Abstract
Quantitative assessment of the ability of the ecosystem service (ES) and its driving forces is of great significance for achieving regional SDGs. In view of the scarcity of existing research that evaluates the sustainability of multiple ES types over a long time series at the township scale in a typical Watertown Region, this study aims to address two key scientific questions: (1) what are the spatiotemporal changes in the ecosystem service supply–demand index (ESSDI) and ecosystem service sustainability index (ESSI) of a typical Watertown Region? and (2) what are the key factors driving the changes in ESSI? To answer the above two questions, this study takes the Yangtze River Delta Integrated Demonstration Zone (YRDIDZ) as the study area, utilizing multi-source remote sensing and other spatiotemporal geographical datasets to calculate the supply–demand levels and sustainable development ability of different ES in the YRDIDZ from 2000 to 2020. The main findings were as follows: (1) From 2000 to 2020, the mean ESSDI values for habitat quality, carbon storage, crop production, water yield, and soil retention all showed a declining trend. (2) During the same period, the mean ESSI exhibited a fluctuating downward trend, decreasing from 0.31 in 2000 to 0.17 in 2020, with low-value areas expanding as built-up areas grew, while high-value areas were mainly distributed around Dianshan Lake, Yuandang, and parts of ecological land. (3) The primary driving factors within the YRDIDZ were human activity factors, including POP and GDP, with their five-period average explanatory powers being 0.44 and 0.26, whereas the explanatory power of natural factors was lower. However, the interaction of POP and soil showed higher explanatory power. The results of this study could provide actionable ways for regional sustainable governance: (1) prioritizing wetland protection and soil retention in high-population-density areas based on targeted land use quotas; (2) integrating ESSI coldspots (built-up expansion zones) into ecological redline adjustments, maintaining high green infrastructure coverage in new urban areas; and (3) establishing a population–soil co-management framework in agricultural–urban transition zones.
1. Introduction
The term ecosystem service (ES) refers to the various resources and services that ecosystems provide through their structure and functions, including the provisioning service, regulating service, cultural service, and supporting service [1,2,3]. ES not only directly meets basic human needs such as food, water, and air, but also indirectly facilitates important ecological processes such as climate regulation, water cycling, soil protection, and biodiversity maintenance. Previous research on ES provides significant scientific and practical significance in today’s society [4,5]. However, due to the intensified global environmental changes, population growth pressures, and the overconsumption of resources, ES, which is fundamental to human survival and development, has experienced gradual degradation, and the ability of regional ES has declined steadily [6,7]. This is particularly evident in China, where, since the implementation of the reform and opening-up policy in 1978, the process of urbanization has accelerated significantly [8,9]. According to the China Statistical Yearbook (2024), the urbanization rate rose from 17.92% to 66.16% in 2023 [10]. Furthermore, the United Nations projects that the percentage of the global urban population will reach 66% by 2050 [11]. The expansion of urban built-up land has encroached on other land types such as paddy fields, forests, and wetlands, significantly diminishing their ES ability [12,13,14]. Therefore, quantitative evaluation of the ability of different ES types and their driving forces has garnered wide attention from both academics and relevant policymakers. This underscores the urgent need for comprehensive assessments of ES to inform sustainable development strategies.
The evaluation of ES has evolved significantly over the past decades, with different methodologies being developed to address various research objectives. To date, numerous scholars globally have conducted studies on ES evaluation, spatiotemporal evolution analysis, driving forces, and related areas. Specifically, in terms of ES evaluation, Tiemann and Ring developed biophysical indicators to assess forest ES [15]; Tedeschi et al. applied systems thinking to enhance regional ES [16]; Cai and Shu integrated system theory to optimize ES in urban ecological development [17]; Yu et al. employed the equivalent factor method to calculate ES of Xining city and found that the ES values declined [18]; Zhou et al. evaluated the cultural ecosystem service of a wetland park using the SolVES model [19]; and Wu and Fan evaluated regional ES from a comprehensive perspective by constructing a comprehensive ecosystem service index [20]. To sum up, the commonly used ES evaluation methods include field observation and experiments [21], remote sensing and spatial analysis technologies [22,23], ecosystem models and simulation [24], economic valuation methods [25,26], statistical and econometric analysis [27], participatory and social survey methods [28], scenario analysis and prediction [29], comprehensive assessment frameworks [30], and emerging technological methods [31,32]. Among these, field monitoring methods require the establishment of long-term ecological research networks, which are time-consuming. Remote sensing technology has the advantage of long-term monitoring at a grid level, which can track ES change trends across any location. To date, remote sensing technology in monitoring ES has achieved significant progress. Kou et al. utilized remote sensing data to obtain land use data to generate ES based on the InVEST model [33]; Garshasbi et al. utilized land use products to evaluate ES of Hyrcanian forests [34]; Wu et al. detected the ES changes in arid and semi-arid areas based on time-series remote sensing images and the Google Earth Engine platform [35]; and Wang et al. analyzed the spatiotemporal variations of the grassland gross ecosystem product based on a machine learning algorithm and multi-source remote sensing data, and found that the grassland gross ecosystem product exhibited an upward trend in Xilinhot city [36]. Generally, researchers focused on different land use types or different ES types. Land use types include wetland [37], forest [38], grassland [39], urban area [40], and glaciers [41], while ES types include cultural ES [42,43], water yield ES [44], carbon sequestration [45,46], biodiversity [47], and supply and demand [48]. Among these, the supply and demand of ES, as a crucial link between ecological processes and human well-being, jointly facilitate the flow of ES from natural systems to social systems. This dynamic effectively represents regional ES sustainability. However, current research on the supply and demand of ES primarily focuses on a limited number of services within large urban agglomerations, while overlooking small-scale studies, such as those at the town scale, that examine multiple ES types. Future studies should prioritize small-scale, multi-ES analyses to better inform localized SDG strategies.
Therefore, in response to these challenges, this paper selected a typical Watertown Region, the Yangtze River Delta Integrated Demonstration Zone (YRDIDZ), as the study area to map its supply and demand situation and ES sustainability from 2000 to 2020. The aims of this study are to answer the following two scientific questions: (1) what are the spatiotemporal changes in the ecosystem service supply–demand index (ESSDI) and ecosystem service sustainability index (ESSI) of a typical Watertown Region? and (2) what are the key factors that influence the changes in ESSI? To achieve these study aims, this study quantifies the spatiotemporal changes in ESSDI and ESSI. Through this analysis, it not only enhances our understanding of spatial and temporal distribution patterns, but also provides actionable insights for SDG planning.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
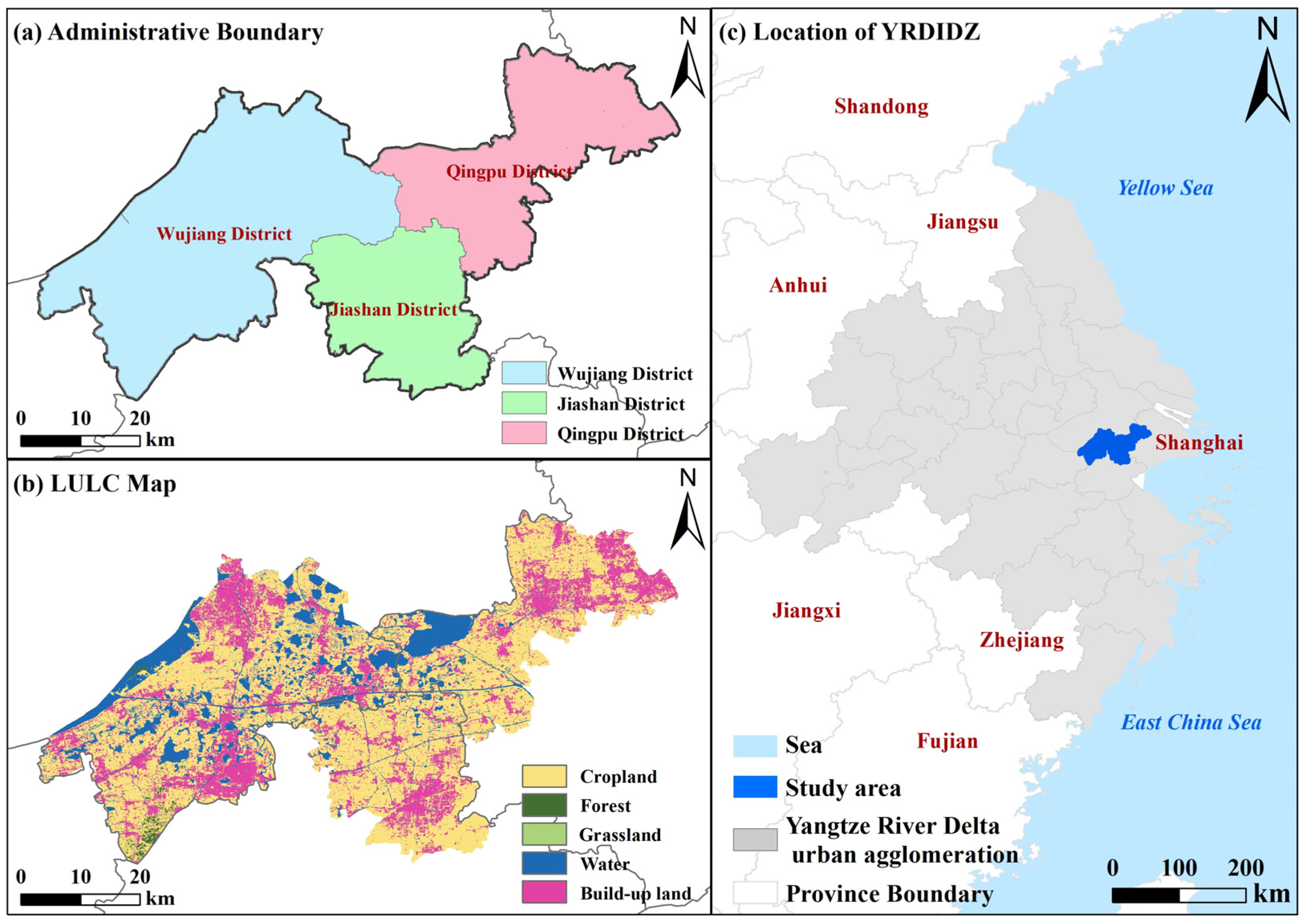
The YRDIDZ, a typical Watertown Region, is strategically positioned at the heart of the Yangtze River Delta, one of China’s most economically dynamic and ecologically significant regions, spanning latitudes 30°52′ to 31°11′ N and longitudes 120°53′ to 121°27′ E. This area encompasses Qingpu District in Shanghai Municipality, Wujiang District in Suzhou city, Jiangsu Province, and Jiashan District in Jiaxing city, Zhejiang Province. Renowned for its intricate water networks (with a density of 6–7 km/km2) and rich ecological resources, this region historically was well-known as a “land of fish and rice”, forming a special river network system within the Yangtze River Delta plain. The YRDIDZ administers 28 towns and covers a total area of approximately 2350 km2 (Figure 1). The terrain is predominantly flat, characterized by a typical subtropical monsoon climate with mild temperatures, abundant rainfall, and an average annual precipitation of 1200 mm. The region experiences four distinct seasons, with an average annual temperature of 16 °C and relative humidity of 75%. As of 2022, the population of the YRDIDZ was approximately 2.57 million, with a total GDP of 451 billion yuan. However, rapid urbanization has exerted immense pressure on the natural environment, resulting in the fragmentation of ecological spaces and a forest coverage rate below the national average, which have hindered the achievement of SDGs [49].
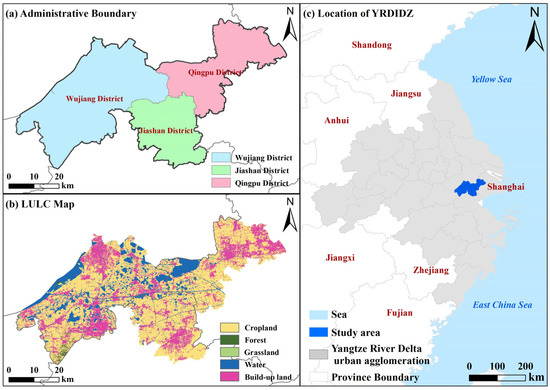
Figure 1.
Study area map. (a) Administrative boundary, (b) LULC map, and (c) location of YRDIDZ.
2.2. Data Sources
To ensure the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the analysis, multiple data sources were utilized in this study. Specifically, the data sources included remote sensing datasets, statistical yearbooks, and administrative division data, as detailed in Table 1. All datasets were rigorously preprocessed to ensure consistency and reliability across the study area.

Table 1.
Used datasets, sources, and brief descriptions.
Based on Table 1, LULC datasets for the year of 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 were used to calculate different ES types. The spatial resolution of the LULC products was 30 m. Precipitation data and evaporation data for the year of 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 were obtained from the China Meteorological Data Service Centre, and were interpolated based on meteorological station monitoring results, with a spatial resolution of 30 m. Depth-to-bedrock data for the year of 2020, representing root depth [50], had a spatial resolution of 100 m. Soil data for the year of 2009, provided by the National Tibetan Plateau Scientific Data Center, included soil name, soil type, soil texture, and soil depth, with a resolution of 1000 m [51]. DEM data for the year of 2009 were acquired from the Geospatial Data Cloud platform, with a resolution of 30 m. Population density data for the years of 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 were acquired from the Worldpop website, which provides annual population density spatial distribution data at a resolution of 100 m. GDP data for the years of 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 were acquired from Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform, which provides GDP spatial distribution data at a resolution of 1000 m [52]. NDVI data for the years of 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 were acquired from National Science & Technology Infrastructure, with a resolution of 30 m [53]. Statistical yearbooks were downloaded from the respective regional governmental websites, including the Qingpu Statistical Yearbook, Jiashan Statistical Yearbook, Wujiang Statistical Yearbook, China Water Resources Bulletin, and China Energy Statistical Yearbook for the years of 2001, 2006, 2011, 2016, and 2021. Administrative division data provided the boundaries of the YRDIDZ at both district and town scales. Given the challenges in acquiring temporally matched depth-to-bedrock, soil, and DEM datasets, coupled with the minimal temporal variation observed in these parameters within the study area over the past two decades, a single-time-period dataset was adopted for the analysis. To ensure consistency across all datasets, a resampling method was applied. Finally, all datasets were processed to a uniform resolution of 30 m and projected in the WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_50N coordinate system.
2.3. Methods
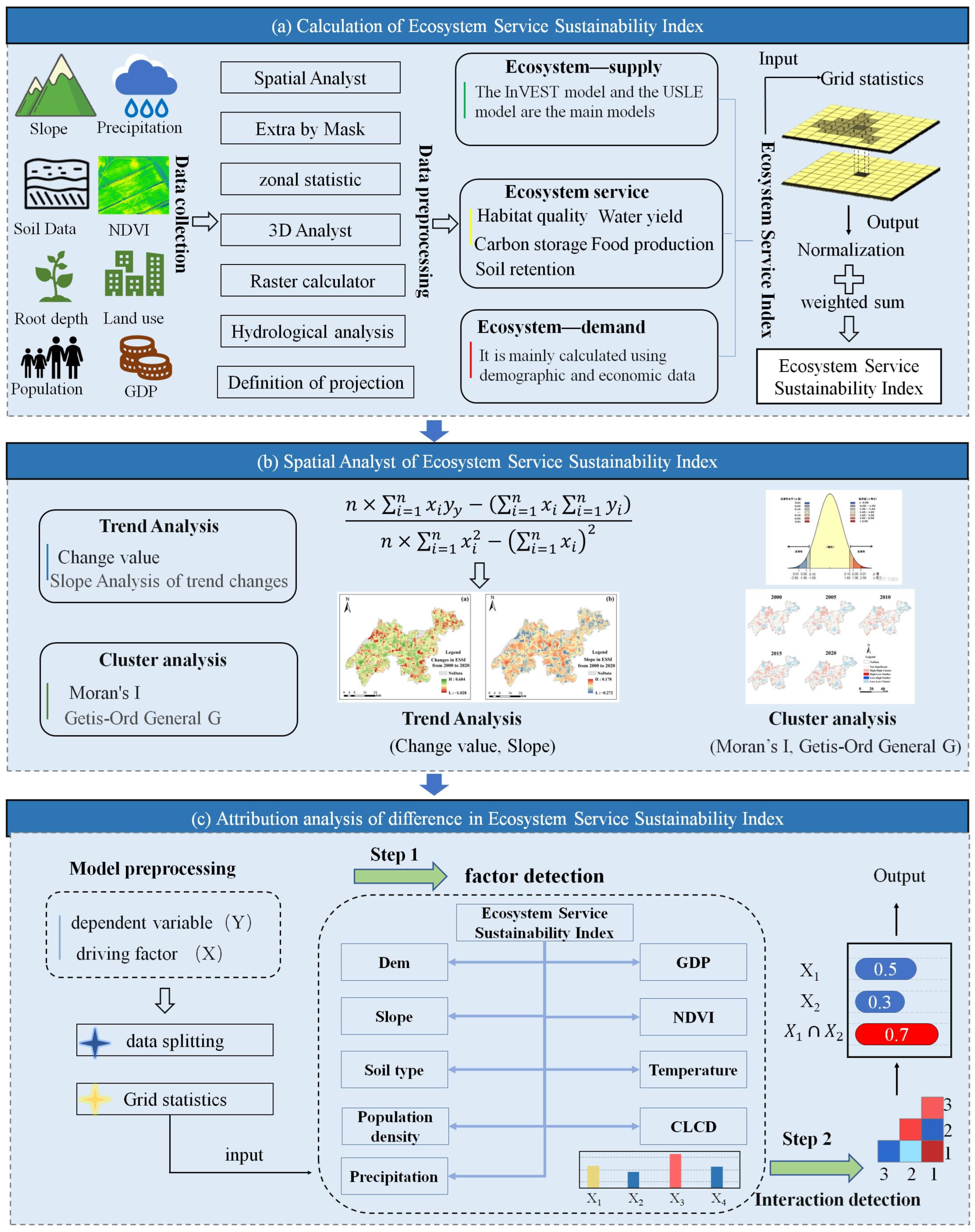
The analysis process mainly includes three parts, which are the calculation of ESSI, spatial analysis of the difference in ESSI, and attribution analysis of the difference in ESSI (Figure 2). The methodology employed in this study comprises five main components: (1) evaluation of the supply of five ES types; (2) evaluation of the demand of five ES types; (3) construction of the ESSDI and ESSI; (4) calculation of the spatial autocorrelation index and change trend values; and (5) calculation of the Geodetector model. Specifically, multiple datasets were collected and processed to calculate the supply and demand capacity of different ES types. These ES types included habitat quality, water yield, carbon storage, crop production, and soil retention. Then, the ESSDI was developed to assess the region’s supply and demand situation of different ES types. Next, a weighted calculation method was applied to build the ESSI to quantitatively evaluate the regional ES sustainable development level. Finally, the Geodetector model was adopted to explore the contributions of different driving factors. In addition, spatiotemporal analysis of ESSI was performed at the town scale. This comprehensive approach provides a robust framework for understanding the dynamics of ES in rapidly urbanizing regions. Section 2.3.1, Section 2.3.2, Section 2.3.3, Section 2.3.4 and Section 2.3.5 provide detailed descriptions of the calculation formulas for each component.
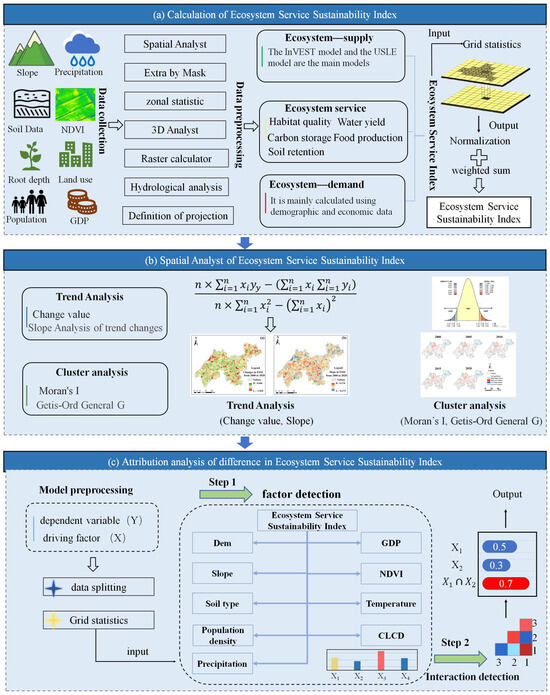
Figure 2.
Analysis process, used datasets, and equations. (a) Calculation of ESSI, (b) spatial analysis of ESSI differences, and (c) attribution analysis of ESSI differences.
2.3.1. Evaluation of the Supply of Five ES Types
Table 2 presents the calculation formulas of the supply of five ES types.

Table 2.
Calculation formulas of the supply of five ES types.
Table 2.
Calculation formulas of the supply of five ES types.
| ES Type | Formulas | Variables | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Service | Habitat Quality [54] | : Habitat degradation degree of grid x in habitat type j. r: Threat source. y: Grid location of threat source r. : Weight of threat factor r (normalized across all threats). : Threat intensity value of threat source r in grid y. : Threat decay function from threat source r in grid y to grid x. : Accessibility/permeability level of threat sources to grid x. : Sensitivity of habitat type j to threat source r (0–1, where 1 = highly sensitive). : Habitat quality of grid x in habitat type j, derived from habitat suitability and degradation. : Habitat suitability index of habitat type j (0–1, where 1 = optimal suitability). h: Half-saturation parameter, controlling the nonlinear response of habitat quality to degradation. | |
| Water Yield [55] | : Annual water yield (mm) for land type j in grid x. : Annual actual evapotranspiration (mm) for land type j in grid x. : Annual precipitation (mm) in grid x. | ||
| Carbon Storage [56] | : Total carbon sequestration (t). : Aboveground biomass carbon stock (t). : Belowground soil carbon stock (t). : Belowground biomass carbon stock (t). : Carbon stock in dead organic matter (t). | ||
| Crop Production [56] | : Allocated food production for grid cell i. : Total food production. : Normalized difference vegetation index for grid cell i. : Sum of the normalized difference vegetation index across all cropland grid cells. | ||
| Soil Retention [56] | : Soil conservation amount for grid cell i. : Potential soil erosion amount for grid cell i. : Actual soil erosion amount for grid cell i. : Rainfall erosivity factor for grid cell i. : Soil erodibility factor for grid cell i. : Slope length factor for grid cell i. : Slope factor for grid cell i. : Water and soil retention factor for grid cell i. : Vegetation coverage factor for grid cell i. | ||
Based on Table 2, the supply of habitat quality was calculated based on the InVEST model [54]. On the basis of existing study [57], both factors were assigned a threat weight of 0.7. The distance–decay functions were linear decay (cropland) and exponential decay (built-up land), respectively. Then, the species habitat preference (HABITAT) and sensitivity to threats (CRP = cropland threat, URB = urban threat) for each LULC type were acquired (Table 3) [57]. In addition, the half-saturation parameter was set to 0.50.

Table 3.
Acquired HABITAT, CRP, and URB values for each LULC type.
The supply of water yield was quantified using the annual water yield module of the InVEST model. This module incorporates factors such as plant-available water, land use types, and soil properties to compute water yield, providing results that are both reliable and closely aligned with real-world conditions. It included precipitation data, evaporation data, root depth data, soil data, and land use data. Among these, precipitation data were acquired based on the Kriging method and meteorological station yearly data. Other datasets were resampled to 30 m. Plant-available water content (PAWC) was calculated based on soil data. Its calculation formula is shown in Equation (9).
where sand%, silt%, and clay% represent the percentage of sand, silt, and clay particles in the soil, respectively. OM denotes the organic matter content of the soil.
In addition, LULC_veg represents the binary code indicating vegetation presence (1 = vegetated, 0 = non-vegetated), root depth (mm) indicates the maximum root depth of dominant vegetation in the LULC class, and Kc shows the crop coefficient [58]. Table 4 shows the biophysical parameter values of different LULC types.

Table 4.
Biophysical parameter values of different LULC types.
The seasonal factor (Z) represents hydrogeological characteristics and the seasonal distribution of precipitation. Its value typically ranges from 1 to 30; in this study, Z = 6.5 was adopted based on regional hydrological conditions. The final modeled outputs were validated against observed surface water yield data from the local Water Resources Bulletin, followed by necessary model calibration.
The carbon storage model within the InVEST model calculates carbon density across various land use types, characterizing the organic carbon content in the ecosystem’s aboveground biomass, belowground biomass, soil, and dead organic matter. The assigned carbon density values (Mg C/ha) for each land use type are summarized in Table 5 [59].

Table 5.
Assigned carbon density values (Mg C/ha) for each LULC type.
For crop production, based on existing research [56], the supply of crop production was estimated by distributing the total crop production based on the ratio of grid-level NDVI to total cropland NDVI.
For soil retention, the calculation of supply was mainly based on the RUSLE equation. For detailed computational formulations, please refer to Reference [60]; a comprehensive description is omitted herein to maintain brevity.
2.3.2. Evaluation of the Demand of Five ES Types
Table 6 shows the calculation formulas of the demand of five ES types.

Table 6.
Calculation formulas of the demand of five ES types.
Table 6.
Calculation formulas of the demand of five ES types.
| ESs Type | Formulas | Variables | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demand Services | Habitat Quality [54] | H: Demand for habitat quality. : Intensity of land use development, which is the percentage of construction land area relative to the total regional land area. : Population density, reflecting the human demand for habitat quality. : GDP per unit area. | |
| Water Yield [55] | : Total water demand (t). : Agricultural irrigation water demand (t). : Industrial water demand (t). : Domestic water demand (t). | ||
| Carbon Storage [61] | : Demand of carbon storage (t). : Per capita carbon emissions (t). : Population density (persons/km2). | ||
| Crop Production [61] | : Food demand. : Per capita food demand. : Population density within the grid. | ||
| Soil Retention [56] | : Actual soil erosion amount for grid cell i. : Rainfall erosivity factor for grid cell i. : Soil erodibility factor for grid cell i. : Slope length factor for grid cell i. : Slope factor for grid cell i. : Water and soil retention factor for grid cell i. : Vegetation coverage factor for grid cell i. | ||
Based on Table 6, habitat quality demand refers to the consumption or desired amount of ES by human society. In this study, this demand is primarily driven by human activities and is calculated based on factors such as population density and land development intensity. Since GDP and population density data are provided at 1 km and 100 m resolutions, respectively, they need to be resampled and recalculated to a 30 m grid. Because the formula employs a logarithmic function, values of population density and GDP below 1 would yield extremely negative outputs, leading to unrealistic negative values in subsequent supply–demand index calculations. To address this, a secondary adjustment was applied: population densities below 1 person per 900 m2 were treated as negligible demand and reassigned a value of 1. This ensured the logarithmic function computes demand as zero, better reflecting real-world conditions.
The demand of carbon storage calculation incorporates population density and per capita energy consumption (in kilograms of standard coal equivalent), multiplied by the carbon emission conversion factor for energy consumption. Based on the relevant literature [62], this conversion factor was assigned a value of 0.67.
For crop production, based on existing research [56], the demand was derived from per capita crop production requirements multiplied by population density.
For water yield, the calculation of demand mainly consisted of three parts, which were agricultural irrigation water demand, industrial water demand, and domestic water demand.
For soil retention, similar to the supply calculation method, the calculation of demand was also based on the RUSLE equation.
2.3.3. Construction of ESSDI and ESSI
After calculating the supply and demand of the five ES types, a normalization method was applied to standardize the results. This study introduced an indicator, the ecosystem service supply–demand Index (ESSDI), to evaluate the balance between the supply and demand of ES in the YRDIDZ. The calculation formula is shown in Equation (15):
where and denote the actual supply and demand of the ith ES type. The ESSDI value ranges from −1 to 1. A value greater than 0 indicates a surplus, while a value less than 0 reflects a deficit or imbalance in the specific ES type.
To measure regional ES sustainability, the ecosystem service sustainability index (ESSI) was also constructed. The calculation formula is shown in Equation (16):
where denotes the weight of ith ES type (set to 0.2 for each type in this study); signifies the ESSDI value of ith ES type.
2.3.4. Calculation of the Spatial Autocorrelation Index and Change Trend Values
Calculation of the Spatial Autocorrelation Index
Spatial autocorrelation refers to the correlation between different locations within spatial data, and is commonly used to investigate the spatial distribution patterns and clustering. Moran’s I coefficient is a widely used metric for this purpose, ranging from −1 to 1. A value greater than 0 indicates positive spatial autocorrelation, while a value less than 0 denotes negative spatial autocorrelation [63,64]. The calculation formula is shown in Equation (17):
where Moran’s I ranges from −1 to 1; i and j represent the indices of polygons, and denotes the spatial weights matrix, which assigns a value of 1 if polygons i and j are adjacent, and 0 if they are not. The variables and correspond to the attribute values at point i and the mean value across the entire study area, respectively.
While Moran’s I coefficient characterizes the degree of spatial autocorrelation, it does not reveal local spatial clustering patterns. Therefore, local autocorrelation indicators, such as Getis–Ord General G* (Gi*) [65,66], LISA (Local Indicator of Spatial Association) [67], and SatScan [68], are used to identify specific clustering conditions. Among these, Gi* is particularly useful for detecting statistically significant spatial clusters, such as hotspots or coldspots, in geographic data. In this study, Gi* was used to analyze the spatial clustering of ESSI. The calculation formulas for Gi* are shown in Equations (18)–(20):
where denotes the spatial weights matrix, which reflects the spatial relationship between the two; is the value of the variable of interest for feature j; and n is the total number of features or locations in the dataset.
Considering that ES is influenced by geographic proximity, Moran’s I ensures spatial dependency is accounted for in subsequent analyses. Gi identified hotspots (high–high clusters) and coldspots (low–low clusters), guiding tailored conservation strategies.
Calculation of the Change Trend Value
The change trend analysis is a useful method to assess the change trend and change intensity of ESSI changes over time. It uses the Ti value to indicate the overall change trend at the gridded level of ESSI [69,70]. If the value of Ti is greater than zero, there exists an improvement in ESSI during the study period. On the contrary, if the value of Ti is less than zero, there exists a deterioration in ESSI during the study period. If the value of Ti equals zero, there exists no change. The calculation formula is shown in Equation (21).
where represents the change trend of ESSI at the ith grid; and n stands for the number of study periods. In this study, it equals 5. denotes the value of ESSI at the ith grid. If is greater than 0, it indicates that ESSI at the ith grid shows an increased change trend. If is less than 0, it indicates that ESSI at the ith grid shows a decreased change trend.
2.3.5. Principles of the Geodetector Model
Spatial stratified heterogeneity is a fundamental characteristic of geographical data. The Geodetector model is a powerful tool for analyzing spatial stratified heterogeneity [71], and uses the q-value to measure the explanatory power of different driving factors. It ranges from 0–1, where a higher value indicates a higher explanatory power. The calculation formula is shown in Equation (22):
where h represents the stratification of the influencing factor; L denotes the total number of strata; Nh and N correspond to the number of units within stratum h and the entire region, respectively; and SSW and SST stand for the sum of within-stratum variances and the total variance across the entire region, respectively. Except for the factor detection, the Geodetector model provides an interaction factor result.
In this study, based on existing research [72,73,74,75], nine potential driving factors were selected to investigate their q-value and interaction q-value. These selected factors were DEM (x1), slope (x2), soil type (Soil) (x3), Population density (POP) (x4), GDP (x5), NDVI (x6), temperature (Tem) (x7), China Land Cover Dataset (CLCD) (x8), and precipitation (Pre) (x9). Among these, for natural factors, DEM and slope affect soil retention and habitat quality, whereas Pre and NDVI determine water yield capacity. For human factors, POP and GDP reflect anthropogenic pressure.
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Change Analysis of ESSDI for the Five ES Types
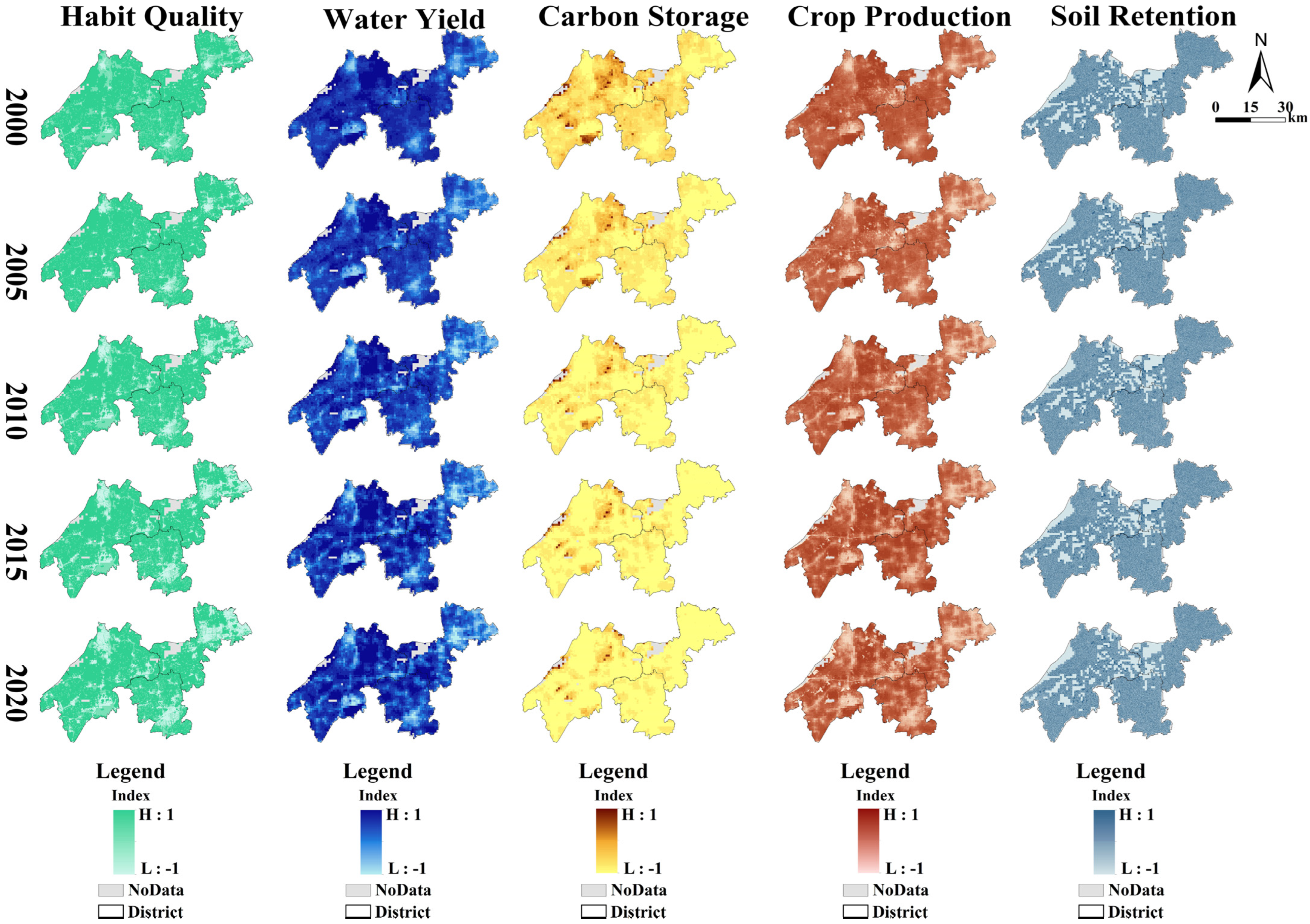
To visualize the spatial distribution of ESSDI values for the five ES types over the past 20 years, ArcGIS 10.8 was used to generate maps, as shown in Figure 3.
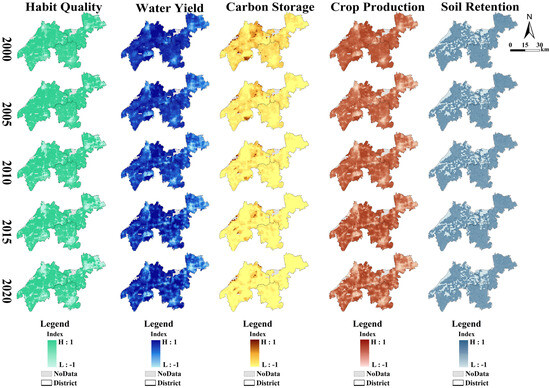
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of ESSDI values for five ES types.
According to Figure 3, in the YRDIDZ zone, the surplus proportions of habitat quality, carbon storage, water yield, and crop production have declined in the past 20 years. Urbanized areas in the eastern, southern, and northwestern sectors of the YRDIDZ exhibited the most pronounced imbalances between supply and demand for these services. Notably, the deficit area for habitat quality expanded significantly from 2010 to 2020. Although the ESSDI value for water yield fluctuated over time, the eastern part of Qingpu District and the southern part of Jiashan District consistently emerged as the primary regions of supply–demand imbalance. The pressure of supply–demand deficits for carbon storage was substantial across the YRDIDZ, with the few areas of balance concentrated near lakes characterized by lower population densities. While the central part of the YRDIDZ maintained a surplus in crop production, the surrounding areas have increasingly been encroached upon by deficit zones in recent years. Due to the intricate river network and dense waterways within the YRDIDZ, the distribution of supply–demand deficits for soil retention was relatively fragmented. The fragmentation of soil retention deficits suggests that localized interventions, such as riparian buffer zones, may be effective in mitigating further degradation. These spatial patterns highlight the growing pressure on ecosystem services in urbanized and densely populated areas, underscoring the need for targeted conservation and restoration efforts.
Using the calculation formulas described earlier, the supply and demand of the five ES types were quantified, and the average ESSDI values were computed. Table 7 presents the average ESSDI values at the district level.

Table 7.
Average ESSDI values of the five ES types at the district level.
According to Table 7, the average ESSDI values for five ES types—habitat quality, carbon storage, crop production, water yield, and soil retention—exhibited a declining trend from 2000 to 2020. Specifically, for habitat quality, the average ESSDI values for the YRDIDZ across the five periods were 0.32, 0.34, 0.29, 0.26, and 0.24, reflecting a decrease of 0.08. This indicates a continuous degradation of regional habitat quality. From 2000 to 2020, ESSDI values were all greater than 0, indicating a surplus state. However, the level of surplus degree was decreased. At the district level, the trends of three districts all showed a decreased trend. For Qingpu District, the ESSDI value decreased from 0.68 in 2000 to 0.42 in 2020, a decline of −0.26. Compared to Jiashan District (−0.18) and Wujiang District (−0.14), the decline in Qingpu District was more severe. All three regions experienced a continuous decline in habitat quality. For carbon storage, the average ESSDI values also showed a continuous decline, with change trend values of −0.25 (Qingpu District), −0.27 (Jiashan District), and −0.30 (Wujiang District). The ESSDI values for the YRDIDZ across the five periods were −0.57, −0.71, −0.78, −0.81, and −0.85. Compared with habitat quality, carbon storage was already in a state of imbalance in 2000, with an initial ESSDI value of −0.57, significantly lower than habitat quality’s 0.32. Overall, carbon storage in the YRDIDZ remained in a significant state of imbalance from 2000 to 2020. For crop production, the average ESSDI value exhibited a fluctuating downward trend, decreasing from 0.39 in 2000 to 0.17 in 2020. At the YRDIDZ level, ESSDI values remained above 0, indicating a surplus. However, at the district level, the trends diverged. Qingpu District experienced a decline of 0.26, from 0.28 in 2000 to 0.02 in 2020. In contrast, Jiashan District and Wujiang District maintained a surplus state throughout the study period, with declines of 0.18 and 0.20, respectively. For soil retention, the average ESSDI values for the YRDIDZ across the five periods were 0.52, 0.51, 0.52, 0.52, and 0.51, showing a slight decrease of 0.0034 from 2000 to 2020. Soil retention remained in a surplus state throughout the study period. At the district level, all three regions exhibited a surplus state with minor fluctuations and minimal differences among them. For water yield, the ESSDI value for the YRDIDZ decreased from 0.51 in 2000 to 0.46 in 2020. However, from 2000 to 2005, the ESSDI value dropped from 0.51 to 0.41 before steadily increasing to 0.46 by 2020. At the district level, the trends mirrored those of the YRDIDZ, with Wujiang District having the highest ESSDI values, followed by Jiashan District and Qingpu District. From 2000 to 2020, three districts were all in a surplus state. Overall, the declining ESSDI trends for habitat quality, carbon storage, crop production, water yield, and soil retention highlight the growing pressure on regional ecosystem services, necessitating targeted interventions to restore balance.
In summary, from 2000 to 2020, the average ESSDI values for all ES types exhibited a declining trend, indicating a reduction in the supply–demand ratio. This trend reflects either a decline in surplus capacity or an intensification of imbalance.
3.2. Spatiotemporal Change Analysis of ESSI from 2000 to 2020 at Different Scales
Using the ESSI calculation formula, the zone statistical method was applied to calculate the average ESSI values at different scales. Table 8 presents the average ESSI values at the YRDIDZ and district scales.

Table 8.
Average ESSI values at different scales.
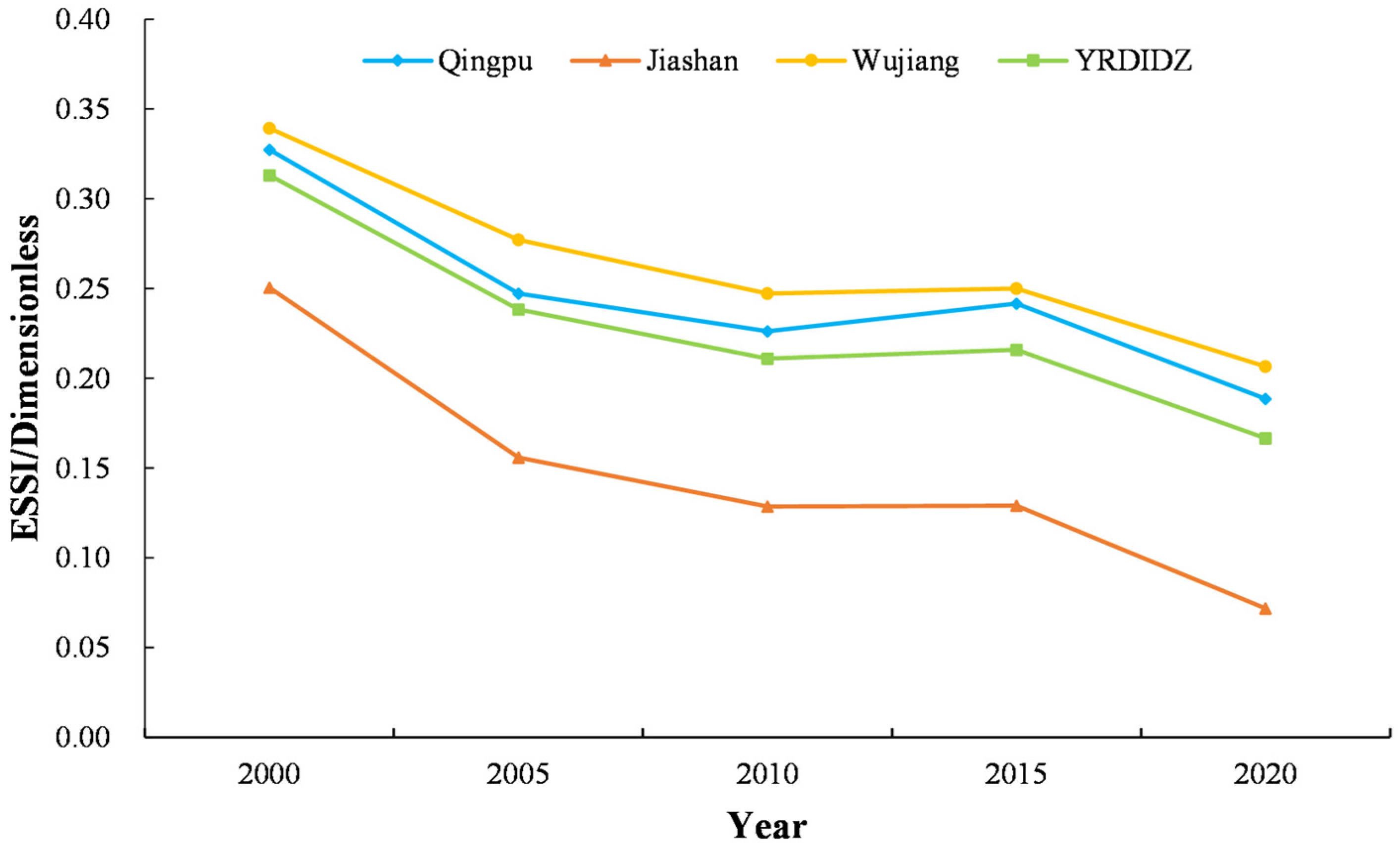
Based on Table 7, the sustainability level of ES types in the YRDIDZ exhibited a declining trend over the past 20 years, with the ESSI value decreasing by 0.15. From 2000 to 2020, the ESSI value was greater than 0. At the district level, all districts’ ESSI values were greater than 0 throughout the study period. Specifically, the ESSI values for the three counties decreased by 0.14 (Qingpu District), 0.18 (Jiashan District), and 0.13 (Wujiang District). Figure 4 illustrates the temporal changes in ESSI from 2000 to 2020. The declining ESSI values across the YRDIDZ and its districts highlight the growing challenges in maintaining ecosystem service sustainability, particularly in urbanized and densely populated areas.
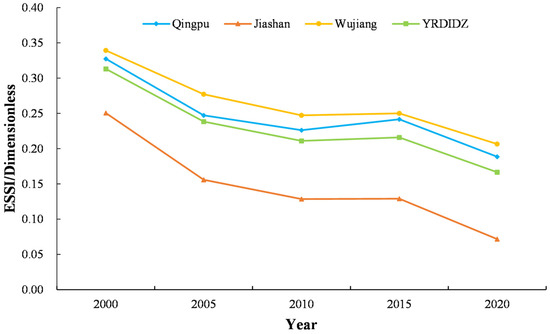
Figure 4.
Line graph of ESSI values for different scales from 2000 to 2020.
As shown in Figure 4, the ESSI values over the past two decades exhibited a fluctuating downward trend. The most significant decline occurred between 2000 and 2005. From 2005 to 2015, the ESSI values showed a fluctuating upward trend, followed by a continued decline from 2015 to 2020. The fluctuating trends in ESSI values highlight the dynamic nature of ecosystem service sustainability, with significant declines in the early 2000s and a partial recovery in the mid-2010s, followed by renewed pressure in recent years.
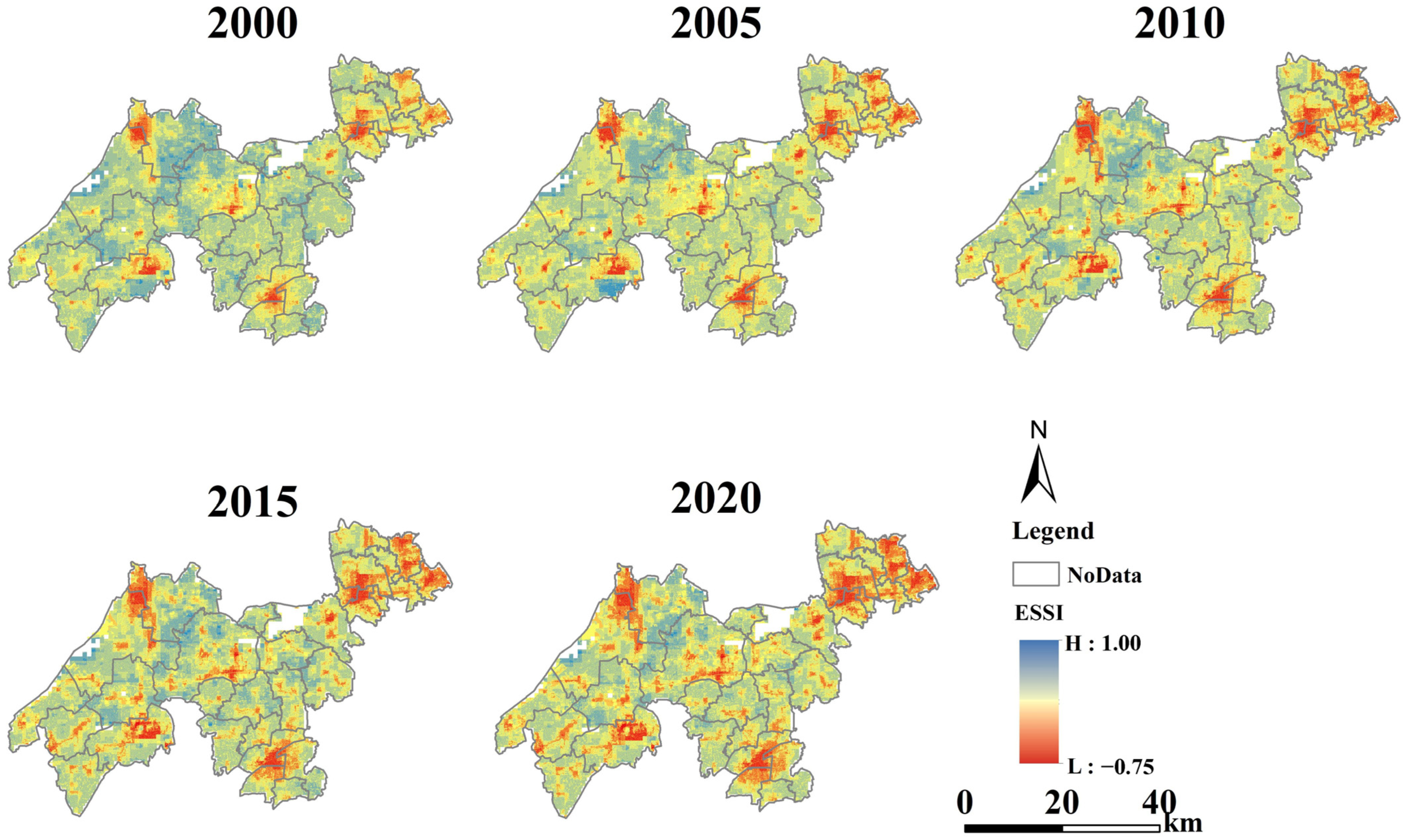
To analyze the spatial distribution of ESSI across different periods, spatial distribution maps were generated using ArcGIS 10.8. Figure 5 illustrates the spatial distribution of ESSI at different periods.
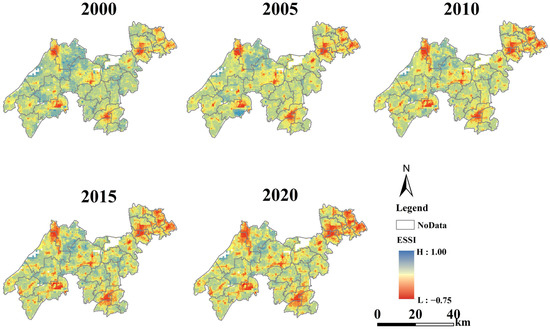
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of ESSI values at different periods.
Based on Figure 5, it was evident that as the years progressed, the sustainability level of ESs within the YRDIDZ was continuously declining, with the area of low sustainability levels expanding annually. Specifically, between 2000 and 2005, the area of low sustainability levels within the YRDIDZ grew at a relatively rapid pace, particularly in the southern part of Wujiang District, the central part of Jiashan District, and the east-central part of the YRDIDZ, all of which experienced varying degrees of expansion. During the period from 2005 to 2020, the spatial distribution of ESSI became relatively more stable, with areas of lower overall levels primarily exhibiting a point-to-area diffusion pattern. The Qingpu urban cluster, the northwestern part of Wujiang District, Shengze town in the south, and the central part of Jiashan District are the main distribution points of low sustainability levels.
Table 9 displays the ESSI values of all towns from 2000 to 2020.

Table 9.
ESSI values of all towns from 2000 to 2020.
As illustrated in Table 9, in the year 2000, the majority of towns were able to maintain a high level of sustainability in their ES ability. However, for Qingpu District, even in 2000, most of its towns exhibited a low level of sustainability in ES ability. Between 2000 and 2005, almost all towns within the YRDIDZ experienced a significant decline in the sustainability level of their ES ability. Some towns, such as Shengze town and Zhenze town in Wujiang District, even transitioned from high to low sustainability levels. From 2015 to 2020, there was another overall decline in the sustainability level of ES within the YRDIDZ, although the rate of decline was lower than that in 2005. In general, the ESSI values for many towns in Qingpu District have consistently decreased, indicating that their ecosystem service sustainability levels have remained at a low level. This is followed by Jiashan District and Wujiang District. However, on a temporal scale, the ESSI values for the vast majority of towns have shown a downward trend from 2000 to 2020.
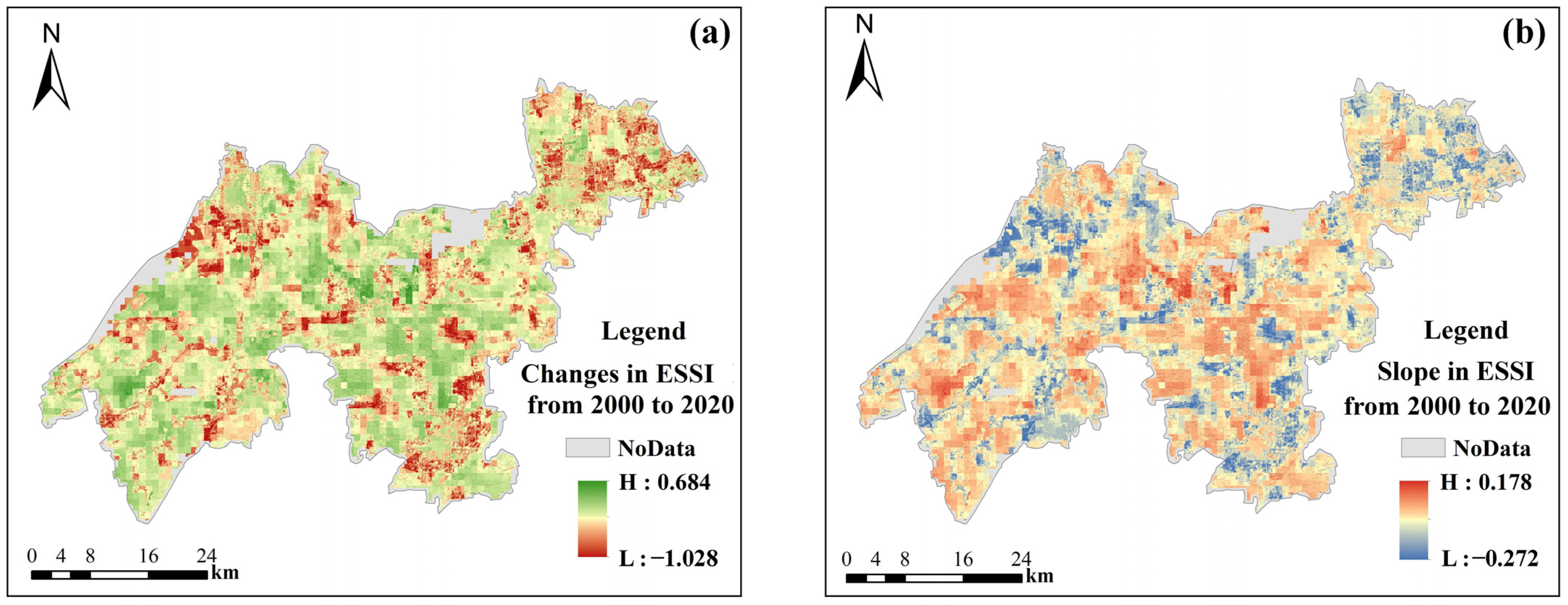
In order to obtain the changes in ESSI from 2000 to 2020, the changes and slope were calculated. Figure 6 represents the changes and slope in ESSI from 2000 to 2020.
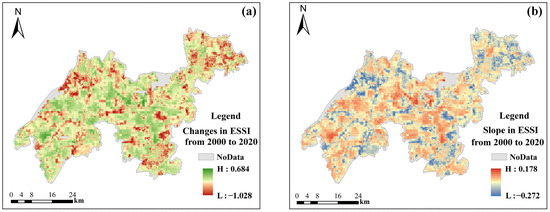
Figure 6.
Changes and slope in ESSI. (a) Changes in ESSI from 2000 to 2020; (b) slope in ESSI from 2000 to 2020.
As illustrated in Figure 6a, the ESSI varied between −1.028 and 0.6840 from 2000 to 2020. Areas with a surplus in ecosystem supply and demand were predominantly located near rivers, lakes, and forested regions, whereas areas with an imbalance were mainly found in developed lands, including the urban areas of Jiashan District and the northern regions of Wujiang District. Within Qingpu District, the ESSI changes were sporadically distributed without distinct high or low clustering zones. Although the spatial extent of ESSI growth areas exceeded that of declining areas, the magnitude of increase was notably less than that of decrease. This, combined with the regional average ESSI over the past two decades, further indicates an overall downward trend in the ESSI values within the YRDIDZ. According to Figure 6b, over the last 20 years, the slope values of ESSI ranged from −0.272 to 0.178, indicating a relatively stable overall trend. Spatially, positive slope values were primarily distributed around Dianshan Lake, Yuandang Lake, Fenhu Lake, Taipu River, and Taihu Lake, as well as in wetland areas within the YRDIDZ. Conversely, negative slope values were mainly found in urban developed lands of Jiashan District, Qingpu District, and Wujiang District.
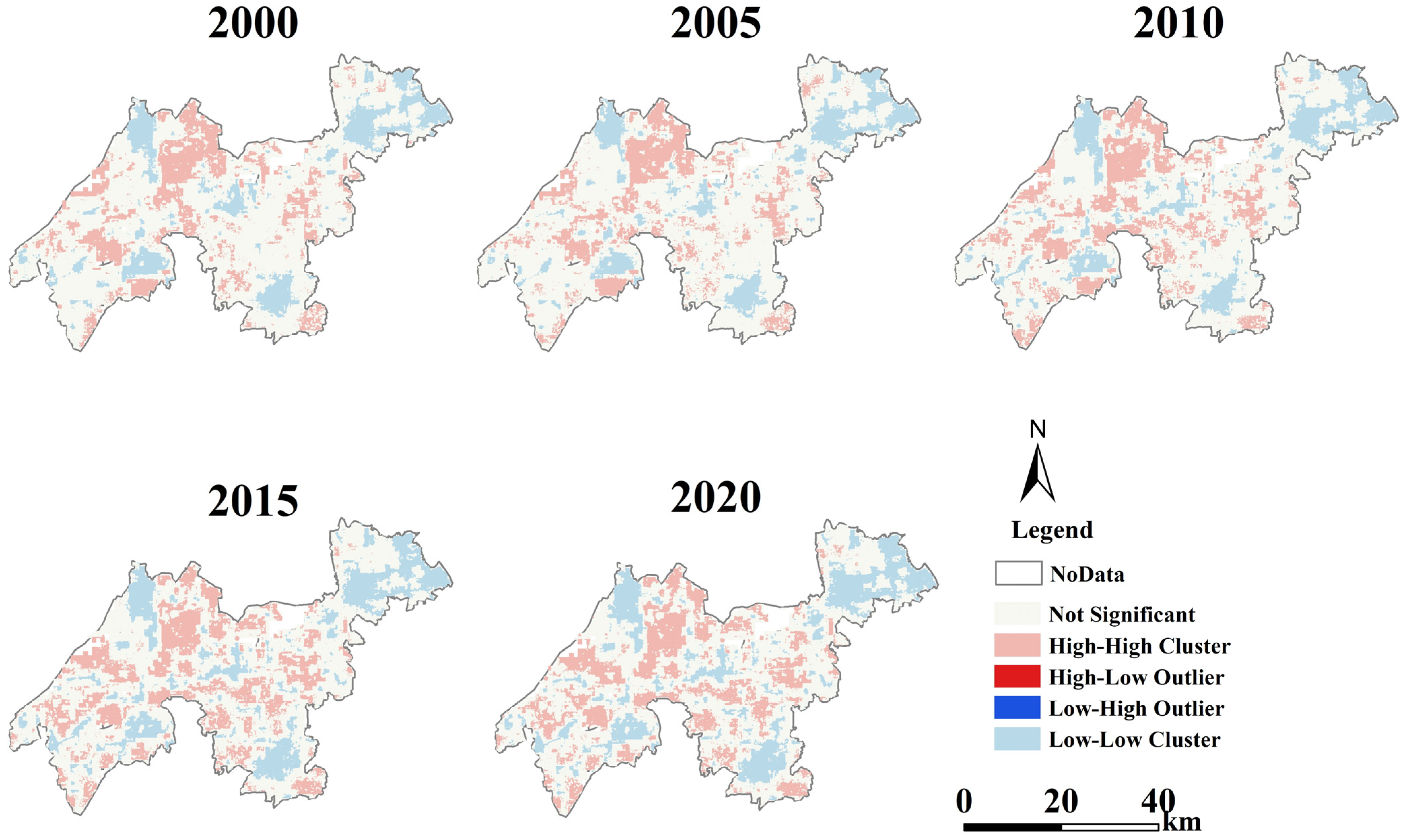
To investigate the spatial autocorrelation situation and the local spatial cluster characteristics, Moran’s I and Gi* indexes were calculated. Specifically, the Moran’s I index values of five periods were 0.9518, 0.9501, 0.9526, 0.9559, and 0.9543, respectively. This indicates that ESSI showed a relatively high spatial cluster effect. In addition, Moran’s I represented an upwards shape, indicating that the spatial cluster effect increased from 2000 to 2020. Figure 7 presents the local spatial cluster result of the Gi* index.
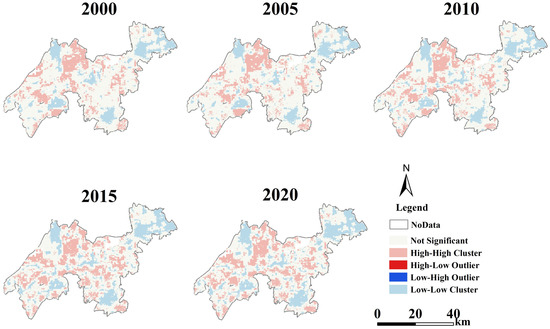
Figure 7.
Local spatial cluster result of the Gi* index from 2000 to 2020.
According to Figure 7, the high–high cluster areas within the YRDIDZ are primarily concentrated along the eastern shore of Taihu Lake, the eastern part of Tongli town, and around wetlands such as Dianshan Lake. The low–low cluster areas are mainly distributed in Shengze town of Wujiang District, the border between Tongli town and Taihu New City, throughout the Qingpu urban cluster, and in the central area of Jiashan urban areas. The low–high and high–low outliers are predominantly scattered and do not exhibit significant clustering characteristics. In terms of spatial extent, the low–low cluster shows a trend of expanding range, especially in the central and southern parts of Jiashan District. Additionally, there is a slight downward trend in the high–high cluster within this region. Furthermore, the extent of high–high cluster areas in the northwestern part of Wujiang District also shows a declining trend. Moreover, the area of low–low cluster in Qingpu District has remained largely unchanged without significant variation.
3.3. Driving Factor Analysis of ESSI
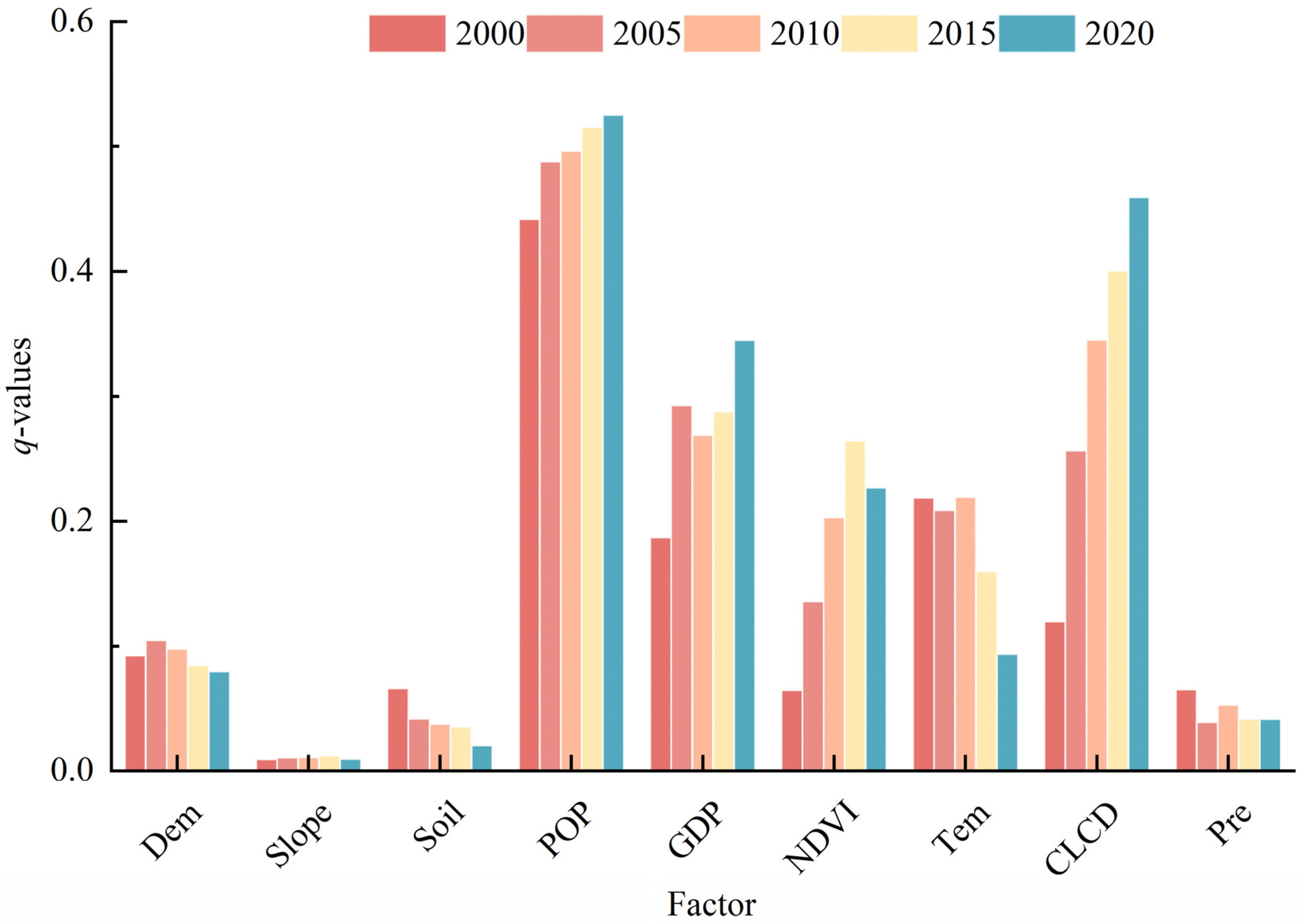
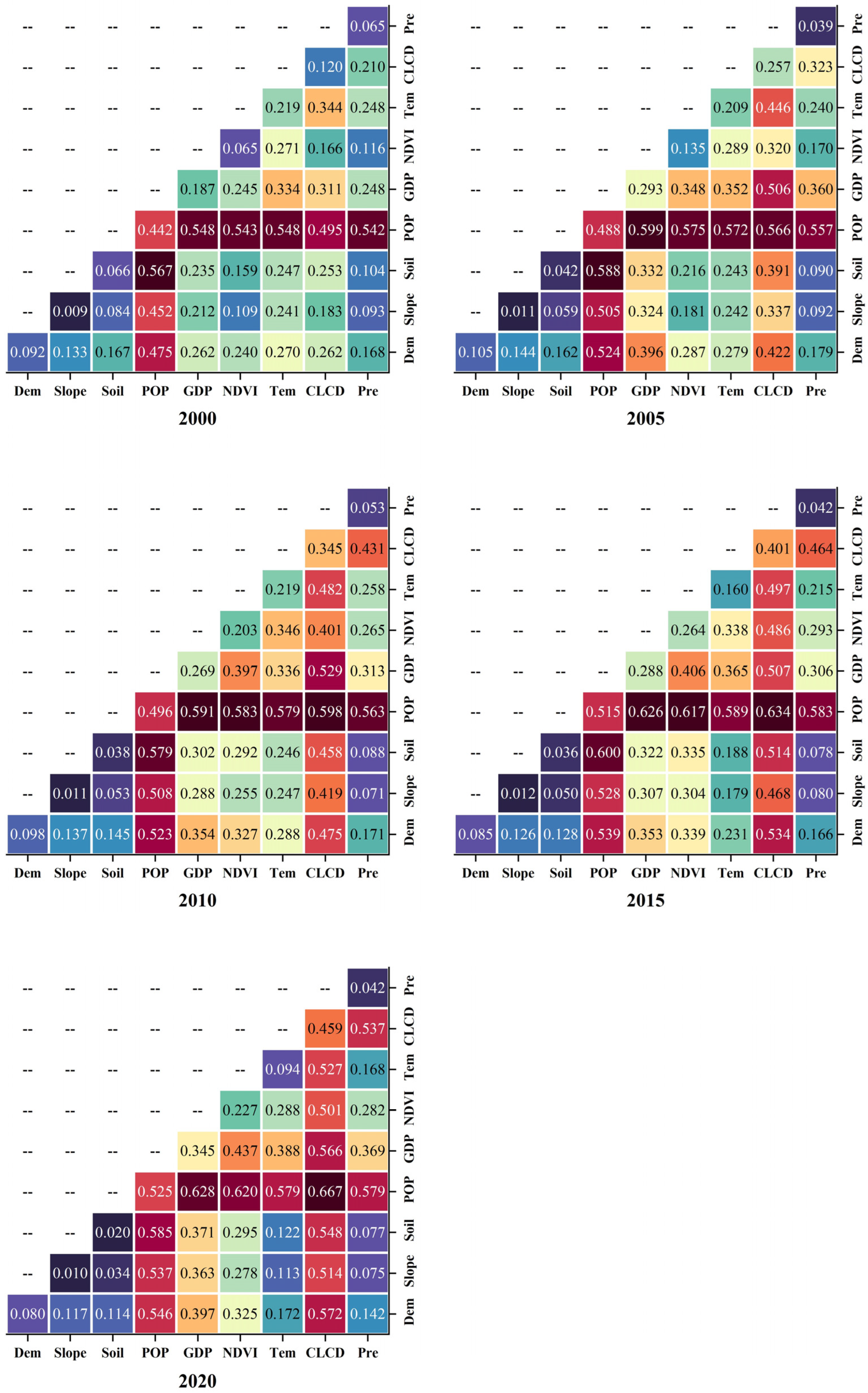
Based on the Geodetector model, the q-values of all selected factors were analyzed. Figure 8 depicts the q-values of each factor in five periods.
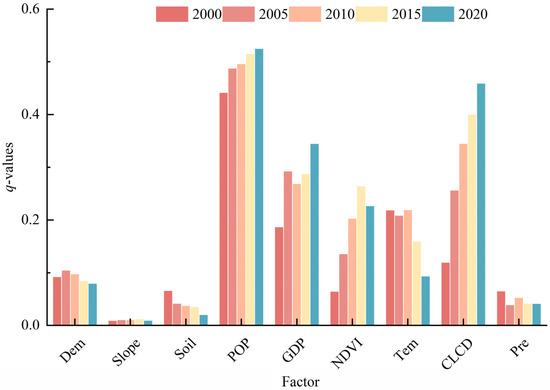
Figure 8.
Five periods’ q-values of each factor.
As depicted in Figure 8, there is a notable disparity in the explanatory power of different factors on the ESSI. Specifically, Dem, Slope, Soil, and Pre exhibit the lowest explanatory power, whereas POP, GDP, and CLCD demonstrate the highest explanatory power, particularly after 2010, where these three indicators rank first, second, and third, respectively. Following these are NDVI, and Tem. From a temporal perspective, compared to the year 2000, by 2020, the explanatory power of all factors had strengthened to some extent. Among these, the GDP indicator experienced the greatest increase in explanatory power, while the POP indicator saw a relatively smaller increase, yet its explanatory power remained the highest in each period. In summary, within the YRDIDZ, socio-economic factors and human activities have a significant impact on the ESSI within the study area, whereas the explanatory power of natural factors is comparatively lower. Generally, the average q-value of each factor from 2000 to 2020 was POP (0.44), GDP (0.26), Soil (0.22), NDVI (0.17), Tem (0.16), Slope (0.13), CLCD (0.12), Pre (0.12), and DEM (0.10), respectively.
In addition to the single factor detection, interaction detection of any two factors at different years were also explored. Figure 9 represents the interaction detection result from 2000 to 2020.
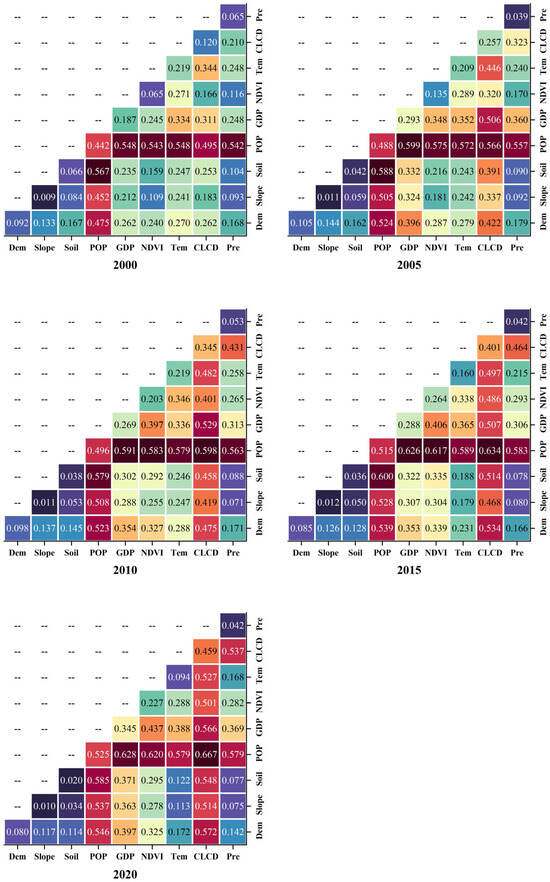
Figure 9.
Interaction detection result from 2000 to 2020.
As illustrated in Figure 9, it is evident that across all study periods, the interaction between the POP factor and other factors consistently manifests as bifactor enhancement. This implies that the interactive effects between the POP factor and other factors exceed the explanatory power of independent factors on the ESSI, particularly the interaction between the POP factor and the Soil factor, which exhibits the highest explanatory capability. This suggests that the spatial variation of ESSI in the study area is not influenced by simple single factors. Notably, while POP and GDP are the two factors with the strongest explanatory power as single factors, the explanatory capability of their interaction is lower than that of the interaction between POP and Soil. Moreover, in the years 2000 and 2015, their interactive explanatory power was also inferior to that of the interaction between POP and Slope.
From a temporal perspective, in the year 2000, among the four pairs with the highest interaction, the interactive explanatory power of the POP and Soil factors was the highest, with a value of 0.567, followed by the interaction between POP and GDP factors (0.548), POP and Tem factors (0.548), and POP and NDVI factors (0.543). In 2005, among the four pairs with the highest interaction, the interactive explanatory power of the POP and GDP factors was the highest, with a value of 0.588, followed by the interaction between POP and GDP factors (0.599), POP and NDVI factors (0.575), and POP and Pre factors (0.4737). In 2010, among the four pairs with the highest interaction, the interactive explanatory power of the POP and Soil factors was the highest, with a value of 0.5402, followed by the interaction between POP and CLCD factors (0.598), POP and GDP factors (0.591), and POP and NDVI factors (0.583). In 2015, among the four pairs with the highest interaction, the interactive explanatory power of the POP and CLCD was the highest, with a value of 0.634, followed by the interaction between POP and GDP factors (0.626), POP and Slope factors (0.617), and POP and NDVI factors (0.617). In 2020, among the four pairs with the highest interaction, the interactive explanatory power of the POP and CLCD factors was the highest, with a value of 0.667, followed by the interaction between POP and GDP factors (0.628), and POP and NDVI factors (0.620).
4. Discussion
4.1. Drivers of ESSDI and ESSI Changes in YRDIDZ
The spatiotemporal evolution patterns of ESSDI and ESSI revealed in this study align with ecosystem service degradation trends observed in rapidly urbanizing regions globally [76,77,78,79,80,81]. However, as a quintessential Jiangnan Watertown Region, the Yangtze River Delta Integration Demonstration Zone (YRDIDZ) exhibits distinct regional specificity derived from its unique natural–human coupled characteristics. Specifically, the ESSDI for habitat quality demonstrated a persistent declining trend. Consistent with Wang et al.’s findings in the Pearl River Delta [76], our analysis identified construction land expansion-induced fragmentation of ecological land as the primary driver of habitat quality degradation in YRDIDZ. Nevertheless, the dense river network characteristic of watertowns confers heightened ecological sensitivity. Between 2000 and 2020, wetland area reduction in the study region—particularly critical for waterbird habitats and water purification—resulted in greater ESSDI declines compared to arid zone studies [35]. This discrepancy underscores the enhanced vulnerability of watertown ecosystems to land use changes.
Regarding water yield, the ESSDI exhibited a fluctuating downward trajectory. Contrary to Yang et al.’s observations in the Pearl River Basin [77], our study revealed a post-2005 recovery trend in water yield ESSDI, partially attributable to integrated watershed management policies implemented following the Taihu Lake cyanobacteria incident. Statistical analyses showed marked improvements in wastewater treatment plant coverage (2000–2020), corroborating the restorative potential of policy interventions on aquatic ecosystem services. These findings challenge conventional “nature-dominated restoration” frameworks, suggesting that engineered measures can enhance supply–demand balance in high-intensity human intervention areas.
In crop production systems, Qingpu District displayed the lowest mean ESSDI, correlating with its land use profile. As per 2024 statistical reports, Qingpu’s rice cultivation area (85.17 km2) remained substantially below that of Wujiang (150.00 km2) and Jiashan (134.67 km2) districts. For soil retention, minimal ESSDI variation across regions likely reflects limited spatial extent and homogeneous soil texture/type characteristics.
Regarding ESSI spatial heterogeneity drivers, while prior studies emphasize GDP and population (POP) pressures on ecosystem service sustainability [82,83,84,85], our study revealed stronger interactive effects between POP and soil factors (q = 0.584). This phenomenon stems from watertown-specific conditions: intensified population agglomeration and persistent polder reclamation in high-density areas. This finding identifies novel regulatory targets for Yangtze River Delta urban–rural integration zones.
4.2. Theoretical Advancements, Limitations and Further Study
This study advances the ecosystem service sustainability assessment methodology and driver analysis while acknowledging limitations. Theoretically, it pioneers a township-scale ESSDI-ESSI index system (30 m spatial resolution) incorporating five ecosystem service types, enabling precise identification of ecological resilience “hotspots” like Jinze Town for targeted governance. Mechanistically, our human–nature coupling analysis via Geodetector revealed POP–Soil synergy (q > 0.5) as a critical ESSI decline driver, surpassing conventional single socio-economic factor frameworks [84,85].
In addition, to enhance regional ES ability, based on the aforementioned analysis, this study proposes the following recommendations to further achieve regional sustainable development goals: Firstly, for the high–high clustering areas of ESSI in Qingpu District, Jiashan District, and Wujiang District, it is necessary to further spatially plan the population distribution pattern to make the spatial distribution more rational. Additionally, during urban construction, the spatial allocation of impervious surfaces and urban green spaces should be balanced to reserve space for regional ecological land, thereby better promoting the harmonious development of human–land relationships. Secondly, when formulating urban planning, the proportion of urban ecological land area must be considered to avoid unlimited urban development. In particular, the area of regional arable land must adhere to the government’s designated red line for arable land, and encroachment on arable land, forest land, and garden land should be prohibited. Lastly, water resources are crucial regional assets, and as a typical area of the watertown, it is essential to protect the significant wetland resources within the region.
Although this study combines multi-source remote sensing and other geospatial data to calculate the spatiotemporal changes in the supply–demand relationship of five ES types in the YRDIDZ from 2000 to 2020, there are still certain shortcomings in the research methodology and time frame that need to be addressed in subsequent studies. Specifically, the following three aspects should be considered: (1) This study only selected five typical types of ecosystem services; however, ecosystems are complex composite systems that include not just these five services but also cultural ecosystem services, among others. Therefore, future evaluations of regional ecosystem services should more comprehensively consider a variety of ecosystem service types. (2) In evaluating ecosystem service types, due to limited spatial data, some calculation methods employed approximate substitutions to represent certain ecosystem service types. With the advent of more emerging technologies, higher quality data acquisition methods are gradually becoming possible, including the emergence of spatiotemporal big data such as social sensing data, providing technical means for more accurate regional ecosystem service evaluations. (3) Limited by data timeliness, this study only analyzed the changes in ESSI in the YRDIDZ from 2000 to 2020. However, since the proposal of the YRDIDZ in 2019, the region has undergone increasingly significant changes in recent years. Therefore, future research should extend the study period to make the evaluation results more current.
4.3. Implications for Global Deltaic Regions
Although this study took the YRDIDZ as the study area, the methodologies and conclusions could provide importance references for global deltaic and rapidly urbanized regions. Firstly, the constructed ESSDI-ESSI index system is suitable for these deltaic regions with fragmented units. The interaction detection results showed that population density and soil type had higher explanatory power, indicating that regions with intensive human activities could exert soil erosion. Secondly, this study found that regions with high ESSI mainly belonged to ecological land and were located in the surrounding areas of large lakes. This could inform regions grappling with similar “aquatic-terrestrial ecotone shrinkage” challenges. It is recommended to delineate a buffer zone from water bodies as priority areas for ecological infrastructure.
5. Conclusions
Based on remote sensing and other geospatial data products, this study evaluated the supply and demand of different ES types from 2000 to 2020. Then, an index named ecosystem service supply–demand index (ESSDI) was constructed to evaluate the supply–demand relationship of different ES types. Next, the ecosystem service sustainability index (ESSI) was also promoted to evaluate the sustainability of regional ES ability. The main research conclusions are as follows: (1) From 2000 to 2020, the mean ESSDI values of habitat quality, carbon storage, crop production, water yield, and soil retention all showed a declining trend. (2) During the same period, the mean ecosystem service sustainability index (ESSI) exhibited a fluctuating downward trend, decreasing from 0.0460 in 2000 to −0.0927 in 2020, with low-value areas expanding as built-up areas grew, while high-value areas were mainly distributed around Dianshan Lake, Yuandang, and parts of Taihu Lake. (3) The primary driving factors within the YRDIDZ were human activity factors, including POP and GDP, with their five-period average explanatory powers being 0.44 and 0.26, respectively, whereas the explanatory power of natural factors was lower. These results of this study could provide actionable ways for regional sustainable governance: (1) prioritizing wetland protection and soil retention in high-population-density areas based on targeted land use quotas; (2) integrating ESSI coldspots (built-up expansion zones) into ecological redline adjustments, maintaining high green infrastructure coverage in new urban areas; and (3) establishing a population–soil co-management framework in agricultural–urban transition zones.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z., C.X. and J.J.; methodology, Z.Z., L.W. (Liang Wang) and W.Z. (Wanglong Zhang); software, Z.Z. and L.W. (Liang Wang); validation, L.W. (Liang Wang), W.Z. (Wanglong Zhang) and Z.Z.; formal analysis, Z.Z., L.W. (Liang Wang) and W.Z. (Wanglong Zhang); investigation, L.W. (Litao Wang); resources, Z.Z. and C.X.; data curation, E.S. and W.Z. (Weiwei Zhang); writing—original draft preparation, Z.Z. and J.J.; writing—review and editing, J.J. and E.S.; visualization, L.W. (Litao Wang); supervision, J.J. and C.X.; project administration, C.X.; funding acquisition, C.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42201132).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank all data providers and platforms for providing the administrative division data and geospatial products.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| CLCD | China Land Cover Dataset |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| ES | Ecosystem Service |
| ESSDI | Ecosystem Service Supply–Demand Index |
| ESSI | Ecosystem Service Sustainability Index |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| Gi* | Getis–Ord General G* |
| InVEST | Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs |
| LULC | Land Use and Land Cover |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| POP | Population Density |
| Pre | Precipitation |
| Tem | Temperature |
| YRDIDZ | Yangtze River Delta Integrated Demonstration Zone |
References
- Danley, B.; Widmark, C. Evaluating conceptual definitions of ecosystem services and their implications. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 126, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, Y.; Pandey, R.; Stringer, L.; Cao, Y.; Bhatt, H.; Luo, R.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Li, S. Characteristics and Framework for Assessing Supply and Demand Relationship for Ecosystem Services Using a Trade-off and Synergy Lens. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 1771–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fentaw, G.; Beneberu, G.; Wondie, A.; Eneyew, B. Ecosystem services of wetlands in the upper Abbay River basin, Ethiopia. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, J. A review of methods for quantifying urban ecosystem services. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2025, 253, 105215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolander, C.; Lundmark, R. A Review of Forest Ecosystem Services and Their Spatial Value Characteristics. Forests 2024, 15, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, L.; Marín, V. Ecosystem services and ecosystem degradation: Environmentalist’s expectation? Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 45, 101177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.; Anderson, S.; Costanza, R.; Kubiszewski, I. The ecological economics of land degradation: Impacts on ecosystem service values. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 129, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, G.; Zwiers, F.; Hu, T. Contribution of urbanization to warming in China. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ferrier, R.; Jenkins, A.; Yuan, J.; Bailey, M.; et al. Forty years of reform and opening up: China’s progress toward a sustainable path. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China Statistical Yearbook (2024); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2024.
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2013 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.; Ren, H.; Zha, C.; Eshetu, S. Monitoring Spatio-Temporal Variations of Ponds in Typical Rural Area in the Huai River Basin of China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, A.; Girardello, M.; Forzieri, G.; Manca, F.; Beck, P.; Cescatti, A.; Strona, G. Assisted tree migration can reduce but not avert the decline of forest ecosystem services in Europe. Glob. Environ. Change 2023, 80, 102676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, S. Ecosystem service decline in response to wetland loss in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 130, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemann, A.; Ring, I. Towards ecosystem service assessment: Developing biophysical indicators for forest ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, L.; Johnson, D.; Atzori, A.; Kaniyamattam, K.; Menendez, H., III. Applying Systems Thinking to Sustainable Beef Production Management: Modeling-Based Evidence for Enhancing Ecosystem Services. Systems 2024, 12, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Shu, C. Integrating System Perspectives to Optimize Ecosystem Service Provision in Urban Ecological Development. Systems 2024, 12, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, L.; Wei, H. Coupling Landscape Connectedness, Ecosystem Service Value, and Resident Welfare in Xining City, Western China. Systems 2023, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Guan, D.; Huang, X.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, M. Evaluation of the cultural ecosystem services of wetland park. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Fan, F. Assessment of ecosystem services in new perspective: A comprehensive ecosystem service index (CESI) as a proxy to integrate multiple ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, D. A comparative analysis of ecosystem service values from various rice farming systems: A field experiment in China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 70, 101664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, H. Simulation and analysis of ecological early-warning of urban construction land expansion based on digital sensing feature recognition and remote sensing spatial analysis technology. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2023, 132, 103484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshetu, S.; Sha, J.; Li, X.; Bao, Z.; Ji, J.; Ji, Z.; Kassaye, A.; Lai, S.; Yang, Y. Ecosystem services dynamics and their influencing factors: Synergies/tradeoffs interactions and implications, the case of upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 938, 173524. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, G.; Day, B.; Binner, A. Multiple-Purchaser Payments for Ecosystem Services: An Exploration Using Spatial Simulation Modelling. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2019, 74, 421–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Verdin, G.; Sanjurjo-Rivera, E.; Galicia, L.; Hernandez-Diaz, J.; Hernandez-Trejo, V.; Marquez-Linares, M. Economic valuation of ecosystem services in Mexico: Current status and trends. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 21, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahimoridi, R.; Kazemi, H.; Kamkar, B.; Nadimi, A.; Hosseinalizadeh, M.; Yeganeh, H. Economic valuation of ecosystem services in canola agroecosystems. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 20, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Shen, X.; Xu, H.; Aili, A. Dynamics of ecosystem service values in the Tarim River Basin. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 12, 1484950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Valette, H.; Mathé, S.; Salles, J. An assessment method of ecosystem services based on stakeholders perceptions: The Rapid Ecosystem Services Participatory Appraisal (RESPA). Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhang, X.; Peng, H. The spatiotemporal changes and trade-off synergistic effects of ecosystem services in the Jianghan Plain of China under different scenarios. Environ. Res. Commun. 2024, 6, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, B. Integrating ecosystem service supply and demand into ecological risk assessment: A comprehensive framework and case study. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2977–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingua, F.; Coops, N.; Griess, V. Valuing cultural ecosystem services combining deep learning and benefit transfer approach. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 58, 101487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, J.; Peng, M.; Li, T.; Wen, D.; Huang, X. Monitoring ecosystem services in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area based on multi-temporal deep learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y. Spatiotemporal analysis of ecological benefits coupling remote sensing ecological index and ecosystem services index. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garshasbi, F.; Ashournejad, Q.; Ghalenoei, N. A comparative assessment of remote sensing based land cover products for economic valuation of ecosystem services of Hyrcanian forests. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 75, 4552–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Mi, J. Detecting the effects of opencast mining on ecosystem services value in arid and semi-arid areas based on time-series remote sensing images and Google Earth Engine (GEE). BMC Ecol. Evol. 2024, 24, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, N.; Han, G.; Li, W.; Batunacun; Bao, Y. Analysis of spatial-temporal variations of grassland gross ecosystem product based on machine learning algorithm and multi-source remote sensing data: A case study of Xilinhot, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 51, e02942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingha, C.; Biber-Freudenberger, L.; Mbanga, L.; Kometa, S. Community-based valuation of wetland ecosystem services: Insights from Bamenda, Cameroon. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2025, 33, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mngadi, M.; Odindi, J.; Mutanga, O.; Sibanda, M. Quantitative remote sensing of forest ecosystem services in sub-Saharan Africa’s urban landscapes: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masenyama, A.; Mutanga, O.; Dube, T.; Bangira, T.; Sibanda, M.; Mabhaudhi, T. A systematic review on the use of remote sensing technologies in quantifying grasslands ecosystem services. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1000–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Lu, M.; Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Yu, D. Multi-scale urban ecosystem service changes and their impact mechanisms on human well-being. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 374, 124117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Su, B.; Beckmann, M.; Fang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, H.; Yan, N.; Volk, M. Emergy-based valuation of glacier ecosystem services: A case from the Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 374, 123966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirons, M.; Comberti, C.; Dunford, R. Valuing Cultural Ecosystem Services. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2016, 41, 545–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comalada, F.; Llorente, O.; Acuña, V.; Saló, J.; Garcia, X. Using georeferenced text from social media to map the cultural ecosystem services of freshwater ecosystems. Ecosyst. Serv. 2025, 72, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Guo, W.; Jiao, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, Y. Development of a decision framework for river health and water yield ecosystem service in watershed. J. Hydrol. 2023, 623, 129773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhao, W.; Ye, J.; Muroki, M.; Pereira, P. Ecosystem carbon sequestration service supports the Sustainable Development Goals progress. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.; Summers, D.; Regan, C.; Abbott, H.; Linden, L.; Frizenschaf, J. Sensitivity analysis in economic evaluation of payments for water and carbon ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 54, 101416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaweepworadej, P.; Evans, K. Tree-cover dynamics in a rapidly urbanising tropical mega-city—Are trees of greater biodiversity and ecosystem service value less likely to be lost? Urban For. Urban Green. 2025, 104, 128669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knegt, B.; Lof, M.; Clec’h, S.; Alkemade, R. Growing mismatches of supply and demand of ecosystem services in the Netherlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, E.; Lin, W.; Li, B.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y. Regional Ecological Security Assessment Based on the Pressure–State–Response Framework: The Demonstration Zone of Yangtze River Delta as an Example. Land 2024, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Wei, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, B. Depth-to-bedrock map of China at a spatial resolution of 100 meters. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environnent Data Center. China Soil Map Based Harmonized World Soil Database (HWSD) (v1.1) (2009); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environnent Data Center: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, D.; Yang, X.; Luo, C. Spatialization Approach to 1km Grid GDP Supported by Remote Sensing. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2005, 7, 120–123. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Dai, J.; Wu, C.; Xia, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Divergent shifts in peak photosynthesis timing of temperate and alpine grasslands in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, V.; Page, S.; Tansey, K.; Jones, L.; Bika, K.; Balzter, H. Tiger Habitat Quality Modelling in Malaysia with Sentinel-2 and InVEST. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Gao, J. Spatial and temporal distribution of supply-demand of ecosystem services in the demonstration zone of green and integrated ecological development of the Yangtze River Delta from the perspective of water-energy-food nexus. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 9430–9445. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Jia, X.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, H.; Wang, H.; Kang, H.; Sun, Y. Spatial-temporal patterns of supply and demand of ecosystem services in the ecological function area of Qin-Ba Mountains. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2023, 32, 2236–2248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Lv, L. Multi-scenario prediction of habitat quality in Nanjing based on FLUS and InVEST models. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2022, 39, 1001–1013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Li, Y.; Du, W. Evaluation on water source conservation capacity and analysis of its variation characteristics of Taihu Lake Basin based on InVEST model. Water Resour. Prot. 2018, 34, 62–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Research of Carbon Storage Changes in Terrestrial Ecosystems Based on InVEST Model in the Yangtze River Delta Region. J. Nanjing Xiaozhuang Univ. 2020, 6, 82–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Tariq, A.; Li, Q.; Ghaffar, B.; Farhan, M.; Jamil, A.; Soufan, W.; Sabagh, A.; Freeshah, M. Soil erosion assessment by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS in an arid zone. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 3105–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Shao, Y.; Pei, B.; Yang, M.; Li, G.; Wen, W.; Yang, K. Spatial-temporal pattern and regional regulation of supply and demand of ecosystem services in the Yangtze River Delta integration demonstration zone. J. East China Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2023, 6, 145–157. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xiang, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, G. Practical Research on Carbon Dioxide Emission Calculation in Iron and Steel Industry. Ind. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2012, 38, 86–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild, M.F. Spatial Autocorrelation. In Catmog 47, Geo Books; University of East Anglia: Norwich, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, D. Spatial Autocorrelation: A Primer. Resource Publications in Geography; Association of American Geographers: Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geogr. Anal. 1992, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics: Distributional Issues and an Application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association-LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulldorff, M. A spatial scan statistic. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 1997, 26, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Jin, B.; Xi, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, R.; Guo, B.; Xu, Z.; et al. Spatiotemporal and Multiscale Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Degree between Economic Development Equality and Eco-Environmental Quality in China from 2001 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pei, T.; Xie, B.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal variation of NDVI in vegetation growing season and its responses to climate factors in mid and eastern Gansu Province from 2008 to 2016. Arid. Land Geogr. 2019, 42, 1427–1435. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Fu, B. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Fu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, Z. Spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem service bundles and the driving factors in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 479, 144006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Meng, X.; Liu, B. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of ecosystem services in the upper Fenhe watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sun, P.; Zhang, J.; Mo, J.; Wang, K. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of ecosystem services’ transformation in the Yellow River basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Hai, X.; Shanguan, Z.; Deng, L. Driving factors of ecosystem services and their spatiotemporal change assessment based on land use types in the Loess Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, W.; Ma, Y.; Bai, X.; Huang, L.; Cheng, S.; Yang, H.; Guo, W. Spatiotemporal dislocation of ecosystem supply and demand services from habitat quality under different development scenarios. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Feng, X.; Yan, H.; Su, M.; Wu, W. Spatiotemporal variation of essential ecosystem services and their trade-off/synergy along with rapid urbanization in the Lower Pearl River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, X.; Fan, Z. Quantitative assessment of the habitat quality dynamics in Yellow River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Tao, Q.; Qiu, J.; Pueppke, S.; Gao, G.; Ou, W. Integrating water quantity- and quality-related ecosystem services into water scarcity assessment: A multi-scenario analysis in the Taihu Basin of China. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 160, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Q. Water Ecosystem Service Quality Evaluation and Value Assessment of Taihu Lake in China. Water 2021, 13, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, F.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Q. The eutrophication variation analysis of Dianshan Lake from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Pollut. Control 2023, 45, 805–809+816. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Han, R.; Yang, S.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Qu, W. Identification of bundles and driving factors of ecosystem services at multiple scales in the eastern China region. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Teng, Y.; Chu, X.; Kumi, M. Spatio-temporal variations of ecosystem services and their drivers in the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Han, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yu, L.; Dong, Y.; Sun, J. Multilevel driving factors affecting ecosystem services and biodiversity dynamics on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 136448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Wu, L.; Li, F.; Lin, C. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Services and the Driving Factors in Urban Agglomerations: Evidence from 12 National Urban Agglomerations in China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 804969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).