Emerging Roles of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. LSEC and Liver Steatosis
2.1. Physiological Role of LSEC in Lipid Transfer
2.2. LSEC Capillarization and Liver Steatosis
2.3. Endothelial Dysfunction and Liver Steatosis
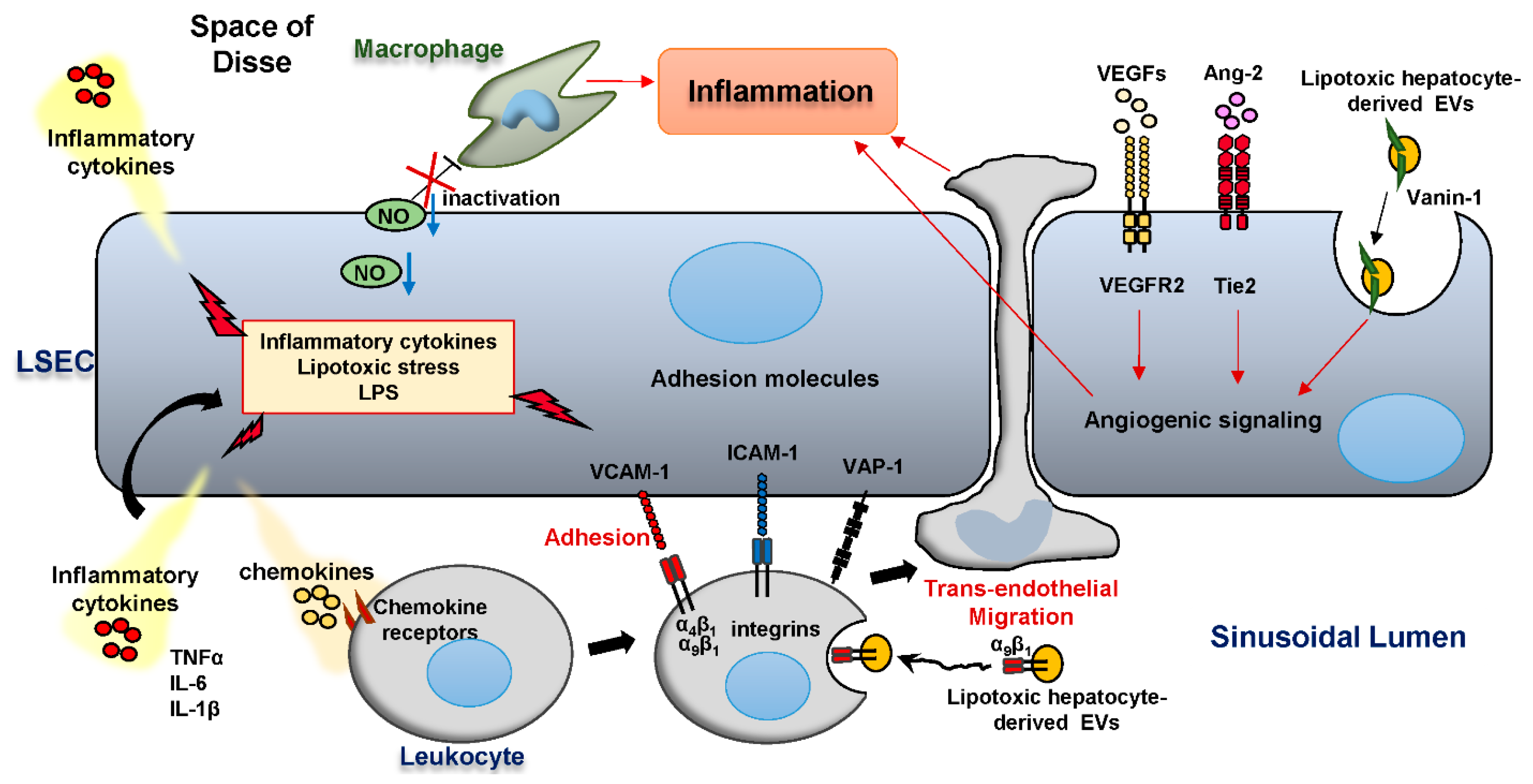
3. LSEC and Liver Inflammation in NASH
3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Roles of LSEC in an Early Stage of NASH
3.2. Pro-Inflammatory Roles of LSEC in NASH
3.3. The Role of LSEC Adhesion Molecules in the Hepatic Leukocyte Recruitment
3.4. Angiogenesis Accelerates Liver Inflammation
4. The Role of LSEC in NASH-Related Fibrosis
Intercellular Communication of LSEC and other Liver Cells via Extracellular Vesicles in NASH Pathogenesis
5. The Role of LSEC in NASH-Associated HCC
6. Conclusions and Reflection
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALD | alcoholic liver disease |
| Ang-2 | angiopoietin-2 |
| CCL | C-C motif chemokine ligand |
| ConA | concanavalin A |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| EV | extracellular vesicle |
| FABP4 | fatty acid binding protein 4 |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HFD | high fat diet |
| HSC | hepatic stellate cells |
| HUVEC | human umbilical vascular endothelial cells |
| ICAM-1 | intracellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| LDL | low density lipoproteins |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| LSEC | liver sinusoidal endothelial cells |
| LYVE-1 | lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 |
| mTOR | mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| NASH | nonalcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NAFLD | nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-kappa B |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| oxLDL | oxidized LDL |
| PEC | peri-tumoral endothelial cells |
| PRR | pattern recognition receptor |
| PLVAP | plasmalemma vesicle-associated protein |
| sIL-6R | soluble interlukine-6 receptor |
| SK1 | sphingosine kinase 1 |
| TECs | tumoral endothelial cells |
| TNFα | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| Tie2 | angiopoietin/tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin-like and EGF-like domains 2 |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| VNN1 | vanin-1 |
| VAP-1 | vascular adhesion protein-1 |
| VCAM-1 | vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VEGFR2 | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 |
| VLCAD | very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase |
| VLDL | very low density lipoproteins |
References
- Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—A global public health perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Ratziu, V.; Loomba, R.; Rinella, M.; Anstee, Q.M.; Goodman, Z.; Bedossa, P.; Geier, A.; Beckebaum, S.; Newsome, P.N.; et al. Obeticholic acid for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Interim analysis from a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 2184–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J. MAFLD: A consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, Y.; Waked, I.; Bollipo, S.; Gomaa, A.; Ajlouni, Y.; Attia, D. What’s in a name? Renaming ‘NAFLD’ to ‘MAFLD’. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Hepatic lipotoxicity and the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The central role of nontriglyceride fatty acid metabolites. Hepatology 2010, 52, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppan, D.; Surabattula, R.; Wang, X.Y. Determinants of fibrosis progression and regression in NASH. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.H.; Hirsova, P.; Tomita, K.; Bronk, S.F.; Werneburg, N.W.; Harrison, S.A.; Goodfellow, V.S.; Malhi, H.; Gores, G.J. Mixed lineage kinase 3 mediates release of C-X-C motif ligand 10-bearing chemotactic extracellular vesicles from lipotoxic hepatocytes. Hepatology 2016, 63, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, K.; Kabashima, A.; Freeman, B.L.; Bronk, S.F.; Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H. Mixed lineage kinase 3 mediates the induction of CXCL10 by a STAT1-dependent mechanism during hepatocyte lipotoxicity. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 3249–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Furuta, K.; Lucien, F.; Gutierrez Sanchez, L.H.; Hirsova, P.; Krishnan, A.; Kabashima, A.; Pavelko, K.D.; Madden, B.; Alhuwaish, H.; et al. Integrin beta1-enriched extracellular vesicles mediate monocyte adhesion and promote liver inflammation in murine NASH. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knolle, P.A.; Wohlleber, D. Immunological functions of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, K.K.; Simon-Santamaria, J.; McCuskey, R.S.; Smedsrod, B. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1751–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahan, R.H.; Porsche, C.E.; Edwards, M.G.; Rosen, H.R. Free fatty acids differentially downregulate chemokines in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Insights into non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoutene, A.; Biquard, L.; Lasselin, J.; Kheloufi, M.; Tanguy, M.; Vion, A.C.; Merian, J.; Colnot, N.; Loyer, X.; Tedgui, A.; et al. A defect in endothelial autophagy occurs in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and promotes inflammation and fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluchowski, N.L.; Becuwe, M.; Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipid droplets and liver disease: From basic biology to clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoutene, A.; Rautou, P.E. Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeve, L.D.; Maretti-Mira, A.C. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell: An Update. Semin. Liver Dis. 2017, 37, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.; Dobbs, B.R.; Rogers, G.W. Lipoproteins and the liver sieve: The role of the fenestrated sinusoidal endothelium in lipoprotein metabolism, atherosclerosis, and cirrhosis. Hepatology 1995, 21, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmer, S.N.; Cogger, V.C.; Fraser, R.; McLean, A.J.; Sullivan, D.; Le Couteur, D.G. Age-related changes in the hepatic sinusoidal endothelium impede lipoprotein transfer in the rat. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrnberger, L.; Hennig, R.; Kremer, W.; Hellerbrand, C.; Goepferich, A.; Kalbitzer, H.R.; Tamm, E.R. Formation of fenestrae in murine liver sinusoids depends on plasmalemma vesicle-associated protein and is required for lipoprotein passage. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Berkel, T.J.; De Rijke, Y.B.; Kruijt, J.K. Different fate in vivo of oxidatively modified low density lipoprotein and acetylated low density lipoprotein in rats. Recognition by various scavenger receptors on Kupffer and endothelial liver cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Oteiza, A.; Sørensen, K.K.; McCourt, P.; Olsen, R.; Smedsrød, B.; Svistounov, D. Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and stabilins in elimination of oxidized low-density lipoproteins. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G71–G81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Virella, M.F.; Virella, G.; Orchard, T.J.; Koskinen, S.; Evans, R.W.; Becker, D.J.; Forrest, K.Y. Antibodies to oxidized LDL and LDL-containing immune complexes as risk factors for coronary artery disease in diabetes mellitus. Clin. Immunol. 1999, 90, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, D. Low density lipoprotein oxidation and its pathobiological significance. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20963–20966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogger, V.C.; Mohamad, M.; Solon-Biet, S.M.; Senior, A.M.; Warren, A.; O’Reilly, J.N.; Tung, B.T.; Svistounov, D.; McMahon, A.C.; Fraser, R.; et al. Dietary macronutrients and the aging liver sinusoidal endothelial cell. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 310, H1064–H1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyao, M.; Kotani, H.; Ishida, T.; Kawai, C.; Manabe, S.; Abiru, H.; Tamaki, K. Pivotal role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in NAFLD/NASH progression. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 1130–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kus, E.; Kaczara, P.; Czyzynska-Cichon, I.; Szafranska, K.; Zapotoczny, B.; Kij, A.; Sowinska, A.; Kotlinowski, J.; Mateuszuk, L.; Czarnowska, E.; et al. LSEC fenestrae are preserved despite pro-inflammatory phenotype of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in mice on high fat diet. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, W.; Tian, L.; Quan, J.; Wang, Y.; Niu, R. oxLDL induces injury and defenestration of human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells via LOX1. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 53, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, J.N.; Cogger, V.C.; Fraser, R.; Le Couteur, D.G. The effect of feeding and fasting on fenestrations in the liver sinusoidal endothelial cell. Pathology 2010, 42, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, A.; Frank, D.N.; Harnke, B.; Bambha, K. Systematic review: Microbial dysbiosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, B.R.; Rogers, G.W.; Xing, H.Y.; Fraser, R. Endotoxin-induced defenestration of the hepatic sinusoidal endothelium: A factor in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis? Liver 1994, 14, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, F.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francque, S.; Verrijken, A.; Mertens, I.; Hubens, G.; Van Marck, E.; Pelckmans, P.; Van Gaal, L.; Michielsen, P. Noncirrhotic human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induces portal hypertension in relation to the histological degree of steatosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 22, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francque, S.; Laleman, W.; Verbeke, L.; Van Steenkiste, C.; Casteleyn, C.; Kwanten, W.; Van Dyck, C.; D’Hondt, M.; Ramon, A.; Vermeulen, W.; et al. Increased intrahepatic resistance in severe steatosis: Endothelial dysfunction, vasoconstrictor overproduction and altered microvascular architecture. Lab. Investig. 2012, 92, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, F.D.; Suzuki, A.; Sanderson, S.O.; Lindor, K.D.; Angulo, P. Prevalence and indicators of portal hypertension in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1028–1033.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baffy, G. Origins of portal hypertension in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, S.; Yang, W.; Winslet, M.C.; Seifalian, A.M. Impairment of hepatic microcirculation in fatty liver. Microcirculation 2003, 10, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammer, A.J.; Anderson, T.; Celermajer, D.S.; Creager, M.A.; Deanfield, J.; Ganz, P.; Hamburg, N.M.; Lüscher, T.F.; Shechter, M.; Taddei, S.; et al. The assessment of endothelial function: From research into clinical practice. Circulation 2012, 126, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateya, S.; Rizzo, N.O.; Handa, P.; Cheng, A.M.; Morgan-Stevenson, V.; Daum, G.; Clowes, A.W.; Morton, G.J.; Schwartz, M.W.; Kim, F. Endothelial NO/cGMP/VASP signaling attenuates Kupffer cell activation and hepatic insulin resistance induced by high-fat feeding. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2792–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasarín, M.; La Mura, V.; Gracia-Sancho, J.; García-Calderó, H.; Rodríguez-Vilarrupla, A.; García-Pagán, J.C.; Bosch, J.; Abraldes, J.G. Sinusoidal endothelial dysfunction precedes inflammation and fibrosis in a model of NAFLD. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Paredes, F.J.; Hernández Mesa, G.; Morales Arraez, D.; Marcelino Reyes, R.; Abrante, B.; Diaz-Flores, F.; Salido, E.; Quintero, E.; Hernández-Guerra, M. Contribution of cyclooxygenase end products and oxidative stress to intrahepatic endothelial dysfunction in early non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Lezana, T.; Raurell, I.; Bravo, M.; Torres-Arauz, M.; Salcedo, M.T.; Santiago, A.; Schoenenberger, A.; Manichanh, C.; Genescà, J.; Martell, M.; et al. Restoration of a healthy intestinal microbiota normalizes portal hypertension in a rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnani, M.; Chen, H.; Barr, V.A.; Quon, M.J. Insulin-stimulated activation of eNOS is independent of Ca2+ but requires phosphorylation by Akt at Ser (1179). J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30392–30398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, J.X.; Yamaguchi, K.; Taruno, A.; Katsuyama, M.; Iwata, K.; Ibi, M.; et al. The NOX1 isoform of NADPH oxidase is involved in dysfunction of liver sinusoids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 115, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, L.; Dombrowski, F.; Lendeckel, U.; Schulz, C.; Gardemann, A.; Keilhoff, G. Impairment of endothelial nitric oxide synthase causes abnormal fat and glycogen deposition in liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1782, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L. Energy metabolism in the liver. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulias, P.T.; Tenopoulou, M.; Greene, J.L.; Raju, K.; Ischiropoulos, H. Nitric oxide regulates mitochondrial fatty acid metabolism through reversible protein S-nitrosylation. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, rs1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knolle, P.A.; Schmitt, E.; Jin, S.; Germann, T.; Duchmann, R.; Hegenbarth, S.; Gerken, G.; Lohse, A.W. Induction of cytokine production in naive CD4(+) T cells by antigen-presenting murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells but failure to induce differentiation toward Th1 cells. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limmer, A.; Ohl, J.; Kurts, C.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Reiss, Y.; Groettrup, M.; Momburg, F.; Arnold, B.; Knolle, P.A. Efficient presentation of exogenous antigen by liver endothelial cells to CD8+ T cells results in antigen-specific T-cell tolerance. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Mates, J.M.; Cheplowitz, A.M.; Hammer, L.P.; Maiseyeu, A.; Phillips, G.S.; Wewers, M.D.; Rajaram, M.V.; Robinson, J.M.; Anderson, C.L.; et al. Blood-borne lipopolysaccharide is rapidly eliminated by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells via high-density lipoprotein. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2390–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrig, A.; Banafsche, R.; Kremer, M.; Hegenbarth, S.; Hamann, A.; Neurath, M.; Gerken, G.; Limmer, A.; Knolle, P.A. Development and functional consequences of LPS tolerance in sinusoidal endothelial cells of the liver. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Armas, M.; Simon-Santamaria, J.; Pettersen, I.; Moens, U.; Smedsrød, B.; Sveinbjørnsson, B. Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) is present in murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) and mediates the effect of CpG-oligonucleotides. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, E.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Krux, F.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. Toll-like receptor-induced innate immune responses in non-parenchymal liver cells are cell type-specific. Immunology 2010, 129, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, F.; Tacke, F. Roles for chemokines in liver disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 577–594.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyachi, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Komiya, C.; Shiba, K.; Shimazu, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Deushi, M.; Osaka, M.; Inoue, K.; Sato, Y.; et al. Roles for cell-cell adhesion and contact in obesity-induced hepatic myeloid cell accumulation and glucose intolerance. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 2766–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.; Lalor, P.F.; Adams, D.H. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells—gatekeepers of hepatic immunity. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.; Johnston, B.; Lee, S.S.; Bullard, D.C.; Smith, C.W.; Beaudet, A.L.; Kubes, P. A minimal role for selectins in the recruitment of leukocytes into the inflamed liver microvasculature. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.H.; Hubscher, S.G.; Fisher, N.C.; Williams, A.; Robinson, M. Expression of e-selectin and e-selectin ligands in human liver inflammation. Hepatology 1996, 24, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalor, P.F.; Sun, P.J.; Weston, C.J.; Martin-Santos, A.; Wakelam, M.J.; Adams, D.H. Activation of vascular adhesion protein-1 on liver endothelium results in an NF-kappaB-dependent increase in lymphocyte adhesion. Hepatology 2007, 45, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinall, A.I.; Curbishley, S.M.; Lalor, P.F.; Weston, C.J.; Blahova, M.; Liaskou, E.; Adams, R.M.; Holt, A.P.; Adams, D.H. CX(3)CR1 and vascular adhesion protein-1-dependent recruitment of CD16(+) monocytes across human liver sinusoidal endothelium. Hepatology 2010, 51, 2030–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, D.A.; Wilson, G.K.; Bailey, D.; Shaw, R.K.; Jalkanen, S.; Salmi, M.; Rot, A.; Weston, C.J.; Adams, D.H.; Shetty, S. Human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells promote intracellular crawling of lymphocytes during recruitment: A new step in migration. Hepatology 2017, 65, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, C.J.; Shepherd, E.L.; Claridge, L.C.; Rantakari, P.; Curbishley, S.M.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Hubscher, S.G.; Reynolds, G.M.; Aalto, K.; Anstee, Q.M.; et al. Vascular adhesion protein-1 promotes liver inflammation and drives hepatic fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefere, S.; Van de Velde, F.; Devisscher, L.; Bekaert, M.; Raevens, S.; Verhelst, X.; Van Nieuwenhove, Y.; Praet, M.; Hoorens, A.; Van Steenkiste, C.; et al. Serum vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 predicts significant liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, R.P.; Liu, Y.; Iyer, S.S.; Liu, S.; Gupta, B.; Desai, C.; Kumar, P.; Smith, T.; Singhi, A.D.; Nusrat, A.; et al. Blocking integrin α(4)β(7)-mediated CD4 T cell recruitment to the intestine and liver protects mice from western diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhood, A.; McGuire, G.M.; Manning, A.M.; Miyasaka, M.; Smith, C.W.; Jaeschke, H. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) expression and its role in neutrophil-induced ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat liver. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1995, 57, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douds, A.C.; Lim, A.G.; Jazrawi, R.P.; Finlayson, C.; Maxwell, J.D. Serum intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in alcoholic liver disease and its relationship with histological disease severity. J. Hepatol. 1997, 26, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essani, N.A.; Fisher, M.A.; Farhood, A.; Manning, A.M.; Smith, C.W.; Jaeschke, H. Cytokine-induced upregulation of hepatic intercellular adhesion molecule-1 messenger RNA expression and its role in the pathophysiology of murine endotoxin shock and acute liver failure. Hepatology 1995, 21, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H.; Farhood, A.; Bautista, A.P.; Spolarics, Z.; Spitzer, J.J.; Smith, C.W. Functional inactivation of neutrophils with a Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) monoclonal antibody protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat liver. Hepatology 1993, 17, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, P.; Sjöström, M.; Söderberg, C.; Kinnman, N.; Stål, P.; Hultcrantz, R. Attenuated liver fibrosis after bile duct ligation and defective hepatic stellate cell activation in neural cell adhesion molecule knockout mice. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonder, C.S.; Norman, M.U.; Swain, M.G.; Zbytnuik, L.D.; Yamanouchi, J.; Santamaria, P.; Ajuebor, M.; Salmi, M.; Jalkanen, S.; Kubes, P. Rules of recruitment for Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes in inflamed liver: A role for alpha-4 integrin and vascular adhesion protein-1. Immunity 2005, 23, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkijärvi, R.; Adams, D.H.; Leino, R.; Möttönen, T.; Jalkanen, S.; Salmi, M. Circulating form of human vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1): Increased serum levels in inflammatory liver diseases. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pober, J.S.; Sessa, W.C. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, B.S.; Nolan, D.J.; Butler, J.M.; James, D.; Babazadeh, A.O.; Rosenwaks, Z.; Mittal, V.; Kobayashi, H.; Shido, K.; Lyden, D.; et al. Inductive angiocrine signals from sinusoidal endothelium are required for liver regeneration. Nature 2010, 468, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; El-Assal, O.N.; Ono, T.; Yamanoi, A.; Dhar, D.K.; Nagasue, N. Sinusoidal endothelial cell proliferation and expression of angiopoietin/Tie family in regenerating rat liver. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Kwon, J.; Popov, Y.; Gajdos, G.B.; Ordog, T.; Brekken, R.A.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Schuppan, D.; Bi, Y.; Simonetto, D.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes fibrosis resolution and repair in mice. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1339–1350.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk Akcora, B.; Storm, G.; Prakash, J.; Bansal, R. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor BIBF1120 ameliorates inflammation, angiogenesis and fibrosis in CCl(4)-induced liver fibrogenesis mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugues, S.; Fernandez-Varo, G.; Muñoz-Luque, J.; Ros, J.; Arroyo, V.; Rodés, J.; Friedman, S.L.; Carmeliet, P.; Jiménez, W.; Morales-Ruiz, M. Antiangiogenic treatment with sunitinib ameliorates inflammatory infiltrate, fibrosis, and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulon, S.; Legry, V.; Heindryckx, F.; Van Steenkiste, C.; Casteleyn, C.; Olievier, K.; Libbrecht, L.; Carmeliet, P.; Jonckx, B.; Stassen, J.M.; et al. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the pathophysiology of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in two rodent models. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulon, S.; Francque, S.; Colle, I.; Verrijken, A.; Blomme, B.; Heindryckx, F.; De Munter, S.; Prawitt, J.; Caron, S.; Staels, B.; et al. Evaluation of inflammatory and angiogenic factors in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cytokine 2012, 59, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, M.V.; Hadziyannis, E.; Tiniakos, D.; Georgiou, A.; Margariti, A.; Kostas, A.; Papatheodoridis, G.V. Serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 30, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefere, S.; Van de Velde, F.; Hoorens, A.; Raevens, S.; Van Campenhout, S.; Vandierendonck, A.; Neyt, S.; Vandeghinste, B.; Vanhove, C.; Debbaut, C.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 promotes pathological angiogenesis and Is a therapeutic target in murine nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1087–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostallari, E.; Shah, V.H. Angiocrine signaling in the hepatic sinusoids in health and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G246–G251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deleve, L.D.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y. Sinusoidal endothelial cells prevent rat stellate cell activation and promote reversion to quiescence. Hepatology 2008, 48, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilscher, M.B.; Sehrawat, T.; Arab, J.P.; Zeng, Z.; Gao, J.; Liu, M.; Kostallari, E.; Gao, Y.; Simonetto, D.A.; Yaqoob, U.; et al. Mechanical stretch increases expression of CXCL1 in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells to recruit neutrophils, generate sinusoidal microthombi, and promote portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 193–209.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, J.; Lemoinne, S.; Boulanger, C.; Durand, F.; Moreau, R.; Valla, D.; Rautou, P.E. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeve, L.D.; Wang, X.; Kanel, G.C.; Atkinson, R.D.; McCuskey, R.S. Prevention of hepatic fibrosis in a murine model of metabolic syndrome with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.G. Cellular sources of extracellular matrix in hepatic fibrosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2008, 12, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ding, Q.; Yaqoob, U.; de Assuncao, T.M.; Verma, V.K.; Hirsova, P.; Cao, S.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Huebert, R.C.; Shah, V.H. Exosome adherence and internalization by hepatic stellate cells triggers sphingosine 1-phosphate-dependent migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 30684–30696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Choi, S.S.; Syn, W.K.; Michelotti, G.A.; Swiderska, M.; Karaca, G.; Chan, I.S.; Chen, Y.; Diehl, A.M. Hedgehog signalling regulates liver sinusoidal endothelial cell capillarisation. Gut 2013, 62, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Bronk, S.F.; Yagita, H.; Gores, G.J. Vismodegib suppresses TRAIL-mediated liver injury in a mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, B.S.; Cao, Z.; Lis, R.; Nolan, D.J.; Guo, P.; Simons, M.; Penfold, M.E.; Shido, K.; Rabbany, S.Y.; Rafii, S. Divergent angiocrine signals from vascular niche balance liver regeneration and fibrosis. Nature 2014, 505, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.H.; Hirsova, P.; Gores, G.J. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis pathogenesis: Sublethal hepatocyte injury as a driver of liver inflammation. Gut 2018, 67, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Verma, V.K.; Morton, L.A.; Shah, V.H.; LaRusso, N.F.; Gores, G.J.; Malhi, H. Extracellular vesicles in liver pathobiology: Small particles with big impact. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2219–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, F.J.; Revenu, C.; Arras, G.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Pegtel, D.M.; Follain, G.; Allio, G.; Goetz, J.G.; Zimmermann, P.; et al. Live tracking of inter-organ communication by endogenous exosomes in vivo. Dev. Cell 2019, 48, 573–589.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, R.P.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Jung, Y.; Omenetti, A.; Syn, W.K.; Choi, S.S.; Cheong, Y.; Fearing, C.M.; Agboola, K.M.; et al. Liver cell-derived microparticles activate hedgehog signaling and alter gene expression in hepatic endothelial cells. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoinne, S.; Cadoret, A.; Rautou, P.E.; El Mourabit, H.; Ratziu, V.; Corpechot, C.; Rey, C.; Bosselut, N.; Barbu, V.; Wendum, D.; et al. Portal myofibroblasts promote vascular remodeling underlying cirrhosis formation through the release of microparticles. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povero, D.; Eguchi, A.; Niesman, I.R.; Andronikou, N.; de Mollerat du Jeu, X.; Mulya, A.; Berk, M.; Lazic, M.; Thapaliya, S.; Parola, M.; et al. Lipid-induced toxicity stimulates hepatocytes to release angiogenic microparticles that require Vanin-1 for uptake by endothelial cells. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Sada, Y.H.; El-Serag, H.B.; Kanwal, F.; Duan, Z.; Temple, S.; May, S.B.; Kramer, J.R.; Richardson, P.A.; Davila, J.A. Temporal trends of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma in the veteran affairs population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 594–601.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, R.; Bugianesi, E. Should we undertake surveillance for HCC in patients with NAFLD? J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.; Poklepovic, A.; Moyneur, E.; Barghout, V. Population-based risk factors and resource utilization for HCC: US perspective. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2010, 26, 2183–2191.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; El-Serag, H.B.; Sada, Y.H.; Kanwal, F.; Duan, Z.; Temple, S.; May, S.B.; Kramer, J.R.; Richardson, P.A.; Davila, J.A. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the absence of cirrhosis in United States veterans is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.; Arroyo, A.G.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; Moreno-Otero, R. Angiogenesis in chronic inflammatory liver disease. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.Y.; Wang, J.D.; Tang, Z.H.; Zhou, X.P.; Quan, Z.W.; Liu, Y.B.; Shen, J. Higher proliferation of peritumoral endothelial cells to IL-6/sIL-6R than tumoral endothelial cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraud, C.; Mogler, C.; Runge, A.; Evdokimov, K.; Lu, S.; Schledzewski, K.; Arnold, B.; Hammerling, G.; Koch, P.S.; Breuhahn, K.; et al. Endothelial transdifferentiation in hepatocellular carcinoma: Loss of Stabilin-2 expression in peri-tumourous liver correlates with increased survival. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boord, J.B.; Maeda, K.; Makowski, L.; Babaev, V.R.; Fazio, S.; Linton, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Combined adipocyte-macrophage fatty acid-binding protein deficiency improves metabolism, atherosclerosis, and survival in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation 2004, 110, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Johnson, R.S.; Distel, R.J.; Ellis, R.; Papaioannou, V.E.; Spiegelman, B.M. Uncoupling of obesity from insulin resistance through a targeted mutation in aP2, the adipocyte fatty acid binding protein. Science 1996, 274, 1377–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Cao, H.; Kono, K.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Furuhashi, M.; Uysal, K.T.; Cao, Q.; Atsumi, G.; Malone, H.; Krishnan, B.; et al. Adipocyte/macrophage fatty acid binding proteins control integrated metabolic responses in obesity and diabetes. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancke, K.; Grubeck, D.; Hauser, N.; Kreienberg, R.; Weiss, J.M. Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein as a novel prognostic factor in obese breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 119, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, K.M.; Kenny, H.A.; Penicka, C.V.; Ladanyi, A.; Buell-Gutbrod, R.; Zillhardt, M.R.; Romero, I.L.; Carey, M.S.; Mills, G.B.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; et al. Adipocytes promote ovarian cancer metastasis and provide energy for rapid tumor growth. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, K.L.; van der Poorten, D.; Xu, A.; Bugianesi, E.; Kench, J.G.; Lam, K.S.; Chisholm, D.J.; George, J. Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein levels relate to inflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laouirem, S.; Sannier, A.; Norkowski, E.; Cauchy, F.; Doblas, S.; Rautou, P.E.; Albuquerque, M.; Garteiser, P.; Sognigbe, L.; Raffenne, J.; et al. Endothelial fatty liver binding protein 4: A new targetable mediator in hepatocellular carcinoma related to metabolic syndrome. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3033–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Adhesion Molecules | Counter-Part Ligands | Preclinical Animal Studies | Clinical Studies | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loss-of-Function | Animal Model | Hepatic Histological Readout | Adhesion Molecule as Biomarker | ||
| VCAM-1/MAdCAM-1 | ITGα4β1 ITGα4β7 ITGα9β1 | α4β1 blockade | HFD-fed mouse | Reduced myeloid cell accumulation [55] | Serum VCAM-1 level correlates with liver fibrosis score in NAFLD [63] |
| α4β7 blockade | WD-fed mouse | Reduced CD4+ T cell recruitment and fibrosis [64] | |||
| β1 blockade | FFC-fed mouse | Reduced MoMF-associated inflammation and fibrosis [10] | |||
| ICAM-1 | ITGαLβ2 ITGαMβ2 | ICAM-1 blockade | I-R injury in rat | Reduced necrosis [65] | Serum ICAM-1 level predicts histological severity in ALD [66] |
| Gal/ET-induced shock in mouse | Reduced necrosis [67] | ||||
| αMβ2 blockade | I-R injury in rat | Reduced necrosis and neutrophil recruitment [68] | |||
| NCAM | NCAM N-cadherin proteoglycans | NCAM−/− | BDL in mouse | Reduced fibrosis [69] | N.A. |
| VAP-1 | Unknown | VAP-1 blockade | ConA treatment in mouse | Reduced Th2 cell recruitment [70] | Serum VAP-1 level: (1) predicts histological severity in NAFLD [62], and (2) is increased in ALD and PBC [71] |
| VAP-1 blockade VAP-1−/− | Diet-induced NAFLD/NASH models, CCl4 model in mice | Reduced inflammatory cell infiltrate and fibrosis [62] | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furuta, K.; Guo, Q.; Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H. Emerging Roles of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Biology 2020, 9, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110395
Furuta K, Guo Q, Hirsova P, Ibrahim SH. Emerging Roles of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Biology. 2020; 9(11):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110395
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuruta, Kunimaro, Qianqian Guo, Petra Hirsova, and Samar H. Ibrahim. 2020. "Emerging Roles of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis" Biology 9, no. 11: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110395
APA StyleFuruta, K., Guo, Q., Hirsova, P., & Ibrahim, S. H. (2020). Emerging Roles of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Biology, 9(11), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110395







