Abstract
Skin aging is a multifactorial process driven by both intrinsic mechanisms—such as telomere shortening, oxidative stress, hormonal decline, and impaired autophagy—and extrinsic influences including ultraviolet radiation, pollution, smoking, and diet. Together, these factors lead to the structural and functional deterioration of the skin, manifesting as wrinkles, pigmentation disorders, thinning, and reduced elasticity. This review provides an integrative overview of the biological, molecular, and clinical dimensions of skin aging, emphasizing the interplay between inflammation, extracellular matrix degradation, and senescence-associated signaling pathways. We examine histopathological hallmarks and molecular markers and discuss the influence of genetic and ethnic variations on aging phenotypes. Current therapeutic strategies are explored, ranging from topical agents (e.g., retinoids, antioxidants, niacinamide) to procedural interventions such as lasers, intense pulsed light, photodynamic therapy, microneedling, and injectable biostimulators. Special attention is given to emerging approaches such as microneedle delivery systems, with mention of exosome-based therapies. The review underscores the importance of personalized anti-aging regimens based on biological age, phototype, and lifestyle factors. As the field advances, integrating mechanistic insights with individualized treatment selection will be key to optimizing skin rejuvenation and preserving long-term dermal health.
Keywords:
aging; skin; dermatology; therapy; histology; biomarkers; laser; health; rejuvenation; light 1. Introduction
Skin aging is a central topic in dermatology, not only due to its esthetic implications but also because of its broader impact on skin health, function, and disease susceptibility. As the largest organ of the human body, the skin serves as a barrier, a sensory interface, and a dynamic regulator of immune and thermoregulatory processes. With age, these functions become progressively compromised, making skin aging a multidimensional challenge. Furthermore, as the global life expectancy increases and cosmetic concerns become more prevalent, understanding the mechanisms and clinical manifestations of skin aging has gained considerable importance for both preventive and therapeutic dermatology [1].
Skin aging is broadly categorized into two distinct but interrelated processes: intrinsic (chronological) aging and extrinsic (environmental) aging. Intrinsic aging reflects the natural, genetically programmed senescence of cells and tissue over time. It is characterized by epidermal thinning, decreased cellular turnover, reduced sebaceous activity, diminished elasticity, and fine wrinkling. This process is largely driven by telomere shortening, oxidative stress, DNA damage, and reduced autophagy, culminating in fibroblast dysfunction and extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation [2,3].
In contrast, extrinsic aging, often referred to as photoaging, is predominantly induced by chronic exposure to environmental insults, particularly ultraviolet (UV) radiation. UV radiation leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), DNA damage, and the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which degrade collagen and disrupt the dermal ECM. Clinically, extrinsic aging is characterized by coarse wrinkles, pigmentation irregularities, solar lentigines, telangiectasias, and actinic elastosis. Other environmental factors, such as pollution, smoking, poor nutrition, and lifestyle habits, further exacerbate these changes by inducing chronic inflammation and accelerating oxidative damage [2].
The impact of aging on skin health extends beyond cosmetic alterations. Age-related changes impair the skin’s barrier function, delay wound healing, reduce resistance to mechanical and thermal stress, and increase the susceptibility to infections and neoplasms. Histologically, aging skin demonstrates a progressive loss of dermal collagen and elastic fiber integrity, the flattening of the dermoepidermal junction, and diminished microvascular and immune functions. These changes collectively contribute to the fragile skin phenotype and complicate dermatologic care in elderly patients [4].
Given its multifactorial nature, the management of skin aging requires a comprehensive understanding of its clinical, histological, and molecular foundations. Some recent works have been published on this topic, focused on addressing different specific aspects of skin aging, such as etiology and treatment [5,6,7,8]. This review aims to provide a wider, transversal, and updated overview of the key features of skin aging, with an emphasis on clinical manifestations, histopathologic correlates, and evidence-based therapeutic strategies. Special attention is given to topical, light-based, mechanical, and minimally invasive interventions that have demonstrated efficacy in mitigating or reversing signs of aging.
2. Clinical Changes in Aging Skin
2.1. Extrinsic Aging
2.1.1. Role of UV and Blue Radiation
Solar radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation comprising three types of energy: visible light (approximately 44%), infrared radiation (around 53%), and a smaller fraction (3–7%) of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. UV radiation is further subdivided into three spectral bands based on the wavelength: UVA (320–400 nm), UVB (280–320 nm), and UVC (100–280 nm). While UVA and UVB reach the Earth’s surface and thus exert significant biological effects on the skin, UVC is almost entirely absorbed by the ozone layer. Immediately adjacent to the UVA band lies blue light (400–490 nm), which partially overlaps with the UVA region due to its location at the high-energy end of the visible spectrum [9]. Blue light originates from both natural sources (i.e., sunlight) and artificial sources such as electronic screens (LEDs, computers, televisions, mobile phones) and medical devices. Although the irradiance of electronic screens is significantly lower—up to 1000 times less than that of solar radiation—chronic and cumulative exposure has prompted investigations into its potential adverse effects on the skin, particularly in facial areas [10].
The different wavelengths and energies of radiation determine its depth of penetration and interactions with the skin. At the tissue level, UVA, due to its longer wavelength, penetrates deeper into the dermis compared to UVB and is therefore more strongly implicated in photoaging. In contrast, UVB, which possesses higher energy and a shorter wavelength, primarily affects the epidermal layer. UV photons damage the skin through two main mechanisms: direct absorption and photosensitization. In direct absorption, cellular chromophores—such as nucleic acids, amino acids (tryptophan and tyrosine), quinones, flavins, porphyrins, and urocanic acid—are capable of absorbing UV radiation and converting this energy into molecular responses that activate cellular mechanisms [11]. Among these mechanisms, the formation of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and 6-4 photoproducts (6-4PPs) is particularly relevant. These DNA lesions interfere with RNA transcription, activate the tumor suppressor gene p53, and induce apoptosis in keratinocytes [12]. Photosensitization involves the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) via UV-activated endogenous or exogenous sensitizers. These free radicals penetrate the cell nucleus and induce oxidative DNA damage and strand breaks, contributing to cellular dysfunction [13]. Oxidative stress subsequently triggers inflammatory pathways and stimulates the overexpression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), particularly MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9, which degrade key components of the extracellular matrix, such as collagen and elastin [14]. Clinically, these changes manifest as a loss of skin elasticity, wrinkle formation, hyperpigmented lesions, and impaired barrier function.
Additionally, UVA1 radiation can induce immediate pigment darkening (IPD), persistent pigment darkening (PPD), and delayed tanning (DT), particularly in individuals with darker skin phototypes (III–VI) [15]. It has been proposed that the rapid onset of pigmentation following visible light exposure is photochemical in nature, while delayed pigmentation is due to neomelanogenesis [16]. Since the primary stimulator of melanogenesis, alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), reduces the UV-induced hydrogen peroxide levels in irradiated melanocytes, a link between pigmentation and oxidative stress has been suggested [17].
Blue light, in turn, induces oxidative stress in dermal tissue mitochondria. In in vitro models, blue light within the 450–490 nm range has been shown to exert cytotoxic effects on human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes, particularly at high intensities (>30 J/cm2) [18]. This form of blue radiation has a high affinity for cutaneous chromophores such as flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and flavoproteins, triggering photoreactions similar to those induced by UVA radiation [19].
At lower intensities, blue light reduces the expression of antimicrobial peptides and slows epidermal regeneration, thereby compromising skin integrity. Additionally, it has been associated with reduced cell viability and increased expression of inflammatory markers at the epidermal level [20].
Moreover, blue light stimulates melanogenesis through the G-protein-coupled membrane receptor opsin-3 [21,22]. In individuals with darker skin, sustained tyrosinase activity leads to the formation of tyrosinase-associated protein complexes, which are responsible for the prolonged hyperpigmentation characteristic of these phototypes [9].
2.1.2. Clinical Manifestations
Although wrinkles are part of intrinsic skin aging, external factors—primarily UVA radiation—significantly contribute to the appearance of deeper and more numerous wrinkles [23,24,25,26].
The increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) activates inflammatory metabolic pathways, proinflammatory cytokines, and degradative enzymes such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), particularly MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9, which degrade type I and III collagen fibers—the main structures responsible for skin firmness and tensile strength [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36].
The degradation of the extracellular matrix prevents the proper regeneration of dermal components, leading to the structural collapse of the skin and the progressive formation of wrinkles and folds [34,35].
Solar lentigines are benign pigmented lesions that result from chronic sun exposure. Histologically, they are characterized by hyperpigmentation of the basal epidermal layer and irregular melanosome distribution. They arise due to melanocytic hyperplasia induced by UV radiation, visible light, and other environmental factors [36,37,38,39,40].
The role of p53 has been demonstrated in the induction of skin pigmentation after UVB exposure, through the increased expression of the pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) transcriptome in keratinocytes. Additionally, stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF1) deficiency in senescent fibroblasts, caused by changes in DNA promoter methylation, acts as a potent stimulus for melanogenic processes, contributing to uneven skin pigmentation [41,42,43].
Solar elastosis is a prominent clinical and histological manifestation of photoaging. It is characterized by dermal thickening with the accumulation of abnormal elastotic material. Similarly to wrinkle formation, ROS generated after UV exposure chronically activate MMPs, particularly MMP-9 and MMP-12, which appear to play a significant role in the development of solar elastosis [44,45,46].
Telangiectasias are visible dilations of superficial capillaries, predominantly found on the cheeks, nose, and auricular regions. Although their association with cutaneous aging, particularly in higher phototypes, is well established, the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. It is hypothesized that various factors, especially UV radiation, may induce the downregulation of angiogenesis inhibitors such as thrombospondin-1, thereby promoting vascular proliferation [47,48,49].
It has also been described that UV radiation can increase the production of nitric oxide at the cutaneous level. Although this phenomenon is considered positive from a cardiovascular perspective, it could facilitate the development of cutaneous telangiectasias by perpetuating vasodilation [50,51,52,53].
2.1.3. Impact of Lifestyle Factors
Extrinsic aging is not solely determined by solar radiation; various lifestyle factors also play a fundamental role in the progressive deterioration of the skin. Among these, environmental pollution, smoking, inadequate nutrition, lack of sleep, and exposure to other sources of radiation, such as infrared and visible blue light, are particularly significant. These factors act synergistically, exacerbating oxidative, inflammatory, and structural damage in the skin.
This set of external factors that act on our skin and can accelerate skin damage and aging has been grouped under the term “exposome”. Below, we will describe in more detail three of the exposome components that have been most strongly linked to skin aging: environmental pollution, smoking, and diet [54].
Environmental Pollution
Multiple environmental pollutants have been associated with an increase in signs of photoaging, including wrinkles and lentigines. Significant contributors include air quality index (AQI) measurements, nitrogen dioxide (NO2), fine particulate matter (PM2.5), exposure to fossil fuels, soot, and traffic-related air pollution [55,56,57,58,59,60]. It is likely that pollution acts synergistically with UV radiation, leading to a significant increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) [54].
Ozone (O3) is probably the most extensively studied environmental compound in dermatology. Although its skin penetration is limited, it can oxidize lipids and proteins in the stratum corneum, deplete endogenous antioxidant mechanisms, and even reduce the efficacy of exogenous antioxidants such as vitamins C and E [61,62,63]. Ozone (O3) has also been studied for its ability to dysregulate inflammatory pathways, particularly the activation of the NF-κB pathway and an increase in interleukin-8 (IL-8) production, thus creating a pro-inflammatory environment. Additionally, O3 exposure can enhance the expression of MMP-9 and COX-2, leading to a reduction in the type I and III collagen levels in the dermis, contributing to the acceleration of skin aging [64,65].
Regarding other environmental pollutants, an epidemiological study associated air pollution with the development of lentigines in both Caucasian and Asian populations. The activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in epidermal cells by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) present in polluted air may explain the underlying pathophysiological mechanism behind these observations [58,66].
Smoking
Tobacco smoke contains more than 4000 potentially toxic chemical substances. The association between smoking and premature skin aging has been documented in numerous studies. This effect appears to be dose-dependent [67,68,69,70,71].
Smoking increases elastic fibers within the reticular dermis, producing changes similar to those observed in solar elastosis. In vitro studies have demonstrated that tobacco use induces the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 3 (MMP-1 and MMP-3), which are involved in collagen degradation. Furthermore, smoking reduces the activity of transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) and the expression of its receptors [72,73,74,75].
A recent meta-analysis concluded that there is a clear association between active smoking and various manifestations of skin aging, although this association is less evident in former smokers [7].
Diet
Water, proteins, and lipids constitute the primary building blocks for skin construction [76,77,78,79]. Although essential in maintaining the cellular structure, excessive lipid intake can alter the skin composition, leading to negative effects [80]. Excessive lipid intake can impair the collagen structure of the skin and delay wound healing. Additionally, it promotes a pro-inflammatory skin environment through increased cytokine production (such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)) and the activation of inflammasome components. Clinically, this phenomenon is reflected in psoriasis, where pro-inflammatory diets rich in lipids exacerbate the disease [81,82,83,84,85].
However, not all effects of lipids are detrimental. Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids have demonstrated beneficial effects in the prevention and treatment of skin inflammation, as well as protective roles against UV radiation and environmental pollutants. Although in vivo evidence remains limited, the effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids have been studied in vitro [79,86,87,88,89].
Processed sugars have been associated with the abnormal glycation of skin components, contributing to skin aging [90,91].
The antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and depigmenting properties of vitamins C and E are well known. Vitamin C, in addition to its antioxidant action, is essential for proper collagen synthesis. The combination of both vitamins improves the stability of vitamin E and enhances its protective action, reducing UV-induced damage and helping to prevent lipid oxidation caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) [92,93,94,95].
The role of vitamin D has gained increasing importance in recent years. The active metabolites of vitamin D3 exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and DNA repair effects. These compounds activate nuclear receptors such as VDR, AhR, LXR, and RORα/γ and also participate in non-genomic mechanisms through the 1,25D3-MARRS receptor. Additionally, they stimulate antioxidant pathways, such as the activation of Nrf2 and DNA repair mechanisms mediated by p53, while simultaneously inhibiting pro-inflammatory pathways like NF-κB. From an inflammatory perspective, vitamin D is capable of regulating B and T lymphocyte activity at the cutaneous level, as well as modulating the production of various pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1, IL-6, IL-9, IL-17) [96,97,98,99,100].
Vitamin D also plays an important role in reducing the activation of the NF-κB pro-inflammatory pathway [101,102]. Furthermore, vitamin D increases the expression of the transcription factor Nrf2, which regulates key antioxidant defense genes such as CAT, SOD-1, and SOD-2 [103,104]. Vitamin D also contributes to the production and activation of p53, enhances other DNA repair mechanisms that reduce UVB-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs), and regulates keratinocyte apoptosis in response to solar damage [105,106,107,108]. In addition to the major nutrients and vitamins, other dietary elements can contribute to reducing skin aging: collagen and its derived peptides, when administered as nutritional supplements, contribute to the synthesis of collagen and hyaluronic acid by dermal fibroblasts and may play a role in reducing oxidative stress [109,110]. Polyphenols exert antioxidant effects, also helping to reduce cutaneous oxidative stress. In a review published by Cao et al., numerous studies are compiled highlighting the antioxidant role of polyphenol-rich extracts [109].
2.2. Intrinsic Aging
2.2.1. Genetic and Hormonal Influences
Skin aging is driven by both intrinsic (chronological) and extrinsic (environmental) factors, with the former being strongly influenced by genetic predisposition and hormonal changes. Below are the main genetic and hormonal alterations associated with cutaneous aging.
Genetic Changes
Genetic predisposition plays a major role in the aging process and the condition of an individual’s skin. Certain genes are involved in the regulation of cellular repair, responses to oxidative stress, and the synthesis of structural proteins such as collagen and elastin. Notably, many of the genes implicated in skin aging exhibit pleiotropy, meaning that they influence multiple phenotypic traits. Among these key genes, single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are predominantly located within a small group of 44 central pleiotropic genes and 32 genes associated with skin pigmentation, many of which are clustered in chromosomal band 16q24.3 [111].
Transcriptomic analyses have further revealed that most of the genes identified in the context of aging are differentially expressed with age, indicating a functional link between gene expression profiles and skin aging [112]. Additionally, genes traditionally linked to skin pigmentation also play significant roles in other skin phenotypes, such as wrinkle formation and loss of elasticity, reinforcing their pleiotropic character [113].
Moreover, familial background can exert a strong influence on aging trajectories. Individuals with family members who exhibit slower aging processes, including better skin condition, are more likely to experience delayed cutaneous aging themselves. This observation further supports the notion that genetic factors play a crucial role in the biological aging process [114].
Hormonal Changes
Menopause leads to significant hormonal alterations, particularly a decline in estrogen levels, which profoundly impacts skin aging due to the presence of estrogen receptors in it. The skin expresses two isoforms of nuclear estrogen receptors: ERα (restricted to sebaceous and eccrine glands) and ERβ (widely distributed in dermal fibroblasts, sebocytes, adipocytes, melanocytes, and keratinocytes) [115]. Estrogen is essential in maintaining skin thickness, hydration, and elasticity. Since the collagen and elastin profiles in the skin mirror the 17β-estradiol levels throughout aging and during and after menopause [116], its decline leads to reduced collagen synthesis, decreased skin hydration, and increased wrinkle formation. Consequently, postmenopausal women typically experience accelerated skin aging characterized by dryness, thinning, and loss of elasticity [117,118].
In men, the age-related decline in testosterone levels also affects skin health. Like estrogen, testosterone helps to maintain skin thickness and sebum production, and its reduction can result in drier skin and diminished elasticity. Although these effects are generally less pronounced than those associated with declining estrogen, they contribute to the overall aging process of the skin [117].
Other hormones, such as growth hormone (GH) and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), also influence skin aging and decline with age [119]. GH stimulates cellular regeneration and repair, while DHEA contributes to sebum production, supporting skin hydration and barrier function [120]. Thus, age-related reductions in these hormones lead to increased skin dryness, decreased elasticity, impaired tissue regeneration, and reduced protection against UV radiation [121].
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), a hormone that mediates the effects of pituitary GH, is primarily produced in the liver but is also locally synthesized by dermal fibroblasts. In senescent fibroblasts, IGF-1 production is significantly reduced, leading to atrophy in connective tissue-rich organs such as the skin and contributing to an aged skin phenotype [122]. Keratinocytes do not synthesize IGF-1 and thus depend on its local availability to maintain homeostasis. Since IGF-1 inhibits the activation of matrix-degrading metalloproteinases (MMPs) [123], its deficiency reduces epidermal cell proliferation and differentiation, resulting in atrophy and compromised barrier function [124].
Oxytocin (OXT), a neuropeptide synthesized in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary, is also produced in various extraneural tissue types. In the cutaneous context, both OXT and its receptor (OXTR) are expressed in human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes. Studies in animal models have demonstrated the protective and anti-inflammatory effects of OXT, including reduced ROS levels, increased glutathione concentrations, and decreased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 [125].
Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine), a hormone secreted by the pineal gland and primarily involved in circadian rhythm regulation, is also produced by extrapineal sites, including the skin. In the skin, melatonin undergoes phototransformation upon UVA/UVB exposure and oxidative stress, generating metabolites such as 6-hydroxymelatonin and acetylserotonine, which have antioxidant properties [126]. Moreover, melatonin exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects, participates in DNA repair by reducing p53 activation, and modulates mitochondrial function via tyrosinase activity [127].
Finally, retinoids—compounds derived from retinol (vitamin A)—exert beneficial effects on nearly all skin cell types. In keratinocytes, they promote differentiation; in fibroblasts, they enhance the expression of collagen types I and III, elastin, fibronectin, and glycosaminoglycans, while reducing collagenase activity; in melanocytes, they suppress tyrosinase activity and melanin production; and, in sebocytes, they inhibit proliferation and lipid synthesis, accounting for their sebosuppressive effects [128]. Although plasma retinol levels do not vary significantly with age [129], its cutaneous functionality is impaired by factors such as UVB exposure, oxidative stress, and aging, since UVB radiation reduces epidermal retinol concentrations and the expression of retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR-α) and gamma (RAR-γ), leading to a functional vitamin A deficiency in the skin [130].
2.2.2. Other Intrinsic Factors Related to Aging
Metabolic Processes
Metabolism influences skin aging through its role in regulating cellular energy production, nutrient supply, and waste removal. As metabolic processes slow with age, cells receive reduced energy and nutrients, impairing their function and regenerative capacity. Diminished metabolic activity also results in the slower elimination of cellular waste, contributing to the accumulation of damaged proteins and lipids in the skin [131]. Additionally, metabolic activity can generate advanced glycation end products (AGEs)—proteins or lipids that become glycated due to exposure to sugars. AGEs can cross-link collagen fibers, making them stiff and less elastic, which contributes to wrinkle formation and reduced skin elasticity [132].
Immune System Deterioration
The immune system plays a crucial role in maintaining skin health by defending against pathogens, supporting wound healing, and regulating inflammation. With aging, the immune system becomes less efficient—a phenomenon known as immunosenescence. This decline results in reduced skin resilience, slower wound healing, and increased susceptibility to infections and cutaneous disorders. Age-related immune dysfunction is characterized by a decrease in both the number and functionality of immune cells, including T lymphocytes and macrophages, which compromises the skin’s ability to respond to insults and repair itself effectively [133]. Moreover, aging is frequently associated with chronic low-grade inflammation. This persistent inflammation is marked by elevated levels of inflammatory markers and cytokines, which can damage skin cells and extracellular matrix components, thereby accelerating the aging process [134].
2.2.3. Clinical Features: Skin Thinning, Dryness, Fine Wrinkles, and Loss of Elasticity
The clinical manifestations of intrinsic photoaging often parallel those of extrinsic photoaging, making it virtually impossible to clearly distinguish between changes caused exclusively by chronological skin aging and those induced by external factors. Cutaneous changes associated with normal aging include impaired barrier function, cutaneous immunosenescence, alterations in cellular turnover and wound healing responses, dysregulation of vasomotor phenomena, changes in sebaceous and sweat gland secretions, alterations in sensitivity and proprioception, and a decreased capacity for vitamin D synthesis, among others. Clinically, this is manifested as skin thinning, dryness, loss of elasticity, increased wrinkling, and pigmentary alterations [135].
Skin thinning is often attributed to intrinsic aging. Histologically, it correlates with the flattening of the dermoepidermal junction and a reduction in the contact surface area between the dermis and the epidermis [2,3,25,136].
Clinically, this results in thinner, more fragile skin, a condition that has been recently described under different terms, such as dermatoporosis, cutaneous insufficiency, or skin failure. This emerging concept refers to the compromised ability of aged skin to repair itself, properly heal wounds, and, in advanced stages, even maintain its own structural integrity [137,138,139,140,141,142,143]. Figure 1 shows a schematic representation of the intrinsic and extrinsic factors of skin aging.
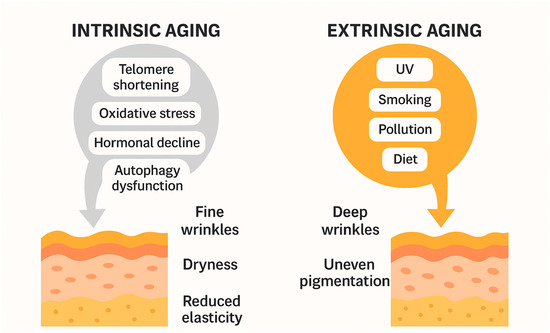
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration comparing intrinsic and extrinsic aging mechanisms.
2.2.4. Differences in Skin Aging Patterns Based on Phototypes
Facial aging in Fitzpatrick skin types V–VI exhibits unique characteristics due to structural and functional differences in the skin and facial skeleton. African American skin is characterized by a thicker stratum corneum, increased fibroblast activity, and larger, more dispersed melanosomes, conferring greater skin thickness, improved elasticity, and natural protection against photoaging. This explains the delayed onset of wrinkles, generally beginning in the fifth decade of life, and their reduced severity compared to individuals with lighter skin tones [136,144,145,146,147,148,149].
Fitzpatrick skin types V–VI present distinct anthropometric characteristics in their facial morphology. A greater forehead height is noted, accompanied by shorter nasal and ear lengths. Additionally, they exhibit a broader nasal base due to an increased alar width, as well as a wider palpebral fissure and mouth width. The lips are generally prominent. Ocular proptosis is also characteristic, with anterior displacement of the eyeballs, resulting in scleral show and increased infraorbital shadowing. Lastly, bimaxillary protrusion—the forward positioning of both jaws—contributes to greater overall facial convexity [148,149,150]. These anatomical features correlate with clinical findings. With age, the midface shows marked eyelid laxity, descent of the malar fat pads, and the early formation of nasolabial folds [136,148,149,151,152]. Although brow ptosis occurs, it tends to be less pronounced than in other ethnic groups [149].
Submental fat accumulation combined with thicker cervical skin contributes to a more obtuse and less defined cervicomental angle with aging. Lip aging is minimal in this population, with less volume loss and reduced perioral lentigo formation. Overall, the aging pattern in this group emphasizes facial volume redistribution more than the formation of fine wrinkles [136,145,148,149]. Asian skin tends to show fewer visible wrinkles during the early decades of life, with a delay in the appearance of fine lines until the fifth decade.
Pigmentary photoaging predominates over wrinkle formation, with the early onset of solar lentigines, melasma, and pigmented seborrheic keratoses. It has been suggested that the higher lipid content of the stratum corneum may enhance the persistence and adverse effects of environmental pollutants [148,149].
East Asians (Chinese, Japanese, Koreans) typically present with a broader facial structure (increased bitemporal and bizygomatic width) and a flatter facial profile. The nasal bridge is usually lower, the upper eyelid is fuller, and the supratarsal crease is lower. Aging in this group includes pronounced malar fat pad descent, infraorbital shadowing, and the predominance of wrinkle formation around the periorbital and perioral areas [136,148,149].
Differences in skin aging depending on phototypes are compiled in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparative table summarizing structural and clinical aging patterns observed in Black, Asian, and Caucasian skin.
3. Alterations in the Histology of Aging Skin
Throughout the aging process, the skin endures intricate structural changes that influence all skin layers and annexes. The histological appearance of a normal epidermis is illustrated in Figure 2. The superficial dermis in individuals under the age of 50 exhibits a porous structure, with collagen fibers that are thin and have varying orientations. However denser, non-oriented collagen fibers are observed in the deep dermis compared to the superficial dermis. These aspects are still present after 50 years, with some changes becoming more apparent as individuals age. The significance of comprehending the fundamental changes in the epidermis and its conjunctive components to gain a more complete understanding of the aging process is underscored by several studies [153,154,155].
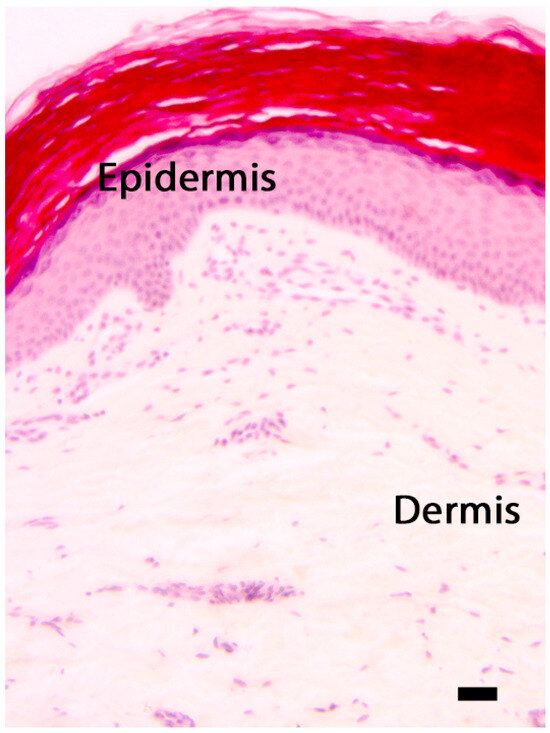
Figure 2.
The skin: morphological differences between the epidermis and the dermis. Hematoxylin–eosin, scale bar = 10 microns. The photograph is the property of one of the authors (SB).
The aging processes of both types of collagen fibers occur at approximately the same age and proceed in tandem with the changes that affect elastic fibers after the age of 50. Collagen fibers endure changes. The process commences with the narrowest fibers being impacted, followed by the fragmentation and rupture of more superficial dermis fibers. This leads to a progressive reduction in the thickness and density of the superficial dermis, resulting in a thicker appearance of collagen fibers. The thinning is a result of the quantitative reduction in collagen fibers, whereas the increased density is a result of the lysation of the narrowest fibers, which vanish almost completely, leaving only slightly bulkier ones [154,155].
The deep dermis also experiences changes, as collagen fibers begin to thicken to a certain extent, thereby supplying the deep dermis with a specific density. This thickening of collagen fibers in the subsurface stratum is a compensatory response to the reduced skin resistance at the surface. Fragmentation processes and the gradual, progressive amplification of collagen fiber fragmentation and lysis occur as the deep dermis matures. Microscopic examinations demonstrate that the lysis of certain collagen fibers induces the formation of spaces between the remaining fibers, which initially appear diminutive but expand in size. The deep dermis becomes more fibrous as collagen fibers become increasingly thick by the age of 70 [154,155].
Histological investigations have demonstrated that collagen fibers are present in the deep dermis in individuals aged 75–80, with the fibrils becoming more flexible and tussled. The strength of collagen fibers is diminished as a result of this process, as they are not as densely packed. The dermis’s resistance to the epidermis is directly impacted by this process, which continues to affect additional structural components [154,155].
Elastic fibers also endure substantial modifications. Elastic fibers are sparse and comparatively long in the superficial dermis in subjects under the age of 50, but they are denser and longer in the deep dermis. Several changes become more apparent as individuals age after 50 years. At the outset, there is a propensity for the fragmentation of a limited number of elastic fibers, both in the superficial and deep dermis. The superficial dermis progressively thins and loses its flaccid appearance by the age of 55. The tinctorial affinity of and quantitative reduction in elastic fibers result in a greater degree of fragmentation [154,155].
Elastic fibers exhibit progressive thickening in the deep dermis, and elastolysis processes are documented. The aspect of fragmentation becomes more apparent during aging, as a result of the more pronounced thickening of elastic fibers and the fact that a few fibers maintain an elongated appearance [154,155].
The fragmentation process has an impact on all elastic fibers, with numerous fragments demonstrating structural modifications and tinctorial affinity. The progressive processes of elastolysis are responsible for the incremental loss of elastic fibers. Significant differences in skin vasculature have been revealed by histological investigations, which implies a direct correlation with skin aging processes. Subjects under the age of 50 exhibit a highly vascularized superficial dermis with a high number of small caliber vessels.
The vasculature is well represented in regions with a thicker epidermis, where the superficial dermis exhibits papillae [154,155]. The diameter of the vessels progressively decreases as a result of discrete but progressive changes in vessel size that occur at the onset of aging processes. As long as the superficial dermis remains relatively lax, study results indicate that the number of vessels does not decrease significantly, even in more advanced stages of aging [154,155].
When the superficial dermis loses its papillary aspect, it becomes thinner and increasingly dense, resulting in a progressive reduction in the size and number of blood vessels. They become scarce and diminutive as the process of senescence advances, resulting in a numerical decline. The progressive reduction in the dermal vasculature is represented by a progressive numerical reduction and a reduction in size, which is a result of modifications to the vascular wall components [154,155].
The degenerative and alterative processes that affect the components of the vascular walls do not affect all vessels simultaneously, as some areas may have a greater number of vessels and progress at a quicker pace. The vessels with the narrowest walls, which are the smallest in all cases examined, seem to be the most susceptible. Alternative processes were also observed in the case of certain larger caliber vessels with denser walls [154,155].
The tendency of thrombus organization to occupy the vessel lumen, which makes circulation more difficult and accentuates processes of stasis and enlargement, suggests the loss of functionality in some vessels. The morphological characteristics of the epidermis indicate that the vasculature is distinct based on the time of investigation [154,155]. Table 2 summarizes the histological alterations that occur during skin aging.

Table 2.
Layer-specific summary of skin aging changes, including approximate age of onset and associated clinical manifestations.
3.1. The Molecular Mechanisms of Skin Aging
3.1.1. Telomere Shortening
Telomeres, which are situated at the termini of linear chromosomes in eukaryotes, are essential for the prevention of degradation or fusion with the chromosomes that surround them. Telomere shortening is indicative of the malfunction of this protective mechanism, which results in cellular senescence and aging. In order to preserve the length of telomeres, telomerase incorporates the telomeric sequence TTAGGG. The DNA damage response (DDR) pathway and downstream effectors, such as cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p16 and p21, are activated by telomeres, which are significant in chronological skin aging. This causes cell cycle arrest. The intrinsic aging-induced cellular senescence that is a result of cell division can be attributed to the gradual shortening of telomeres [156,157].
3.1.2. Oxidative Stress and MMPs
The relationship between skin aging and oxidative stress and/or matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) has been the subject of numerous studies over the past three decades. The chronological aging process is significantly influenced by reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are essential for mitochondrial aerobic metabolism. Skin inflammation and wrinkle formation are induced by ROS in sun-protected regions. The transmembrane signaling pathway is disrupted by oxidative stress, resulting in DNA damage and an increase in the expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and MMPs. MMPs, a superfamily of zinc-containing metalloproteinases, have the ability to degrade ECM molecules, thereby decreasing collagen synthesis. The oxidation of macromolecules, including cellular lipids, proteins, and DNA, is also a consequence of elevated ROS levels, which results in cellular dysfunction. The primary biomarker of aging is oxidative protein damage, which is frequently observed in the photodamaged epidermis. Lipofuscin accumulates as the cell matures, resulting in the formation of “age spots”. Lipofuscin serves as a redox-active site for free radicals and proteasome inhibitors, thereby initiating a cycle that contributes to protein aggregation [156,157].
Increased ROS also results in the oxidation of macromolecules, such as cellular lipids, proteins, and DNA, leading to cellular dysfunction with aging.
3.1.3. The Role of Cytokines in Aging Skin
The activation of numerous inflammatory signaling pathways through surface receptors such as epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors, transforming growth factor (TGF) receptor, Toll-like receptors, interleukin 1 (IL-1) receptor, and TNF receptor is a critical feature of the skin aging process by cytokines. Major cytokines secreted by keratinocytes include interleukins, colony-stimulating factors (CSFs), TGF-α, TGF-β, TNF-α, and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). Through the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), UV radiation can either directly or indirectly activate signaling, resulting in inflammation and age-related diseases, including type 2 diabetes, arthritis, and dementia [156,157]. TNF-α, a primary effector cytokine in cutaneous proinflammatory processes, induces the elevation of MMP-9 and inhibits collagen synthesis. The epidermis is irreversibly damaged as a result of persistent exposure to TNF-α, which disrupts MMP-9 production. Multiple pathways, such as NF-κB, AP1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α), and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf-2), are associated with elevated TNF-α levels [156,157]. The IL-1 levels in the epidermis increase with age, which in turn triggers age-related processes by promoting skin inflammation. The synthesis of IL-1 decreases with age, while the IL-1 related proinflammatory response is stimulated by IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra). Key transcription factors associated with inflammatory and immune responses, including NF-κB, AP-1, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and MAPKs, are induced by IL-1 and IL-6. The pathogenesis of numerous age-related maladies is linked to IL-18, a cytokine from the IL-1 superfamily [156,157]. In the dermal fibroblasts of the aged human epidermis, cysteine-rich protein 61 (CCN1), an ECM-associated matricellular protein, can be induced. This process stimulates MMP-1 production and downregulates the TGF-β type II receptor, thereby preventing TGF-β signaling, which is essential in maintaining ECM homeostasis.
3.1.4. Regulation of Autophagy
Autophagy (ATG) is a critical cell self-digestion mechanism that transports harmful or damaged proteins, lipids, and other cellular constituents to the lysosome for enzymatic degradation. It is composed of five primary stages: initiation, nucleation, elongation, fusion, and payload degradation. The activity of ATG-related proteins, LC3, and GABA type A receptor-associated protein is regulated by the ubiquitin-like conjugation system. Autophagic processes prevent stress-induced cellular senescence and extend the replicative lifespan of cells. Nevertheless, the relationship between ATG and epidermis degeneration remains ambiguous. Aging and ATG are distinct processes, as indicated by numerous investigations [154,155,156,157].
3.1.5. Skin Aging and Apoptosis
Apoptosis, a process that eliminates damaged cells without inducing inflammation, can be a double-edged weapon in the context of aging. The persistence of functionally deficient post-mitotic cells can result from the resistance of aging cells to apoptosis that can develop during low-level chronic stress events. Host defense mechanisms can exacerbate anti-apoptotic signaling, resulting in a senescent, pro-inflammatory phenotype, as aging cells are significantly resistant to apoptosis. The primary cause of age-related resistance to apoptosis is a functional deficiency in the p53 network. p53 is a transcription factor that serves as a gatekeeper for DNA mutations, and DNA damage activates checkpoint pathways and DNA repair mechanisms. In the extracellular matrix (ER), the stress recognition system experiences a decline as it ages, thereby preventing apoptosis. In a murine model, it was found that the functional activity of p53 decreases as it ages, and the premature aging that is induced by the forced activation of p53 does not correspond to a physiological aging process [156,157].
3.1.6. The Function of MicroRNAs in the Aging of the Skin
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that are involved in a variety of biological and pathological processes, including aging, and regulate the translation of mRNAs. Their expression can function as a biomarker of aging, including chronological aging and photoaging, as well as age-related maladies. The regulation of molecules implicated in the insulin-like growth factor 1 and mTOR signaling pathways is related to the role of miRNAs in skin aging. During replicative senescence, an analysis of age-associated cutaneous mRNAs in keratinocytes revealed an increase in the expression of miR-130, miR-138, and miR-181a/b, which target the p63 and sirtuin 1 mRNAs. The upregulation of miR-137 and miR-668 is linked to β-galactosidase activity, whereas miR-191 can obstruct the G1–S phase transition, resulting in cell cycle arrest and a quiescent state. In senescent epidermis fibroblasts, miRNA deregulation is linked to the decreased expression of transmembrane receptors and ECM components. Senescent dermal fibroblasts exhibit elevated miRNA levels, which influence all stages of the cellular life cycle. Through the downregulation of integrin alpha 5, miR-152 has the potential to reduce dermal fibroblast adhesion. The expression of the B-Myb transcription factor is regulated by the upregulation of the miR-29 and miR-30 miRNA families during fibroblast senescence. The downregulation of critical molecules in the TGF-β signaling pathway is associated with the overexpression of miR-449 and miR-9 in Langerhans cells, which leads to a reduction in the function of Langerhans cells [156,157].
3.1.7. The Microbiome of the Skin
The human microbiome, which encompasses all microorganisms identified in human tissue, is an essential element of the epidermal barrier system. It is home to viruses, fungi, and up to one million bacteria per square centimeter of surface area. Aging is one of the numerous pathologic conditions that can result from imbalances in the epidermis microbiota. The epidermis microbiome’s composition is contingent upon demographic characteristics, physiological conditions, antibacterial treatment, and preservation measures. Research has demonstrated that the epidermis microbiome undergoes changes and diversification as individuals age, with elderly individuals exhibiting a greater degree of alpha diversity and a greater susceptibility to pathogenic invasion. The density of lipophilic bacteria on the skin increases with sebaceous levels during puberty, whereas the density is reduced in geriatric skin. It has been demonstrated that the microbial distribution on the cranium varies among age categories, with Firmicutes being more prevalent in the youngest age group. Moreover, significant disparities in the microbial composition of the geriatric and younger groups were observed in age-related microbiota profiles for intrinsic skin aging and photoaging, The elevated enrichment of nine microbial communities and 18 pathways in the skin microbiome is a significant factor in skin aging [156,157]. A schematic representation of the molecular markers of skin aging is depicted in Figure 3.
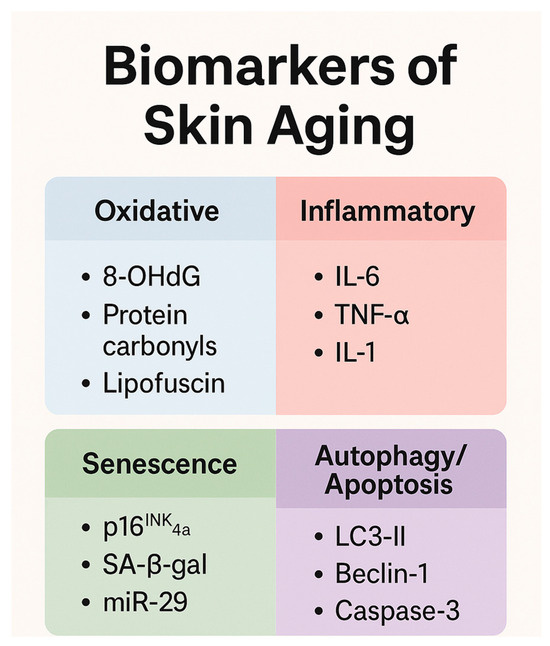
Figure 3.
Summary of key biomarkers involved in skin aging, grouped by pathophysiological pathway.
4. Therapeutic Approaches to Skin Aging
4.1. Topical Therapies
Topical cosmetics are the main approach regarding non-invasive strategies for the treatment of skin aging. Their mechanisms vary from stimulating cellular turnover and collagen synthesis to reducing oxidative stress or improving epidermal barrier function. A well-structured regimen can significantly delay the visible signs of aging and enhance skin quality [158].
As some of the most studied actives, retinoids (vitamin A derivatives) stand as the gold standard in treating skin aging. Retinol, the most commonly used form in over-the-counter formulations, promotes epidermal renewal and dermal collagen production, visibly improving fine lines, rough texture, and pigmentation. Clinical studies confirm its efficacy in long-term use [159]. Nevertheless, retinoids are associated with skin irritation and teratogenicity, making them unsuitable during pregnancy and for patients with sensitive skin. In such cases, alternative agents like glycolic acid and azelaic acid offer evidence-based and well-tolerated options [158,160].
Retinaldehyde is a first-generation retinoid used in cosmeceuticals as a direct precursor of retinoic acid. It offers greater biological potency than retinol while maintaining better skin tolerability compared to retinoic acid, thus providing an optimal balance between efficacy and safety. Clinical studies have shown that concentrations of 0.05–0.1% improve the epidermal thickness, skin elasticity, and hydration, with effects comparable to glycolic acid peels and good tolerability even with long-term use. Its low irritancy combined with its ability to induce both epidermal and dermal remodeling makes retinaldehyde a key active ingredient in anti-aging formulations [158,160].
Glycolic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) of low molecular weight. Glycolic acid acts as a chemical exfoliant by loosening corneocyte adhesions, promoting epidermal renewal, and stimulating dermal fibroblasts. This dual action enhances the skin texture and decreases wrinkles and pigmentation [161]. Concentrations of around 10% in formulations with a pH above 3.5 are typically used for anti-aging purposes in daily care products. Long-term use leads to dermal thickening and wrinkle reduction, with studies demonstrating efficacy even after 12 months of use. Higher concentrations are used in dermatologic procedures such as chemical peels. However, gradual introduction is advised due to glycolic acid’s potential irritative effects, especially in sensitive skin types [159,160,161].
Azelaic acid is a dicarboxylic acid that exhibits anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antibacterial, and depigmenting properties. Azelaic acid downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibits tyrosinase, being a valuable agent against both “inflammaging” and hyperpigmentation [162]. Azelaic acid is photostable, non-photosensitizing, and safe for use during pregnancy and lactation. The typical concentrations of azelaic acid range from 10% to 20%, with good tolerance, making azelaic acid a viable long-term option for low-irritation routines [162,163].
Another essential pillar in aging prevention is the use of topical antioxidants, especially in combination with broad-spectrum sunscreens. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is the most researched topical antioxidant, with proven benefits in neutralizing free radicals, stimulating collagen production, and inhibiting melanogenesis [158,159]. In addition to pure ascorbic acid, modern formulations increasingly include botanical antioxidants, such as flavonoids, polyphenols, and carotenoids from fruits, vegetables, and algae. The synergistic use of antioxidants in the morning, followed by sunscreen, provides enhanced photoprotection against both ultraviolet and visible light-induced oxidative damage [159].
A multifunctional ingredient of interest is niacinamide (vitamin B3). This water-soluble vitamin acts as a precursor to NAD+/NADH, which are essential coenzymes for cellular energy metabolism, DNA repair, and oxidative stress regulation. Niacinamide has demonstrated broad-spectrum effects: it improves fibroblast proliferation and dermal matrix integrity, increases collagen and elastin synthesis, and strengthens epidermal barrier function by reducing transepidermal water loss [164]. Niacinamide also possesses anti-inflammatory properties and the ability to inhibit melanosome transfer to keratinocytes, making it effective in treating hyperpigmentation disorders such as melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation [165]. Niacinamide is well tolerated in all skin types and typically used in concentrations from 2% to 10%. Its formulation versatility, photostability, and affordability make it one of the most widely adopted ingredients in modern anti-aging skincare [166].
Finally, any topical anti-aging strategy must be completed with hydration and barrier maintenance. Aging skin is more vulnerable to transepidermal water loss and barrier disruption due to lipid deficiency and the thinning of the stratum corneum. Topical products containing humectants (e.g., glycerin, hyaluronic acid), emollients, and barrier-restoring agents (e.g., ceramides, cholesterol, fatty acids) play a complementary role in maintaining skin and improving the efficacy of antiaging products [159].
4.2. Light-Based Therapies
4.2.1. Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)
Intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy is a widely used non-invasive technique for skin rejuvenation, particularly effective in treating the clinical manifestations of photoaging, such as dyschromia, telangiectasias, lentigines, and overall skin texture irregularities. Unlike lasers, which operate at a single wavelength, IPL devices emit non-coherent, broad-spectrum light typically ranging from 500 to 1200 nm. This light can be filtered to selectively target chromophores such as melanin and hemoglobin, enabling the simultaneous treatment of pigmentary and vascular lesions with a single device [167].
The mechanism of action of IPL is based on the principle of selective photothermolysis. Energy from the light source is absorbed by specific targets in the skin, generating heat and leading to the controlled destruction of undesired tissue structures, such as pigmented lesions or dilated capillaries, while sparing the surrounding healthy tissue. In addition, IPL has been shown to stimulate dermal fibroblasts and increase collagen synthesis, likely through sublethal thermal injury and the activation of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway. This dermal remodeling contributes to improved skin elasticity and reduced fine lines, thereby complementing its pigment-corrective effects [167,168].
Clinical studies have reported significant improvements in skin tone, pigmentation uniformity, and surface smoothness following IPL treatments, with high patient satisfaction and minimal downtime. Typically, a series of three to six sessions spaced 3–4 weeks apart is recommended to achieve optimal results. Maintenance sessions may be performed every 6–12 months depending on the degree of photodamage and patient expectations [168].
One of the advantages of IPL is its relatively favorable safety profile. Side effects are generally mild and transient, including erythema, edema, and a sensation of warmth during and shortly after the procedure. The risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or blistering is low when appropriate settings are used and when patients adhere to strict photoprotection post-treatment. Nonetheless, caution is advised in patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV–VI, who are more prone to pigmentary alterations [167].
In comparative studies, IPL has demonstrated efficacy similar to that of certain non-ablative lasers for pigmentary and vascular components of photoaging. However, for deeper wrinkles and advanced dermal laxity, IPL may be less effective than ablative laser modalities. Emerging protocols increasingly combine IPL with other energy-based devices, such as fractional lasers or radiofrequency, to maximize the therapeutic outcomes by targeting multiple aging pathways simultaneously [167,168].
4.2.2. Laser Therapies
Laser technologies for skin rejuvenation can be broadly categorized into ablative and non-ablative modalities, each with distinct mechanisms and clinical implications. Ablative lasers, such as CO2 (10,600 nm) and Er:YAG (2940 nm), target water as their chromophore, leading to the vaporization of epidermal and dermal structures. These induce robust collagen remodeling and are highly effective in treating moderate-to-severe photoaging but are associated with longer recovery periods and higher risks of adverse effects such as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and infection [167]. Fractional ablative CO2 lasers (FACL), which create microscopic zones of ablation surrounded by intact tissue, have emerged as the gold standard due to their balance of efficacy and safety. Expert consensus underscores the importance of individualized treatment parameters, particularly for Fitzpatrick phototypes III–IV, and the use of prophylactic antimicrobials and post-procedural skincare to mitigate complications [169].
Non-ablative lasers, including neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) (1064 nm), Er:Glass, and diode lasers, act primarily through dermal coagulation, without disrupting the epidermis. These systems offer reduced downtime and lower risk profiles but generally require more treatment sessions to achieve comparable outcomes. Meta-analyses reveal no statistically significant difference in efficacy between ablative and non-ablative lasers when assessed for overall wrinkle reduction and patient satisfaction, although ablative systems trend toward higher improvement rates in more severe photoaging. Notably, combining different laser wavelengths—such as Nd:YAG with potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) or Er:YAG—can enhance the treatment response while minimizing adverse effects. These combinations yield higher quartile improvement and satisfaction rates, along with reduced pain and erythema compared to monotherapies [170,171,172].
4.2.3. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) involves the application of a topical photosensitizing agent—most commonly 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or methyl-aminolevulinate (MAL)—followed by illumination with a specific light source to activate the photosensitizer. This leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species, resulting in selective damage to target cells. PDT has been extensively evaluated for its efficacy in treating actinic keratoses and has gained interest in the context of photoaging. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials supports its utility in reducing fine wrinkles and mottled pigmentation and improving skin texture, particularly with MAL-based regimens [173].
Clinical trials indicate that PDT is a safe and effective non-invasive option for facial photodamage, with MAL-based protocols yielding more consistent outcomes and higher-quality evidence than ALA. The efficacy of PDT appears enhanced when combined with red or blue light sources, which optimize protoporphyrin IX (PpIX) activation. Despite its benefits, PDT is associated with transient adverse effects such as burning, erythema, and edema, and its tolerability is sometimes limited by procedure-related discomfort. Nonetheless, its dual action—targeting both neoplastic and degenerative changes—positions PDT as a unique and valuable modality within the spectrum of skin rejuvenation treatments [174,175].
4.3. Mechanical Rejuvenation Techniques
4.3.1. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive, mechanical exfoliation technique that is widely used in cosmetic dermatology for superficial skin resurfacing. It utilizes abrasive crystals or diamond-tipped devices combined with vacuum suction to remove the stratum corneum, promoting epidermal regeneration and enhancing the skin texture. This controlled exfoliation induces a cascade of repair processes, including increased cell turnover, fibroblast activation, and neocollagenesis, which contribute to improved skin smoothness, tone, and radiance [176].
Although microdermabrasion is considered less aggressive than other resurfacing methods, it has shown efficacy in addressing mild photoaging signs such as dullness, fine lines, and irregular pigmentation. The procedure is generally well tolerated, with minimal downtime and rare adverse effects, making it suitable for individuals seeking gradual esthetic improvement. However, its superficial mode of action limits its impact on deeper dermal structures or moderate-to-severe rhytids, and it is often combined with other modalities to enhance the outcomes [176].
4.3.2. Microneedling
Microneedling, also known as percutaneous collagen induction therapy, involves the creation of controlled microinjuries to the skin using fine needles, typically delivered through dermarollers or motorized pens. These microchannels stimulate a wound healing response characterized by the release of growth factors, upregulation of collagen types I and III, and remodeling of the extracellular matrix. It is particularly effective in improving skin texture, reducing fine wrinkles, and treating scars, including atrophic acne scars [176,177].
Recent studies have explored microneedling in combination with adjuvant treatments, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP), polynucleotides, and exosomes, to amplify the regenerative effects. A randomized controlled study evaluating microneedling with PRP for periorbital rejuvenation reported subjective improvements in skin homogeneity and texture in over 70% of patients, despite a lack of statistically significant changes in dermatologist-assessed photonumeric scales [178,179].
Microneedle patch technology represents a novel evolution of this technique, offering the precise, painless, and self-administered transdermal delivery of bioactive agents. These dissolvable or hydrogel-based microneedle arrays have been developed to deliver antioxidants, extracellular vesicles, mRNA, or stem-cell derived products directly into the dermis to combat photoaging at the molecular level. Preclinical studies suggest that microneedle patches loaded with adipose-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) can promote collagen remodeling, reduce oxidative stress, and enhance the epidermal structure, making them a promising strategy for anti-aging interventions [176,180,181].
4.3.3. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels induce the controlled chemical exfoliation of the skin using caustic agents that vary in their depth of penetration—from superficial (epidermal) to medium and deep (papillary to reticular dermis). These peels remove damaged layers of skin, stimulate epidermal regeneration, and trigger dermal remodeling via fibroblast activation and collagen neosynthesis. The most commonly used agents in esthetic dermatology include glycolic acid (GA) and trichloroacetic acid (TCA), each with distinct penetration profiles and clinical indications [176].
Superficial peels with glycolic acid (typically 20–70%) are effective for fine lines, dyspigmentation, and mild textural irregularities. Medium-depth peels with TCA (20–35%) are more effective for photoaging signs such as deeper rhytids and solar lentigines, but they require more downtime and carry a higher risk of side effects such as erythema, edema, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin types [182].
A split-face comparative study evaluating 70% GA versus 30–35% TCA for photodamage and acne scarring demonstrated significant improvements with both agents in terms of elasticity, hydration, and wrinkle reduction. However, TCA achieved superior reductions in wrinkle depth, while GA exhibited better tolerability and fewer adverse effects, especially in patients with sensitive or Fitzpatrick IV–VI skin. Additionally, combination protocols (e.g., 70% GA followed by 15% TCA) have been shown to enhance the peel depth and efficacy while maintaining a favorable safety profile, optimizing the results with less irritation [183].
Chemical peels remain a cornerstone of mechanical skin rejuvenation due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to address a broad spectrum of photodamage. Patient selection, pre-peel priming (e.g., retinoids), and post-peel care are critical in maximizing outcomes and minimizing risks, particularly in higher-risk phototypes or when using medium-depth peels.
4.4. Injectable and Minimally Invasive Procedures
Injectable and minimally invasive procedures provide effective and customizable strategies to address the visible signs of facial aging. These include botulinum toxin injections, dermal fillers, and biostimulatory or mesotherapy-based treatments.
Botulinum toxin type A (BT) is the most widely used procedure for esthetic purposes. BT acts by inhibiting acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction, resulting in temporary muscle relaxation and the softening of dynamic wrinkles. BT is used for glabellar lines, forehead creases, and crow’s feet. Several botulinum toxin formulations are currently approved for wrinkle treatment, each differing slightly in their onset, diffusion properties, and duration of effect, requiring individualized application depending on the treatment area and patient response [184].
Hyaluronic acid-based dermal fillers are primarily used to restore facial volume lost with age or to enhance features such as the lips and cheekbones, aiming to re-establish the youthful “inverted triangle” of facial proportions. The injection technique, anatomical plane, and choice of filler depend on the product’s density, viscosity, and cross-linking characteristics. Lower-density gels may be used for fine lines or superficial corrections, while high-density fillers are more appropriate for deeper structural support. Some formulations also stimulate neocollagenesis, offering both volumizing and regenerative effects [185].
Mesotherapy is a classic used technique in esthetic dermatology. Unlike neurotoxins or volumizing fillers, mesotherapy acts on the skin’s biological environment rather than on the muscles or deep structural volume. Mesotherapy consists of microinjections spaced approximately 1 cm apart into the dermis, delivering substances such as vitamins, amino acids, peptides, or hyaluronic acid. This treatment is generally safe and well tolerated and aims to improve skin quality, hydration, and elasticity over time [186].
5. Conclusions
Skin aging is a complex, multifactorial process driven by the convergence of intrinsic biological mechanisms—such as telomere attrition, hormonal decline, and oxidative stress—and extrinsic factors including UV radiation, pollution, and lifestyle. These processes culminate in the progressive structural and functional deterioration of the skin, characterized by collagen loss, dermal thinning, pigmentary changes, and impaired barrier and immune function. Clinically, the manifestations are heterogeneous and vary across phototypes, highlighting the need for individualized approaches.
In recent years, anti-aging dermatology has transitioned from a purely cosmetic focus to a regenerative and preventive discipline grounded in molecular biology and tissue remodeling. Topical agents such as retinoids, antioxidants, and niacinamide remain central in maintaining epidermal homeostasis, while energy-based devices, injectable biostimulators, and advanced delivery systems (e.g., microneedle patches, exosome-based therapies) offer increasingly precise and synergistic treatment options. These modalities not only target visible signs of aging but also modulate the underlying inflammatory, oxidative, and metabolic pathways.
The future of anti-aging dermatology lies in personalization. The integration of omics data (genomics, epigenetics, transcriptomics, microbiome) with clinical and lifestyle factors will enable stratified interventions tailored to individual aging trajectories. This precision-based approach has the potential to redefine therapeutic goals—shifting from the correction of age-related features to the preservation of skin health, resilience, and biological youth.
Ultimately, successful anti-aging strategies must be comprehensive, evidence-based, and patient-centric. Beyond esthetics, they should aim to restore skin function, prevent age-related vulnerability, and enhance quality of life in an aging population. As our understanding deepens, dermatologists are uniquely positioned to lead this evolution—bridging science and individualized care to meet the demands of modern longevity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.N.-R., M.F.-G. and S.B.; methodology, J.N.-R., M.F.-G. and S.B.; software, M.L.H.-B. and A.P.-G.; validation, J.N.-R., M.F.-G. and S.B.; formal analysis J.N.-R., M.F.-G. and S.B.; investigation, J.N.-R., M.F.-G. and S.B.; resources, M.L.H.-B. and A.P.-G.; data curation, M.L.H.-B. and A.P.-G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.N.-R., M.F.-G. and S.B.; writing—review and editing, J.N.-R., M.F.-G. and S.B.; visualization, M.L.H.-B. and A.P.-G.; supervision, J.N.-R., M.F.-G. and S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lai-Cheong, J.E.; McGrath, J.A. Structure and Function of Skin, Hair and Nails. Medicine 2009, 37, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavkin, J.; Ellis, D.A.F. Aging Skin: Histology, Physiology, and Pathology. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 19, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Structural Characteristics of the Aging Skin: A Review. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2007, 26, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.; Geyer, S.; Weninger, W.; Guimberteau, J.; Wong, J.K. The Dynamic Anatomy and Patterning of Skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorteau, J.; Chevalier, F.P.; Fromy, B.; Lamartine, J. Functional integrity of aging skin, from cutaneous biology to anti-aging strategies. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boismal, F.; Serror, K.; Dobos, G.; Zuelgaray, E.; Bensussan, A.; Michel, L. Skin aging: Pathophysiology and innovative therapies. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Q.Y.A.; Chew, F.T. Defining Skin Aging and Its Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T. Molecular Insights of Human Skin Epidermal and Dermal Aging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2023, 112, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, G.; Dhaliwal, A.; Brar, A.S.; Sreedevi, M.; Ahmadi, Y.; Irfan, M.; Golbari, R.; Zumárraga, D.; Yateem, D.; Lysak, Y.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of the Role of UV Radiation in Photoaging Processes Between Different Types of Skin. Cureus 2025, 17, e81109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gálvez, E.N.; Aguilera, J.; Solis, A.; De Gálvez, M.V.; De Andrés, J.R.; Herrera-Ceballos, E.; Gago-Calderon, A. The Potential Role of UV and Blue Light from the Sun, Artificial Lighting, and Electronic Devices in Melanogenesis and Oxidative Stress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2022, 228, 112405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, E.; Geisler, A.N.; Nguyen, J.; Kohli, I.; Hamzavi, I.; Lim, H.W.; Jagdeo, J. Visible Light. Part I: Properties and Cutaneous Effects of Visible Light. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughery, M.F.; Wilson, H.E.; Sewell, A.; Stevison, S.; Wyrick, J.J. The Surprising Diversity of UV-Induced Mutations. Adv. Genet. 2024, 5, 2300205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, F. Photoprotection and Skin Pigmentation: Melanin-Related Molecules and Some Other New Agents Obtained from Natural Sources. Molecules 2020, 25, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.I.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.J. Protective Role of Caesalpinia Sappan Extract and Its Main Component Brazilin against Blue Light–Induced Damage in Human Fibroblasts. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 7025–7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campiche, R.; Curpen, S.J.; Lutchmanen-Kolanthan, V.; Gougeon, S.; Cherel, M.; Laurent, G.; Gempeler, M.; Schuetz, R. Pigmentation Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Skin and How to Protect against Them. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2020, 42, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.W.; Kohli, I.; Ruvolo, E.; Kolbe, L.; Hamzavi, I.H. Impact of Visible Light on Skin Health: The Role of Antioxidants and Free Radical Quenchers in Skin Protection. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, S27–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Jeong, S.A.; Choi, H.S.; Ro, S.; Lee, J.S.; Park, J.K. Protective Effects of Ginsenoside Rg2 and Astaxanthin Mixture against UVB-Induced DNA Damage. Anim. Cells Syst. 2018, 22, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Trullas, C.; Jourdan, E. Cell and Tissue-Based Models for Evaluating the Cutaneous Impact of Visible Light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2024, 19, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losi, A.; Gardner, K.H.; Möglich, A. Blue-Light Receptors for Optogenetics. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 10659–10709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Rentero, M.; López Sánchez, A.; Nicolás-Morala, J.; Alcaraz-Laso, P.; Zhang, N.; Juarranz, Á.; González, S.; Carrasco, E. The Effect of Fernblock® in Preventing Blue-Light-Induced Oxidative Stress and Cellular Damage in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Is Associated with NRF2 Induction. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2024, 23, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.; Choi, E.H.; Atanaskova Mesinkovska, N. The Expression of Opsins in the Human Skin and Its Implications for Photobiomodulation: A Systematic Review. Photoderm. Photoimm. Photomed. 2020, 36, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo, M.; Mataix, M.; Alonso-Juarranz, M.; Lorrio, S.; Villalba, M.; Rodríguez-Luna, A.; González, S. The Aqueous Extract of Polypodium Leucotomos (Fernblock®) Regulates Opsin 3 and Prevents Photooxidation of Melanin Precursors on Skin Cells Exposed to Blue Light Emitted from Digital Devices. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansary, T.M.; Hossain, M.R.; Kamiya, K.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Inflammatory Molecules Associated with Ultraviolet Radiation-Mediated Skin Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Duan, E. Fighting against Skin Aging: The Way from Bench to Bedside. Cell Transpl. 2018, 27, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors in Skin Ageing: A Review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2008, 30, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsou, F.; Trakatelli, M.; Patsatsi, A.; Kalokasidis, K.; Sotiriadis, D. Extrinsic Aging: UV-Mediated Skin Carcinogenesis. Derm. Endocrinol. 2012, 4, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Richa; Kumar, A.; Tyagi, M.B.; Sinha, R.P. Molecular Mechanisms of Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced DNA Damage and Repair. J. Nucleic Acids 2010, 2010, 592980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutmann, J.; Morita, A.; Chung, J.H. Sun Exposure: What Molecular Photodermatology Tells Us About Its Good and Bad Sides. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davinelli, S.; Bertoglio, J.C.; Polimeni, A.; Scapagnini, G. Cytoprotective Polyphenols Against Chronological Skin Aging and Cutaneous Photodamage. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, G. Intracellular Signaling Mechanisms Involved in the Biological Effects of the Xanthophyll Carotenoid Astaxanthin to Prevent the Photo-aging of the Skin in a Reactive Oxygen Species Depletion-independent Manner: The Key Role of Mitogen and Stress-activated Protein Kinase 1. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manicone, A.; Mcguire, J. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Modulators of Inflammation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, W.C.; Wilson, C.L.; López-Boado, Y.S. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Modulators of Inflammation and Innate Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.-W.; Kwon, S.-H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Na, J.-I.; Huh, C.-H.; Choi, H.-R.; Park, K.-C. Molecular Mechanisms of Dermal Aging and Antiaging Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, T.; Little, E.; Quan, H.; Qin, Z.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Elevated Matrix Metalloproteinases and Collagen Fragmentation in Photodamaged Human Skin: Impact of Altered Extracellular Matrix Microenvironment on Dermal Fibroblast Function. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1362–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, T.E.; Miller, A.H.; Wang, J. Collagen Scaffolds in Bone Sialoprotein-Mediated Bone Regeneration. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 812718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansel, J.; Perry, P.; Brown, J.; Damm, D.; Phan, T.; Hart, C.; Luger, T.; Hefeneider, S. Cytokine Modulation of Keratinocyte Cytokines. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1990, 94, s101–s107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortonne, J.-P. Pigmentary Changes of the Ageing Skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 1990, 122, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoczyńska, A.; Budzisz, E.; Trznadel-Grodzka, E.; Rotsztejn, H. Melanin and Lipofuscin as Hallmarks of Skin Aging. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2017, 2, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, D.; Hachiya, A.; Takano, K.; Hicks, R.; Visscher, M.O.; Kitahara, T.; Hase, T.; Takema, Y.; Yoshimori, T. Autophagy Has a Significant Role in Determining Skin Color by Regulating Melanosome Degradation in Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2416–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, C.; Cohen, C.; Chagnoleau, C.; Flouret, V.; Bourreau, E.; Bernerd, F. Key Regulatory Role of Dermal Fibroblasts in Pigmentation as Demonstrated Using a Reconstructed Skin Model: Impact of Photo-Aging. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, D.; Hachiya, A.; Amano, Y.; Ohuchi, A.; Kitahara, T.; Takema, Y. The Essential Role of P53 in Hyperpigmentation of the Skin via Regulation of Paracrine Melanogenic Cytokine Receptor Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4343–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.; Widlund, H.R.; Feige, E.; Lin, J.Y.; Wilensky, D.L.; Igras, V.E.; D’Orazio, J.; Fung, C.Y.; Schanbacher, C.F.; Granter, S.R.; et al. Central Role of P53 in the Suntan Response and Pathologic Hyperpigmentation. Cell 2007, 128, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.E.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, T.J.; Kang, H.Y. Senescent Fibroblasts Drive Ageing Pigmentation: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Senile Lentigo. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4620–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarialho-Kere, U.; Kerkelä, E.; Jeskanen, L.; Ranki, A.; Vaalamo, M.; Hasan, T.; Pierce, R.; Starcher, B.; Raudasoja, R.; Oikarinen, A. Accumulation of Matrilysin (MMP-7) and Macrophage Metalloelastase (MMP-12) in Actinic Damage. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulopoulos, A.K. Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases 9 and 12 in Actinic Cheilitis. World J. Exp. Med. 2013, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, P.; Calles, C.; Benesova, T.; Macaluso, F.; Krutmann, J. Photoprotection beyond Ultraviolet Radiation—Effective Sun Protection Has to Include Protection against Infrared A Radiation-Induced Skin Damage. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 23, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, K.; Kadoya, K.; Kajiya, K.; Hong, Y.-K.; Detmar, M. Ultraviolet B Irradiation of Human Skin Induces an Angiogenic Switch That Is Mediated by Upregulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and by Downregulation of Thrombospondin-1. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Kim, Y.K.; Cho, K.H.; Chung, J.H. Infrared Exposure Induces an Angiogenic Switch in Human Skin That Is Partially Mediated by Heat: IR Induces Angiogenesis in Human Skin in Vivo. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 155, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Oh, Y.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, K.H.; Chung, J.H. Ultraviolet Radiation Attenuates Thrombospondin 1 Expression via PI3K-Akt Activation in Human Keratinocytes. Photochem. Photobiol. 2006, 82, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-M.; Huang, A.; Kaley, G.; Sun, D. eNOS Uncoupling and Endothelial Dysfunction in Aged Vessels. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H1829–H1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barolet, A.C.; Litvinov, I.V.; Barolet, D. Light-Induced Nitric Oxide Release in the Skin beyond UVA and Blue Light: Red & near-Infrared Wavelengths. Nitric Oxide 2021, 117, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliman, G.; Lowe, D.; Cohen, H.; Felton, S.; Raj, K. Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Production of Nitric Oxide:A Multi-Cell and Multi-Donor Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opländer, C.; Volkmar, C.M.; Paunel-Görgülü, A.; Van Faassen, E.E.; Heiss, C.; Kelm, M.; Halmer, D.; Mürtz, M.; Pallua, N.; Suschek, C.V. Whole Body UVA Irradiation Lowers Systemic Blood Pressure by Release of Nitric Oxide From Intracutaneous Photolabile Nitric Oxide Derivates. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuks, K.B.; Hüls, A.; Sugiri, D.; Altug, H.; Vierkötter, A.; Abramson, M.J.; Goebel, J.; Wagner, G.G.; Demuth, I.; Krutmann, J.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone and Skin Aging: Results from Two German Cohort Studies. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flament, F.; Bourokba, N.; Nouveau, S.; Li, J.; Charbonneau, A. A Severe Chronic Outdoor Urban Pollution Alters Some Facial Aging Signs in Chinese Women. A Tale of Two Cities. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flament, F.; Ye, C.; Amar, D. Assessing the Impact of an Aerial Chronic Urban Pollution (UP) on Some Facial Signs of Differently-aged Chinese Men. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2019, 41, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Xue, C.-H.; Hwang, S.K.; Li, W.-H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.-Z. Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter Associated with Senile Lentigo in Chinese Women: A Cross-sectional Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüls, A.; Vierkötter, A.; Gao, W.; Krämer, U.; Yang, Y.; Ding, A.; Stolz, S.; Matsui, M.; Kan, H.; Wang, S.; et al. Traffic-Related Air Pollution Contributes to Development of Facial Lentigines: Further Epidemiological Evidence from Caucasians and Asians. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Hüls, A.; Vierkötter, A.; Yuan, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, W.; Li, J.; et al. Indoor PM2.5 Exposure Affects Skin Aging Manifestation in a Chinese Population. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierkötter, A.; Schikowski, T.; Ranft, U.; Sugiri, D.; Matsui, M.; Krämer, U.; Krutmann, J. Airborne Particle Exposure and Extrinsic Skin Aging. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2719–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, L.; Valacchi, G. Antioxidants and the Response of Skin to Oxidative Stress: Vitamin E as a Key Indicator. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 15, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valacchi, G.; Pagnin, E.; Corbacho, A.M.; Olano, E.; Davis, P.A.; Packer, L.; Cross, C.E. In Vivo Ozone Exposure Induces Antioxidant/Stress-Related Responses in Murine Lung and Skin. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valacchi, G.; Van Der Vliet, A.; Schock, B.C.; Okamoto, T.; Obermuller-Jevic, U.; Cross, C.E.; Packer, L. Ozone Exposure Activates Oxidative Stress Responses in Murine Skin. Toxicology 2002, 179, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valacchi, G.; Sticozzi, C.; Belmonte, G.; Cervellati, F.; Demaude, J.; Chen, N.; Krol, Y.; Oresajo, C. Vitamin C Compound Mixtures Prevent Ozone-Induced Oxidative Damage in Human Keratinocytes as Initial Assessment of Pollution Protection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valacchi, G.; Pecorelli, A.; Belmonte, G.; Pambianchi, E.; Cervellati, F.; Lynch, S.; Krol, Y.; Oresajo, C. Protective Effects of Topical Vitamin C Compound Mixtures against Ozone-Induced Damage in Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1373–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutmann, J.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Pan, X.; Crawford, M.; Sore, G.; Seite, S. Pollution and Skin: From Epidemiological and Mechanistic Studies to Clinical Implications. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 76, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvy, J.-M.D.; Guinot, C.; Preziosi, P.; Vaillant, L.; Tenenhaus, M.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Tschachler, E. Epidemiologic Determinants of Skin Photoaging: Baseline Data of the SU.VI.MAX. Cohort. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000, 42, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Youn, C.S.; Park, B.J.; Kim, K.H.; Park, K.C.; Cho, K.H.; Eun, H.C. Cutaneous Photodamage in Koreans: Influence of Sex, Sun Exposure, Smoking, and Skin Color. Arch. Dermatol. 2001, 137, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Ernster, V.L.; Grady, D.; Miike, R.; Black, D.; Selby, J.; Kerlikowske, K. Facial Wrinkling in Men and Women, by Smoking Status. Am. J. Public Health 1995, 85, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadunce, D.P.; Burr, R.; Gress, R.; Kanner, R.; Lyon, J.L.; Zone, J.J. Cigarette Smoking: Risk Factor for Premature Facial Wrinkling. Ann. Int. Med. 1991, 114, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raduan, A.; Luiz, R.; Manela-Azulay, M. Association between Smoking and Cutaneous Ageing in a Brazilian Population. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2008, 22, 1312–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, A. Tobacco Smoke Causes Premature Skin Aging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 48, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Just, M.; Ribera, M.; Monsó, E.; Lorenzo, J.C.; Ferrándiz, C. Effect of Smoking on Skin Elastic Fibres: Morphometric and Immunohistochemical Analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Morita, A.; Tsuji, T. Alterations of Extracellular Matrix Induced by Tobacco Smoke Extract. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2000, 292, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Ono, Y.; Nakata, S.; Shintani, Y.; Sakakibara, N.; Morita, A. Tobacco Smoke Extract Induces Premature Skin Aging in Mouse. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 46, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.; Palma, L.; Tavares Marques, L.; Bujan Varela, J. Dietary Water Affects Human Skin Hydration and Biomechanics. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 8, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, B.; Volaklis, K.; Fuchs, D.; Burtscher, M. Role of Dietary Protein and Muscular Fitness on Longevity and Aging. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Rao, E.; Sun, Y.; Grossmann, M.E.; Morris, R.J.; Cleary, M.P.; Li, B. Epidermal Fatty Acid Binding Protein Promotes Skin Inflammation Induced by High-Fat Diet. Immunity 2015, 42, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balić, A.; Vlašić, D.; Žužul, K.; Marinović, B.; Bukvić Mokos, Z. Omega-3 Versus Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in the Prevention and Treatment of Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meksiarun, P.; Maeda, Y.; Hiroi, T.; Andriana, B.B.; Sato, H. Analysis of the Effects of Dietary Fat on Body and Skin Lipids of Hamsters by Raman Spectroscopy. Analyst 2015, 140, 4238–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, D.F.; Sarandy, M.M.; Novaes, R.D.; Freitas, M.B.; Do Carmo Gouveia Pelúzio, M.; Gonçalves, R.V. High-Fat Diet and Alcohol Intake Promotes Inflammation and Impairs Skin Wound Healing in Wistar Rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 4658583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, D.F.; Sarandy, M.M.; Novaes, R.D.; Da Matta, S.L.P.; Gonçalves, R.V. Effect of a High-Fat Diet and Alcohol on Cutaneous Repair: A Systematic Review of Murine Experimental Models. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaid, M.; Singh, T.; Prasad, R.; Katiyar, S.K. Intake of High-Fat Diet Stimulates the Risk of Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Skin Tumors and Malignant Progression of Papillomas to Carcinoma in SKH-1 Hairless Mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 274, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, D.; Franz, S.; Popkova, Y.; Anderegg, U.; Schiller, J.; Schwede, K.; Lorz, A.; Simon, J.C.; Saalbach, A. High-Fat Diet Exacerbates Early Psoriatic Skin Inflammation Independent of Obesity: Saturated Fatty Acids as Key Players. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, Y.; Yamakuchi, M.; Fukushige, T.; Ibusuki, A.; Hashiguchi, T.; Kanekura, T. High-fat Diet Exacerbates Imiquimod-induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis in Mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-H.; Kim, J.; Jung, S.; Sung, K.; Son, Y.-K.; Bae, J.M.; Kim, B.-H. Alleviation of Ultraviolet B-Induced Photoaging by 7-MEGATM 500 in Hairless Mouse Skin. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 35, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkrishna, A.; Nain, P.; Chauhan, A.; Sharma, N.; Gupta, A.; Ranjan, R.; Varshney, A. Super Critical Fluid Extracted Fatty Acids from Withania Somnifera Seeds Repair Psoriasis-Like Skin Lesions and Attenuate Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) Release. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, Y.J.; Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Zhen, A.X.; Madushan Fernando, P.D.S.; Kang, H.K.; Ahn, Y.S.; Hyun, J.W. Effect of Fermented Fish Oil on Fine Particulate Matter-Induced Skin Aging. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J. Modulating Effect of Fatty Acids and Sterols on Skin Aging. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 57, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draelos, Z.D. Aging Skin: The Role of Diet: Facts and Controversies. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 31, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Katta, R. Sugar Sag: Glycation and the Role of Diet in Aging Skin. Ski. Ther. Lett. 2015, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Brescoll, J.; Daveluy, S. A Review of Vitamin B12 in Dermatology. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullar, J.; Carr, A.; Vissers, M. The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schempp, C.M.; Meinke, M.C.; Lademann, J.; Ferrari, Y.; Brecht, T.; Gehring, W. Topical Antioxidants Protect the Skin from Chemical-induced Irritation in the Repetitive Washing Test: A Placebo-controlled, Double-blind Study. Contact Dermat. 2012, 67, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xu, X.-G.; Li, Y.-H.; Wang, B.; Gao, X.-H.; Chen, H.-D.; Yatskayer, M.; Oresajo, C. Protective Effects of a Topical Antioxidant Complex Containing Vitamins C and E and Ferulic Acid against Ultraviolet Irradiation-Induced Photodamage in Chinese Women. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2013, 12, 464–468. [Google Scholar]
- Skrobot, A.; Demkow, U.; Wachowska, M. Immunomodulatory Role of Vitamin D: A Review. In Current Trends in Immunity and Respiratory Infections; Pokorski, M., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1108, pp. 13–23. ISBN 978-3-030-01634-0. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.F.; Das, L.M.; Ahsanuddin, S.; Qiu, Y.; Binko, A.M.; Traylor, Z.P.; Debanne, S.M.; Cooper, K.D.; Boxer, R.; Lu, K.Q. Oral Vitamin D Rapidly Attenuates Inflammation from Sunburn: An Interventional Study. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Marepally, S.R.; Goh, E.S.Y.; Cheng, C.Y.S.; Janjetovic, Z.; Kim, T.-K.; Miller, D.D.; Postlethwaite, A.E.; Slominski, A.T.; Tuckey, R.C.; et al. Investigation of 20S-Hydroxyvitamin D3 Analogs and Their 1α-OH Derivatives as Potent Vitamin D Receptor Agonists with Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postlethwaite, A.E.; Tuckey, R.C.; Kim, T.-K.; Li, W.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Myers, L.K.; Brand, D.D.; Slominski, A.T. 20S-Hydroxyvitamin D3, a Secosteroid Produced in Humans, Is Anti-Inflammatory and Inhibits Murine Autoimmune Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 678487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöbke, T.K.; Sorg, B.L.; Steinhilber, D. Vitamin D in Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjetovic, Z.; Tuckey, R.C.; Nguyen, M.N.; Thorpe, E.M.; Slominski, A.T. 20,23-dihydroxyvitamin D3, Novel P450scc Product, Stimulates Differentiation and Inhibits Proliferation and NF-κB Activity in Human Keratinocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 223, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjetovic, Z.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Tuckey, R.C.; DeLeon, D.A.; Nguyen, M.N.; Pfeffer, L.M.; Slominski, A.T. 20-Hydroxycholecalciferol, Product of Vitamin D3 Hydroxylation by P450scc, Decreases NF-κB Activity by Increasing IκBα Levels in Human Keratinocytes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, M.; Werner, S. Nrf2—A Regulator of Keratinocyte Redox Signaling. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiprasongsuk, A.; Janjetovic, Z.; Kim, T.-K.; Jarrett, S.G.; D’Orazio, J.A.; Holick, M.F.; Tang, E.K.Y.; Tuckey, R.C.; Panich, U.; Li, W.; et al. Protective Effects of Novel Derivatives of Vitamin D3 and Lumisterol against UVB-Induced Damage in Human Keratinocytes Involve Activation of Nrf2 and P53 Defense Mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Dixon, K.M.; Deo, S.S.; Holliday, C.J.; Slater, M.; Halliday, G.M.; Reeve, V.E.; Mason, R.S. Photoprotection by 1,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Is Associated with an Increase in P53 and a Decrease in Nitric Oxide Products. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, K.M.; Sequeira, V.B.; Deo, S.S.; Mohan, R.; Posner, G.H.; Mason, R.S. Differential Photoprotective Effects of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and a Low Calcaemic Deltanoid. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2012, 11, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, V.B.; Rybchyn, M.S.; Gordon-Thomson, C.; Tongkao-On, W.; Mizwicki, M.T.; Norman, A.W.; Reeve, V.E.; Halliday, G.M.; Mason, R.S. Opening of Chloride Channels by 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Contributes to Photoprotection against UVR-Induced Thymine Dimers in Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.; Gupta, R.; Dixon, K.M.; Deo, S.S.; Choong, S.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Bishop, J.E.; Ishizuka, S.; Norman, A.W.; Posner, G.H.; et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D and Three Low-Calcemic Analogs Decrease UV-Induced DNA Damage via the Rapid Response Pathway. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 89–90, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ge, C. Diet and Skin Aging—From the Perspective of Food Nutrition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Qian, J.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; He, S.; Ma, H. Bioavailability and Bioavailable Forms of Collagen after Oral Administration to Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3752–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, X.; Blay, N.; Cortés, B.; Carreras, A.; Iraola-Guzmán, S.; De Cid, R. Skin Phototype and Disease: A Comprehensive Genetic Approach to Pigmentary Traits Pleiotropy Using PRS in the GCAT Cohort. Genes 2023, 14, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, D.; Fabris, F.; Doherty, A.; Freitas, A.A.; De Magalhães, J.P. Ageing Transcriptome Meta-Analysis Reveals Similarities and Differences between Key Mammalian Tissues. Aging 2021, 13, 3313–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, T.; Boateng, S.T.; Uddin, M.B.; Banang-Mbeumi, S.; Yadav, R.K.; Bock, C.R.; Folahan, J.T.; Siwe-Noundou, X.; Walker, A.L.; King, J.A.; et al. The PI3K-Akt-mTOR and Associated Signaling Pathways as Molecular Drivers of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Skin Diseases: Update on Therapeutic Strategy Using Natural and Synthetic Compounds. Cells 2023, 12, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, R.S.; Bin Dayel, S.; Abahussein, O.; El-Sherbiny, A.A. Influences on Skin and Intrinsic Aging: Biological, Environmental, and Therapeutic Insights. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e16688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollina, U.; Abdel-Naser, M.B.; Ganceviciene, R.; Zouboulis, C.C. Receptors of Eccrine, Apocrine, and Holocrine Skin Glands. Dermatol. Clin. 2007, 25, 577–588, ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lephart, E.D.; Naftolin, F. Factors Influencing Skin Aging and the Important Role of Estrogens and Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs). Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lephart, E.D.; Naftolin, F. Menopause and the Skin: Old Favorites and New Innovations in Cosmeceuticals for Estrogen-Deficient Skin. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodby, B.; Penta, K.; Pecorelli, A.; Lila, M.A.; Valacchi, G. Skin Health from the Inside Out. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartke, A.; Hascup, E.; Hascup, K.; Masternak, M.M. Growth Hormone and Aging: New Findings. World J. Mens Health 2021, 39, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, H.D.; Cooke, P.S. Targeting Estrogen Signaling and Biosynthesis for Aged Skin Repair. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1281071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, B.; Moradi, R.; Mirzavi, F.; Barati, M.; Soleimani, A.; Jaafari, M.-R.; Zarghami, N. The Protection Role of Human Growth Hormone on Skin Cells Following Ultraviolet B Exposure. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2024, 257, 112961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laron, Z. Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1): A Growth Hormone. Mol. Pathol. 2001, 54, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, P.; Singh, K.; Krug, L.; Koroma, A.; Hainzl, A.; Bloch, W.; Kochanek, S.; Wlaschek, M.; Schorpp-Kistner, M.; Angel, P.; et al. Persistent JunB Activation in Fibroblasts Disrupts Stem Cell Niche Interactions Enforcing Skin Aging. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, S.R.; Thumiger, S.P.; Werther, G.A.; Wraight, C.J. Epidermal Homeostasis: The Role of the Growth Hormone and Insulin-like Growth Factor Systems. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 737–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, M.; Stegemann, A.; Paus, R.; Kleszczyński, K.; Maity, P.; Wlaschek, M.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Endocrine Controls of Skin Aging. Endocr. Rev. 2025, 46, 349–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocheva, G.; Slominski, R.M.; Janjetovic, Z.; Kim, T.-K.; Böhm, M.; Steinbrink, K.; Reiter, R.J.; Kleszczyński, K.; Slominski, A.T. Protective Role of Melatonin and Its Metabolites in Skin Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Hu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Y. The Influence of Circadian Rhythms on DNA Damage Repair in Skin Photoaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendimenico, G.J.; Mezick, J.A. Pharmacological Effects of Retinoids on Skin Cells. Ski. Pharmacol. 1993, 6 (Suppl. 1), 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinobu, T.; Tamai, H.; Tanabe, T.; Murata, T.; Manago, M.; Mino, M.; Hirahara, F. Plasma Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta-Carotene, and Retinol Levels in the Institutionalized Elderly Individuals and in Young Adults. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1994, 64, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Budzianowska, A.; Banaś, K.; Budzianowski, J.; Kikowska, M. Antioxidants to Defend Healthy and Youthful Skin—Current Trends and Future Directions in Cosmetology. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaccio, F.; D′Arino, A.; Caputo, S.; Bellei, B. Focus on the Contribution of Oxidative Stress in Skin Aging. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgutka, K.; Tkacz, M.; Tomasiak, P.; Tarnowski, M. A Role for Advanced Glycation End Products in Molecular Ageing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Yu, Y.; Sun, S.; Lu, C.; Zhai, J.; Lei, Y.; Bai, F.; Wang, R.; Chen, J. Immune Alterations with Aging: Mechanisms and Intervention Strategies. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, R.; Hu, A.; Bollag, W.B. The Skin and Inflamm-Aging. Biology 2023, 12, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, J.M. Clinical Aspects of Aging Skin: Considerations for the Wound Care Practitioner. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2020, 33, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, S.; Maymone, M.B.C.; Vashi, N.A. Aging in Skin of Color. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 37, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.M. Skin Failure: An Emerging Concept. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, L.; Abadir, P.; Brem, H.; Carter, M.; Conner-Kerr, T.; Davidson, J.; DiPietro, L.; Falanga, V.; Fife, C.; Gardner, S.; et al. Chronic Wound Repair and Healing in Older Adults: Current Status and Future Research. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langemo, D.K.; Brown, G. Skin Fails Too: Acute, Chronic, and End-Stage Skin Failure. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2006, 19, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.J.; Martin, P. Wound Repair at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3209–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenske, N.A.; Lober, C.W. Structural and Functional Changes of Normal Aging Skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1986, 15, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.M. Unavoidable Pressure Injuries, Terminal Ulceration, and Skin Failure: In Search of a Unifying Classification System. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2017, 30, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, J.M.; Miller, R.A. Chronic Skin Fragility of Aging: Current Concepts in the Pathogenesis, Recognition, and Management of Dermatoporosis. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2018, 11, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McKnight, A.; Momoh, A.; Bullocks, J. Variations of Structural Components: Specific Intercultural Differences in Facial Morphology, Skin Type, and Structures. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2009, 23, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brissett, A.; Naylor, M. The Aging African-American Face. Facial Plast. Surg. 2010, 26, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.C. Skin of Color: Biology, Structure, Function, and Implications for Dermatologic Disease. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 46, S41–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, W.; Carlisle, K. The Architecture of Black and White Facial Skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1991, 24, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexis, A.F.; Obioha, J.O. Ethnicity and Aging Skin. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2017, 16, s77–s80. [Google Scholar]
- Vashi, N.A.; de Castro Maymone, M.B.; Kundu, R.V. Aging Differences in Ethnic Skin. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2016, 9, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, S. Ethnic and Gender Considerations in the Use of Facial Injectables: Asian Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 22S–27S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.P.; Olson, K.L. Anthropometric Facial Analysis of the African American Woman. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2001, 3, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talakoub, L.; Wesley, N.O. Differences in Perceptions of Beauty and Cosmetic Procedures Performed in Ethnic Patients. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2009, 28, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Férnandez-Guarino, M.; Naharro-Rodriguez, J.; Bacci, S. Disturbances in the Skin Homeostasis: Wound Healing, an Undefined Process. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnal-Forné, M.; Molina-García, T.; Ortega, M.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Molina, P.; Ferrández-Izquierdo, A.; Sepulveda, P.; Bodí, V.; Ríos-Navarro, C.; Ruiz-Saurí, A. Changes in Human Skin Composition Due to Intrinsic Aging: A Histologic and Morphometric Study. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2024, 162, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonta, M.; Daina, L.; Muţiu, G. The Process of Ageing Reflected by Histological Changes in the Skin. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2013, 54, 797–804. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.R.; Korolchuk, V.I. Biochemistry and Cell Biology of Ageing: Part II Clinical Science; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2019; Volume 91, ISBN 9789811336805. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Hong, Y.; Kim, M. Structural and Functional Changes and Possible Molecular Mechanisms in Aged Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, K.; Hallock, K.; Lam, C. Photoaging and Topical Rejuvenation. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2023, 50, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draelos, Z.; Bogdanowicz, P.; Saurat, J.-H. Top Weapons in Skin Aging and Actives to Target the Consequences of Skin Cell Senescence. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNatale, L.; Idkowiak-Baldys, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Gonzalez, A.; Stephens, T.J.; Jiang, L.I.; Li, W.; Basson, R.; Bayat, A. Novel Rotational Combination Regimen of Skin Topicals Improves Facial Photoaging: Efficacy Demonstrated in Double-Blinded Clinical Trials and Laboratory Validation. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 724344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-C.; Yang, J.-H. Dual Effects of Alpha-Hydroxy Acids on the Skin. Molecules 2018, 23, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, B.C.; Wu, W.; Rosen, T. Azelaic Acid: Evidence-Based Update on Mechanism of Action and Clinical Application. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2015, 14, 964–968. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Shang, J.; Gu, Z.; Gong, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Azelaic Acid: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 2359–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boo, Y.C. Mechanistic Basis and Clinical Evidence for the Applications of Nicotinamide (Niacinamide) to Control Skin Aging and Pigmentation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, C.; Hadjab, F.; Porcello, A.; Lourenço, K.; Scaletta, C.; Abdel-Sayed, P.; Hirt-Burri, N.; Applegate, L.A.; Laurent, A. Mechanistic Insights into the Multiple Functions of Niacinamide: Therapeutic Implications and Cosmeceutical Applications in Functional Skincare Products. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madaan, P.; Sikka, P.; Malik, D.S. Cosmeceutical Aptitudes of Niacinamide: A Review. Recent Adv. Anti-Infect. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour Mohammad, A.; Gholizadeh Mesgarha, M.; Seirafianpour, F.; Karimi, Y.; Sodagar, S.; Afraie, M.; Goodarzi, A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Efficacy, Safety, and Satisfaction Rates of Laser Combination Treatments vs Laser Monotherapy in Skin Rejuvenation Resurfacing. Lasers Med. Sci. 2023, 38, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seirafianpour, F.; Pour Mohammad, A.; Moradi, Y.; Dehghanbanadaki, H.; Panahi, P.; Goodarzi, A.; Mozafarpoor, S. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials Comparing Efficacy, Safety, and Satisfaction between Ablative and Non-Ablative Lasers in Facial and Hand Rejuvenation/Resurfacing. Lasers Med. Sci. 2022, 37, 2111–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, N.; Pajk, F.; Vizintin, Z. Full-Face Skin Resurfacing Using a Combination of Fractional and Full Spot Ablative 2940 Nm Erbium Laser. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.; Lee, Y.H.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, W.-S. Split-Face Comparison of the Picosecond 1064-Nm Nd:YAG Laser Using a Microlens Array and the Quasi-Long-Pulsed 1064-Nm Nd:YAG Laser for Treatment of Photoaging Facial Wrinkles and Pores in Asians. Lasers Med. Sci. 2020, 35, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, E.V.; Tidwell, W.J.; Guss, L.; Sutton, A.V. Study of a 532/1064 Fractional Picosecond Laser for Facial Rejuvenation. Dermatol. Surg. 2022, 48, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna-Rico, E.; Lluch-Galcera, J.J.; Pérez-García, B.; Naharro-Rodríguez, J.; Azcárraga-Llobet, C.; Company-Quiroga, J.; Boixeda, P. Assessing the Safety and Efficacy of a New 532-Nm and 1064-Nm Laser Device with Variable Sequencing and Cryogen Spray Cooling for Rosacea Treatment. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q. Positive Effects of Low-Dose Photodynamic Therapy with Aminolevulinic Acid or Its Methyl Ester in Skin Rejuvenation and Wound Healing: An Update. J. Biophoton. 2023, 16, e202200293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panova, O.S.; Dubensky, V.V.; Petunina, V.V.; Beimanova, M.A.; Sanches, E.A.; Gelfond, M.L.; Shilov, B.V.; Belkharoeva, R.K. Photodynamic reparative skin regeneration using application of photosensitizer gel based on chlorin e6. Biomed. Photon. 2021, 10, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayan, G.V.; Podoplekina, N.D.; Glagoleva, E.N.; Petrishchev, N.N.; Galagudza, M.M. Autofluorescence Spectroscopy in Photodynamic Therapy for Skin Rejuvenation: A Theranostic Approach in Aesthetic Medicine. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2024, 45, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moubayed, S.P.; Desroches, M.-L.; Deane, E.C. Nonsurgical Facial Esthetic Procedures. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2025, 58, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, S.; Xie, G. Comparing the Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Alone Versus Combined With Microneedles or Radiofrequency for Neck Wrinkle Treatment. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e16651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlich, G.; Skorochod, R.; Sabo, E.; Saigal, R.; Dahan, E.; Wolf, Y. The Efficacy of Thermal Mechanical Fractional Injury System for Facial Rejuvenation: Subjective, Objective and Image Analysis Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e70063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuskiatti, W.; Wannawittayapa, T.; Buranaporn, P.; Wanitphadeedecha, R.; Lizarondo, F.P.J.; Nokdhes, Y. The Efficacy and Safety of Synchronized Radiofrequency and High Intensity Facial Electrical Stimulation in Improving Facial Skin Laxity and Quality in Asians. Lasers Surg. Med. 2025, 57, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Xiang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, W.-X.; Lv, X.-L. Recent Developments in Using Microneedle Patch Technology as a More Efficient Drug Delivery System for Treating Skin Photoaging. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boca, A.; Fanian, F.; Smit, R.; Redaelli, A.; Goorochurn, R.; Issa, H.; Sukmanskaya, N.; Philippon, V.; Dell’ Avanzato, R. Evaluation of the Performance and Safety of a New Micro-Needle Technology in Comparison With the Classic Needle on the Antiaging Effects of a Biorevitalizing Solution: A Randomized Split Face/Neck Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 3974–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, M.; Mucha, P.; Rotsztejn, H. Comparative Study of 15% Trichloroacetic Acid Peel Combined with 70% Glycolic Acid and 35% Trichloroacetic Acid Peel for the Treatment of Photodamaged Facial Skin in Aging Women. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjhi, M.; Sagar, V.; Yadav, P.; Dabas, G.; Gupta, A.; Pratap, P. A Comparative Study of 70% Glycolic Acid and 30% Trichloroacetic Acid Peel in the Treatment of Facial Atrophic Acne Scars: A Split-Face Study. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2024, 17, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, S.; Baker, M.R.; Chatterjee, S.; Kumar, H. Botulinum Toxin: An Update on Pharmacology and Newer Products in Development. Toxins 2021, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, L.N.; Gupta, A. Hyaluronic Acid Fillers for Midface Augmentation: A Systematic Review. Facial Plast. Surg. 2021, 37, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostkowska, E.; Poleszak, E.; Wojciechowska, K.; Dos Santos Szewczyk, K. Dermatological Management of Aged Skin. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).