Abstract
Background: The injection of dermal fillers for facial esthetics has become a very popular procedure. Although usually safe in the hands of the experienced user, filler injections may bear a risk of unwanted side effects. Material and Methods: This is a narrative review of dermal filler migration after facial injections. We performed research on the literature on Pubmed and Google Scholar. Inclusion criteria were observational studies, case reports, and clinical trials which investigated the association of facial filler injections to filler migration. Animal studies have not been considered. Intravascular injections were excluded. Results: We identified 28 reports that met the inclusion criteria. The age range of affected patients was 21 to 86 years (mean ± standard deviation: 47 ± 14.8 years). Women were 25 times more reported than males. Hyaluronic acid and polyalkylimide were the most commonly encountered filler substances. Injections into the nose, lips, nasolabial folds, and forehead (including glabella) are more often reported for filler migration than injections into the cheeks. Tear-trough correction bears a risk for orbital migration. The delay from injection to presentation of filler migration was highly variable. Very late filler migration was more commonly seen with permanent fillers than non-permanent products. Conclusions: Filler migration distant from the injection site can occur even several years after the primary treatment. All filler types can be involved. Permanent fillers bear a higher risk of very late filler migration. Migration of permanent fillers needs surgical treatment, while HA fillers respond to hyaluronidase injections. Detailed knowledge of facial anatomy, safer injection techniques, and filler qualities are preventive measures.
1. Introduction
The use of fillers in esthetic medicine has grown faster than any other procedure, reflecting a trend for minimally invasive procedures. The fillers represent versatile tools in facial rejuvenation, contouring, and volumizing. They can be classified according to substance(s), biophysical characteristics, crosslinking methods, and longevity of lifting effect [1,2,3].
Temporary fillers include collagen and hyaluronic acid (HA)-based products. Semipermanent (also known as biostimulatory) fillers are calcium hydroxyapatite (CaH), polycaprolactone, and poly-D, L-lactic acid (PDLLA). Polymethyl-methacrylate (PMMA), polyalkylimide, polyacrylamide, paraffin, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), and other silicones are the substances used as permanent fillers. Paraffin was one of the first substances used as filler, but safety issues and dissatisfying long-term outcomes made it disappear in medical esthetics. On the contrary, silicones have never been approved for use as filler, but sometimes they are still used off-label [2].
There is no ideal filler. The adverse events can be classified into acute or immediate (during and shortly after injection), early (up to 2 weeks after injection), delayed (>2 weeks to 12 months), late (>1 year), and localized or generalized [4]. The most common adverse events of the immediate or early type of reaction are injection pain, bruising, and temporary redness, while nodules and granulomas are usually delayed or late reactions. Vascular compromise is an acute and severe adverse event caused by intraarterial or intravenous injections, extraluminal pressure of filler material, or indirect vascular trauma. Fortunately, both abscess formation and vascular occlusion are much less frequent [5,6]. The rate of adverse events is widely dependent on the skills and experience of the user. Another problem is the participation of laypersons without medical understanding in illicit filler injections [7,8,9]. The general complication rate of filler injections in experienced hands is less than 5% [10]. A summary of possible adverse events after facial filler injection is given in Table 1 [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33].

Table 1.
Possible adverse events associated with facial filler injection (Ref.: reference(s)).
While HA fillers may be removed by injecting the enzyme hyaluronidase, permanent filler reactions often warrant surgery for complete removal. The kinetics of HA degradation by hyaluronidase is dependent on crosslinking filler technology, but not the concentration of HA [35]. Permanent fillers have been associated with possible delayed adverse events occurring even years after injection and with unwanted systemic side effects including myalgia, arthralgia, fever, lymphadenopathy, and malaise [36,37]. A great danger for patients arises from the use of illegal injectable fillers [38].
To ensure patient safety and avoid mistakes, various guidelines have been developed [39,40,41].
In this narrative review, we will focus on a lesser-known and rarer adverse event after facial filler injections, i.e., the delayed filler migration or displacement, often observed weeks to years after injection. Filler migration is defined as filler material found remote from the original site of injection. To narrow this review, we excluded inadvertently intravascular injections that might also cause filler migration as an acute severe adverse event.
2. Materials and Methods
We performed research on the literature through Pubmed and Google Scholar. Inclusion criteria were observational studies, case reports, and clinical trials which investigated the association of facial filler injections to filler migration. Animal studies have not been considered. The search string, designed to cover the primary themes of the review and optimized for high sensitivity, was (dermal fillers [Title/Abstract] OR AND (facial esthetics [Title/Abstract] AND migration [Title/Abstract] OR filler migration [Title/Abstract]. Exclusion criteria were intravascular injection, acute displacement, vascular compromise, and infection. The identified articles were included for further analysis if the title or the abstract showed the matching keywords. We decided not to specify a year range for the selection of articles. The articles were excluded if they contained only abstracts, and were not in the English or German language. Papers published in conferences, books, or book chapters were also excluded. We also searched further from the references of the articles which showed our area of concern (Figure 1).
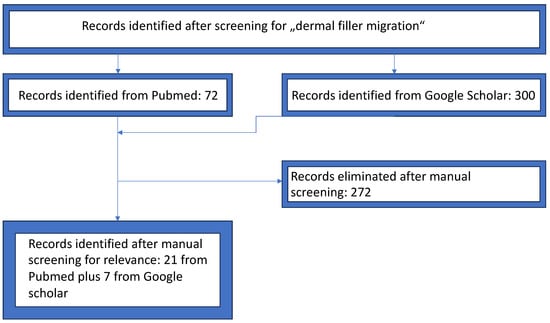
Figure 1.
PRISMA selection flowchart.
Filler migration was defined as the presence of filler at a location distant from the injection site without accidental intravascular injection.
3. Results
Initially, we identified 43 papers. After the first check, 22 papers were excluded according to the exclusion criteria. Analyzing these papers, 7 additional reports were found [42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70]. A summary is provided in Table 2.

Table 2.
Reported cases of filler migration after facial esthetic procedures (Ref.: reference).
The age range was 21 to 86 years (mean ± standard deviation: 47 ± 14.8 years). Women were 25 times more reported than males. HA and polyalkylimide were the most commonly encountered filler substances. CaH, PDLLA, PDMS, and other silicones, and PMMA and polyacrylamide were identified in selected cases. Injections into the nose, lips, nasolabial folds, and forehead (including glabella) seem to be more often reported for filler migration than injections into the cheeks. While nasolabial folds and lips are major targets for filler placement, the nose and forehead are less commonly treated. Muscular activity is highest on the lips followed by glabella. On the cheeks, deep injections are favored for facial contouring in contrast to the other areas mentioned. Deposition of fillers into deep midfacial fat pads bears obviously a lower risk for filler migration. Tear trough correction carries a risk for orbital migration.
The delay from injection to presentation of filler migration was highly variable, from 2 weeks to 60 years. The extremely late presentation of filler migration was associated with the use of permanent fillers like silicones, polyalkylimide, PMMA, and polyacrylamide. However, there was a single case report with filler migration presenting 16 years after injection of HA [55].
The clinical presentation varied from nodules to tumor-like masses, some with inflammation, edema, and pain. The possible differential diagnoses ranged from granulomatous to inflammatory disorders, soft tissue infection, cysts, and tumors. Imaging by diagnostic ultrasound or MRI had been reported in several cases. Confirmation of diagnosis was done by histopathology. MRI revealed significantly more lesions due to filler migration than clinically suspected [61]. In an ultrasound study on 57 patients after facial implantation of a permanent filler, lymphatic spread migration to cervical lymph nodes was observed in 34 patients (59.6%) [57].
Treatment was not reported for all patients. Before the final diagnosis was confirmed, corticosteroids and antibiotics have often been prescribed. They were of limited success. In the case of HA, hyaluronidase injections were employed, but in some patients, surgery had been performed since the diagnosis was unsure. For permanent fillers, surgery was the treatment of choice.
Hyaluronidase works faster on HA filler when applied early, and in late reactions, multiple and higher dosages might work well. For semipermanent fillers no specific drug therapy is available. Hydrolysis will eventually decompose PLLA but it is a slow process. In some cases, CaH may need minor surgery, e.g., on the vermillion border, but the injection in the lips is no longer recommended. In the case of most permanent fillers, the particulate material is embedded in a scaffold of collagen fibers which becomes tighter with time.
In addition, we added four patients to our own practice, 3 women and 1 man. Three developed subcutaneous nodules after permanent fillers (silicon and PMMA), and one female presented with subcutaneous nodules after PDLLA injection by a beautician (Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4).
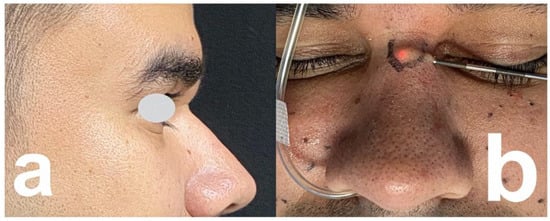
Figure 2.
A 33-year-old man. (a) PMMA injected in glabella with displacement to radix. (b) In-tralesional laser treatment.
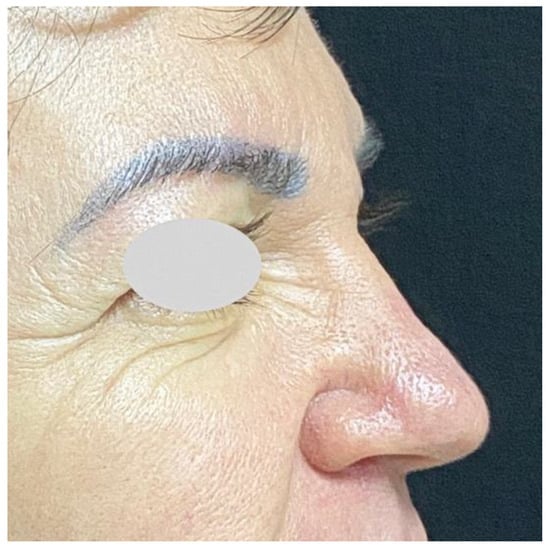
Figure 3.
55-year-old woman. Silicone injected 12 years ago into the glabella by an esthetician. Displacement to radix and nasal dorsum.
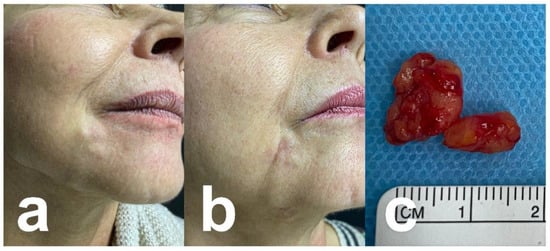
Figure 4.
A 64-year-old woman. (a) PMMA migration (originally injected 20 years ago in mouth commissure) with subcutaneous nodules. (b) After surgical excision. (c) Surgical specimen.
Due to the variability in clinical presentation, the range of possible differential diagnoses is broad. They include soft tissue infections including abscess and cellulite (erysipelas), atypical mycobacterial infections, herpes zoster, and mycetoma [4,12,15,18]. Non-infectious differential diagnoses include sarcoidosis, scars, xanthelasma, temporal arteritis, neurogenic ulcer, and keratoacanthoma [16,25,28]. Benign and malignant tumors must be considered in other cases such as parotid pleomorphic adenoma, cutaneous cysts, facial granuloma, and pseudo-lymphoma on the benign spectrum, and basal cell carcinoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, cutaneous lymphoma or metastasis as malignancies [42,71,72,73].
4. Discussion
Amongst possible adverse events of dermal filler injections, migration of filler material is a relatively rare and delayed adverse event [54,55,56,57,58,61]. Considering polyacrylamide filler, migration has been observed in up to 3% of cases [67]. Clinical evidence of filler migration may not be observed unless a secondary complication, such as granuloma, edema, or cysts, developed.
Migration of filler material may result in an unsightly appearance, chronic inflammation, infection, and vascular compromise with disastrous complications including stroke and blindness. Filler migration can be induced by several mechanisms. Common but avoidable is poor injection technique due to lacking skills and poor knowledge of anatomy. Further technical errors are high-volume injection, too-fast injection under pressure, and/or the use of a too-small needle or cannula. Other factors contributing to migration include pressure-induced displacement through massage, muscle activity, gravity, and spreading through the lymphatic system (migrated granulomas) [56]. A neuroradiological study suggested that the risk of migration of filler material tends to be lower with the injection of smaller droplets [74].
The formation of foreign body granulomas is dependent upon macrophage function. The major subtypes are M1 with pro-inflammatory activity and pro-fibrotic M2. An in vitro study using different preparations of a commercially available HA filler, experimental HA filler material, and permanent fillers, and Aquamid® and Bio-Alcamid® investigated gene expression patterns after incubation with human TPH-1 monocytes [75]. M0 macrophages responded with a small increase in interleukin (IL)-1β and chemokine CCL18 to HA, but a strong IL-1β and CCL18 response to both non-resorbable fillers. In contrast to HA, Bio-Alcamid® also stimulated further pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-3, IL-4, interferon (IFN) type 1, and macrophage markers [76]. In a second trial, both HA fillers and Bio-Alcamid® were injected into a 3D human Phenion® Full-Thickness Skin model. Both resorbable and non-resorbable fillers induced an up-regulation of cytokines and chemokines, suggesting an acute inflammatory tissue response. Details, however, were different between HA and permanent filler. Bio-Alcamid® increased significant tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8, whereas the response to HA fillers was markedly less pronounced [77]. As a rule, particulated fillers bear a higher risk of granuloma formation compared to non-particulated products [78].
Most granulomas develop around injection sites. In these cases, migration is not involved. However, granuloma formation distant from the primary injection is a consequence of the migration of filler material. In the case of permanent fillers, the degradation of larger particles allows phagocytosis by macrophages [79]. Transendothelial migration of macrophages has been demonstrated using near-infrared techniques such as fluorescence reflectance imaging and fluorescence-mediated tomography in experimentally induced permanent filler granulomas (polyacrylamide) [80]. With indocyanine green-labeled monocytes and near-infrared laser angiography, infectious and non-infectious inflammation could be differentiated in an animal model [81].
Aesthetic facial subunits reveal a different risk of filler migration due to variations in static and dynamic anatomy [82]. In addition, the injection plane in facial tissue is important for the longevity of the volumizing effect after filler placement. Injections into midfacial deep fat and lateral temporal-cheek superficial fat compartments provide better longevity compared to the perioral region and chin, in reverse suggesting a lower risk of filler migration in general [83].
Intravascular injections have not been considered in this review since they are acute adverse events in contrast to the other mechanisms of filler migration [15,25]. Here, we present suggested mechanisms of migration or displacement in special areas, corresponding to anatomy:
Injections in the glabella: In the case of strong glabella lines, the nasal bridge is particularly subject to the activity of corrugator supercilii and procerus muscles. Repeated muscle contractions may become responsible for the migration of filler injected in the glabella or radix [42]. Examples are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
Injections into the forehead: Potential mechanisms of filler displacement include migration of the filler through the galea aponeurosis and orbital septum by gravity and facial muscle movement. Fillers injected into the forehead may migrate along the tissue plane formed by the galea and the posterior orbicularis fascia functions to the upper eyelid. Facial muscle movement and gravity are involved. In addition, postoperative massage of the injection sites has also been considered, but this would account for migration in a closer timeframe after the injection [60].
Injections in the temple: The superior boundary of the buccal space is connected to the deep temporal fat pad. The anterior buccal extension inserts into the cheeks. With increasing age buccal extension may develop a pseudo-prolapse into the buccal space of the anterior cheek which can facilitate filler migration from the temple to the cheeks [47].
Injections close to the eye: Injection of fillers in the vicinity of the eye can facilitate their migration under the conjunctiva, most probably due to lymphatic spread [44].
Injection for tear trough augmentation: The tear trough is the landmark of the medial border of sub-orbicularis oculi fat. Tear trough deformities are located between the palpebral and orbital parts of the orbicularis oculi. With age, the orbicularis retaining ligament separating deep and superficial fat pads gets weaker, which may lead to herniation of orbital fat. Injections above the deep plane and too close to the orbital rim can cause unwanted filler migration into the lower eyelid [84]. In a systematic review, the frequency of filler migration in this area was 7.7% [45].
Injections into nasolabial folds: In contrast to other facial regions subcutaneous fat is dispersed. The muscles of facial expression form a strong network of collagenous fibers with a direct connection to the skin. Filler injected into the nasolabial fold may migrate due to gravity and muscular movement into the labiomental sulcus. Displacement of filler material from nasolabial folds has been reported in 0.5% of cases [85,86]. An example is shown in Figure 4.
There are rare reports of filler migration after distant injection for gluteal enhancement liquid silicone or PMMA [51,87,88]. Distant migration of polyacrylamide has been observed after breast augmentation to the axilla, chest wall, abdominal wall, and peritoneum [89]. Some aspects must be considered in these cases: (a) much larger volumes were applied compared to facial esthetics, and (b) PMMA, silicone, and polymethacrylate are permanent fillers. (c) Silicones are used off-label since they have never been FDA-approved for esthetics. It is lesser known that even HA can persist in subcutaneous adipose tissue for several years, which explains very rare documented cases of late filler migration after injection of HA [55,90].
Nonetheless, filler migration or displacement has been reported with both temporary and permanent fillers. The differential diagnosis of the resulting clinical symptomatology is broad and includes infectious, inflammatory, cystic, and neoplastic disorders. Often, patients are not aware of the filler products that have been used. Sometimes, different products were applied simultaneously. It is important to specify the filler material by imaging techniques and/or histopathology. While HA-induced lesions may be treated with intralesional hyaluronidase injections, permanent fillers often need surgery [91]. Occasionally, an allergy to hyaluronidase has been observed. One risk factor is a previous sensitization to bee or wasp venom [92].
We have recently described a combined technique of neodymium (Nd)-YAG laser application followed by minor surgery to remove PMMA particles avoiding extensive surgery, even in such delicate localizations such as the nose and the lips (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5) [93,94]. The laser energy is released intralesional using a 300–600 µm blunt fiber embedded in a micro-cannula. The skin temperature is controlled during the procedure to prevent burning. The laser energy causes fragmentation of PMMA particles, which can subsequently be removed by a blunt suction cannula with negative pressure. Satisfaction with this procedure was high.
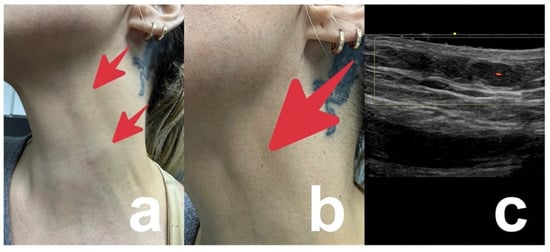
Figure 5.
40-year-old women with subcutaneous nodules on the neck 4 months after injections of PDLLA into middle and lower face by a beautician (red arrows). Intralesional corticosteroids applied by the beautician did not improve the nodules but caused localized skin atrophy. (a) Overview. (b) Detail. (c) Doppler ultrasound showing the subcutaneous nodule but excluding lymphadenopathy.
In summary, dermal filler material may spread to distant body sites from the point of injection by vascular transport (blood vessels and lymphatic vessels), along anatomical structures like ligaments and fasciae, by gravity or muscular activity, and along with inflammatory reactions through intracellular transport by macrophages.
Diagnosis of filler migration depends upon medical history and careful clinical examination. Due to the variability in the clinical presentation, numerous differential diagnoses must be excluded. Localization of filler material in deeper tissue layers is supported by imaging techniques. High-frequency ultrasound has been used to localize and identify dermal fillers in the face [95,96]. For HA hypoechoic or anechoic structures are characteristic, while CaH, polycaprolactone, silicon oil, and PMMA demonstrate hyperechoic deposits [97].
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows not only the localization of filler material but supports the identification of the type of filler material responsible. HA filler show hyperintense signals on T2 W sequences and hypointense signals on T1 W sequences because of their water binding capacity. In contrast, CaH shows low to intermediate signals, and PDLLA T2 W images are hypointense [98].
For final confirmation of a diagnosis of filler migration, histopathology is essential. Since biopsy is an invasive technique, patients sometimes refuse. However, in the case of placement of various or unknown filler materials, it remains the gold standard in diagnostics [5,97,99].
5. Conclusions
Filler migration is a less common adverse event seen after injectable filler placement. It can occur on every body part. We focused in this review on facial filler treatment since this is the most common site of application. The migration often occurs with a delay of weeks to years after implantation and is not restricted to certain filler products. However, the management of filler migration differs between HA and permanent fillers. While HA can be removed by intralesional injection of hyaluronidase, permanent filler removal needs surgery. The invasiveness of such a procedure can be reduced by prior intralesional application of the Nd-YAG laser [93,94]. Since the clinical symptoms of filler migration are not uniform, a broad range of differential diagnoses must be considered.
For patient safety, qualified knowledge of anatomy, dermal filler materials, and injection techniques are most important. For beginners, we recommend attending qualified courses by established, serious providers to increase their knowledge and skills. Early recognition and management of unwanted side effects are of great importance to minimize risks of an unfortunate outcome [7,39,40,41].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, visualization, and writing—original draft preparation, A.G. and U.W.; methodology, investigation, and data procession, A.G. and U.W.; supervision and writing—review and editing, A.G. and U.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper if applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are free and available on PUBMED© and Google Scholar©.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jiang, B.; Ramirez, M.; Ranjit-Reeves, R.; Baumann, L.; Woodward, J. Noncollagen dermal fillers: A summary of the clinical trials used for their FDA approval. Dermatol. Surg. 2019, 45, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.H.; Beynet, D.P.; Gharavi, N.M. Overview of deep dermal fillers. Facial Plast. Surg. 2019, 35, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollina, U.; Goldman, A. Hyaluronic acid dermal fillers: Safety and efficacy for the treatment of wrinkles, aging skin, body sculpturing and medical conditions. Clin. Med. Rev. Ther. 2011, 3, 107–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, H.J.; Kim, B.Y.; Ryu, S.I.; Kim, N.Y.; Ko, J.Y.; Ro, Y.S.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, J.E. New classification of late and delayed complications after dermal filler: Localized or generalized? J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2020, 22, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, J.; Walker, L.; Ali, S.R.; Whitaker, I.S. An illustrated anatomical approach to reducing vascular risk during facial soft tissue filler administration—A review. JPRAS Open 2022, 36, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollina, U.; Goldman, A. Facial vascular danger zones for filler injections. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena, L.; Requena, C.; Christensen, L.; Zimmermann, U.S.; Kutzner, H.; Cerroni, L. Adverse reactions to injectable soft tissue fillers. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 64, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povolotskiy, R.; Oleck, N.C.; Hatzis, C.M.; Paskhover, B. Adverse events associated with aesthetic dermal fillers: A 10-year retrospective study of FDA data. Am. J. Cosmet. Surg. 2018, 35, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadari, H.; Krompouzos, G.; Kassir, M.; Gupta, M.; Wollina, U.; Katsambas, A.; Lotti, T.; Jafferany, M.; Navarini, A.A.; Berg, R.V.; et al. Complication of soft tissue fillers: Prevention and management review. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2020, 19, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelke, L.W.; Van Den Elzen, H.J.; Canninga, M.; Neumann, M.H.A. Complications after treatment with polyalkylimide. Dermatol. Surg. 2009, 35 (Suppl. 2), 1625–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, Z.; Trikha, S.; Etemad-Shahidi, S.; Virmani, S.; Denning, C.; Al-Mukhtar, Y.; Rennie, C.; Penny, A.; Jamali, Y.; Parrish, N.C.E. Case series and review on managing abscesses secondary to hyaluronic acid soft tissue fillers with recommended management guidelines. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Balassiano, L.K.A.; Cavallieri, F.A.; Munhoz, G.; Tembra, M.F.; Ramos-E-Silva, M. Not so “happy bump”: A complication due to hyaluronic acid. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 6308–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, M.; Lopez-Gehrke, I.; Villarica-Hayano, W.; Suwanchinda, A.; Galadari, H. Nonscarring alopecia after temporal lifting technique with dermal fillers. JAAD Case Rep. 2023, 37, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.W.; Shiuey, E.; Briceño, C.A.; Lee, V. Acute diplopia after glabellar hyaluronic acid filler injection. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2023, 31, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colon, J.; Mirkin, S.; Hardigan, P.; Elias, M.J.; Jacobs, R.J. Adverse events reported from hyaluronic acid dermal filler injections to the facial region: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 2023, 15, e38286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soares, D.; Bowhay, A.; Blevins, L.W.; Patel, S.M.; Zuliani, G.F. Patterns of filler-induced facial skin ischemia: A systematic review of 243 cases and introduction of the FOEM scoring system and grading scale. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 151, 592e–608e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.M.; Mueller, M.A.; Hu, A.C.; Evans, G.R.D. Asymptomatic stroke after hyaluronic acid filler injection: Case report and literature review. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2021, 41, NP602–NP608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Convery, C.; Davies, E.; Murray, G.; Walker, L. Delayed-onset nodules (DONs) and considering their treatment following use of hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2021, 14, E59–E67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trinh, L.N.; McGuigan, K.C.; Gupta, A. Delayed complications following dermal filler for tear trough augmentation: A systematic review. Facial Plast. Surg. 2022, 38, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Zheng, Q.; Hu, J. Dizziness and pain after temporal augmentation with hyaluronic acid. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2023; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, M.K.; Maeng, M.M.; Khzam, R.A.; Dubovy, S.R.; Johnson, T.E. Recurrent periorbital edema associated with retained foreign body after filler injection. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 39, e30–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.; Xie, H.; Wang, G.; An, Y. Risk comparison of filler embolism between polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and hyaluronic acid (HA). Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2019, 43, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoud, C.; Lossos, C.; Ali, S.Z. Polymethylmethacrylate-induced foreign body reaction presenting as bilateral parotid lesions: A case report of dermal filler adverse reaction diagnosed on fine needle aspiration. Cytopathology 2023, 34, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland-Warmann, M.J. Hypersensitivity reaction to Hyaluronic Acid Dermal filler following novel Coronavirus infection—A case report. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, R.A.; Oliveira, L.Q.; Martelli-Júnior, H.; Pires, F.R.; Carvas, J.B.; Rogerio, V.E.; Rabelo, V.D.; Coletta, R.D. Adverse reactions to the injection of face and neck aesthetic filling materials: A systematic review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2023, 28, e278–e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.; Nieto-Lopez, F.; Rueda-Carrasco, J. Lipoteichoic acid and molecular weight of hyaluronic acid could explain the late inflammatory response trigger by hyaluronic acid fillers. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 5610–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Lee, J.J.; Patton, T.; Choudhary, S. Facial sclerosing lipogranuloma after self-injection of homemade tissue filler: An alarming new practice. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Álvarez, J.; Lebrón-Martín, J.A.; Fernández-Freire, L.R.; Dorado, T.Z.; Morillo, J.S.G. Cutaneous and ganglion sarcoidosis induced by polycaprolactone facial filler: A new expression of ASIA syndrome? Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2021, 8, 002652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mario, M.; Ettore, L.; Bernardi, S.; Becelli, R.; Filippo, G. Vascular complications with necrotic lesions following filler injections: Literature systematic review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023; 101499, epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, N.W.M.; Dhar, A.; Cameron-Strange, A. The perils of penile enhancement: Case report of a fulminant penile infection. BMC Urol. 2021, 21, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanasarnaksorn, W.; Thanyavuthi, A.; Prasertvit, P.; Rattanakuntee, S.; Jitaree, B.; Suwanchinda, A. Case series of tongue necrosis from vascular complications after chin augmentation with hyaluronic acid: Potential pathophysiology and management. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, J.M.; Matayoshi, S. Visual loss after aesthetic facial filler injection: A literature review on an ophthalmologic issue. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2022, 85, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Ng, C.Y. Vitiligo associated with polycaprolactone-based collagen stimulator filler. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 24, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Kollipara, R.; Hoss, E.; Goldman, M.P. Lower eyelid xanthelasma following hyaluronic acid filler injections to the tear troughs. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 3190–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, P.A.; Buhren, B.A.; Bölke, E.; Philipp-Dormston, W.G.; Homey, B.; Schrumpf, H. Time- and dose-dependent effects of hyaluronidase on the degradation of different hyaluronan-based fillers in vitro. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 151, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, L.; Ulrich, F.; Raffoul, W.; Rossi, S.A. Management of a large quantity of permanent gluteal copolyamide fillers (Aqualift/Activegel): Literature review and algorithm. Aesthet. Surg. J. Open Forum. 2022, 4, ojac051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, A.; Staub, H.; Wollina, U. Hypercalcemia due to polymethylmethacrylate injections? (Literature review and case reports). Georgian Med. News. 2018, 282, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chayangsu, O.; Wanitphakdeedecha, R.; Pattanaprichakul, P.; Hidajat, I.J.; Evangelista, K.E.R.; Manuskiatti, W. Legal vs. illegal injectable fillers: The adverse effects comparison study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydenrych, I.; De Boulle, K.; Kapoor, K.M.; Bertossi, D. The 10-Point Plan 2021: Updated concepts for improved procedural safety during facial filler treatments. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 779–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeltzer, A.; Geeroms, M.; Antoniazzi, E.; Giunta, G.; De Baerdemaeker, R.; Hendrickx, B.; Hamdi, M. The “ART” of facial filler injections: Avoid, recognize, and treat hyaluronic acid-induced complications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.H.; Fitzgerald, R.; Cox, S.E.; Butterwick, K.; Murad, M.H.; Humphrey, S.; Carruthers, J.; Dayan, S.H.; Donofrio, L.; Solish, N.; et al. Preventing and treating adverse events of injectable fillers: Evidence-based recommendations from the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Multidisciplinary Task Force. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magacho-Vieira, F.N.; Santana, A.P. Displacement of hyaluronic acid dermal filler mimicking a cutaneous tumor: A case report. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Di Carmine, M.; Marchetti, M.; Lorusso, F.; Amore, R.; Amuso, D. Dermal cosmetic migration after lip augmentation procedure: Clinical management and histological analysis in a case report with review of the literature. Surgeries 2023, 4, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, H.; Masarwa, D.; Sapir, S.; Kaiserman, I. Subconjuctival mobile mass after hyaluronic acid filler injection. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 30, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed-Azzam, S.; Burkat, C.; Mukari, A.; Briscoe, D.; Joshi, N.; Scawn, R.; Alon, E.; Hartstein, M. Filler migration to the orbit. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2021, 41, NP559–NP566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almukhtar, R.; Fitzgerald, R.; Cotofana, S.; Fabi, S. Migration of hyaluronic acid–based soft tissue filler from the temples to the cheeks—An anatomic explanation. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 1526–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dryden, S.C.; Gabbard, R.D.; Meador, A.G.; Stoner, A.E.; Klippenstein, K.A.; Wesley, R.E. A case of orbital granuloma secondary to dermal filler injection. Cureus 2021, 13, e20606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczorowski, M.; Nelke, K.; Łuczak, K.; Hałoń, A. Filler migration and florid granulomatous reaction to hyaluronic acid mimicking a buccal tumor. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, e78–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlHarbi, Z.A.; Alkatan, H.M.; Alsuhaibani, A.H. Long-term outcomes of surgically removed migrated polyalkylimide (Bio-Alcamid) filler to the periorbital area. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 33, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, R.; Mukari, A.; Krausz, J.; Hartstein, M.E.; Azzam, S.H. Orbit mass secondary to migration of dermal hyaluronic acid filler. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtahi-Naeini, B.; Faghihi, G.; Shahmoradi, Z.; Saffaei, A. Filler migration and extensive lesions after lip augmentation: Adverse effects of polydimethylsiloxane filler. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Chiang, C.P.; Wu, B.Y.; Gao, H.W. Filler migration to the forehead due to multiple filler injections in a patient addicted to cosmetic fillers. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2017, 19, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.S. Delayed onset filler complication: Two case reports and literature review. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 30, e12513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.Y.; Lee, K.C.; Jang, Y.H.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, W.J. A case of the migration of hyaluronic acid filler from nose to forehead occurring as two sequential soft lumps. Ann. Dermatol. 2016, 28, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, D.R.; Stoica, B. Filler migration: A number of mechanisms to consider. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 31, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Ryu, J.; Kim, O.; Yoon, J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, J. Clinical implications of ultrasound artifacts in the cervicofacial area following injection of permanent facial fillers. J. Med. Ultrason. 2015, 42, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grippaudo, F.R.; Di Girolamo, M.; Mattei, M.; Pucci, E.; Grippaudo, C. Diagnosis and management of dermal filler complications in the perioral region. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2014, 16, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J. Pseudocyst of the neck after facial augmentation with liquid silicone injection. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, e474–e475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, Y.S.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.S. Periorbital lipogranuloma related to filler migration: A rare complication of facial fillers. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2014, 16, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadouch, J.A.; Nolthenius, C.J.T.; Kadouch, D.J.; van der Woude, H.J.; Karim, R.B.; Hoekzema, R. Complications after facial injections with permanent fillers: Important limitations and considerations of MRI evaluation. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2014, 34, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrabi-Farahani, S.; Lerman, M.A.; Noonan, V.; Kabani, S.; Woo, S.-B. Granulomatous foreign body reaction to dermal cosmetic fillers with intraoral migration. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2014, 117, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, S.; Lawrence, N.; Donofrio, L.; Cox, S.E. Delayed migration of hyaluronic acid fillers: A new complication? Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathoo, N.A.; Rassmussen, S.; Dolman, P.J.; Rossman, D.W. Periocular mass lesions secondary to dermatologic fillers: Report of 3 cases. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 49, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; Mehta, P.; Adesanya, O.; Ahluwalia, H.S. Migrated periocular filler masquerading as arteriovenous malformation: A diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 29, e18–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulart, J.M.; High, W.A.; Goldenberg, G. Evidence of calcium hydroxylapatite migration: Distant nodule formation in the setting of concurrent injection with nonanimal stabilized hyaluronic acid. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 65, e65–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.H.; Malhotra, R. Long-term orbitofacial complications of polyalkylimide 4% (Bio-Alcamid). Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 25, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Sung, M.S.; Kim, N.J.; Choung, H.K.; Khwarg, S.I. Eyelid mass secondary to injection of calcium hydroxylapatite facial filler. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 24, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, K.R. Radiesse nodule of the lips from a distant injection site: Report of a case and consideration of etiology and management. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2007, 6, 846–847. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, R.B.; Hage, J.J.; van Rozelaar, L.; Lange, C.A.; Raaijmakers, J. Complications of polyalkylimide 4% injections (Bio-Alcamid): A report of 18 cases. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2006, 59, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda-Lari, A. Augmentation of the malar area with polyacrylamide hydrogel: Experience with more than 1300 patients. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2008, 28, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, A.; Gray, M.L.; Westra, W.H.; Teng, M.S.; Rosenberg, J.D. Dermal filler presenting as parotid mass: A case report. Head Neck Pathol. 2021, 15, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syunyaeva, Z.; Kahnert, K.; Kauffmann-Guerrero, D.; Huber, R.M.; Tufman, A. Dermal filler injections mimic tumor activity during immune checkpoint inhibition. Respiration 2018, 95, 362–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, K.; Prabhu, I.S.; Bradley, K.M. Fluorodeoxyglucose activity associated with a cosmetic poly-L-lactide filler: A potential confounder on positron emission tomography and computed tomography. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginat, D.T.; Schatz, C.J. Imaging features of midface injectable fillers and associated complications. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanput, W.; Mes, J.J.; Wichers, H.J. THP-1 cell line: An in vitro cell model for immune modulation approach. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, W.H.; Jennen, D.; Keizers, P.H.J.; Hodemaekers, H.M.; Vermeulen, J.P.; Bakker, F.; Schwillens, P.; van Herwijnen, M.; Jetten, M.; Kleinjans, J.C.S.; et al. Evaluation of adverse effects of resorbable hyaluronic acid fillers: Determination of macrophage responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennen, D.G.J.; van Herwijnen, M.; Jetten, M.; Vandebriel, R.J.; Keizers, P.; Geertsma, R.E.; de Jong, W.H.; Kleinjans, J.C.S. Transcriptomic analysis in human 3D skin model injected with resorbable hyaluronic acid fillers reveals foreign body response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneke, E. Adverse effects of fillers. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, L.G.; Stolz, W.; Schroeder, J.A. Electron microscopic documentation of late changes in permanent fillers and clinical management of granulomas in affected patients. Dermatol. Surg. 2009, 35 (Suppl. 2), 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenblätter, M.; Ehrchen, J.; Varga, G.; Sunderkötter, C.; Heindel, W.; Roth, J.; Bremer, C.; Wall, A. In vivo optical imaging of cellular inflammatory response in granuloma formation using fluorescence-labeled macrophages. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Christensen, J.M.; Brat, G.A.; Johnson, K.E.; Chen, Y.; Buretta, K.J.; Cooney, D.S.; Brandacher, G.; Lee, W.P.; Li, X.; Sacks, J.M. Monocytes loaded with indocyanine green as active homing contrast agents permit optical differentiation of infectious and non-infectious inflammation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, P.A.; Filler, T. Static and dynamic anatomy of the face, in particular eyebrows, eyelids and lips. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2022, 56, 306–312. [Google Scholar]
- Master, M.; Roberts, S. Long-term MRI follow-up of hyaluronic acid dermal filler. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2022, 10, e4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollina, U.; Goldman, A. Correction of tear trough deformity by hyaluronic acid soft tissue filler placement inferior to the lateral orbital thickening. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruglikov, I.; Trujillo, O.; Kristen, Q.; Isac, K.; Zorko, J.; Fam, M.; Okonkwo, K.; Mian, A.; Thanh, H.; Koban, K.; et al. The facial adipose tissue: A revision. Facial Plast. Surg. 2016, 32, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oranges, C.M.; Brucato, D.; Schaefer, D.J.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Harder, Y. Complications of nonpermanent facial fillers: A systematic review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2021, 9, e3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, A.; Tran, T.; Cibulas, A.T.; Warden, D.; Danger, F.J.; Scherer, K.; Wasyliw, C. Filler migration and granuloma formation after gluteal augmentation with free-silicone injections. Cureus 2018, 10, e3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, H.L.; Wang, I.; Meehan, S.; Sanchez, M.; Smith, G.P. Gluteal silicone injections leading to extensive filler migration with induration and arthralgia. Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 21, 13030/qt4xf2m886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, I.S.; Song, Y.S.; Choi, K.U.; Ahn, H.Y. Distant migration of gel filler: Imaging findings following breast augmentation. Skeletal. Radiol. 2022, 51, 2223–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.V.; Urman, D.S.; Cabral, E.S.; Shim, E.K.; Bennett, R.G. Hyaluronic acid filler incidentally found during Mohs micrographic surgery: Observations in 36 patients regarding skin depth, degradation size, and estimated persistence time. Dermatol. Surg. 2022, 48, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzany, B.; Becker-Wegerich, P.; Bachmann, F.; Erdmann, R.; Wollina, U. Hyaluronidase in the correction of hyaluronic acid-based fillers: A review and a recommendation for use. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2009, 8, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guliyeva, G.; Huayllani, M.T.; Kraft, C.; Lehrman, C.; Kraft, M.T. Allergic complications of hyaluronidase injection: Risk factors, treatment strategies, and recommendations for management. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, A.; Wollina, U.; Machado, D.; Marionwic, D. Laser in the treatment of granulomas on the nose produced by polymethylmethacrylate: A case series. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, A.; Wollina, U. Polymethylmethacrylate-induced nodules of the lips: Clinical presentation and management by intralesional neodymium: YAG laser therapy. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.; Su, X.; Hu, J.; Chai, H. High-frequency ultrasound of facial filler materials in the nasolabial groove. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2022, 46, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, H.; Su, X.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Dou, M.; Hu, J. High-frequency ultrasound imaging findings of different mental injectable soft tissue fillers. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2022, 46, 2995–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelke, L.W.; Cassuto, D.; Velthuis, P.; Wortsman, X. Nomenclature proposal for the sonographic description and reporting of soft tissue fillers. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.G.; Jardim, L.C.; Schuch, L.F.; Silveira, F.M.; Wagner, V.P.; Pires, F.R.; Santos, J.N.D.; Martins, M.D. Foreign body reactions related to orofacial esthetic fillers: A systematic review. Oral Dis. 2023; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lu, H.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Qi, Z. The histologic reaction and permanence of hyaluronic acid gel, calcium hydroxylapatite microspheres, and extracellular matrix bio gel. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).