Research on the Impact of Digital Innovation Ecosystem Niche Suitability for High-Quality Economic Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Analysis
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Theoretical Analysis
3. Variable Selection and Model Construction
3.1. Variable Selection
3.1.1. Independent Variable: Niche Suitability of DIES
3.1.2. Dependent Variable: High-Quality Economic Development
3.1.3. Control Variable
3.2. Model Construction
3.3. Data Source
4. Empirical Analyses
4.1. Niche Suitability Analysis of DIES
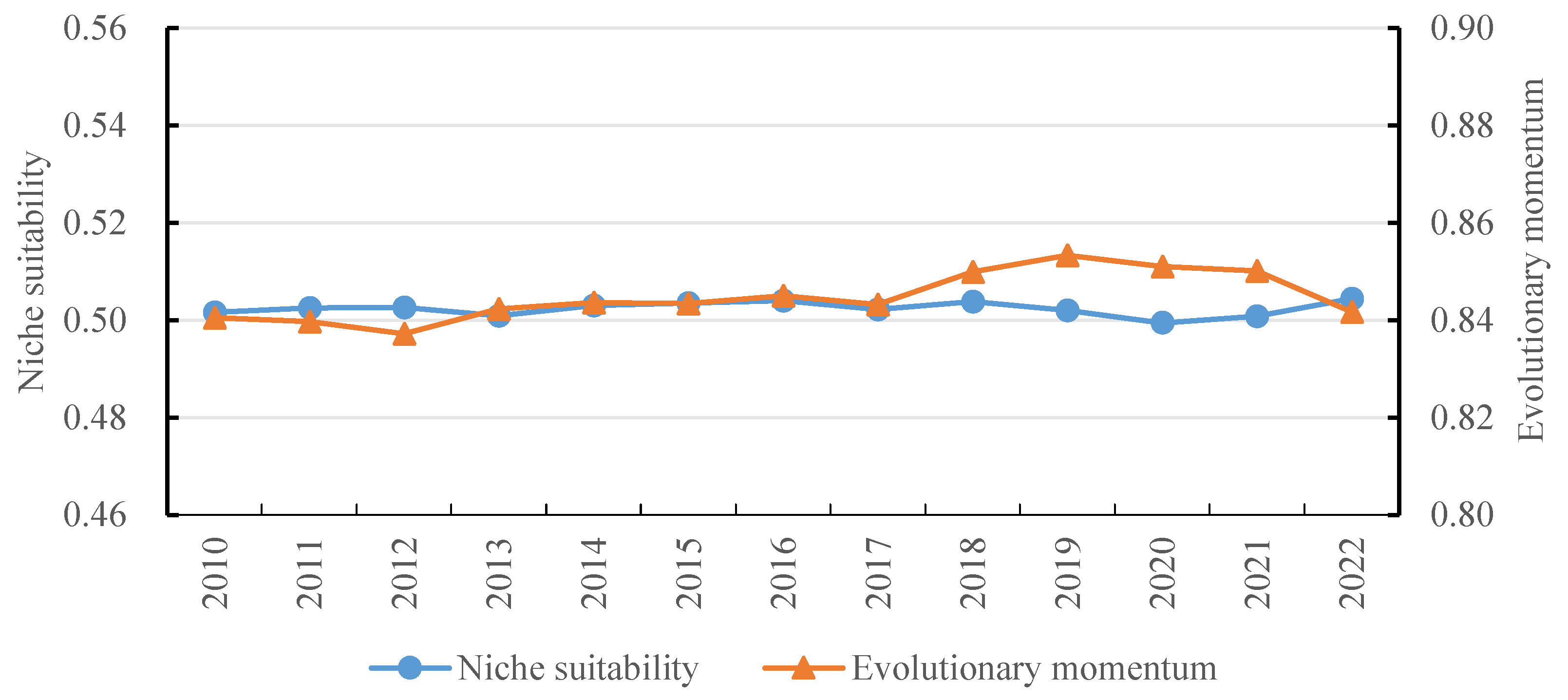
4.1.1. Overall Analysis of Niche Suitability on DIES
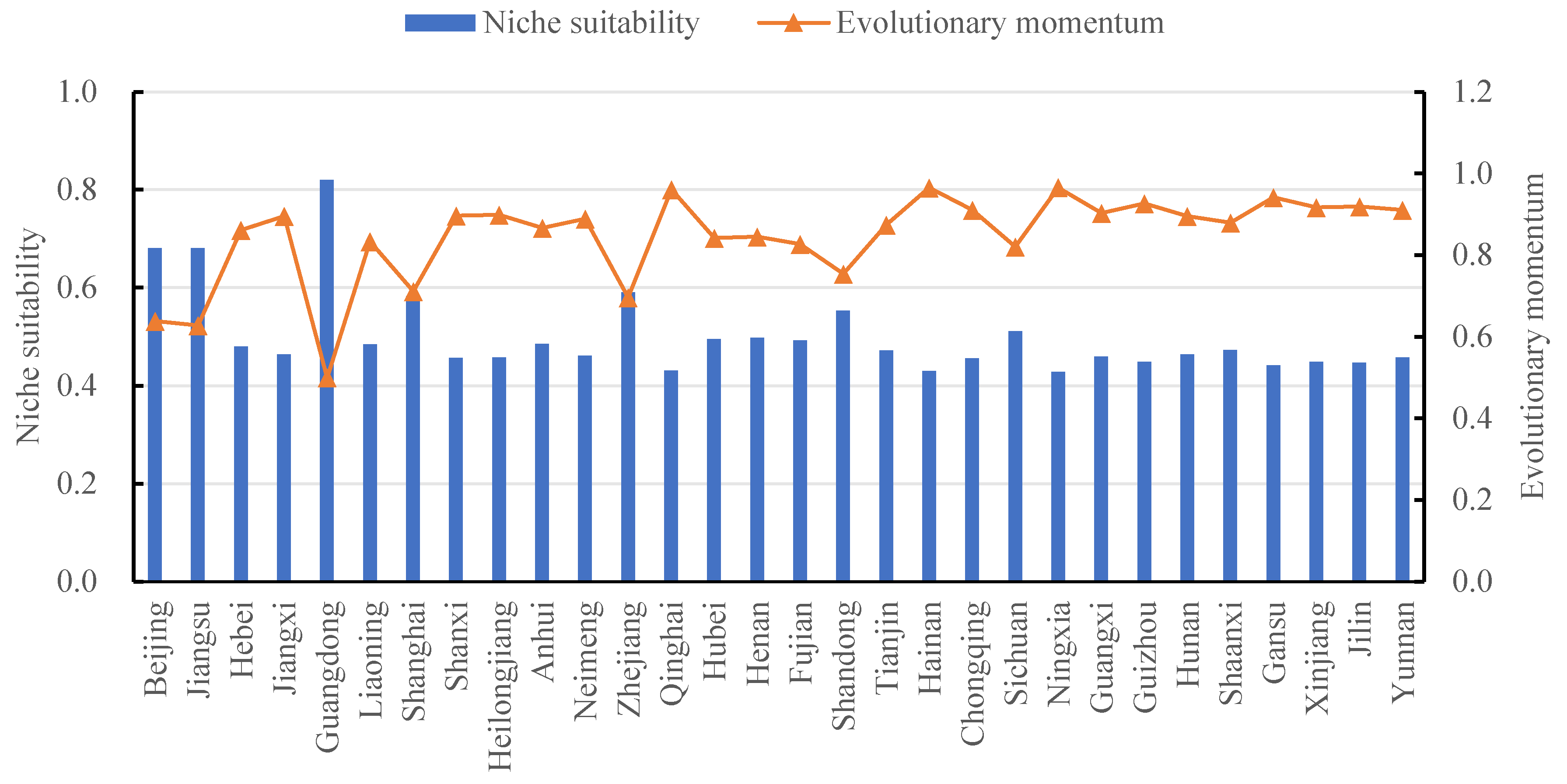
4.1.2. Analysis of Regional Difference in Niche Suitability of DIES
4.2. The Impact of DIES Niche Suitability on HQ Economic Development
4.2.1. Descriptive Statistics of Variables
4.2.2. Static Regression Results Analysis
4.2.3. Analysis of Dynamic Regression Results
4.3. Robustness Test
5. Conclusion and Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Contributions
5.2. Practical Implications
6. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.Y. Research on health evaluation and early warning of regional digital innovation ecosystem. Soft Sci. 2023, 37, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagna, J.M.; Bhada, S.V. Strategic Adoption of Digital Innovations Leading to Digital Transformation: A Literature Review and Discussion. Systems 2024, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarikka-Stenroos, L.; Ritala, P. Network management in the era of ecosystems: Systematic review and management frame work. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 67, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, S.; Lyytinen, K.; Majchrzak, A.; Michael, S. Digital innovation management: Reinventing innovation management research in a digital World. MIS Q. 2017, 41, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritala, P.; Agouridas, V.; Assimakopoulos, D.; Gies, O. Value creation and capture mechanisms in innovation ecosystems: A comparative case study. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2013, 63, 244–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, F. Predators and Prey: A new ecology of competition. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1993, 71, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adner, R. Match your innovation strategy to your innovation ecosystem. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2006, 84, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Adner, R.; Kapoor, R. Value creation in innovation ecosystems: How the structure of technological interdependence affects firm performance in new technology generations. Strateg. Manag. J. 2010, 31, 306–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolloch, M.; Dellermann, D. Digital Innovation in the Energy Industry: The Impact of Controversies on the Evolution of Innovation Ecosystems. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 136, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Watanabe, C. Japanese and US Perspectives on the National Innovation Ecosystem. Technol. Soc. 2008, 30, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, R.; Ghosh, A.; Rosenakopf, L. Competition-cooperation interplay during multi firm technology coordination: The effect of firm heterogeneity on conflict and consensus in a technology standards organization. Strateg. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 3193–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.L.; Davis, J.P.; Chhabra, Y. Entrepreneurial innovation: Killer apps in the iPhone ecosystem. Soc. Sci. Electron. Publ. 2014, 104, 255–259. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, K.H.; Mu, R.P. The digital innovation ecosystems: Theory building and a research agenda. Sci. Res. Manag. 2021, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suseno, Y.; Laurell, C.; Sick, N. Assessing value creation in digital innovation ecosystems: A social media analytics approach. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2018, 27, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhao, Y.H. Governance mechanism of digital innovation ecosystem. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2021, 39, 965–969. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, L.J.; Liu, J.T.; Xiao, Y.X.; Kong, D.Q. Research on symbiosis model of digital innovation ecosystem. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2022, 40, 1481–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Z.; Zhao, S.L.; Zhang, P.Y. The Niche-fitness Theory and Its Application to the Systems of Crop Growth. J. Lanzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 1993, 29, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, H. The niche-fitness model of crop population and its application. Ecol. Model. 1997, 104, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.L.; Wang, D.P.; Zhou, C. Sustainability evaluation of regional innovation system based on synthetic niche-fitness. Syst. Eng.-Theory Pract. 2011, 31, 927–935. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.Y.; Chen, G.J.; Liu, Q.L. The Innovation Niche Fitness and Evolution of High-tech Industry Innovation Ecosystem. Syst. Eng. 2018, 36, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.J.; Hu, Y.R.; Ma, W.M. Ecological system suitability of regional innovation and correlation of economic development. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2013, 21, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walrave, B.; Talmar, M.; Podoynitsyna, K.S.; Romme, A.G.L.; Verbong, G.P.J. A multi-level perspective on innovation ecosystems for path-breaking innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2018, 136, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.Y.; Zeng, Z.M.; Yang, B. Research on the spatial relationship between niche suitability and innovation performance of high-tech industry innovation ecosystem. Forum Sci. Technol. China 2022, 12, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Lu, C.Q. Research on regional innovation ecosystem and innovation efficiency based on niche adaptability. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2017, 36, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.; Han, Q. Does the Innovation-Driven Promote the High-Quality Development of Urban Economy? Sci. Sci. Manag. ST 2022, 43, 88–106. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.S.; Zhao, X.Y. Firms’ technological strategies in an innovation ecosystem: A dynamic inter-action between leading firms and following firms based on evolutionary game theory and multi-agent simulation. J. Manag. Sci. China 2022, 25, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xia, M.; Li, X.; Lin, H.; Xie, Z. How innovation ecosystem synergy degree influences technology innovation performance—Evidence from China’s high-tech industry. Systems 2022, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.D.; Lu, C.X. The impact of innovation ecosystem resilience on high-quality economic development. Forum Sci. Technol. China 2023, 321, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lu, J.Y. What kind of digital innovation ecosystem can improve regional innovation performance: An analysis based on NCA and QCA. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy 2022, 39, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.F.; Wang, B. Does digital technology promote China’s global value chain position. Int. Econ. Trade Res. 2020, 36, 35–51. [Google Scholar]
- Papadomikolaki, E.; Tezel, A.; Yitmen, I.; Hilletofth, P. Blockchain innovation ecosystems orchestration in construction. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2023, 123, 672–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, X.; Bo, Y. How can regional innovation ecosystem affect innovation level? An Fs-QCA analysis. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2024, 36, 4067–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K. Science, technology and innovation ecosystem transformation toward society 5.0. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 220, 107460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brea, E. A framework for mapping actor roles and their innovation potential in digital ecosystems. Technovation 2023, 125, 102783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.Y.; Lin, Z.F.; Liu, X.L. Green finance and economic growth quality: Construction of general equilibrium model with resource constraints and empirical test. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2022, 30, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.F.; Jie, X.H. Measurement of China’s high-quality development and analysis of provincial status. J. Quant. Technol. 2020, 35, 26–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, S.H. Study on the measurement of economic high-quality development level in China in the new era. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2018, 35, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Y.; Shen, K.R. Modernized economic system, total factor productivity and High-Quality development. Shanghai J. Econ. 2018, 6, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.Q.; Chu, C.J.; Gao, J.N. Effect of environmental regulation and industrial structure upgrading on high-quality economic development. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 30, 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.M.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhu, J.D. Study on the measurement and high-quality economy development effect of national innovation driving force. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2019, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, G.Y.; Zhang, J.P. The estimation of China’s provincial capital stock: 1952–2000. Econ. Res. J. 2004, 39, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Deng, F. Digital technology, factor structure transformation and high-quality economic development. Soft Sci. 2023, 37, 9–14+22. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.L.; Zhang, S. Research on mechanism of high-quality foreign trade contribute to high-quality economic development. Asia-Pac. Econ. Rev. 2023, 1, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X. Digital economy, resource misallocation and total factor productivity. Financ. Trade Res. 2022, 33, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Yang, Y.Q.; Luo, X.Y.; Wen, T. The spatial correlation network and formation mechanism of China’s high-quality economic development. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 1920–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
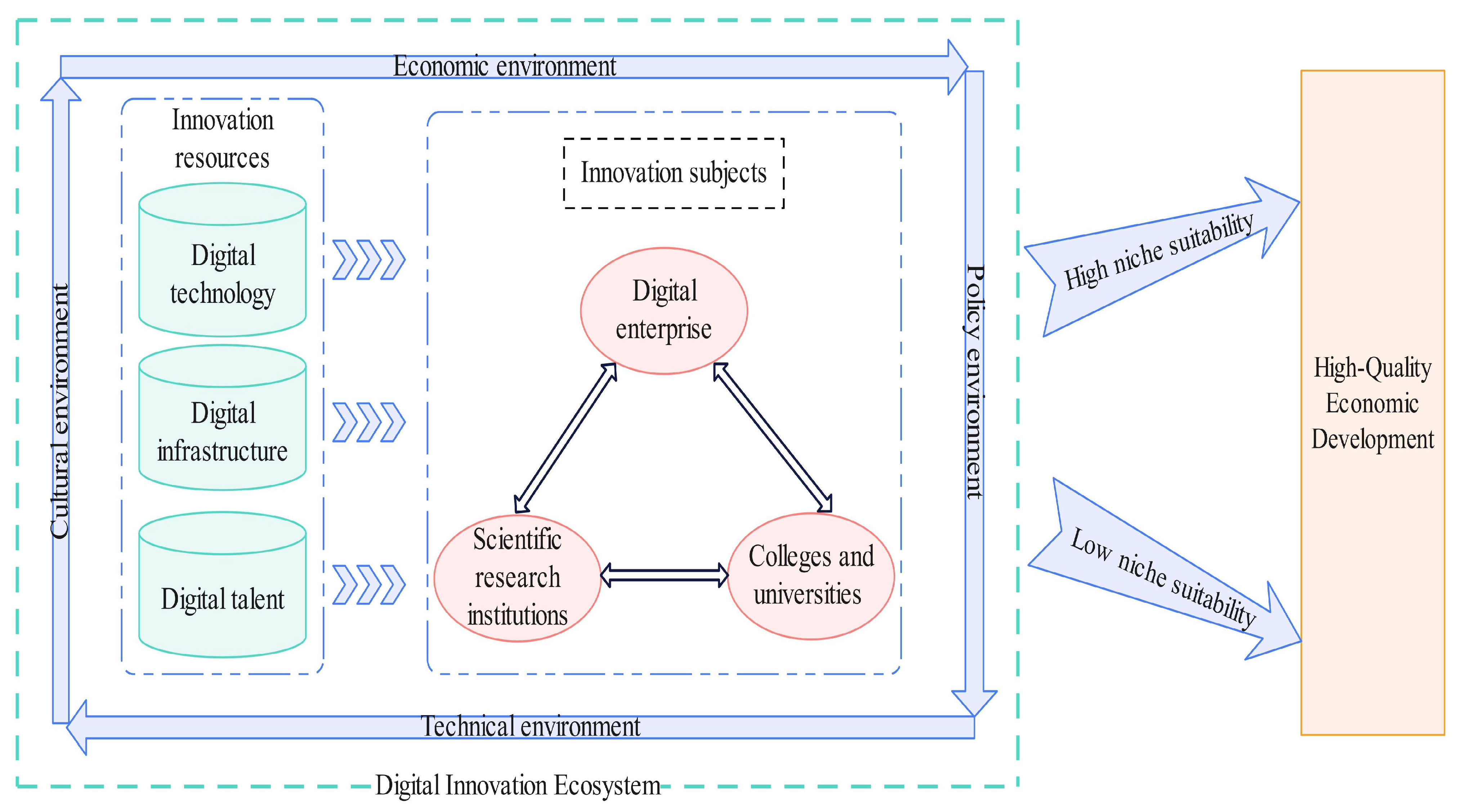
| Evaluation Objective | Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Explanation of Indicators | Unit of Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Niche suitability of DIES | Innovation subjects | Digital enterprise | Number of digital enterprises | units |
| Colleges and universities | Number of colleges and universities | units | ||
| Scientific research institutions | Number of scientific research institutions | units | ||
| Innovation resources | Digital infrastructure | Long-distance cable line length | km | |
| Internet broadband access ports | 10,000 unit | |||
| Number of mobile phone base stations | units | |||
| Digital technology | Internet penetration rate | percentage | ||
| Mobile phone penetration rate | sets/100 people | |||
| Digital talent | People employed in the ICT industry | 10,000 people | ||
| Innovation environment | Economic environment | Per capita GDP of each region | yuan | |
| Per capita disposable income of urban and rural residents | yuan | |||
| Per capita consumption expenditure of urban and rural residents | yuan | |||
| Policy environment | Local government expenditure on science and technology | billions of yuan | ||
| Local fiscal expenditure on education | billions of yuan | |||
| Cultural environment | Number of public libraries | units | ||
| Technical environment | Number of three major patent applications | item | ||
| Technical contract turnover | billions of yuan |
| District | Niche Suitability | Ranking | District | Niche Suitability | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.6807 | 2 | Fujian | 0.4925 | 10 |
| Jiangsu | 0.6804 | 3 | Shandong | 0.5536 | 6 |
| Hebei | 0.4803 | 13 | Tianjin | 0.4720 | 15 |
| Jiangxi | 0.4642 | 16 | Hainan | 0.4299 | 29 |
| Guangdong | 0.8203 | 1 | Chongqing | 0.4555 | 23 |
| Liaoning | 0.4842 | 12 | Sichuan | 0.5115 | 7 |
| Shanghai | 0.5830 | 5 | Ningxia | 0.4286 | 30 |
| Shanxi | 0.4571 | 22 | Guangxi | 0.4597 | 19 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.4578 | 20 | Guizhou | 0.4470 | 26 |
| Anhui | 0.4852 | 11 | Hunan | 0.4642 | 17 |
| Neimeng | 0.4613 | 18 | Shaanxi | 0.4726 | 14 |
| Zhejiang | 0.5906 | 4 | Gansu | 0.4415 | 27 |
| Qinghai | 0.4310 | 28 | Xinjiang | 0.4486 | 24 |
| Hubei | 0.4951 | 9 | Jilin | 0.4470 | 26 |
| Henan | 0.4976 | 8 | Yunnan | 0.4576 | 21 |
| District | Evolutionary Momentum | Ranking | District | Evolutionary Momentum | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.6383 | 28 | Fujian | 0.8271 | 23 |
| Jiangsu | 0.6270 | 29 | Shandong | 0.7532 | 25 |
| Hebei | 0.8605 | 19 | Tianjin | 0.8740 | 17 |
| Jiangxi | 0.8956 | 13 | Hainan | 0.9647 | 2 |
| Guangdong | 0.4994 | 30 | Chongqing | 0.9104 | 9 |
| Liaoning | 0.8332 | 22 | Sichuan | 0.8200 | 24 |
| Shanghai | 0.7107 | 26 | Ningxia | 0.9656 | 1 |
| Shanxi | 0.8961 | 12 | Guangxi | 0.9025 | 10 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.8988 | 11 | Guizhou | 0.9189 | 6 |
| Anhui | 0.8664 | 18 | Hunan | 0.8956 | 14 |
| Neimeng | 0.8888 | 15 | Shaanxi | 0.8791 | 16 |
| Zhejiang | 0.6954 | 27 | Gansu | 0.9414 | 4 |
| Qinghai | 0.9599 | 3 | Xinjiang | 0.9164 | 7 |
| Hubei | 0.8420 | 21 | Jilin | 0.9262 | 5 |
| Henan | 0.8448 | 20 | Yunnan | 0.9104 | 8 |
| Code | Mean | Sd | HQ | Suita | open | ftrade | fas | urb | fin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQ | 0.7537 | 0.1525 | 1 | ||||||
| Suita | 0.5024 | 0.0879 | 0.439 *** | 1 | |||||
| open | 0.2640 | 0.2551 | 0.219 *** | 0.431 *** | 1 | ||||
| ftrade | 0.2071 | 0.2400 | 0.467 *** | 0.374 *** | 0.385 *** | 1 | |||
| fas | 0.3406 | 0.2530 | −0.117 ** | 0.187 *** | −0.286 *** | −0.200 *** | 1 | ||
| urb | 0.5949 | 0.1239 | 0.525 *** | 0.410 *** | 0.442 *** | 0.428 *** | 0.056 | 1 | |
| fin | 1.4777 | 0.4495 | −0.207 *** | −0.065 | −0.052 | −0.265 *** | 0.457 *** | −0.462 *** | 1 |
| Variables | HQ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| Suita | 0.626 *** (0.0353) | 0.483 *** (0.0963) | 0.534 *** (0.0946) | 0.609 *** (0.0727) |
| open | 0.151 * (0.0670) | 0.192 * (0.0748) | 0.269 ** (0.126) | |
| ftrade | 0.380 *** (0.0634) | 0.429 *** (0.0660) | 0.273 *** (0.0749) | |
| fas | −0.109 (0.0614) | −0.184 * (0.0921) | −0.242 * (0.0648) | |
| urb | 0.534 *** (0.0603) | 1.574 *** (0.244) | 0.492 ** (0.149) | |
| fin | −0.161 *** (0.0420) | −0.325 *** (0.0928) | −0.354 *** (0.0811) | |
| _cons | 0.159 *** (0.0141) | 0.105 *** (0.0263) | 0.124 *** (0.0360) | 0.207 *** (0.0497) |
| Province control | NO | NO | YES | YES |
| Time control | NO | NO | NO | YES |
| N | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| R-squared | 0.5466 | 0.6337 | 0.7365 | 0.8446 |
| Variables | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| System GMM | Differential GMM | OLS | FE | |
| HQ-1 | 0.724 *** (0.125) | 0.651 *** (0.0561) | 0.750 *** (0.1484) | 0.658 *** (0.0852) |
| Suita | 0.627 *** (0.0952) | 0.563 *** (0.0441) | 0.628 *** (0.0831) | 0.616 *** (0.0770) |
| open | 0.260 ** (0.116) | 0.324 * (0.119) | 0.233 ** (0.0840) | 0.193 ** (0.0726) |
| ftrade | 0.268 *** (0.108) | 0.173 * (0.02134) | 0.368 *** (0.0517) | 0.178 ** (0.0544) |
| fas | −0.150 * (0.0622) | −0.0494 * (0.0192) | −0.0813 * (0.0360) | −0.0485 * (0.0476) |
| urb | 0.246 ** (0.0973) | 0.255 ** (0.0728) | 0.253 *** (0.0519) | 0.244 *** (0.0468) |
| fin | −0.1259 ** (0.0552) | −0.211 ** (0.0188) | −0.0816 * (0.0350) | −0.241 *** (0.0625) |
| _cons | 0.226 * (0.0398) | 0.171 * (0.0334) | 0.305 *** (0.0625) | 0.162 * (0.0767) |
| AR (1) | 0.044 | 0.064 | ||
| AR (2) | 0.456 | 0.594 | ||
| N | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 |
| Sargan Test | 0.228 | 0.235 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Fang, Y.; Liu, J. Research on the Impact of Digital Innovation Ecosystem Niche Suitability for High-Quality Economic Development. Systems 2025, 13, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050352
Ma Y, Fang Y, Liu J. Research on the Impact of Digital Innovation Ecosystem Niche Suitability for High-Quality Economic Development. Systems. 2025; 13(5):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050352
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yabing, Yongheng Fang, and Jiamin Liu. 2025. "Research on the Impact of Digital Innovation Ecosystem Niche Suitability for High-Quality Economic Development" Systems 13, no. 5: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050352
APA StyleMa, Y., Fang, Y., & Liu, J. (2025). Research on the Impact of Digital Innovation Ecosystem Niche Suitability for High-Quality Economic Development. Systems, 13(5), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050352







