mTanh: A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Vanishing Gradient Tolerant Activation Function †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Inkjet-Printing Technology
- 1.
- pattern design—creating the desired pattern using an editing tool;
- 2.
- printing—using an inkjet printer to deposit the ink onto the substrate;
- 3.
- curing—solidifying or treating the printed element to ensure stability.
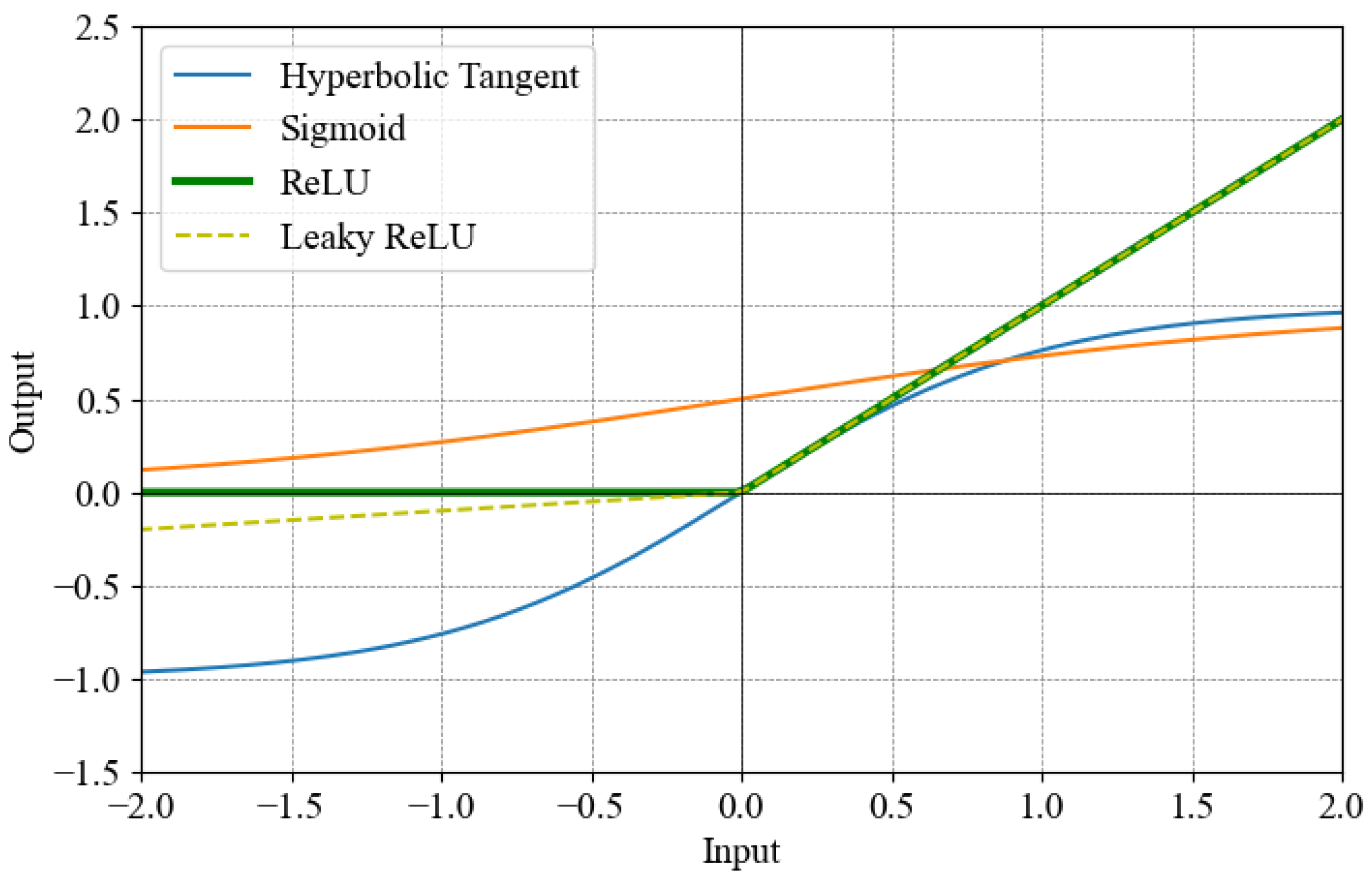
2.2. Activation Function
2.3. Vanishing Gradient Problem
3. Inkjet-Printed Activation Function
3.1. System Architecture
3.2. Fabrication Process
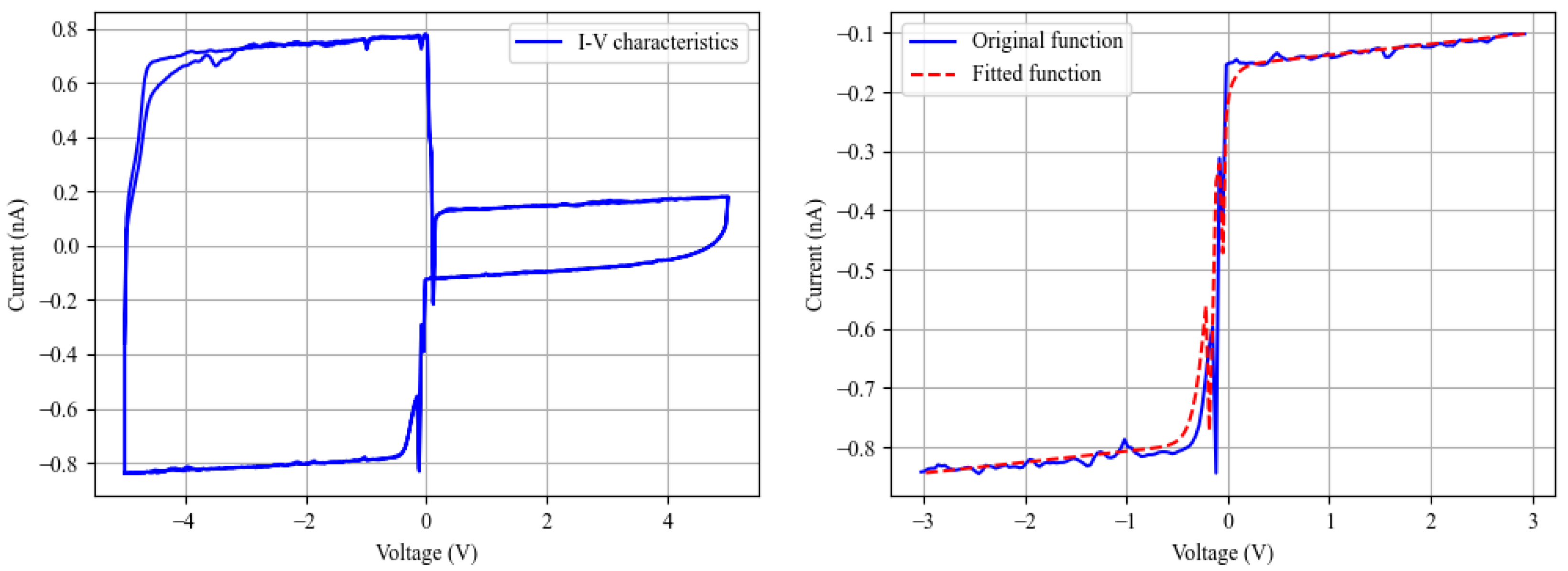
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Curve Fitting
4. Experiment with Neural Networks
4.1. Neural Network Feasibility Study
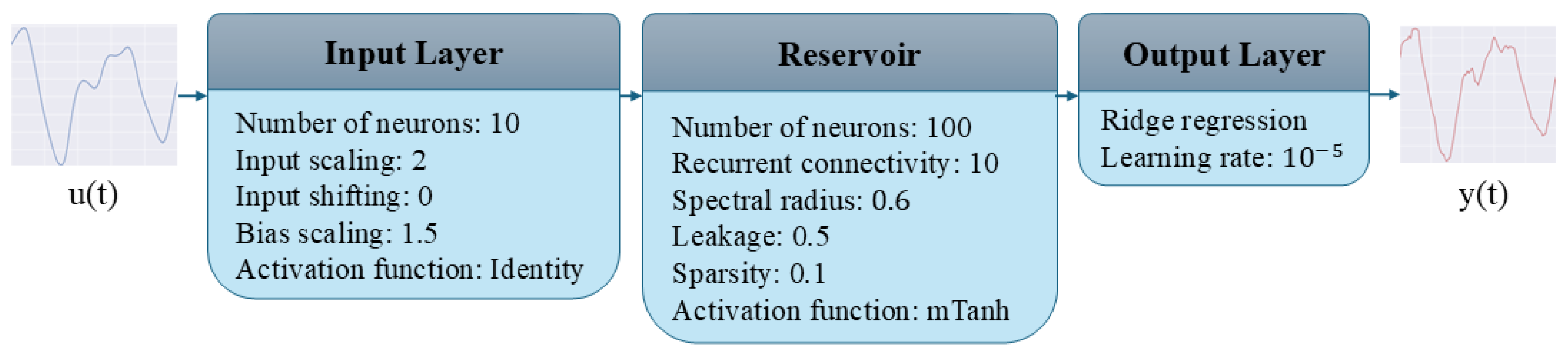
4.1.1. Echo State Network
4.1.2. Hyperparameter Optimization
4.1.3. Dataset
4.2. Vanishing Gradient Resistance
4.2.1. Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP)
4.2.2. Dataset
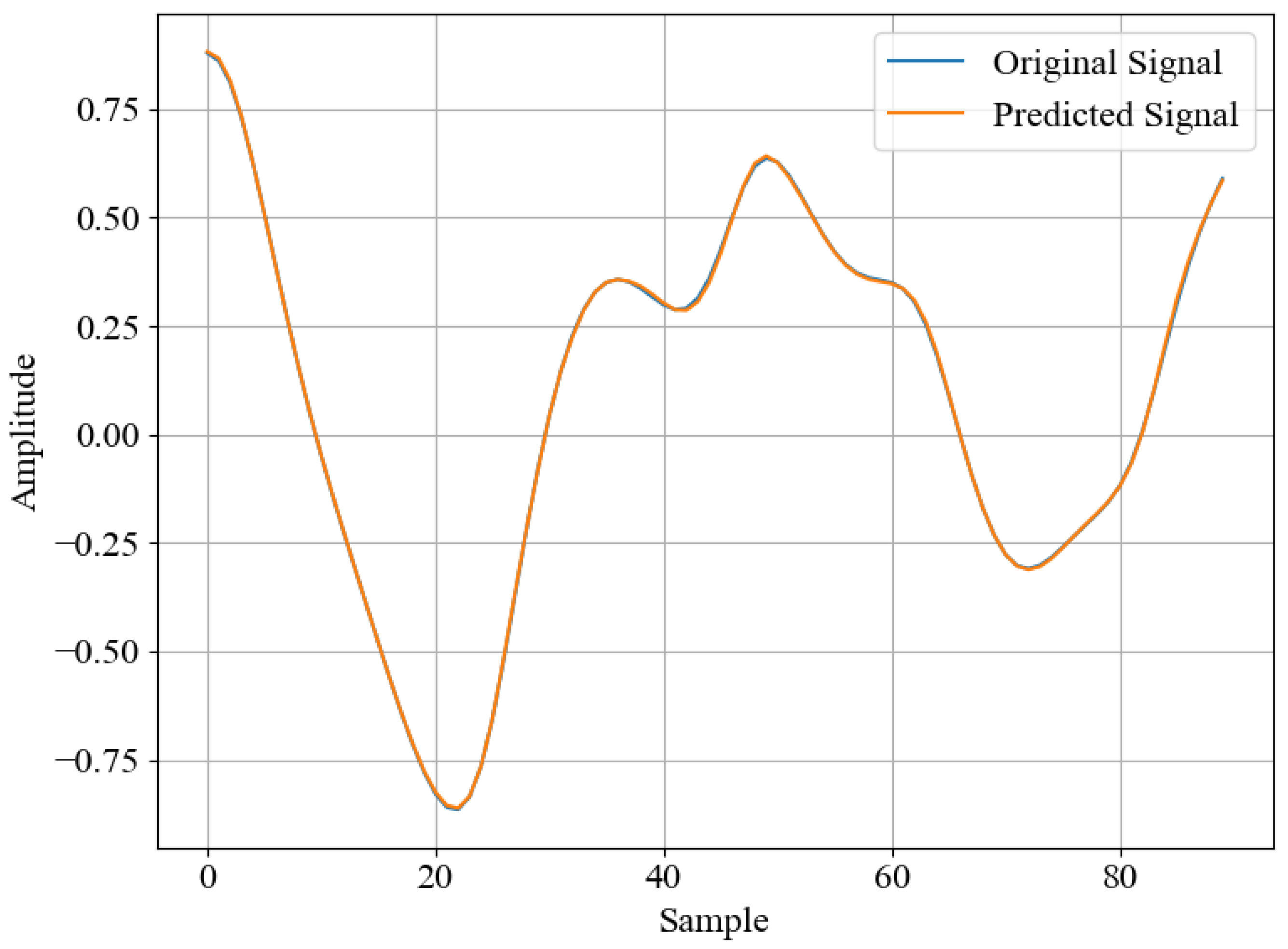
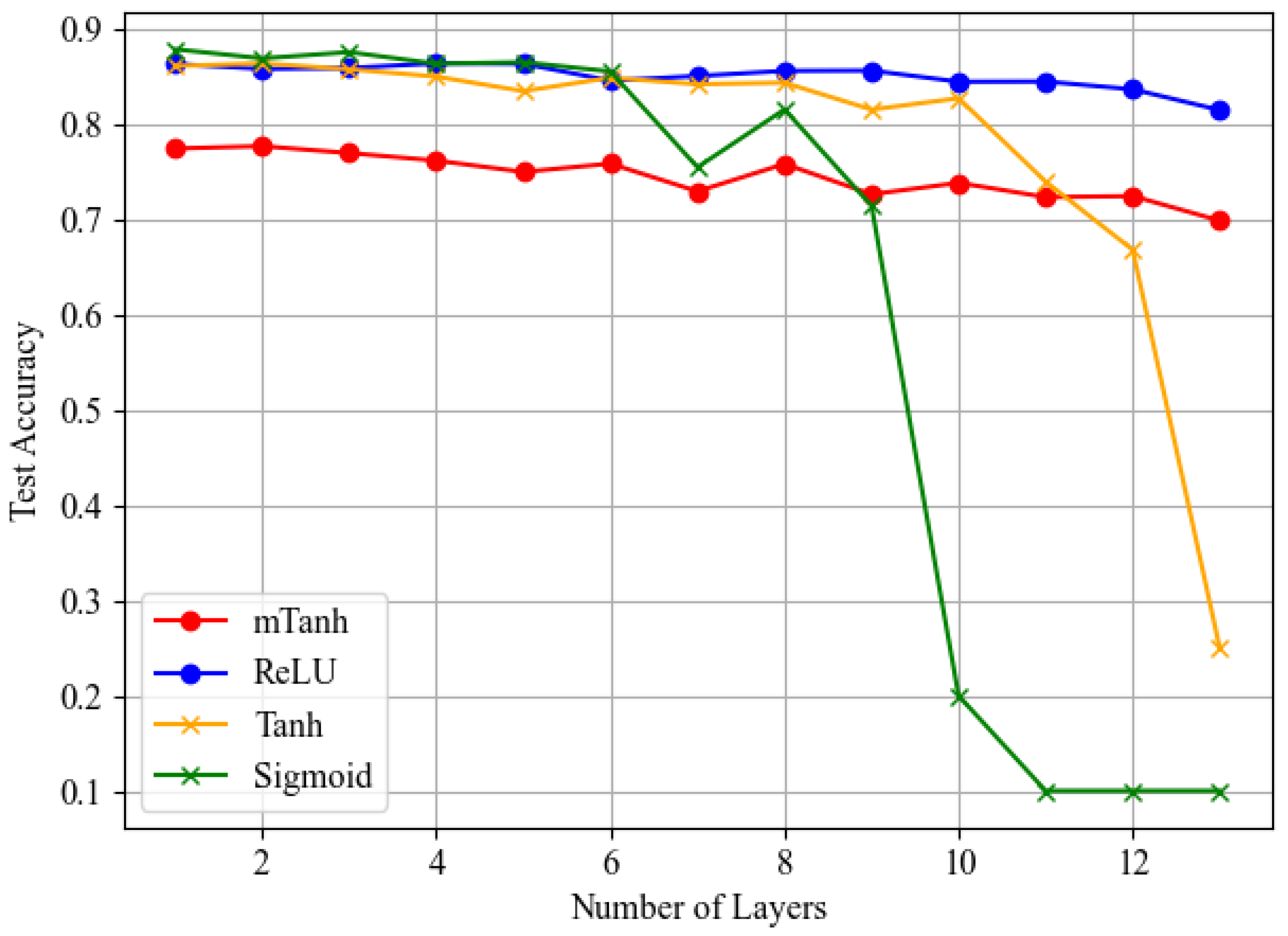
5. Results and Discussion
- n is the total number of data points;
- represents the actual observed value;
- represents the predicted value.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VGP | Vanishing Gradient Problem |
| MLP | Multi Layer Perceptron |
| ESN | Echo State Network |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| hBN | Hexagonal Boron Nitride |
| PET | Polyethylene Terephthalate |
| IJP | Inkjet-Printed |
References
- IEEE. Executive Summary. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Roadmap for Devices and Systems; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Jia, A.B.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, S.X. Emerging Electrochromic Materials and Devices for Future Displays. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 14679–14721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, A.K.; Hoang, A.T.; Xu, D.; Hong, J.; Kim, B.J.; Ji, S.; Ahn, J.H. 2D Materials in Flexible Electronics: Recent Advances and Future Prospectives. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 318–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Feng, B.; Huo, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, W.; Peng, J.; Li, Z.; Du, C.; Wang, W.; Zou, G.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Meets Flexible Sensors: Emerging Smart Flexible Sensing Systems Driven by Machine Learning and Artificial Synapses. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, S.G. Inkjet Printing Next-Generation Flexible Devices: Memristors, Photodetectors and Perovskite LEDs. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de Barcelona, Departament d’Enginyeria Electrònica i Biomèdica, Barcelona, Spain, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dankoco, M.; Tesfay, G.; Bènevent, E.; Bendahan, M. Temperature sensor realized by inkjet printing process on flexible substrate. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2016, 205, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.T.; Huang, K.Y.; Lin, D.T.; Liao, W.C.; Lin, H.W.; Hu, Y.C. A flexible proximity sensor fully fabricated by inkjet printing. Sensors 2010, 10, 5054–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Jung, M.; Kim, B.; Kim, J.; Shin, K.; Kwon, O.S.; Jeon, S. Low-voltage, high-sensitivity and high-reliability bimodal sensor array with fully inkjet-printed flexible conducting electrode for low power consumption electronic skin. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmaleki, H.; Haugen, A.B.; Merhi, Y.; Nygaard, J.V.; Agarwala, S. Inkjet-printed flexible piezoelectric sensor for self-powered biomedical monitoring. Mater. Today Electron. 2023, 5, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Haider, M.R. Impact Localization in Inkjet-Printed Tactile Grid Sensor with Echo State Network. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 67th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Springfield, MA, USA, 11–14 August 2024; pp. 1070–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Zhu, X.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Sun, D.; Gu, W. A grid-less flexible tactile sensing system based on deep neural network for two-point localization and shape recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 18259–18266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, R.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xia, J.; et al. Crack-across-pore enabled high-performance flexible pressure sensors for deep neural network enhanced sensing and human action recognition. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8358–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Islam, S.; Haider, M.; Opu, M.; Gardner, S.; Pullano, S. A Low-Cost Flexible Inkjet-Printed Echo State Network for Impact Localization. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 26–28 June 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, S.; Lai, S.; Cosseddu, P.; Bonfiglio, A. An Inkjet-Printed, Ultralow Voltage, Flexible Organic Field Effect Transistor. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1600212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Lopez, F.; Gao, T.Z.; Kraft, U.; Zhu, C.; Öhlund, T.; Pfattner, R.; Feig, V.R.; Kim, Y.; Wang, S.; Yun, Y.; et al. Inkjet-printed stretchable and low voltage synaptic transistor array. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubb, M.P.; Subbaraman, H.; Park, S.; Akinwande, D.; Chen, R.T. Inkjet Printing of High Performance Transistors with Micron Order Chemically Set Gaps. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adry, T.Z.; Akter, S.; Eliza, S.; Gardner, S.D.; Haider, M.R. An Inkjet-Printed Flexible Memristor Device for Echo State Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), Knoxville, TN, USA, 1–3 July 2024; pp. 740–744. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Vescio, G.; Gonzalez-Torres, S.; Lopez-Vidrier, J.; Frieiro, J.L.; Pazos, S.; Jing, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, S.D.; Ascorbe-Muruzabal, J.; et al. Inkjet-printed h-BN memristors for hardware security. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 9985–9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, M.; Kiazadeh, A.; Deuermeier, J.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Martins, R.; Carlos, E. Inkjet printed IGZO memristors with volatile and non-volatile switching. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.; Kiazadeh, A.; Martins, R.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Carlos, E. Printed Memristors: An Overview of Ink, Materials, Deposition Techniques, and Applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2024, 10, 2400212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Scholz, A.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Marques, G.C.; Aghassi-Hagmann, J. A Fully Inkjet-Printed Unipolar Metal Oxide Memristor for Nonvolatile Memory in Printed Electronics. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 2023, 70, 3051–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.D.; Haider, M.R. An inkjet-printed artificial neuron for physical reservoir computing. IEEE J. Flex. Electron. 2022, 1, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Haider, M.R. A Low-Cost Minimally-Processed Inkjet-Printed Nonlinear Element for Reservoir Computing. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), Knoxville, TN, USA, 1–3 July 2024; pp. 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S. The vanishing gradient problem during learning recurrent neural nets and problem solutions. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness -Knowl.-Based Syst. 1998, 6, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, G.; Song, D.; Carbonell, J.G. The exploding gradient problem demystified-definition, prevalence, impact, origin, tradeoffs, and solutions. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1712.05577v4. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.L.; Hannun, A.Y.; Ng, A.Y. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In Proceedings of the ICML, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–19 June 2013; Volume 30, p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Pascanu, R. Understanding the exploding gradient problem. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1211.5063. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; van Gelder, J.; van de Ven, B.; Amitonov, S.V.; De Wilde, B.; Ruiz Euler, H.C.; Broersma, H.; Bobbert, P.A.; Zwanenburg, F.A.; van der Wiel, W.G. Classification with a disordered dopant-atom network in silicon. Nature 2020, 577, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, H. The “echo state” approach to analysing and training recurrent neural networks-with an erratum note. Bonn Ger. Ger. Natl. Res. Cent. Inf. Technol. Gmd Tech. Rep. 2001, 148, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier, D.J.; Bollt, E.; Griffith, A.; Barbosa, W.A.S. Next generation reservoir computing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.W.; Brewer, G.A.; Lai, Y.C. Reservoir-computing based associative memory and itinerancy for complex dynamical attractors. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, L.; Peng, H. An image classification method based on Echo State Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Neuromorphic Computing (ICNC), Wuhan, China, 15–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Dong, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, P.; Gallicchio, C.; et al. Echo state graph neural networks with analogue random resistive memory arrays. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2023, 5, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yao, P.; Hao, Z.; Gao, B.; Qian, H.; et al. Memristor-based fully analog reservoir computing system for power-efficient real-time spatiotemporal signal processing. Nat. Electron. 2022, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, P.; Jalalvand, A.; Stone, S.; Birkholz, P. PyRCN: A toolbox for exploration and application of Reservoir Computing Networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 113, 104964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, L.; Mackey, M. Mackey-glass equation. Scholarpedia 2010, 5, 6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Hyper Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Loss | Categorical cross entropy |
| Learning rate | 0.005 |
| Batch size | 10 |
| Validation split | 0.2 |
| Activation Function | Score | Mean Squared Error |
|---|---|---|
| ReLU | 0.993 | |
| Leaky ReLU | 0.995 | |
| Tanh | 0.989 | |
| mTanh | 0.986 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akter, S.; Haider, M.R. mTanh: A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Vanishing Gradient Tolerant Activation Function. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2025, 15, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea15020027
Akter S, Haider MR. mTanh: A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Vanishing Gradient Tolerant Activation Function. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications. 2025; 15(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea15020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkter, Shahrin, and Mohammad Rafiqul Haider. 2025. "mTanh: A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Vanishing Gradient Tolerant Activation Function" Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications 15, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea15020027
APA StyleAkter, S., & Haider, M. R. (2025). mTanh: A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Vanishing Gradient Tolerant Activation Function. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications, 15(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea15020027








