Anti-Aging Efficacy of a Multi-Peptides–Silybin Complex: Mechanistic Insights and a 56-Day Clinical Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Product
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Antibodies and Reagents
2.4. Instruments
2.5. UV Irradiation and Drug Treatment
2.6. MTT Assay
2.7. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
2.8. Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining
2.9. Western Blot (WB) Assay
2.10. Victoria Blue (VB) Staining
2.11. Clinical Study
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
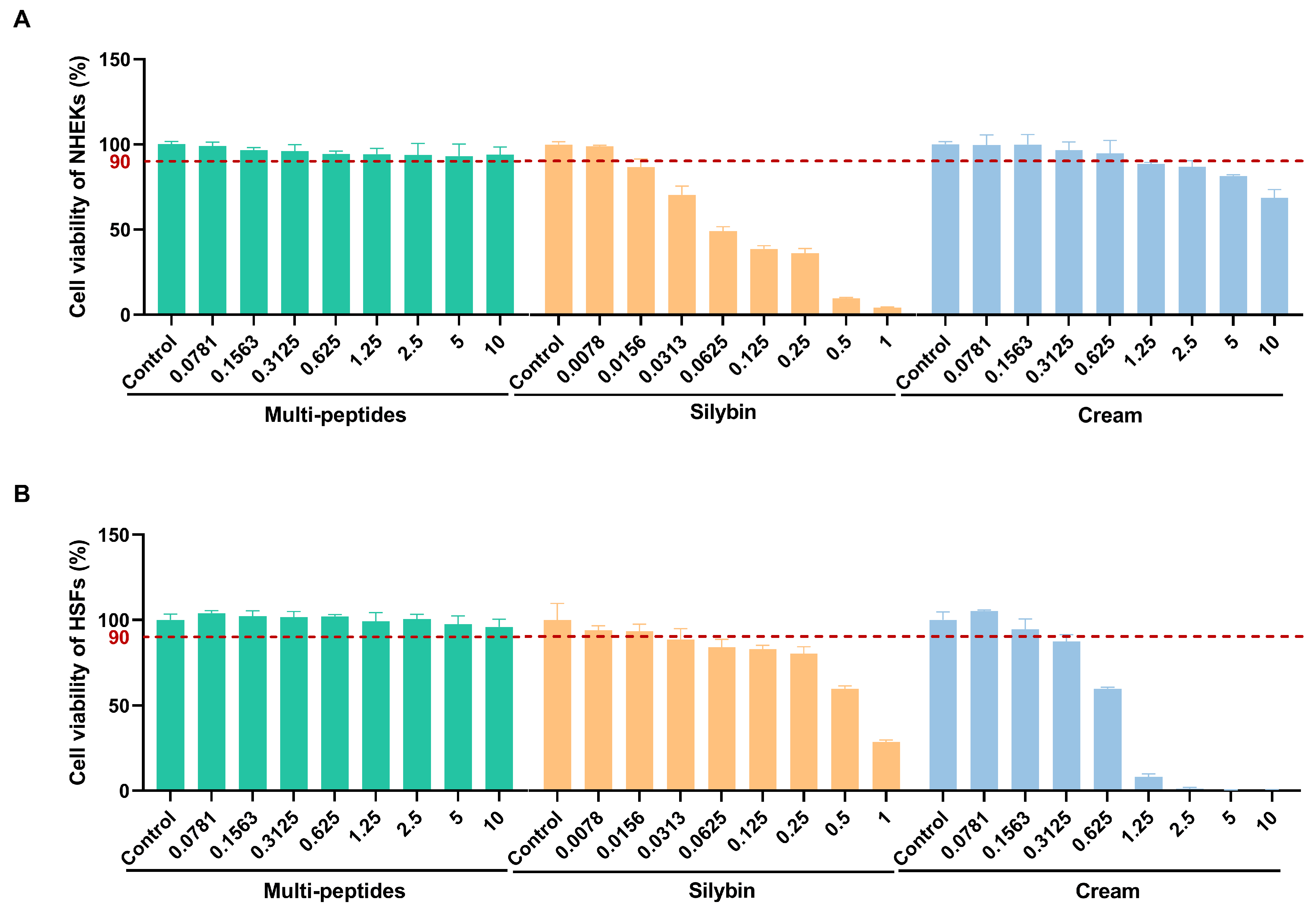
3.1. Cell Viability
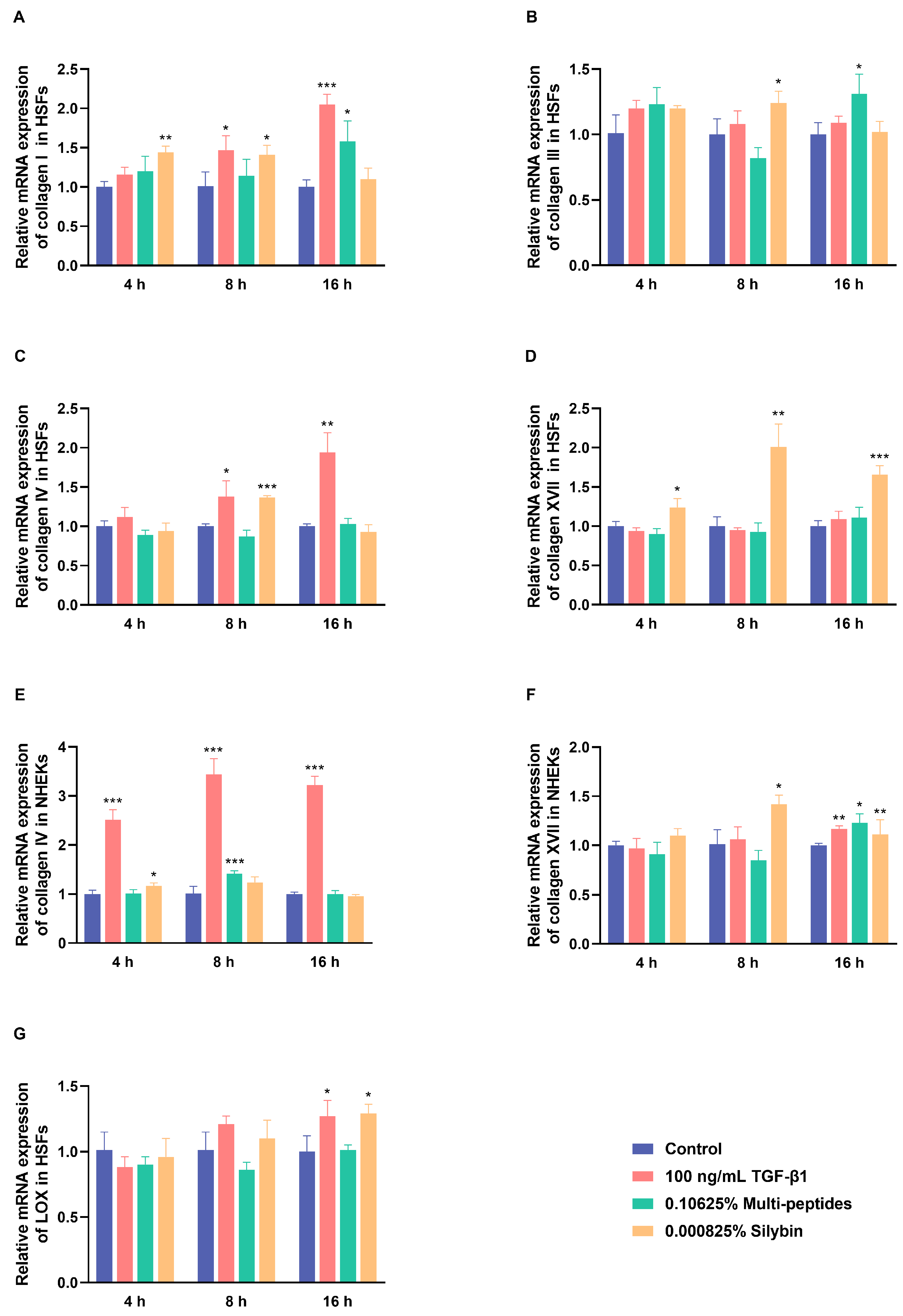
3.2. Rapidly Transcriptional Activation of Anti-Aging Proteins by Multi-Peptides and Silybin
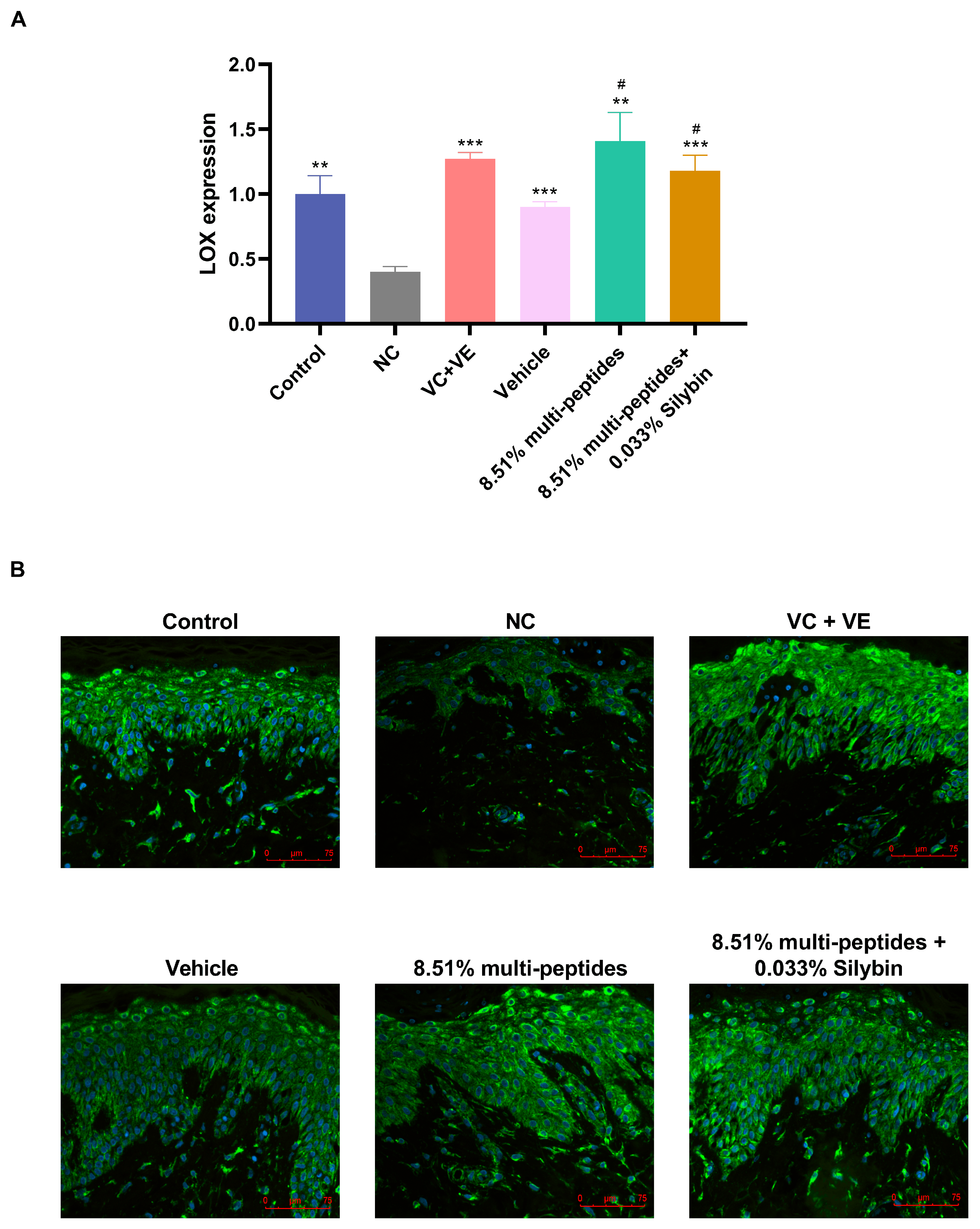
3.3. Restoration of UV-Damaged ECM Proteins by Multi-Peptides and Silybin
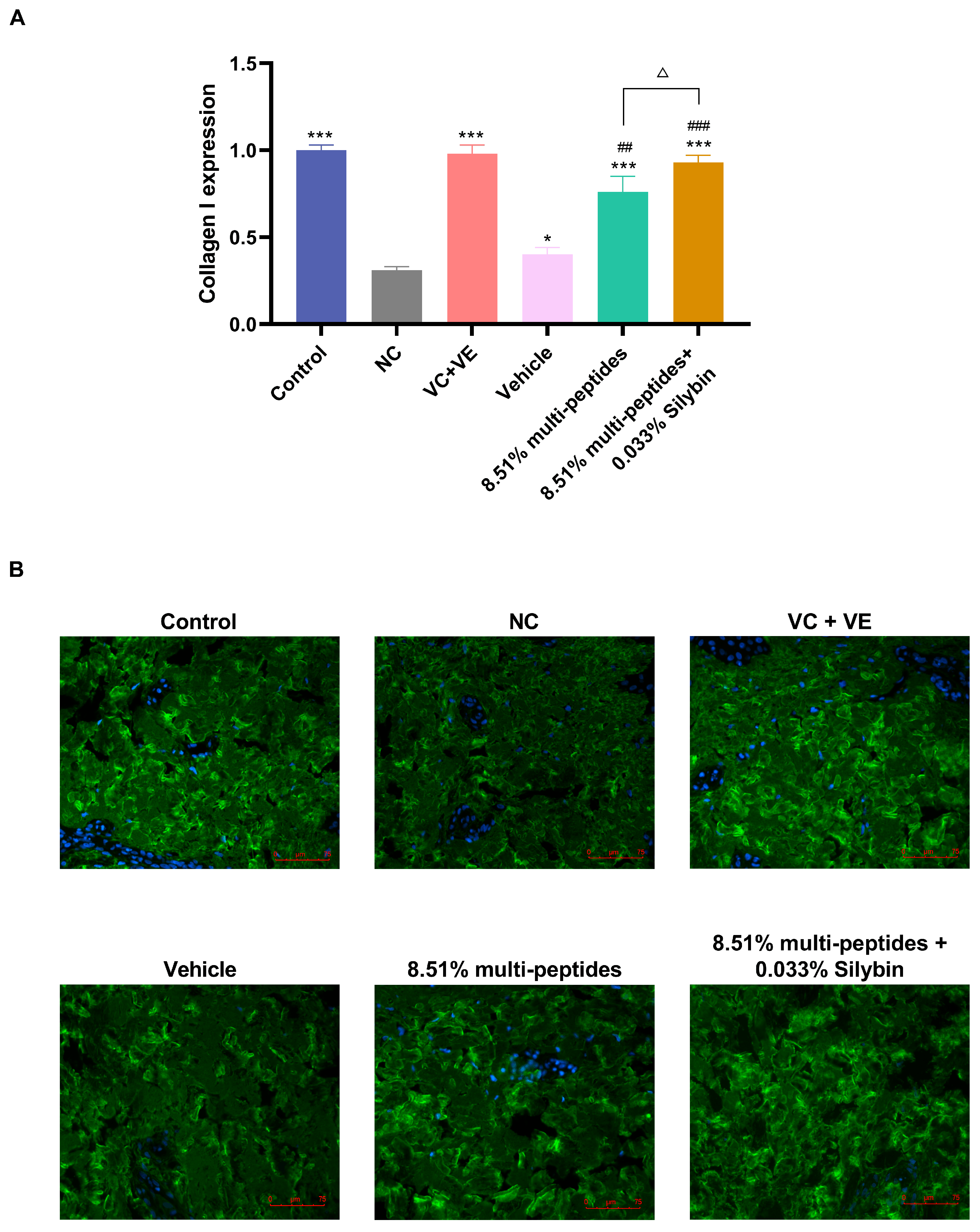
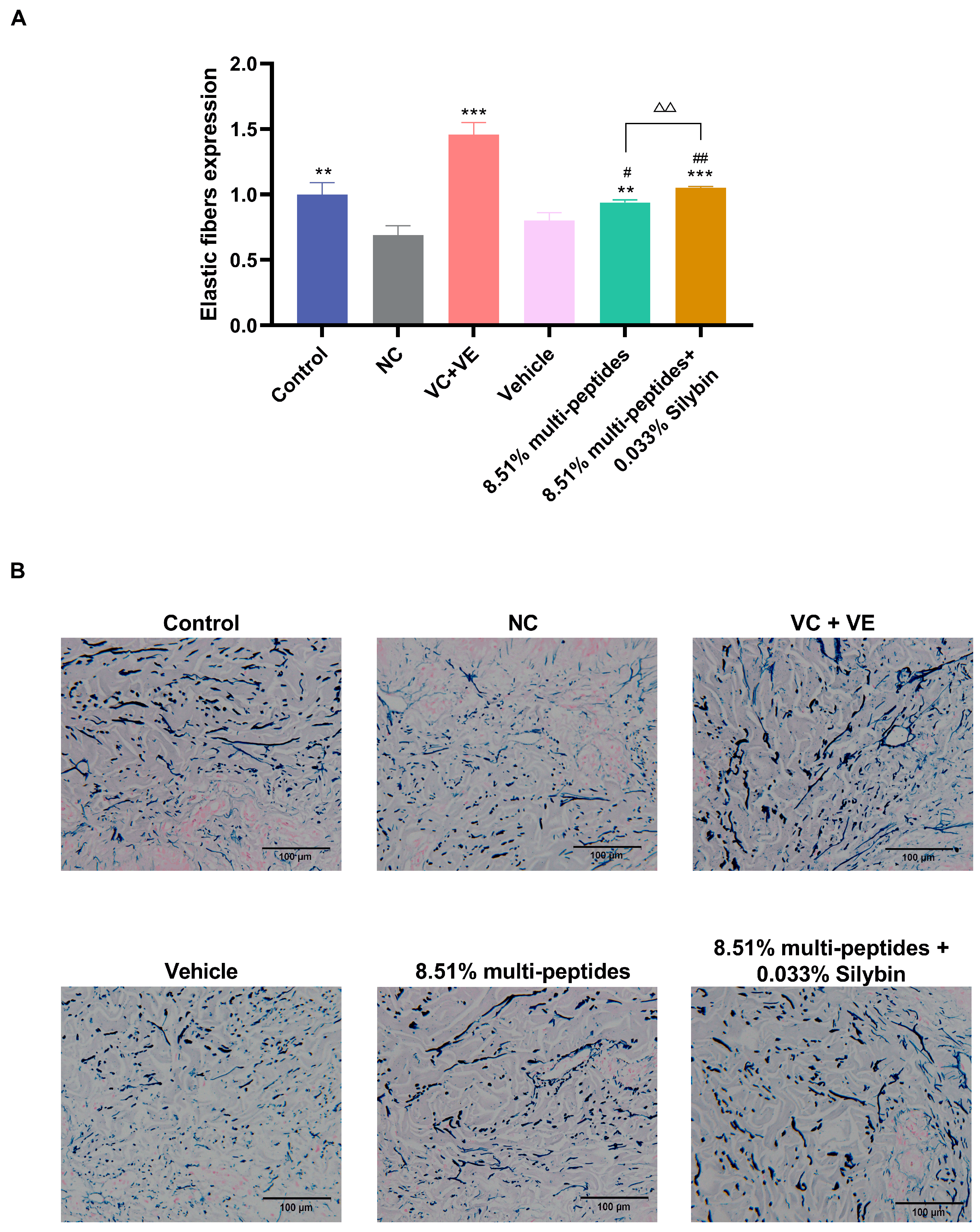
3.4. Rapid In Vitro Activation of Anti-Aging Proteins by the Cream Containing Multi-Peptides and Silybin
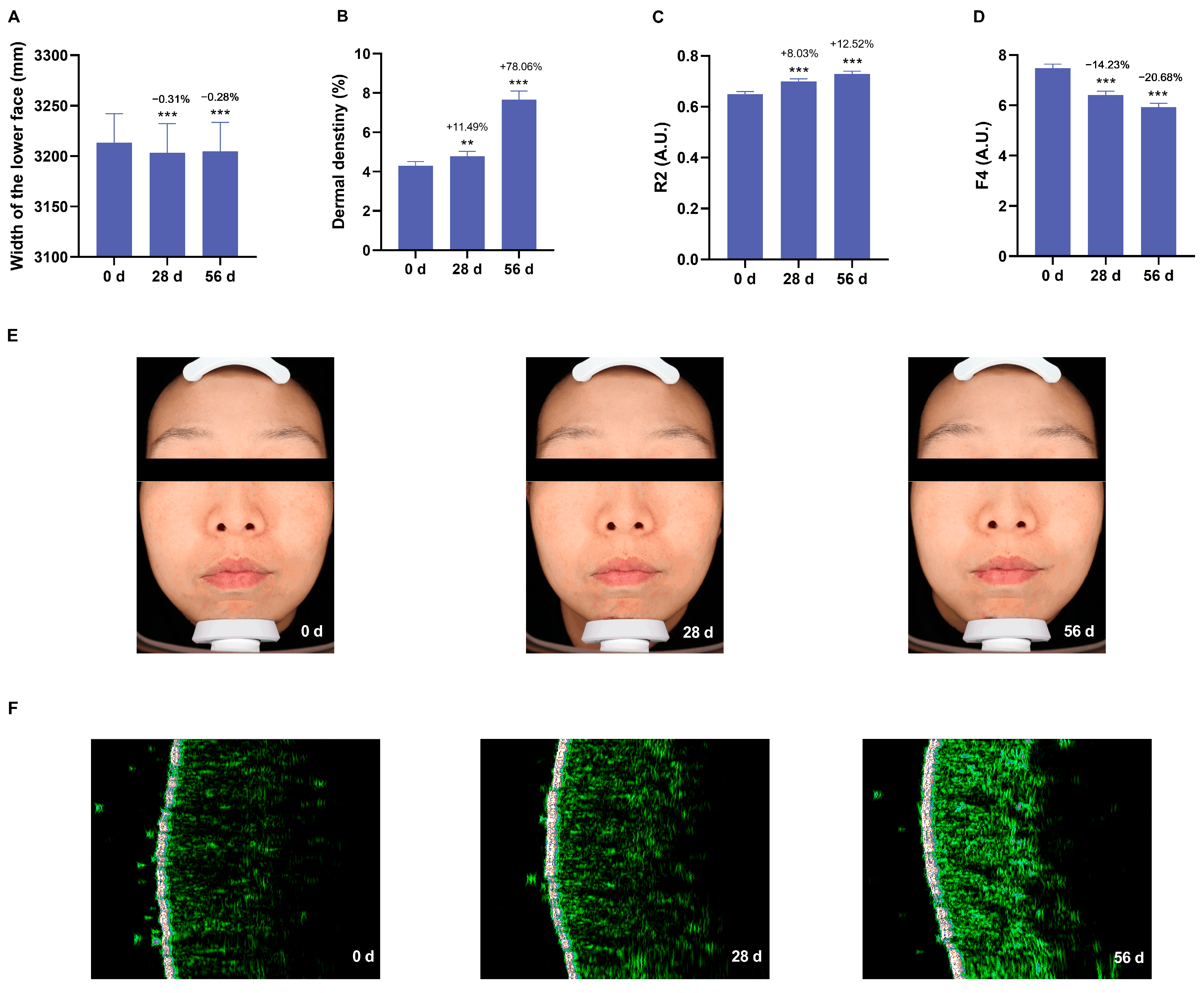
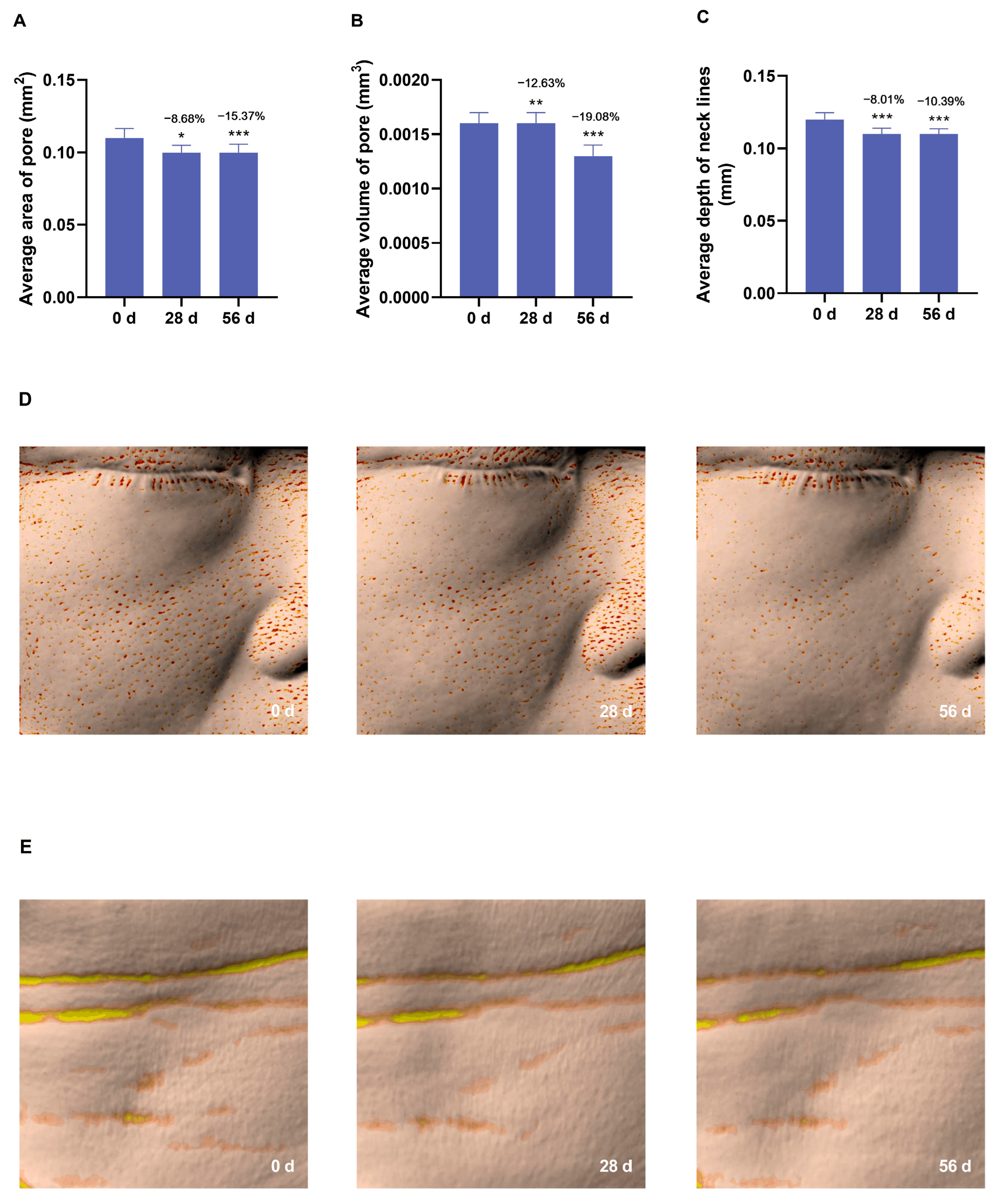
3.5. Anti-Aging Effects of the Cream on Skin
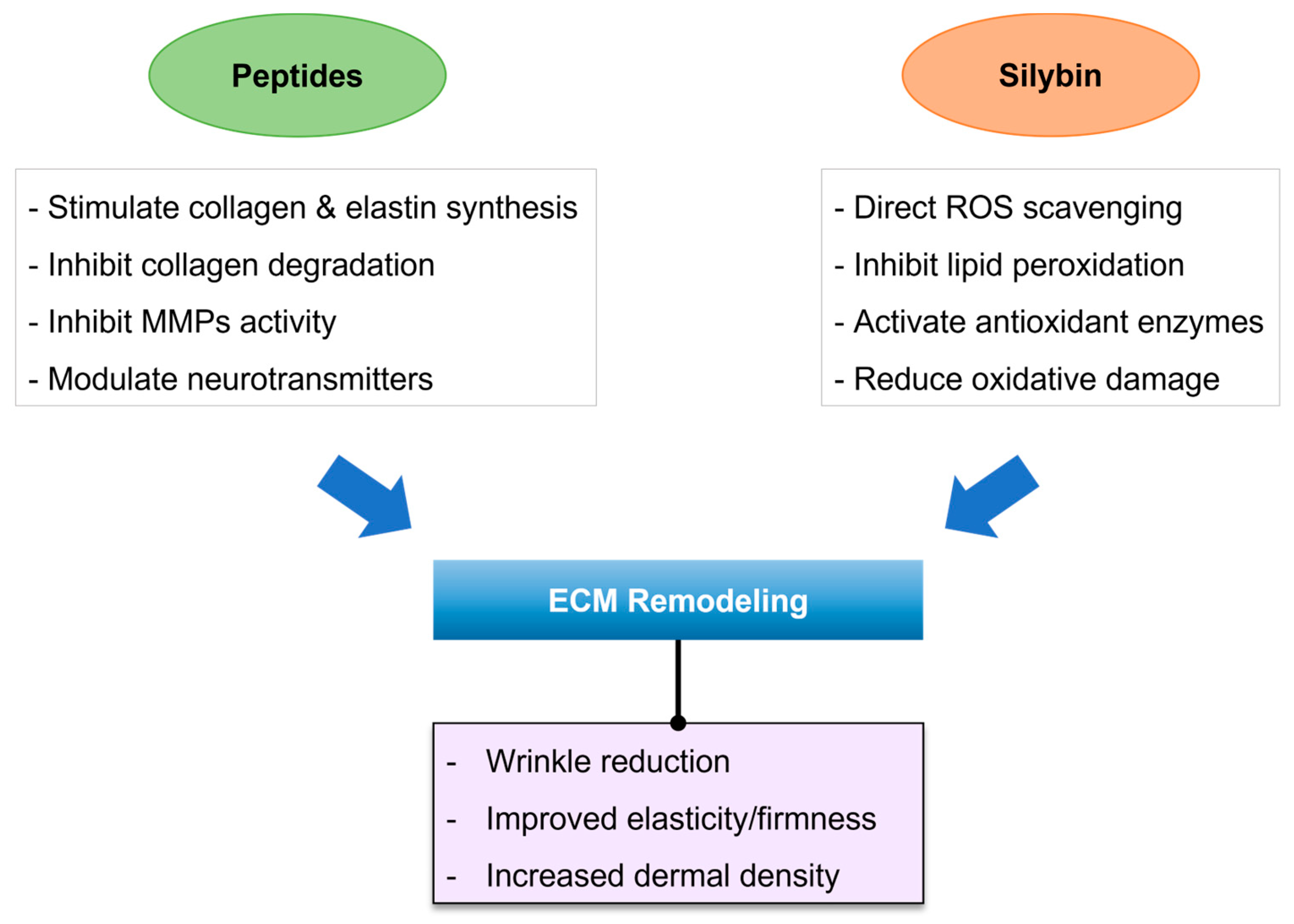
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| LOX | Lysyl oxidase |
| DEJ | Dermal–epidermal junction |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| AGEs | Advanced glycation end products |
| HSFs | Human skin fibroblasts |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| NHEKs | Normal human epidermal keratinocytes |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| VC | Vitamin C |
| VE | Vitamin E |
| TGF | Transforming growth factor |
| UVA | Ultraviolet A |
| UVB | Ultraviolet B |
| NC | Negative control |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| IF | Immunofluorescence |
| IPP | Image-Pro® Plus |
| IOD | Integrated optical density |
| MOD | Mean optical density |
| WB | Western blot |
| VB | Victoria blue |
| RH | Relative humidity |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SE | Standard error |
References
- Chung, J.H.; Seo, J.Y.; Choi, H.R.; Lee, M.K.; Youn, C.S.; Rhie, G.E.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, K.H.; Park, K.C.; Eun, H.C. Modulation of Skin Collagen Metabolism in Aged and Photoaged Human Skin In Vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 117, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.; Gartstein, V.; Kligman, A.M.; Montagna, W.; Ridder, G.M. Age, sunlight, and facial skin: A histologic and quantitative study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1991, 25, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Datta, S.C.; Varani, J.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittie, L.; Fisher, G.J. Natural and Sun-Induced Aging of Human Skin. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a015370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.J. Molecular mechanisms of ageing in connective tissues. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2001, 122, 735–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behmoaras, J.; Slove, S.; Seve, S.; Vranckx, R.; Sommer, P.; Jacob, M.P. Differential expression of lysyl oxidases LOXL1 and LOX during growth and aging suggests specific roles in elastin and collagen fiber remodeling in rat aorta. Rejuvenation Res. 2008, 11, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäki, J.M. Lysyl oxidases in mammalian development and certain pathological conditions. Histol. Histopathol. 2009, 24, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenizo, V.; Andre, V.; Reymermier, C.; Sommer, P.; Damour, O.; Perrier, E. LOXL as a target to increase the elastin content in adult skin: A dill extract induces the LOXL gene expression. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 15, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarani-Contri, M.; Vincenzi, D.; Quaglino, D., Jr.; Mori, G.; Pasquali-Ronchetti, I. Localization of human placenta lysyl oxidase on human placenta, skin and aorta by immunoelectronmicroscopy. Matrix 1989, 9, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flagler, M.J.; Tamura, M.; Laughlin, T.; Hartman, S.; Ashe, J.; Adams, R.; Kozak, K.; Cresswell, K.; Mullins, L.; Jarrold, B.B.; et al. Combinations of peptides synergistically activate the regenerative capacity of skin cells in vitro. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widgerow, A.D.; Ziegler, M.E.; Shafiq, F. TriHex 2.0—Advancing Skin Health Science and the TriHex Technology. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e16690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorouhi, F.; Maibach, H.I. Role of topical peptides in preventing or treating aged skin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 31, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorouhi, F.; Maibach, H.I. Topical Peptides and Proteins for Aging Skin. In Textbook of Aging Skin; Farage, M.A., Miller, K.W., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1865–1896. ISBN 978-3-662-47398-6. [Google Scholar]
- Namjoshi, S.; Benson, H.A.E. Cyclic peptides as potential therapeutic agents for skin disorders. Pept. Sci. 2010, 94, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, Y.Y.; Gui, B.; Arnison, P.G.; Wang, Y.; Reaney, M.J.T. Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) bioactive compounds and peptide nomenclature: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Xing, H.Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Yu, X.Y. An Anti-Wrinkle Cyclic Hexapeptide Compound and Its Preparation Method. CN114634554A, 6 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.L.; Huang, P.; Sun, B.X.; Liu, Z.B.; Wang, Y. A Linseed Extract with Skin Anti-Aging Effect, Its Preparation Method and Application. CN116172921A, 30 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Jabbar, O.; Kashmoola, M.A.; Mustafa Al-Ahmad, B.E.; Mokhtar, K.I.; Muhammad, N.; Abdul Rahim, R.; Qouta, L.A. The Effect of Flaxseed Extract on Skin Elasticity of The Healing Wound In Rabbits. IIUM Med. J. Malays. 2019, 18, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New ingredients for skin and hair care launched at in-cosmetics. Pharm Cosmet Rev. 2010, 37, 14. [CrossRef]
- Murphy-Ullrich, J.E.; Poczatek, M. Activation of latent TGF-β by thrombospondin-1: Mechanisms and physiology. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2000, 11, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schagen, S.K. Topical Peptide Treatments with Effective Anti-Aging Results. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnamaeian, M.; Vilcinskas, A. Short antimicrobial peptides as cosmetic ingredients to deter dermatological pathogens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8847–8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A.M.; Sakuma-Oyama, Y.; Oyama, N.; Black, M.M. Collagen XVII/BP180: A collagenous transmembrane protein and component of the dermoepidermal anchoring complex. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2005, 30, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Lu, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Pioneering ionic liquids in neuro-soothing: Enhanced transdermal delivery of collagen peptides and their synergistic anti-aging functions. Mater Today Bio 2025, 31, 101527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Nie, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Deng, H. Peptides in Cosmetics: From Pharmaceutical Breakthroughs to Skincare Innovations. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, P.; Mo, J.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Zhu, W.; Du, Z. Ferulic acid in synergy with retinol alleviates oxidative injury of HaCaT cells during UVB-induced photoaging. Aging 2024, 16, 7153–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.S.; Magalhães, M.C.; Oliveira, R.; Sousa-Lobo, J.M.; Almeida, I.F. Trends in the Use of Botanicals in Anti-Aging Cosmetics. Molecules 2021, 26, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajnochová Svobodová, A.; Gabrielová, E.; Michaelides, L.; Kosina, P.; Ryšavá, A.; Ulrichová, J.; Zálešák, B.; Vostálová, J. UVA-photoprotective potential of silymarin and silybin. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2018, 310, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, S.; Yamaguchi, K. Silybin from Silybum Marianum Seeds Inhibits Confluent-Induced Keratinocytes Differentiation as Effectively as Retinoic Acid without Inducing Inflammatory Cytokine. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 45, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boira, C.; Chapuis, E.; Lapierre, L.; Tiguemounine, J.; Scandolera, A.; Reynaud, R. Silybum marianum Extract: A Highly Effective Natural Alternative to Retinoids to Prevent Skin Aging Without Side Effects. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e16613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, R.; Pasalar, P.; Kamalinejad, M.; Dehpour, A.R.; Tavangar, S.M.; Paknejad, M.; Mehrabani Natanzi, M.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Ahmadi Ashtiani, H.R.; Akbari, M.; et al. The effect of silymarin (Silybum marianum) on human skin fibroblasts in an in vitro wound healing model. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckvall, H.; Wassberg, C.; Berne, B.; Ponten, F. Similar UV responses are seen in a skin organ culture as in human skin in vivo. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 11, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yang, R.; Wu, L.; Tang, S.; Wei, B.; Guo, L.; He, L.; Feng, Y. Atractylodes macrocephala polysaccharides regulate the innate immunity of colorectal cancer cells by modulating the TLR4 signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 7111–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriyama, S.; Ogura, Y.; Nishikawa, S.; Hosoi, J.; Amano, S. Regeneration of collagen fibrils at the papillary dermis by reconstructing basement membrane at the dermal-epidermal junction. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, T.R.; Bird, D.; Baker, A.M.; Barker, H.E.; Ho, M.W.; Lang, G.; Erler, J.T. LOX-mediated collagen crosslinking is responsible for fibrosis-enhanced metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-m.; Yoo, B.-Y.; Seo, Y.-K. Wound-healing effects of human dermal components with gelatin dressing. J. Biomater. Appl. 2017, 32, 716–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, D.G. Practical Statistics for Medical Research; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1991; ISBN 0-412-27630-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Kong, L.; Wu, J.; Wu, W.; Ma, L.; Jiang, S.; Ren, W.; et al. A review of the botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, synthetic biology and comprehensive utilization of Silybum marianum. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1417655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haytoglu, N.S.; Gurel, M.S.; Erdemir, A.; Falay, T.; Dolgun, A.; Haytoglu, T.G. Assessment of skin photoaging with reflectance confocal microscopy. Skin. Res. Technol. 2014, 20, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, F.; Palacios, S.; Alemañ, N.; Guerrero, F. Changes of the basement membrane and type IV collagen in human skin during aging. Maturitas 1996, 25, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langton, A.K.; Halai, P.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Sherratt, M.J.; Watson, R.E.B. The impact of intrinsic ageing on the protein composition of the dermal-epidermal junction. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2016, 156, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Zhu, H.; Wei, J. Anti-aging effect of low molecular weight recombinant humanized collagen on photo-aging by activating adherence junction signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0329460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szauter, K.M.; Cao, T.; Boyd, C.D.; Csiszar, K. Lysyl oxidase in development, aging and pathologies of the skin. Pathol. Biol. 2005, 53, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, A. Elastic fibers during aging and disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 66, 101255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Yoon, S.; Kim, S.; Jung, J.; Kor, M.; Shin, K.; Lim, C.; Han, H.S.; Lee, H.; Park, K.-Y.; et al. Anti-Wrinkle Benefits of Peptides Complex Stimulating Skin Basement Membrane Proteins Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierckx, S.; Patrizi, M.; Merino, M.; González, S.; Mullor, J.L.; Nergiz-Unal, R. Collagen peptides affect collagen synthesis and the expression of collagen, elastin, and versican genes in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1397517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Furmanczyk, M.; Ramos, D.; Ribes, A.; Pons, L.; Bustos, J.; de Henestrosa, A.R.F.; Granger, C.; Jourdan, E. Natural Retinol Analogs Potentiate the Effects of Retinal on Aged and Photodamaged Skin: Results from In Vitro to Clinical Studies. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 2299–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hong, M.; Huang, Y. Synergy of GHK-Cu and hyaluronic acid on collagen IV upregulation via fibroblast and ex-vivo skin tests. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akulinina, I.; Stefanaki, I.; Pavlíčková, E.; Maiolino, M.; Hajduk, S.; Sápy, M.; Mertin, B.; Rijo, H.; Tekeli, Ö.; Valois, A.; et al. Topical formulation containing peptides and vitamin C in ampoules improves skin aging signs: Results of a large, international, observational study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 3910–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Evaluation Item | Score 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 28 d | 56 d | |
| Pruritus | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Burning | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Tightness | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.19 |
| Tingling | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Dryness/scaling | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Edema | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Desquamation | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Erythema | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Evaluation Item | Consumer Satisfaction 1 | |
|---|---|---|
| 28 d | 56 d | |
| Improvement in pore-related concerns | 81% | 90% |
| Improved jawline definition | 81% | 90% |
| Reduction of nasolabial folds | 81% | 90% |
| Reduction of glabellar lines | 84% | 87% |
| Reduction of neck lines | 84% | 84% |
| Reduction in submental fat | 81% | 87% |
| Improved skin firmness and elasticity | 87% | 90% |
| Refined and smoother skin | 87% | 87% |
| Mild and non-irritating | 87% | 97% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Hu, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Ye, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Liao, F.; Li, Y.; Sun, P. Anti-Aging Efficacy of a Multi-Peptides–Silybin Complex: Mechanistic Insights and a 56-Day Clinical Evaluation. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12050223
Zhang H, Hu H, Xu C, Wang L, Ye Y, Huang J, Chen Y, Liao F, Li Y, Sun P. Anti-Aging Efficacy of a Multi-Peptides–Silybin Complex: Mechanistic Insights and a 56-Day Clinical Evaluation. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(5):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12050223
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hong, Huiping Hu, Chenlan Xu, Lina Wang, Ying Ye, Jiefang Huang, Yuyan Chen, Feng Liao, Yanan Li, and Peiwen Sun. 2025. "Anti-Aging Efficacy of a Multi-Peptides–Silybin Complex: Mechanistic Insights and a 56-Day Clinical Evaluation" Cosmetics 12, no. 5: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12050223
APA StyleZhang, H., Hu, H., Xu, C., Wang, L., Ye, Y., Huang, J., Chen, Y., Liao, F., Li, Y., & Sun, P. (2025). Anti-Aging Efficacy of a Multi-Peptides–Silybin Complex: Mechanistic Insights and a 56-Day Clinical Evaluation. Cosmetics, 12(5), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12050223






