0.5 V CMOS Inverter-Based Transconductance Amplifier with Quiescent Current Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
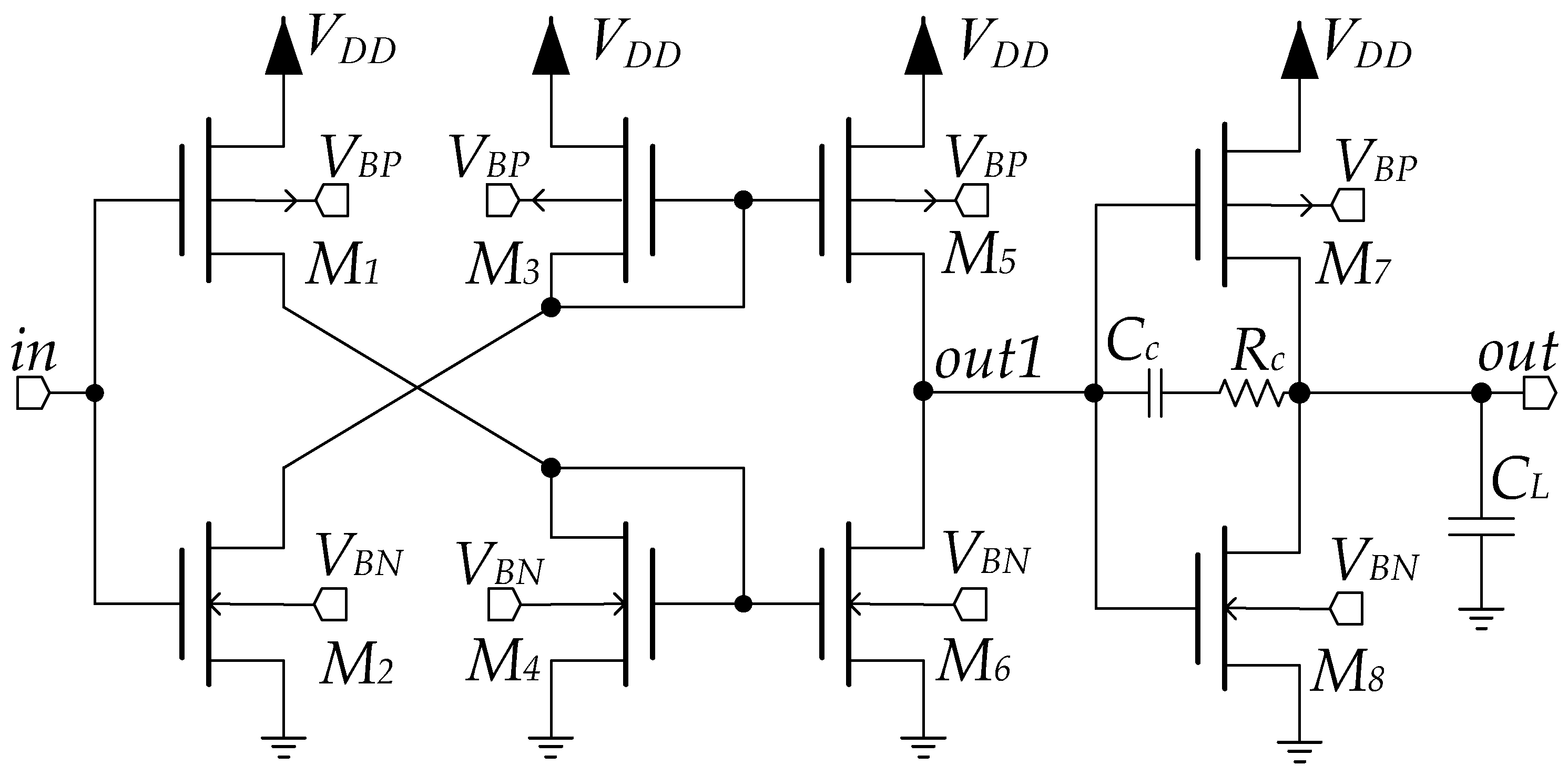
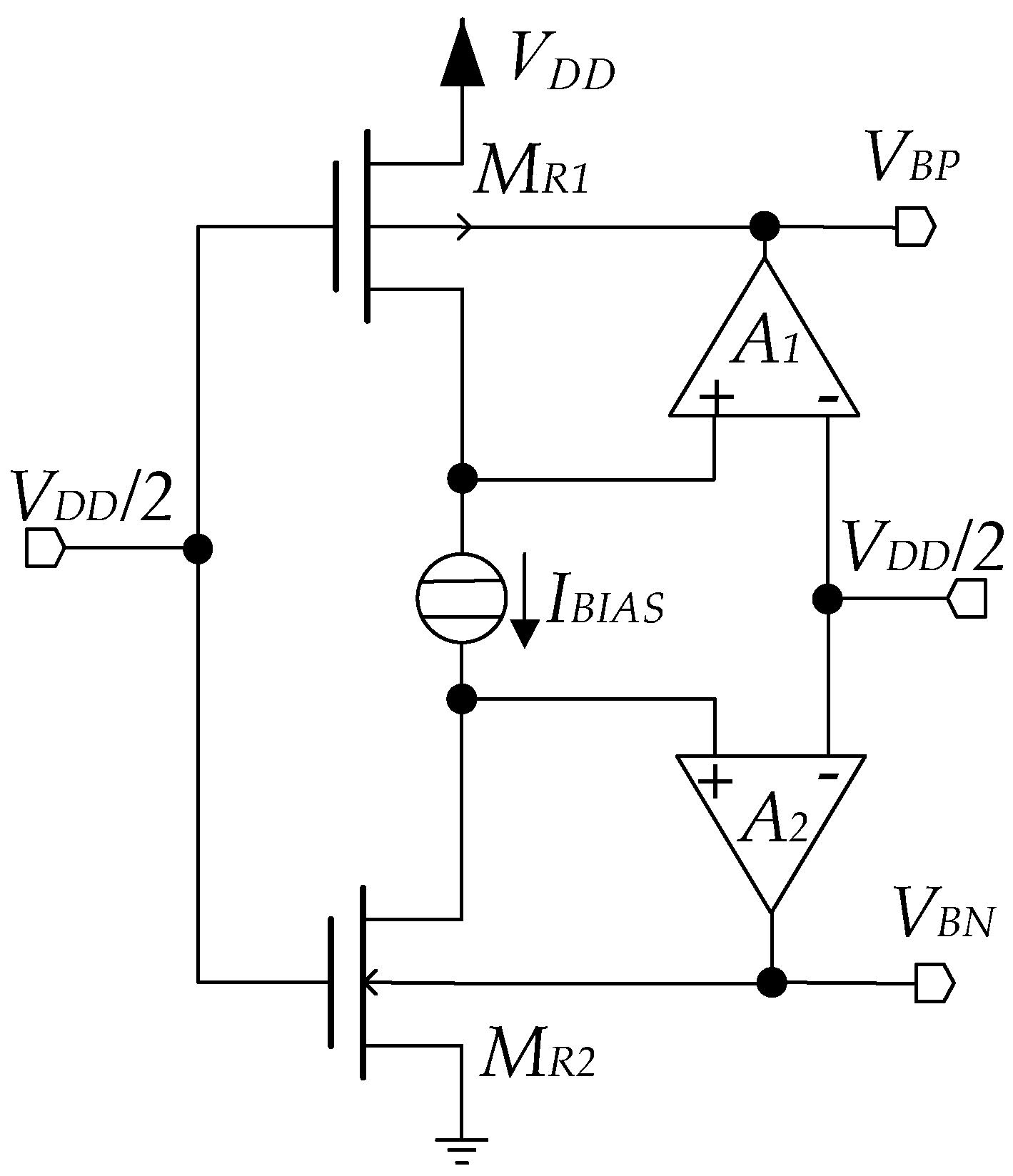
2. The Proposed Solution
- (a)
- assigned aspect ratios (W/L)R1 and (W/L)R2;
- (b)
- ID1,2 = kIBIAS, where k is the ratio of the transistors aspect ratio as in (1);
- (c)
- VSGR1 = VGSR2 = VDD/2;
- (d)
- VSDR1 = VDSR2 = VDD/2, assuming ideal input virtual short in A1 and A2.
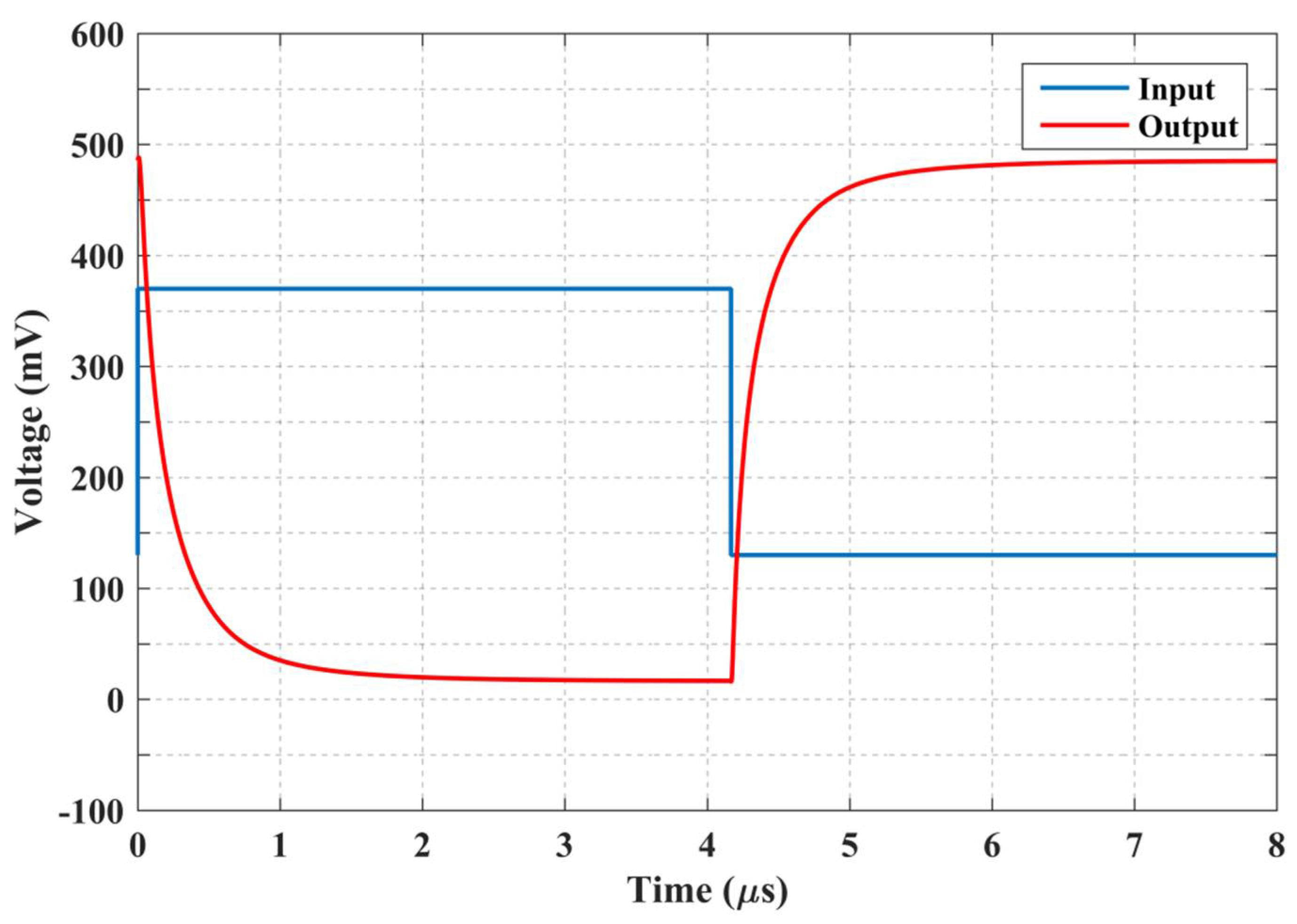
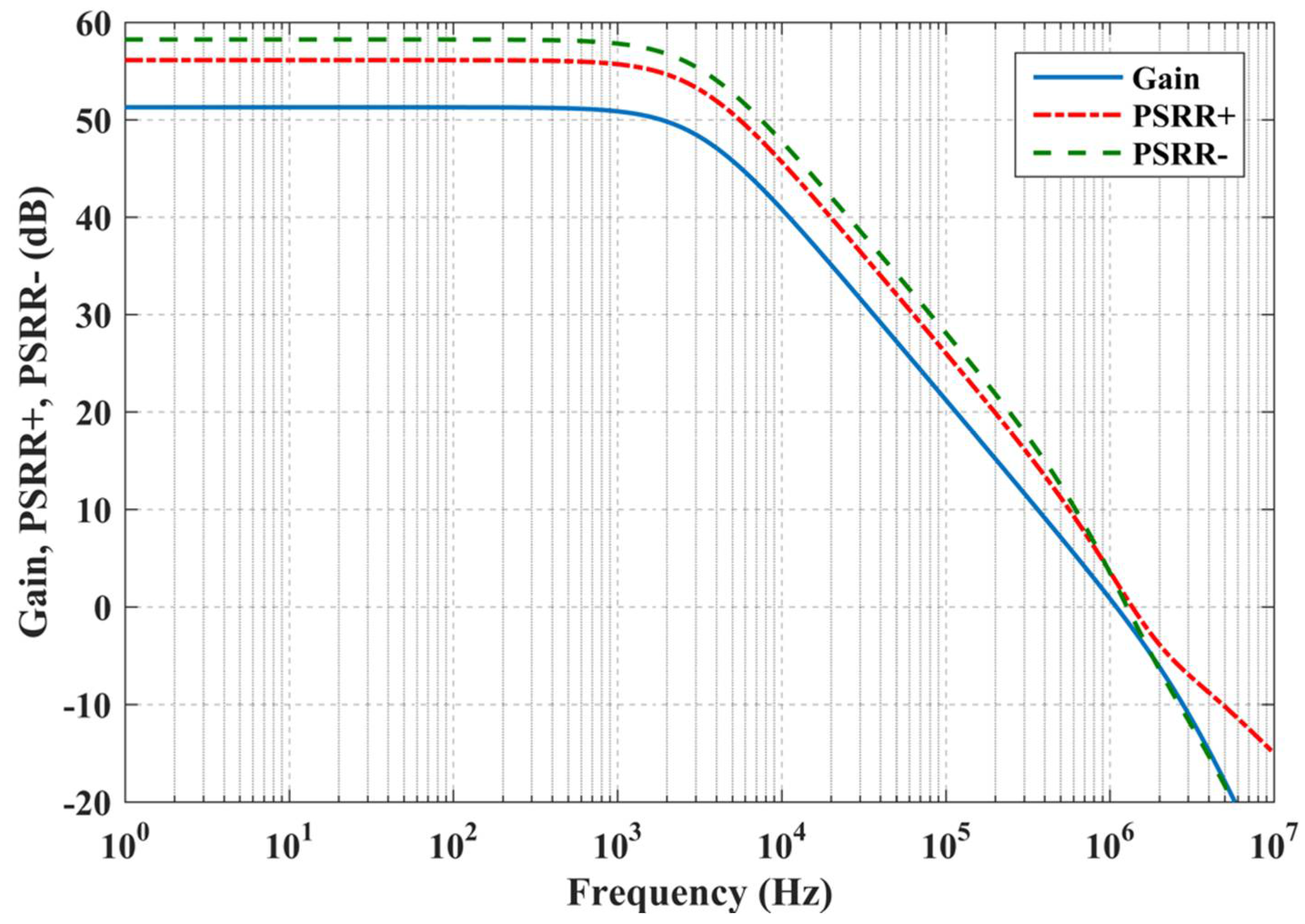
3. Validation Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vittoz, E.; Fellrath, J. CMOS analog integrated circuits based on weak inversion operations. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1977, 12, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.R.A.; Sahoo, B.D.; Dutta, A. A Wideband 2–5 GHz Noise Canceling Subthreshold Low Noise Amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 65, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Islam, S.K. Low-Voltage Bulk-Driven Operational Amplifier With Improved Transconductance. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 2084–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Hussein, S.M.; Hashim, Y.; Tang, K.-T. An Enhanced Input Differential Pair for Low-Voltage Bulk-Driven Amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2021, 29, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Lopez-Martin, A.; Carvajal, R.; Chavero, F. Very low-voltage analog signal processing based on quasi-floating gate transistors. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2004, 39, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, J.M.A.; Lopez-Martin, A.J.; Acosta, L.; Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Carvajal, R.G. Using Floating Gate and Quasi-Floating Gate Techniques for Rail-to-Rail Tunable CMOS Transconductor Design. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2011, 58, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.; Cassia, M. 1-V power supply CMOS cascode amplifier. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2001, 36, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Tsividis, Y.; Kinget, P. 0.5-V analog circuit techniques and their application in OTA and filter design. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2005, 40, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, J.; Duque-Carrillo, J.; Torelli, G.; Ausin, J. Constant-gm constant-slew-rate high-bandwidth low-voltage rail-to-rail CMOS input stage for VLSI cell libraries. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2003, 38, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, A.D.; Pennisi, S.; Scotti, G.; Trifiletti, A. 0.9-V Class-AB Miller OTA in 0.35-µm CMOS With Threshold-Lowered Non-Tailed Differential Pair. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 64, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Paik, D.; Lee, S.; Miyahara, M.; Matsuzawa, A. An Ultra-Low-Voltage 160 MS/s 7 Bit Interpolated Pipeline ADC Using Dynamic Amplifiers. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Flynn, M.P. A 100 MS/s, 10.5 Bit, 2.46 mW Comparator-Less Pipeline ADC Using Self-Biased Ring Amplifiers. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chandrakasan, A.P.; Lee, H.S. A 12 b 5-to-50 MS/s 0.5-to-1 V Voltage Scalable Zero-Crossing Based Pipelined ADC. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.; Steyaert, M.S.J. A 250 mV 7.5 W 61 dB SNDR SC ∆Σ Modulator Using Near-Threshold-Voltage-Biased Inverter Amplifiers in 130 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaul, F.M.; Chandrakasan, A.P. A Noise-Efficient 36 nV/Hz Chopper Amplifier Using an Inverter-Based 0.2-V Supply Input Stage. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 3032–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ytterdal, T. A 54-µW Inverter-Based Low-Noise Single-Ended to Differential VGA for Second Harmonic Ultrasound Probes in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2016, 63, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.A.; Xu, Y.P. A Low-Power, High CMRR Neural Amplifier System Employing CMOS Inverter-Based OTAs With CMFB Through Supply Rails. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 724–737. [Google Scholar]
- Crovetti, P.S. A Digital-Based Virtual Voltage Reference. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2015, 62, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, O.; Crovetti, P.S.; Alioto, M. Fully Synthesizable Low-Area Digital-to-Analog Converter With Graceful Degradation and Dynamic Power-Resolution Scaling. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 2865–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Mostafa, I. A Process-Tolerant, Low-Voltage, Inverter-Based OTA for Continuous-Time Σ∆ ADC. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2016, 24, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J. An Inverter-Based Continuous Time Sigma Delta ADC With Latency-Free DAC Calibration. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2020, 67, 3630–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, P.; Crovetti, P.; Klimach, H.; Bampi, S.; Aiello, O.; Alioto, M. 300 mV-Supply, sub-nW-Power Digital-Based Operational Transconductance Amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rodovalho, L.H.; Aiello, O.; Rodrigues, C.R. Ultra-Low-Voltage Inverter-Based Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Voltage Gain Enhancement by Improved Composite Transistors. Electronics 2020, 9, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodovalho, L.H.; Ramos Rodrigues, C.; Aiello, O. Self-Biased and Supply-Voltage Scalable Inverter-Based Operational Transconductance Amplifier with Improved Composite Transistors. Electronics 2021, 10, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W. CMOS inverter as analog circuit: An overview. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2019, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palani, R.K.; Harjani, R. Inverter-Based Circuit Design Techniques for Low Supply Voltages; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K. An Inverter-Based Analog Front-End for a 56-Gb/s PAM-4 Wireline Transceiver in 16-nm CMOS. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Lett. 2018, 12, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qiao, Z.; Li, Q. Inverter-Based Subthreshold Amplifier Techniques and Their Application in 0.3-V ∆Σ-Modulators. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Monsurró, P.; Scotti, G.; Trifiletti, A.; Pennisi, S. Biasing technique via bulk terminal for minimum supply CMOS amplifiers. Electron. Lett. 2005, 41, 779–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsurró, P.; Pennisi, S.; Scotti, G.; Trifiletti, A. Exploiting the Body of MOS Devices for High Performance Analog Design. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2011, 11, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| VDD | 0.5 V |
| IBIAS | 60 nA |
| (W/L)R1, (W/L)1, (W/L)3, (W/L)5 | 990/90 nm/nm |
| (W/L)R2, (W/L)2, (W/L)4, (W/L)6 | 210/90 nm/nm |
| (W/L)7 | 4 × (990/90) nm/nm |
| (W/L)8 | 4 × (210/90) nm/nm |
| RC, CC | 50 kΩ, 1.5 pF |
| A1, A2 | 40 dB |
| CL//RL | 1 pF//1.5 MΩ |
| VDD | 0.5 V |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| gm1 | 3.55 μA/V |
| rO1 | 7.7 MΩ |
| gm2 | 18.12 μA/V |
| rO2 | 1.47 MΩ |
| Parameter | μ | σ | σ/μ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vout (mV) | 250.1 | 11.8 | 4.7% |
| IDD (nA) | 488.1 | 93.7 | 19.2% |
| DC Gain (dB) | 51.3 | 0.56 | 1.1% |
| UGF (MHz) | 1.13 | 0.34 | 30.1% |
| PM (degrees) | 68.9 | 5.2 | 7.5% |
| PSRR+ (dB) | 56.1 | 0.56 | 1% |
| PSRR- (dB) | 58.2 | 0.56 | 0.9% |
| 1% Ts+/Ts- (ns) 1 | 522/348 | 206/135 | 39.5/38.8% |
| Corner T = −20 °C | TT | FF | FS | SF | SS |
| Vout (mV) | 244.4 | 248.6 | 229.7 | 264.7 | 249.3 |
| IDD (nA) | 256 | 475 | 243 | 227 | 104 |
| DC Gain (dB) | 49.8 | 52 | 50 | 50.4 | 47.4 |
| UGF (MHz) | 0.67 | 1.58 | 0.63 | 0.59 | 0.22 |
| PM (degrees) | 69.2 | 64.6 | 69 | 69.9 | 76.9 |
| PSRR+ (dB) | 54.4 | 56.7 | 54.7 | 55.2 | 52 |
| PSRR- (dB) | 56.9 | 58.9 | 57.1 | 57.4 | 54.7 |
| 1% Ts+/Ts- (ns) | 685/438 | 272/182 | 566/337 | 854/336 | 2632/880 |
| Corner T = 27 °C | TT | FF | FS | SF | SS |
| Vout (mV) | 249.9 | 244.5 | 249.3 | 249.9 | 250 |
| IDD (nA) | 488 | 579 | 505 | 479 | 485 |
| DC Gain (dB) | 51.3 | 51.7 | 52.1 | 50.4 | 51 |
| UGF (MHz) | 1.09 | 1.68 | 1.13 | 1.08 | 0.88 |
| PM (degrees) | 69.2 | 64.3 | 69.5 | 69 | 73.1 |
| PSRR+ (dB) | 56.1 | 56.7 | 56.9 | 55.2 | 55.7 |
| PSRR- (dB) | 58.2 | 58.5 | 59.8 | 58.9 | 58.3 |
| 1% Ts+/Ts- (ns) | 520/319 | 240/207 | 506/322 | 519/321 | 719/490 |
| Corner T = 80 °C | TT | FF | FS | SF | SS |
| Vout (mV) | 255.8 | 249.1 | 233.9 | 277.1 | 259.8 |
| IDD (nA) | 1177 | 2417 | 1338 | 1061 | 621 |
| DC Gain (dB) | 52.6 | 53 | 53 | 52.1 | 51.5 |
| UGF (MHz) | 2.2 | 5.68 | 2.5 | 1.98 | 0.97 |
| PM (degrees) | 74.3 | 77.3 | 75.8 | 73.3 | 73.4 |
| PSRR+ (dB) | 57.4 | 57.7 | 57.9 | 56.7 | 56.3 |
| PSRR- (dB) | 59.4 | 59.7 | 59.8 | 58.9 | 58.4 |
| 1% Ts+/Ts- (ns) | 356/235 | 130/123 | 230/239 | 233/210 | 838/436 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ballo, A.; Pennisi, S.; Scotti, G. 0.5 V CMOS Inverter-Based Transconductance Amplifier with Quiescent Current Control. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2021, 11, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea11040037
Ballo A, Pennisi S, Scotti G. 0.5 V CMOS Inverter-Based Transconductance Amplifier with Quiescent Current Control. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications. 2021; 11(4):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea11040037
Chicago/Turabian StyleBallo, Andrea, Salvatore Pennisi, and Giuseppe Scotti. 2021. "0.5 V CMOS Inverter-Based Transconductance Amplifier with Quiescent Current Control" Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications 11, no. 4: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea11040037
APA StyleBallo, A., Pennisi, S., & Scotti, G. (2021). 0.5 V CMOS Inverter-Based Transconductance Amplifier with Quiescent Current Control. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications, 11(4), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea11040037








