Abstract
Human skin homeostasis is partly maintained by a complex microscopic ecosystem known as the microbiota. Together, the skin host and microbiota form a synergistic evolutionary unit referred to as ‘skin holobiont’, which can be modulated by various stresses. By extracting organic wild yellow gentian roots enhanced through fermentation of a rare and resistant bacterium, Sphingomonas faeni, a cosmetic active ingredient was developed to rebalance the holobiont functions as well as hydric and lipidic skin content. Indeed, gentian-fermented extract (GFE) boosts hyaluronic acid (HA) biosynthesis in vitro, stimulates the HA receptor, CD44, and allows water storage and retention through its signaling cascade by epidermal reinforcement. Importantly, GFE also increases lipid synthesis by +147% in vitro, which was confirmed clinically on volunteers with dehydrated and dry skin who presented an increase in hydration and skin surface lipids after 28 days of treatment. Furthermore, a metaproteomic study highlighted that there is a slow-down of skin barrier and antioxidant proteins from both human and microbial origins, with age and dehydration, that can be reversed by GFE after 56 days. In conclusion, acting on the HA metabolism and specific microbiota species, GFE rebalances the skin holobiont for a reinforced and rehydrated skin with optimal lipid content.
1. Introduction
It is now well known that microorganisms present at the skin surface play a strong role in the proper functioning of the skin. More precisely, mutual relations between the skin and its microbial ecosystem, as well as their responses to environmental impacts, are of great importance as dysbiosis contributes often to skin diseases [1]. It has also been shown that water content is a factor that influences the microbiota composition. Indeed, microbiota communities are diverse in different skin body sites: moist, sebaceous and dry [2]. During adulthood, and in the absence of drastic shifts in external factors, the individual skin microbiota shows temporal stability [3] despite the large interindividual variability [4], suggesting that mutualistic and commensal interactions exist between skin microorganisms, but also between skin microorganisms and their host. Subsequently, the maintenance of skin moisturization should also imply proper interactions between skin microbiota and its host. A lack of studies on the topic required us to perform a metaproteomic analysis in order to determine the relationships between hydration level, skin microbiota diversity and holobiont functions. Holobiont comes from the Greek word “holos” which means “all” and “bios” meaning “life”. It represents an assemblage of a host organism and its microbial ecosystem [5]. The skin holobiont represents the interface between our organism and its external environment. Its first mission is to be a defense barrier against daily and various (physical, mechanical and biological) stresses while preserving exchanges with our environment. Besides its protective role, another main function of the skin is to maintain proper skin hydration [6].
The skin barrier has a double role: to prevent the penetration of outside elements and the evaporation of water from the skin. These specific functions rely on a dynamic homeostasis that needs to be maintained. Skin hydration is defined as water content present within the stratum corneum (SC), the outermost skin layer which is composed of corneocytes embedded into a lipid-filled intercellular area. Skin water content relies on a combination of two distinct mechanisms: hydration, meaning the ability of the skin to retain stored water, and moisturization, meaning the skin’s ability to prevent water loss [7]. Therefore, skin water homeostasis depends on a precise balance between water retention in the dermis, mainly through hyaluronic acid (HA), and the skin’s ability to lock in moisture, partly by the SC and its lipid content [8]. Indeed, HA has very interesting hygroscopic properties essential for water storage in the dermis and epidermis. Furthermore, through its signaling cascade binding one of its receptors, cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44), HA is also critical for skin barrier maintenance. Indeed, the HA/CD44 glycoprotein conjugate influences the formation of the lamellar bodies which are expressed from keratinocytes to form the lipid lamellar bilayer of the SC [9].
Addressing skin dehydration and dryness, plants and microorganisms able to resist desiccated and cold environments such as Gentiana lutea, a mountain plant that grows best with altitude [10], and Sphingomonas faeni (S. faeni), a rare bacteria isolated from the aerobiome [11], were studied. Gentian roots are known for their content in secoiridoids such as gentiopicroside and amarogentin which give drinks made from gentian roots their bitter taste [12]. Another secoiridoid of interest is swertiamarin, as it has been demonstrated to reduce levels of free radicals [13]. Roots also contain iridoids, including loganic acid, which is able to activate antioxidant enzymes and reduce ROS levels [14]. Therefore, swertiamarin and loganic acid, strong antioxidants, are of particular interest as they can assist in protecting HA that can be degraded by free radicals [15]. Gentiana lutea roots also contain sugars such as monosaccharides (glucose, fructose), disaccharides (saccharose, gentiobiose) and trisaccharides (gentianose), which can be used as substrates for various microorganisms. S. faeni is widely described in the literature as a “psychrotolerant” bacterium [16], i.e., capable of growing at temperatures close to 0 °C, despite having an optimum growth temperature of over 20 °C. This cold tolerance is attributed to the accumulation of lipids as a first strategy adopted to increase membrane fluidity [16,17]. Based on its unique composition and ability to resist desiccated and cold environments thanks to defense mechanisms, S. faeni represents an innovative source for the development of new skincare solutions specifically dedicated to dry and dehydrated skins.
In the present study, age and dehydration were taken as putative modulators or stressors of the holobiont functions to determine the impact of stresses on skin holobiont protein interactions and find a natural topical solution to rebalance the observed modulations. Thus, an active cosmetic ingredient, GFE, based on Gentiana lutea roots fermentation by S. faeni, was developed. In vitro, GFE acts on hyaluronic acid production and protection, as well as epidermal lipid synthesis. Clinically GFE increases, on dehydrated volunteers, skin hydration and skin surface lipids versus a placebo. Thanks to a metaproteomic study aiming at deciphering the main biological functions modulated between aged dehydrated and young skins, the restorative properties of GFE on skin holobiont were demonstrated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fermented Extract Production (In-House Experiments)
Yellow Gentiana lutea roots were locally and sustainably harvested in France by a gentian association. Roots were ground into pieces between 0.1 and 1 cm and extracted in an ethanol–water (water heated to 55 °C) mixture (50% v/v). Extract was then decolorized with activated charcoal, clarified, concentrated by evaporation of the alcohol, purified on a XAD-16N resin column and clarified again to obtain a first purified gentiana extract, rich in antioxidant molecules. In order to enrich amino acids and lipids without degrading antioxidant molecules, fermentation was conducted in parallel. Thus, gentian roots were fermented by adding water and bacterial culture containing Sphingomonas faeni which was isolated from the aerobiota of the Puy De Dôme station (France) [11]. The fermentation was performed for 10 days and the fermented extract was clarified to remove gentian roots before mixing into the ethanolic purified gentian extract to obtain the final gentian fermented extract (GFE). The latter was finally stabilized in water/propanediol (50/50) to solubilize both antioxidant molecules from the ethanolic extract and the fermented aqueous one. GFE is characterized by the following molecules (% on a dry matter basis; DM): Loganic acid ≥ 2%/DM; Swertiamarin ≥ 1%/DM; Amino acids ≥ 0.5%/DM; Polar lipids: Presence. Based on laboratory analysis, GFE also contains minor bitter compounds from iridoid family, polyphenols including flavonoids, sugars and few proteins.
2.2. In Vitro Evaluation of Biological Activity (In-House Experiments)
2.2.1. Hyaluronic Acid Dosage
Normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) and normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK) isolated from 55-year-old donors were incubated during 72 h with GFE 0.5%. HA dosage was then conducted on supernatants by solid phase sandwich ELISA (DHYAL0, Biotechne, Minneapolis, MN, USA) with absorbance measurement at 450nm (Fluoroskan Ascent FL, Thermo Fisher Scientific™, Waltham, MA, USA). A dosage of total proteins with BCA method was conducted for normalization. Each condition was conducted in 3 (NHEK) or 6 (NHDF) replicates and variations of HA releases were expressed as percentage of untreated cells (control). Concerning statistical analysis, the results are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was assessed using Student’s t-test and significant differences compared to the control are indicated as follows: * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001.
2.2.2. Epifluorescence Microscopy for CD44 and Lipids Quantification
Immunodetection and quantification of CD44 were performed on NHEK (n ≥ 4) from 55-year-old donors treated 48 h with GFE 0.5% or D-panthenol 0.3% or nothing (control). Topical D-panthenol is a well-known molecule that acts like a moisturizer [18]. The variations of CD44 expression were expressed as percentage of untreated cells (control). CD44 was detected by immunostaining using specific primary monoclonal antibody (O/N, 4 °C; 14-0441-82, Invitrogen™, Waltham, MA, USA) and a secondary antibody coupled to a green fluorochrome (45 min, room temperature; A11006, Invitrogen™).
Quantification of lipids synthesis was performed by staining lipids with a lipid-specific green fluorescent dye (BODIPY dye, D3922, Invitrogen™) in NHEK (n = 3) treated (or not, control condition) with GFE 0.5% during 48 h.
Pictures were acquired with an epifluorescence microscope (Leica®, Wetzlar, Germany) using strictly the same acquisition time and resolution (20× objective). Quantification of fluorescence staining was performed using ImageJ software (1.54f version, NIH) on 2 distinct images per replicate by integration of the specific fluorescence signal normalized by the number of cells (Hoechst staining), and then expressed as percentage of relative fluorescent unit normalized to untreated NHEK (control). Concerning statistical analysis, the results are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was assessed using Student’s t-test and significant differences compared to the control are indicated as follows: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
2.3. In Vivo Evaluation of Biological Activity
2.3.1. Skin Benefit Evaluation
This study was performed by EUROFINS Dermscan/Pharmascan (Villeurbanne, France), which is authorized as a clinical investigation center by the French Health Authorities, on cosmetic products defined by article L. 5131-1 of the French Public Health Code, in accordance with Decree n° 2017-884 of 9 May 2017 modifying some regulatory requirements concerning research involving human subjects. Thus, this trial adhered to the principles of good clinical practices and the declaration of Helsinki. According to local and European regulatory guidelines (Official Journal of the European Union of 10 March 2010, paragraph 1.2.9), this type of trial testing on active cosmetics does not require ethics committee approval or the competent authority’s authorization.
The objective of the clinical study was to evaluate the action of GFE on skin lipidic and hydric balance. One group of 20 healthy female volunteers (phototype II/III: 60%/40%) aged between 42 to 52 years old (mean: 48 years old) was recruited (Group 1). Among them, a sub-panel of sebum-deficient skin was identified (n = 10), with sebum <100 μg/cm2 on forehead, measured by Sebumeter® (Courage & Khazaka, Köln, Germany) [18]. Beyond general inclusion criteria, the group had specific inclusion criteria related to skin hydration and measured using a Corneometer® (Courage & Khazaka, Köln, Germany) : 100% of included volunteers presented dehydrated skin [19].
The study was an intra-individual study, meaning each volunteer being her own control. Volunteers applied (randomized split-face application) the gel containing 1% GFE twice a day (in the morning and in the evening) on one half of the face and the placebo formula at the same rate on the other half of the face. Both products were used in replacement of any usual daily skincare routine. Volunteers were allowed to apply (except on visiting days) usual cleansing, make up and body skincare products. The evaluation of the in vivo effects of GFE-containing gel and placebo (so on both sides of the face for each volunteer) was performed at D0 (before the study) and after 28 days (D28, with last application being carried out the previous day) through different methods: MoistureMap® (Courage & Khazaka, Köln, Germany) to evaluate cutaneous hydration rate on forehead [7] and Sebumeter® (Courage & Khazaka, Köln, Germany) to evaluate skin surface lipids on forehead [20].
2.3.2. Metaproteomic Analysis
A metaproteomic study was performed by PHYLOGENE (Bernis, France) to identify skin host/microbiota protein interactions and determine changes occurring in holobiont functions and diversity in dehydrated skin. Ability of GFE to counteract observed differences was also assessed. The principle of a metaproteomic study is to analyze simultaneously proteins from host and its microbiota allowing the deciphering of their interactions. Swabs were collected at day 0 from 20 younger (25–35 yo) women and from 20 older (42–54 yo) women with dehydrated skin at D0 and 56 days after application of GFE.
Group 2, identified as the younger group with all skin types that did not apply any product, was included in this clinical study as a control for metaproteomic analysis and a tend-to-be reference. Group 1 composed of the same 20 volunteers presenting dehydrated skin and described previously was also sampled for this metaproteomic analysis. A skin surface sampling was carried out on the cheek with swabs on the volunteers of the two groups at D0. A second cheek sampling was performed on group 1 after 56 days of GFE application. Then, evaluation of skin metaproteome was implemented on samples from group 1 and group 2 at D0 to assess impact of age and dehydration on skin holobiont. Then, evaluation was performed between group 1 at D0 and D56 in order to assess the effect of GFE on skin microbiota diversity and holobiont functions. Proteins, whatever their taxonomic origin, were extracted from skin swabs and digested. Resulting peptidic mixtures (500 ng) were injected and analyzed using nano-LC HRAM MS technology (nano chromatography PepMap100 C18 column (Thermo Fisher Scientific™, Waltham, MA, USA); 2.5% to 35% acetonitrile gradient; coupled with High Resolution Accurate Mass Spectrometer Q-Exactive Plus, Thermo at a resolution of 70,000 for MS scan and 17,500 for MS/MS scan). Peptides extracts were labeled with isobaring tags which allowed multiplex samples before injection. This method is based on peptides labelling by the Tandem Mass Tag® (TMT®) (Thermo Fisher Scientific™, Waltham, MA, USA) reagent after sample trypsin digestion. During MS/MS fragmentation, the reagent generates a fragment ion with known mass. Different isobaric (same mass) TMT® reagents are available and each generates fragment ions of different masses. By doing so, they are used to label peptides coming from different digestions that can be mixed in a 1:1 ratio and analyzed in the same LC-MS/MS run. The comparison of ion fragment quantities produced by the different labelling then allows the relative protein quantification. Protein identification was possible thanks to a database sequence alignment followed by bioinformatic analysis.
After protein identification and quantification, for taxonomic analysis, peptides were assigned to the Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA) by submitting their sequences to Unipept tool 1. Then, each protein was assigned to the most precise LCA of its peptides. Identified taxa were gathered in 3 different taxonomic groups: host (all Metazoa), bacteria and fungi. The abundance of each taxon was calculated as the sum of associated protein abundances. Those abundances were used as input data to measure alpha and beta diversity. Alpha-diversity measures the intra-sample diversity. Indexes used in this analysis were Shannon and Simpson indexes, which take into account both taxa abundances and evenness [21,22]. Statistical differences between groups were evaluated by a Wilcoxon test. Beta-diversity measures inter-sample diversity and sample separation according to their microbiota composition. Distance metrics used in this analysis were Bray–Curtis [23]. Statistical differences between groups were measured by PERMANOVA using “adonis” function.
Taxa abundances were calculated by summing abundances of all associated proteins. Differentially abundant species were identified by measuring the median fold change and adjusted p-value of all associated proteins. In the following studies, taxa considered as differentially abundant were these with a p-value ≤ 0.05 and a fold change ≥1.2 or ≤0.833.
Functional involvement of proteins from various species was analyzed. Each function was associated to a score corresponding to the sum of its related protein abundances in each sample. Literature analysis allows clustering of identified proteins significantly regulated between conditions according to their main functions. Here, clustered proteins were represented by a black square if the expression was significantly upregulated or a white square if significantly downregulated (p < 0.05).
2.4. Statistical Analyses
For each parameter, mean values and standard deviations were calculated for each time point by product. To assess the change from the baseline value, a paired t-test was performed on the outcome (Ti-T0) for each product. The normality assumption was checked using a Shapiro–Wilk test (p = 0.01); in case of rejection, a Wilcoxon signed rank test was carried out instead with a significance set at p-value < 0.05. In addition, to test whether the products differed statistically significantly, a paired t-test (or a Wilcoxon signed rank test) was carried out on the variable (Ti-T0)B-(Ti-T0)A with a significance set at p-value < 0.05. The software used were EXCEL (version 16.63) and SAS 9.4.
3. Results
3.1. GFE Improves Hyaluronic Acid Pathway In Vitro
Normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) and normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK) isolated from 55-year-old donors were incubated during 72 h with GFE 0.5%. Figure 1a,b shows HA synthesis quantification by specific ELISA in NHDF and NHEK, respectively. As shown, GFE 0.5% increases HA release by 32% (p < 0.05) as compared to untreated keratinocytes (control). HA synthesis in fibroblasts treated with GFE 0.5% was also higher than in untreated NHDF (control) by +62% (p < 0.001).
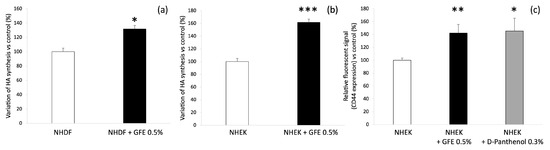
Figure 1.
GFE improves hyaluronic acid and CD44 synthesis; (a) HA synthesis by NHDF after GFE 0.5% treatment; (b) HA synthesis by NHEK after GFE 0.5% treatment; (c) Quantification of CD44 synthesis in NHEK after treatment with GFE 0.5% or D-panthenol 0.3%; Mean ± SD, statistical significance: *** p < 0.001 vs. control; ** p < 0.01 vs. control; * p < 0.05 vs. control.
Immunodetection and quantification of the HA receptor, CD44, was performed on NHEK from 55-year-old donors treated 48 h with GFE 0.5% or D-panthenol 0.3% or nothing (control). As shown in Figure 1c, GFE 0.5% induces CD44 synthesis by +42% in treated keratinocytes as compared to the untreated ones (control). Thus, CD44 stimulation with GFE is comparable to that obtained with D-panthenol, a pure molecule known to promote skin hydration [18].
3.2. GFE Increases Lipid Synthesis In Vitro
Quantification of lipid synthesis was performed by staining lipids with a lipid-specific green fluorescent dye (BODIPY dye, Thermo Fisher Scientific™, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) in NHEK (n = 3) treated (or not, control condition) with GFE 0.5% during 48 h. Figure 2 shows that GFE 0.5% increases lipid synthesis by +147% in treated keratinocytes as compared to untreated ones (control).
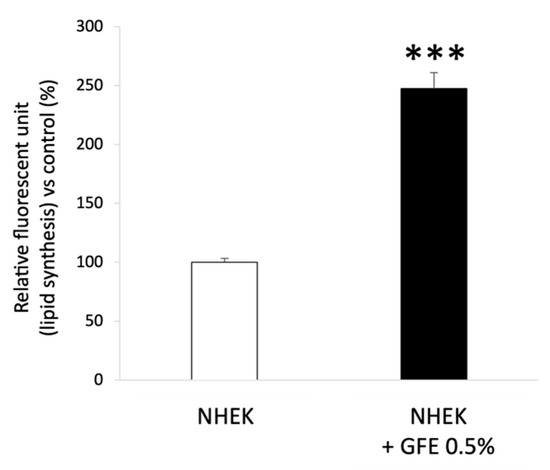
Figure 2.
Quantification of lipid synthesis after GFE treatment in NHEK; Mean ± SD, statistical significance: *** p < 0.001 vs. control.
3.3. GFE Stimulates Hydration on Dry Skins
The efficacy of GFE 1% on moisturization was evaluated by MoistureMap® (Courage & Khazaka, Köln, Germany) on all dehydrated volunteers from group 1. As shown in Figure 3, after 28 days of application, the overall studied group showed a significant increase in skin hydration of +7.3% in the area treated with GFE 1% compared to the placebo (p < 0.05; 68% of volunteers with improvement). Moreover, the sebum-deficient sub-panel displays a stronger hydration rate, with an increase of 12.5% with GFE 1% as compared to the placebo (p < 0.01, 89% of volunteers with improvement). Compared to D0, the placebo does not have any significant impact in both studied groups whereas GFE induces a significant increase of 10% in the dehydrated panel (p < 0.05; 79% of volunteers with improvement).
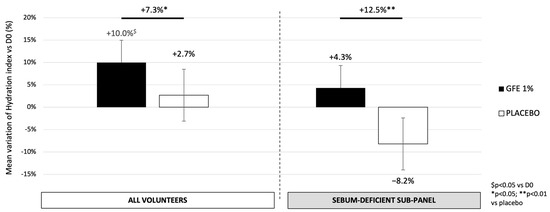
Figure 3.
Variation of skin hydration evaluated by MoistureMap® (Courage & Khazaka, Köln, Germany) after 28 days of treatment with GFE or placebo. Mean ± SEM, statistical significance: * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. placebo; $ p < 0.05 vs. D0.
3.4. GFE Protects or Restores the Skin Surface Lipids According to Skin Condition
By using the Sebumeter® (Courage & Khazaka, Köln, Germany) to evaluate skin surface lipids on the forehead, as shown in Figure 4, GFE 1% treatment increases the skin surface lipid quantity by 27% as compared to the placebo (p = 0.01), meaning that active treatment allows protection of the skin lipid surface in dehydrated skins. In the sebum-deficient sub-panel, the effect is even more pronounced, with an increase of 23% vs. D0 and thus 43% in the treated area compared to the placebo (p < 0.05). GFE is able to restore skin surface lipidic film in dry skins.
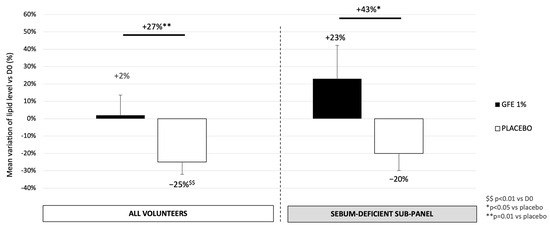
Figure 4.
Variation of skin surface lipids evaluated by Sebumeter® (Courage & Khazaka, Köln, Germany) after 28 days of treatment with GFE® or placebo. Mean ± SEM, statistical significance: * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. placebo; $$ p < 0.01 vs. D0.
3.5. GFE Restores in Older Dehydrated Skin the Holobiotic Characteristics of Younger Skin and Stimulates Beneficial Bacteria Species
A mass spectrometry-based metaproteomic process was conducted to sequence proteins from bacterial, fungi and human origin followed by taxonomic, functional and statistical analysis. Proteins from humans, bacteria and fungi were clustered according to their functions and expression modulation. In all conditions, more than six thousand proteins were identified and analyzed. Among them, more than eight hundred proteins such as (non-exhaustive list): filaggrin, S100A2, HSP A4L, cornifin, hornerin, serpinB8, ferritin, defensin α1, glutathione S-transferase, guanine deaminase, antibacterial proteins from S. epidermidis, A6NI72 (ROS generation), FRP3, NQO2, TP53, etc... were demonstrated as significantly regulated and then clustered according to their main functions if known (Supplementary Tables S1 and S2). Functional analysis showed that identified proteins linked to antioxidant responses and skin barrier were significantly downregulated with age and dehydration (Figure 5, left panel). Interestingly, these functions were reactivated after GFE application (Figure 5, right panel).
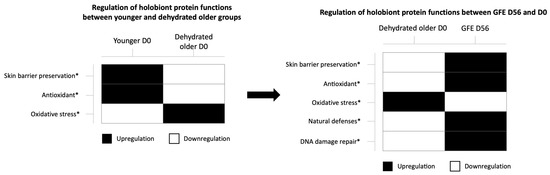
Figure 5.
Regulation of protein functions between younger and dehydrated older groups (left panel) and dehydrated older group treated or not during 56 days (right panel); proteins from humans, bacteria and fungi were clustered according to their functions and expression modulation (downregulated: white, upregulated: black), * p < 0.05.
GFE restored youthful protein functions by upregulating proteins involved in skin barrier preservation and antioxidant activity, while downregulating oxidative stress proteins, after 56 days of treatment in older dehydrated skin. Moreover, treated skins also showed an improvement of natural skin defenses and DNA damage repair, by upregulation of associated proteins from both human and microbial origin. For example, antibacterial proteins from S. epidermidis were upregulated in vivo by GFE 1%. As shown in Figure 6, GFE also stimulated abundances of some specific bacterial species. Particularly, after applying GFE 1% during 56 days, older dehydrated skins showed an increase in S. epidermidis and Ralstonia species abundances, by, respectively, +39% and +45% (Figure 6a,b). It is noteworthy that Alpha diversity, which measures intra-individual diversity, was measured using Shannon and Simpson indexes (Shannon, 1998; Simpson, 1949). As indicated in Figure S4, it was not significantly modulated with 56 days of treatment with GFE 1%.
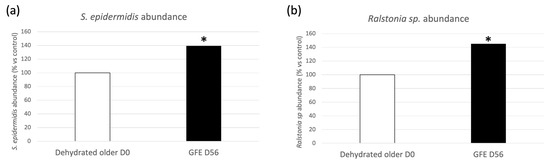
Figure 6.
S. epidermidis (a) and Ralstonia sp (b) abundance before and after treatment with 1% GFE, * p < 0.05.
4. Discussion
The present study reveals that GFE rebalances the skin holobiont for a rehydrated and lipid-replenished skin, without disturbing the microbiota diversity. It restores a youthful holobiont profile in older dehydrated skin boosting an abundance of hydration-linked bacterial species and regulating major protein functions involved in skin barrier preservation, through action on skin lipidic composition and hyaluronic acid (HA) stimulation.
Numerous studies demonstrated the interest in using fermented plant extracts for cosmetic purposes. For example, the bio-fermented Aframomum angustifolium extract allowed better hydration of the stratum corneum and improved dermal–epidermal connectivity in treated skins [24]. Fermented grape stem extracts can be used in moisturizing cosmetic formulations and also to complement the treatment of dry and sensitive skin [25]. It is noteworthy that this study also enhanced the interest in the use of fermentation in cosmetic application as it contributes to extending potential applications. Indeed, our group previously demonstrated the efficacy of a gentian active ingredient as an anti-aging eye contour [26]. The present study demonstrates for the first time the impact of fermentation on active properties, especially on skin holobiont.
Indeed, as demonstrated by these results, GFE enhances HA synthesis both in fibroblasts and keratinocytes, showing that GFE allows water retention in both skin compartments. Moreover, GFE increases CD44 synthesis leading to HA-mediated epidermal barrier function reinforcement. HA aids in water retention thanks to its ability to bind to its main receptor, cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44), a transmembrane glycoprotein. Importantly, CD44 is highly expressed both in the dermal and epithelial compartments of adult skin under the condition of normal tissue homeostasis [27,28]. The HA/CD44 glycoprotein conjugate influences the formation of the lamellar bodies which are expressed from keratinocytes to form the lipid lamellar bilayer of the SC [9]. In addition, CD44 controls the formation and proper assembly of tight junctions which are essential in holding keratinocytes together in the epidermis and emerging SC [29]. The HA/CD44 conjugate also induces keratinocyte differentiation [30]. It has also been suggested that CD44 may retain hyaluronan in the keratinocyte pericellular matrix, thus participating by itself in normal differentiation and the epidermal barrier function [31]. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are involved in the degradation of HA [32], thus promoting skin inflammation and lack of water, accelerating skin aging. As shown in the Supplementary Information, GFE upregulates in NHEK the expression of tight junctions and dermo-epithelial markers (Figures S1 and S2) and improves HA protection against free radicals’ degradation (Figure S3), maintaining water binding both in the dermis and the epidermis. As explained above, GFE contains active molecules which have demonstrated their efficiency in biological assays. Indeed, swertiamarin was shown to reduce ROS and superoxide anion levels as well as interferon and inflammatory factors via the cGAS-STING pathway [33]. It also inhibits lipid peroxidation and reduces the level of inflammatory mediators by activating the defense system of nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) and inhibiting nuclear factor-κ B (NF-κB) [34]. Interestingly, GFE also contains loganic acid, which was shown to exhibit a protective effect through its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects via inactivating the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway and activating the SIRT1/Nrf2 pathways [35]. Thus, it is highly likely that GFE acts on the HA/CD44 pathway through inactivation of NF-κB downregulation and Nrf2 upregulation.
Importantly, GFE is efficient on both dehydrated and dry skins by stimulating overall moisture, protecting or restoring the skin surface lipids according to skin condition, in vitro and in vivo. Skin surface lipids have been found to be an important determinant in the water-holding properties of the stratum corneum [36]. Skin hydration and skin surface lipids quantity are considered to be important factors in skin health. More precisely, a right balance between these two components plays a central role in protecting and preserving skin integrity [37].
Skin dehydration is a temporary condition that can affect all skin types (normal, oily and dry). It can be influenced by environmental conditions (e.g., a desiccated environment during sleep or in an airplane, a cold and dry winter, etc.) and is due to excessive water loss [38,39]. Dehydrated skin is clinically characterized by fine lines, also called dehydration wrinkles, producing a dull complexion and sometimes even a lack of elasticity [40]. Dehydrated skins thus lack water, whereas dry skins lack lipids due to an underproduction of skin surface lipids [41]. The permeability barrier is localized to the outer layer of the epidermis. It consists of corneocytes surrounded by a neutral lipid-enriched extracellular matrix primarily composed of ceramides, cholesterol and free fatty acids. The hydrophobic extracellular lipid matrix provides the principal barrier to the transcutaneous movement of water and electrolytes [42]. The hydrophobic nature of lipids from intercorneocyte spaces prevents water from leaving corneocytes [43]. Interestingly, during this late stage of epidermal differentiation, cells become embedded in a lipid ceramide-rich matrix which seals intercellular spaces between the fully differentiated cornified keratinocytes. This process maintains a waterproof barrier on the skin surface [44,45].
Finally, by studying holobiont protein interactions and microbial diversity thanks to a metaproteomic analysis [46], GFE demonstrates an ability to preserve global skin microbiome diversity (as shown in Supplementary Figure S4), while increasing Staphyloccocus epidermidis and Ralstonia species abundances (Figure 6). S. epidermidis has a well-known role in skin health and barrier function. More precisely, it has been shown that it secretes a sphingomyelinase that facilitates the host production of ceramides to help maintain skin integrity and prevent water loss of damaged skin by acting on the lipid metabolism [47]. Ralstonia sp. is barely known in the literature. Ma et al. have recently shown that Ralstonia sp. abundance is increased in skins considered ideal which have a better water–oil balance and barrier function, as well as a higher hydration content compared to undesirable skins [48]. Interestingly, a recent study confirms the direct link between improvement of the skin barrier function, surface moisture content and an increased ratio of the relative abundance of commensal bacteria, such as Staphylococcus epidermidis and Ralstonia. Thus, stimulating an abundance of S. epidermidis and Ralstonia sp. contributes to skin barrier homeostasis and skin hydration maintenance, which confirms the results obtained here [49]. Preserving microbiota diversity at genus level is key to maintaining skin homeostasis. Indeed, a disruption to that delicate balance (due to barrier alteration or imbalance between symbionts and pathogens for example) may lead to an impaired skin function or even to diseases including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis or cutaneous lupus [50]. Further investigations would be worth conducting to address GFE efficacy towards such skin pathologies in which microbiota, hydration and lipid imbalance have been highlighted [51,52,53].
In conclusion of this study, GFE, an active ingredient obtained from wild yellow gentian roots enhanced by fermentation with S. faeni leaves the skin deeply hydrated, particularly through its rebalancing action on skin holobiont protein functions and the preservation (or restoration, according to skin type) of skin lipidic structure.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cosmetics11040132/s1, Figure S1: Relative expression of genes related to epidermal differentiation and cell cohesion in keratinocytes after GFE treatment; Figure S2: Relative expression of genes related to DEJ in keratinocytes and fibroblasts after GFE treatment; Figure S3: Relative expression of genes related to antioxidant defense in keratinocytes and fibroblasts after GFE treatment; Figure S4: Alpha diversity according to Shannon and Simpson indexes between dehydrated older at D0 and after 56 days of GFE application [21,22,23]; Tables S1 and S2: list of proteins identified by metaproteomic analysis in, on one hand, younger (n = 20) versus older (n = 20) volunteers and, on the other hand, in GFE-treated volunteers at D56 vs. D0 (n = 20), respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.N.R., A.D.-Z. and J.-Y.B.; methodology, L.N.R., A.D.-Z. and J.-Y.B.; validation, J.-D.A. and J.-Y.B.; formal analysis, L.N.R., A.D.-Z., C.R., C.B., Y.L., S.B. and I.M.; investigation, L.N.R., A.D.-Z., C.R., C.B., Y.L., S.B. and I.M.; writing—original draft preparation, L.N.R. and J.-D.A.; writing—review and editing, L.N.R., A.D.-Z. and J.-D.A.; supervision, J.-Y.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because, according to local and European regulatory guidelines (Official Journal of the European Union of 10 March 2010, paragraph 1.2.9), this type of trial testing on active cosmetics does not require ethics committee approval or the competent authority’s authorization.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data are available upon demand.
Acknowledgments
Authors sincerely thank Adriana Albano from Greentech US for spelling checks and correcting English.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors L.N.R., C.R., C.B., Y.L., J.-D.A. and J.-Y.B are employed by Greentech S.A.; author A.D.-Z. is employed by Greencell S.A.; authors S.B. and I.M. are employed by Phylogene S.A. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Skowron, K.; Bauza-Kaszewska, J.; Kraszewska, Z.; Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, N.; Grudlewska-Buda, K.; Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Radtke, L.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Human Skin Microbiome: Impact of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors on Skin Microbiota. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The Human Skin Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Byrd, A.L.; Park, M.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Kong, H.H.; Segre, J.A. Temporal Stability of the Human Skin Microbiome. Cell 2016, 165, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouslimani, A.; Porto, C.; Rath, C.M.; Wang, M.; Guo, Y.; Gonzalez, A.; Berg-Lyon, D.; Ackermann, G.; Moeller Christensen, G.J.; Nakatsuji, T.; et al. Molecular Cartography of the Human Skin Surface in 3D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2120–E2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, R.; Margulis, L.; Berlanga, M. Symbiogenesis: The Holobiont as a Unit of Evolution. Int. Microbiol. Off. J. Span. Soc. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douladiris, N.; Vakirlis, E.; Vassilopoulou, E. Atopic Dermatitis and Water: Is There an Optimum Water Intake Level for Improving Atopic Skin? Child. Basel Switz. 2023, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidado, I.M.; Qassem, M.; Triantis, I.F.; Kyriacou, P.A. Review of Advances in the Measurement of Skin Hydration Based on Sensing of Optical and Electrical Tissue Properties. Sensors 2022, 22, 7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, F. Skin hydration and hyaluronic acid. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 137 (Suppl. 1), S23–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguignon, L.Y.W.; Ramez, M.; Gilad, E.; Singleton, P.A.; Man, M.-Q.; Crumrine, D.A.; Elias, P.M.; Feingold, K.R. Hyaluronan-CD44 Interaction Stimulates Keratinocyte Differentiation, Lamellar Body Formation/Secretion, and Permeability Barrier Homeostasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, O.; Mayo, S.; Rodríguez, A.; Casquero, P. Effect of Soil in the Growth of Gentiana Lutea Radical System in North Mountain of Léon (Spain). Acta Hortic. 2012, 955, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, P.; Canet, I.; Sancelme, M.; Wirgot, N.; Deguillaume, L.; Delort, A.-M. Screening of Cloud Microorganisms Isolated at the Puy de Dôme (France) Station for the Production of Biosurfactants. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 16, 12347–12358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberham, A.; Schwaiger, S.; Stuppner, H.; Ganzera, M. Quantitative Analysis of Iridoids, Secoiridoids, Xanthones and Xanthone Glycosides in Gentiana Lutea L. Roots by RP-HPLC and LC-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhamad Fadzil, N.S.; Sekar, M.; Gan, S.H.; Bonam, S.R.; Wu, Y.S.; Vaijanathappa, J.; Ravi, S.; Lum, P.T.; Dhadde, S.B. Chemistry, Pharmacology and Therapeutic Potential of Swertiamarin—A Promising Natural Lead for New Drug Discovery and Development. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 2721–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzydzan, O.; Brodyak, I.; Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Sybirna, N. Loganic Acid, an Iridoid Glycoside Extracted from Cornus Mas L. Fruits, Reduces of Carbonyl/Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Plasma and Restores Antioxidant Balance in Leukocytes of Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mellitus. Life 2020, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltés, L.; Mendichi, R.; Kogan, G.; Schiller, J.; Stankovska, M.; Arnhold, J. Degradative Action of Reactive Oxygen Species on Hyaluronan. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, H.-J.; Denner, E.B.M.; Buczolits, S.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M.; Bennasar, A.; Kämpfer, P. Sphingomonas Aurantiaca Sp. Nov., Sphingomonas Aerolata Sp. Nov. and Sphingomonas Faeni Sp. Nov., Air- and Dustborne and Antarctic, Orange-Pigmented, Psychrotolerant Bacteria, and Emended Description of the Genus Sphingomonas. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, N.; Anesio, A.M.; Rafiq, M.; Holtvoeth, J.; Bull, I.; Haleem, A.; Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F. Temperature Driven Membrane Lipid Adaptation in Glacial Psychrophilic Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, F.; Heller, A.; Rippke, F.; Tausch, I. Topical Use of Dexpanthenol in Skin Disorders. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 3, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuang, V.; Rona, C.; Distante, F.; Berdasca, E. The Use of a Capacitance Device to Evaluate the Hydration of Human Skin. J. Appl. Cosmetol. 1997, 15, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Luebberding, S.; Krueger, N.; Kerscher, M. Skin Physiology in Men and Women: In Vivo Evaluation of 300 People Including TEWL, SC Hydration, Sebum Content and Skin Surface pH. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. Communication Theory of Secrecy Systems. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1949, 28, 656–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.; Curtis, J. An Ordination of the Upland Forest Communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albouy, M.; Aubailly, S.; Jeanneton, O.; Marteau, C.; Sobilo, L.; Boulgana, R.; Bru, G.; Bellanger, M.; Leblanc, E.; Dos Santos, M.; et al. Skin-Protective Biological Activities of Bio-Fermented Aframomum Angustifolium Extract by a Consortium of Microorganisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1303198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanek-Wandzel, N.; Zarębska, M.; Wasilewski, T.; Hordyjewicz-Baran, Z.; Zajszły-Turko, E.; Tomaka, M.; Bujak, T.; Ziemlewska, A.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z. Kombucha Fermentation as a Modern Way of Processing Vineyard By-Products into Cosmetic Raw Materials. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2023, 45, 834–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, J.-Y.; Cabannes, M.; Bouton, C.; Carre, M.; Bridon, E.; Filaire, E. In Vitro, Ex Vivo and Clinical Approaches to Evaluate the Potential Effect of Gentiana Lutea Extract on Skin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2023, 45, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.A.; Bouchard, T.; St John, T.; Wayner, E.; Carter, W.G. Human Keratinocytes Express a New CD44 Core Protein (CD44E) as a Heparan-Sulfate Intrinsic Membrane Proteoglycan with Additional Exons. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tammi, M.; Tammi, R. Distribution of Hyaluronan and Its CD44 Receptor in the Epithelia of Human Skin Appendages. Histochemistry 1992, 98, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, N.; Haftek, M.; Niessen, C.M.; Behne, M.J.; Furuse, M.; Moll, I.; Brandner, J.M. CD44 Regulates Tight-Junction Assembly and Barrier Function. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.V.; Holtz, R.; Riemer, J. Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Stimulates the in Vitro Expression of CD44 Proteins but Not HAS1 Proteins in Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes (NHEKs) and Is HA Molecular Weight Dependent. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasonen-Seppänen, S.; Karvinen, S.; Törrönen, K.; Hyttinen, J.M.T.; Jokela, T.; Lammi, M.J.; Tammi, M.I.; Tammi, R. EGF Upregulates, Whereas TGF-Beta Downregulates, the Hyaluronan Synthases Has2 and Has3 in Organotypic Keratinocyte Cultures: Correlations with Epidermal Proliferation and Differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valachová, K.; Hassan, M.E.; Šoltés, L. Hyaluronan: Sources, Structure, Features and Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; He, D.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Gong, L.; Tang, C.; Peng, H.; Qiu, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, T.; et al. Swertiamarin Relieves Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury by Limiting DNA Damage. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Xia, R.; Zhang, P.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z.; Khan, A.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, W.; Liu, L. Swertiamarin or Heat-Transformed Products Alleviated APAP-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Modulation of Apoptotic and Nrf-2/NF-κB Pathways. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.N.; Prasad, N.; Puppala, E.R.; Panda, S.R.; Jain, S.; Ravichandiran, V.; Singh, M.; Naidu, V.G.M. Loganic Acid Protects against Ulcerative Colitis by Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB Mediated Inflammation and Activating the SIRT1/Nrf2 Anti-Oxidant Responses in-Vitro and in-Vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 122, 110585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, G.; Kuno, H.; Kawai, M. Stratum Corneum Lipids Serve as a Bound-Water Modulator. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilion, J.V.; Khanna, S.; Anasseri, S.; Laney, C.; Mayrovitz, H.N. Physiological, Pathological, and Circadian Factors Impacting Skin Hydration. Cureus 2022, 14, e27666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.I.; Han, J.; Lee, M.; Seo, J.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, E. A Study of Skin Characteristics According to Humidity during Sleep. Skin Res. Technol. 2019, 25, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duplan, H.; Nocera, T. Skin hydration and hydrating products. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 145, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, M.; Oguri, M.; Kuwahara, T.; Takahashi, M. Effect of Exposure of Human Skin to a Dry Environment. Skin Res. Technol. 2002, 8, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Man, M.-Q.; Li, T.; Elias, P.M.; Mauro, T.M. Aging-Associated Alterations in Epidermal Function and Their Clinical Significance. Aging 2020, 12, 5551–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radner, F.P.; Grond, S.; Haemmerle, G.; Lass, A.; Zechner, R. Fat in the Skin: Triacylglycerol Metabolism in Keratinocytes and Its Role in the Development of Neutral Lipid Storage Disease. Dermatoendocrinol 2011, 3, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Yasuda, R.; Sayo, T.; Ishikawa, O.; Inoue, S. Hyaluronan Exists in the Normal Stratum Corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefèvre-Utile, A.; Braun, C.; Haftek, M.; Aubin, F. Five Functional Aspects of the Epidermal Barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evrard, C.; Lambert de Rouvroit, C.; Poumay, Y. Epidermal Hyaluronan in Barrier Alteration-Related Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaduta, O.; Dvanajscak, Z.; Zybailov, B. Metaproteomics-An Advantageous Option in Studies of Host-Microbiota Interaction. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hunt, R.L.; Villaruz, A.E.; Fisher, E.L.; Liu, R.; Liu, Q.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; Li, M.; Otto, M. Commensal Staphylococcus Epidermidis Contributes to Skin Barrier Homeostasis by Generating Protective Ceramides. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 301–313.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Niu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Bai, T.; Yang, S.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Shao, L. The Characteristics of the Skin Physiological Parameters and Facial Microbiome of “Ideal Skin” in Shanghai Women. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.-Y.; Yuan, C.; Yan, B.; Humbert, P.; Quan, Z.-X. Effects of Investigational Moisturizers on the Skin Barrier and Microbiome Following Exposure to Environmental Aggressors: A Randomized Clinical Trial and Ex Vivo Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yu, X.; Cheng, G. Human Skin Bacterial Microbiota Homeostasis: A Delicate Balance between Health and Disease. mLife 2023, 2, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Lu, J.; Tai, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z. The Epidermal Lipid-Microbiome Loop and Immunity: Important Players in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Adv. Res. 2024, S2090-1232(24)00088-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filatov, V.; Sokolova, A.; Savitskaya, N.; Olkhovskaya, M.; Varava, A.; Ilin, E.; Patronova, E. Synergetic Effects of Aloe Vera Extract with Trimethylglycine for Targeted Aquaporin 3 Regulation and Long-Term Skin Hydration. Mol. Basel Switz. 2024, 29, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosik-Kozioł, A.; Nakielski, P.; Rybak, D.; Frączek, W.; Rinoldi, C.; Lanzi, M.; Grodzik, M.; Pierini, F. Adhesive Antibacterial Moisturizing Nanostructured Skin Patch for Sustainable Development of Atopic Dermatitis Treatment in Humans. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 32128–32146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).