Unraveling the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Microbiota in Skin Health and Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction: A Comprehensive View on Skin Care
1.1. The Skin as a Barrier and Immune System
1.2. The Gut Microbiota: A Key Player in Systemic Health Regulation
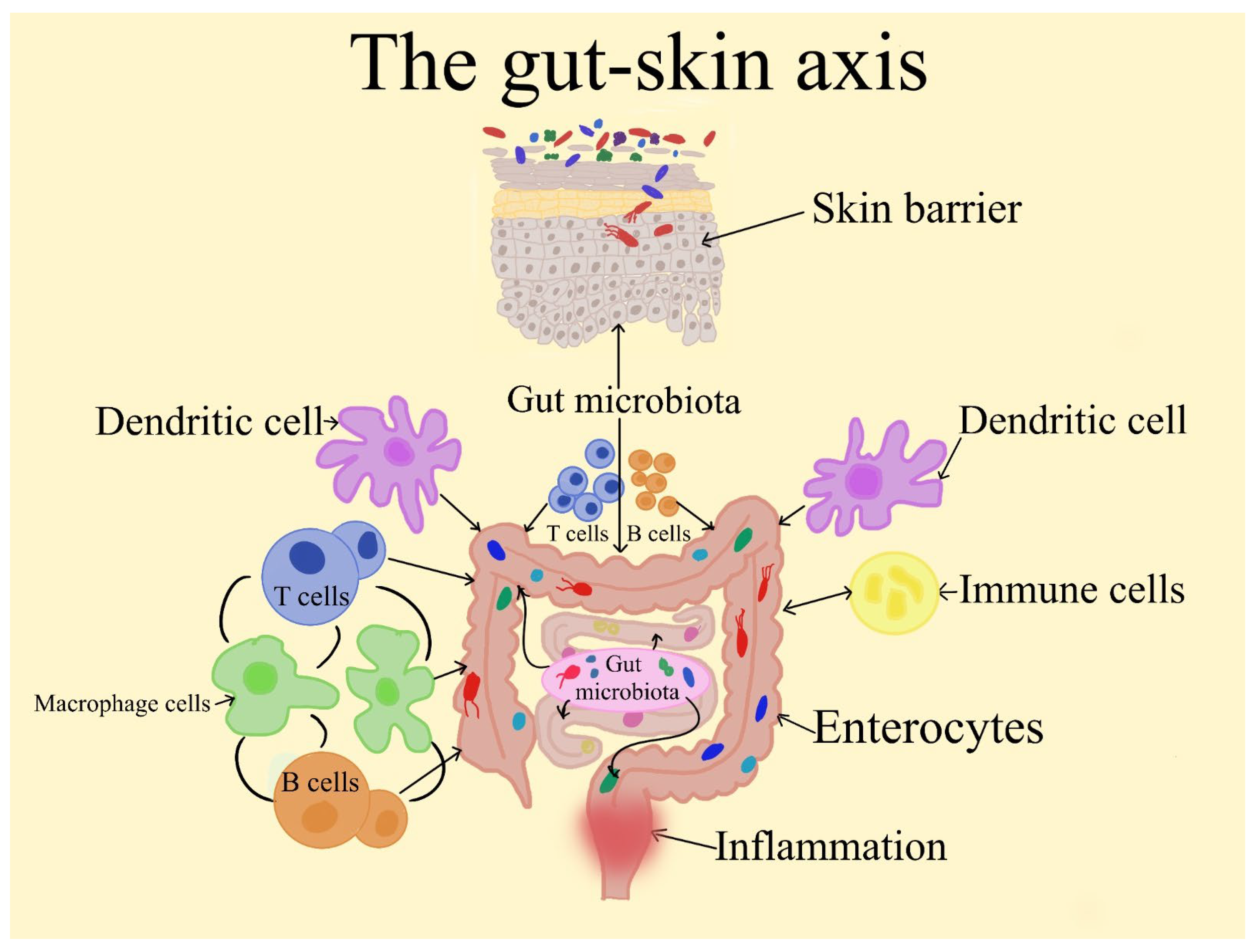
1.3. The Gut–Skin Axis’ Emergence
1.4. Scope of the Review
2. The Gut Microbiome: Composition, Function, and Dysbiosis
2.1. Normal Gut Microbiota Composition
2.2. Functional Roles of the Gut Microbiome
2.3. Gut Dysbiosis: Definition and Consequences
3. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting the Gut Microbiome for Skin Health
3.1. Dietary Interventions
3.2. Probiotics
3.3. Prebiotics
3.4. Postbiotics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yousef, H.; Alhajj, M.; Sharma, S. Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis. 2017. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk470464 (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Agarwal, S.; Krishnamurthy, K. Histology, skin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, H.; Miao, J.H.; Alhajj, M.; Badri, T. Histology, skin appendages. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Romanovsky, A.A. Skin temperature: Its role in thermoregulation. Acta Physiol. 2014, 210, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, E.; Lewis, C.J.; Hernandez, J.G.; Gentile, P.; Ferreira, A.M. Layer-by-layer assembly: Advancing skin repair, one layer at a time. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 13908–13923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresma, J.A.S. Organization of the skin immune system and compartmentalized immune responses in infectious diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00034-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Merana, G.R.; Harris-Tryon, T.; Scharschmidt, T.C. Skin immunity: Dissecting the complex biology of our body’s outer barrier. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimnejad, N.; Jaafar, D.; Goodarzi, H. The past, present, future: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of human skin diseases. Physiologia 2024, 4, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Gao, X.; Xie, W. Research progress in skin aging, metabolism, and related products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zgutka, K.; Tkacz, M.; Tomasiak, P.; Tarnowski, M. A role for advanced glycation end products in molecular ageing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, H.; Ward, M.; Stitt, A.W. AGEs, RAGE, and diabetic retinopathy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2011, 11, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ooi, X.Y.; Parvus, M.N.; Valdez, L.; Tsin, A. Advanced Glycation End Products: Formation, Role in Diabetic Complications, and Potential in Clinical Application. In The Eye and Foot in Diabetes; Grigsby, J., Derbel, F., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, R.; Parveen, A.; Kang, M.-C.; Hong, S.-M.; Kim, S.Y. Glyoxal-derived advanced glycation end products (GO-AGEs) with UVB critically induce skin inflammaging: In vitro and in silico approaches. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreou, E.; Papaneophytou, C. Boosting Immunity Through Nutrition and Gut Health: A Narrative Review on Managing Allergies and Multimorbidity. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. Microbial dysbiosis in the skin microbiome and its psychological consequences. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.R.; Akter, S.; Tamanna, S.K.; Mazumder, L.; Esti, I.Z.; Banerjee, S.; Akter, S.; Hasan, M.R.; Acharjee, M.; Hossain, M.S. Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: Gut-skin axis observed through the lenses of therapeutics and skin diseases. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2096995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafian, M.; Ding, N.; Holmes, E.; Hart, A. Effect on the Host Metabolism. In The Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Shah, Y.A.; Hussain, M.; Rabail, R.; Socol, C.T.; Hassoun, A.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Rusu, A.V. Human gut microbiota in health and disease: Unveiling the relationship. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 999001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, S.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7493–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manach, C.; Donovan, J.L. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of dietary flavonoids in humans. Free Radic. Res. 2004, 38, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalbert, A.; Williamson, G. Dietary intake and bioavailability of polyphenols. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2073S–2085S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: Major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Mârza, S.M.; Papuc, I. The immunomodulatory effects of vitamins in cancer. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1464329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Bai, Y.; Zha, L.; Ullah, N.; Ullah, H.; Shah, S.R.H.; Sun, H.; Zhang, C. Mechanism of the gut microbiota colonization resistance and enteric pathogen infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 716299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiertsema, S.P.; van Bergenhenegouwen, J.; Garssen, J.; Knippels, L.M. The interplay between the gut microbiome and the immune system in the context of infectious diseases throughout life and the role of nutrition in optimizing treatment strategies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, V.V.; Sarath, A.P.; Kerkar, Z. Gut microbiome in dermatology–A narrative review. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2025, 1094, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.A.; Monteleone, G.; McLaughlin, J.T.; Paus, R. The gut-skin axis in health and disease: A paradigm with therapeutic implications. Bioessays 2016, 38, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi Shirazi, M.; Sadeghi, S. Avicenna (980–1037 AD) and Nocturnal Itching: Exploring Gut-Skin Connection. J. Adv. Med. Biomed. Res. 2024, 32, 393–396. [Google Scholar]
- Bowe, W.P.; Logan, A.C. Acne vulgaris, probiotics and the gut-brain-skin axis-back to the future? Gut Pathog. 2011, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.; Luthra, A.; Tardif, M.; Dashi, A.; Worsley, O. The Bidirectional Gut-Skin Axis: Emerging Evidence and Potential Skin Health Implications. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2024, 75, 633–659. [Google Scholar]
- Huseini, H.F.; Rahimzadeh, G.; Fazeli, M.R.; Mehrazma, M.; Salehi, M. Evaluation of wound healing activities of kefir products. Burns 2012, 38, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéniche, A.; Benyacoub, J.; Buetler, T.M.; Smola, H.; Blum, S. Supplementation with oral probiotic bacteria maintains cutaneous immune homeostasis after UV exposure. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2006, 16, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poutahidis, T.; Kearney, S.M.; Levkovich, T.; Qi, P.; Varian, B.J.; Lakritz, J.R.; Ibrahim, Y.M.; Chatzigiagkos, A.; Alm, E.J.; Erdman, S.E. Microbial symbionts accelerate wound healing via the neuropeptide hormone oxytocin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreouzi, M.; Theodorakis, N.; Nikolaou, M.; Feretzakis, G.; Anastasiou, A.; Kalodanis, K.; Sakagianni, A. Skin microbiota: Mediator of interactions between metabolic disorders and cutaneous health and disease. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, H.J.; de Goffau, M.C. The human gut microbiota. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 902, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Cintoni, M.; Raoul, P.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Pulcini, G.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. Food components and dietary habits: Keys for a healthy gut microbiota composition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel-Muroz, A.; Akulinin, M.; Shilova, P.; Tyakht, A.; Klimenko, N. Stability of human gut microbiome: Comparison of ecological modelling and observational approaches. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 4456–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassarella, M.; Blaak, E.E.; Penders, J.; Nauta, A.; Smidt, H.; Zoetendal, E.G. Gut microbiome stability and resilience: Elucidating the response to perturbations in order to modulate gut health. Gut 2021, 70, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.V.-A. Gut microbiome composition and diversity are related to human personality traits. Hum. Microbiome J. 2020, 15, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Moles, L.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Bustos, G.; De Vos, W.M.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Fuentes, S.; Jiménez, E. Bacteriological and immunological profiling of meconium and fecal samples from preterm infants: A two-year follow-up study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Schwartz, B. Interactions between dietary antioxidants, dietary Fiber and the gut microbiome: Their putative role in inflammation and cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, J.K.; Waters, J.L.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Koren, O.; Blekhman, R.; Beaumont, M.; Van Treuren, W.; Knight, R.; Bell, J.T. Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 2014, 159, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Lozupone, C.A.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. Worlds within worlds: Evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.B.; Tolonen, A.C.; Xavier, R.J. Human genetic variation and the gut microbiome in disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syromyatnikov, M.; Nesterova, E.; Gladkikh, M.; Smirnova, Y.; Gryaznova, M.; Popov, V. Characteristics of the gut bacterial composition in people of different nationalities and religions. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pessemier, B.; Grine, L.; Debaere, M.; Maes, A.; Paetzold, B.; Callewaert, C. Gut–skin axis: Current knowledge of the interrelationship between microbial dysbiosis and skin conditions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boix-Amorós, A.; Badri, M.H.; Manasson, J.; Blank, R.B.; Haberman, R.H.; Neimann, A.L.; Girija, P.V.; Hernandez, A.J.; Heguy, A.; Koralov, S.B. Alterations in the cutaneous microbiome of patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis reveal similarities between non-lesional and lesional skin. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Zhu, W.; Kuang, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. Skin and gut microbiome in psoriasis: Gaining insight into the pathophysiology of it and finding novel therapeutic strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 589726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Wang, X.; Cai, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Min, W.; Qian, Q.; Zeng, Y. Research progress on the correlation of atopic dermatitis with gut microbiota. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beam, A.; Clinger, E.; Hao, L. Effect of diet and dietary components on the composition of the gut microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Yang, H. Factors affecting the composition of the gut microbiota, and its modulation. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaka, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Tobe, K. The gut microbiome: A core regulator of metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 256, e220111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tan, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, D.; Feng, W.; Peng, C. Functions of gut microbiota metabolites, current status and future perspectives. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Pérez, O.; Cruz-Ramón, V.; Chinchilla-López, P.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. The role of the gut microbiota in bile acid metabolism. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Bajaj, J.S. Bile acids and the gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 30, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.L.; Patterson, A.D. The gut microbiome: An orchestrator of xenobiotic metabolism. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, C. Modulation of gut microbiota and immune system by probiotics, pre-biotics, and post-biotics. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 634897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, M.; Piermattei, A.; Di Sante, G.; Migliara, G.; Delogu, G.; Ria, F. Immunomodulation by gut microbiota: Role of Toll-like receptor expressed by T cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 586939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieryńska, M.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L.; Struzik, J.; Mielcarska, M.B.; Gregorczyk-Zboroch, K.P. Integrity of the intestinal barrier: The involvement of epithelial cells and microbiota—A mutual relationship. Animals 2022, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Bodduluri, S.R.; Baby, B.V.; Hegde, B.; Kotla, N.G.; Hiwale, A.A.; Saiyed, T.; Patel, P.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Enhancement of the gut barrier integrity by a microbial metabolite through the Nrf2 pathway. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyszkowski, R.; Mehrzad, R. Inflammation: A multifaceted and omnipresent phenomenon. In Inflammation and Obesity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- DeGruttola, A.K.; Low, D.; Mizoguchi, A.; Mizoguchi, E. Current understanding of dysbiosis in disease in human and animal models. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ja, H. The causes of intestinal dysbiosis: A review. Altern. Med. Rev. 2004, 9, 180–197. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Han, X.; Huang, W.; You, Y.; Zhan, J. Gut dysbiosis during early life: Causes, health outcomes, and amelioration via dietary intervention. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7199–7221. [Google Scholar]
- Hrncir, T. Gut microbiota dysbiosis: Triggers, consequences, diagnostic and therapeutic options. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, W. Dietary fiber intake and gut microbiota in human health. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimentarius, C. Guidelines on Nutrition Labelling CAC/GL 2-1985 as Last Amended 2010; Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme, Secretariat of the Codex Alimentarius Commission; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- de Menezes, E.W.; Giuntini, E.B.; Dan, M.C.T.; Sardá, F.A.H.; Lajolo, F.M. Codex dietary fibre definition–Justification for inclusion of carbohydrates from 3 to 9 degrees of polymerisation. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.-J.; Chau, C.-F. Classification and regulatory perspectives of dietary fiber. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.M.; Champ, M.M.-J.; Cloran, S.J.; Fleith, M.; Van Lieshout, L.; Mejborn, H.; Burley, V.J. Dietary fibre in Europe: Current state of knowledge on definitions, sources, recommendations, intakes and relationships to health. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 149–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.A.; Grant, L.J.; Gidley, M.J.; Mikkelsen, D. Gut fermentation of dietary fibres: Physico-chemistry of plant cell walls and implications for health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deehan, E.C.; Duar, R.M.; Armet, A.M.; Perez-Muñoz, M.E.; Jin, M.; Walter, J. Modulation of the gastrointestinal microbiome with nondigestible fermentable carbohydrates to improve human health. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaker, B.R.; Tuncil, Y.E. A perspective on the complexity of dietary fiber structures and their potential effect on the gut microbiota. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 3838–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Besten, G.; Van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvallet, C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Gurry, T.; Irizarry, R.A.; Alm, E.J. Meta-analysis of gut microbiome studies identifies disease-specific and shared responses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, M.; Thomas, A.; Reisetter, A.C.; Scholtens, D.M.; Wolever, T.M.; Josefson, J.L.; Layden, B.T. Maternal short-chain fatty acids are associated with metabolic parameters in mothers and newborns. Transl. Res. 2014, 164, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürholz, K.; Hofmann, J.; Iljazovic, A.; Häger, J.; Lucas, S.; Sarter, K.; Strowig, T.; Bang, H.; Rech, J.; Schett, G. Dietary short-term fiber interventions in arthritis patients increase systemic SCFA levels and regulate inflammation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Chu, Y.; Li, J.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, B.; Shi, L. Intestinal butyrate-metabolizing species contribute to autoantibody production and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Marion, T.; Tong, Y.; Zaiss, M.M.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y. Resistant starch intake alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by modulating gut microbiota and promoting concomitant propionate production. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 116, 102564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wan, J.; Choe, U.; Pham, Q.; Schoene, N.W.; He, Q.; Li, B.; Yu, L.; Wang, T.T. Interactions between food and gut microbiota: Impact on human health. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 389–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasaniha, R.; Olof, H.; Voisin, A.; Armstrong, K.; Wine, E.; Vasanthan, T.; Armstrong, H. Diversity of fibers in common foods: Key to advancing dietary research. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, D.; Michael, M.; Rajput, H.; Patil, R. Dietary fibre in foods: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.-W.; Yu, E.-Z.; Feng, Q. Soluble dietary fiber, one of the most important nutrients for the gut microbiota. Molecules 2021, 26, 6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Introducing the concept of prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Scott, K.P.; Rastall, R.A.; Tuohy, K.M.; Hotchkiss, A.; Dubert-Ferrandon, A.; Gareau, M.; Murphy, E.F.; Saulnier, D.; Loh, G. Dietary prebiotics: Current status and new definition. Food Sci. Technol. Bull. Funct. Foods 2010, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davani-Davari, D.; Negahdaripour, M.; Karimzadeh, I.; Seifan, M.; Mohkam, M.; Masoumi, S.J.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Prebiotics: Definition, types, sources, mechanisms, and clinical applications. Foods 2019, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Trijp, M.P.; Rios-Morales, M.; Logtenberg, M.J.; Keshtkar, S.; Afman, L.A.; Witteman, B.; Bakker, B.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Schols, H.; Hooiveld, G.J. Detailed Analysis of Prebiotic Fructo-and Galacto-Oligosaccharides in the Human Small Intestine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 21152–21165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ren, F. The role of probiotics in skin health and related gut–skin axis: A review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, G.; Verde, L.; Zink, A.; Muscogiuri, G.; Albanesi, C.; Paganelli, A.; Barrea, L.; Scala, E. Plant-based foods for chronic skin diseases: A focus on the Mediterranean diet. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2025, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, H.; Tan, J. Effects of diet on acne and its response to treatment. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, O.E.; Camera, E.; Flori, E.; Ottaviani, M. Insulin and the sebaceous gland function. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1252972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkembi, B.; Huppertz, T. Glycemic responses of milk and plant-based drinks: Food matrix effects. Foods 2023, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, T.; Ali, F.R.; Carolides, S.; Al-Niaimi, F. Rosacea and diet: What is new in 2021? J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2021, 14, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Manfredini, M.; Barbieri, M.; Milandri, M.; Longo, C. Probiotics and Diet in Rosacea: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, Y.; Fulmali, D.G. Relationship between atopic dermatitis and food allergy in children. Cureus 2022, 14, e33160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balić, A.; Vlašić, D.; Žužul, K.; Marinović, B.; Bukvić Mokos, Z. Omega-3 versus omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory skin diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.; Eng, P.A.; Borelli, S.; Kägi, R.; Zimmermann, C.; Zahner, C.; Drewe, J.; Hess, L.; Ferrari, G.; Lautenschlager, S. Gamma-linolenic acid levels correlate with clinical efficacy of evening primrose oil in patients with atopic dermatitis. Adv. Ther. 2014, 31, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Marani, A.; Martina, E.; Diotallevi, F.; Radi, G.; Offidani, A. Psoriasis as an immune-mediated and inflammatory systemic disease: From pathophysiology to novel therapeutic approaches. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, N.; Hoashi, T.; Saeki, H. Nutrition and psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Pu, H.; Voss, M. Overview of anti-inflammatory diets and their promising effects on non-communicable diseases. Br. J. Nutr. 2024, 132, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranchida, N.; Molinari, F.; Franco, G.A.; Cordaro, M.; Di Paola, R. Potential Role of Dietary Antioxidants During Skin Aging. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogerakou, T.; Antoniadou, M. The Role of Dietary Antioxidants, Food Supplements and Functional Foods for Energy Enhancement in Healthcare Professionals. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-H.; Khnykin, D. Fatty acid transporters in skin development, function and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2014, 1841, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimarco, A.; Landry, M.J.; Gardner, C.D. Ultra-processed foods, weight gain, and co-morbidity risk. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 11, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-y.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Li, L.; Guo, M.-m.; He, Y.-f.; Dong, Y.-m.; Meng, H.; Yi, F. Advanced glycation end products in the skin: Molecular mechanisms, methods of measurement, and inhibitory pathways. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 837222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Global impacts of western diet and its effects on metabolism and health: A narrative review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, S.; Durante-Mangoni, E. Unraveling the puzzle: Health benefits of probiotics—A comprehensive review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, A.; Chen, A.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, S.; Chen, D.; Yu, R. Lactobacillus for the treatment and prevention of atopic dermatitis: Clinical and experimental evidence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1137275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maftei, N.-M.; Raileanu, C.R.; Balta, A.A.; Ambrose, L.; Boev, M.; Marin, D.B.; Lisa, E.L. The potential impact of probiotics on human health: An update on their health-promoting properties. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-E.; Zheng, P.; Ye, S.-Z.; Ma, X.; Liu, E.; Pang, Y.-B.; He, Q.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Li, W.-Q.; Zeng, J.-H. Microbiome: Role in inflammatory skin diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 1057–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.; Huang, C.; Radi, R.; Moll, S.B.; Jules, E.; Arbiser, J.L. Skin barrier function: The interplay of physical, chemical, and immunologic properties. Cells 2023, 12, 2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, I.; Ramser, A.; Isham, N.; Ghannoum, M.A. The gut microbiome as a major regulator of the gut-skin axis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeebuddin, M.; Karnati, R.K.; Shiroorkar, P.N.; Nagaraja, S.; Asdaq, S.M.B.; Khalid Anwer, M.; Fattepur, S. Topical probiotics: More than a skin deep. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, M.; Huang, M.; Zhong, Q. The Bacteriocins Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Promising Applications in Promoting Gastrointestinal Health. Foods 2024, 13, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak-Kopeć, P.; Śliżewska, K. The effect of probiotics on the production of short-chain fatty acids by human intestinal microbiome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, C.M.; Lee, Y.-M. Revolutionizing cosmetic ingredients: Harnessing the power of antioxidants, probiotics, plant extracts, and peptides in personal and skin care products. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, V.; Sarkar, R.; Verma, D.; Das, A. Probiotics in Dermatology: An Evidence-based Approach. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2024, 15, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutema, I.A.M.P.; Latarissa, I.R.; Widowati, I.G.A.R.; Sartika, C.R.; Ciptasari, N.W.E.; Lestari, K. Efficacy of Probiotic Supplements and Topical Applications in the Treatment of Acne: A Scoping Review of Current Results. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2025, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, R.D.; Pontefract, B.A.; Mishcon, H.R.; Black, C.A.; Sutton, S.C.; Theberge, C.R. Gut microbiome: Profound implications for diet and disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merenstein, D.; Pot, B.; Leyer, G.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Preidis, G.A.; Elkins, C.A.; Hill, C.; Lewis, Z.T.; Shane, A.L.; Zmora, N. Emerging issues in probiotic safety: 2023 perspectives. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2185034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek-Wicher, R.; Junka, A.; Paleczny, J.; Bartoszewicz, M. Clinical trials of probiotic strains in selected disease entities. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 8854119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Li, T.; Yang, S.; Ma, L.; Cai, B.; Jia, Q.; Jiang, H.; Bai, T.; Li, Y. The prebiotic effects of fructooligosaccharides enhance the growth characteristics of Staphylococcus epidermidis and enhance the inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2025, 47, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randeni, N.; Bordiga, M.; Xu, B. A Comprehensive Review of the Triangular Relationship among Diet–Gut Microbiota–Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Habsi, N.; Al-Khalili, M.; Haque, S.A.; Elias, M.; Olqi, N.A.; Al Uraimi, T. Health Benefits of Prebiotics, Probiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorakkattu, P.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Shah, K.; Babu, K.S.; Mundanat, A.S.; Deliephan, A.; Deokar, G.S.; Santivarangkna, C.; Nirmal, N.P. Postbiotics: Current trends in food and pharmaceutical industry. Foods 2022, 11, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.; De Paepe, K.; Van de Wiele, T. Postbiotics and their health modulatory biomolecules. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida, C.V.; Antiga, E.; Lulli, M. Oral and topical probiotics and postbiotics in skincare and dermatological therapy: A concise review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.-J.; Iwasa, M.; Han, K.-I.; Kim, W.-J.; Tang, Y.; Hwang, Y.J.; Chae, J.R.; Han, W.C.; Shin, Y.-S.; Kim, E.-K. Heat-killed Enterococcus faecalis EF-2001 ameliorates atopic dermatitis in a murine model. Nutrients 2016, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, H.; Jung, B.J.; You, G.E.; Jang, S.; Chung, D.K. Lipoteichoic acid isolated from Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits melanogenesis in B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munteanu, C.; Turti, S.; Marza, S.M. Unraveling the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Microbiota in Skin Health and Disease. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12040167
Munteanu C, Turti S, Marza SM. Unraveling the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Microbiota in Skin Health and Disease. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(4):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12040167
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunteanu, Camelia, Sabina Turti, and Sorin Marian Marza. 2025. "Unraveling the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Microbiota in Skin Health and Disease" Cosmetics 12, no. 4: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12040167
APA StyleMunteanu, C., Turti, S., & Marza, S. M. (2025). Unraveling the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Microbiota in Skin Health and Disease. Cosmetics, 12(4), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12040167






