Abstract
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiations represents a significant risk factor and may lead to various skin disorders, premature aging, and an increased susceptibility to skin cancers. Recently, probiotics have emerged as promising candidates for fortifying the skin’s natural defences through their diverse mechanisms. The aim of the present work was exploring the potential of five heat-treated probiotics (SkinbacTM, Probiotical Research S.r.l., Novara, Italy), as protective agents against UVA and UVB damages on human keratinocyte line (HaCaT) and human skin 3D model (Phenion® Full-Thickness Skin Model, Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, Dusseldorf, Germany). The protective role toward artificially induced oxidative stress was evaluated by determining the residual viability after UV exposure and analyzing gene expression of markers involved in apoptosis (Tumor protein 53), inflammation/immunosuppression (Interleukin 6), oxidative stress (oxidative stress response enzyme heme oxygenase 1), investigated using quantitative real-time PCR. Additionally, we examined the protective effects of these strains, testing them on Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes (NHEK) irradiated with UVC, specifically, evaluating the expression of tight junction proteins, including claudin 1, claudin 4, and occludin, by ELISA. The tested heat-treated probiotics effectively protected from UVA, UVB, and UVC damage on all end points analyzed, revealing their capacity to enhance barrier protection in cases of damage and their potential for innovative skincare strategies centered around probiotic-based formulations for enhanced protection against UV-induced skin damage.
1. Introduction
Sunlight comprises an electromagnetic spectrum of different wavelengths, including short wavelength, high-energy rays, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, visible light (VL), and long-wavelength, low-energy rays, infrared radiation (IRR) [1,2]. The UV spectrum includes three regions that are classified based on wavelength and their effect on living organisms [3]. UVA represents the majority of the spectrum that reaches the Earth; it is a low-energy radiation, and its wavelength is between 320 and 400 nm. This radiation penetrates skin and induces reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, which lead to oxidative stress in the cells, by damaging nucleic acids, membrane lipids, and proteins, also leading to abnormal cell proliferation [1,3,4]. UVB is a higher-energy radiation that hits our skin in a lower amount, but the shorter wavelength (280–320 nm) has potentially more dangerous effects, as it has a direct mutagenic effect on DNA, and it is therefore considered a potent carcinogen [3,4]. UVC is the highest-energy radiation, with wavelength from 100 to 280 nm. Very little of this radiation reaches the Earth’s surface [3], but this amount is increasing due to the atmospheric ozone layer reduction. Therefore, it is an upcoming environmental concern [4]. While adequate and limited exposure to UV light can provide health benefits [1], prolonged and unprotected exposure may pose humans at high risk for dermatological disorders, skin inflammation, and cancer or eye damage [1,5]. In addition to these risks, UV exposure is associated with increased skin aging (photoaging). In fact, through ROS formation in the skin, UVB upregulates the activator protein 1 (AP-1) and, consequently, the matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and downregulates procollagen biosynthesis, causing skin aging, loss of elasticity, and wrinkle formation [6,7].
In the skin resides a multitude of microorganisms, namely the skin microbiome, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. The skin microbiome composition, and the role that these microbes play, varies based on the body sites which they inhabit [8]. In general, they contribute in protecting the host from harmful situations, supporting skin barrier function, defending from the invading pathogens, controlling inflammation, and modulating the immune system [9]. In recent years, the use of microorganisms to modulate the skin microbiome as possible intervention for dermatological diseases has started to be investigated. However, the use of probiotics, which are defined by the International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) as ‘live microorganisms that, when administrated in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host’ [10], is not feasible in cosmetic formulations [11]. The main challenge is to keep them alive during the product’s shelf life while respecting the microbiological limits for cosmetics (ISO 2014) [11]. Thus, a new way to deliver beneficial metabolites derived from probiotics topically, overcoming the problem of viability, is the use of ‘postbiotics’. These are defined by the ISAPP as ‘a preparation of inanimate (non-viable) microorganisms and/or their components that confers a health benefit on the host’ [12]. The roles of probiotics and post-biotics in skin health have been recently investigated [13]. They play a role in skin repair and wound healing, increase the epithelial barrier, inhibit directly or by competitive exclusion pathogens, combat biofilm formation, and stimulate the immune system. Recently, several studies have investigated how certain probiotics or postbiotics may contribute to the protection from UV-induced photodamage and oxidative stress in skin [11,14,15,16,17], but only a few of these have tried to explain the molecular mechanisms through which they act on skin by enhancing its natural defenses.
In this context, our study strives to deepen the mechanism by which five heat-treated probiotic strains contribute to protect skin, in particular the epidermis, from oxidative stress, inflammation, and damage artificially induced by UV radiation. To investigate this, we used in vitro models (2D cell lines and a 3D full-thickness skin model) that were stimulated with UV light and selectively treated with the five heat-treated strains. The effects were investigated through a viability assay, transcriptomic, and proteomic analyses. With this work, we aim to contribute valuable insights that may lay the foundation for innovative skincare strategies focused on probiotic-based formulations for enhanced skin protection against UV-induced damage.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Heat-Treated Probiotics
The bacterial strains Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Skinbac™ SB01, Limosilactobacillus reuteri Skinbac™ SB02, Bifidobacterium breve Skinbac™ SB03, Ligilactobacillus salivarius Skinbac™ SB04, and Bifidobacterium animalis spp. lactis Skinbac™ SB05 (Probiotical Research S.r.l., Novara, Italy) underwent thermal inactivation at temperatures exceeding 75 °C for 30–90 min. Following heat treatment, the strains were processed via spray-drying and subsequently analyzed using flow cytometry with two fluorophores, TO and PI, to determine the total fluorescent units (TFU). This quantification enabled standardization to a final concentration of 109 TFU per gram. The resulting powders were stored at 4 °C for further analysis of their postbiotic properties.
2.2. Human Immortalized HaCaT Keratinocyte Cell Line Culture
The human immortalized HaCaT keratinocyte cell line (BS CL 168) was obtained from Istituto Zooprofilattico (Brescia, Italy). The cells were grown in a 25 cm2 tissue culture flask, in RPMI-1640 medium (Sigma Aldrich, Milan, Italy) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Sigma Aldrich, Milan, Italy) 2 mM L-glutamine, penicillin (100 U mL−1)/streptomycin (100 U mL−1), and 50 mg mL−1 gentamicin. The cells were incubated in a humidified, 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37 °C. When ca. 80% of confluence was reached, cells were harvested with trypsin/EDTA and seeded at a density of 5 × 104 cells per well into 96 well plates for 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide proliferation (MTT) assay, or at a density of 1 × 106 cells per well into 24 well plates for RNA extraction.
2.3. Primary Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes
Cryopreserved Human Adult Epidermal Keratinocytes (NHEK-Ad) from a single donor, obtained by Lonza (catalog #00192627), were grown in a 25 cm2 tissue culture flask, in KGM™ Gold Keratinocyte Basal Medium (Lonza, Basilea, Switzerland) supplemented with 0.50 mL Hydrocortisone, 0.50 mL Transferrin, 0.25 mL Epinephrine, 0.50 mL GA-100, 2 mL BPE, 0.50 mL hEGF, and 0.50 mL insulin (Lonza, Basilea, Switzerland). The cells were incubated in a humidified, 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37 °C. When ca. 80% of confluence was reached, cells were harvested with trypsin/EDTA and seeded at a density of 105 cells per well into 24-well plates and then used for the subsequent experiments with a UV-C lamp, SkinbacTM heat-treated probiotics, and proteomic analysis.
2.4. 3D Phenion® Full-Thickness Skin Model
3D Phenion® full-thickness skin models (FTSM) (diameter 140 mm, thickness 2.6–3.8 mm) were purchased from Henkel (Phenion® FT; Dusseldorf, Germany) and cultured in small Petri dishes (3.5 cm in diameter) filled with 4 mL pre-warmed air-liquid-interface (ALI) medium, provided by the manufacturer. Tissues were subjected to experiments after the overnight equilibration at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
2.5. UVA/UVB Light Damage of HaCaT Cell Line and 3D Phenion® Full-Thickness Skin Model
HaCaT cell line, seeded in 96-well plates, or overnight equilibrated 3D Phenion® full-thickness skin models, were exposed to UV radiation (UVA: 18 J cm−2 or 10 J cm−2 and UVB: 0.2 J cm−2 or 0.025 J cm−2) in the Irradiation chamber BS-02 (Opsytec Dr. Gröbel GmbH, Ettlingen, Germany) in a dose-controlled mode. Twenty-four hours after UV exposure, the basal medium was removed from the wells and replaced with fresh medium or with the heat-treated probiotics samples diluted in the medium at the following concentrations: 2 × 106 heat-treated strains mL−1 for HaCaT cell line and 2 × 107 heat-treated strains mL−1 for the FTSM. Each sample was tested in triplicate, and untreated cells were used as control.
2.6. Study of Recovery from UVA/UVB Light Damage of HaCatT Cell Line and 3D Phenion® Full-Thickness Skin Model with MTT Assay
After 24- or 48-h incubation with the heat-treated probiotics, we proceeded by evaluating cell viability with the MTT assay, performed according to the method of Mosmann [18] with slight modifications. For the HaCaT cell line, the medium was removed and 100 µL of MTT reagent was applied to the cells (0.05 mg mL−1 in RPMI 1640 medium without phenol-red). The plate was incubated for 3 h in the dark at 37 °C, 5% CO2. Afterwards, the MTT solution was aspirated and 100 µL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were added to dissolve the purple formazan product. The solution was shaken in the dark for 15 min at room temperature. For 3D Phenion® FTSM, the tissue was washed with PBS and excessive liquid was removed by slightly drying on a sterile filter paper disc. Thereafter, three cuts were realized on it to allow penetration of MTT solution in the skin model. The so-cut 3D model was placed in a 24 well-plate containing 1 mL of MTT solution (0.05 mg mL−1 diluted in ALI medium) and was incubated for 3 h at 37 °C, 5% CO2. After the incubation period, the tissues were removed from the wells containing MTT solution and dried on a filter paper. Then, they were transferred into a new 24 well-plate containing 1 mL of 2-propanol. The plate was incubated for another 3 h at room temperature on a shaker (approx. 250 rpm). Thereafter, the tissue was removed from the wells and 1 mL of 2-propanol was added to the eluate of each well. The plate was shaken to obtain a homogeneous solution. Then, three aliquots of 200 µL were transferred into a new 96-well plate. The absorbance of the solutions was read in a microplate reader (BioTek Instruments Inc., Bad Friedrichshall, Germany) at 570 nm and 630 nm (reference wavelength). Data were expressed as cell viability percentage, compared to the control cells, as per the following formula:
% cell viability/ctrl = (Abs sample/Abs ctrl) × 100
2.7. RNA Extraction and Real-Time-PCR of HMOX1, IL-6, and TP53 Genes on 3D Phenion® Full-Thickness Skin Model
After exposure of 3D Phenion® FTSM to UV radiation (UVA 10 J cm−2, UVB 0.025 J cm−2) in the Irradiation chamber BS-02 (Opsytec Dr. Gröbel GmbH) in a dose-controlled mode and treatment with SkinbacTM heat-treated probiotics 2 × 107 heat-treated strains mL−1 diluted in ALI medium for 24 or 48 h, the FTSM was cut into two identical pieces using a sharp scalpel. The pieces were inserted into 2 mL tubes containing 1 mL of Trizol™ (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and the tissue was disrupted into the ULTRA-TURRAX® T 25 digital (IKA-Werke GmbH & Co. KG, Staufen, Germany) for about 30 s. Total RNA was extracted from the 3D skin models according to the method described by Chomczynski and Mackey [19]. Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized by reverse transcriptase using commercial kit “PrimeScriptTM RT Reagent Kit (perfect Real Time)” (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan). Produced amplicons were quantified through the monitoring of the fluorescence emitted during reaction by using the TaqMan® (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA) probes system. Gene expression of HMOX1, IL-6, and TP53 were evaluated through quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The following TaqMan probes were used: Hs01110250-m1 (HMOX1), Hs00985639_m1 (IL-6), Hs01034249_m1 (TP53), and Hs99999905_m1 (GAPDH) as housekeeping gene. The obtained data were analyzed according to the 2−ΔΔCt method [20].
2.8. UVC Light Damage of NHEK
Human Adult Epidermal Keratinocytes (NHEK), seeded in 24-well plates, were added with 107 heat-treated strains mL−1, incubated at 37 °C for 24 h, and then exposed to UVC radiation (30 J cm−2) using a UVC lamp (VWR part of Avantor, Radnor, PA, USA). One hour after UV exposure, expression of tight junctions Occludin (OCLN), Claudin 1 (CLDN1), and Claudin 4 (CLDN4) was assessed by ELISA (Assay Genie, Dublin, Ireland). The ELISA assay was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, samples and standards were added to pre-coated wells, followed by incubation with specific antibodies and a substrate solution, and the absorbance was measured at the specified wavelength to determine analyte concentrations.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Data from each experiment were subjected to statistical analysis using Student’s t-test; p-values less than 0.05 or 0.01 were considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Study of Recovery from UVA/UVB Light Damage of HaCaT Cell Line with MTT Assay
The MTT assay is a simple method to investigate the metabolic activity of cells cultivated in vitro and their consequent viability. In our study, it was used to investigate the change in viability of cells after UVA and UVB exposure and subsequent treatment with the SkinbacTM heat-treated probiotics. As expected, a decrease in cell viability was observed after UVA and UVB exposure (18 J cm−2 and 0.2 J cm−2, respectively), likely due to the induced photodamage. On the other hand, the treatment with SkinbacTM helped cells recover from the damage, demonstrated by a statistically significant difference compared to the UV-damaged cells (p < 0.05). Data are shown in Figure 1A,B.
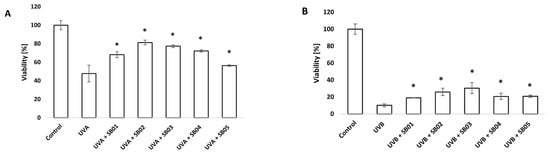
Figure 1.
Viability of HaCaT cell line analyzed with MTT assay, after UVA 18 J cm−2 (A) and UVB 0.2 J cm−2 (B) exposure and consequent 24 h treatment with SkinbacTM heat-treated probiotics diluted in the medium at 2 × 106 heat-treated strains mL−1. Columns correspond to the average value of three independent samples; error bars represent SEM. Asterisks indicate significant difference compared to cells treated only with UV radiation (* = p < 0.05).
3.2. Study of Recovery from UVA/UVB Light Damage of 3D Phenion® Full-Thickness Skin Model with MTT Assay
We further investigated the effect of UVA and UVB radiation on the 3D Phenion® FTSM. As previously shown, a decrease in cell viability 24 h after UVA exposure (10 J cm−2) was confirmed on the FTSM. In this case, only SB01 and SB05 improved the viability of FTSM with a statistically significant difference. The effect of UVB (0.025 J cm−2) exposure on viability was not evident after 24 h treatment, but a significant decrease in viability compared to untreated control was shown 48 h after treatment. In this second case, all the SkinbacTM taken in analysis could help the tissue in recovery from UVB damages, as demonstrated by the statistically significant difference of viability compared to the control treated with UVB alone (Figure 2A,B)
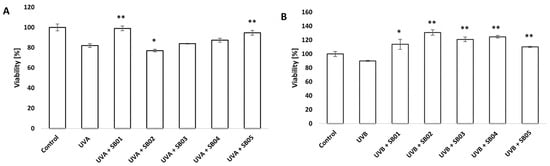
Figure 2.
Viability of 3D Phenion® full-thickness skin model analyzed with MTT assay, after UVA 10 J cm−2 (A) exposure and consequent 24 h treatment with SkinbacTM heat-treated probiotics, and UVB 0.025 J cm−2 (B) exposure and consequent 48 h treatment with SkinbacTM heat-treated probiotics. SkinbacTM were diluted in the medium at 2 × 107 heat-treated strains mL−1. Columns correspond to the average value of three independent samples; error bars represent SEM. Asterisks indicate significant difference compared to cells treated only with UV radiation (* = p < 0.05; ** = p < 0.01).
3.3. Gene Expression of HMOX1, IL-6, and TP53 in the 3D Phenion® Full-Thickness Skin Model
After exposure of 3D Phenion® FTSM to UV radiation (UVA 10 J cm−2, UVB 0.025 J cm−2) and treatment with SkinbacTM heat-treated probiotics (2 × 107 heat-treated strains mL−1) diluted in ALI medium for 24 or 48 h, RNA was extracted and qRT-PCR was used to determine the relative gene expression, as described in the previous section. Figure 3 show data relative to gene expression of HMOX1, a gene encoding for Heme oxigenase 1, an essential enzyme in heme catabolism. Mammalian heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1), one of two isoforms of heme oxygenase (Hmox; EC 1.14.99.3) that catabolize cellular heme to biliverdin, carbon monoxide, and free iron, is strongly upregulated during stress, and it is considered one of the most sensitive and reliable indicators of cellular oxidative stress [21]. SB03 and SB04 were able to significantly downregulate the expression of HMOX1 in the 3D FTSM after oxidative stress induction with UVB after 24 h. SB01 and SB02 showed a tendency to downregulate the expression of HMOX1 in the 3D skin model, but without statistical significance. UVA treatment did not show an upregulation of this gene, and neither was it observed after 48 h of treatment with UVB.
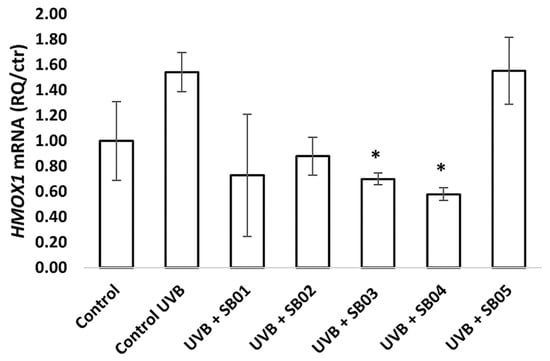
Figure 3.
Gene-expression analysis of HMOX1 determined by qRT-PCR of 3D Phenion® full-thickness skin model irradiated with UVB (0.025 J cm−2) and treated for 24 h with SkinbacTM SB01, SB02, SB03, SB04, and SB05 2 × 107 heat-treated strains mL−1, diluted in ALI medium. Columns correspond to the average value of two independent samples; error bars represent SEM. Asterisks indicate significant difference compared to cells treated only with UV radiation (* = p < 0.05).
Figure 4 presents IL-6 expression data of 3D FTSM. This gene encodes for the cytokine Interleukin 6, which functions in inflammation, and it is known to be induced by UV radiation [22]. Our data confirms this statement and demonstrates the ability of the heat-treated probiotics to reduce the expression of this gene, suggesting potential anti-inflammatory properties. Statistically, only the reduction obtained with SB03 and SB04 can be considered significant, though SB01 and SB02 also showed a tendency to reduce the expression of this gene.
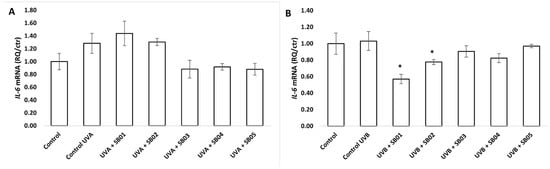
Figure 4.
(A,B) Gene-expression analysis of IL-6 determined by qRT-PCR of 3D Phenion® full-thickness skin model irradiated with UVA (10 J cm−2) and UVB (0.025 J cm−2) and treated for 24 h with SkinbacTM SB01, SB02, SB03, SB04, and SB05 diluted in ALI medium at 2 × 107 heat-treated strains mL−1. Columns correspond to the average value of two independent samples; error bars represent SEM. Asterisks indicate significant difference compared to cells treated only with UV radiation (* = p < 0.05).
UV radiation has been shown to induce the expression of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene and is known to produce “signature” mutations in p53 in human and mouse skin cancers and in the tumor-suppressor gene patched in human basal cell carcinoma [23]. The function of p53 is to induce DNA repair when needed and/or induce apoptosis if the damage is too great; in this way, the protein suppresses tumor development. All the heat-treated probiotics inhibited UV-induced expression of gene encoding p53 24 h post UVB irradiation, suggesting a positive role in skin tumor prevention (Figure 5). UVA did not significantly influence the expression of TP53.
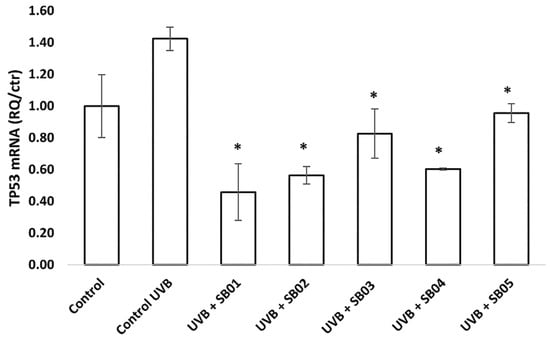
Figure 5.
Gene-expression analysis of TP53 determined by qRT-PCR of 3D Phenion® full-thickness skin model irradiated with UVB (0.025 J cm−2) and treated for 24 h with SkinbacTM SB01, SB02, SB03, SB04, and SB05 2 × 107 heat-treated strains mL−1, diluted in ALI medium. Columns correspond to the average value of two independent samples; error bars represent SEM. Asterisks indicate significant difference compared to cells treated only with UV radiation (* = p < 0.05).
3.4. Study of Protection from UVC Light Damage of NHEK
Cellular extracts were utilized to investigate the modulation of key tight junction (TJ) proteins by probiotics, employing ELISA assays for precise measurement. Following UVC-induced damage, the probiotics displayed distinct capacities to enhance the expression of critical TJ proteins, including Claudin-1, Claudin-4, and Occludin (Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8), compared to the positive control. These proteins are fundamental in preserving the integrity and function of the skin barrier, as well as in supporting vital cellular processes such as differentiation, proliferation, and permeability regulation. The observed upregulation of Claudin-1, Claudin-4, and Occludin in response to probiotic treatment highlights a potential mechanism through which these microorganisms strengthen the skin’s natural defense. Additionally, the promotion of tight junction repair by probiotics, as indicated in the graphs, suggests their role in accelerating recovery from UV-induced damage, reinforcing the importance of TJ proteins in maintaining skin homeostasis.
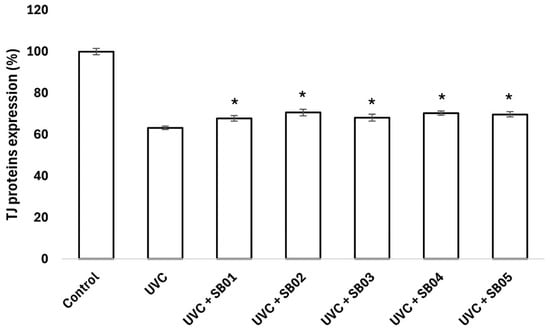
Figure 6.
Claudin-1 protein expression of NHEK-Ad cells analyzed with ELISA assay, after treatment with SkinbacTM SB01, SB02, SB03, SB04, and SB05 107 heat-treated strains mL−1 and UVC 30 J cm−2 exposure. Columns correspond to the average value of two independent samples; error bars represent SEM. Asterisks indicate significant difference compared to cells treated with UVC radiation (* = p < 0.05).
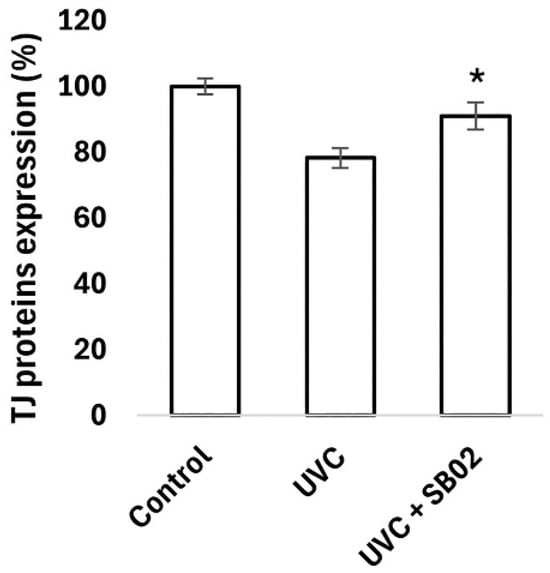
Figure 7.
Claudin-4 protein expression of NHEK-Ad cells analyzed with ELISA assay, after treatment with SkinbacTM SB02 107 heat-treated strains mL−1 and UVC 30 J cm−2 exposure. Columns correspond to the average value of two independent samples; error bars represent SEM. Asterisks indicate significant difference compared to cells treated with UVC radiation (* = p < 0.05).
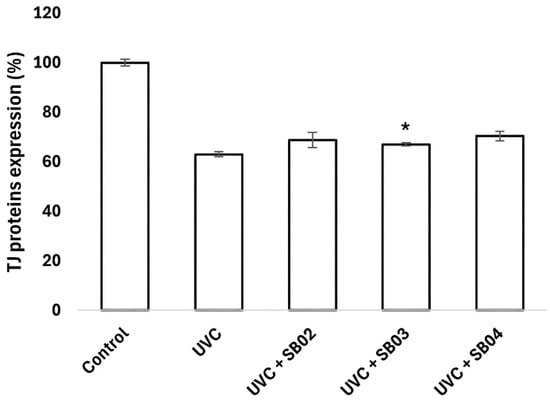
Figure 8.
Occludin protein expression of NHEK-Ad cells analyzed with ELISA assay, after treatment with SkinbacTM SB02, SB03, and SB04 107 heat-treated strains mL−1 and UVC 30 J cm−2 exposure. Columns correspond to the average value of two independent samples; error bars represent SEM. Asterisks indicate significant difference compared to cells treated with UVC radiation (* = p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
UV radiation is one of the best-studied environmental factors contributing to the skin exposome [2], inducing skin damage and aging (hence, the term “photoaging”), and is a causative factor in melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers [24]. Photoprotection is necessary for preventing skin alterations. The modern approach combines the usage of physical or chemical sunscreens that act at a primary level to absorb or reflect UV radiation, with secondary-level protection consisting of active ingredients (e.g., antioxidants) that cooperate in controlling skin damage [25]. The skin microbiome has a significant impact on dermal health [26], and the usage of probiotics and postbiotics may influence it beneficially [13]. Several studies have also highlighted their role in counteracting the negative effects induced by UV light, primarily through their capacity to produce antioxidant compounds or enzymes, UV-absorbing compounds, and photolyases [11,14,25,27,28,29,30].
Our study aimed to investigate how five heat-treated probiotic strains (Skinbac™ SB01, Skinbac™ SB02, Skinbac™ SB03, Skinbac™ SB04, Skinbac™ SB05) contribute to protect skin from oxidative stress, inflammation, and damage caused by UV radiation.
To elucidate this, we first studied how UVA and UVB rays influence cell viability of a human keratinocyte cell line and a human full-thickness skin model. It is well-documented that prolonged exposure to UV radiation in skin induces an auto-regulated program of cell death (p53 dependent apoptosis), which aims to prevent the replication of DNA-damaged cells [31]. As expected, UVA and UVB treatment reduced cell viability of HaCaT cells. The consequent 24 h treatment with SkinbacTM heat-treated probiotics helped cells recover, significantly increasing their viability (Figure 1A,B). To further consolidate these findings, the 3D Phenion® FTSM (Phenion® FT; Dusseldorf, Germany) was also employed, which better mimics the in vivo conditions. In fact, this model comprises epidermal keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts organized in a multilayered skin equivalent that resembles human skin structure and tissue functionality. Similarly, the treatment of FTSM with UVA and UVB showed a tendency to decrease its viability, though less pronounced than in the case of the HaCaT cell line. Cultivating the model with the heat-treated probiotics confirmed their positive role. In fact, all the strains significantly increased the viability, except for SB02, SB03, SB04 after treatment with UVA (Figure 2A,B).
Transcriptomic analysis helped reveal the mechanism regulating programmed cell death. In fact, TP53 gene (encoding for Tumor Protein 53) was upregulated in samples treated with UVB rays, as previously reported [31], while all the heat-treated strains were able to downregulate its expression, further consolidating their potential role in DNA repair and cell damage recovery, thereby preventing apoptosis (Figure 5).
The second gene that we took into account was HMOX1, which encodes for the antioxidant enzyme heme oxygenase 1, considered an indicator of cellular oxidative stress [21] that can be induced by several environmental stimuli, including UV radiation [32]. In our study, UVB upregulated the expression of this gene in the FTSM, while SkinbacTM SB01, SB02, SB03, and SB04 downregulated its expression, with the latter two showing statistical significance (Figure 3). We hypothesized that the probiotics produced antioxidant metabolites that remained stable after heat-treatment, and when absorbed by the FTSM participated in the process of ROS scavenging, contributing to reduce the skin cell response to stress induced by UV irradiation. Similarly, UVA and UVB irradiation showed a tendency to increase the expression of the IL-6 gene compared to control. This response is expected. Previous studies reported the increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines expression in skin after UV irradiation [16,22,31]. Here we show that certain strains of SkinbacTM can help decrease the inflammatory response of skin to UV exposure.
Finally, we examined tight junction (TJ) protein expression. Following UVC-induced damage, the probiotics enhanced the expression of critical TJ proteins, including Claudin-1, Claudin-4, and Occludin (Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8) compared to the positive control. These proteins are fundamental not only in preserving skin barrier integrity and function but also in vital cellular processes such as differentiation, proliferation, and permeability regulation [33]. Tight junctions are essential for maintaining skin homeostasis by preventing the passage of harmful substances and ensuring proper cell signaling. The probiotic-driven upregulation of these proteins suggests a mechanism by which these beneficial microorganisms strengthen the skin’s natural defenses. Furthermore, by promoting the repair of damaged TJ structures, probiotics may accelerate recovery from UV-induced skin damage.
It is worth noting that our experimental design incorporated UVC radiation testing as a “worst-case scenario” approach [34]. While UVC rays are less prevalent in the environment compared to UVA and UVB due to atmospheric filtration, they are significantly more energetic and potentially more damaging to cellular structures [35]. This methodological choice offers substantial advantages: by subjecting materials to the most intense form of ultraviolet radiation, we rigorously test their robustness under extreme conditions [36]. If Skinbac™ demonstrates adequate protection against UVC rays, it likely exhibits even greater efficacy against the less energetic UVA and UVB rays [34]. Additionally, such stress testing helps identify potential failure points, providing greater confidence before moving on to more specific tests [36]. This approach aligns with established R&D protocols, where stress testing methodologies anticipate critical issues. Using UVC radiation accelerates and amplifies potential damage, allowing rapid assessment of product efficacy and resilience under conditions far more severe than normal sun exposure [35].
5. Conclusions
This study highlights the significant potential of heat-treated probiotics to mitigate the adverse effects of UV radiation on the skin. By enhancing cell viability, modulating critical genes associated with oxidative stress and inflammation, and restoring tight junction protein integrity, these strains demonstrate a multifaceted approach to skin protection. The ability of specific probiotics to downregulate genes like TP53 and HMOX1, while also attenuating inflammatory markers such as IL-6, underscores their role in DNA repair, ROS scavenging, and reducing pro-inflammatory responses.
From a practical perspective, these findings pave the way for innovative applications in dermatological and cosmetic industries. Heat-treated probiotics, like the Skinbac™ strains, could be incorporated into topical formulations, sunscreens, or oral supplements aimed at promoting skin health, preventing photoaging, and accelerating recovery from UV-induced damage. Their stability and efficacy even after heat treatment make them particularly attractive for industrial scaling and product development.
Author Contributions
G.M., D.P., A.A. and M.P. conceptualized the study. G.M., A.A., A.V. and G.D., contributed to methodology. G.M. and A.A. worked on the formal analysis. G.M., A.A., A.V. and G.D. carried out the investigation. G.M., A.A., M.P. and D.P. wrote the original draft. M.P., F.R. and D.P. reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported equally by Giuliani S.p.A. and Probiotical S.p.A.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Giammaria Giuliani of Giuliani S.p.A. (Milano, Italy) and Vera Mogna from Probiotical S.p.A. (Novara, Italy) for their trust in the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this study received funding from Giuliani S.p.A. and Probiotical S.p.A. G.M. and D.P. are employed by Giuliani S.p.A.; F.R. serves as a consultant for Giuliani S.p.A.; A.A., A.V., G.D. and M.P. are employed by Probiotical Research Srl. The authors declare that, despite these financial and commercial relationships, the research was conducted with complete scientific autonomy and independence. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, interpretation of results, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. All scientific decisions were made independently by the research team, and the study protocol, methodology, and conclusions reflect solely the scientific judgment of the authors.
References
- Chen, D.; Ai, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ao, Y.; Rong, J.; Li, G. Protective effects of Cu/Zn-SOD and Mn-SOD on UVC radiation-induced damage in NIH/3T3 cells and murine skin. Acta Histochem. 2023, 125, 152030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krutmann, J.; Bouloc, A.; Sore, G.; Bernard, B.A.; Passeron, T. The skin aging exposome. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 85, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, B.; Cockerell, C.J. Pathobiology of actinic keratosis: Ultraviolet-dependent keratinocyte proliferation. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, S10–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ying, W. NAD+ administration profoundly decreases UVC-induced skin damage by attenuating oxidative stress. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2023, 15, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer, G.P. Mechanisms of UV-induced mutations and skin cancer. Genome Instab. Dis. 2020, 1, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapetsas, A.; Voulgaridou, G.P.; Konialis, M.; Tsochantaridis, I.; Kynigopoulos, S.; Lambropoulou, M.; Stavropoulou, M.I.; Stathopoulou, K.; Aligiannis, N.; Bozidis, P.; et al. Propolis Extracts Inhibit UV-Induced Photodamage in Human Experimental In Vitro Skin Models. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laga, A.C.; Murphy, G.F. The Translational Basis of Human Cutaneous Photoaging. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, C.V.; Antiga, E.; Lulli, M. Oral and Topical Probiotics and Postbiotics in Skincare and Dermatological Therapy: A Concise Review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ácsová, A.; Hojerová, J.; Martiniaková, S. Efficacy of postbiotics against free radicals and UV radiation. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, S.; Ali, S.A. Probiotics and postbiotics play a role in maintaining dermal health. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 3966–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COSSMA. Postbiotics Anti-Ageing Care [Internet]. 2020. Available online: https://www.cossma.com/ingredients/article/postbiotics-anti-ageing-care-36102.html (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; Cao, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhou, H.; Yu, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Ma, P.; et al. Hydrogel sunscreen based on yeast /gelatin demonstrates excellent UV-shielding and skin protection performance. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 205, 111885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Chen, M.; Xue, L.; Wang, J.; Ye, Q.; Wu, S.; Yang, R.; Zhao, H.; et al. Exploration of the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-Photoaging Effect of Limosilactobacillus fermentum XJC60. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 838060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Rath, G. Formulation and evaluation of UV protective synbiotic skin care topical formulation. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2019, 21, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods. 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomczynski, P.; Mackey, K. Short technical reports. Modification of the TRI reagent procedure for isolation of RNA from polysaccharide- and proteoglycan-rich sources. Biotechniques 1995, 19, 942–945. [Google Scholar]
- Vigetti, D.; Viola, M.; Karousou, E.; Rizzi, M.; Moretto, P.; Genasetti, A.; Clerici, M.; Hascall, V.C.; De Luca, G.; Passi, A. Hyaluronan-CD44-ERK1/2 regulate human aortic smooth muscle cell motility during aging. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 4448–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poss, K.D.; Tonegawa, S. Reduced stress defense in heme oxygenase 1-deficient cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10925–10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Song, X.; Bi, Z.; Chu, W.; Wan, Y. UV-induced NF-kappaB activation and expression of IL-6 is attenuated by (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in cultured human keratinocytes in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soehnge, H.; Ouhtit, A.; Ananthaswamy, O.N. Mechanisms of induction of skin cancer by UV radiation. Front. Biosci. 1997, 2, d538–d551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nichols, J.A.; Katiyar, S.K. Skin photoprotection by natural polyphenols: Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and DNA repair mechanisms. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2010, 302, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souak, D.; Barreau, M.; Courtois, A.; André, V.; Duclairoir Poc, C.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Gault, M. Challenging Cosmetic Innovation: The Skin Microbiota and Probiotics Protect the Skin from UV-Induced Damage. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Prajapat, G.; Abrar, M.; Ledwani, L.; Singh, A.; Agrawal, A. Cyanobacteria as efficient producers of mycosporine-like amino acids. J. Basic Microbiol. 2017, 57, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Chen, T.H.; Butcher, A.M.; Trzoss, L.L.; Nam, S.J.; Shirakawa, K.T.; Zhou, W.; Oh, J.; Otto, M.; Fenical, W.; et al. A commensal strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis protects against skin neoplasia. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, N.; Berman, B.; Ceilley, R.I.; Kircik, L.H. Understanding the Role of Photolyases: Photoprotection and Beyond. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2017, 16, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Allhorn, M.; Arve, S.; Brüggemann, H.; Lood, R. A novel enzyme with antioxidant capacity produced by the ubiquitous skin colonizer Propionibacterium acnes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Trink, A.; Giuliani, G.; Rinaldi, F. Protective Effects of Sunscreen (50+) and Octatrienoic Acid 0.1% in Actinic Keratosis and UV Damages. J. Investig. Med. 2022, 70, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Nisar, M.F.; Lin, M.; Zhong, J.L. Heme Oxygenases: Cellular Multifunctional and Protective Molecules against UV-Induced Oxidative Stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5416728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, N.; Brandner, J.M. Barriers and more: Functions of tight junction proteins in the skin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1257, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Orazio, J.; Jarrett, S.; Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Scott, T. UV Radiation and the Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12222–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, D.L.; Saladi, R.N.; Fox, J.L. Ultraviolet radiation and skin cancer. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, J. The product stress testing approach. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2004, 9, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).