Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, and Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of the Traditional Medicinal Plant Matthiola incana (L.) R. Br.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Plant Material and Extraction
2.3. Cytotoxic Activity
2.3.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.3.2. MTT Bioassay
2.3.3. LDH Release
2.4. Antioxidant Activity: Superoxide Radical Scavenging Activity
2.5. Enzyme Inhibition Activity
2.5.1. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Inhibition
2.5.2. Monoamine Oxidase A (MAO-A) Inhibition
2.5.3. Tyrosinase (TYR) Inhibition
2.5.4. Lipase Inhibition
2.5.5. Inhibition of α-Glucosidase (α-GLU)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
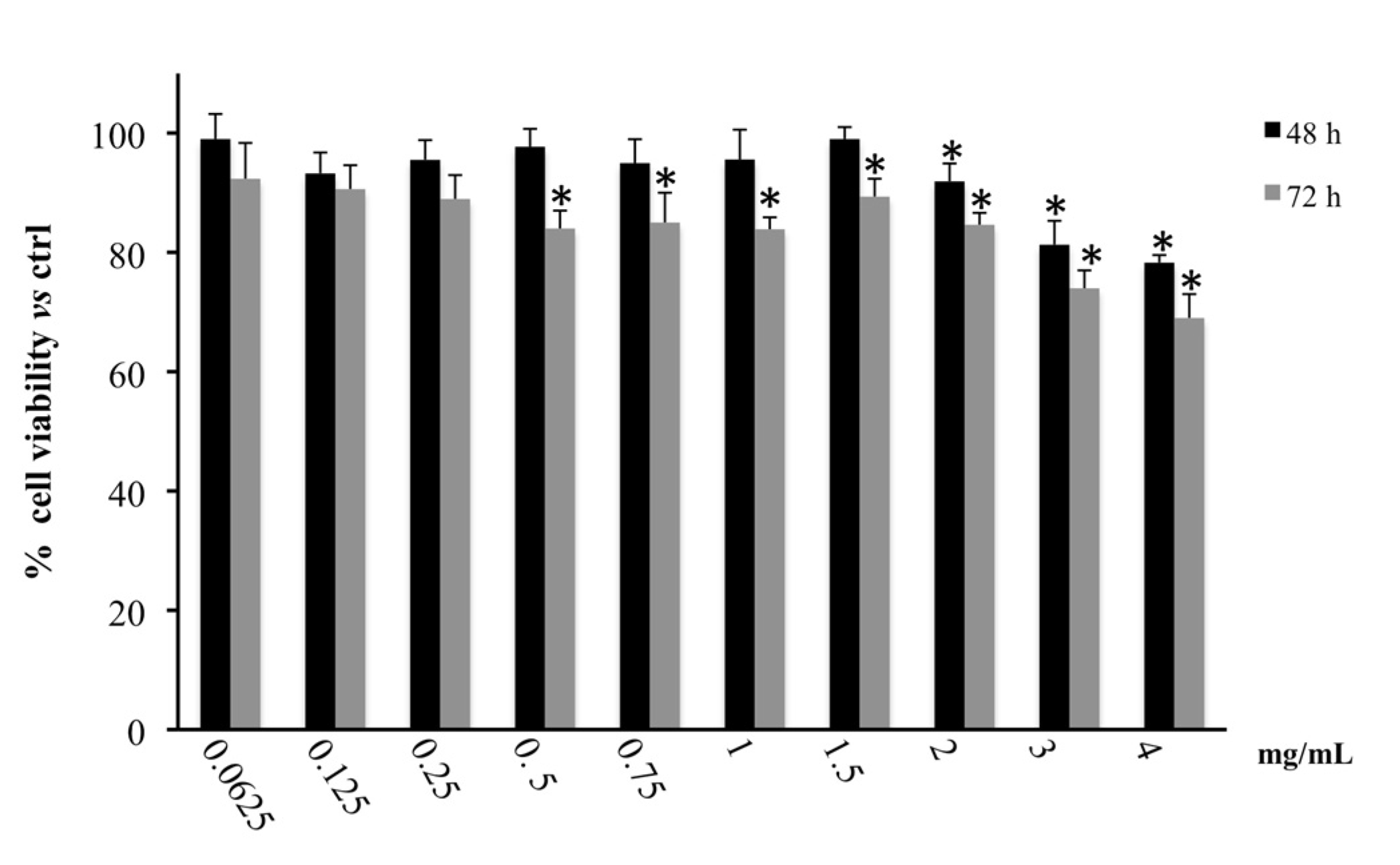
3.1. Cytotoxic Activity
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
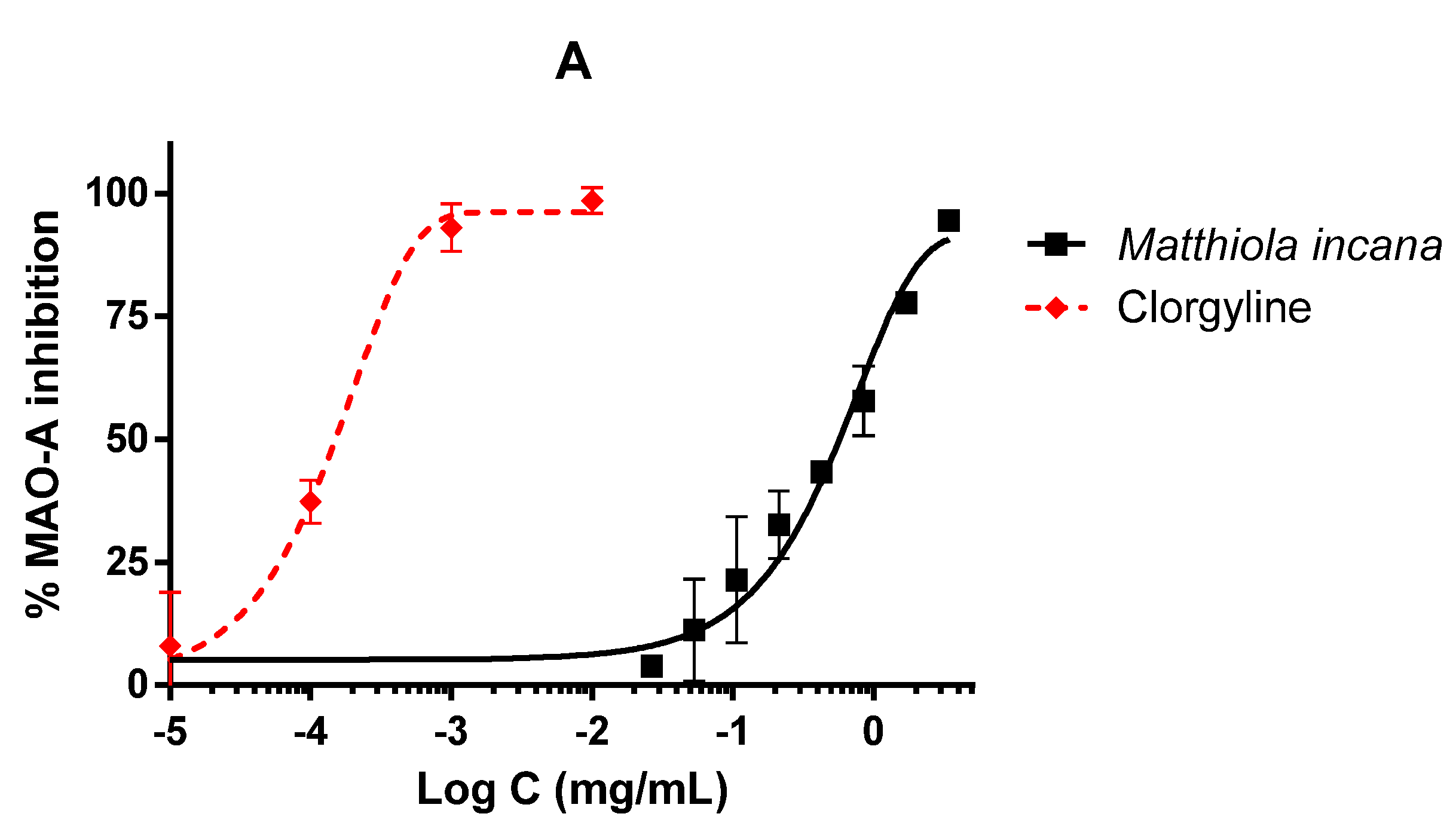
3.3. Inhibitory Activities on CNS Enzymes
3.4. Inhibitory Activities on α-Glucosidase (α-GLU) and Lipase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiersema, J.H.; León, B. World Economic Plants: A Standard Reference; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; p. 436. [Google Scholar]
- Glen, H.F. Cultivated plants of Southern Africa; Jacana Education: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2002; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Emami, S.A.; Sahebkar, A.; Tayarani-Najaran, N.; Tajarani-Najaran, Z. Cancer and its treatment in main ancient books of Islamic Iranian traditional medicine (7th to 14th Century AD). Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2012, 14, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Govind, P. Ethnomedicinal plants for prevention and treatment of tumours. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2009, 3, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Houghton, P.J.; Osibogun, M.I. Flowering plants used against snakebite. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1993, 39, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, R.N.; Nayar, S.L.; Chopra, I.C. Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants; Council of Scientific and Industrial Research: New Delhi, India, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Rasool, N.; Afzal, S.; Riaz, M.; Rashid, U.; Rizwan, K.; Zubair, M.; Ali, S.; Shahid, M. Evaluation of antioxidant activity, cytotoxic studies and GC-MS profiling of Matthiola incana (stock flower). Legume Res. 2013, 36, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cerón Martínez, C.E. Plantas medicinales de los Andes ecuatorianos. In Botánica Económica de los Andes Centrales Moraes; Øllgaard, M.R., Kvist, B., Borchsenius, L.P., Balslev, F.H., Eds.; Universidad Mayor de San Andrés: La Paz, Bolivia, 2006; Volume 42, pp. 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Jerves-Andrade, L.; Leòn-Tamariz, F.; Penaherrera, E.; Cuzco, N.; Tobar, V.; Ansaloni, R.; Wilches, L.M. Medicinal plants used in South Ecuador for gastrointestinal problems: An evaluation of their antibacterial potential. J. Med. Plant Res. 2014, 8, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Macía, M.J.; García, E.; Vidaurre, P.J. An ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants commercialized in the markets of La Paz and En Alto, Bolivia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 97, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, C.; Ballero, M.; Maxia, A. Le piante medicinali utilizzate contro le patologie epidermiche in Ogliastra (Sardegna centro-orientale). Atti Soc. Toscana Sci. Nat. Resid. Pisa Mem. Ser. B 2006, 113, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, T.K. Edible Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Plants; Springer Science & Business Media: New Delhi, India, 2014; Volume 7, pp. 633–637. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Deng, M.; Lv, Z.; Peng, Y. Evaluation of antioxidant activities of extracts from 19 Chinese edible flowers. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, X.B.; Tian, D.Q.; Fang, X.P.; Yu, Y.M.; Zhu, H.Q.; Ge, Y.Y.; Ma, G.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Xiao, W.F.; et al. Antioxidant properties and color parameters of herbal teas in China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 87, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, N.; Cavò, E.; Ragusa, S.; Cacciola, F.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L.; Marino, A.; Cincotta, F.; Condurso, C.; Taviano, M.F. Phytochemical characterization and biological activities of a hydroalcoholic extract obtained from the aerial parts of Matthiola incana (L.) R.Br. subsp. incana (Brassicaceae) growing wild in Sicily (Italy). Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1800677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerit, J.; Edeas, M.; Bricaire, F. Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2004, 5, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregório, B.M.; De Souza, D.B.; de Morais Nascimento, F.A.; Pereira, L.M.; Fernandes-Santos, C. The potential role of antioxidants in metabolic syndrome. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Cong, W.; Ji, S.; Rothman, S.; Maudsley, S.; Martin, B. Metabolic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finberg, J.P.M.; Rabey, J.M. Inhibitors of MAO-A and MAO-B in Psychiatry and Neurology. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Yamashita, D.; Takeda, Y.; Yonemori, S. Screening for tyrosinase inhibitors among extracts of seashore plants and identification of potent inhibitors from Garcinia subelliptica. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampi, R.R.; Tampi, D.J.; Ghori, A.K. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for delirium in older adults. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Dement. 2016, 31, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessesen, D.H.; Van Gaal, L.F. Progress and challenges in anti-obesity pharmacotherapy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaviva, R.; Sorrenti, V.; Santangelo, R.; Cardile, V.; Tomasello, B.; Malfa, G.; Vanella, L.; Amodeo, A.; Mastrojeni, S.; Pugliese, M.; et al. Effects of extract of Celtis aetnensis (Tornab.) Strobltwigs in human colon cancer cell cultures. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfa, G.A.; Tomasello, B.; Sinatra, F.; Villaggio, G.; Amenta, F.; Avola, R.; Renis, M. “Reactive” response evaluation of primary human astrocytes after methylmercury exposure. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Les, F.; Prieto, J.M.; Arbonés-Mainar, J.M.; Valero, M.S.; López, V. Bioactive properties of commercialised pomegranate (Punica granatum) juice: Antioxidant, antiproliferative and enzyme inhibiting activities. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, V.; Les, F.; Iannarelli, R.; Caprioli, G.; Maggi, F. Methanolic extract from red berry-like fruits of Hypericum androsaemum: Chemical characterization and inhibitory potential of central nervous system enzymes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 94, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Les, F.; Arbonés-Mainar, J.M.; Valero, M.S.; López, V. Pomegranate polyphenols and urolithin A inhibit α-glucosidase, dipeptidyl peptidase-4, lipase, triglyceride accumulation and adipogenesis related genes in 3T3-L1 adipocyte-like cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 220, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergent, T.; Ribonnet, L.; Kolosova, A.; Garsou, S.; Schaut, A.; De Saeger, S.; Van Peteghem, C.; Larondelle, Y.; Pussemier, L.; Schneider, Y.J. Molecular and cellular effects of food contaminants and secondary plant components and their plausible interactions at the intestinal level. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 813–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, K.; Vázquez-Salgado, A.M.; Duran-Camacho, G.; Dominguez-Martinez, I.; Benjamín-Rivera, J.A.; Fernández-Vega, L.; Carmona Sarabia, L.; Cruz García, A.; Pérez-Deliz, F.; Méndez Román, J.A.; et al. Iron and copper intracellular chelation as an anticancer drug strategy. Inorganics 2018, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, N.; Filocamo, A.; Ragusa, S.; Cacciola, F.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L.; Celano, M.; Maggisano, V.; Taviano, M.F. Chemical characterization and biological activities of phenolic-rich fraction from cauline leaves of Isatis tinctoria L. (Brassicaceae) growing in Sicily, Italy. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hor, S.L.; Teoh, S.L.; Lim, W.L. Plant polyphenols as neuroprotective agents in Parkinson’s disease Targeting Oxidative Stress. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reglodi, D.; Renaud, J.; Tamas, A.; Tizabi, Y.; Socías, S.B.; Del-Bel, E.; Raisman-Vozari, R. Novel tactics for neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease: Role of antibiotics, polyphenols and neuropeptides. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 155, 120–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidaro, M.C.; Astorino, C.; Petzer, A.; Carradori, S.; Alcaro, F.; Costa, G.; Artese, A.; Rafele, G.; Russo, F.M.; Petzer, J.P.; et al. Kaempferol as selective human MAO-A inhibitor: Analytical detection in calabrian red wines, biological and molecular modeling studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Flores, A.; Fernández, L. Analysis of monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymatic activity by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection combined with an assay of oxidation with a peroxidase and its application to MAO inhibitors from foods and plants. J. Chromatogr. B. Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1073, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Treis, A.; Patenge, N.; Fiesel, F.C.; Springer, W.; Kahle, P.J. Parkin protects against tyrosinase-mediated dopamine neurotoxicity by suppressing stress-activated protein kinase pathways. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 1700–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, Y.N.G.; Hwang, S.H.; Wang, Z.; Lim, S.S. Screening of Peruvian medicinal plants for tyrosinase inhibitory properties: Identification of tyrosinase inhibitors in Hypericum laricifolium Juss. Molecules 2017, 22, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Tao, G.-J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Z.-P. Investigating the inhibitory activity and mechanism differences between norartocarpetin and luteolin for tyrosinase: A combinatory kinetic study and computational simulation analysis. Food Chem. 2017, 223, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr Bouzaiene, N.; Chaabane, F.; Sassi, A.; Chekir-Ghedira, L.; Ghedira, K. Effect of apigenin-7-glucoside, genkwanin and naringenin on tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in B16F10 melanoma cells. Life Sci. 2016, 144, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finicelli, M.; Squillaro, T.; Di Cristo, F.; Di Salle, A.; Melone, M.A.B.; Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G. Metabolic syndrome, Mediterranean diet, and polyphenols: Evidence and perspectives. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5807–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.-Y.; Tain, Y.-L.; Yu, H.-R.; Huang, L.-T. The effects of resveratrol in the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaniv, Z.; Schafferman, D.; Shamir, I.; Madar, Z. Cholesterol and triglyceride reduction in rats fed Matthiola incana seed oil rich in (n-3) fatty acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, R.; Bidel, L.P.R.; Rugani, N.; Perrier, V.; Carrière, F.; Dubreucq, E.; Jay-Allemand, C. Inhibition of CpLIP2 lipase hydrolytic activity by four flavonols (galangin, kaempferol, quercetin, myricetin) compared to orlistat and their binding mechanisms studied by quenching of fluorescence. Molecules 2019, 24, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priscilla, D.H.; Roy, D.; Suresh, A.; Kumar, V.; Thirumurugan, K. Naringenin inhibits α-glucosidase activity: A promising strategy for the regulation of postprandial hyperglycemia in high fat diet fed streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 210, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, G.; Pan, J.; Wang, Y. α-Glucosidase inhibition by luteolin: Kinetics, interaction and molecular docking. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şöhretoğlu, D.; Sari, S. Flavonoids as alpha-glucosidase inhibitors: Mechanistic approaches merged with enzyme kinetics and molecular modelling. Phytochem. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Inhibition Kinetics of Flavonoids on Yeast α-Glucosidase Merged with Docking Simulations. Protein Pept. Lett. 2010, 17, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ado, M.A.; Abas, F.; Mohammed, A.S.; Ghazali, H.M. Anti- and pro-lipase activity of selected medicinal, herbal and aquatic plants, and structure elucidation of an anti-lipase compound. Molecules 2013, 18, 14651–14669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, J.; Xie, X.; Tong, Z.; Li, B.; Li, G.; Lu, G.; Li, W. Naringenin protects against acute pancreatitis in two experimental models in mice by NLRP3 and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 3232491, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, K.; Yuan, C.; Xing, R.; Ni, J.; Hu, G.; Chen, F.; Wang, X. Luteolin protects mice from severe acute pancreatitis by exerting HO-1-mediated anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Villarreal, D.; Camacho, A.; Castro, H.; Ortiz-Lopez, R.; de la Garza, A.L. Anti-obesity effects of kaempferol by inhibiting adipogenesis and increasing lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 75, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taviano, M.F.; Miceli, N.; Acquaviva, R.; Malfa, G.A.; Ragusa, S.; Giordano, D.; Cásedas, G.; Les, F.; López, V. Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, and Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of the Traditional Medicinal Plant Matthiola incana (L.) R. Br. Biology 2020, 9, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9070163
Taviano MF, Miceli N, Acquaviva R, Malfa GA, Ragusa S, Giordano D, Cásedas G, Les F, López V. Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, and Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of the Traditional Medicinal Plant Matthiola incana (L.) R. Br. Biology. 2020; 9(7):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9070163
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaviano, Maria Fernanda, Natalizia Miceli, Rosaria Acquaviva, Giuseppe Antonio Malfa, Salvatore Ragusa, Deborah Giordano, Guillermo Cásedas, Francisco Les, and Víctor López. 2020. "Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, and Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of the Traditional Medicinal Plant Matthiola incana (L.) R. Br." Biology 9, no. 7: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9070163
APA StyleTaviano, M. F., Miceli, N., Acquaviva, R., Malfa, G. A., Ragusa, S., Giordano, D., Cásedas, G., Les, F., & López, V. (2020). Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, and Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of the Traditional Medicinal Plant Matthiola incana (L.) R. Br. Biology, 9(7), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9070163









