Ultra-Low Power, Process-Tolerant 10T (PT10T) SRAM with Improved Read/Write Ability for Internet of Things (IoT) Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
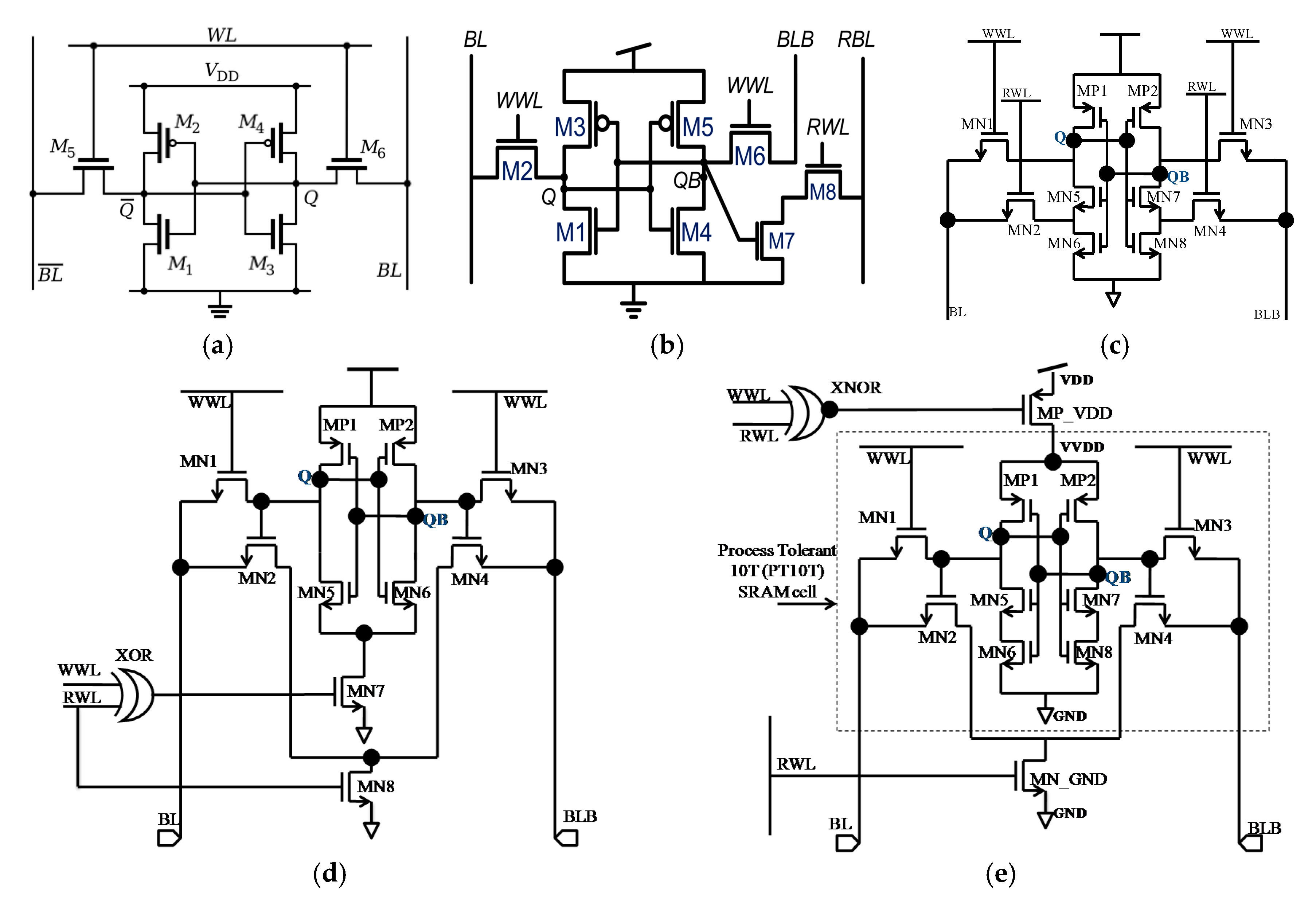
2. Related Work and Motivation
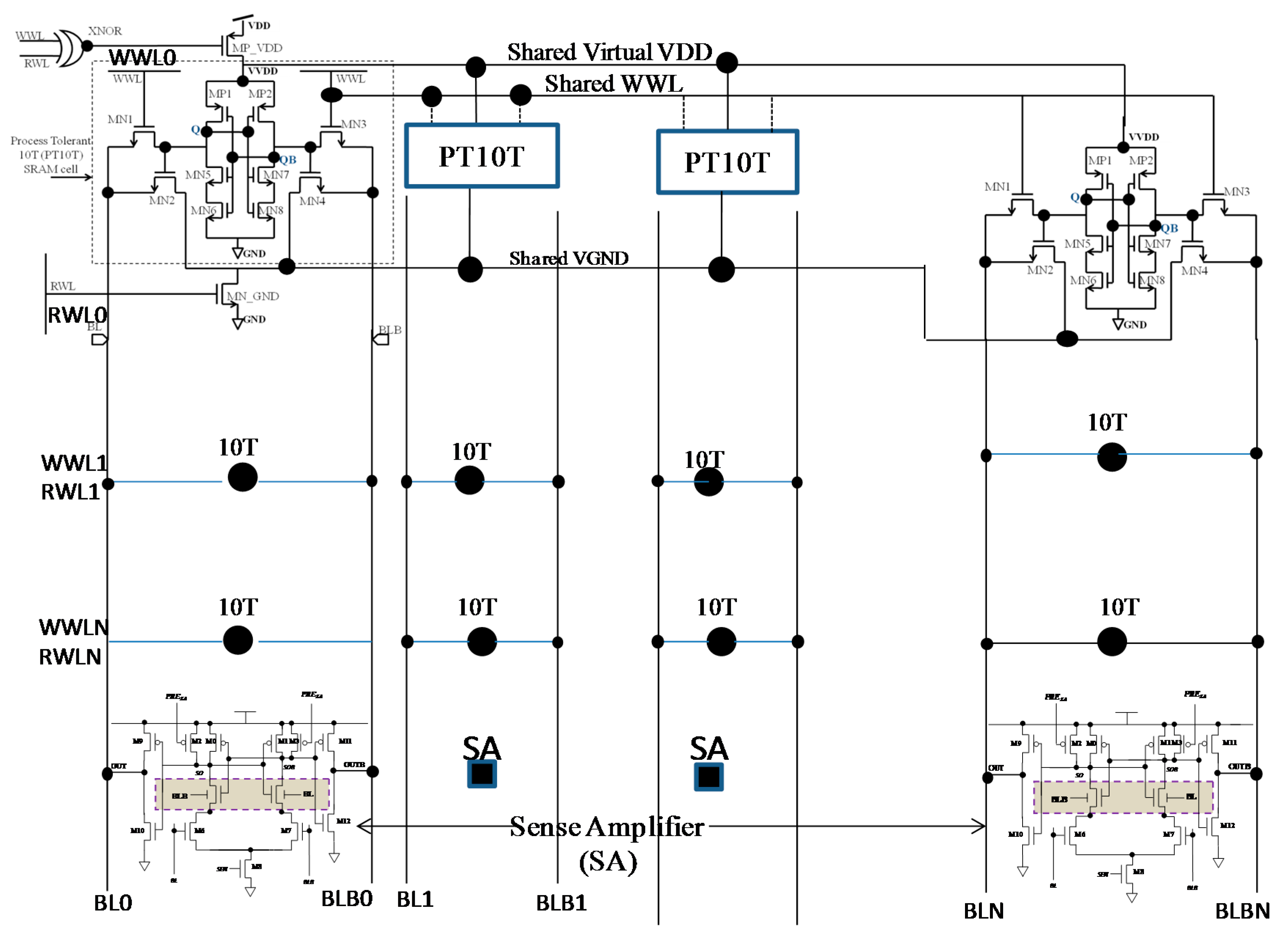
3. Architecture of 10T SRAM Cell
4. 10T SRAM Cell-Based 8 kb Macroblock and Area Overhead
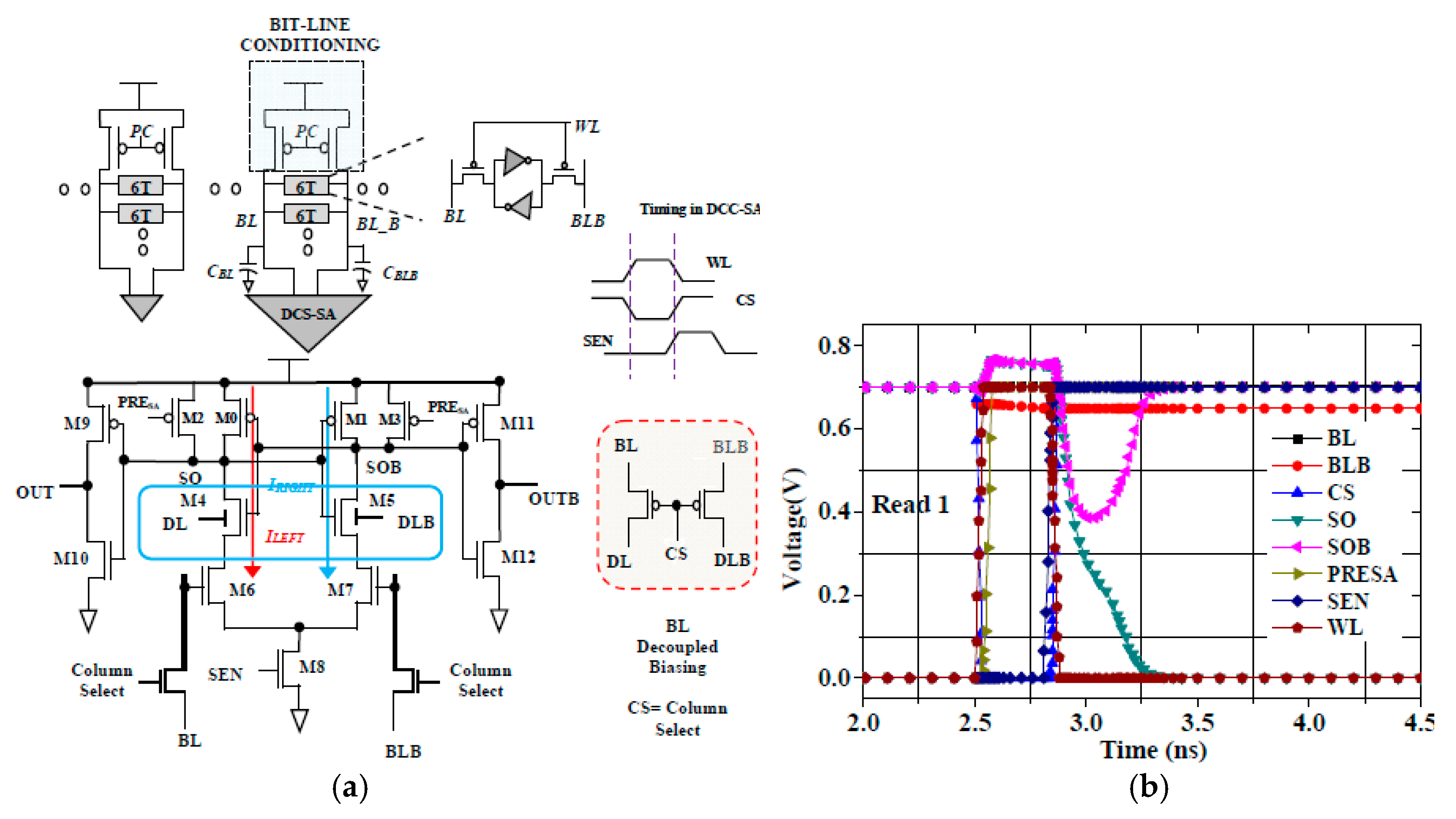
5. Operations and Working of 10T SRAM
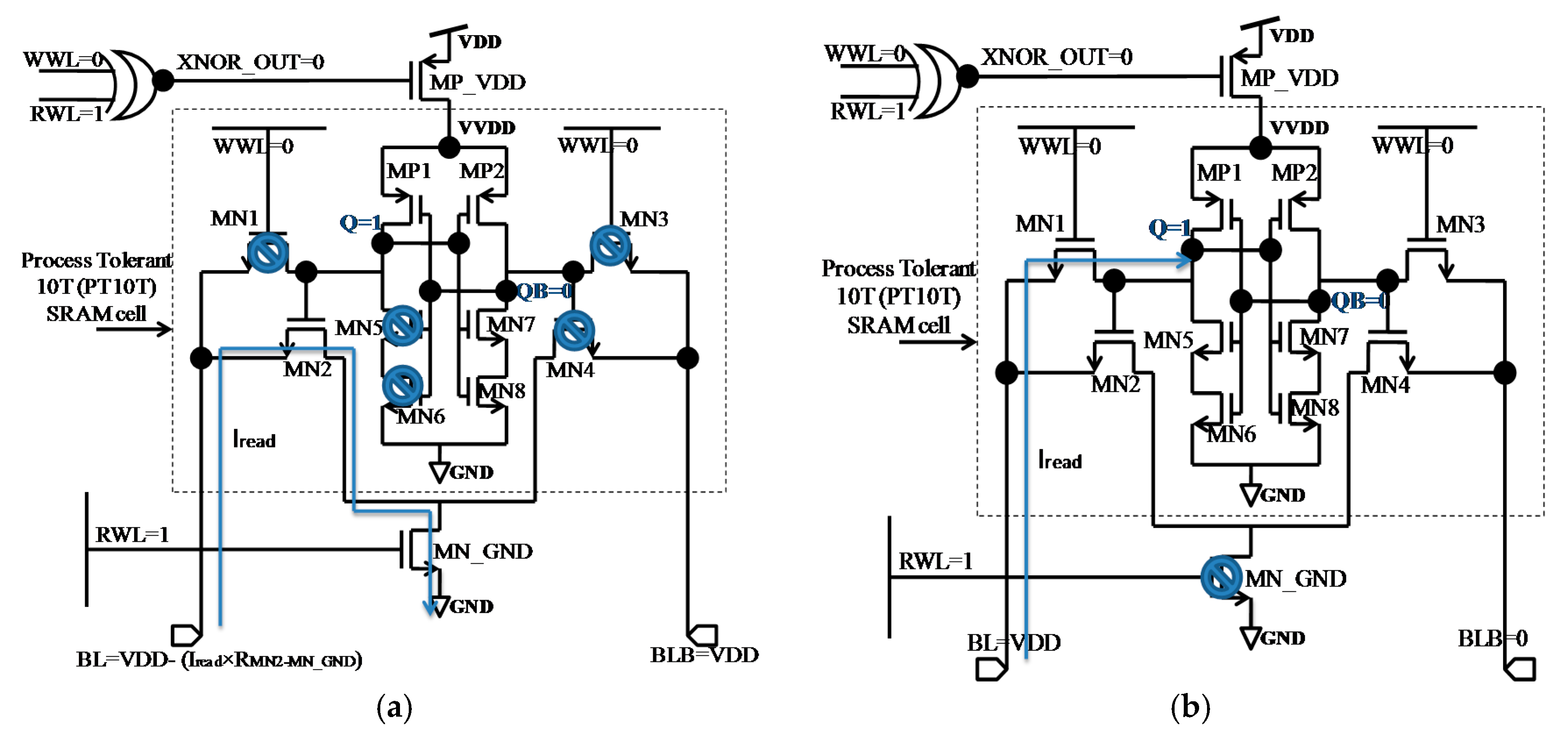
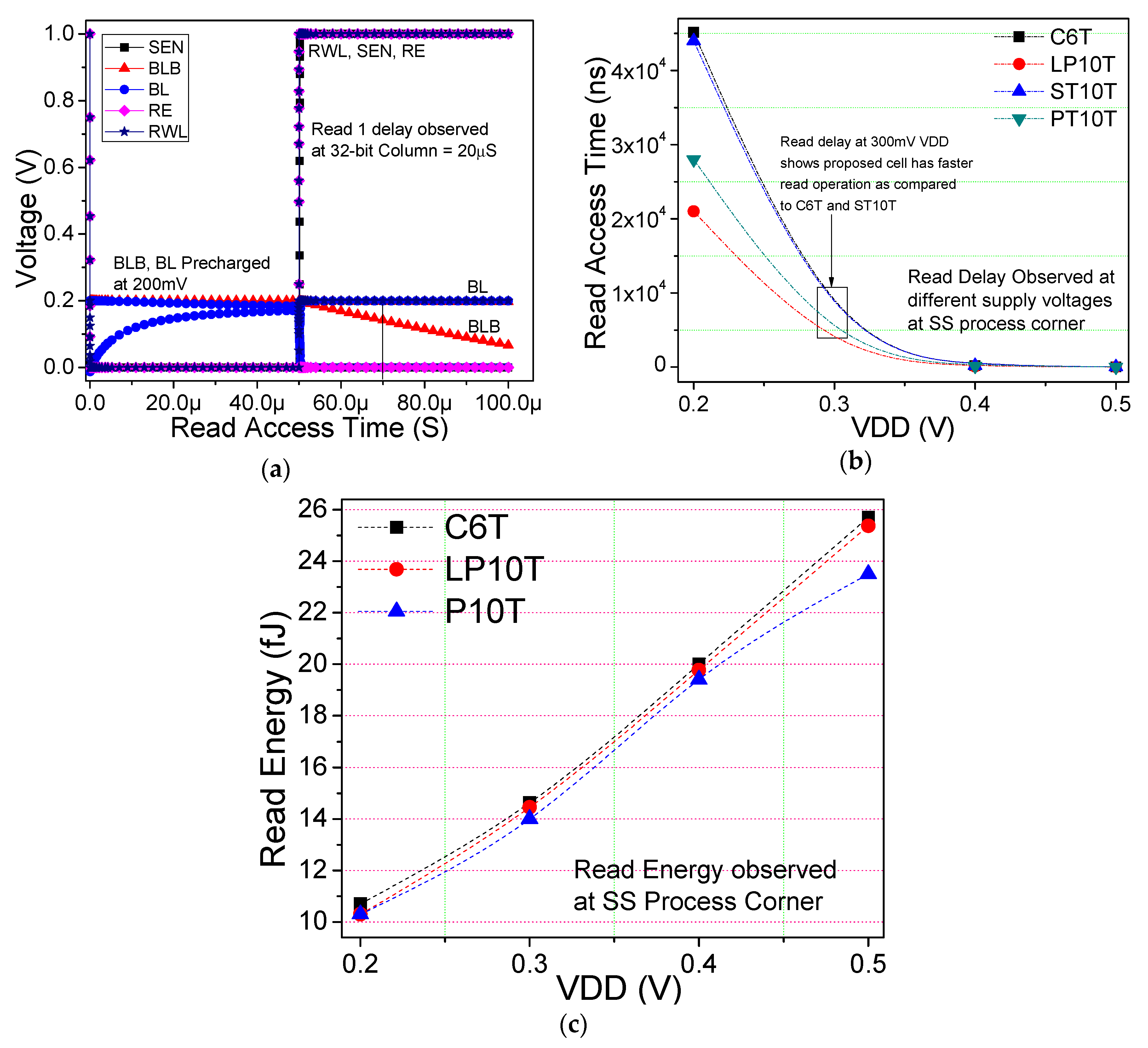
5.1. Read Operation
5.2. Write Operation
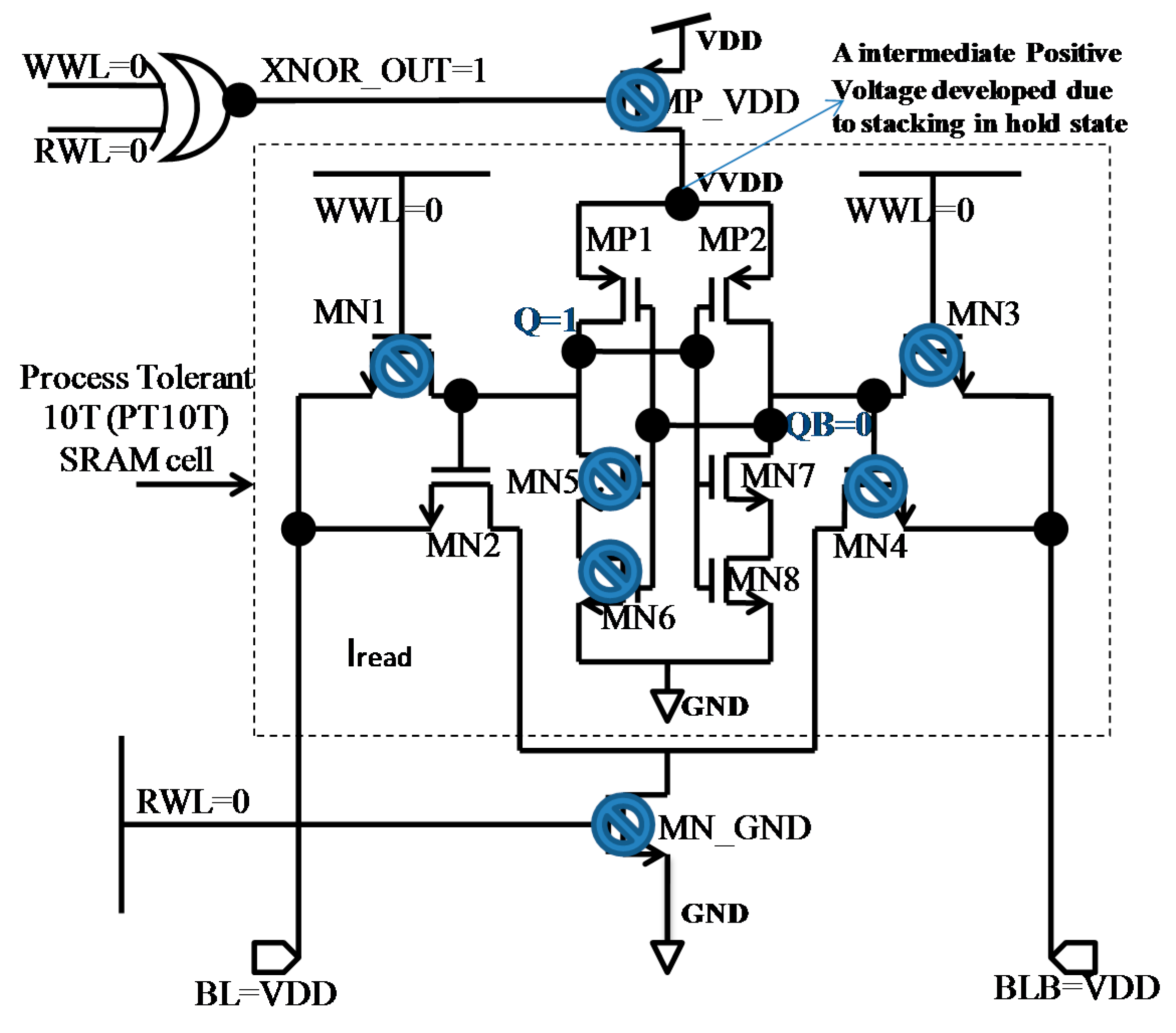
5.3. Data Retention
6. Simulation Results of PT10T SRAM
6.1. Simulation Setup
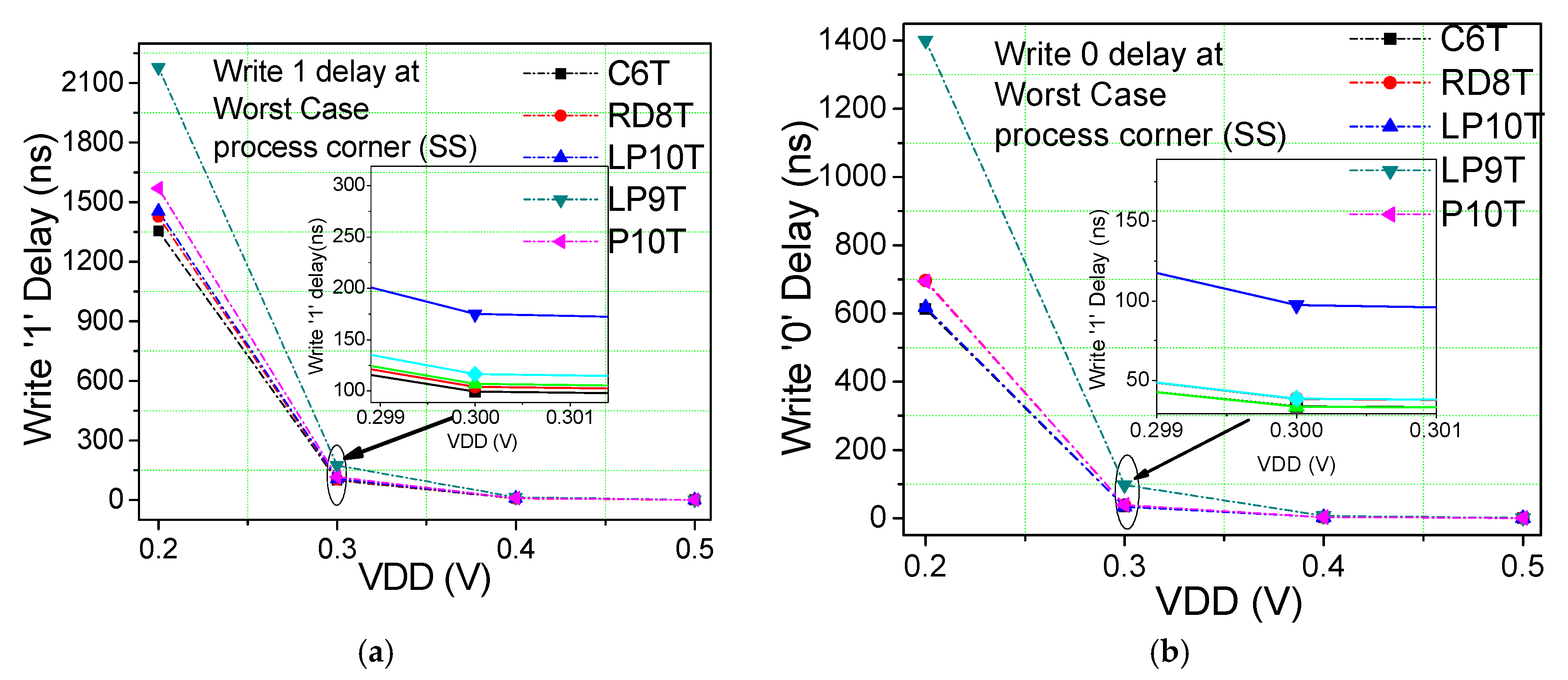
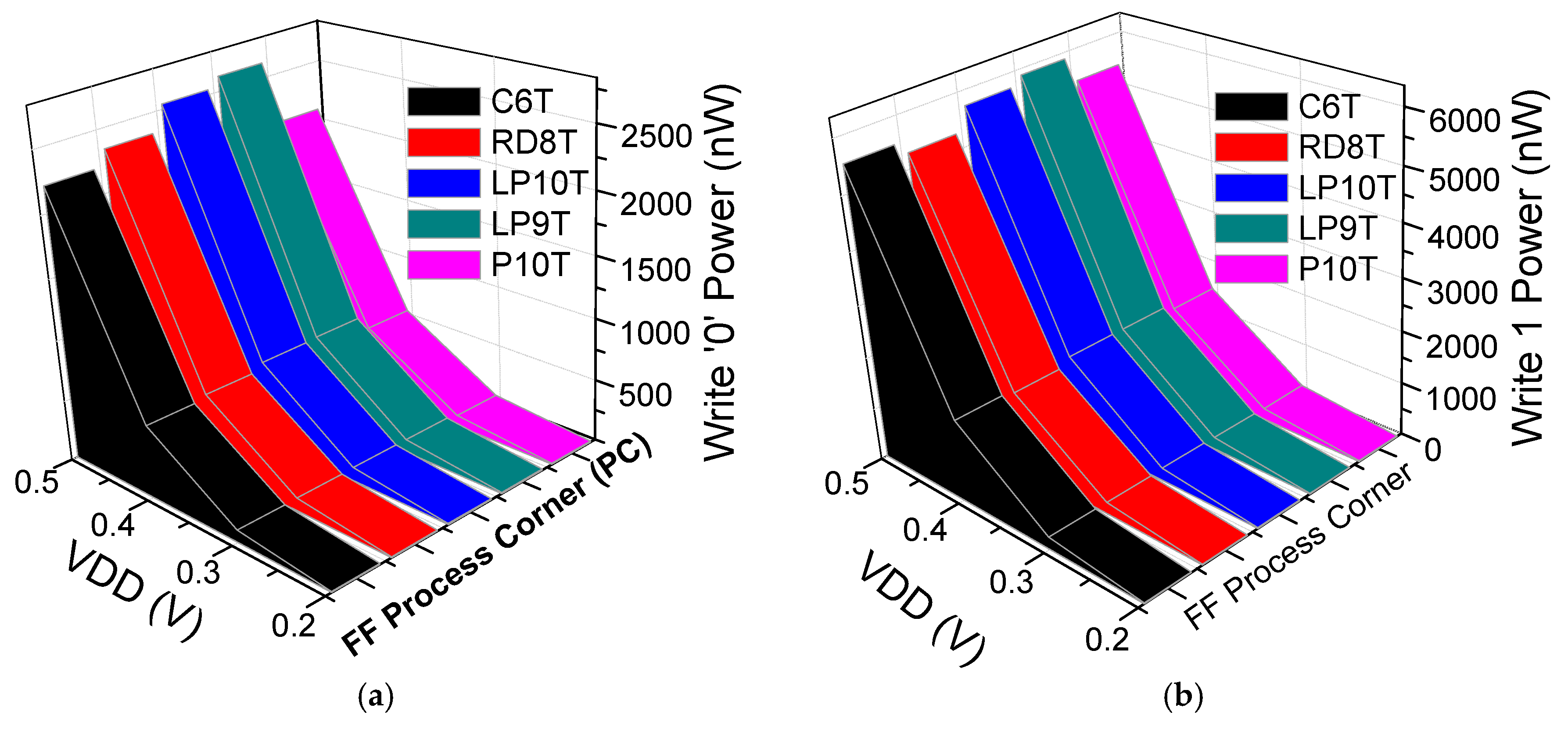
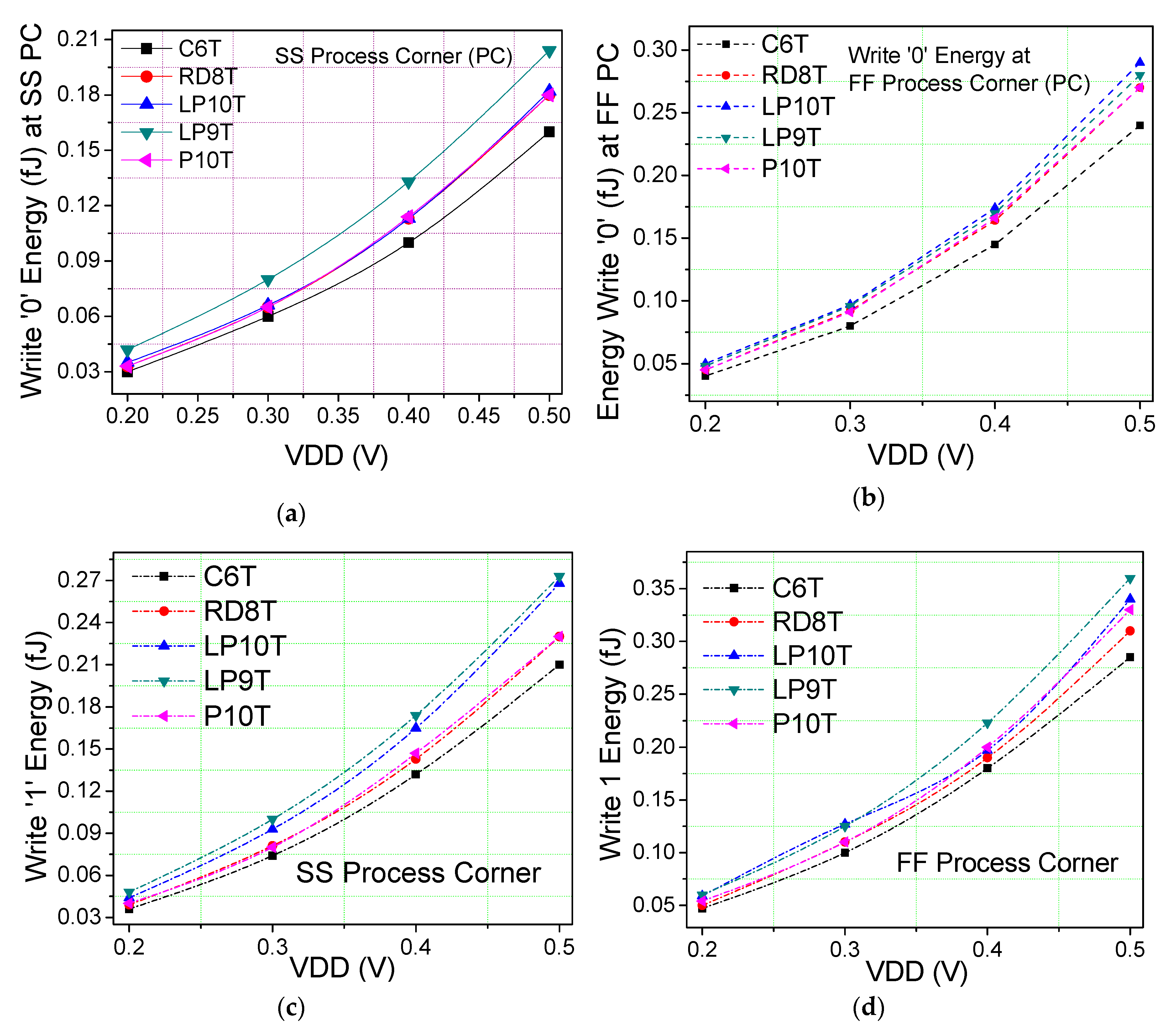
6.2. Write and Read Analysis
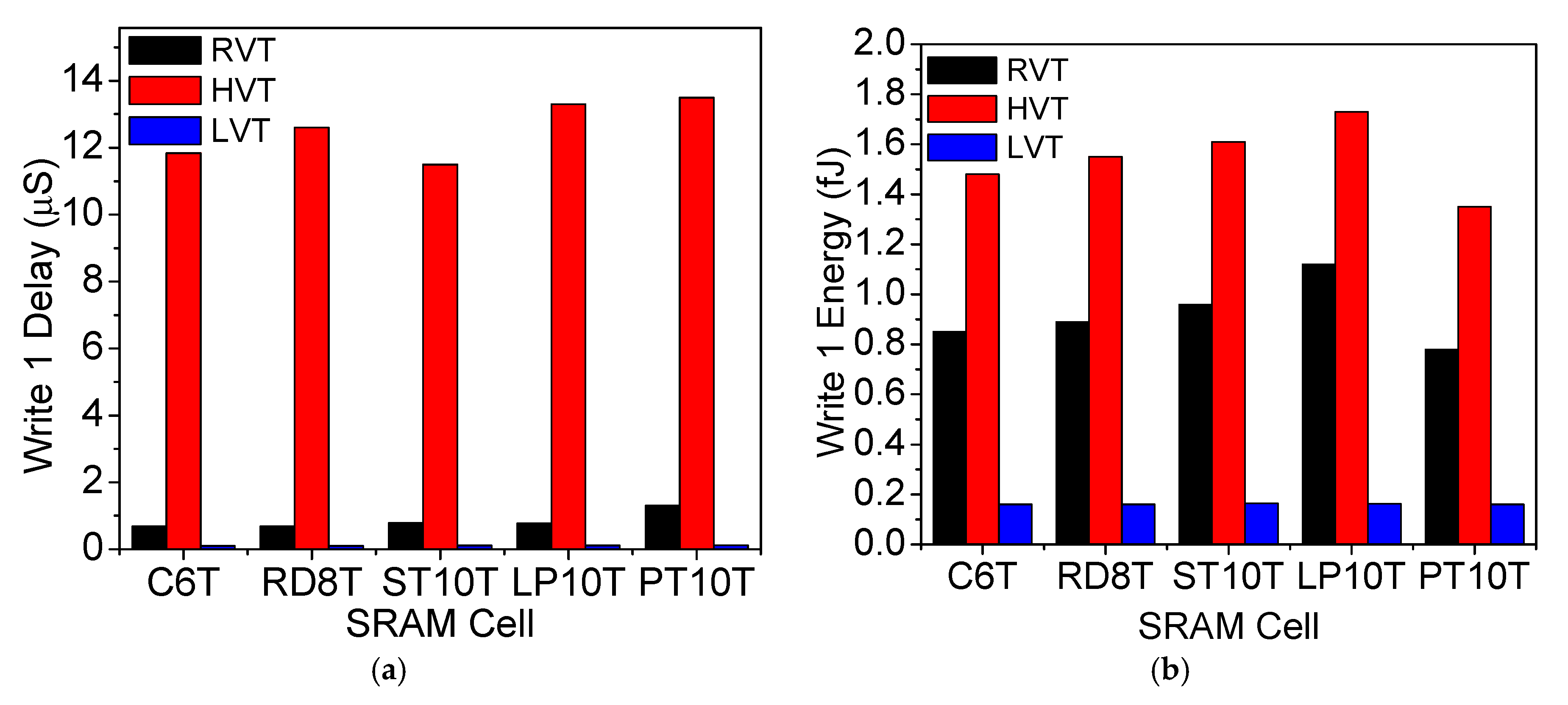
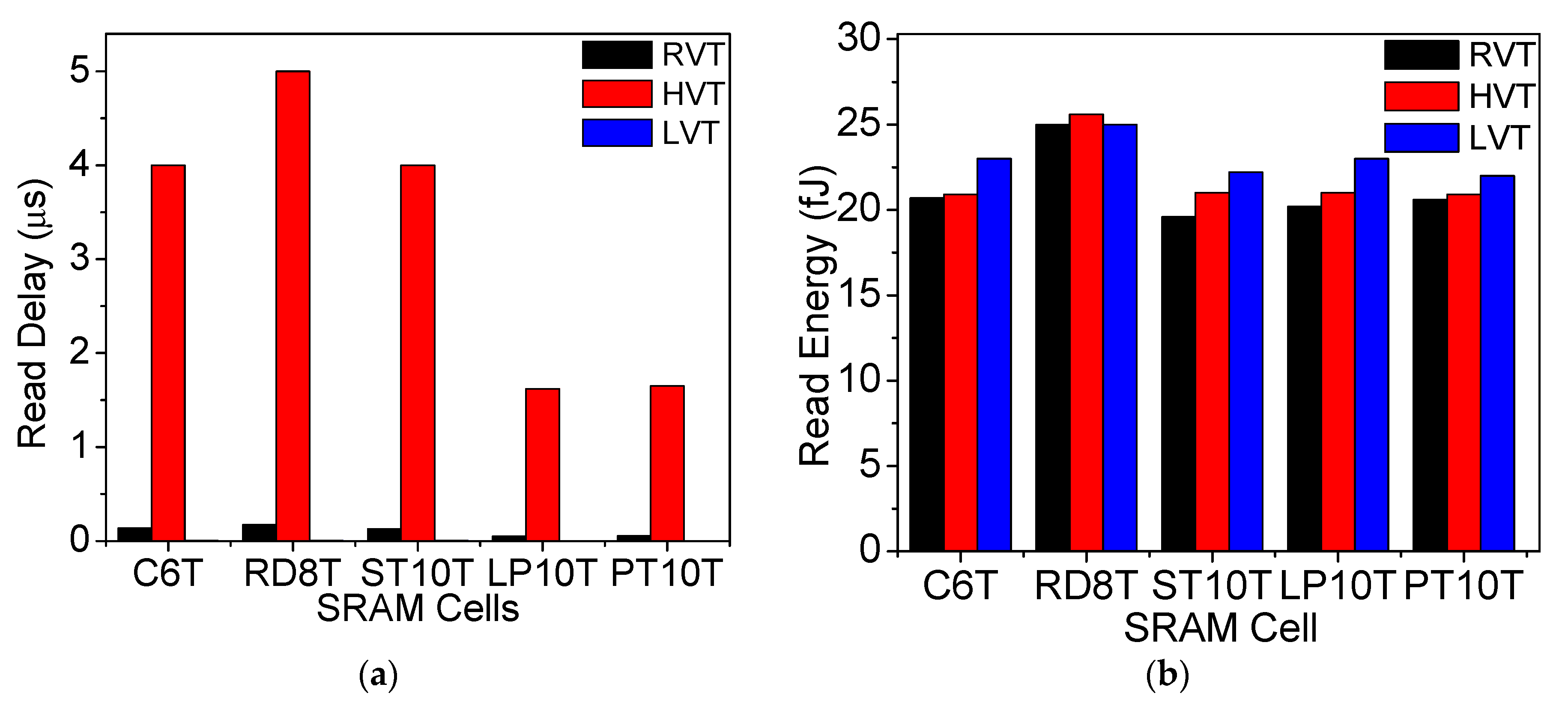
6.3. Write and Read Analysis at Different Threshold Voltage Transistors
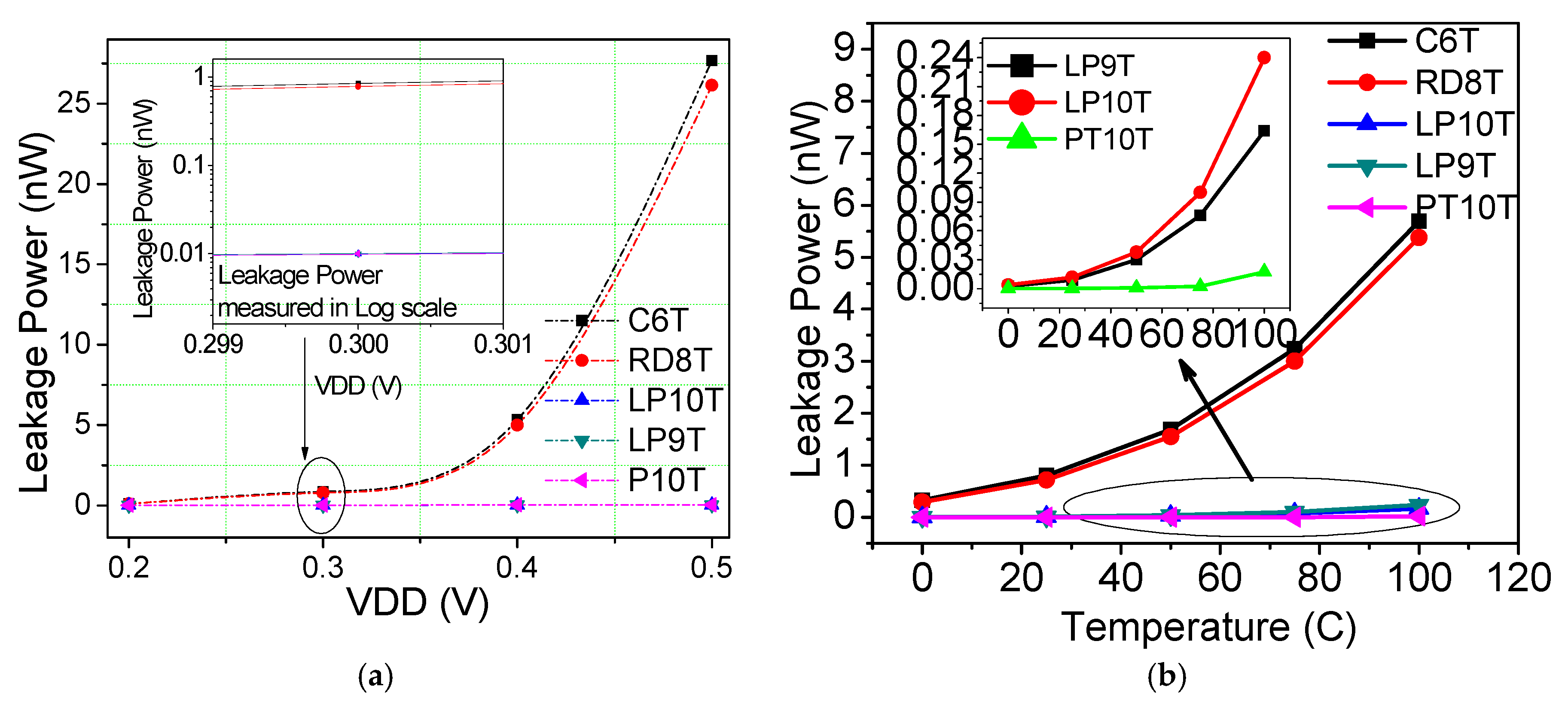
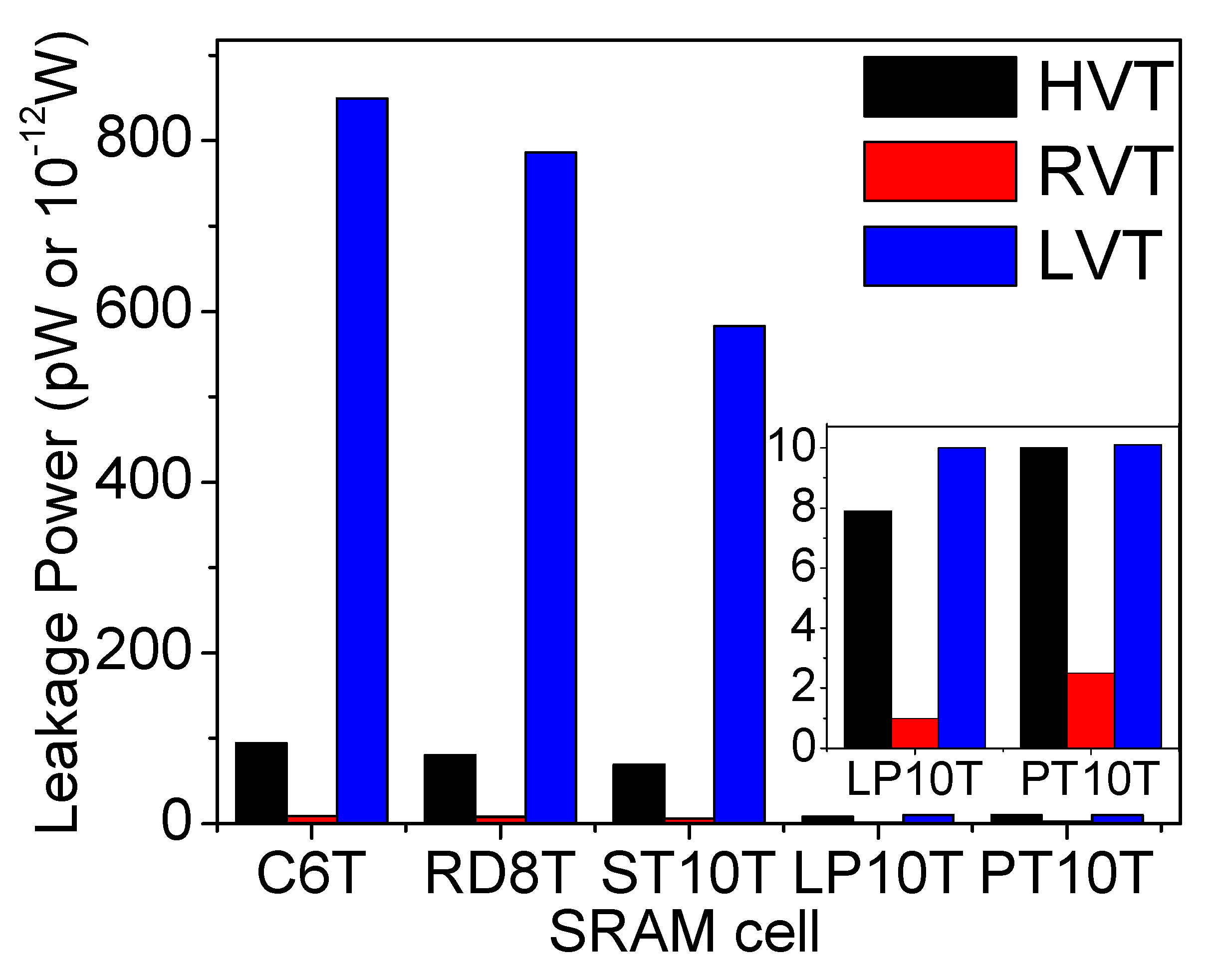
6.4. Standby or Leakage Power
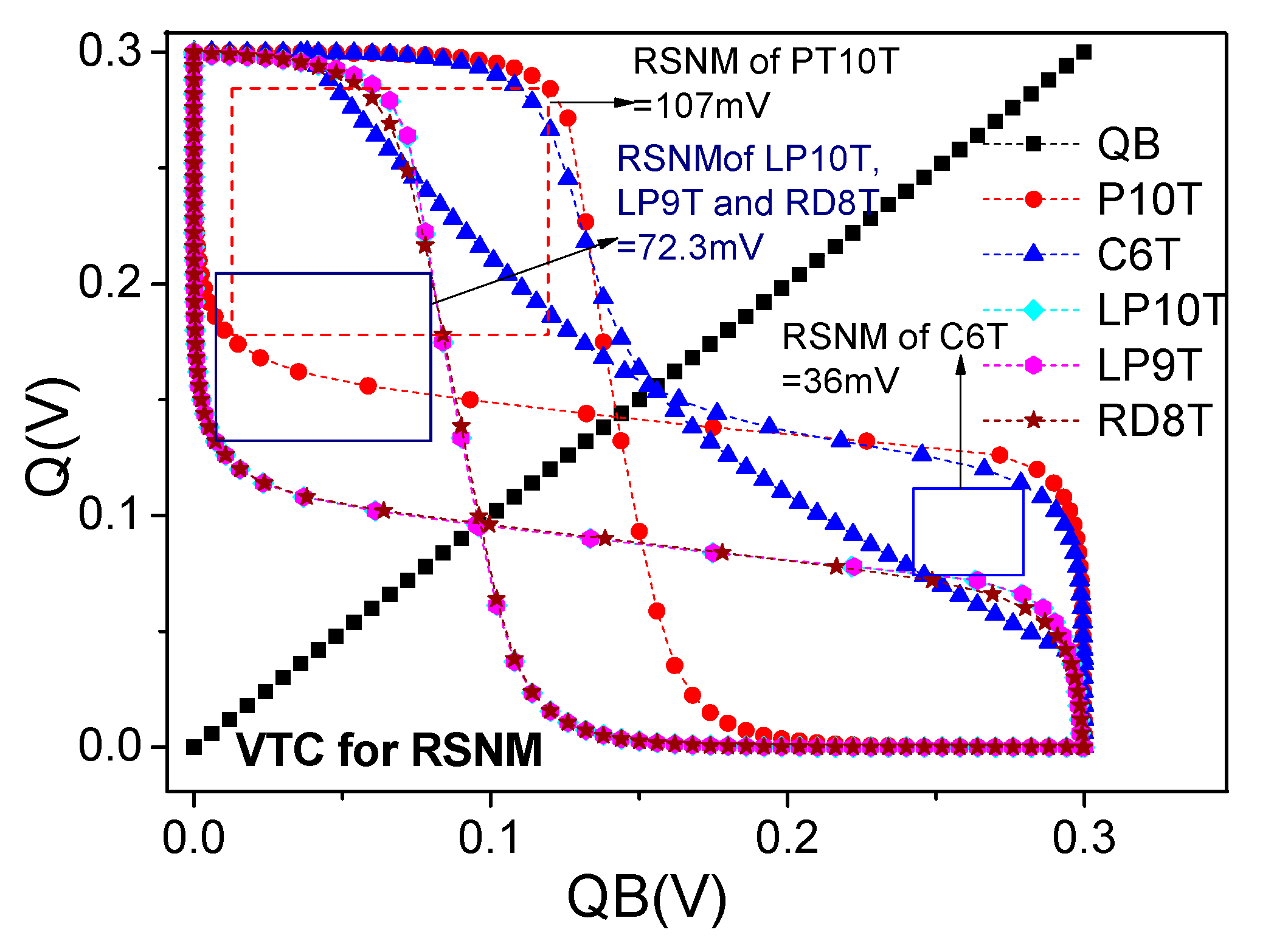
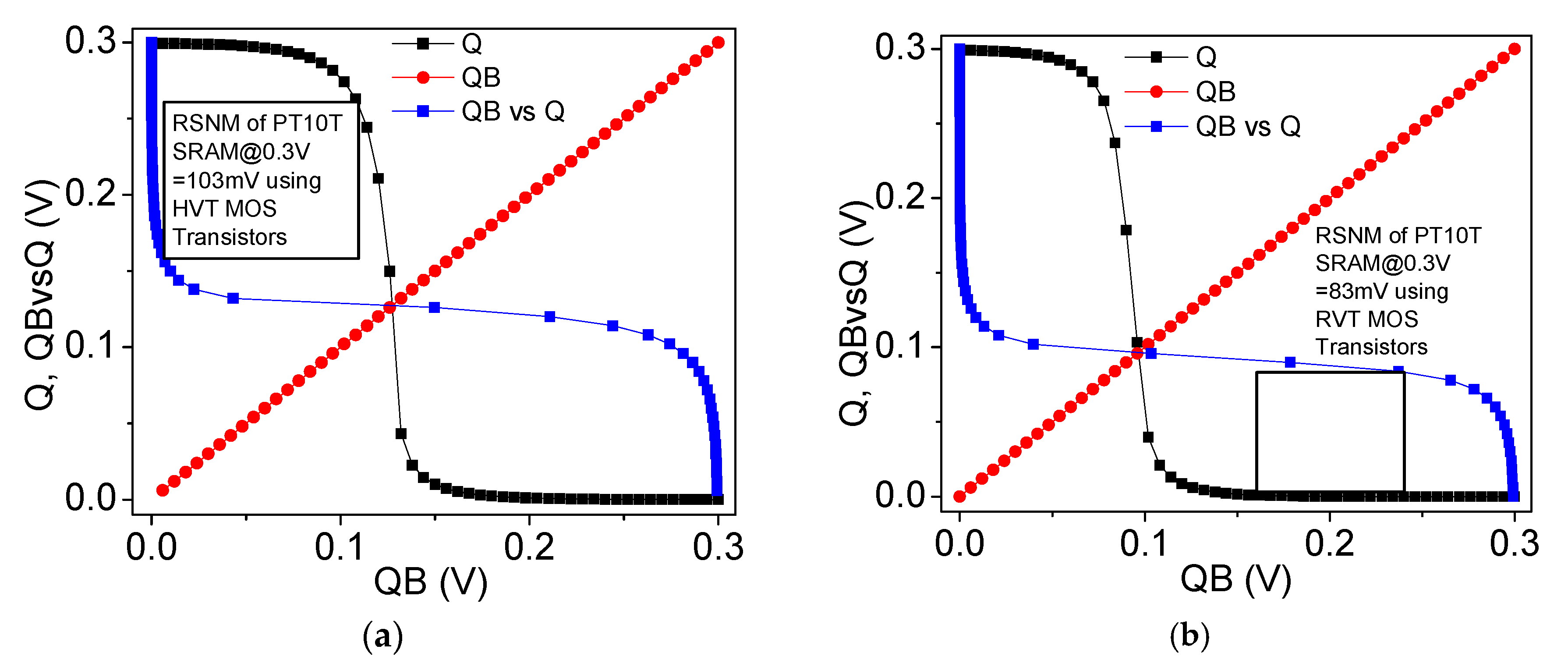
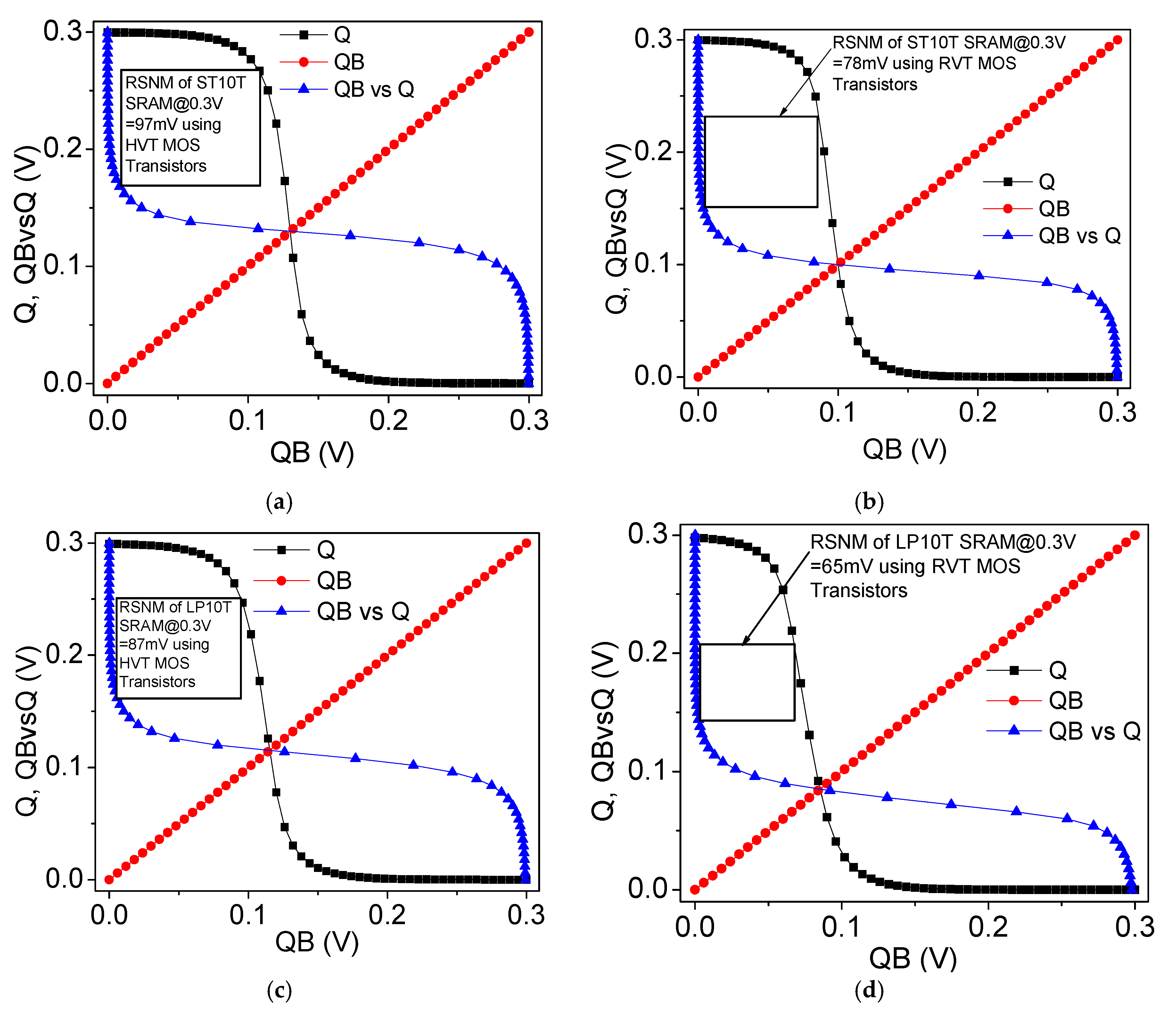
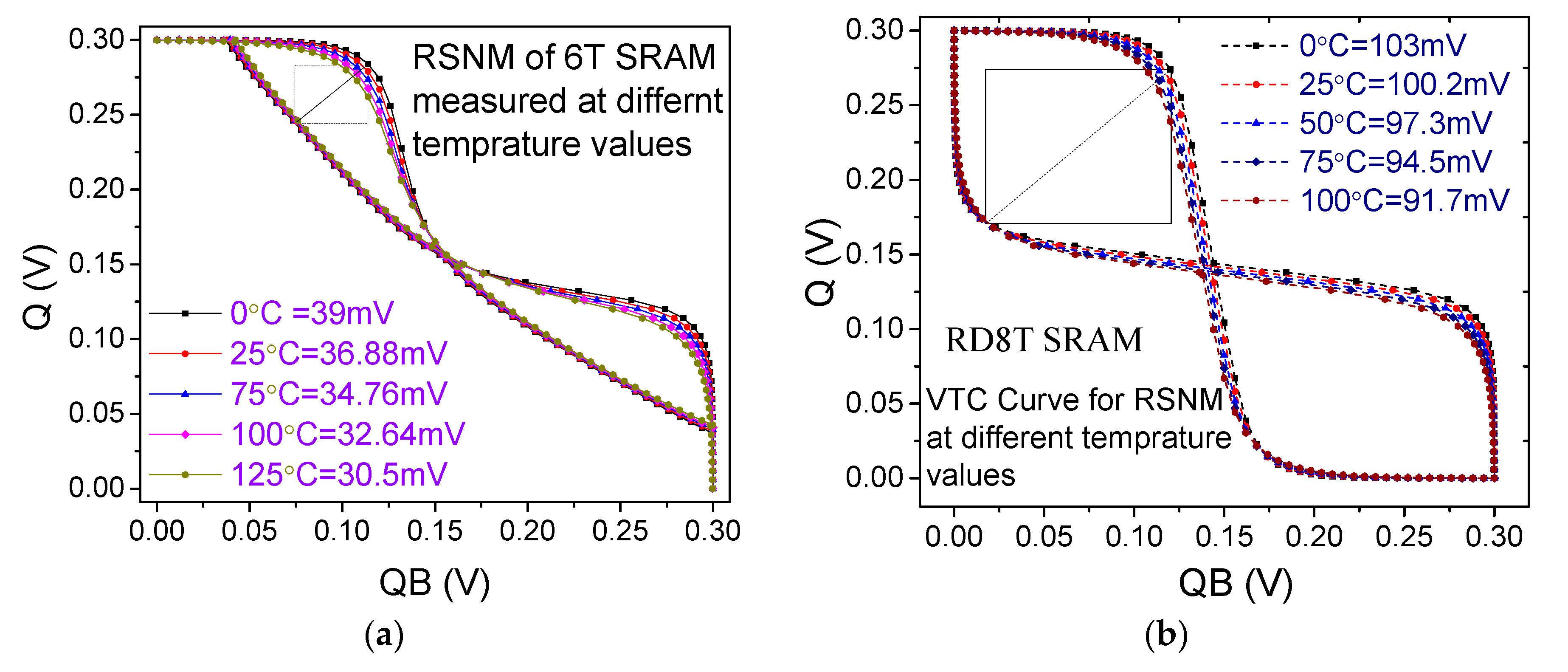
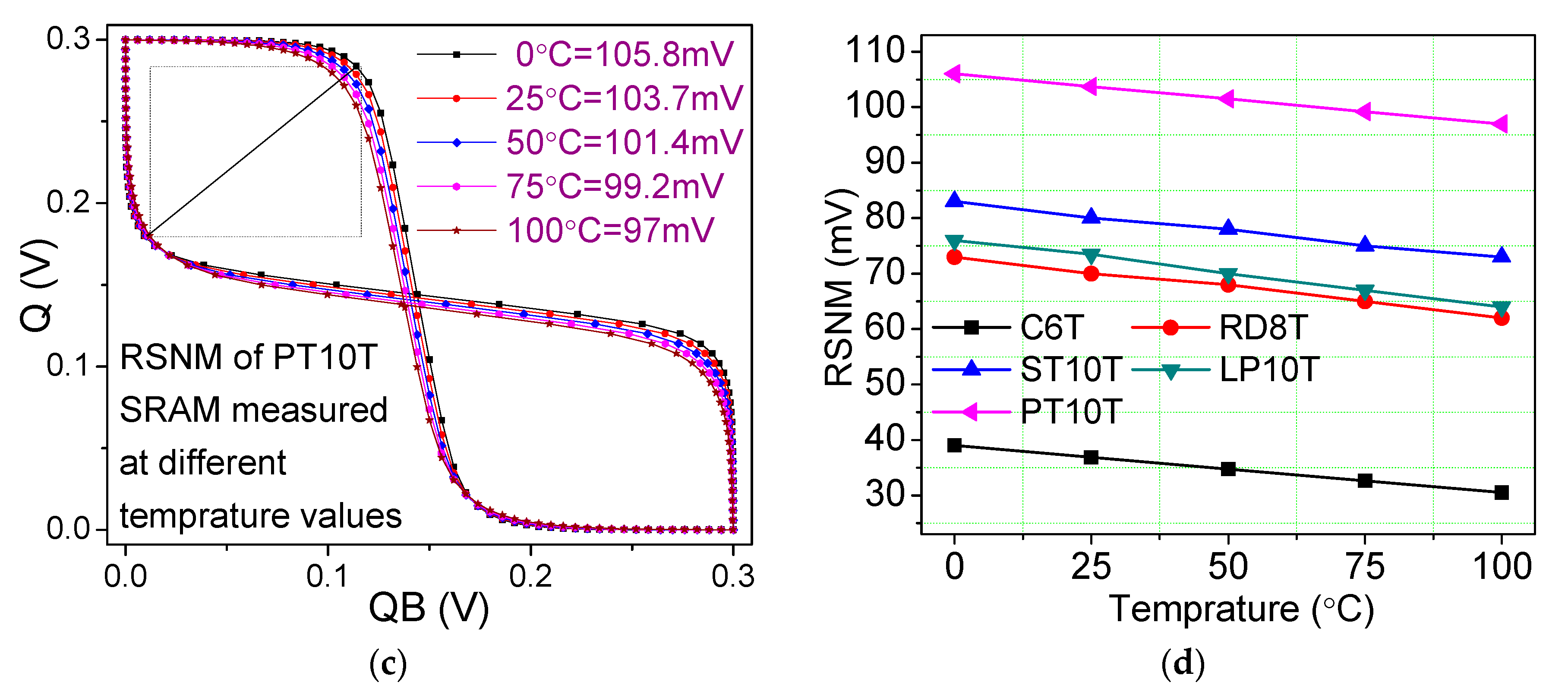
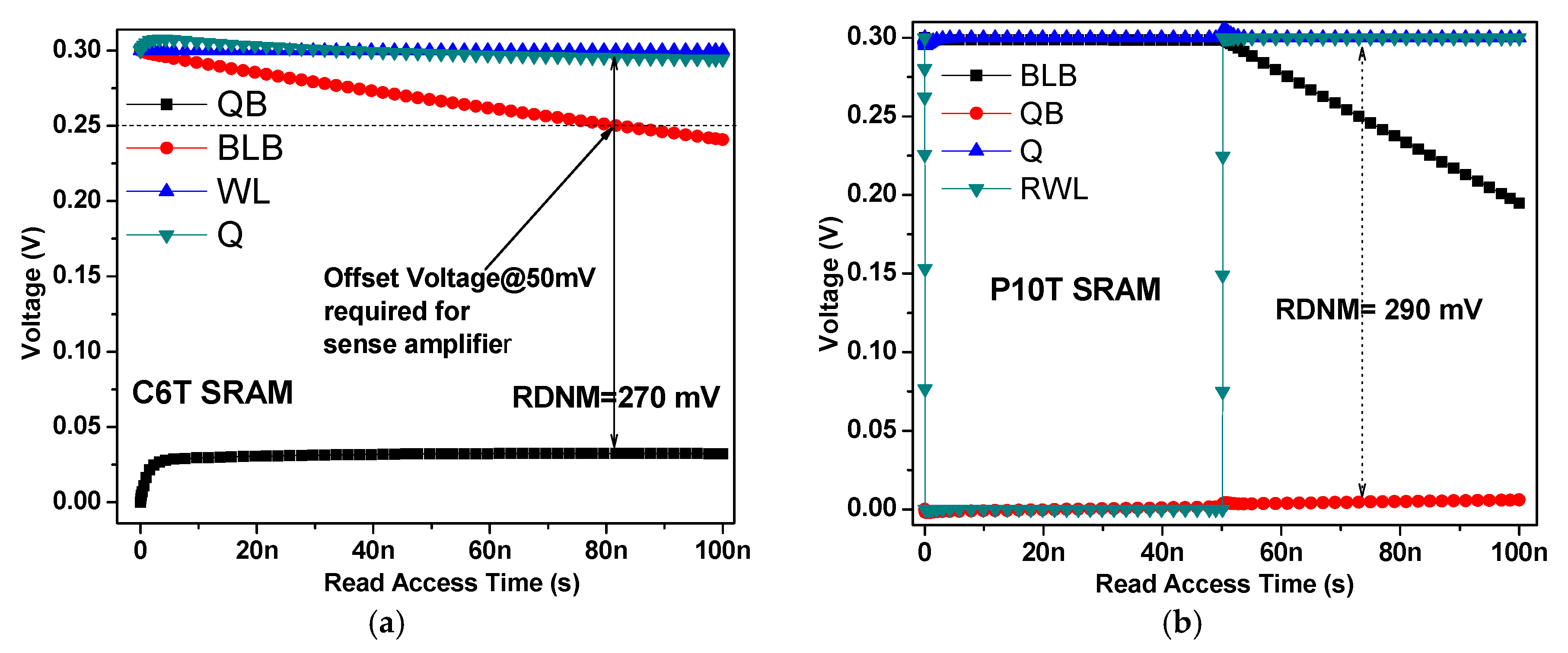
6.5. Read Static Noise Margin (RSNM) and Dynamic Read Margin (DRM)
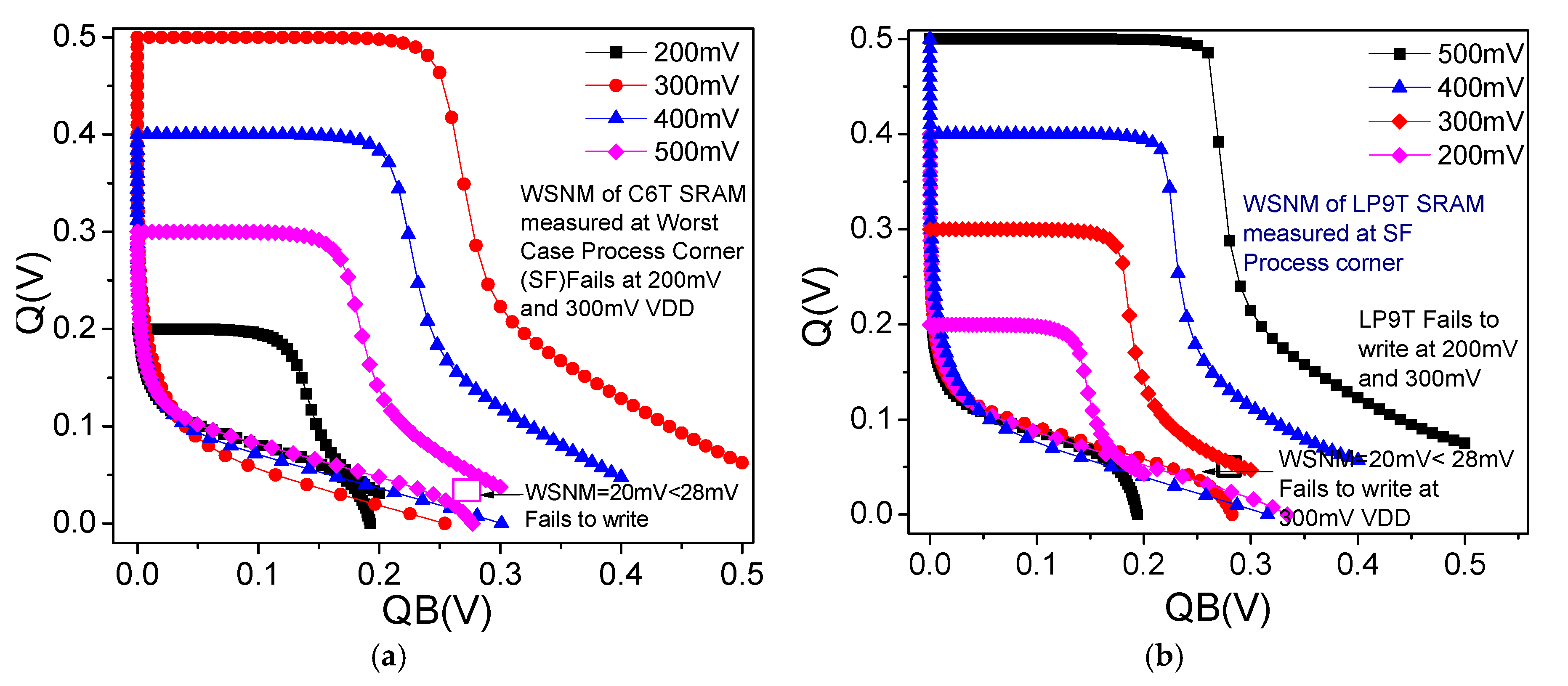
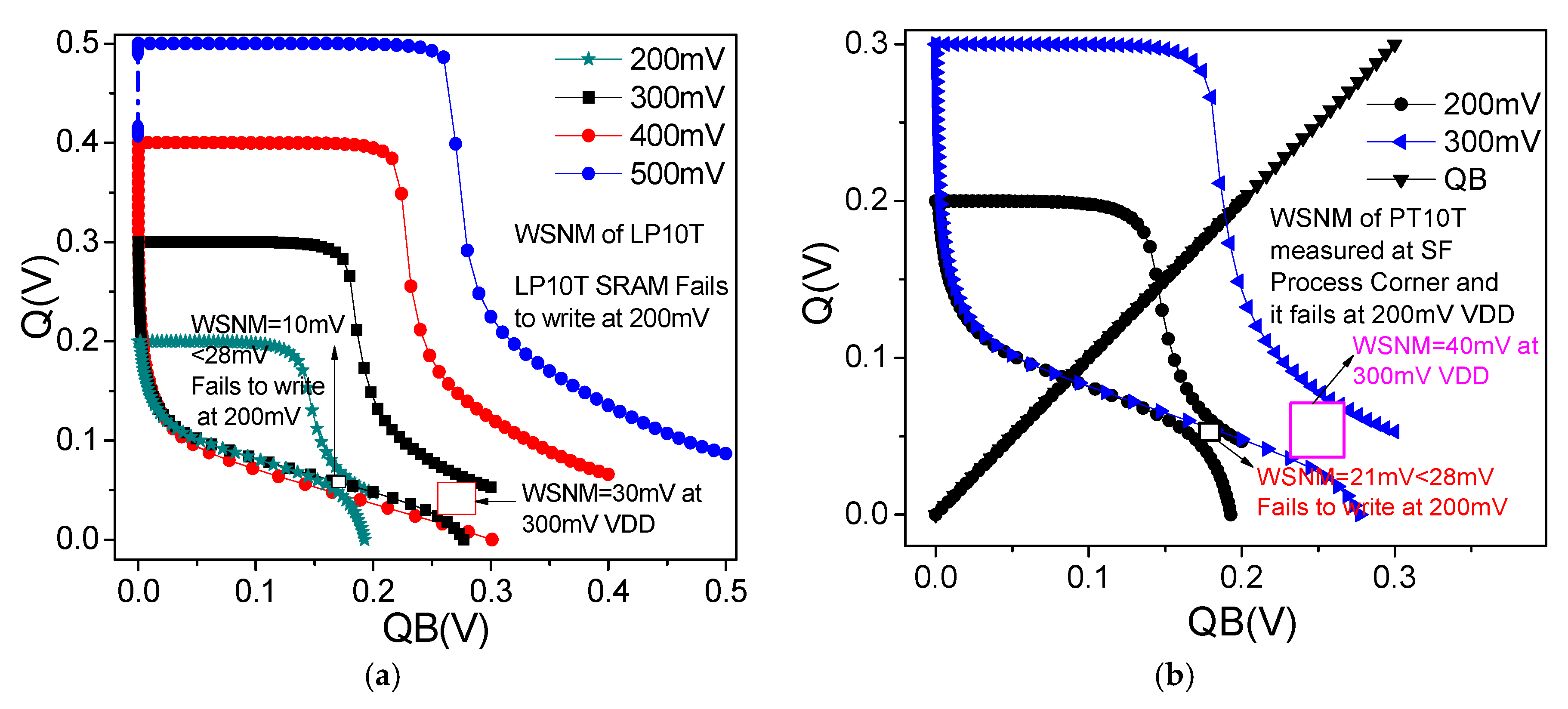
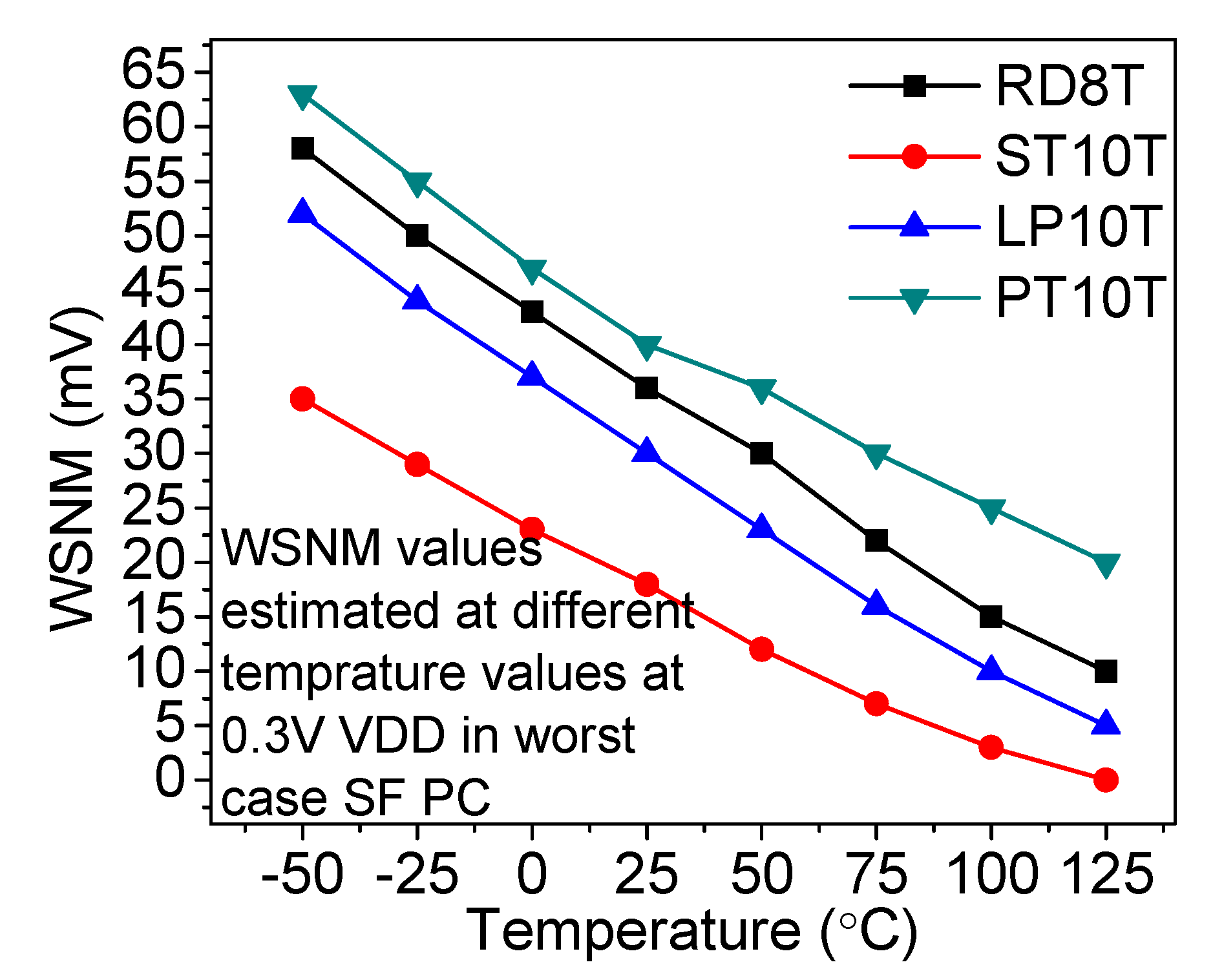
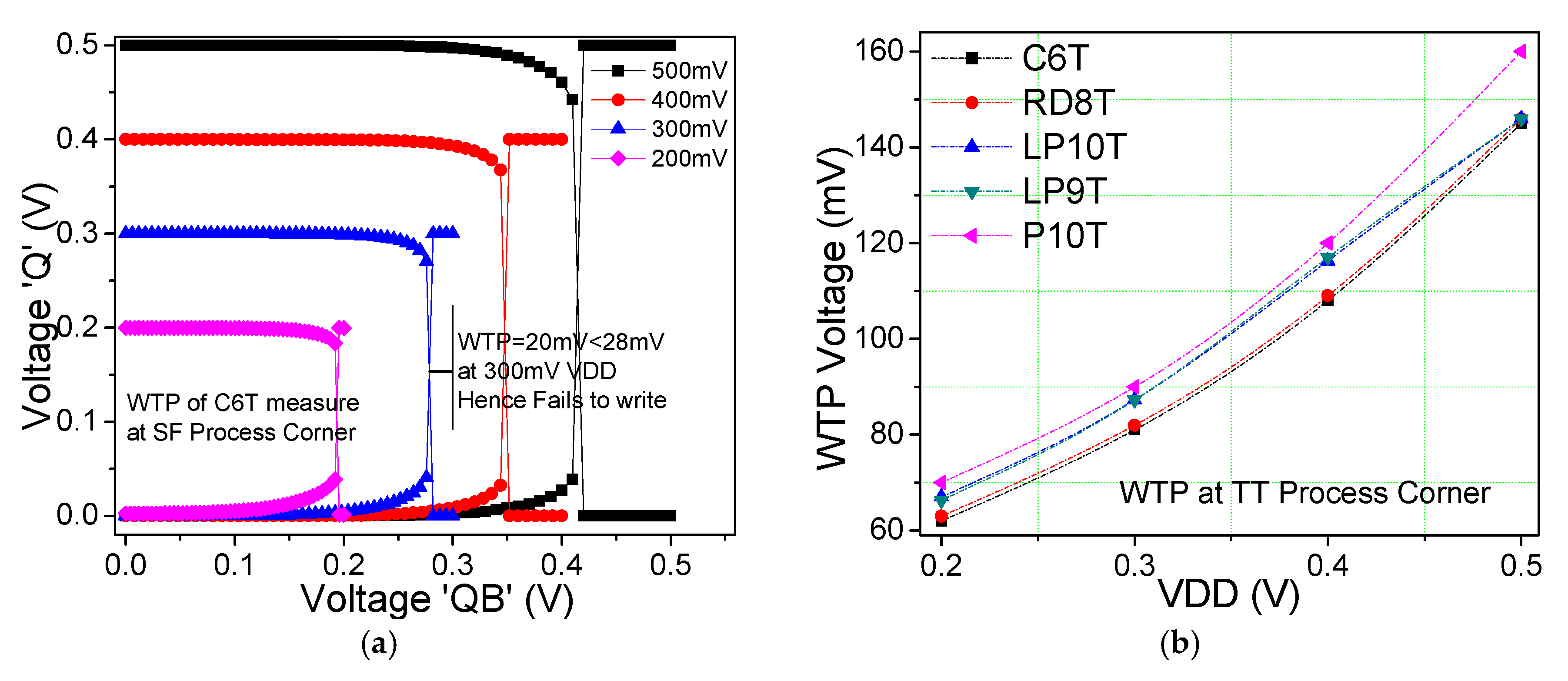
6.6. WSNM and Write Trip Point (WTP)
6.7. Comparison to FinFET-Based SRAM
6.8. Inter- and Intra-Die Variations
7. Summary of Results
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klinefelter, A.; Roberts, N.E.; Shakhsheer, Y.; Gonzalez, P.; Shrivastava, A.; Roy, A.; Craig, K.; Faisal, M.; Boley, J.; Oh, S.; et al. 21.3 a 6.45 µw self powered IoT SoC with integrated energy-harvesting power management and ULP asymmetric radios. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Shakhsheer, Y.; Silver, J.D.; Klinefelter, A.; Nagaraju, M.; Boley, J.; Pandey, J.; Shrivastava, A.; Carlson, E.J.; et al. A battery less 19 µw MICS/ISM-Band energy harvesting body sensor node SoC for ExG applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoun, B.H.; Wang, A.; Chandrakasan, A. Modeling and sizing for minimum energy operation in subthreshold circuits. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2005, 40, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.N.; Yahya, F.B.; Calhoun, B.H. Optimizing SRAM bit-cell reliability and energy for IoT applications. In Proceedings of the 17th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 14–16 March 2016; pp. 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, G.; Gattani, A. Memory Plays a Vital Role in Building the Connected World; Electronic Design: Hong Kong, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kursun, V.; Friedman, E.G. Multi-Voltage CMOS Circuit Design; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, K.; Prasad, S.C. Low-Power CMOS VLSI Circuit Design; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, J.P.; Roy, K. Ultralow-voltage process-variation-tolerant schmitt-trigger-based SRAM design. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2012, 20, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, S.A.; Kursun, V. Low power and robust 7t dual-v t SRAM circuit. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–21 May 2008; pp. 1452–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, M.-F.; Wu, J.-J.; Chen, K.-T.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lee, R.; Liao, H.J.; Yamauchi, H. A differential data-aware power-supplied 8T SRAM cell with expanded write/read stabilities for lower VDDmin applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Islam, A. Variation tolerant differential 8t SRAM cell for ultralow power applications. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2016, 35, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Islam, A. 9-t SRAM cell for reliable ultralow-power applications and solving Multibit soft-error issue. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2016, 16, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Hasan, M. Leakage characterization of 10T SRAM cell. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2012, 59, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reniwal, B.S.; Singh, P.; Vijayvargiya, V.; Vishvakarma, S.K. A new sense amplifier design with improved input referred offset characteristics for energy-efficient SRAM. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE International Conference on Embedded Systems and VLSI Design, Hyderabad, India, 7–11 January 2017; pp. 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Reniwal, B.S.; Vijayvargiya, V.; Singh, P.; Vishvakarma, S.K.; Dwivedi, D. Dataline Isolated Differential Current Feed/Mode Sense Amplifier for Small Icell SRAM Using FinFET. In Proceedings of the 25th Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI (GLSVLSI), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 20–22 May 2015; pp. 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Reniwal, B.S.; Bhatia, P.; Vishvakarma, S.K. Design and investigation of variability aware sense amplifier for low power, high speed SRAM. Microelectron. J. 2017, 59, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, J.P.; Kim, K.; Park, S.P.; Roy, K. Process variation tolerant SRAM array for ultra low voltage applications. In Proceedings of the 45th IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 8–13 June 2008; pp. 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Raychowdhury, A.; Roy, K. Accurate estimation of total leakage current in scaled CMOS logic circuits based on compact current modeling. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Design Automation Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 2–6 June 2003; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Cao, Y.; Markovic, D.; Vladimirescu, A.; Rabaey, J. SRAM leakage suppression by minimizing standby supply voltage. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design, San Jose, CA, USA, 22–24 March 2004; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Nalam, S.; Calhoun, B.H. Analyzing static and dynamic write margin for nanometer SRAMs. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Low Power Electronics & Design, Bangalore, India, 11–13 August 2008; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Balasubramanian, S.; Zlatanovici, R.; King, T.; Nikolic, B. FinFET-based SRAM design. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–10 August 2005; pp. 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Jeong, H.; Song, S.C.; Wang, J.; Yeap, G.; Jung, S.O. Single Bit-Line 7T SRAM Cell for Near-Threshold Voltage Operation with Enhanced Performance and Energy in 14 nm FinFET Technology. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2016, 63, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Agarwal, A.; Chen, Q.; Roy, K. SRAMs in Scaled Technologies under Process Variations: Failure Mechanisms, Test & Variation Tolerant Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 10–13 September 2006; pp. 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kim, K.; Mahmoodi, H.; Roy, K. Design of a Process Variation Tolerant Self-Repairing SRAM for Yield Enhancement in Nanoscaled CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
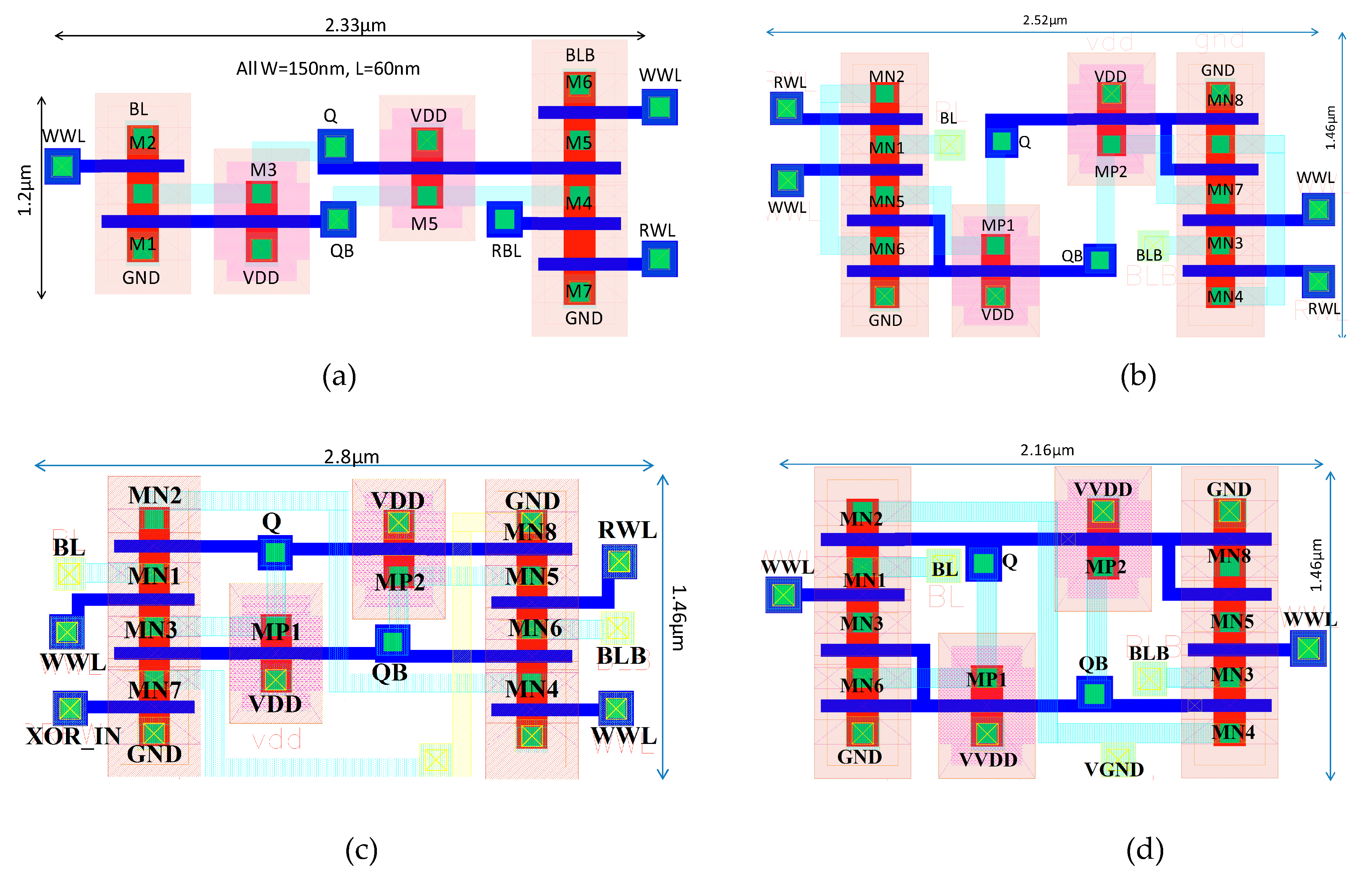
| SRAM | Numbers of MOS Transistors Used | Layout Area [Width (W) × Height (H)] |
|---|---|---|
| C6T | 6 (2 LVT/HVT/RVT p-MOS, 4 LVT/HVT/RVT n-MOS) | 1 × (2.33 µm × 1 µm = 2.33 µm2) |
| RD8T | 8 (2 LVT/HVT/RVT p-MOS, 6 LVT/HVT/RVT n-MOS) | 1.2 × (2.33 µm × 1.2 µm = 2.8 µm2) |
| ST10T [8] | 10 (2 LVT/HVT/RVT p-MOS, 8 LVT/HVT/RVT n-MOS) | 1.58 × (2.52 µm × 1.46 µm = 3.68 µm2) |
| LP10T [13] | 10 (2 LVT/HVT/RVT p-MOS, 8 LVT/HVT/RVT n-MOS) | 1.71 × (2.8 µm × 1.46 µm = 4 µm2) |
| PT10T | 10 (2 LVT/HVT/RVT p-MOS, 8 LVT/HVT/RVT n-MOS) | 1.35 × (2.16 µm × 1.46 µm = 3.15 µm2) |
| Operation | WWL | RWL | BL | BLB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Write 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Write 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Read 1 | 0 | 1 | Discharging | 1 |
| Read 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Discharging |
| Hold | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| SRAM | Cell Layout Area [Width (W) × Height (H)] | 8-Kb (Kilo-Bit) Layout Area Using 2 Metal-1 Poly Layer Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| C6T | 2.33 µm2 | 18.75 mm2 (1×) |
| RD8T | 2.8 µm2 | 22.63 mm2 (1.2×) |
| ST10T [8,17] | 3.68 µm2 | 29.60 mm2 (1.58×) |
| LP10T [13] | 4.0 µm2 | 32.17 mm2 (1.71×) |
| PT10T | 3.15 µm2 | 25.34 mm2 (1.35×) |
| Merits SRAM | Write Access Time | Read Access Time | Leakage Power | Write Energy | Read Energy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FinFET-C6T (14 nm) | 0.25 ns | 31.4 ns | 1.16 µW | 231.8 fJ | 301.6 fJ |
| FinFET-RD8T (14 nm) | 0.19 ns | 48.3 ns | 1.52 µW | 281.7 fJ | 190 fJ |
| FinFET-ST10T (14 nm) | 0.23 ns | 44.9 ns | 1.32 µW | 316.3 fJ | 293 fJ |
| Bulk CMOS-PT10T (65 nm) | 116.3 ns | 1000 ns | 0.084 µW | 160 fJ | 22 fJ |
| SRAM Merits | WSNM (mV) | RSNM (mV) | RDNM (mV) | WTP (mV) | Worst Case (All Cells Are in Holding State) Leakage Power | Write ‘1’ Energy (pJ) | Read Energy (fJ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6T | 20 | 36 | 220 | 81 | 6.8 µW | 0.16 | 23 |
| RD8T | 32 | 72.3 | 299.5 | 82 | 6.3 µW | 0.16 | 25 |
| LP9T [12] | 20 | 72.3 | 295 | 87.3 | 90 nW | 0.17 | 23.5 |
| LP10T [13] | 30 | 72.3 | 299 | 87.25 | 81 nW | 0.163 | 23 |
| ST10T [17] | 35 | 103 | 268 | 82 | 4.66 µW | 0.17 | 22.2 |
| PT10T | 40 | 107 | 290 | 90 | 84 nW | 0.16 | 22 |
| SRAM | C6T | C8T | ST10T [8,17] | LP10T [13] | PT10T | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Merits | RVT | HVT | LVT | RVT | HVT | LVT | RVT | HVT | LVT | RVT | HVT | LVT | RVT | HVT | LVT | |
| Write 1 Delay (ns) SS PC | 683 | 11,840 | 99.43 | 687 | 12,600 | 104 | 786 | 11,500 | 110 | 770 | 13,300 | 107 | 1300 | 13,500 | 116.3 | |
| Write 1 Power (pW) SS PC | 124 | 12.56 | 1.6 | 130 | 12.34 | 1.6 | 122 | 14 | 1.5 | 146 | 13 | 1.52 | 70 best | 10 best | 1.5 best | |
| Write 1 Energy (pJ) SS PC | 0.85 | 1.48 | 0.16 | 0.89 | 1.55 | 0.16 | 0.96 | 1.61 | 0.17 | 1.12 worst | 1.73 worst | 0.163 worst | 0.78 best | 1.35 best | 0.16 same | |
| Read Delay SS PC (µs) | 138 | 4000 | 2.3 | 174 | 5000 | 3 | 130 | 4000 | 2.3 | 50 | 1620 | 1 | 53 | 1650 | 1 | |
| Read Power SS PC (pW) | 150 | 5.23 | 10,000 | 144 | 5.12 | 8330 | 151 | 5.22 | 9660 | 405 worst | 13 worst | 23,000 worst | 390 | 12.7 | 22,000 | |
| Read Energy SS PC (fJ) | 20.7 | 20.9 | 23 | 25 | 25.6 | 25 | 19.6 | 21 | 22.2 | 20.2 | 21 | 23 | 20.6 | 20.9 best | 22 best | |
| Leakage Power (nW) | 752 | 72 | 6800 | 640 | 64 | 6288 | 552 | 46.4 | 4660 | 64 | 8 | 80 | 80 | 20 | 84 | |
| RSNM (mV) FS PC | 10 | 21.5 | 36 | 100 | 80 | 72 | 97 | 78 | 103 | 87 | 68 | 72 | 103 best | 83 best | 107 best | |
| WSNM (mV) SF PC | 20 | Fails | 20 | 28 | Fails | 30 | 33 | Fails | 35 | 30 | 33 | 30 | 40 best | 30 | 40 best | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, P.; Vishvakarma, S.K. Ultra-Low Power, Process-Tolerant 10T (PT10T) SRAM with Improved Read/Write Ability for Internet of Things (IoT) Applications. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2017, 7, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea7030024
Singh P, Vishvakarma SK. Ultra-Low Power, Process-Tolerant 10T (PT10T) SRAM with Improved Read/Write Ability for Internet of Things (IoT) Applications. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications. 2017; 7(3):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea7030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Pooran, and Santosh Kumar Vishvakarma. 2017. "Ultra-Low Power, Process-Tolerant 10T (PT10T) SRAM with Improved Read/Write Ability for Internet of Things (IoT) Applications" Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications 7, no. 3: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea7030024
APA StyleSingh, P., & Vishvakarma, S. K. (2017). Ultra-Low Power, Process-Tolerant 10T (PT10T) SRAM with Improved Read/Write Ability for Internet of Things (IoT) Applications. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications, 7(3), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea7030024