Abstract
Digital orientation has attracted significant attention from policymakers and researchers due to its potential to drive innovation success. While prior research has largely examined the impact of digital orientation on specific types of innovation from a static lens, a holistic and dynamic perspective on its relationship with firms’ overall innovation performance remains limited. Drawing on dynamic capabilities theory, this study aims to bridge this gap by developing a moderated mediation model that incorporates the mediating role of digital capabilities and the moderating effect of environmental dynamism in the relationship between digital orientation and firms’ overall innovation performance. Using survey data from 368 Chinese firms, this study employs hierarchical regression analysis and the bootstrap method to test the hypotheses. The results indicate that digital orientation promotes digital capabilities (encompassing digital sensing, digital integrative, and digital transforming capabilities), which in turn facilitates firms’ overall innovation performance. Also, the effect of digital capabilities on innovation performance is moderated by environmental dynamism. This study contributes to the existing literature by offering a holistic and dynamic lens to elucidate the link between digital orientation and innovation performance, while also providing managerial insights for firms seeking to adopt digital orientation to boost innovation success in the evolving digital environments.
1. Introduction
Innovation is a key pathway for firms to achieve competitive advantage [1]. In recent years, the infusion of emerging digital technologies has increasingly become a crucial external force enabling innovation processes and outcomes [2,3]. However, the application of digital technologies does not always lead to innovation success [4]. This is worth considering, given that reports indicate that over 80% of digital efforts fail to achieve intended goals [4]. For example, companies such as General Electric, Procter & Gamble, and Ford have invested heavily in developing digital products, services, and infrastructures, yet they have encountered significant performance challenges and shareholder opposition [5]. Why have so many digital innovation initiatives failed to meet expectations? Such failures are frequently attributable to inadequate strategic coherence. Specifically, digital projects may be undertaken disparately, exhibit insufficient integration with the firm’s core competitive strategy, or proceed without a clear roadmap for converting technological potential into sustainable competitive advantage. Accordingly, recent perspectives argue that digital success is not solely contingent upon technological application but also relies on a cohesive strategic orientation guiding digital initiatives [6,7,8].
Against this backdrop, digital orientation has emerged as a new strategic orientation concept, referring to a firm’s deliberate strategic positioning to harness the opportunities presented by emerging digital technologies [6,9,10]. Recent studies suggest that digital orientation can enhance competitive advantage and drive the innovation success of firms [11,12]. However, existing research has predominantly examined the impact of digital orientation on specific types of innovation, such as service innovation, digital process innovation, and supply chain innovation [13,14,15], while devoting relatively little attention to its influence on the overall innovation performance of firms. Achieving high overall innovation performance is a complex undertaking, influenced by a diverse set of factors spanning both external conditions (e.g., government policy, market dynamics, and technology advancements) and internal characteristics (e.g., corporate strategy, R&D resources and capabilities, and organizational structure and culture) [2,3,7]. Although prior research has broadly examined the antecedents of overall firm innovation, existing studies provide limited insight into how digital orientation systematically affects the overall firm innovation performance [11,12]. Therefore, to address this gap and provide a more holistic perspective on the role of digital orientation in shaping firms’ innovation outcomes, this study poses the first research question (RQ1): What is the relationship between digital orientation and firms’ overall innovation performance?
Moreover, this study seeks to elucidate the underlying mechanisms through which digital orientation influences innovation performance, an issue that has received limited scholarly attention in the extant literature. While existing research, primarily grounded in the knowledge-based view, argues that digital orientation enhances innovation by facilitating knowledge acquisition and creation [6,14,16], this perspective may not fully capture how digitally oriented firms dynamically adjust resources and capabilities to drive innovation within fast-paced digital environments. Dynamic capabilities theory offers a crucial complementary perspective, emphasizing the firm’s ability to integrate, reconfigure, and create resources in response to environmental shifts [17]. In addition, recent studies indicate that effective competition in the digital era necessitates dynamic capabilities tailored for digital transformation, yet this remains an underexplored area [18,19]. Responding to calls to identify the dynamic capabilities for digital transformation, this study focuses on digital capabilities, viewed as critical dynamic capabilities that enable firms to leverage digital technologies in support of core business activities [19,20]. Consistent with traditional strategic orientation studies, which argue that strategic orientation provides potential value that is actualized into a competitive advantage through the effective deployment of corresponding organizational capabilities, we anticipate that digital orientation will drive significant performance improvements through digital capabilities [21,22,23]. However, little is known in the existing literature about the mediating role of digital capabilities in the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance [12,15]. To further unravel the “black box” linking digital orientation and innovation performance, this study proposes the second research question (RQ2): How do digital capabilities mediate the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance?
Furthermore, firms are influenced by the external environment, even if top managers are internally motivated to develop digital orientation and digital capabilities. Environmental dynamism refers to the instability or volatility of a firm’s external environment [24], serves as a critical driver in the formation and evolution of dynamic capabilities, as well as influencing firms’ strategic choices [17]. A high level of environmental dynamism requires firms to continuously respond to changes in market demand, technological iterations, and shifts in competitive landscapes, thereby placing greater demands on their strategic adaptability and dynamic capabilities [25,26]. Given the disruptive nature of digital technologies, which is reflected in accelerated innovation cycles, blurred industry boundaries, and evolving customer expectations fueled by ubiquitous data and connectivity, incorporating environmental dynamism becomes essential for understanding the interplay among digital orientation, digital capabilities, and innovation performance. In essence, the environmental dynamism that firms face today is amplified or fundamentally shaped by these digital disruptions, making its contingent role critical to investigate. However, the contingent role of environmental dynamism in this relationship remains largely unexplored [26]. Accordingly, to fill this gap, this study proposes the third research question (RQ3): How does environmental dynamism moderate the relationships among digital orientation, digital capabilities, and innovation performance?
To address the aforementioned questions, this study develops a moderated mediation model grounded in dynamic capabilities theory. We conceptualize digital capabilities as comprising three sub-capabilities: digital sensing, digital integrative, and digital transformation capabilities. These correspond to the sensing, seizing, and reconfiguring dimensions of the dynamic capabilities framework [20,27,28]. We propose that digital capabilities, along with their sub-capabilities, serve as mediating variables in the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance. Environmental dynamism functions as a moderating variable, influencing the relationships among digital orientation, dynamic capabilities, and innovation performance. We collected questionnaire survey data from 368 Chinese enterprises and employed hierarchical regression analysis and the bootstrap method to test the hypotheses.
Our research contributes to theory and practice in four ways. First, we respond to the calls in the existing literature for further investigation into the influence of digital orientation [10,29]. Unlike prior studies that predominantly focused on specific types of innovation, our study provides a more holistic perspective on the role of digital orientation in promoting firms’ overall innovation performance [10,29]. Second, we address calls to identify dynamic capabilities for digital transformation by providing novel insights into the role of digital capabilities [18,19]. Drawing on dynamic capabilities theory, our study empirically demonstrates that digital capabilities act as a key mediator in the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance, thus shedding light on the underlying mechanisms through which digital orientation influences innovation performance. Third, our study offers new knowledge on how environmental dynamism moderates the relationships among digital orientation, digital capabilities, and innovation performance, thereby enriching the understanding of the contextual effects of these relationships [12,30]. Fourth, our research encourages practitioners to strengthen digital capabilities under the guidance of digital orientation, thus effectively fostering innovation success in dynamic digital environments.
2. Theory and Hypotheses
2.1. Dynamic Capabilities Theory
The acquisition and sustenance of competitive advantage by firms in dynamic environments has long been a central concern for both scholars and practitioners. Grounded in the resource-based view, the dynamic capabilities theory argues that a firm’s competitive advantage arises not only from its valuable, rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable resources, but also depends on its ability to integrate, reconfigure, and create new resource stocks in an ever-changing environment [17]. Dynamic capabilities are typically viewed as higher-order capabilities that govern the rate of change in ordinary capabilities, making them more difficult for competitors to replicate [27,28]. Teece proposed that dynamic capabilities consist of three dimensions: sensing, seizing, and reconfiguring. The sensing dimension involves identifying and assessing internal and external changes; the seizing dimension focuses on taking action to exploit opportunities or mitigate threats; and the reconfiguring dimension emphasizes the continuous strategic renewal of assets and organizational structures [27,28].
Warner and Wäger argue that the ubiquity of new digital technologies is changing the very nature and purpose of dynamic capabilities, necessitating the establishment of dynamic capabilities for digital transformation within firms. In this context, the concept of digital capabilities has emerged, referring to a firm’s ability to leverage digital technologies to support business activities [20,31,32]. This study draws on the dynamic capabilities theory to categorize digital capabilities into three sub-capabilities: digital sensing, digital integrative, and digital transforming capabilities. These three sub-capabilities directly correspond to the sensing, seizing, and reconfiguring dimensions of dynamic capabilities theory, respectively. Digital sensing capabilities refer to the ability to apply digital technologies to scan the external environment and sense opportunities and threats, emphasizing firms’ high sensitivity and rapid responsiveness (aligning with the sensing dimension). Digital integrative capabilities refer to a firm’s ability to effectively assimilate, enhance, and apply digital technologies within the organization [31,33], thereby enabling seizing opportunities through the adaptation and enhancement of existing resources and practices (aligning with the seizing dimension). Digital transforming capability refers to a firm’s ability to leverage digital technologies for the continuous transformation of resources, processes, and organizational structures [19,34], ensuring that firms can achieve ongoing renewal in rapidly changing market environments (aligning with the reconfiguring dimension).
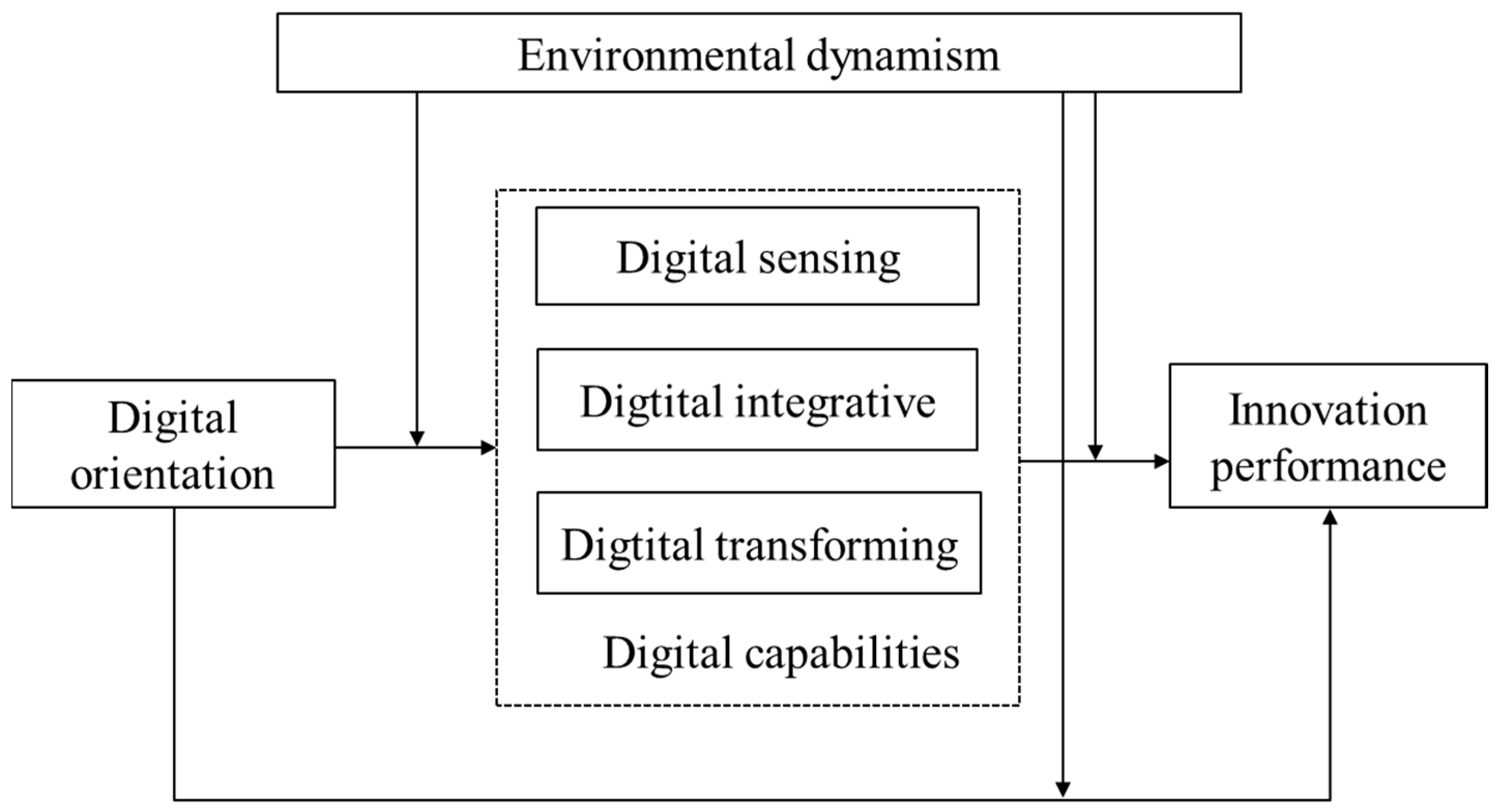
Managerial cognition serves as a crucial micro-foundation of dynamic capabilities [35]. Digital orientation as a manifestation of a firm’s strategic cognition profoundly influences the cultivation of digital capabilities. Digital capabilities reflect the resource actions firms undertake to implement digital orientation. The driving force of digital orientation on innovation performance will be realized through the development of digital capabilities. Furthermore, dynamic capabilities theory suggests that environmental dynamism is a critical contextual factor influencing the relationships among strategic orientation, digital capabilities, and innovation performance. Therefore, drawing on dynamic capabilities theory, this study constructs a moderated mediation model (as illustrated in Figure 1). The research framework establishes a direct link between digital orientation and innovation performance, proposing that digital capabilities play a mediating role in this relationship, while environmental dynamism serves as a positive moderating factor.
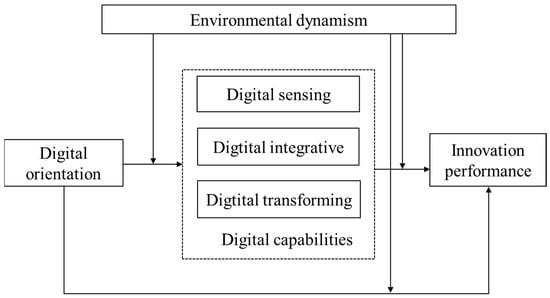
Figure 1.
The theoretical model.
2.2. Digital Orientation and Innovation Performance
Strategic orientation refers to the overall strategic direction of a company, reflecting the values and beliefs in conducting business and guiding its activities to achieve sustained superior performance [36,37,38]. The main categories of strategic orientation in existing research include market orientation [37], learning orientation [39,40], technology orientation [41,42], and entrepreneurship orientation [43]. In recent years, emerging digital technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) have been widely applied to business optimization, customer experience enhancement, operational process simplification, and the creation of new business models [19]. Against this backdrop, Digital orientation has emerged as a new strategic orientation concept and is gradually attracting scholarly attention [6,9,10].
Digital orientation reflects a company’s openness and commitment to integrating and leveraging digital technologies [29]. Recent studies have shown that digital orientation plays a crucial role in overcoming operational challenges, enhancing customer experiences, and fostering innovation across products, services, and processes [11,44]. It enables firms to sense, understand, and apply emerging digital technologies throughout the innovation journey [18]. Specifically, tools like big data analytics, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence empower companies to identify market trends and customer needs with precision, thus uncovering new opportunities for innovation [3,45,46]. Moreover, digital twin and simulation technologies allow firms to design, test, and refine innovative solutions within virtual environments. These tools not only minimize resource waste and trial-and-error costs but also increase the likelihood of successful innovations [2,47]. Additionally, digital platforms create novel opportunities for collaboration, access to new markets, and the acquisition of critical resources, offering firms fresh avenues for innovation [21,48,49]. In conclusion, digital orientation is instrumental in optimizing both the innovation process and its outcomes, ultimately boosting overall innovation performance. Thus, these arguments lead to the following hypothesis:
H1.
Digital orientation is positively related to innovation performance.
2.3. Digital Capacities and Innovation Performance
Dynamic capabilities theory suggests that firms should proactively cultivate the ability to integrate, adapt, and create new resource reserves to adapt to evolving environments [17]. Recent studies suggest that effective competition in the digital era requires firms to develop new dynamic capabilities for digital transformation [18,19,50]. Digital capabilities are regarded as emerging dynamic capabilities in the digital context, with an emphasis on data-driven decision-making, agile responsiveness, and value co-creation [19,20,51]. The core of digital capabilities lies in how firms leverage digital technologies to sense environmental changes, integrate internal and external resources, and reconfigure resources and capabilities [19,51]. Recent research highlights that digital capabilities not only enhance firms’ operational functions but also play an indispensable role in driving innovation processes [21,48].
Leveraging digital sensing capabilities allows for real-time monitoring of market dynamics, consumer demands, and competitor behaviors, facilitating the identification of potential innovation opportunities and forecasting of possible digital disruptions [19,21]. Digital integrative capabilities enable firms to identify and acquire valuable digital elements and seamlessly integrate them with traditional innovation elements. This integration process minimizes the search and transaction costs associated with innovation elements and promotes the formation of highly creative and well-structured innovation configurations [29,52]. Although sensing and integrative capabilities facilitate the identification and creation of innovation opportunities, converting these opportunities into tangible outcomes necessitates digital transforming capabilities. Firms with robust digital transforming capabilities tend to develop digital collaboration networks, redesign flexible organizational structures, and enhance employees’ digital maturity [19]. These efforts further optimize innovation processes, expand innovation networks, and nurture the development of innovative talent. Thus, these arguments lead to the following hypotheses:
H2.
Digital capabilities are positively related to innovation performance.
H2a.
Digital sensing capabilities are positively related to innovation performance.
H2b.
Digital integrative capabilities are positively related to innovation performance.
H2c.
Digital transforming capabilities are positively related to innovation performance.
2.4. Digital Orientation and Digital Capacities
Digital orientation serves as a critical driving force in shaping the development of firms’ digital capabilities. It shapes the selection, configuration, and interconnection of digital initiatives, offering a clear strategic direction for digital capability development [23,52]. Moreover, digitally oriented firms are more inclined to leverage digital technologies and resources to solve problems or create value, thus fostering an environment conducive to the development of digital capabilities [11,53]. From the sensing dimension of dynamic capabilities theory, digital orientation encourages firms to employ digital technologies to uncover hidden insights from vast datasets, thereby enhancing their digital sensing capabilities [19]. From the seizing dimension, digital orientation guides firms in implementing digital solutions and integrating new digital components into existing products and services, thus enhancing their digital integrative capabilities [3,53]. From the reconfiguring dimension, digital orientation advocates for organizational renewal and transformation, thereby driving the development of digital transforming capabilities [54]. Thus, these arguments lead to the following hypotheses:
H3.
Digital orientation is positively related to digital capabilities.
H3a.
Digital orientation is positively related to digital sensing capabilities.
H3b.
Digital orientation is positively related to digital integrative capabilities.
H3c.
Digital orientation is positively related to digital transforming capabilities.
2.5. Mediating Role of Digital Capabilities
Past research has shown that strategic orientation does not automatically lead to improved performance but rather fosters certain behaviors that, in turn, influence performance outcomes [38]. Digital orientation directs firms to leverage and develop digital technologies and resources, thereby facilitating the cultivation of digital capabilities [23]. Digital capabilities could serve as an effective deployment mechanism for digital orientation, reflecting a firm’s ability to align digital initiatives with its strategic digital objectives [23,52]. Drawing from dynamic capabilities theory, digital capabilities enhance firm performance through two key mechanisms: perceptive mechanisms, which capture market intelligence via digital sensing capabilities, and responsive mechanisms, which integrate and reconfigure resources and processes through digital integrative and transforming capabilities [31,55]. We argue that digital capabilities—encompassing sensing, integrative, and transforming capabilities—serve as a critical bridge between digital orientation and innovation performance, elucidating how digital orientation can be translated into enhanced innovation outcomes. Thus, these arguments lead to the following hypotheses:
H4.
Digital capabilities play a positive mediating role in the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance.
H4a.
Digital sensing capabilities serve as a positive mediator in the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance.
H4b.
Digital integrative capabilities positively mediate the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance.
H4c.
Digital transforming capabilities positively mediate the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance.
2.6. Moderating Role of Environmental Dynamism
Environmental dynamism refers to the instability or volatility of a firm’s external environment [24], reflecting the extent to which the external environment is characterized by short product life cycles and frequent changes in demand, production, and regulations [30,56,57]. According to dynamic capabilities theory, firms need to continuously reconfigure and update their resources and capabilities to adapt to environmental changes [27]. We predict that when environmental dynamism is high, the positive influence of digital orientation on digital capabilities will be more pronounced. This is because, in highly dynamic environments, traditional competitive advantages become weakened or obsolete, thus challenging firms as they confront the “capability gap” between their current and optimal resource configurations [58]. This challenge may compel digitally oriented firms to urgently develop digital capabilities to reshape their competitive advantage [56,59].
Furthermore, we expect that in highly dynamic environments, the role of digital orientation in enhancing innovation performance will be more prominent. Specifically, under conditions of rapid change and uncertainty, digital orientation enables firms to remain strategically forward-looking and digitally responsive to innovation opportunities presented by market and technological shifts. Additionally, we expect environmental dynamism to positively moderate the relationship between digital capabilities and innovation performance. High environmental dynamism heightens uncertainty and accelerates the pace of change, making continuous adaptation essential for firm survival and success. Digital capabilities, as key dynamic capabilities, are the primary means through which firms adapt to such turbulence. To address survival challenges and pursue superior performance, firms that possess strong digital capabilities are more likely to proactively scan the external environment, sense emerging trends, and integrate digital resources to support innovation activities. Therefore, the contribution of digital capabilities to innovation performance becomes increasingly crucial and valuable when the environment demands constant adaptation [60,61]. Thus, these arguments lead to the following hypotheses:
H5a.
Environmental dynamism positively moderates the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance.
H5b.
Environmental dynamism positively moderates the relationship between digital capabilities and innovation performance.
H5c.
Environmental dynamism positively moderates the relationship between digital orientation and digital capabilities.
3. Methodology
3.1. Sample and Data Collection
To validate the assumptions of our model, we conducted a questionnaire survey in China. Given the immense scale and rapid development of China’s digital economy, along with its leading position in various application fields, studying the digital transformation of Chinese enterprises offers a highly representative case. According to the “Accenture 2024 China Digital Transformation Index” report, an increasing number of Chinese companies are committed to using digital technologies to reshape their business models, optimize operational functions, and drive innovation in products and services. Furthermore, Chinese firms face underdeveloped legal frameworks, extensive government intervention in business activities, and a rapidly changing business environment, all of which collectively intensify environmental dynamism [62]. These trends not only reflect China’s unique position in the global digital transformation but also mirror broader global trends in digitalization. Therefore, studying the experiences of Chinese enterprises provides valuable insights into the core drivers and evolutionary patterns of the global digital wave, as well as revealing potential opportunities and challenges.
Additionally, we selected senior executives (including CEOs, vice presidents, general managers, and senior directors) as respondents because they play a crucial role in strategic decision-making and the implementation of digital initiatives. While their specific operational perspectives may vary based on their functional roles, these senior executives share a common strategic responsibility in driving the firm’s digital transformation and innovation efforts. This common strategic responsibility ensures a sufficiently consistent perspective for measuring firm-level strategy and capabilities. Specifically, these executives have the authority to decide on the adoption and implementation of digital orientation, drive the development of digital capabilities, and steer firm-wide innovation initiatives. Moreover, senior executives are responsible for monitoring external opportunities and challenges and responding promptly. Consequently, senior executives possess a comprehensive understanding of digital orientation, digital capabilities, environmental dynamism, and innovation performance, making them ideal respondents for this study.
To obtain a representative sample, we collaborated with a survey agency called Credamo, which provides a professional platform to assist clients in conducting surveys. The survey was conducted over two months, from January to February 2024, and a total of 446 questionnaires were collected during this period. We excluded questionnaires with the following characteristics: (1) completion time of less than 100 s; (2) missing key information; and (3) responses exhibiting obvious patterns. After these exclusions, 368 valid questionnaires remained, yielding an effective response rate of 82.5%. Table 1 presents the basic demographic information of the respondents. The sample comprises private firms (67.7%), state-owned firms (25%), and foreign-owned firms and other types (7.3%), spanning industries such as manufacturing (53.3%) and information transmission, software, and IT services (36.7%).

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of the samples (N = 368).
3.2. Measurement Scales
In this study, all measurement items were adapted from established scales in prior research (see Table A1 in Appendix A). The adaptation was necessary as the survey targeted Chinese respondents, necessitating a Chinese version of the questionnaire to align with the local context. To ensure linguistic and conceptual accuracy, we employed a back-translation method with the assistance of professional bilingual translators to convert the English questionnaire into Chinese. Following the initial design, we conducted interviews with five experts in innovation, entrepreneurship, and strategic management, along with senior executives from ten companies, to ensure both face and content validity. These experts and executives evaluated the questionnaire’s structure, wording, and terminology, providing valuable feedback and suggestions. Based on the experts’ input, we refined the question stems. Meanwhile, feedback from the senior executives led us to enhance the descriptions of the measures by incorporating specific examples of digital technology applications.
All research variables were measured using a five-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (“Strongly Disagree”) to 5 (“Strongly Agree”). The measurement of digital orientation (DO) was adapted from the work of Arias-Pérez et al. [6] and Arias-Pérez and Vélez-Jaramillo [53]. Digital capabilities (DCs) were conceptualized as a second-order multidimensional construct, comprising three first-order dimensions: digital sensing capabilities (DSCs), digital integrative capabilities (DICs), and digital transforming capabilities (DTCs), each measured by five items. The measurement scale for digital sensing capabilities was developed based on the work of Kump et al. [34]. The measurement of digital integrative capabilities was adapted from the work of Weigelt [63]. The measurement of digital transforming capabilities was adapted from the work of Kump et al. [34]. Innovation performance was measured based on the work of Chen et al. [64]. The scale for environmental dynamism (ED) was derived from the work of Azadegan et al. [56]. To avoid the influence of extraneous variables on the causal relationships between the core variables, we controlled for firm age, firm size, ownership type, industry category, and manager gender [65,66,67].
3.3. Common Method Bias
To address the risk of common method bias (CMB), we implemented several procedural controls prior to data collection, including simplifying survey questions and items, clarifying ambiguous concepts with examples, ensuring respondent anonymity, and separating items measuring independent and dependent variables. Beyond these procedural remedies, we employed statistical techniques to assess the presence of CMB. First, we adopted Harman’s single–factor test to verify the data’s CMB. A principal component analysis without rotation extracted six factors, which collectively explained 69.18% of the total variance. The first factor explained 30.004% of the variance, which is below the 50% threshold [68], indicating that CMB was not a significant concern. Second, we used the confirmatory factor analysis approach to Harman’s one-factor test. When all items were loaded on a single factor, the fit indices were as follows: χ2/df = 9.286; CFI = 0.458; NFI = 0.432; RMSEA = 0.15; SRMR = 0.1631. These indices were far from acceptable thresholds, further supporting the conclusion that CMB was unlikely to influence the results. Third, we used an unmeasured latent variable technique to estimate the extent to which common method bias might be an issue in our model [69]. We estimated two competing confirmatory factor analysis models. Model 1 includes only the substantive factors and their loadings, which provided the following fit indices: χ2/df = 1.766; CFI = 0.951; NFI = 0.895; RMSEA = 0.046; SRMR = 0.0528. Incorporating factors and loadings for both substantive and method variables, Model 2 achieved the following fit indices: χ2/df = 1.762; CFI = 0.952; NFI = 0.896; RMSEA = 0.046; SRMR = 0.0532. Based on the comparison, we can conclude that the difference in fit between the two models is not significant. Although these tests cannot definitively eliminate the possibility of CMB, they offer compelling evidence that CMB is unlikely to influence our data.
3.4. Reliability and Validity
This study used SPSS 27.0 and AMOS 27.0 to test the reliability and validity of the sample data. As presented in Table 2, the reliability analysis revealed that both Cronbach’s alpha coefficients and composite reliability (CR) values for all variables exceeded 0.8, indicating good reliability of the measurements. In terms of validity, the measurement items used in this study were adapted from established scales and underwent pretesting, demonstrating high content validity. Additionally, Confirmatory Factor Analysis was conducted to assess the convergent validity of each latent variable, with all measurement items showing factor loadings and Average Variance Extracted (AVE) values greater than 0.5, meeting the critical value requirements and indicating good convergent validity among the variables. The results of the discriminant validity test indicated that the square root of the AVE for each variable was greater than the absolute value of the correlation coefficient between that variable and all other variables, confirming good discriminant validity [70]. The results are shown in Table 3. Discriminant validity was further assessed using the Heterotrait–Monotrait Ratio (HTMT), with the results showing that all HTMT correlation values were below the critical threshold of 0.85, further reinforcing the robustness of discriminant validity. Finally, the model fit indices (χ2/df = 1.766; CFI = 0.951; NFI = 0.895; RMSEA = 0.046; SRMR = 0.0528) showed good performance, indicating that the questionnaire design and structural model of this study reached a satisfactory level.

Table 2.
Reliability and validity analysis.

Table 3.
Mean, standard deviation, correlation matrix, and the square root of AVE.
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis
Table 3 presents the results of the descriptive statistical analysis and correlation analysis of the variables in this study. As shown in Table 3, digital orientation and digital capabilities are both positively correlated with innovation performance, and there is also a positive correlation between digital orientation and digital capabilities. This provides preliminary support for the regression analysis. In addition, the study checked for multicollinearity problems between the variables by calculating the VIF values for each model. The results show that all VIF values are well below 10, indicating that there is no serious multicollinearity problem.
4.2. Hypotheses Testing
In this study, the hypotheses were tested using hierarchical regression analysis and bootstrap in SPSS 27.0. Hypothesis 1 predicts that digital orientation is positively related to innovation performance. The results in Model 2, Table 4, show that digital orientation has a positive relationship with innovation performance (β = 0.739 ***, p < 0.001). Thus, Hypothesis 1 is supported.

Table 4.
Main effect and mediating effect test.
Hypothesis 2 predicts that digital capabilities are positively associated with innovation performance. As shown in Table 4, Model 3, the results indicate a positive and statistically significant coefficient for digital capability (β = 0.800 ***, p < 0.001), demonstrating a strong positive effect of digital capability on innovation performance. Therefore, Hypothesis 2 is confirmed. Additionally, Hypotheses 2a, 2b, and 2c propose that the three sub-dimensions of digital capabilities, namely digital sensing, digital integrative, and digital transforming capabilities, each exert a positive influence on innovation performance. The analysis of Model 4 in Table 4 reveals significant positive coefficients for digital sensing capabilities (β = 0.210 ***, p < 0.001), digital integrative capabilities (β = 0.148 ***, p < 0.001), and digital transforming capabilities (β = 0.485 ***, p < 0.001). These results confirm that each sub-dimension of digital capabilities significantly and positively contributes to firms’ innovation performance. Accordingly, Hypotheses 2a, 2b, and 2c are confirmed.
Hypothesis 3 posits that digital orientation is positively associated with digital capabilities. As shown in Table 4, Model 8, the findings reveal a significant positive relationship between digital orientation and digital capabilities (β = 0.386 ***, p < 0.001, R2 = 0.321), providing robust evidence in support of Hypothesis 3. Additionally, Hypotheses 3a, 3b, and 3c propose that digital sensing, digital integrative, and digital transforming capabilities, respectively, are positively influenced by digital orientation. The analysis of Models 9, 10, and 11 in Table 4 confirms significant positive coefficients for digital orientation’s impact on digital sensing capabilities (β = 0.364 ***, p < 0.001), digital integrative capabilities (β = 0.205 ***, p < 0.001), and digital transforming capabilities (β = 0.589 ***, p < 0.001), respectively. These results provide compelling support for Hypotheses 3a, 3b, and 3c.
Hypothesis 4, 4a, 4b, and 4c propose that digital capabilities and the three sub-dimensions mediate the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance. To examine this proposed mediation, the study utilized a step-by-step methodology to assess the mediating effects. This procedure requires the fulfillment of several conditions. First, the independent variable (digital orientation) must demonstrate a significant relationship with the dependent variable (innovation performance). As evidenced in Table 4, Model 2, digital orientation exerts a positive and statistically significant influence on innovation performance, satisfying this initial condition. Second, the independent variable (digital orientation) must significantly affect the hypothesized mediator (digital capabilities). Models 8–11 in Table 4 reveal that digital orientation has a positive and significant impact on digital capabilities overall, as well as on the three sub-dimensions. Third, the mediator must significantly influence the dependent variable. Models 3 and 4 in Table 4 establish a significant, positive association, showing that enhanced digital capabilities (both overall and the specific sub-dimensions: sensing, integrative, transforming) are associated with improved innovation performance. These findings support the mediating role of digital capabilities (Hypotheses 4, 4a, 4b, and 4c) in the connection between digital orientation and innovation performance. Subsequent analysis incorporating the mediators (Models 5 and 6) revealed a diminished, yet still statistically significant, direct influence of digital orientation on innovation performance. This pattern confirms that digital capabilities, along with their constituent sub-dimensions, partially mediate the link between digital orientation and innovation performance. To further validate the mediating effect, a bootstrap analysis was conducted using SPSS PROCESS software 4.2 (5000 samples, CI = 95%). As reported in Table 5, the total effect of digital orientation on innovation performance is 0.7394, with the direct effect being 0.6132, accounting for 82.92%, and the indirect effect being 0.1263, accounting for 17.08%. Additionally, the 95% confidence intervals for all models do not include 0. Therefore, it can be concluded that digital capabilities partially mediate the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance. These findings provide strong support for Hypothesis 4 and its sub-hypotheses 4a, 4b, and 4c.

Table 5.
Bootstrap test (mediation effect).
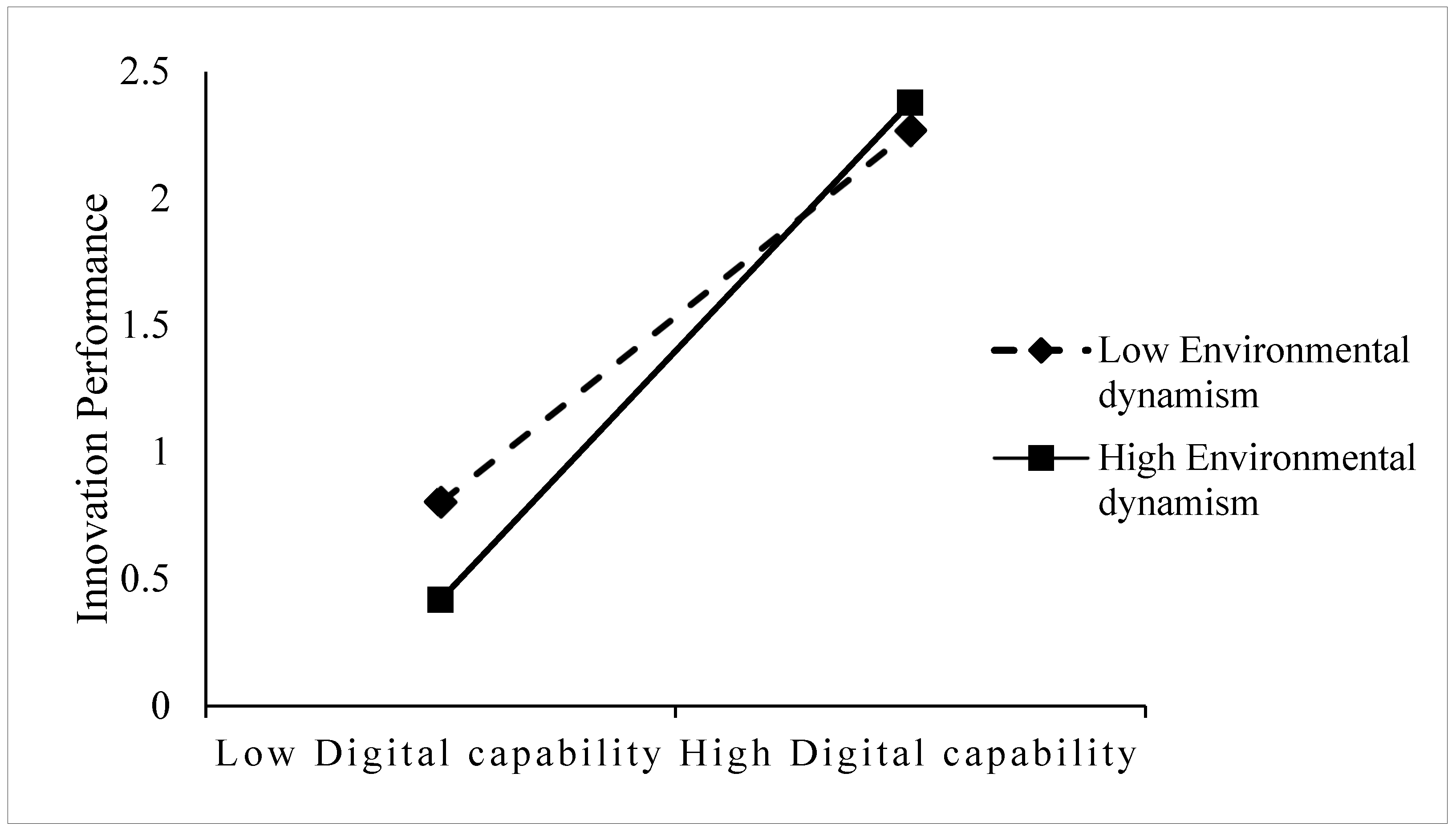
Hypothesis 5a states that environmental dynamism positively moderates the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance. As shown in Table 6, Model 2, the interaction term digital orientation × environmental dynamism is not significant (β = −0.077, p > 0.05), indicating that environmental dynamism does not exhibit a significant moderating effect on the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance. Therefore, Hypothesis 5a is not supported. Hypothesis 5b posits that environmental dynamism positively moderates the relationship between digital capabilities and innovation performance. As shown in Table 6, Model 4, the interaction term digital capabilities × environmental dynamism has a significant positive effect on innovation performance (β = 0.248 **, p < 0.01), indicating that higher environmental dynamism strengthens the positive impact of digital capabilities on innovation performance. Thus, H5b is supported. To further illustrate the moderating effect of environmental dynamism, a simple slope analysis was conducted. Environmental dynamism was divided into two levels: one standard deviation above (high environmental dynamism) and one standard deviation below (low environmental dynamism) the mean. The results, presented in Figure 2, show that under high environmental dynamism conditions, the slope of the digital capabilities–innovation performance relationship is steeper, indicating a stronger positive effect. In contrast, under low environmental dynamism conditions, the slope is flatter, suggesting a weaker association between digital capabilities and innovation performance. These findings confirm that environmental dynamism positively moderates the relationship between digital capabilities and innovation performance, providing further evidence to support H5b. Hypothesis 5c suggests that environmental dynamism positively moderates the relationship between digital orientation and digital capabilities. However, as shown in Table 6, Model 6, the interaction term digital orientation × environmental dynamism is not significant (β = −0.027, p > 0.05), indicating that environmental dynamism does not have a significant moderating effect on the relationship between digital orientation and digital capabilities. Therefore, H5c is not supported.

Table 6.
Moderating test results.
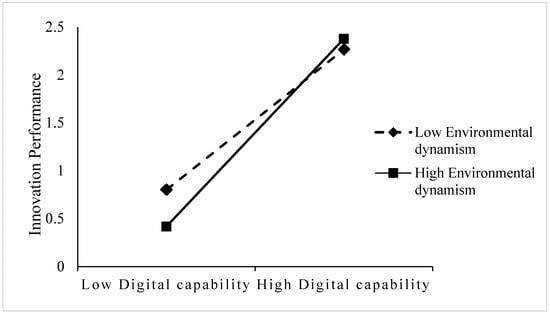
Figure 2.
The moderating effect of environmental dynamism.
Overall, the empirical results indicate that environmental dynamism significantly moderates the relationship between digital capabilities and innovation performance but does not significantly moderate the relationships between digital orientation and innovation performance or between digital orientation and digital capabilities. From the perspective of dynamic capabilities theory, this finding can be attributed to the role of digital capabilities in enhancing a firm’s adaptability in dynamic environments. Specifically, digital capabilities enable firms to swiftly sense and respond to external changes, thereby fostering greater competitive advantages in dynamic contexts. In contrast, digital orientation, as a long-term strategic orientation, follows stable implementation pathways and focuses on consistent goals, making it less responsive to environmental fluctuations.
5. Discussion and Implications
This study investigates the relationship between digital orientation and firm innovation performance by exploring the mediating mechanism of digital capabilities and the moderating role of environmental dynamism. Through rigorous empirical testing of research hypotheses, we provide valuable theoretical and practical implications.
5.1. Theoretical Implications
The research findings make several theoretical contributions. First, this study extends the current literature by shifting focus from individual digital initiatives to the broader role of digital orientation, an area identified by existing research as needing further exploration [10,29]. While prior studies have mainly examined the impact of digital orientation on specific types of innovation, research on its relationship with overall firm-level innovation performance remains scarce [13,16]. We provide new insights into this relationship from a holistic perspective, thereby deepening the understanding of how digital orientation influences firms’ overall innovation performance.
Second, we address calls to identify dynamic capabilities oriented toward digital transformation by providing new knowledge on the role of digital capabilities [18,19]. We categorize digital capabilities into digital sensing, digital integrative, and digital transforming capabilities, offering a comprehensive framework for understanding the role of digital capabilities. In addition, in contrast to prior studies that predominantly adopt a knowledge-based perspective to examine the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance, we unpack the “black box” of this relationship through the lens of dynamic capabilities theory [14,16]. Our findings reveal that digital capabilities act as a key mediating mechanism linking digital orientation and innovation performance. In doing so, we also align with calls for further research into the mediating role of dynamic capabilities constructs in this relationship [12], while extending the application of dynamic capabilities theory in the digital context.
Third, we respond to recent calls for research on the external contextual factors influencing innovation within digital transformation [12,33]. We provide new insights into how environmental dynamism moderates the relationships among digital orientation, digital capabilities, and innovation performance, an area that has rarely been examined in prior research [12,60]. Our findings reveal that environmental dynamism positively moderates the relationship between digital capabilities and innovation performance. However, it does not significantly moderate the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance, nor does it affect the relationship between digital orientation and digital capabilities. This may be attributed to the fact that digital capabilities are inherently adaptive mechanisms designed to swiftly sense and respond to environmental shifts. Turbulent environments increase uncertainty and the imperative for adaptation, thereby amplifying the value derived from dynamic capabilities. In contrast, digital orientation represents a more fundamental, long-term strategic posture, and may exert a relatively stable influence on innovation performance and digital capabilities, making it less susceptible to environmental changes. Notably, this finding aligns with Ranjan (2024), who similarly reported a non-significant direct digital orientation × environmental dynamism interaction, even while finding a significant three-way interaction involving capabilities. This further suggests that the influence of environmental dynamism on translating digital orientation into innovation performance likely manifests primarily through mechanisms involving specific capabilities [12,33].
5.2. Practical Implications
Our research offers several insights for managers seeking to gain a competitive advantage in the digital age. First, our research findings indicate that digital orientation is a critical prerequisite for the cultivation of digital capabilities and innovation success. We encourage firms to cultivate a strong digital orientation by focusing on three key areas: strengthening top management commitment, building a robust technological foundation, and fostering a supportive organizational culture. Reinforcing top management commitment can be achieved by recruiting leaders and key personnel with digital expertise and vision, clearly articulating the strategic significance and roadmap of digital transformation to all employees and allocating necessary resources to digital initiatives. Building a robust technological foundation requires strategic investment in scalable and integrated digital infrastructure—such as cloud platforms, advanced data analytics tools, and enterprise resource planning systems—that can effectively underpin the implementation of digital orientation. Fostering a supportive organizational culture involves promoting a mindset that embraces digital experimentation and views failure as a learning opportunity, reinforced through internal training programs that build a shared digital vision and enhance digital literacy across the workforce.
Second, our research findings demonstrate that the improvement in innovation performance driven by digital orientation is limited. Many well-designed strategic orientations fail due to poor execution. To translate digital orientation into superior innovation performance and sustained competitive advantage, firms should invest in developing digital capabilities, including digital sensing, digital integrative, and digital transforming capabilities. Regarding digital sensing capability, firms should proactively use data analytics tools (e.g., business intelligence tools and customer sentiment analysis tools) to extract valuable insights from large datasets. This facilitates monitoring market trends, customer feedback, and competitor activities in real time, thereby identifying potential innovation opportunities and threats. Digital integrative capability can be strengthened by establishing dedicated digital units that guide and collaborate with other departments in implementing digital initiatives. This cross-functional coordination not only reinforces overall IT utilization and data management but also facilitates the establishment of routines for effectively assimilating and leveraging new digital solutions within existing business processes. These efforts help organizations better seize innovation opportunities and mitigate emerging threats. Enhancing digital transforming capability requires not only improving overall digital maturity but also fostering organizational agility. This involves exploring new digital business models and establishing flexible, adaptable internal structures that enable rapid resource reconfiguration and process adjustments in response to emerging digital opportunities.
Third, the results regarding the moderating effect of environmental dynamism provide managers with valuable insights into how environmental factors influence innovation performance. Given that developing digital capabilities is essential for firms to adapt to environmental turbulence, we advise innovation-seeking firms to view the development of digital capabilities as an ongoing, adaptive strategic routine, rather than a one-off project. Specifically, managers should continuously assess the intensity and nature of environmental dynamism and evaluate its implications for innovation. Based on this assessment, firms should then set targeted priorities and allocate resources strategically for strengthening digital capabilities that are most critical for navigating their particular environment and seizing context-specific opportunities. By aligning digital capabilities development plans with environmental dynamism, firms can better harness their amplified value during turbulent periods and maximize their impact on innovation performance.
Finally, our findings also have significant implications for policymakers aiming to foster an innovation-driven economy in the digital era. First, recognizing the foundational role of digital orientation in initiating successful digital transformation and innovation, policymakers should focus on promoting digital awareness and capabilities across firms. This could involve government initiatives such as digital leadership training programs for executives and managers, disseminating best practices in digitalization, and providing subsidies to support the adoption of advanced digital technologies. Second, policy interventions should prioritize the development of an ecosystem that facilitates the widespread cultivation of digital capabilities. Key measures include investing in future-proof digital infrastructure, optimizing data governance frameworks, and implementing digital talent development initiatives that align workforce skills with the evolving demands of the digital economy. Finally, in light of increasing environmental dynamism, policymakers are encouraged to promote flexible and adaptive regulatory frameworks that enable firms to respond effectively to emerging digital opportunities, while simultaneously ensuring data privacy, cybersecurity, and the ethical use of digital technologies.
5.3. Limitations and Future Research
This study has several limitations that warrant further investigation in future research. First, this study relies on cross-sectional data, which cannot fully capture the dynamic causal relationships among variables. Future research could adopt a dynamic longitudinal research design to capture the dynamic and ongoing nature of digital transformation and firm innovation. Second, although this study is based on data from Chinese firms, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to some extent, we contend that the global representativeness of Chinese firms’ digital transformation, together with the universal applicability of the theoretical logic underpinning digital enablement for innovation, suggests that our findings could offer valuable insights for firms in other countries and regions. Nevertheless, empirical validation through future studies incorporating samples from diverse national and regional settings (including developed economies) is crucial to assess the cross-cultural applicability of our model. Additionally, considering the sample size of 368, future research with larger and more diverse samples would help further enhance confidence in the robustness of the observed relationships. Third, while we hypothesized a positive moderating role of environmental dynamism, the empirical results reveal a more nuanced relationship. Specifically, the moderating effect on digital capabilities was significant, whereas the expected moderation on digital orientation was not supported. This suggests the possibility of non-linear or threshold effects, and future research could investigate these effects to gain a deeper understanding of the boundary conditions of environmental dynamism in the context of digital transformation. Fourth, grounded in dynamic capabilities theory, this study analyzes the internal mechanisms through which digital orientation influences innovation performance. However, the internal mechanisms in the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance are complex. Future research could examine additional potential mediating or moderating factors to extend this research, such as organizational learning, organizational agility, and intellectual capital.
5.4. Conclusions
Grounded in dynamic capabilities theory, this study explores the influence of digital orientation on innovation performance by examining the mediating role of digital capabilities and the moderating effect of environmental dynamism. Survey data were collected from 368 Chinese firms, and hierarchical linear regression, along with the bootstrap method, was employed to test the hypotheses. The empirical results indicate that digital orientation and digital capabilities exert significant positive effects on innovation performance. Further analysis reveals that digital capabilities serve as a key mediator in the relationship between digital orientation and innovation performance, acting as a crucial link that translates strategic intent into tangible innovation outcomes. Moreover, environmental dynamism positively moderates the relationship between digital capabilities and innovation performance, suggesting that the impact of digital capabilities on innovation performance is amplified in more dynamic environments. In summary, the findings encourage firms to actively adopt digital orientation and strengthen digital capabilities to enhance innovation performance in turbulent market environments.
Author Contributions
X.Z.: writing—review and editing, writing—original draft, conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology. Z.W.: writing—review and editing, writing—original draft, supervision, funding acquisition, conceptualization. W.L.: writing—original draft, formal analysis, investigation, visualization, data curation. F.G.: writing—original draft, visualization, investigation, data curation. P.W.: writing—original draft, visualization, investigation, data curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, HUST: 2020WKYXZX008.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Survey items.
Table A1.
Survey items.
| Construct | Items (1 = Strongly Disagree; 5 = Strongly Agree) |
|---|---|
| Digital orientation | Developing a clear vision regarding how new digital technologies contribute to business value |
| Integrating business strategy and digital strategy | |
| Enabling functional area and general management’s ability to understand value of new digital technology investments | |
| We constantly keep current with new digital technology innovations | |
| We are able to and continue to experiment with new digital technologies as necessary | |
| We have a climate that is supportive of trying out new ways of using digital technologies | |
| We constantly seek new ways to enhance the effectiveness of digital technology use | |
| Digital capabilities | |
| Digital sensing | Our company uses business intelligence and industry research tools to identify the best practices in the market |
| Our company uses market intelligence platforms to monitor the current market situation in real-time | |
| Our company uses digital technologies to systematically search for information on the current market situation | |
| Our company knows how to utilize digital means to access new information | |
| Our company uses digital competitive intelligence analysis tools to have an eye on our competitors’ activities at all times | |
| Digital integrative | Our company is able to acquire the digital tools needed by the organization |
| Our company possesses sufficient internal information technology skills to proficiently use digital tools | |
| Our company is capable of customizing standardized “off-the-shelf” digital technologies as needed | |
| Our company could leverage digital means to optimize business processes and the allocation of resources | |
| Our company could extend digital technologies to independently develop new products, services, and processes | |
| Digital transforming | By defining clear responsibilities, our company successfully implements plans for digital transformation in our company |
| Even when unforeseen interruptions occur, digital transformation projects are seen through consistently in our company | |
| Decisions on planned digital transformation projects are pursued consistently in our company | |
| In the past, our company has demonstrated our strengths in implementing digital transformation | |
| In our company, digital transformation projects can be put into practice alongside the daily business | |
| Environmental dynamism | Major changes in the modes of production and/or service provision |
| A high rate of innovation | |
| Major changes in consumer demographics | |
| Frequent and major changes in government regulations | |
| An increasing amount of spending on research and development | |
| Innovation Performance | Our company can improve the quality of its products and services through innovation |
| Our company can accelerate the commercialization pace of new products and services through innovation | |
| Our company can make considerable profits from its new products and services | |
| Our company can develop new technology to improve its operational processes | |
| Our company can purchase new instruments or equipment to accelerate productivity |
References
- Al-Khatib, A.W.; Al-ghanem, E.M. Radical Innovation, Incremental Innovation, and Competitive Advantage, the Moderating Role of Technological Intensity: Evidence from the Manufacturing Sector in Jordan. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2021, 34, 344–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füller, J.; Hutter, K.; Wahl, J.; Bilgram, V.; Tekic, Z. How AI Revolutionizes Innovation Management—Perceptions and Implementation Preferences of AI-Based Innovators. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 178, 121598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, S.; Wright, M.; Feldman, M. The Digital Transformation of Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Progress, Challenges and Key Themes. Res. Policy 2019, 48, 103773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oludapo, S.; Carroll, N.; Helfert, M. Why Do so Many Digital Transformations Fail? A Bibliometric Analysis and Future Research Agenda. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 174, 114528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.H.; Westerman, G. Why so Many High-Profile Digital Transformations Fail. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2018, 9, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Arias-Pérez, J.; Juan, V.-O.; Cepeda-Cardona, J. Strategic Orientation toward Digitalization to Improve Innovation Capability: Why Knowledge Acquisition and Exploitation through External Embeddedness Matter. J. Knowl. Manag. 2021, 25, 1319–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capatina, A.; Bleoju, G.; Kalisz, D. Falling in Love with Strategic Foresight, Not Only with Technology: European Deep-Tech Startups’ Roadmap to Success. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, G. The Technology Fallacy: People Are the Real Key to Digital Transformation. Res.–Technol. Manag. 2019, 62, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khin, S.; Ho, T.C. Digital Technology, Digital Capability and Organizational Performance: A Mediating Role of Digital Innovation. Int. J. Innov. Sci. 2018, 11, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, S.; Canhoto, A.; Molinillo, S.; Pera, R.; Budhathoki, T. Conceptualising a Digital Orientation: Antecedents of Supporting SME Performance in the Digital Economy. J. Strateg. Mark. 2018, 26, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardito, L.; Raby, S.; Albino, V.; Bertoldi, B. The Duality of Digital and Environmental Orientations in the Context of SMEs: Implications for Innovation Performance. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 123, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, P. Unraveling the Mystery of the Link between Digital Orientation and Innovation Performance: The Interplay of Digital Business Capability and Environmental Dynamism. Technovation 2024, 131, 102966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajeddini, K.; Hussain, M.; Gamage, T.C.; Papastathopoulos, A. Effects of Resource Orchestration, Strategic Information Exchange Capabilities, and Digital Orientation on Innovation and Performance of Hotel Supply Chains. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2024, 117, 103645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nie, Y.; Guo, M.; Liu, H. Digital Orientation and Innovation Outputs in Collaboration Networks: Inside the Black Box. J. Knowl. Econ. 2023, 15, 732–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Kohtamäki, M.; Peng, X.; Kong, X. How Digital Orientation Impacts Service Innovation in Hotels: The Role of Digital Capabilities and Government Support. Tour. Econ. 2024, 31, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Lei, X. How Digital Orientation Promotes Digital Process Innovation from the Perspectives of Knowledge and Capability: Evidence from China. J. Knowl. Manag. 2024; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J.; Pisano, G.; Shuen, A. Dynamic Capabilities and Strategic Management. Strateg. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, G. Understanding Digital Transformation: A Review and a Research Agenda. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2019, 28, 118–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.S.R.; Wäger, M. Building Dynamic Capabilities for Digital Transformation: An Ongoing Process of Strategic Renewal. Long Range Plan. 2019, 52, 326–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annarelli, A.; Battistella, C.; Nonino, F.; Parida, V.; Pessot, E. Literature Review on Digitalization Capabilities: Co-Citation Analysis of Antecedents, Conceptualization and Consequences. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 166, 120635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenamor, J.; Parida, V.; Wincent, J. How Entrepreneurial SMEs Compete through Digital Platforms: The Roles of Digital Platform Capability, Network Capability and Ambidexterity. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 100, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, P.; Hoque, M.E.; Shah, N.U.; Candra, A.H.; Hashim, N.M.H.N.; Abdullah, N.L. Entrepreneurial Orientation and Performance of SMEs: The Roles of Marketing Capabilities and Social Media Usage. J. Entrep. Emerg. Econ. 2021, 15, 379–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, D.; Rosin, A.F.; Stubner, S.; Pinkwart, A. The Influence of a Digital Strategy on the Digitalization of New Ventures: The Mediating Effect of Digital Capabilities and a Digital Culture. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2024, 62, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamba, S.F.; Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Akter, S. The Performance Effects of Big Data Analytics and Supply Chain Ambidexterity: The Moderating Effect of Environmental Dynamism. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 222, 107498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Bhatti, S.H.; Gölgeci, I.; Arslan, A. Digital Platform Capability and Organizational Agility of Emerging Market Manufacturing SMEs: The Mediating Role of Intellectual Capital and the Moderating Role of Environmental Dynamism. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 177, 121513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendig, D.; Kleine-Stegemann, L.; Schulz, C.; Eckardt, D. The Effect of Green Startup Investments on Incumbents’ Green Innovation Output. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. Explicating Dynamic Capabilities: The Nature and Microfoundations of (Sustainable) Enterprise Performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2007, 28, 1319–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. The Foundations of Enterprise Performance: Dynamic and Ordinary Capabilities in an (Economic) Theory of Firms. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2014, 28, 328–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindermann, B.; Beutel, S.; Garcia de Lomana, G.; Strese, S.; Bendig, D.; Brettel, M. Digital Orientation: Conceptualization and Operationalization of a New Strategic Orientation. Eur. Manag. J. 2021, 39, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrdoda, Y.; Balzano, M.; Marzi, G. Learn to Survive Crises: The Role of Firm Resilience, Innovation Capabilities and Environmental Dynamism. Technol. Soc. 2023, 74, 102285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Roh, T. Digitalization Capability and Sustainable Performance in Emerging Markets: Mediating Roles of in/out-Bound Open Innovation and Coopetition Strategy. Manag. Decis. 2023; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, Y. Conceptual Method and Empirical Practice of Building Digital Capability of Industrial Enterprises in the Digital Age. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2022, 69, 1902–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, L.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qi, P. How Do Digitalization Capabilities Enable Open Innovation in Manufacturing Enterprises? A Multiple Case Study Based on Resource Integration Perspective. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 184, 122019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kump, B.; Engelmann, A.; Kessler, A.; Schweiger, C. Toward a Dynamic Capabilities Scale: Measuring Organizational Sensing, Seizing, and Transforming Capacities. Ind. Corp. Change 2018, 28, 1149–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Saunila, M.; Ukko, J.; Rantala, T.; Rantanen, H. Shaping Digital Innovation Via Digital-Related Capabilities. Inf. Syst. Front. 2023, 25, 1063–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, S.P.; van Herk, H.; Verhagen, T.; Weltevreden, J.W. Strategic Orientations and Digital Marketing Tactics in Cross-Border e-Commerce: Comparing Developed and Emerging Markets. Int. Small Bus. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, H. Market Orientation and Product Innovation: The Mediating Role of Technological Capability. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2020, 24, 1233–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Clauss, T.; Issah, W.B. Entrepreneurial Orientation and New Venture Performance in Emerging Markets: The Mediating Role of Opportunity Recognition. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2022, 16, 769–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.E.; Mukherjee, D.; Gattermann Perin, M. Learning Orientation and Competitive Advantage: A Critical Synthesis and Future Directions. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 144, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meekaewkunchorn, N.; Szczepańska-Woszczyna, K.; Muangmee, C.; Kassakorn, N.; Khalid, B. Entrepreneurial Orientation and SME Performance: The Mediating Role of Learning Orientation. Econ. Sociol. 2021, 14, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Solis, E.R.; Llonch-Andreu, J.; Malpica-Romero, A.D. How Beneficial Are Relational Capital and Technology Orientation for Innovation? Evidence from Mexican SMEs. Int. J. Innov. Stud. 2022, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masa’deh, R.; Al-Henzab, J.; Tarhini, A.; Obeidat, B.Y. The Associations among Market Orientation, Technology Orientation, Entrepreneurial Orientation and Organizational Performance. Benchmarking Int. J. 2018, 25, 3117–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, S.; Vonmetz, K.; Bullini Orlandi, L.; Zardini, A.; Rossignoli, C. Digital Entrepreneurship: The Role of Entrepreneurial Orientation and Digitalization for Disruptive Innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 193, 122638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Saunila, M.; Ukko, J. Digital Orientation, Digital Maturity, and Digital Intensity: Determinants of Financial Success in Digital Transformation Settings. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2022, 42, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, J.; Cui, L. The Impact of Digital Technologies on Economic and Environmental Performance in the Context of Industry 4.0: A Moderated Mediation Model. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 229, 107777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, X. Navigating Strategic Balance: CEO Big Data Orientation, Environmental Investment, and Technological Innovation in Chinese Manufacturing. Systems 2024, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, R.C.; Haftor, D.M.; Staniewski, M.W. AI-Enabled Business Models for Competitive Advantage. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfat, C.E.; Raubitschek, R.S. Dynamic and Integrative Capabilities for Profiting from Innovation in Digital Platform-Based Ecosystems. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Tao, M. Knowledge Absorption Capacity’s Efficacy to Enhance Innovation Performance through Big Data Analytics and Digital Platform Capability. J. Innov. Knowl. 2022, 7, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, C.; Reinhardt, L.B.; Schreiber, D.; Eberle, L. Dynamic Capabilities for Digital Transformation in an Enterprise Business. Benchmarking Int. J. 2024; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, J.; Castillo-Vergara, M.; Geldes, C.; Carbajal Gamarra, F.M.; Flores, A.; Heredia, W. How Do Digital Capabilities Affect Firm Performance? The Mediating Role of Technological Capabilities in the “New Normal”. J. Innov. Knowl. 2022, 7, 100171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, M.; Han, Z.; Beata, G.; Bresciani, S.; Wang, T. Effects of Digital Orientation on Organizational Resilience: A Dynamic Capabilities Perspective. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2023; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Pérez, J.; Vélez-Jaramillo, J. Ignoring the Three-Way Interaction of Digital Orientation, Not-Invented-Here Syndrome and Employee’s Artificial Intelligence Awareness in Digital Innovation Performance: A Recipe for Failure. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 174, 121305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braojos, J.; Weritz, P.; Matute, J. Empowering Organisational Commitment through Digital Transformation Capabilities: The Role of Digital Leadership and a Continuous Learning Environment. Inf. Syst. J. 2024, 34, 1466–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jin, W. Impact of Digital Capabilities on Entrepreneurial Performance in SMEs. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadegan, A.; Patel, P.C.; Zangoueinezhad, A.; Linderman, K. The Effect of Environmental Complexity and Environmental Dynamism on Lean Practices. J. Oper. Manag. 2013, 31, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bhatia, M.S. Environmental Dynamism, Industry 4.0 and Performance: Mediating Role of Organizational and Technological Factors. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2021, 95, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wu, S.; Luo, X. (Robert) How Does Big Data Analytics Capability Affect Firm Performance? Unveiling the Role of Organisational Resilience and Environmental Dynamism. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2024, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Wu, L.; Lowry, P.B.; Kumar, A.; Tan, K.H. Digitalization and Network Capability as Enablers of Business Model Innovation and Sustainability Performance: The Moderating Effect of Environmental Dynamism. J. Inf. Technol. 2023, 39, 687–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Mariani, M. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Capabilities and the R&D Performance of Organizations: The Moderating Role of Environmental Dynamism. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 11522–11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Paulraj, A.; Dai, J.; Irawan, C.A. Digital Integration Capability Asymmetry and Buyer Product Innovation: The Contingent Roles of Environmental Dynamism and Innovative Climate. Int. J. Oper. Amp Prod. Manag. 2024, 45, 756–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.A.; O’Kane, C.; Chen, G. Business Ties, Political Ties, and Innovation Performance in Chinese Industrial Firms: The Role of Entrepreneurial Orientation and Environmental Dynamism. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 121, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, C. The Impact of Outsourcing New Technologies on Integrative Capabilities and Performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2009, 30, 595–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Lin, M.-J.J.; Chang, C.-H. The Positive Effects of Relationship Learning and Absorptive Capacity on Innovation Performance and Competitive Advantage in Industrial Markets. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2009, 38, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chung, J. Women in Top Management Teams and Their Impact on Innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 183, 121883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Cai, Z.; Liu, H. Online-Offline Channel Integration and Innovation Ambidexterity: Roles of Top Management Team and Environmental Dynamism. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 160, 113792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, Y. The Double-Edged Sword Effect of Social Media Usage on New Product Development Performance: Evidence from Chinese Firms. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2021, 26, 265–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Podsakoff, N.P.; Williams, L.J.; Huang, C.; Yang, J. Common Method Bias: It’s Bad, It’s Complex, It’s Widespread, and It’s Not Easy to Fix. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psychol. Organ. Behav. 2024, 11, 17–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).