A Novel and Reliable Analysis Method Utilizing Hennosides to Improve the Quality Assessment of Lawsonia inermis L. Material Used in Cosmetic Formulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Plant Materials
2.3. Extraction of Lawsonia inermis L. Material
2.3.1. Maceration of Henna Raw Material
2.3.2. Ethanolic Extraction of Henna Raw Material for Hennoside Isolation
2.3.3. Hot Aqueous Extraction of Henna Raw Material for Acidic Hydrolysis
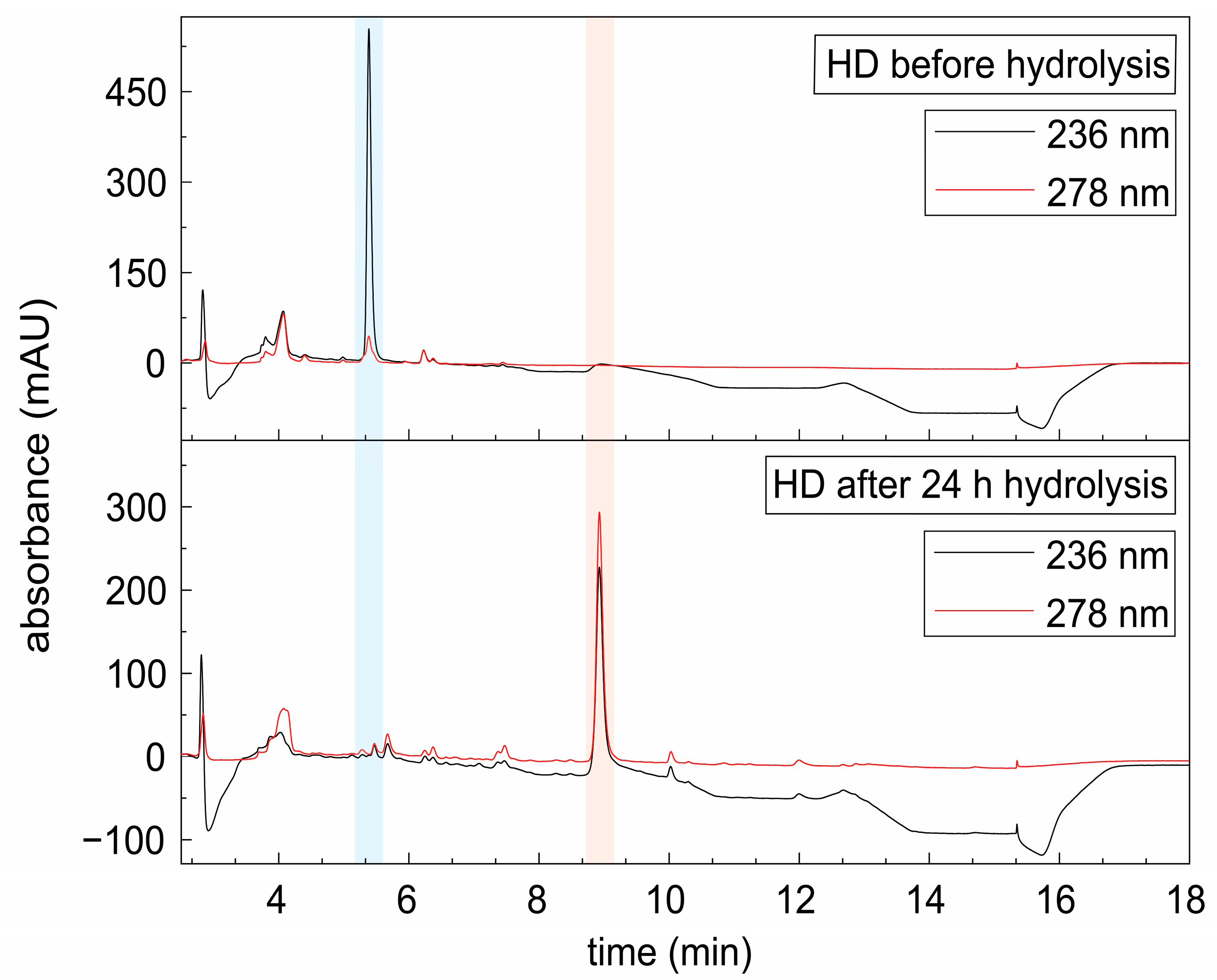
2.3.4. Acidic Hydrolysis of Hennoside in Henna Extract
2.4. Hennoside Isolation via RP Column Chromatography
2.5. Characterization of Isolated Hennoside Material
2.5.1. ESI-TOF Analysis of Isolated Hennoside Fractions
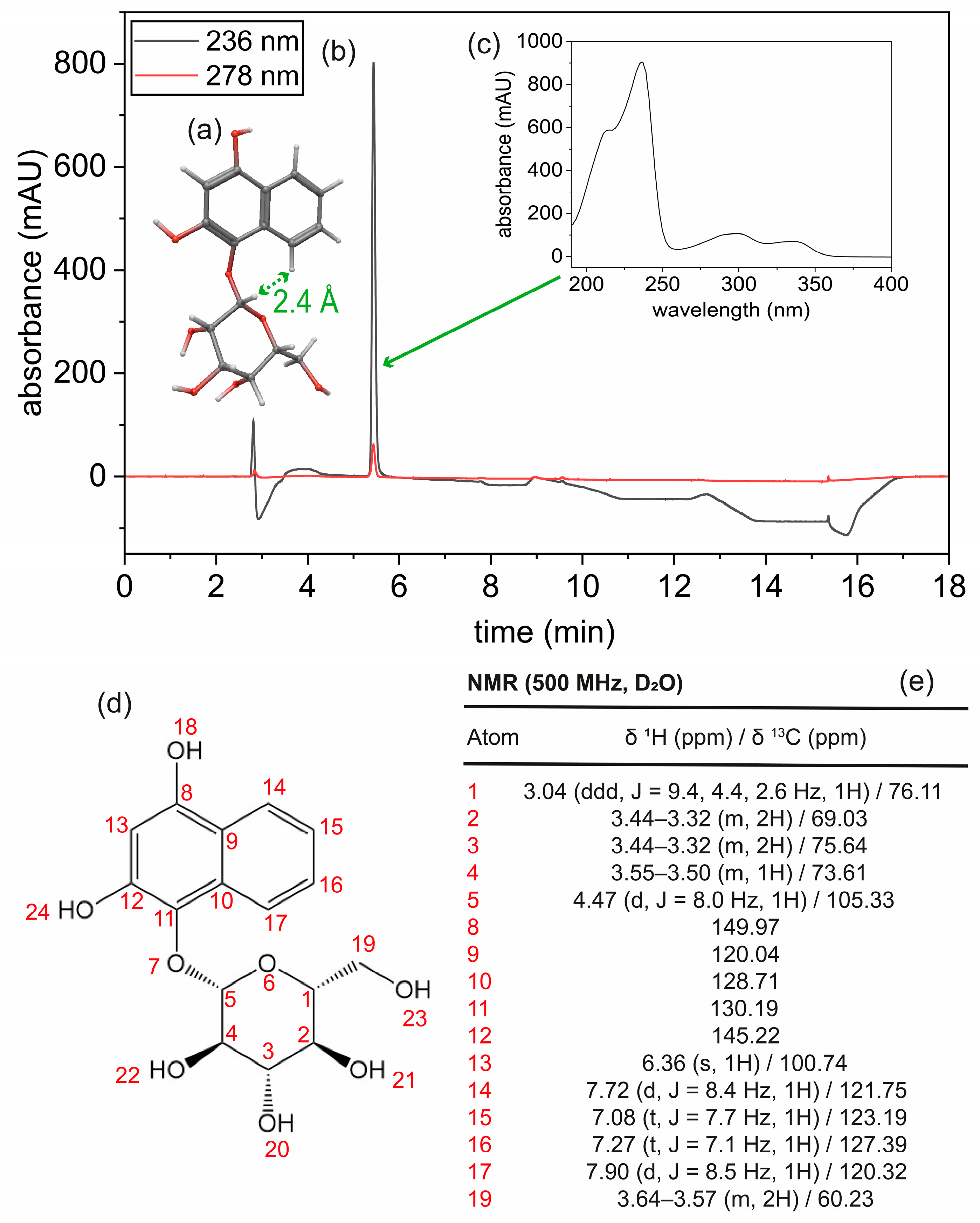
2.5.2. 3D Structural Analysis of Isolated Hennoside by NMR
2.6. Analysis of Lawsonia inermis L. Extracts by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.6.1. Standard Preparation and Method Validation
2.6.2. Quantification of Hennoside and Lawsone in Henna Extracts
3. Results and Discussion
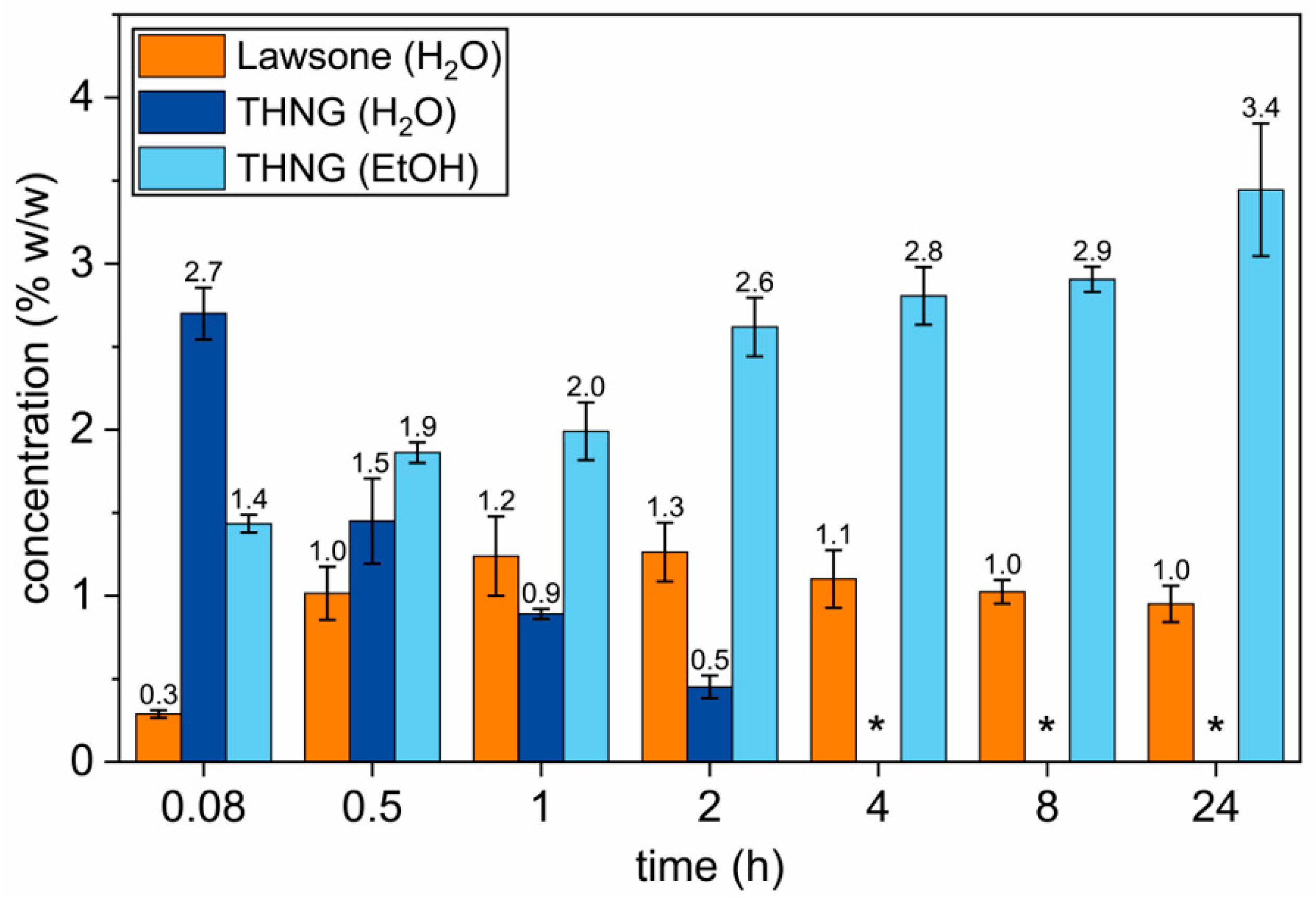
3.1. Sensitivity of Lawsone Release from Lawsonia inermis L. Material
3.2. Structure Determination and Characterization of Isolated Hennoside Sample
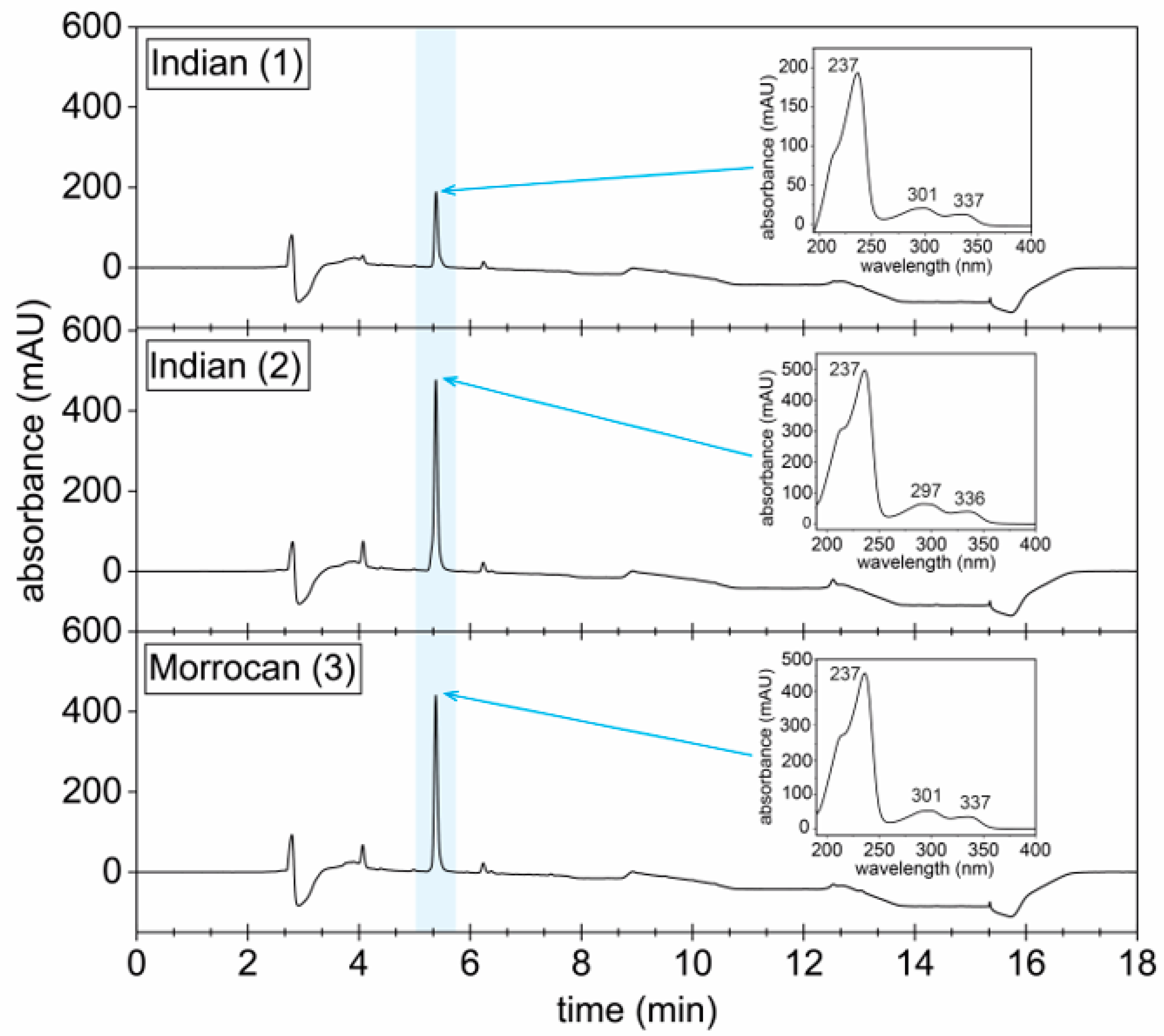
3.3. Development of a Hennoside Quantification Method via HPLC
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| COSY | Homonuclear Correlation Spectroscopy |
| conc.Lawsone | Lawsone concentration |
| conc.THNG | 1,2,4-trihydroxynaphthalene-1-O-glucoside concentration |
| Csp | Concentration spiked sample |
| Cun | Concentration unspiked sample |
| Cadd | Fixed Concentration of sample added for sample spiking |
| EE | Ethanolic Soxhlet Extract |
| ESI-TOF | Electrospray Ionization-Time of Flight |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| FID | Free Induction Decay |
| HCl | Hydrochloric Acid |
| HD | Heat-Denatured Aqueous Extract |
| HMBC | Heteronuclear Multiple-Bond Correlation |
| HPLC-MS-MS | High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| HRESIMS | High Resolution Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry |
| HSQC | Heteronuclear Single Quantum Coherence |
| IPA | Isopropyl alcohol |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| LOQ | Limit of Quantification |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| NOESY | Nuclear Overhauser Effect Spectroscopy |
| RLPA | Response 1,2,4-trihydroxynaphthalene-1-O-glucoside Peak Area |
| RLPH | Response 1,2,4-trihydroxynaphthalene-1-O-glucoside Peak Height |
| RP-HPLC | Reverse Phase-High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| RP-TLC | Reverse Phase-Thin Layer Chromatography |
| RSD | Relative Standard Deviation |
| SCCS | Scientific Committee of Consumer Safety |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| THNG | 1,2,4-trihydroxynaphthalene-1-O-glucoside |
| UPW | Ultra-Pure Water |
| UV | Ultra-Violet |
References
- Kolling, C.; Ribeiro, J.L.D.; de Medeiros, J.F. Performance of the cosmetics industry from the perspective of Corporate Social Responsibility and Design for Sustainability. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 30, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, S.A.; Olaniyi, O.O.; Oladoyinbo, T.O.; Ajayi, N.D.; Olaniyi, F.G. Sustainable Sourcing of Organic Skincare Ingredients: A Critical Analysis of Ethical Concerns and Environmental Implications. Asian J. Adv. Res. Rep. 2024, 18, 65–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, R.A.; Saplacan, Z.; Alt, M.A. Social media goes green-the impact of social media on green cosmetics purchase motivation and intention. Information 2020, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turati, F.; Pelucchi, C.; Galeone, C.; Decarli, A.; La Vecchia, C. Personal hair dye use and bladder cancer: A meta-analysis. Ann. Epidemio.l 2014, 24, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck, H.G.; Stadelhofer, J.W. Industrial Aromatic Chemistry: Raw Materials Processes Products; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, V.; Sharma, U.; Rawat, D.; Benson, D.; Singh, M.; Sharma, R.S. Fast-changing life-styles and ecotoxicity of hair dyes drive the emergence of hidden toxicants threatening environmental sustainability in Asia. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukkanna, K.S.; Stone, N.M.; Ingram, J.R. Para-phenylenediamine allergy: Current perspectives on diagnosis and management. J. Asthma Allergy 2017, 10, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komboonchoo, S.; Bechtold, T. A study on the dyeing characteristics and electrochemical behaviour of lawsone-indigo mixtures. Color. Technol. 2011, 127, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheer Kumar, K.; Begum, A.; Shashidhar, B.; Meenu, M.; Mahender, C.; Sai Vamsi, K. Formulation and Evaluation of 100% Herbal Hair Dye. Int. J. Adv. Res. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari, S.S.; Prabha, T.; Begum, S.S.; Sivakuamr, T.; Saranraj, P.; Manivannan, V.; Kumar, B.A. Formulation and evaluation, comparison of herbal hair dye with marketed formulation. Ann. Phytomed. Int. J. 2021, 10, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patni, P.; Gahtori, A.; Bhandari, P.; Dimri, T.; Ahmad, M. The Herbal Hue: Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Hair Dye. Pharmacogn. Res. 2024, 16, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directorate General for Health & Consumers. In Opinion on Lawsonia inermis (Henna): COLIPA n° C169; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alem, F.Z.; Gita, S.A.; Cougnaud, L.; Affnar, C.; Nounah, I.; Youssef, B.; de Oliveira, A.L.; Charrouf, Z.; Rhourri-Frih, B. Lawsone quantification in Lawsonia inermis L. by HPLC-MS: How does the temperature and pluviometry affect lawsone concentration? Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 158, 112960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhouafli, Z.; Ben Jannet, H.; Mahjoub, B.; Leri, M.; Guillard, J.; Saidani Tounsi, M.; Stefani, M.; Hayouni, E.A. 1,2,4-trihydroxynaphthalene-2-O-β-D-glucopyranoside: A new powerful antioxidant and inhibitor of Aβ42 aggregation isolated from the leaves of Lawsonia inermis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 3, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsouna, A.B.; Trigui, M.; Culioli, G.; Blache, Y.; Jaoua, S. Antioxidant constituents from Lawsonia inermis leaves: Isolation, structure elucidation and antioxidative capacity. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwama, T.; Watanabe, K.; Monthakantirat, O.; Luecha, P.; Noguchi, H.; Watanabe, K.; Umehara, K. Naphthalene glycosides in the Thai medicinal plant Diospyros mollis. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 72, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thanh, N.; Thao, N.P.; Dat, L.D.; Huong, P.T.T.; Lee, S.H.; Jang, H.D.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Van Kiem, P.; Van Minh, C.; et al. Two new naphthalene glucosides and other bioactive compounds from the carnivorous plant Nepenthes mirabilis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Quek, S.Y.; Fedrizzi, B.; Kilmartin, P.A. Characterization of free and glycosidically bound volatile compounds from tamarillo (Solanum betaceum Cav.) with considerations on hydrolysis strategies and incubation time. LWT 2020, 124, 109178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Nishimura, O.; Hara-Nishimura, I.; Nishimura, M.; Matsubara, H. Tissue and Intracellular Localization of Indican and the Purification and Characterization of Indican Synthase from Indigo Plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2000, 41, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duroux, L.; Delmotte, F.M.; Lancelin, J.-M.; Ravis, K.; Jay-Allemand, C. Insight into naphthoquinone metabolism: β-glucosidase-catalysed hydrolysis of hydrojuglone β-D-glucopyranoside. Biochem. J. 1998, 333, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavepour, N.; Bayati, M.; Rahimi, M.; Aliahmadi, A.; Nejad Ebrahimi, S. Optimization of aqueous extraction of henna leaves (Lawsonia inermis L.) and evaluation of biological activity by HPLC-based profiling and molecular docking techniques. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 195, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A. Merck molecular force field. I. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. J. Comput. Chem. 1996, 17, 490–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. ICH Q2(R2) Guideline on Validation of Analytical Procedures—Step 5; EMA/CHMP/ICH/82072/2006; Committee for Medical Products for Human Use: London, UK, 2024.
- Derksen, G.C.H.; Bechtold, T. Natural Colorants—Quinoid, Naphthoquinoid, and Anthraquinoid Dyes. In Handbook of Natural Colorants, 2nd ed.; Bechtold, T., Mussak, R., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2023; pp. 271–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, J.; Kini, M.; Mhaskar, S.; Sangle, P. Estimation of Lawsone Release from Lawsonia inermis Leaf Powder. Trends Agric. Sci. 2022, 1, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafaatullah, A.Q.; Setyorini, D.; Ganing, M.; Panjaitan, R.; Azizah, N. Optimization and Kinetics Extraction of Natural Dyes from Henna Leaves (Lawsonia inermis L.) with Ultrasonic Assistance. J. Kim. Sains Apl. 2023, 26, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslovarić, I.; Ilić, V.; Drvenica, I.; Stančić, A.; Mojsilović, S.; Kukolj, T.; Bugarski, D.; Saso, L.; Nicoletti, M. Insight into the Biological Activity of Hennosides—Glucosides Isolated from Lawsonia inermis (henna): Could They Be Regarded as Active Constituents Instead. Plants 2021, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tříska, J.; Vrchotová, N.; Sýkora, J.; Moos, M. Separation and identification of 1,2,4-trihydroxynaphthalene-1-O-glucoside in Impatiens glandulifera royle. Molecules 2013, 18, 8429–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Kano, K.; Ikeda, T. Kinetic analysis and mechanistic aspects of autoxidation of catechins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1569, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Linearity in the Range of (µg mL−1) | LOD (µg mL−1) | LOQ (µg mL−1) | Recovery (%) | Precision (% RSD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05–11.0 | 0.015 | 0.05 | 93 | 0.77 |
| Linearity in the Range of (µg mL−1) | LOD (µg mL−1) | LOQ (µg mL−1) | Recovery (%) | Precision (% RSD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2–12.0 | 0.06 | 0.2 | 93 | 0.54 |
| min | UPW + 0.1% v/v Formic Acid (A) | Acetonitrile % (B) | Flow Rate (mL min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80 | 20 | 1 |
| 5 | 60 | 40 | 1 |
| 6 | 60 | 40 | 1 |
| 8 | 40 | 60 | 1 |
| 10 | 40 | 60 | 1 |
| 11 | 20 | 80 | 1 |
| 13 | 20 | 80 | 1 |
| 13.1 | 80 | 20 | 1 |
| 18 | 80 | 20 | 1 |
| Time | Lawsone (% w/w) ± SD | THNG (% w/w) ± SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aqueous Extract | Ethanolic Extract | Aqueous Extract | Ethanolic Extract | |
| 5 min | 0.3 ± 0.02 | <0.05 | 2.7 ± 0.16 | 1.4 ± 0.05 |
| 30 min | 1.0 ± 0.16 | <0.05 | 1.5 ± 0.26 | 1.9 ± 0.06 |
| 1 h | 1.2 ± 0.24 | <0.05 | 0.9 ± 0.03 | 2.0 ± 0.17 |
| 2 h | 1.3 ± 0.18 | <0.05 | 0.5 ± 0.07 | 2.6 ± 0.18 |
| 4 h | 1.1 ± 0.17 | <0.05 | <0.2 | 2.8 ± 0.17 |
| 8 h | 1.0 ± 0.07 | <0.05 | <0.2 | 2.9 ± 0.08 |
| 24 h | 1.0 ± 0.11 | <0.05 | <0.2 | 3.4 ± 0.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dallmann, N.; Vill, V.; Straske, F. A Novel and Reliable Analysis Method Utilizing Hennosides to Improve the Quality Assessment of Lawsonia inermis L. Material Used in Cosmetic Formulations. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12030099
Dallmann N, Vill V, Straske F. A Novel and Reliable Analysis Method Utilizing Hennosides to Improve the Quality Assessment of Lawsonia inermis L. Material Used in Cosmetic Formulations. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(3):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12030099
Chicago/Turabian StyleDallmann, Nele, Volkmar Vill, and Fabian Straske. 2025. "A Novel and Reliable Analysis Method Utilizing Hennosides to Improve the Quality Assessment of Lawsonia inermis L. Material Used in Cosmetic Formulations" Cosmetics 12, no. 3: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12030099
APA StyleDallmann, N., Vill, V., & Straske, F. (2025). A Novel and Reliable Analysis Method Utilizing Hennosides to Improve the Quality Assessment of Lawsonia inermis L. Material Used in Cosmetic Formulations. Cosmetics, 12(3), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12030099








