1. Introduction
Medicinal plants are sources of various nutrients and also have therapeutic values, therefore they can be used to synthesize and develop drugs [
1]. The medicinal importance of plants is dependent on their phytochemical constituents like alkaloids, phenolics, flavonoids, tannins, saponins, and essential oils [
2].
Phoenix dactylifera L., commonly known as date palm, belongs to the Arecaceae family and its fruit (dates) has been used in folk medicines for many heart diseases and also for antifungal and antibacterial purposes [
3]. They are a rich source of sugars (glucose and fructose), vitamins (A, C, and B complex), fibers, minerals, and phenolic compounds having potent antioxidant activity [
4]. There are almost 35 countries worldwide which produce dates and their composition varies according to the variety and degree of ripening [
5].
Phoenix dactylifera L. consists of polyphenols like cinnamic acid and their derivatives in which ρ coumaric acid, ferulic acid, and sinapic acids are major compounds [
6]. The darker color variety of the date fruit has a higher concentration of polyphenols compared to the lighter variety [
4]. The date palm kernel contains phytohormones; thus, it produces a significant anti-wrinkle effect and can be used in antiaging products [
7]. Date fruits are rich in phenolics and also possess antioxidant activity. Date seeds can also be used in skin products, as they can yield a moisturizing oil with different essential fatty acids [
8].
The aim of the present study was to formulate a stable emulsion containing the Phoenix dactylifera L. extract and to evaluate its effect on different skin parameters like melanin, erythema, hydration, sebum, and elasticity. The effects produced by this cream were compared with the effects produced by a base without Phoenix dactylifera L. extract.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Plant Material
Phoenix dactylifera L. fruit (Family: Arecaceae) purchased from the local market was used as plant material.
2.1.2. Chemicals
Paraffin oil (Merck, Germany). ABIL-EM 90 (Cetyl Dimethicone copolyol with HLB 5, Franken Chemical, Germany), Lemon oil (Pakistan), Phoenix dactylifera L. fruit extract (methanolic), and distilled water (prepared in the laboratory of the Pharmacy Department, the Islamia University of Bahawalpur, Bahawalpur, Pakistan).
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Extraction of the Plant Material
The extract was taken by soaking the 100 g of chopped fruit in 900 mL of 80% methanol for 24 h. Then the sample was stirred for 15 min and then filtered first through eight layers of muslin cloth and then through Whatman filter paper #01. Afterwards, the dark yellowish colored extract was obtained by evaporating the filtrate to one-third of the initial volume at 40 °C under reduced pressure by using a rotary vacuum evaporator.
2.2.2. Determination of Antioxidant Capacity
Antioxidant activity (free radical scavenging activity) of
Phoenix dactylifera L. fruit extract was determined using the DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl hydrazyl) method. The extract was diluted with an equal volume of DPPH (5 µL) using methanol (analytical grade) and kept in an incubator (37 °C) for half an hour. Then, the absorption of the sample was measured at 517 nm and compared with Vitamin C (Control). The activity of free radicals in the form of % inhibition was calculated by using the equation
The antioxidant activity of Phoenix dactylifera L. fruit extract was 89%.
2.2.3. Formulation Development
The oil phase was prepared by heating paraffin oil (16%) and ABIL EM90 (2.5%) to 75 ± 1 °C. At the same time, the aqueous phase (water) (q.s) was heated to the same temperature. The
Phoenix dactylifera L. extract was added to the aqueous phase. The aqueous phase was subsequently added to the oil phase drop by drop with continued stirring at 2000 rpm by a mechanical mixer for 15 min until the entire aqueous phase was added. During this stirring time, two to three drops of fragrance (fruit oil) were added to yield a good fragrance to the emulsion. The test and placebo compositions are detailed in
Table 1.
After continuous stirring for 15 min at 2000 rpm, the speed of the mixer was reduced to 1000 rpm for a period of 10 min for homogenization. The speed of the mixer was then further reduced to 500 rpm for a further 5 min until the emulsion cooled at room temperature.
The same method was used to formulate the base without the addition of Phoenix dactylifera L. fruit extract.
2.2.4. Emulsion Stability Test
The stability tests were performed for both emulsions at different time intervals during 28 days. The conditions used were 8 ± 0.1 °C (in refrigerator), 25 ± 0.1 °C, 40 °C, 40 °C ± 75% relative humidity and 50 ± 0.1°C (in incubator). The physical characteristics (color, liquefaction, phase separation) of both the base and formulation were evaluated. The formulation was stable with respect to all these parameters.
2.2.5. Evaluation of the Emulsion on Human Skin
Eleven female volunteers with an age range of 23–30 years (mean age 25.5) were selected for inclusion in the study. To determine any possible reactions to the creams, a patch test was performed on the forearms of each individual volunteer and after 48 h, results were recorded for any skin irritancy.
On the next day, two creams (placebo cream and cream with extract) were provided to each volunteer. Each cream was marked “right” and “left” for application to the “right” and “left” cheek, respectively and volunteers applied it once daily at bedtime. Volunteers were instructed to apply the creams for eight weeks and to return for measurements on Weeks 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 8. This study was approved by the Board of Studies, Department of Pharmacy, the Islamia University of Bahawalpur and all the volunteers agreed and signed an informed consent before start of the study.
2.2.6. Patch Test
The patch test was performed on the forearms of each volunteer on the first day of skin testing. For this purpose, a 5 × 4 cm region was marked on both the forearms of each volunteer with the help of a scale. The zero value of skin melanin and erythema were noted with the help of a Mexameter. Small amounts of base and formulation were applied separately on each forearm on the marked area and the area was covered with surgical dressing. Dressings were removed after 48 h and measurements of melanin and erythema values were performed on both forearms.
2.2.7. Mathematical Analysis
The following formula was used to calculate the percentage changes for the individual values of different parameters.
where T
A = Individual value of any parameter after Weeks 1, 2, 3, 6, and 8; T
B = Baseline value of particular parameter.
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
The measured values obtained for different parameters (skin moisture, sebum, melanin, erythema, and elasticity) were analyzed statistically using SPSS 12.0 version (paired samples t-test for variation between the two preparations; two-way ANOVA for variation between different time intervals) at 5% level of significance.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Stability Tests for Base and Formulation
Samples of base and formulation were kept at different storage conditions and their stability was studied. The tests were performed at 8 °C, 25 °C, 40 °C, 40 °C with 75% relative humidity, and 50 °C. Both the base and the formulation were stable against different storage conditions.
Organoleptic parameters relating to stability (color, liquefaction, phase separation) and centrifugation test results are presented in the
Table 2.
There was no change in the color of base and formulation at all storage temperatures. As far as the viscosity and phase separation of the emulsions is concerned, there was a slight change in the base after 21 weeks at 40 °C with 75% relative humidity and 50 °C, while that change was observed in the formulation only at 50 °C.
The
Phoenix dactylifera L. extract has very good antibacterial and antifungal activity. It contains high levels of tannins and phenolic compounds—such as ferulic acid, ρ-coumaric acid, ρ-hydroxybenzoic acid, certain oxidative enzymes, steroids, flavonoids, etc.—which are responsible for antibacterial activity. They have reported antibacterial activity against gram negative bacteria like K-pneumonia and
E. coli [
9]. Presence of different polyphenols are responsible for its antifungal activity especially against
Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Albedinis (Foa) [
10]. Most probably, due to the presence of
Phoenix dactylifera L. extract in the formulation (off-white formula) stabilizes it at high temperatures when compared to base (white formula).
The presence of a lipophilic emulsifier, such as Abil EM 90, also stabilizes the emulsions at high temperatures [
11].
The thermal kinetic energy overcomes the gravitational energy of the emulsions and is responsible for stabilizing the emulsions against phase separation [
12].
3.2. Dermatological Tests
3.2.1. Melanin
Skin color is determined by pigmentation and protects the body against UV radiations. It is due to the presence of a pigment named melanin. Melanin is synthesized by melanocytes and stored in melanosomes. Melanosomes are spread into the skin by melanocytes with the help of dendrites and with the spread of these melanosomes, the melanin also spreads [
13].
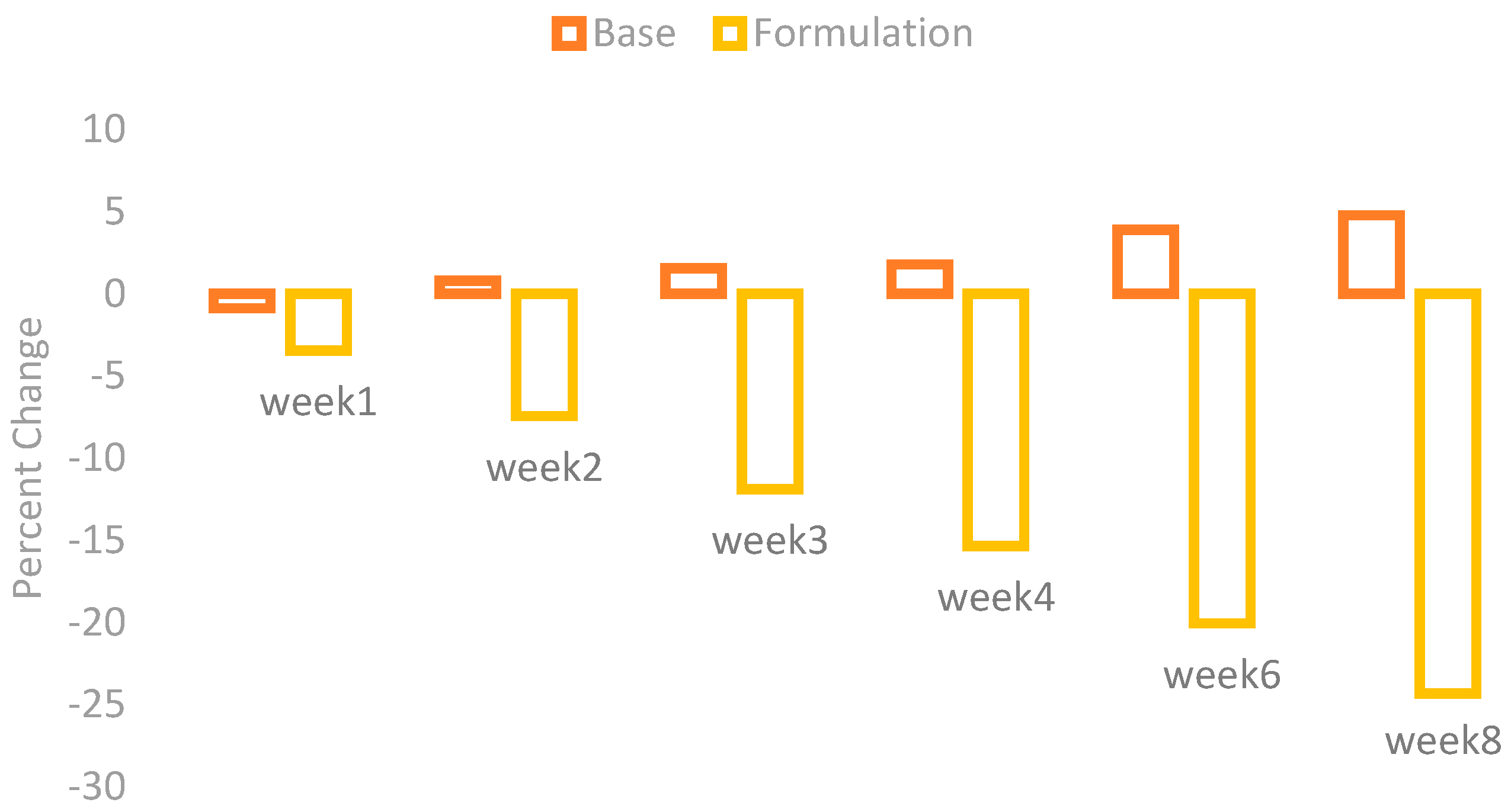
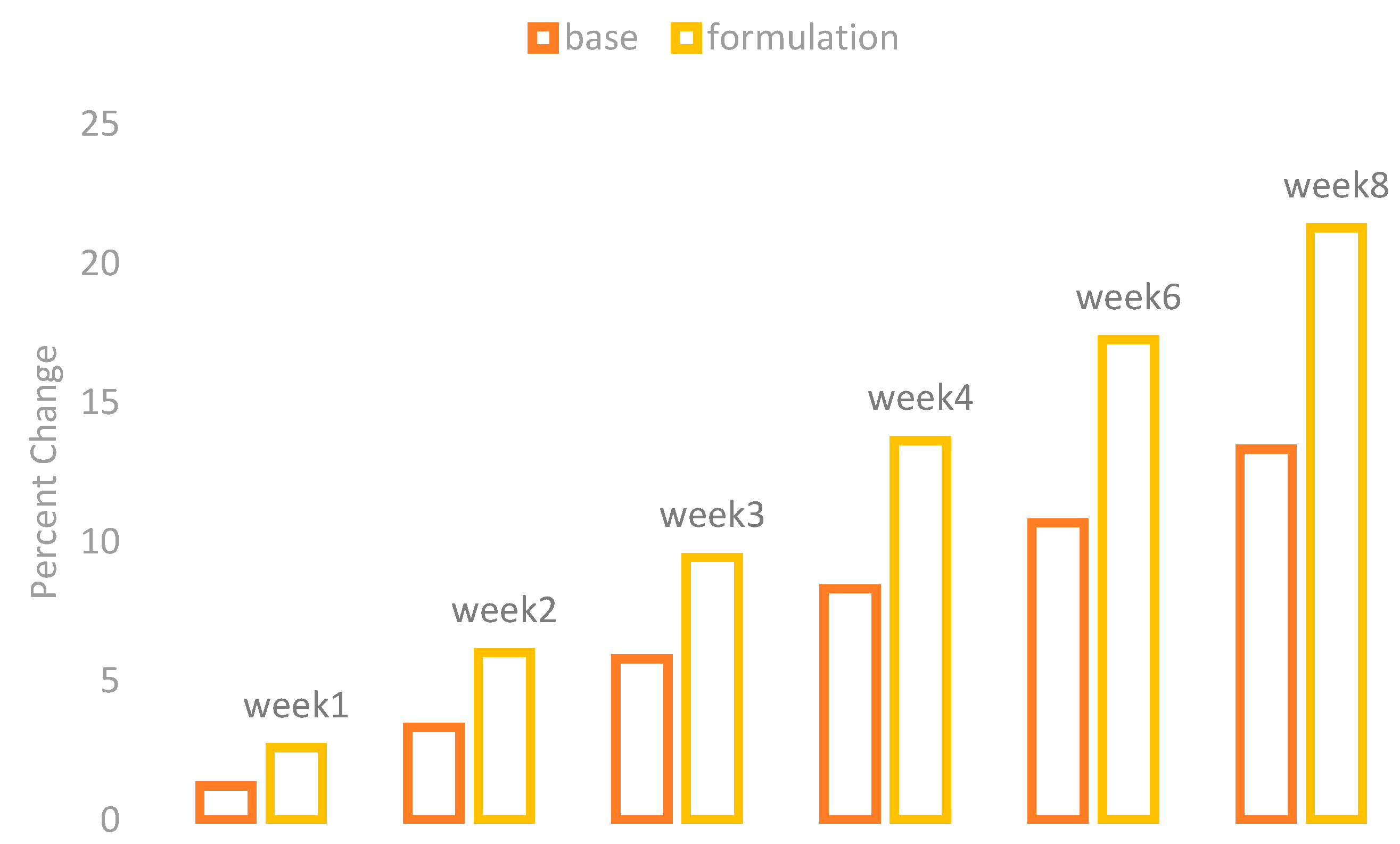
The melanin values of the skin of the cheeks were measured by using a Mexameter MX 18 (Courage + Khazaka, Cologne, Germany). These values were measured on the first day before the application of base and formulation and then on Weeks 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8. The percentage changes in the skin melanin after the application of base and formulation are given in
Figure 1.
The effect of base and formulation on the production of skin melanin were observed. There was an increase in the skin melanin with the application of base while a significant decrease was observed with the application of formulation from Weeks 1 to 8.
When ANOVA was applied with the 5% level of significance, it showed a significant result with time. With the paired sample t-test, the result showed that there are significant variances after two weeks in the effects of base and formulation.
In the fruit of
Phoenix dactylifera L., the presence of polyphenolic compounds and flavonoid glycosides of luteolin, quercetin, and apigenin is the reason behind the antioxidant activity of this fruit. The antioxidant activity of the fruit varies depending upon the variety and the method of extraction [
3].
3.2.2. Erythema
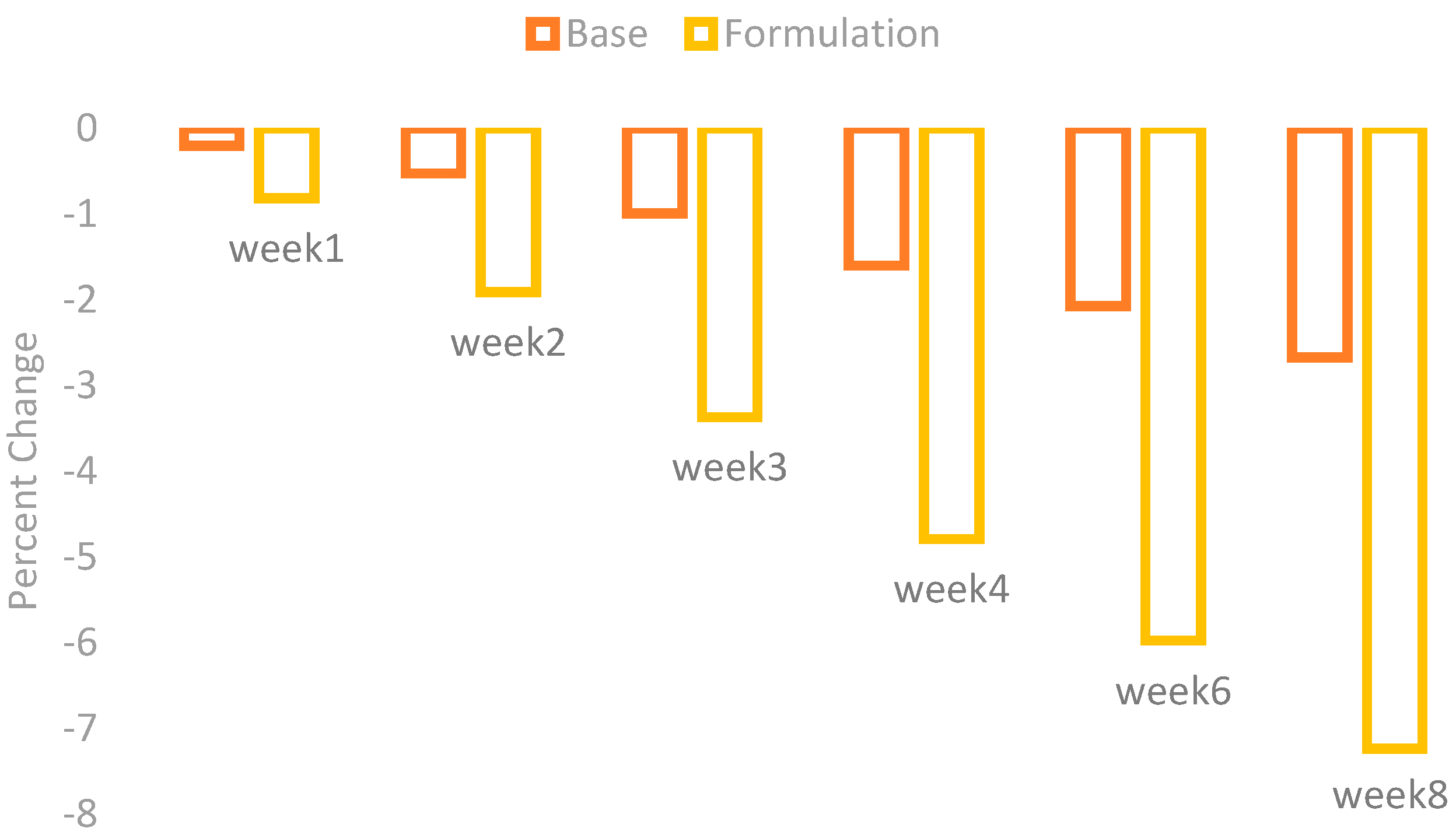
The changes in erythema were observed by using a Mexameter MX 18 after the application of base and formulation. The percentage changes in the skin erythema are given in the
Figure 2.
There was an irregular decrease in erythema after application of the base, while application of the formulation showed a marked decrease with the passage of time.
When the ANOVA test was performed it showed a mild decrease in skin erythema contents with the application of base and a significant decrease with the application of formulation. The paired sample t-test also showed significant variances after four weeks in the results of effects of base and formulation.
The extract of
Phoenix dactylifera L. fruit has superoxide and hydroxyl radical scavenging activity. So, it has an antioxidant and antimutagenic property [
14]. This is the cause of erythematic properties of the formulation.
3.2.3. Skin Moisture Content
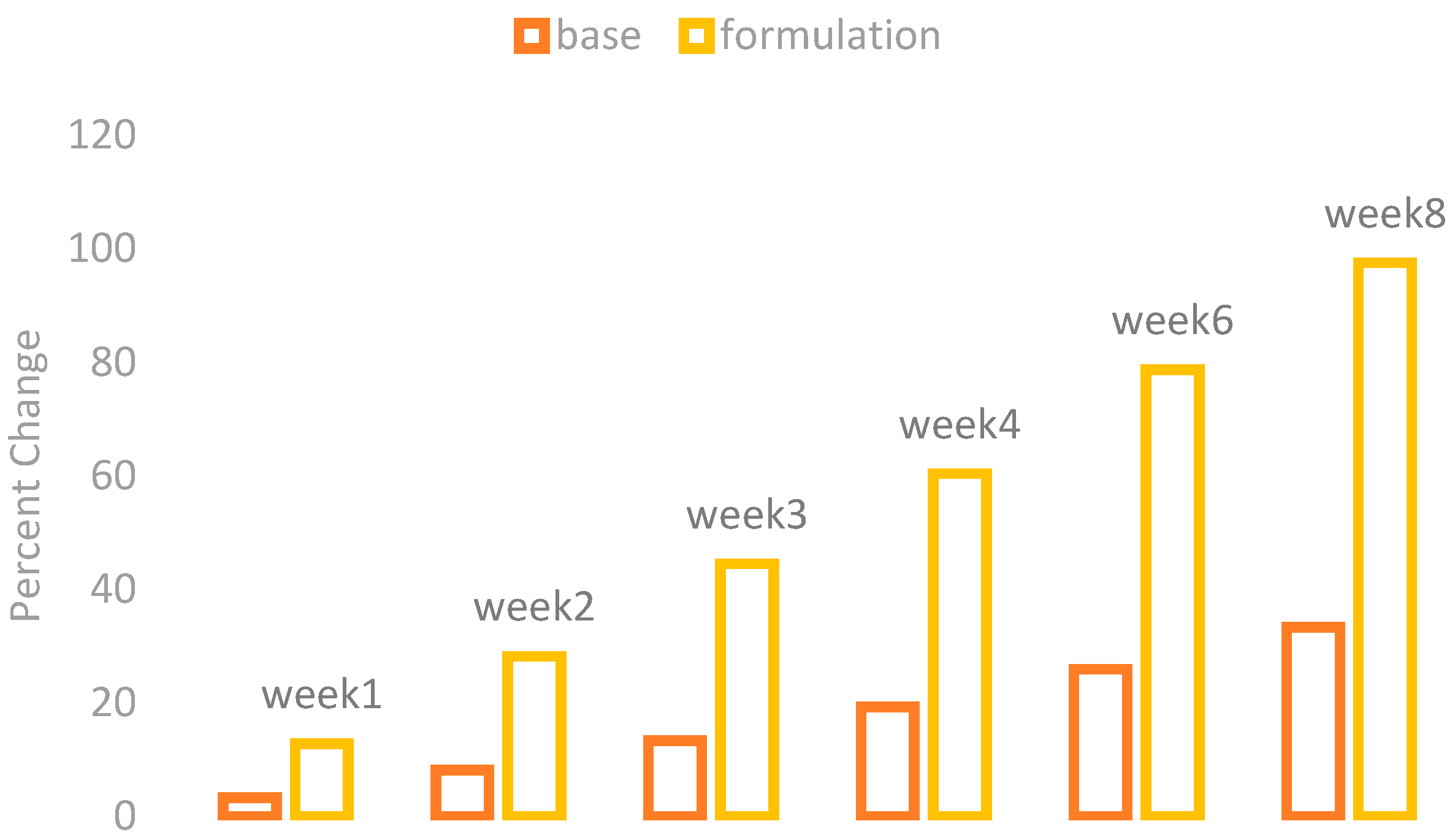
The changes in the skin moisture contents were observed by using a Corneometer CM 825 (Courage + Khazaka) after the application of base and formulation. The percentage changes in the skin moisture are given in
Figure 3.
The application of base showed a mild increase in the skin moisture contents while the application of formulation showed a marked increase in the skin moisture contents.
With ANOVA, the result found in the base application was not significant, while the formulation showed a significant result. The paired sample t-test also showed significant variances after three weeks in the results of effects of base and formulation.
The presence of phenolic acids and vitamins like ascorbic acid and vitamin E is reported in the flesh and the pit of the date palm (
Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruit [
15]. This helps in stimulating dermal fibroblasts, which increases collagen synthesis, resulting in an improvement of the hydration level.
3.2.4. Skin Sebum Content
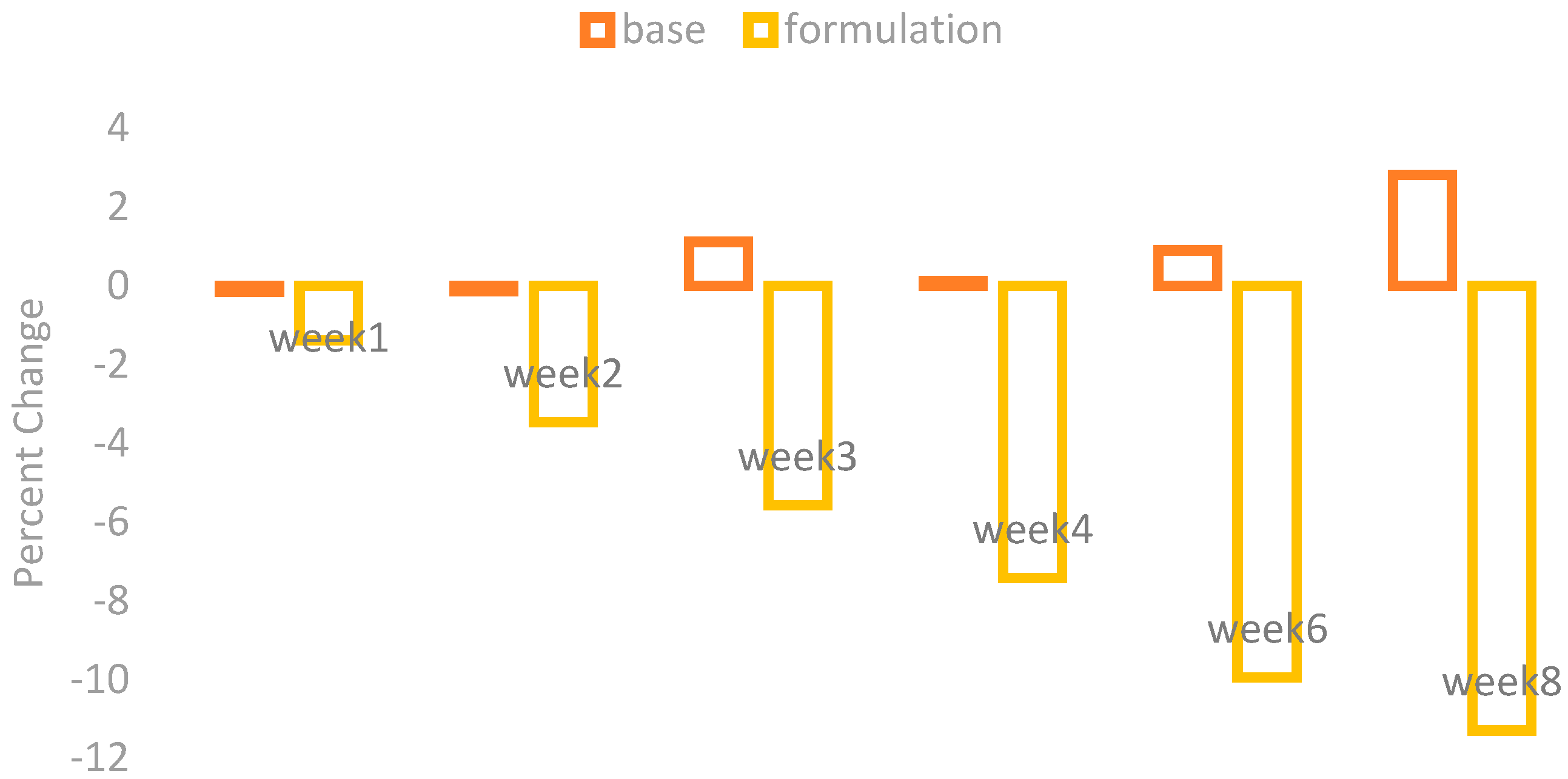
The changes in the skin sebum contents were observed by using a Sebumeter SM 815 (Courage + Khazaka) after the application of base and formulation. The percentage changes in the skin sebum are given in
Figure 4.
The application of base showed an irregular increase and little decrease in the skin sebum contents while the application of formulation showed a marked decrease in the skin sebum contents.
With ANOVA, the result yielded by the base was not significant, while the formulation showed a significant result after four weeks. The paired sample t-test showed insignificant variances in the results of effects of base and formulation.
Dates are rich in many types of fatty acids and among those oleic and linoleic acid are the most important [
16]. These fatty acids inhibit the enzyme α-1 reductase, which causes a decreased production of sebum [
17].
3.2.5. Skin Elasticity
The changes in the skin elasticity contents were observed by using an Elastometer EM 25 (Courage + Khazaka) after the application of base and formulation. The percentage changes in the skin elasticity are given in
Figure 5.
The application of base showed a mild increase in the skin elasticity while the application of formulation showed a marked increase in the skin elasticity.
With ANOVA, a significant result was found after the application of base and formulation. The paired sample t-test also showed significant variances after one week in the results of effects of base and formulation.
Different types of minerals and vitamins, especially vitamin C, are present in date fruits [
18]. Vitamin C has a proven anti-aging activity because it induces the enzyme collagenase 1 and enhances collagen production [
19].
4. Conclusions
The conclusion of this study is that a topical cream containing Phoenix dactylifera L. fruit extract has different effects on different skin parameters. It can produce a decrease in skin melanin contents (whitening effects), decrease in skin erythema contents (anti-inflammatory effect), decrease in skin sebum contents (anti-acne effects), increase in skin moisture contents (moisturizing effect), and an increase in skin elasticity (anti-aging effects).
A further study is needed on this plant in order to use it to treat different skin disorders.
Acknowledgments
Authors are highly thankful to Cosmin Moldovan, University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Târgu Mures, Târgu-Mureş, Romania for his valuable effort in improving this manuscript for English editing.
Author Contributions
N.A. conceived and designed the experiments; S.M. performed the experiments; T.M. and J.I. contributed analysis tools and wrote the paper; all four authors analyzed the data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rasool Hassan, B. Medicinal Plants (Importance and Uses). Pharm. Anal. Acta 2012, 3, e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaiah, D.; Devi, T.; Bono, A.; Sarbatly, R. Studies on phytochemical constituents of six Malaysian medicinal plants. J. Med. Plants Reseach. 2009, 3, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Khanavi, M.; Saghari, Z.; Mohammadirad, A.; Khademi, R.; Hadjiakhoondi, A.; Abdollahi, M. Comparison of antioxidant activity and total phenols of some date varieties. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 17, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, E.A.; Tawfik, M.S.; Abu-Tarboush, H.M. Phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of various date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruits from Saudi Arabia. Food Nutr. 2011, 2, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Manickavasagan, A.; Essa, M.M.; Sukumar, E. Dates: Production, Processing, Food, and Medicinal Values; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, A.; Embarek, G.; Kokkalou, E.; Kefalas, P. Phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of the Algerian ripe date palm fruit (Phoenix dactylifera). Food Chem. 2005, 89, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauza, E.; Dal Farra, C.; Berghi, A.; Oberto, G.; Peyronel, D.; Domloge, N. Date palm kernel extract exhibits antiaging properties and significantly reduces skin wrinkles. Int. J. Tissue React. 2001, 24, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- El Hadrami, A.; Al-Khayri, J.M. Socioeconomic and traditional importance of date palm. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2012, 24, 371–385. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, R.S.; Al-Daihan, S. Antibacterial properties of different cultivars of Phoenix dactylifera L. and their corresponding protein content. Ann. Biol. Res. 2012, 3, 4751–4757. [Google Scholar]
- Boulenouar, N.; Marouf, A.; Cheriti, A. Antifungal activity and phytochemical screening of extracts from Phoenix dactylifera L. cultivars. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerregaard, S.; Vermehren, C.; Söderberg, I.; Frokjaer, S. Accelerated stability testing of a water-in-oil emulsion. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2001, 22, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, C.-A. Investigation on the Thermal Stability of Technical and Cosmetic Emulsions. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Aachen, Aachen, Germany, April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, D.; Liechti, C.; Zülli, F. Stimulation of melanin synthesis for tanning and protection. SÖFW-J. 2006, 132, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Vayalil, P.K. Antioxidant and antimutagenic properties of aqueous extract of date fruit (Phoenix dactylifera L. Arecaceae). J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2002, 50, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaira, N.; Ferchichi, A.; Mrabet, A.; Sghairoun, M. Chemical composition of the flesh and the pit of date palm fruit and radical scavenging activity of their extracts. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 2202–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biglar, M.; Khanavi, M.; Hajimahmoodi, M.; Hassani, S.; Moghaddam, G.; Sadeghi, N.; Oveisi, M.R. Tocopherol content and fatty acid profile of different Iranian date seed oils. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Khan, B.A.; Mahmood, T.; Parveen, R.; Qayum, M.; Anwar, M. Formulation and evaluation of antisebum secretion effects of sea buckthorn w/o emulsion. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agboola, O.S.; Adejumo, A.L. Nutritional Composition of the Fruit of the Nigerian Wild Date Palm, Phoenix dactylifera. World J. Dairy Food Sci. 2013, 8, 196–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ganceviciene, R.; Liakou, A.I.; Theodoridis, A.; Makrantonaki, E.; Zouboulis, C.C. Skin anti-aging strategies. Derm. Endocrinol. 2012, 4, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).