Commercial Formulation of Chlorpyrifos Alters Neurological Behaviors and Fertility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Dose Justification
2.5. Behavioral Studies
2.5.1. Exploratory Behavior
2.5.2. Sexual Behavior
2.6. Fertility Test
2.7. Analgesic Effects
2.8. Muscle Strength and Coordination
2.9. Blood Acetylcholinesterase Activity
2.10. Serum Follicular-Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Luteinizing Hormone (LH), and Testosterone Levels
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavior and External Features
3.1.1. Exploratory Behavior
3.1.2. Sexual Behavior
3.2. Effects on Fertility
3.3. Serum FSH, LH, and Testosterone Levels
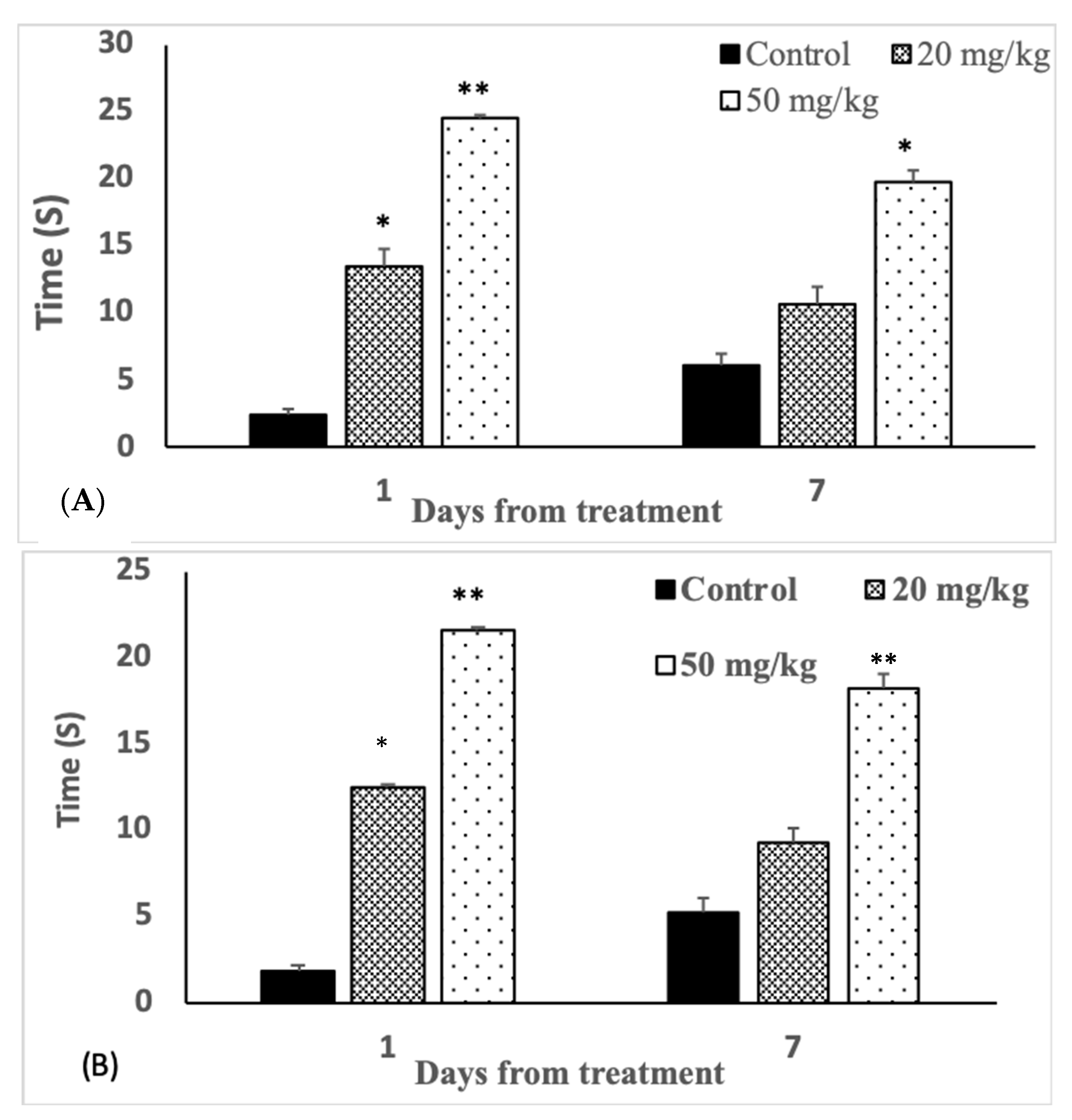
3.4. Analgesic Effects
3.5. Muscle Strength and Coordination
3.6. Blood Acetylcholinesterase Level
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Dose (mg/Kg) | No: Rats Treated | No: Died |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 6 | 0 |
| 2 | 6 | 0 |
| 20 | 6 | 0 |
| 100 | 6 | 6 |
| 200 | 6 | 6 |
References
- Sankoh, A.I.; Whittle, R.; Semple, K.T.; Jones, K.C.; Sweetman, A.J. An assessment of the impacts of pesticide use on the environment and health of rice farmers in Sierra Leone. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Bashir, S.; Irshad, M.; Gupta, S.D.; Dogra, T.D. Effects of acute dimethoate administration on antioxidant status of liver and brain of experimental rats. Toxicology 2005, 206, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiris, L.D.C.; Jayathunga, Y.N.A.; Ratnasooriya, W.D. Antireproductive effects in male rats exposed to methamidophos. Ceylon J. Sci. Biol. Sci. 1995, 24, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Slotkin, T.A.; Seidler, F.J. Developmental neurotoxicity of organophosphates targets cell cycle and apoptosis, revealed by transcriptional profiles in vivo and in vitro. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2012, 34, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Delfino, R.T.; Ribeiro, T.S.; Figueroa-Villar, J.D. Organophosphorus compounds as chemical warfare agents: A review. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 407–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P.; Borges, E.; Dutta, S.; Krajewska-Kulak, E. Decline in sperm count in European men during the past 50 years. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasooriya, W.D.; Jayathunga, Y.N.A.; Peiris, L.D.C. Monocrotophos impairs the fertility of male rats. Med. Sci. Res. 1995, 24, 403–406. [Google Scholar]
- Colović, M.B.; Krstić, D.Z.; Lazarević-Pašti, T.D.; Bondžić, A.M.; Vasić, V.M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Pharmacology and toxicology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.J.; Hein, N.D.; Wijeyesakere, S.J.; Fink, J.K.; Makhaeva, G.F. Neuropathy target esterase (NTE): Overview and future. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 203, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P.; Nwagha, U.; Dutta, S.; Krajewska-Kulak, E.; Izuka, E. Evidence for decreasing sperm count in African population from 1965 to 2015. Afr. Health Sci. 2017, 17, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudavidanage, E.P.; Peiris, D.D. Exposure of judo 40 alters DNA integrity and sperm function of rat Multidisciplinary. EPRA Intern. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2016, 9, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Policy Studies of Sri Lanka (IPS); Cultivation Ministry of Agriculture, Sri Lanka. Better Water, Sustainable Agriculture and Better Lives for Sri Lanka. Paddy Cultivation. Available online: http://www.ips.lk/talkingeconomics/2016/03/22/better-water-sustainable-agriculture-and-better-lives-for-sri-lanka/ (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Schipani, V. The Facts on Chlorpyrifos. Available online: https://www.factcheck.org/2017/04/the-facts-on-chlorpyrifos/ (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Menike, A.M.W.; Shanthini, R.; Kalpage, C.S.; Karunaratne, D.G.G.P.; Kankanamge, A. Chlorpyrifos contamination of fresh water in a commercial vegetable cultivation area in Sri Lanka and factors affecting contamination. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2012, 40, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, Y.; Sabach, S.; Zivan, O.; Dubowski, Y. Key environmental processes affecting the fate of the insecticide chloropyrifos applied to leaves. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dores, E.F.G.C.; Spadotto, C.A.; Weber, O.L.S.; Dalla Villa, R.; Vecchiato, A.B.; Pinto, A.A. Environmental Behavior of Chlorpyrifos and Endosulfan in a Tropical Soil in Central Brazil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3942–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Residue of chlorpyrifos and cypermethrin in vegetables and probabilistic exposure assessment for consumers in Zhejiang Province, China. Food Control 2014, 36, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhees, J.R.; Rohlman, D.S.; Lein, P.J.; Pieper, A.A. Neurotoxicity in Preclinical Models of Occupational Exposure to Organophosphorus Compounds. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuwet, P.; Prapamontol, T.; Chantara, S.; Thavornyuthikarn, P.; Montesano, M.; Whiteheadjr, R.; Barr, D. Concentrations of urinary pesticide metabolites in small-scale farmers in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 407, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, D.T.; Connell, D.; Miller, G.; Chu, C. Probabilistic assessment of chlorpyrifos exposure to rice farmers in Viet Nam. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajah, A.; Thiruchelvam, S. Factors affecting pesticide use by farmers in Vavuniya District. Trop. Agric. Res. 2007, 19, 380–388. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Yokoyama, K. Teratogenicity and developmental toxicity of chlorpyrifos. Reprod. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinham, B. Prolonged exposure to some agricultural pesticides may increase the risk of lung cancer in agricultural workers. Evid. Based Healthc. Public Health 2005, 9, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, M.; du Mortier, C.; Sokolic, T.; Cirelli, A.F. Studies on the Persistence of a Commercial Formulation of Chlorpyrifos on an Agricultural Soil from Provincia de Buenos Aires, República Argentina. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, M.; du Mortier, C.; Fernández Cirelli, A. Behavior of Insecticide Chlorpyrifos on Soils and Sediments with Different Organic Matter Content from Provincia de Buenos Aires, República Argentina. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, P.M.C.S.; van Gestel, C.A.M. Comparative sensitivity of Eisenia andrei and Perionyx excavatus in earthworm avoidance tests using two soil types in the tropics. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1609–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.I.; Van Wijngaarden, R.P.A.; Roessink, I.; Van den Brink, P.J. Effects of time-variable exposure regimes of the insecticide chlorpyrifos on freshwater invertebrate communities in microcosms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Yadav, A.S.; Cheema, N. Genotoxic Effects of Chlorpyrifos in Freshwater Fish Cirrhinus mrigala Using Micronucleus Assay. Adv. Biol. 2016, 2016, 9276963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, K.R.; Giesy, J.P.; Kendall, R.J.; Best, L.B.; Coats, J.R.; Dixon, K.R.; Hooper, M.J.; Kenaga, E.E.; McMurry, S.T. Chlorpyrifos: Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment for Birds and Mammals in Corn Agroecosystems. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2001, 7, 497–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, D.C.; Dhanushka, T. Low doses of chlorpyrifos interfere with spermatogenesis of rats through reduction of sex hormones. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20859–20867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrieri, L.; Della Seta, D.; Canoine, V.; Fusani, L. Developmental exposure to xenoestrogen enhances spatial learning in male rats. Horm. Behav. 2007, 51, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosthuizen, M.K.; Scheibler, A.-G.; Charles Bennett, N.; Amrein, I. Effects of Laboratory Housing on Exploratory Behaviour, Novelty Discrimination and Spatial Reference Memory in a Subterranean, Solitary Rodent, the Cape Mole-Rat (Georychus capensis). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Liang, Y.J.; Sun, Y.J.; Hou, W.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Long, D.X.; Xu, M.Y.; Wu, Y.J. Subchronic neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos, carbaryl, and their combination in rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 29, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccaroni, M.; Della Seta, D.; Farabollini, F.; Fusani, L.; Dessì-Fulgheri, F. Developmental Exposure to Very Low Levels of Ethynilestradiol Affects Anxiety in a Novelty Place Preference Test of Juvenile Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 30, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, C.L.; Isles, A.R.; Humby, T. Measuring risk-taking in mice: Balancing the risk between seeking reward and danger. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 39, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, R.D.; Todd, S.W.; Lumsden, E.; Mullins, R.J.; Mamczarz, J.; Fawcett, W.P.; Gullapalli, R.P.; Randall, W.R.; Pereira, E.F.R.; Albuquerque, E.X. Developmental neurotoxicity of the organophosphorus insecticide chlorpyrifos: From clinical findings to preclinical models and potential mechanisms. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Arredondo, E.; Solís-Heredia, M.d.J.; Rojas-García, E.; Hernández-Ochoa, I.; Quintanilla-Vega, B. Sperm chromatin alteration and DNA damage by methyl-parathion, chlorpyrifos and diazinon and their oxon metabolites in human spermatozoa. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 25, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatem, K.S.; Quinn, J.L.; Phadke, A.; Yu, Q.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Nagaraju, K. Behavioral and Locomotor Measurements Using an Open Field Activity Monitoring System for Skeletal Muscle Diseases. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 51785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.R.; Nemes, C. The exploratory behaviour of rats in the hole-board apparatus: Is head-dipping a valid measure of neophilia? Behav. Processes 2008, 78, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terçariol, P.R.G.; Godinho, A.F. Behavioral effects of acute exposure to the insecticide fipronil. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 99, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmo, A. Male rat sexual behavior. Brain Res. Brain Res. Protoc. 1997, 1, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasoonya, W.D.; Peiris, L.D.C.; Amarasekera, A.S. Analgesic activities of Murraya koengnigii leaf extract. Med. Sci. Res. 1994, 22, 837–840. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnasooriya, W.D.; Peiris, L.D.C.; Jayathunga, Y.N.A. Analgesic and sedative action of monchrotophos following oral administration in rats. Med. Sci. Res. 1995, 23, 401–403. [Google Scholar]
- Antokhin, A.M.; Gainullina, E.T.; Ryzhikov, S.B.; Taranchenko, V.F.; Yavaeva, D.K. Rapid method for measurement of acetylcholinesterase activity. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 147, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, H.J. The Recovery of Plasma Cholinesterase and Erythrocyte Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Workers after Over-exposure to Dichlorvos. Occup. Med. (Chic. Ill). 2000, 50, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaga, K.; Dharmani, C. Sources of exposure to and public health implications of organophosphate pesticides. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2003, 14, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, H.M.T.T.; Tannhauser, S.L.; Tannhauser, M.A.L.L.; Tannhauser, M.A.L.L. The Effects of GABAergic Drugs on Grooming Behaviour in the Open Field. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1994, 74, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, J. Tests for emotionality in rats and mice: A review. Anim. Behav. 1973, 21, 205–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavanja, M.C.R.; Hoppin, J.A.; Kamel, F. Health Effects of Chronic Pesticide Exposure: Cancer and Neurotoxicity. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2004, 25, 155–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durcan, M.J.; Lister, R.G. Does directed exploration influence locomotor activity in a hole board test. Behav. Neural Biol. 1989, 51, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, R.L.; Alugubelly, N.; de Leon, K.; Loyant, L.; Mohammed, A.N.; Patterson, M.E.; Ross, M.K.; Rowbotham, N.E. Inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase by chlorpyrifos in juvenile rats results in altered exploratory and social behavior as adolescents. Neurotoxicology 2020, 77, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beazley-Long, N.; Durrant, A.M.; Swift, M.N.; Donaldson, L.F. The physiological functions of central nervous system pericytes and a potential role in pain. F1000Research 2018, 7, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, A.V. Repeated Exposures to Subthreshold Doses of Chlorpyrifos in Rats: Hippocampal Damage, Impaired Axonal Transport, and Deficits in Spatial Learning. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, J.G.; Taffy Copeman, H. Soman and sarin induce a long-lasting naloxone-reversible analgesia in mice. Life Sci. 1984, 34, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Dick, R.B.; Howell, R.J.; Chrislip, D.W.; Hines, C.J.; Reid, T.M.; Lehman, E.; Laber, P.; Krieg, E.F.; Knott, C. Neurologic function among termiticide applicators exposed to chlorpyrifos. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, A.V.; Gearhart, D.A.; Beck, W.D.; Truan, J.N.; Middlemore, M.-L.M.-L.; Williamson, L.N.; Bartlett, M.G.; Prendergast, M.A.; Sickles, D.W.; Buccafusco, J.J. Chronic, intermittent exposure to chlorpyrifos in rats: Protracted effects on axonal transport, neurotrophin receptors, cholinergic markers, and information processing. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Jenkins, B.; Ames, R.G.; O’Malley, M.; Chrislip, D.; Russo, J. Chronic neurological sequelae to organophosphate pesticide poisoning. Am. J. Public Health 1994, 84, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.; McConnell, R.; Wesseling, C.; Cuadra, R.; Delgado, E.; Torres, E.; Keifer, M.; Lundberg, I. Muscular strength and vibration thresholds during two years after acute poisoning with organophosphate insecticides. Occup. Environ. Med. 2004, 61, e4. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Naughton, S.X.; Wulff, H.; Singh, V.; Beck, W.D.; Magrane, J.; Thomas, B.; Kaidery, N.A.; Hernandez, C.M.; Terry, A.V., Jr. Diisopropylfluorophosphate Impairs the Transport of Membrane-Bound Organelles in Rat Cortical Axons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 356, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambali, S.; Ayo, J. Vitamin C attenuates chronic chlorpyrifos-induced alteration of neurobehavioral parameters in Wistar rats. Toxicol. Int. 2012, 19, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nostrandt, A.C.; Padilla, S.; Moser, V.C. The Relationship of Oral Chlorpyrifos Effects on Behavior, Cholinesterase Inhibition, and Muscarinic Receptor Density in Rat. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1997, 58, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.E.; Richards, P.G. The potential for toxic effects of chronic, low-dose exposure to organophosphates. Toxicol. Lett. 2001, 120, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.P.; Tsutsui, K.; Mohanty, B. Endocrine disrupting pesticides impair the neuroendocrine regulation of reproductive behaviors and secondary sexual characters of red munia (Amandava amandava). Physiol. Behav. 2017, 173, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plant, T.M.; Marshall, G.R. The functional significance of FSH in spermatogenesis and the control of its secretion in male primates. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 764–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, J.; Urakawa, S.; Hori, E.; de Araujo, M.F.P.; Sakuma, Y.; Ono, T.; Nishijo, H. Neuronal Responses in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell during Sexual Behavior in Male Rats. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 1672–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, L.; Stoks, R. Chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative damage is reduced under warming and predation risk: Explaining antagonistic interactions with a pesticide. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 226, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, G.E.; McArthur, S. Estrogen actions in the brain and the basis for differential action in men and women: A case for sex-specific medicines. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 155–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanushka, M.A.T.; Peiris, L.D.C. Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Acephate on Human Sperm. J. Toxicol. 2017, 2017, 3874817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, L.D.C.; Chathu, P.; Perera, D.D.B.D.; Moore, H.D. 1,3-Dinitrobenze-Induced Genotoxicity Through Altering Nuclear Integrity of Diploid and Polyploidy Germ Cells. Dose-Response 2019, 17, 155932581987676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, L.D.; Moore, H.D. Evaluation of effects of 1,3-dinitrobenzene on sperm motility of hamster using computer assisted semen analysis (CASA). Asian J. Androl. 2001, 3, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, A.L.; Sahu, C.R. Emblica officinalis Garten fruits extract ameliorates reproductive injury and oxidative testicular toxicity induced by chlorpyrifos in male rats. Springerplus 2013, 2, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris-John, R.J.; Wickremasinghe, R. Impact of low-level exposure to organophosphates on human reproduction and survival. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauh, V.A.; Perera, F.P.; Horton, M.K.; Whyatt, R.M.; Bansal, R.; Hao, X.; Liu, J.; Barr, D.B.; Slotkin, T.A.; Peterson, B.S. Brain anomalies in children exposed prenatally to a common organophosphate pesticide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7871–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cognez, N.; Warembourg, C.; Zaros, C.; Metten, M.-A.; Bouvier, G.; Garlantézec, R.; Charles, M.-A.; Béranger, R.; Chevrier, C. Residential sources of pesticide exposure during pregnancy and the risks of hypospadias and cryptorchidism: The French ELFE birth cohort. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 76, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Ehrenstein, O.S.; Ling, C.; Cui, X.; Cockburn, M.; Park, A.S.; Yu, F.; Wu, J.; Ritz, B. Prenatal and infant exposure to ambient pesticides and autism spectrum disorder in children: Population based case-control study. BMJ 2019, l962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasinghe, J.; Yu, Q.; Connell, D. Assessment of Health Risk in Human Populations Due to Chlorpyrifos. Toxics 2014, 2, 92–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Post Treatment Day 1 | Post Treatment Day 7 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 20 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | Control | 20 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | |
| Locomotion | 16.0 ± 1.8 | 3.8 ± 1.5 ** | 5.8 ± 1.69 ** | 21.2 ± 2.7 | 19.6 ± 2.5 | 8.0 ± 2.56 ** |
| Rearing | 14.5 ± 3.1 | 6.2 ± 1.58 ** | 2.1 ± 0.72 ** | 7.5 ± 8.22 | 8.22 ± 1.39 | 3.4 ± 1.18 * |
| Frequency of head dipping | 7.7 ± 1.34 | 3.6 ± 1.32 * | 2.0 ± 0.77 ** | 11.6 ± 1.0 | 6.6 ± 0.08 | 3.5 ± 1.23 ** |
| Time/head dip (s) | 1.2 ± 0.36 | 2.1 ± 0.17 * | 2.5 ± 0.13 * | 1.9 ± 0.31 | 1.7 ± 0.21 | 2.3 ± 0.40 * |
| Behavioral Indices | Post-Treatment Day 1 | Post-Treatment Day 7 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 20 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | Control | 20 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | |
| % Mounted | 100 | 80 | 18 * | 100 | 84 | 66 |
| % Intromitted | 100 | 54 * | 18 ** | 100 | 79 | 42 * |
| % Ejaculated | 100 | 45 * | 23 ** | 100 | 58 * | 38 * |
| % Copulatory efficiency | 85 | 60 * | 19 ** | 90 | 68 | 40 * |
| No: of intromissions until the first ejaculation | 17 | 13.5 | 4 ** | 18.5 | 14 | 11 |
| Mounting latency (S) | 44 | 300 ** | 750 ** | 52 | 250 | 650 * |
| Intromission latency (S) | 32 | 400 ** | 700 ** | 30 | 38 | 700 * |
| Ejaculatory latency (S) | 205 | 600 * | 950 ** | 210 | 410 | 850 * |
| Inter-copulatory interval | 74 | 420 ** | 760 ** | 64 | 102 | 418 * |
| Fertility Indices | Post-Treatment Day 1 | Post-Treatment Day 7 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 20 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | Control | 20 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | |
| Libido index | 100 | 66.7 | 33.5 ** | 100 | 77.8 | 55.3 * |
| Fertility index | 100 | 77.7 | 22.2 ** | 100 | 75.5 | 35.2 * |
| Pre-implantation loss | 22.2 ± 4.3 | 20.2 ± 4.2 | 45.1 ± 3.8 * | 20.6 ± 6.2 | 11.8 ± 5.3 | 48.5 ± 8.3 * |
| Post implantation loss | 20.6 ± 6.2 | 16.2 ± 9.2 | 18.1 ± 6.8 | 3.02 ± 0.8 | 12.6 ± 6.3 | 9.9 ± 4.5 * |
| Implantation index | 11.7 ± 0.5 | 11.6 ± 0.7 | 10.0 ± 1.7 | 12.2 ± 0.7 | 11.2 ± 0.8 | 10.3 ± 1.6 |
| Treatment | Post Treatment Day 1 | Post Treatment Day 7 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 20 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | Control | 20 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | |
| Testosterone | 4.0 ± 0.74 | 3.6 ± 0.09 | 2.3 ± 0.55 ** | 3.6 ± 0.14 | 4.4 ± 0.04 | 2.9 ± 0.15 * |
| FSH | 2.76 ± 0.63 | 3.7 ± 0.07 | 2.3 ± 0.45 ** | 3.4 ± 0.12 | 4.0 ± 0.03 | 3.0 ± 0.15 |
| LH | 3.9 ± 0.71 | 3.2 ± 0.08 | 2.2 ± 0.32 ** | 4.7 ± 0.64 | 4.5 ± 0.08 | 3.7 ± 0.25 * |
| Parameters | Post Treatment Day 1 | Post Treatment Day 7 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 20 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | Control | 20 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | |
| Bar test (seconds) | 40.0 ± 5.74 | 36.7 ± 7.09 | 23.3 ± 6.55 ** | 36.6 ± 4.14 | 44.0 ± 3.04 | 34.0 ± 4.15 |
| Bridge test (seconds) | 39.8 ± 1.71 | 37.2 ± 4.8 | 22.0 ± 4.2 ** | 47.8 ± 3.64 | 45.7 ± 4.8 | 35.7 ± 3.25 * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kudavidanage, E.P.; Dissanayake, D.M.I.; Keerthirathna, W.L.R.; Nishshanke, N.L.W.; Peiris, L.D.C. Commercial Formulation of Chlorpyrifos Alters Neurological Behaviors and Fertility. Biology 2020, 9, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9030049
Kudavidanage EP, Dissanayake DMI, Keerthirathna WLR, Nishshanke NLW, Peiris LDC. Commercial Formulation of Chlorpyrifos Alters Neurological Behaviors and Fertility. Biology. 2020; 9(3):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleKudavidanage, Enoka P., D. M. I. Dissanayake, W. L. Rangi Keerthirathna, N. Lasni Wathima Nishshanke, and L. Dinithi C. Peiris. 2020. "Commercial Formulation of Chlorpyrifos Alters Neurological Behaviors and Fertility" Biology 9, no. 3: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9030049
APA StyleKudavidanage, E. P., Dissanayake, D. M. I., Keerthirathna, W. L. R., Nishshanke, N. L. W., & Peiris, L. D. C. (2020). Commercial Formulation of Chlorpyrifos Alters Neurological Behaviors and Fertility. Biology, 9(3), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9030049