Abstract
Leukocytes play a major role in combating infections either by phagocytosis, release of antimicrobial granules, or extracellular trap (ET) formation. ET formation is preceded by a certain leukocyte cell death form, known as ETosis, an evolutionarily conserved mechanism of the innate immune system also observed in marine mammals. Besides several biomolecules and microbial stimuli, marine mammal ETosis is also trigged by various terrestrial protozoa and metazoa, considered nowadays as neozoan parasites, which are circulating in oceans worldwide and causing critical emerging marine diseases. Recent studies demonstrated that pinniped- and cetacean-derived polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) and monocytes are able to form different phenotypes of ET structures composed of nuclear DNA, histones, and cytoplasmic peptides/proteases against terrestrial apicomplexan parasites, e.g., Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum. Detailed molecular analyses and functional studies proved that marine mammal PMNs and monocytes cast ETs in a similar way as terrestrial mammals, entrapping and immobilizing T. gondii and N. caninum tachyzoites. Pinniped- and cetacean leukocytes induce vital and suicidal ETosis, with highly reliant actions of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX), generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and combined mechanisms of myeloperoxidase (MPO), neutrophil elastase (NE), and DNA citrullination via peptidylarginine deiminase IV (PAD4).This scoping review intends to summarize the knowledge on emerging protozoans in the marine environment and secondly to review limited data about ETosis mechanisms in marine mammalian species.
1. Introduction
Early innate immune responses are important mechanisms of the host defense against infections, either protecting non-vertebrate organisms or synergizing adaptive immunity in vertebrate animals [1,2]. These responses are performed by anatomical and physiological barriers (e.g., mucociliary blanket), antimicrobial factors (e.g., complement, lysozyme, lactoferrin, defensins and reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates), and by professional mononuclear phagocytes (e.g., polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), monocytes, macrophages), all of them representing the first line of defense against a vast number of potentially pathogenic agents [3]. These leukocytes are able to entrap, phagocytize, and damage invasive microorganisms, but at the same time they release cytokines/chemokines [4,5,6,7], which are responsible for further leukocyte recruitment, starting acute systematic immune responses and inflammation processes [8,9,10,11].
Marine mammals, especially cetaceans (whales and dolphins), sirenians (manatees and dugongs), pinnipeds (seals, sea lions, sea leopards and walruses), polar bears, and sea otters are the only mammalian species which spend all or majority of their lives in marine environments. Marine mammals can not only be found in the open ocean, but also in freshwaters of lakes [12] and rivers [13], thereby diversifying the potential contact with humans, domestic animals and anthropozoonotic pathogens [14].
Further, marine mammals are highly valuable with respect to comparative and evolutionary immunology since they are the only descendants of primitive terrestrial mammals which returned to the sea and their immune system was initially adapted to a terrestrial existence, including host–parasite interactions that have been re-evolved in aquatic ecosystems [15]. Several studies have described the mechanisms involved in cetacean and pinniped innate immune system [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25], highlighting the importance of leukocytes as forefront of defense against infections [26,27], which is highly important for inflammation resolution and/or wound healing [28]. Moreover, anthropogenic immunosuppression can seriously affect leukocyte counts and generate differences in immune reactions between individuals from the same marine group, e.g., in sirenians, sea otters, pinnipeds, and cetaceans, thereby causing mass mortalities of classical terrestrial pathogens, such as Morbillivirus and Toxoplasma gondii in marine ecosystems worldwide [11,29,30,31,32,33].
Therefore, this review focuses on both, oceanic emerging neozoan parasites and on the innate immune system of pinniped/cetacean mammals. It additionally reviews the innate effector defense mechanism of ETosis and summarizes very limited data on T. gondii- and Neospora caninum-induced ETosis in pinnipeds and cetaceans, thereby highlighting the relevance of this ancient, conserved and effective defense mechanism against these parasites currently circulating in marine environments [31,32,33,34,35,36,37].
2. Marine Environment Affected by Emerging Neozoan Parasites
Oceans are currently threatened by the presence of opportunistic emerging neozoan pathogens (i.e., viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites) affecting both animal and human health and welfare [36,37]. Typical terrestrial neozoan parasites, such as apicomplexan parasites T. gondii, N. caninum, Sarcocystis canis, and Cryptosporidium spp. (i.e., C. parvum, C. hominis) as well as enteropathogenic protozoans, like Giardia intestinalis, Balantidium spp., and Entamoeba spp., have been reported in wild populations of diverse marine mammals [38,39,40,41,42,43,44] and in different marine ecosystems in past decades [13,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49], causing lethal infections not only in sea otters [31,32] and large whales [36,49,50,51,52], but also in pinnipeds [53] and dolphins [34,42].
Occurrence of coccidian parasitoses such as toxoplasmosis, neosporosis, and sarcocystosis are quite problematic in marine mammals reflecting contamination status of oceans and coastal waters with infectious sporulated oocysts [31,34,35,54]. As recorded for terrestrial mammalians, congenital toxoplasmosis has also been reported in cetaceans, such as the Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops aduncus) [55]. Additionally, Dubey et al. [56] showed T. gondii tissue cyst formation in striped dolphins (Stenella coeruleoalba). Obviously, a high contamination of aquatic ecosystems with infectious oocysts of T. gondii-, N. caninum-, S. canis-, and C. parvum, and cysts of G. intestinalis, Entamoeba spp., or Balantidium spp. will facilitate infections in wild marine mammals [31,37,56]. Moreover, movements and migration of uninfected marine mammals into areas with endemic oocyst/cyst contamination prompted by environmental changes, such as “El Niño” events and/or global warming, might result in disease outbreaks as demonstrated for terrestrial mammals [57]. Additionally, direct and indirect contacts between humans and marine mammals are nowadays more frequent, especially due to urbanization expansion along the coasts, tourist activities like whale- and dolphin-watching, aquatic sport activities, rehabilitation and research practices involving maintenance of sick or injured marine mammals, and the contact of marine mammals with pathogens from domestic pets and livestock [58].
To date, a large number of parasite species have gained importance as opportunistic neozoan infections in the marine environment [36,47,49,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66]. Particularly, T. gondii and Sarcocystis neurona stages in brain tissue were associated with encephalitis in stranded harbor seals [65,66]. Consequently, specific antibodies against the apicomplexan parasites, such as N. caninum, T. gondii, and S. neurona, were recently reported in dolphins [50,55,63,64,65,66,67,68,69], whales [51,70], sea otters [31,71] and seals [44,59] confirming a rather wide ocean contamination. Whilst the contamination of oceanic environment and coastal waters with sporulated oocysts and infective cysts is quite obvious [31,41], molecular mechanisms of host innate and adaptive immune responses of marine mammals against these neozoans are still unclear.
3. Cetacean/Pinniped Leukocytes of the Innate Immune System
The innate immune system is one of the two main branches of host defense in vertebrates, with the other one being the adaptive immune system. The innate immune system is evolutionary older and is known as the dominant immune system, acting as a first line of defense against invasive pathogens [26]. The innate immune system of mammals is mainly composed of professional phagocytes (i.e., PMNs, monocytes and macrophages) and highly immunoreactive host epithelial- and host endothelial cells covering mucosal and vessel surfaces of the body.
The innate immune system of cetaceans/pinnipeds mainly includes PMNs and monocytes, which represent 22–72% and 0–11% of the circulating leukocytes, respectively [38,72,73,74,75,76]. As seen in terrestrial mammals, also eosinophils, mast cells, basophils, and macrophages are found in marine mammals [39,76]. Leukocyte morphology in healthy marine and terrestrial mammals are quite similar, but with some notable exceptions [73,74,75,76,77,78,79]. PMNs of most marine mammals have round to oval granules that either do not stain or stain as pale pink within heterophilic granulocytes using Wright-Giemsa [75,77]. These heterophilic granules contain myeloperoxidase (MPO) and neutrophil elastase (NE), which are also typical terrestrial mammalian PMN-derived antimicrobial proteins, identified in PMNs of humans, horses, cattle, goats, and dogs [80,81,82,83,84].
Interestingly, cetaceans have much higher eosinophil counts than most other mammals, including pinnipeds [76,79]. Eosinophils in tissues react to chemoattractants generated in response to parasites, as recently reported for other terrestrial mammalian species [47,85]. They release eosinophil-derived peroxidase from their granules and interact by hydrogen peroxide to perform respiratory burst activities with halide ions or via extracellular trap (ET) formation [85,86]. This complex, combined with other oxygen species and the major basic protein (MBP) being released from secondary granules, enables eosinophils to display bactericidal and parasiticidal activities [85,87,88]. Marine mammal effector mechanisms of leukocytes, such as phagocytosis and respiratory burst resulting in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, have been well investigated [13,14,15,16,17,18,22,89] and show similar pathogen killing capacities as leukocytes of terrestrial mammals [90,91,92,93,94].
As described for terrestrial mammalians, age-related variations in leukocyte composition have also been recorded for marine mammals. As such, Hasselmeier et al. [93] reported that more than half of a free-living harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) pup population in the Northern Sea showed a proportion of at least 10% monocytes in the blood during the winter, while yearlings totally lacked this cell type during the spring season. Differences in numbers, activation status, and monocyte-mediated phagocytosis were most probably due to diverse stress pressure and/or concomitant indiscernible infections [93].
4. ETosis in Terrestrial and Marine Mammals
The paradigm of how mammalian PMNs combat, entrap, and kill pathogenic agents has deeply been changed after the landmark publication of Brinkmann et al. [80]. The discovery of DNA-based antimicrobial ETs not only revolutionized our knowledge on early host innate immune reactions, but changed understanding of their functions in metabolic, autoimmune, reproductive, thromboimmune, tumoral, and inflammatory disorders [94,95,96,97,98,99]. ET-related DNA-structures have widely been studied in context of diverse PMN-derived antibacterial effector defense mechanisms, and were originally named as neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Meanwhile, other types of professional phagocytes, such as mast cells [100,101,102], eosinophils [103], macrophages [104,105,106,107], basophils [108,109], and monocytes [110,111,112,113],were also described as capable for ET extrusion. The process of leukocyte-mediated ET release into extracellular space is known in literature as ETosis [80,114].
Mammalian ETosis can be induced by a variety of potent stimulators, including soluble molecules (e.g., granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)/complement factor 5a [114,115], activated platelets [116], toll-like receptors (TLRs) [117], interleukin 8 (IL-8), interferon gamma (IFNγ) [118], lipopolysaccharides (LPS) [80], phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) [119,120], zymosan [38,82], singlet oxygen [121], fragment crystallizable receptor (Fc receptor) [122,123,124], mycotoxins [125],and invasive pathogens (e.g., bacteria [80,104,126], fungi [122,123,127], viruses [128,129], and parasites [27,111,130,131,132]).
Efficient mammalian ETosis requires mature leukocytes with physiological activities of reactive oxygen species (ROS), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX), neutrophil elastase (NE), myeloperoxidase (MPO) and peptidylarginine deiminase type IV (PAD4) [83,133,134,135,136,137]. Upon respective stimulation of leukocytes, the nuclear envelope disintegrates, thereby permitting the mixture of chromatin with granular proteins/peptides [80]. NE and MPO degrade nuclear histones (H1, H2A/H2B, H3, H4) and stimulate chromatin decondensation [134] through hypercitrullination of specific histones via PAD4, which allows electrostatic coiling of chromatin [135,138]. DNA complexes being decorated with granular proteins/peptides and nuclear histones are consequently extruded from dying cells in fine structures to the extracellular environment (Figure 1). This mechanism is known as suicidal ETosis [139] and lytic ETosis was found associated with other ROS-related activation mechanisms, which have also been observed in leukocytes of marine mammals [140]. Moreover, mammalian ETosis requires the activation of intracellular signaling pathways, frequently involving mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), such as Raf-MEK-ERK kinases as well as p38 MAPK routes [136,137,141]. Additionally, ETosis revealed as a calcium-dependent process in various vertebrate species [137,142,143,144].
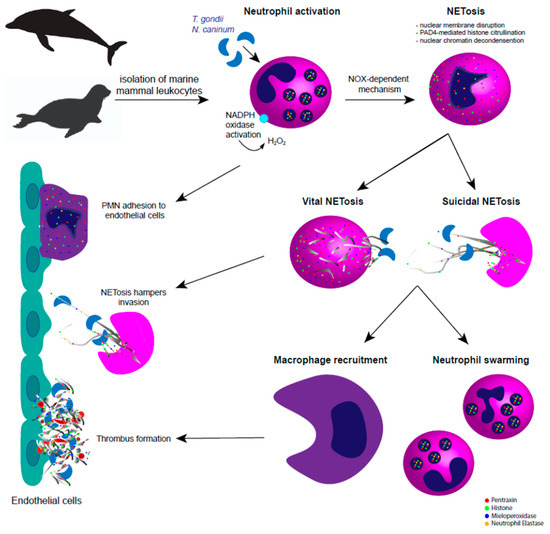
Figure 1.
Apicomplexan-triggered neutrophil extracellular traps (NETosis) in pinniped and cetacean species. In the pinniped and cetacean system, tachyzoite-derived extracellular traps (ETosis) is dependent on nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX) pathways, via reactive oxygen species (ROS) activation and histone citrullination via peptidylarginine deiminase IV (PAD4). Marine mammal-triggered vital and suicidal ETosis result in effective entrapment of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum tachyzoites, thereby hampering active invasion of host endothelial cells. After extracellular trap (ET) release, complementary immune mechanisms take place to keep the homeostasis and to hamper ETosis-mediated collateral tissue damage, such as macrophage recruitment, polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) swarming, chemotaxis, activation of endothelium, and immunothrombosis.
As stated above, suicidal ETosis is mainly known as NOX-dependent cell death pathway [26,82,111,136,137], however, NOX-independent suicidal ETosis has been also reported [121,145,146]. NOX-independent suicidal ETosis includes a considerable lower activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK/MAPK) and rather moderate levels of protein kinase B (PKB or AKT) activation, i.e., of molecules known to be important regulators of autophagy and oncogenic processes. Meanwhile, the activation of p38 appears similar in both, lytic and non-lytic ETosis [126,144,145,147]. Interestingly, even singlet oxygen can stimulate mammalian ETosis in a NOX-independent manner [121]. Irrespective of NOX-dependency, parasites may either be immobilized or entrapped within sticky DNA fibers [27] or be killed via the local high concentration of effector molecules [130].
Since the description of Malawista et al. [148] in which enucleated PMNs survived after being confronted with invasive pathogens despite their short lifespan, posterior studies confirmed these findings proving that some leukocytes do not necessarily succumb during ETosis [103,126,149]. In this context, Yousefi et al. [103] demonstrated that eosinophils and certain PMN subpopulations release ETs of mitochondrial sources without losing their vitality, known as non-lytic or vital ETosis. Consequently, Yipp et al. [150] verified that PMNs which performed vital NETosis were still viable and retained their capability to engulf bacteria via phagocytosis. However, the exact routes of vital ETosis through NOX-independent mechanisms and the release of mitochondrial DNA are not clear yet. Interestingly, NOX-independent vital ETosis seems faster than NOX-dependent suicidal ETosis and seem to rely on a vesicular-based pathway leading to nuclear DNA release, known as vesicular ETosis [97,126,145].
Furthermore, in vitro and in vivo release of different phenotypes of ETs depends on stimulus and probably simultaneously involves several molecular pathways. Recently, three different phenotypes of ETs have been described in PMNs and eosinophils, e.g., the so-called aggregated (aggETs), spread (sprETs), and diffuse (diffETs) ETs [83,151]. Consistent with these findings, aggETs, sprETs, and diffETs have been also recently observed in pinnipeds and dolphins [38,39,40].
While a vast amount of investigations have been performed unveiling precise cellular processes occurring during suicidal, vital and vesicular ETosis, many aspects concerning receptors and signaling pathways being involved in these effector mechanisms are still unresolved. The same holds true for studies on pinniped/cetacean-derived ETosis.
In line with ultrastructural scanning electron microscopy (SEM) findings on terrestrial mammals, marine mammal-derived suicidal ETosis was also described in response to neozoan T. gondii and N. caninum (Figure 2 and Supplementary Materials). These data demonstrate that this cell death process is most probably an early, well-conserved and ancient host innate defense mechanism. Prior to suicidal ETosis, dolphin-and pinniped-derived PMNs and monocytes firmly attached to and subsequently entrapped N. caninum/T. gondii tachyzoites by releasing sticky ETs [38,39]. Thereby active tachyzoite host cell invasion was impeded, as already shown for other apicomplexans in vitro and in vivo [32,85,111,137]. Considering that T. gondii and N. caninum are obligate intracellular parasites and rely on host cell metabolism modulation for successful proliferation [152,153,154,155,156], the blockage of tachyzoite-derived host cell invasion via suicidal ETosis seems to be a crucial antiparasitic effect. Thus, ETosis-mediated inhibition host cell invasion might indeed exhibit a detrimental impact on parasitic development and outcome of disease as postulated elsewhere (for reviews refer to [27,47]). As already demonstrated for other terrestrial mammals, such as dogs [83,157], cattle [158], goats [82,159,160], and sheep [161], the DNA nature of ETs was also confirmed for pinniped- and cetacean-derived leukocytes since treatments with deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) resulted in a significant reduction of T. gondii and N. caninum-triggered ETosis [38,39].
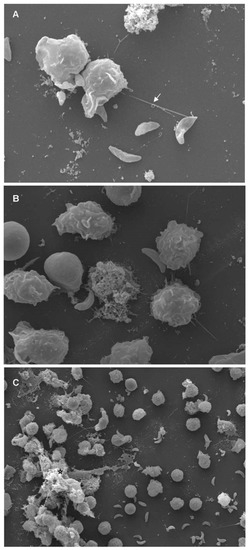
Figure 2.
Toxoplasma gondii-triggered cetacean extracellular traps (ETosis) visualized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) were isolated from whole blood and confronted with viable T. gondii tachyzoites (ratio 1:4) for 60 min on poly-L-lysine (Sigma Aldrich)-pretreated 10 mm coverslips (10 mm of diameter; Nunc) (Please see Supplementary Materials). Samples were fixed in a medium containing formaldehyde 2% (Merck) and 2.5 % glutaraldehyde (Merck), post-fixed in 1 % osmium tetroxide, washed with distilled water before dehydration and critical point dry with CO2-application, and sprinkled with gold particles. The specimens were examined using scanning electron microscope (Philips ® XL30, Philips, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). (a) Vital cetacean PMNs extruded a neutrophil extracellular trap (NET)-like delicate filament (white arrow), attached to a T. gondii-tachyzoite. (b) Many activated PMNs changed their habitual round morphology after they entered in contact with tachyzoites. (c) Conglomerate of parasites being entrapped in a rather thicker DNA meshwork of cetacean-PMN-released fibers (black star).
It seems obvious that ETosis might be of relevance in marine mammals since the persistence of T. gondii in marine environments is nowadays growing through increased ocean contamination, by the facultative life cycle of this parasite, by a wide spectrum of suitable hosts and additional vertical transmission routes. Thus, an expansion of land-to-sea parasite colonization leading to frequent infections in marine mammals, such as sea otters or pinnipeds [162], will probably occur in future. The same might be true for the closely related euryxenous N. caninum, which shares similar aspects of biology and pathogenicity with T. gondii [39].
Interestingly, previous reports on NOX-derived intracellular ROS and dose-dependent ETosis triggered by in human [163] and bovine [111] PMNs were also confirmed for pinniped- and cetacean-triggered suicidal ETosis [38,39]. These observations might be associated with the pathogenicity of toxoplasmosis and neosporosis in marine mammals, since overwhelming suicidal ETosis may harm host tissues by different mechanisms, but especially through release of MPO, histones, chromatin, pro-inflammatory peptides/proteases, and oxidants, which, in turn, might trigger endothelial activation, apoptosis or necrosis in affected tissues or organs [164,165]. In contrast to parasite-induced NETosis in terrestrial mammals, pinniped-derived ETosis triggered by T. gondii revealed to be time-dependent [38]. However, N. caninum-induced ETosis in dolphins revealed as time-independent [39]. Observed differences might rely on the activation status of PMNs and final break-up of the cell membrane, i.e., each marine mammal species might require different time spans to fulfill the NETotic cascade [113], which is probably related with duration of vital and/or lethal ETosis as already demonstrated for other non-marine mammalian host species [147,150,166].
Inhibition of NOX-activity in pinniped- and cetacean-derived phagocytes via diphenylene iodondium (DPI) pre-treatments resulted in a significant diminishment of suicidal ETosis, thereby indicating NOX-dependency of this process. Accordingly, marine mammalian PMNs and monocytes appear to be capable of NOX activation, ROS production, and of performing ROS-dependent phagocytic activities [17,23,93,167]. Moreover, harbor seal (P. vitulina)-derived PMNs/monocytes and dolphin (Tursiops truncatus)-derived PMNs were proven to rapidly undergo lethal ETosis (within 10 min of exposure) against vital T. gondii-tachyzoites [38,40]. Thus, these cell types represent one of the fastest acting immune cell type undergoing ETosis, so far.
In line with pinniped/cetacean immune system, mammalian ETosis being performed in response to Eimeria bovis, C. parvum, and Besnoitia besnoiti stages is also known as a NOX-dependent mechanism [26,136,137,158,168], which finally leads to extrusion of nuclear and cytoplasmic granule enzymes, and the formation of DNA-enriched fibers being adorned with histones and granular proteins. For the latter, a variety of molecules was meanwhile identified to be present in ETosis, including NE, MPO, pentraxin, lactoferrin, cathepsin G, α-defensin, azurocidin, lysozyme, cathelicidins (LL-37), bacterial permeability-increasing protein (BPI), peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRPs), and other PMN granular components (for reviews see [26,27,47,169]). Whether these molecules are also found in marine mammal-triggered ETosis needs further investigations to be elucidated. Furthermore, it remains unclear whether NOX-independent suicidal ETosis is also performed by pinniped/cetacean leukocytes. The same holds true for any receptors (e.g., TLRs, CD11b) or ligands to be involved in apicomplexan-mediated ETosis [136].
5. Conclusions
Despite a vast number of investigations on terrestrial mammalian-triggered ETosis, it still remains enigmatic in pinniped/cetacean species, and various aspects of their nature and significance in vivo remain to be elucidated. Thus, specific signaling pathways or granular molecules leading to parasite entrapment by marine mammal-mediated ETosis are still unclear. The molecular composition of marine mammal-derived ETosis showed the presence of antimicrobial NE, MPO, and global histones, but their antimicrobial/antiparasitic role in vivo is actually unsolved. The actual role of different phenotypes of ETs in marine mammals in vivo also requests further detailed studies, in particular with respect to the impact of pro-inflammatory antimicrobial components, accumulating in high concentrations in organs and tissues in the case of aggETs. In the same way, further studies are required concerning the different molecular activation mechanisms involved in ETosis, not only those ones associated with the leukocyte type involved in this process, but also the intraspecific differences between the diverse pathogenic agents and even between the marine mammals should be considered.
As also true for terrestrial mammalian-derived ETosis, the question why only a proportion of activated PMNs/monocytes are undergoing ETosis in response to parasites still has to be answered. Furthermore, the involvement of ETosis in several diseases (e.g., metabolic-, autoimmune-, reproductive-, tumor- and coagulopathy-related disorders) is another enigmatic field to be considered in marine mammals. In conclusion, we call for more detailed investigations in this fascinating field to better understand molecular aspects underlying degradation and regulation of marine mammal-derived ETosis. This investigation is of paramount importance given that ETosis releases vast amount of potent pro-inflammatory molecules into the system, which might have detrimental (in case of uncontrolled release) but also beneficial effects for the host by entrapping and inhibiting dissemination of parasites.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2079-7737/8/1/12/s1, Supplementary Material: Scanning electron microscopy—Materials and methods applied for figure 2.
Author Contributions
R.V.-B., L.M.R.S., and I.C. performed the experiments. A.T. and C.H. contributed with the review conceptualization. R.V.-B., L.M.R.S., I.C., A.T., and C.H. cooperated in the research design and manuscript review. All the authors contributed with the formal analysis, investigation, and checked the final manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Brigitte Hofmann and Dr. Christin Ritter (Institute for Parasitology, JLU-Giessen, Germany) for their technical assistance in the in vitro culture of T. gondii and N. caninum. Further, we deeply acknowledge Anika Seipp and Ulrich Gärtner (Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology, JLU Giessen, Germany) for their excellent assistance in scanning electron microscopy analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in the present study.
References
- Abbas, A.K.; Litchman, A.H.; Pillai, S. Cellular and Molecular Immunology; Elsevier/Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Riera Romo, M.; Pérez-Martínez, D.; Castillo Ferrer, C. Innate immunity in vertebrates: An overview. Immunology 2016, 148, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.P.; Schrenzel, M.D.; McKnight, M.L.; Reidarson, T.H.; Hanni, K.D.; Stott, J.L.; Ferrick, D.A. Molecular cloning and sequencing of interleukin 6 cDNA fragments from the harbour seal (Phoca vitulina), killer whale (Orcinus orca), and southern sea otter (Enhydra lutris nereis). Immunogenetics 1996, 43, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrendt, J.H.; Hermosilla, C.; Hardt, M.; Failing, K.; Zahner, H.; Taubert, A. PMN-mediated immune reactions against Eimeria bovis. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 151, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taubert, A.; Wimmers, K.; Ponksuksili, S.; Jimenez, C.A.; Zahner, H.; Hermosilla, C. Microarray-based transcriptional profiling of Eimeria bovis-infected bovine endothelial host cells. Vet. Res. 2010, 41, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abi Abdallah, D.S.; Denkers, E.Y. Neutrophils cast extracellular traps in response to protozoan parasites. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, D.; Muñoz, M.C.; Molina, J.M.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Silva, L.M.R.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Ruiz, A. Eimeria ninakohlyakimovae induces NADPH oxidase-dependent monocyte extracellular trap formation and upregulates IL-12 and TGF-α, IL-6 and CCL2 gene transcription. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 227, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature 2007, 449, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonfara, S.; Siebert, U.; Prange, A.; Colijn, F. The impact of stress on cytokine and haptoglobin mRNA expression in blood samples from harbour porpoises (Phocoena phocoena). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2007, 87, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuschke, A.; Valentine-Thon, E.; Griesel, S.; Fonfara, S.; Siebert, U.; Prange, A. Immunological impact of metals in harbor seals (Phoca vitulina) of the North Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7568–7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beineke, A.; Siebert, U.; Wohlsein, P.; Baumgärtner, W. Immunology of whales and dolphins. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 133, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton-Robb, K.; Gershwin, L.; Thompson, R.; Austin, J.; Owen, K.; McKechnie, S. A new dolphin species, the Burrunan dolphin Tursiops australis sp. nov., endemic to southern Australian coastal waters. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermosilla, C.; Silva, L.M.R.; Navarro, M.; Taubert, A. Anthropozoonotic endoparasites in free-ranging “urban” South American sea lions (Otaria flavescens). J. Vet. Med. 2016, 7507145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompa, S.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Ceballos, G. Global distribution and conservation of marine mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13600–13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavagnolo, R.Z. The immunology of marine mammals. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1979, 3, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, K.; Aoki, M.; Akiyoshi, H.; Asaki, H.; Shimada, T.; Ohashi, F. Evaluation of the polymorphonuclear cell functions of bottlenose dolphins. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, K.; Akiyoshi, H.; Aoki, M.; Shimada, T.; Ohashi, F. Relationship between transportation stress and polymorphonuclear cell functions of bottlenose dolphins, Tursiops truncatus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2007, 69, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, M.; Morsey, B.; Mori, C.; Nambiar, P.R.; De Guise, S. PCBs and TCDD, alone and in mixtures, modulate marine mammal but not B6C3F1 mouse leukocyte phagocytosis. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2005, 68, 635–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.; Morsey, B.; De Guise, S. Modulation of the respiratory burst by organochlorine mixtures in marine mammals, humans, and mice. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2007, 70, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, O.V. Peculiarities of phagocytosis in bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) during the period of adaptation to the captivity conditions. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2005, 403, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellisso, S.C.; Muñoz, M.J.; Carballo, M.; Sanchez-Vizcaino, J.M. Determination of the immunotoxic potential of heavy metals on the functional activity of bottlenose dolphin leukocytes in vitro. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 121, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Perrin, W.F. Bryde´s whale: Balaenoptera edeni/brydei. InEncyclopaedia of Marine Mammals, 2nd ed.; Perrin, W.F., Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 158–163. ISBN 9780123735539. [Google Scholar]
- Frouin, H.; Lebeuf, M.; Hammill, M.; Fournier, M. Phagocytosis in pup and adult harbour, grey and harp seals. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 134, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwacke, L.H.; Twiner, M.J.; De Guise, S.; Balmer, B.C.; Wells, R.S.; Townsend, F.I.; Rotstein, D.C.; Varela, R.A.; Hansen, L.J.; Zolman, E.S.; et al. Eosinophilia and biotoxin exposure in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from a coastal area impacted by repeated mortality events. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogh, M.J.; Spoon, T.; Ridgway, S.H.; Jensen, E.; Van Bonn, W.; Romano, T.A. Simultaneous measurement of phagocytosis and respiratory burst of leukocytes in whole blood from bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) utilizing flow cytometry. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 144, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps: Is immunity the second function of chromatin? J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.M.R.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Burgos, R.A.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Far beyond phagocytosis: Phagocyte-derived extracellular traps act efficiently against protozoan parasites in vitro and in vivo. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 5898074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Espinosa, O.; Rojas-Espinosa, O.; Moreno-Altamirano, M.M.; López-Villegas, E.O.; Sánchez-García, F.J. Metabolic requirements for neutrophil traps formation. Immunology 2015, 145, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, S. Morbillivirus infections in aquatic mammals. J. Comp. Pathol. 1998, 119, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.; Wohlsein, P.; Beineke, A.; Haas, L.; Greiser-Wilke, I.; Siebert, U.; Fonfara, S.; Harder, T.; Stede, M.; Gruber, A.D.; et al. Phocine distemper in German seals, 2002. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, P.A.; Miller, M.A.; Kreuder, C.; James, E.R.; Mazet, J.; Dabritz, H.; Jessup, D.A.; Gulland, F.; Grigg, M.E. Transmission of Toxoplasma: Clues from the study of sea otters as sentinels of Toxoplasma gondii flow into the marine environment. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Miller, W.A.; Conrad, P.A.; James, E.R.; Melli, A.C.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Dabritz, H.A.; Packham, A.E.; Paradies, D.; Harris, M.; et al. Type X Toxoplasma gondii in wild mussel and terrestrial carnivores from coastal California: New linkages between terrestrial mammals, runoff and toxoplasmosis of sea otters. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlsein, P.; Puff, C.; Kreutzer, M.; Siebert, U.; Baumgärtner, W. Distemper in a dolphin. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1959–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Fair, P.A.; Sundar, N.; Velmurugan, G.; Kwok, O.C.; McFee, W.E.; Majumdar, D.; Su, C. Isolation of Toxoplasma gondii from bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. History of the discovery of the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bressem, M.F.; Raga, J.A.; Di Guardo, G.; Jepson, P.D.; Duignan, P.J.; Siebert, U.; Barrett, T.; Santos, M.C.; Moreno, I.B.; Siciliano, S.; et al. Emerging infectious diseases in cetaceans worldwide and the possible role of environmental stressors. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2009, 86, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinertz, S.; Hermosilla, C.; Ziltener, A.; Kreicker, S.; Hirzmann, J.; Abdel-Ghaffar, F.; Taubert, A. Gastrointestinal parasites of free-living Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus) in the Northern Red Sea, Egypt. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichel, M.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Sánchez-Contreras, G.; Rubio-García, A.; Magdowski, G.; Gärtner, U.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Harbour seal (Phoca vitulina) PMN and monocytes release extracellular traps to capture the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 50, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villagra-Blanco, R.; Silva, L.M.R.; Aguilella-Segura, A.; Arcenillas-Hernández, I.; Martínez-Carrasco, C.; Seipp, A.; Gärtner, U.; Ruiz de Ybañez, R.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Bottlenose dolphins (Tursiopstruncatus) do also cast neutrophilextracellular traps against the apicomplexan parasite Neosporacaninum. Int. J. Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2017, 6, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlau, M.; Conejeros, I.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Zhou, E.; Gärtner, U.; Ternes, K.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Institute of Parasitology; Justus Liebig University Giessen: Giessen, Germany, 2019; unpublished data. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, M.J. How we all kill whales. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resendes, A.R.; Juan-Salles, C.; Almeria, S.; Majo, N.; Domingo, M.; Dubey, J.P. Hepatic sarcocystosis in a striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba) from the Spanish Mediterranean coast. J. Parasitol. 2002, 88, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes-Hanks, J.M.; Rickard, L.G.; Panuska, C.; Saucier, J.R.; O’Hara, T.M.; Dehn, L.; Rolland, R.M. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia spp. in five marine mammal species. J. Parasitol. 2005, 91, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Kakumoto, C.; Kobayashi, M.; Saito, S.; Kariya, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Xuan, X.; Igarashi, I.; Suzuki, M. Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in seals around Hokkaido, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2007, 69, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raga, J.A.; Fernandez, M.; Balbuena, J.A.; Aznar, F.J. Parasites. In Encyclopaedia of Marine Mammals, 2nd ed.; Perrin, W.F., Thewissen, H.G.M., Würsing, B., Eds.; Academic Press Elsevier Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 821–830. ISBN 9780123735539. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, L.; Johnson, C.K.; Lambourn, D.M.; Gibson, A.K.; Haman, K.H.; Huggins, J.L.; Sweeny, A.R.; Sundar, N.; Raverty, S.A.; Grigg, M.E. A novel Sarcocystis neurona genotype XIII is associated with severe encephalitis in an unexpectedly broad range of marine mammals from the northeastern Pacific Ocean. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermosilla, C.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Silva, L.M.R.; Ruiz, A.; Taubert, A. The intriguing host innate immune response: Novel anti-parasitic defence by neutrophil extracellular traps. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermosilla, C.; Silva, L.M.R.; Kleinertz, S.; Prieto, R.; Silva, M.A.; Taubert, A. Endoparasite survey of free-swimming baleen whales (Balaenoptera musculus, B. physalus, B. borealis) and sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) using non/minimally invasive methods. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermosilla, C.; Hirzmann, J.; Silva, L.M.R.; Brotons, J.M.; Cerdá, M.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Ewers, C.; Taubert, A. Occurrence of anthropozoonotic parasitic infections and faecal microbes in free-ranging sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) from the Mediterranean Sea. Parasitol. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inskeep, W., II; Gardiner, C.H.; Harris, R.K.; Dubey, J.P.; Goldston, R.T. Toxoplasmosis in Atlantic bottle-nosed dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J. Wildl. Dis. 1990, 26, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omata, Y.; Umeshita, Y.; Watarai, M.; Tachibana, M.; Sasaki, M.; Murata, K.; Yamada, T.K. Investigation for presence of Neospora caninum, Toxoplasma gondii and Brucella-species infection in killer whales (Orcinus orca) mass-stranded on the coast of Shiretoko, Hokkaido. Jpn. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2006, 68, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzariol, S.; Marker, F.; Mignone, W.; Serracca, L.; Goria, M.; Marsili, L.; DiGuardo, G.; Casalone, C. Dolphin Morbillivirus and Toxoplasma gondii co-infection in a Mediterranean fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus). BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezón, O.; Hall, A.J.; Vincent, C.; Pabon, M.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Dubey, J.P.; Almería, S. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in North-eastern Atlantic harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) and grey seal (Halichoerus grypus). Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 179, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massie, N.G.; Ware, M.W.; Villegas, E.; Black, M. Uptake and transmission of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts by migratory, filter-feeding fish. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 169, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, J.E.; Dubey, J.P. Congenital toxoplasmosis in a Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops aduncus). J. Parasitol. 2002, 88, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Morales, J.A.; Sundar, N.; Velmurugan, G.V.; González-Barrientos, C.R.; Hernández-Mora, G.; Su, C. Isolation and genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba) from Costa Rica. J. Parasitol. 2007, 93, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daszak, P.; Cunningham, A.A.; Hyatt, A.D. Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife–threats to biodiversity and human health. Science 2000, 287, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulland, F.M.; Hall, A.J. Is marine mammal health deterioring? Trends of global reporting of marine mammal disease. EcoHealth 2007, 4, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Review of Neospora caninum and neosporosis in animals. Korean J. Parasitol. 2003, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buergelt, C.D.; Bonde, R.K. Toxoplasmic meningoencephalitis in a West Indian manatee. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1983, 183, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, M.E.; Roch, P.D.; Stabler, M.; Chan, W. Giardiasis in ringed seals from the western Arctic. J. Wildl. Dis. 1997, 33, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.P.; Nolan, S.; Gulland, F.M.D. Antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria isolated from pinnipeds stranded in central and northern California. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1998, 29, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- LaPointe, J.M.; Gulland FM, D.; Haines, D.M.; Barr, B.C.; Duignan, P.J. Placentitis due to Coxiella burnetii in a Pacific harbor seal (Phoca vitulina richardsi). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1999, 11, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pelt, R.W.; Dietrich, R.A. Staphylococcal infection and toxoplasmosis in a young harbor seal. J. Wildl. Dis. 1973, 9, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holshuh, H.J.; Sherrod, A.E.; Taylor, C.R.; Andrews, B.E.; Howard, E.B. Toxoplasmosis in a feral northern fur seal. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1985, 187, 1229–1230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- LaPointe, J.M.; Duignan, P.J.; Marsh, A.E.; Gulland, F.M.; Barr, B.C.; Naydan, D.K.; King, D.P.; Farman, C.A.; Huntingdon, K.A.B.; Lowenstine, L.J. Meningoencephalitis due to a Sarcocystis neurona-like protozoan in Pacific harbour seals (Phoca vitulina richardsi). J. Parasitol. 1999, 84, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowater, R.O.; Norton, J.; Johnson, S.; Hill, B.; O’Donoghue, P.; Prior, H. Toxoplasmosis in Indo-Pacific humpbacked dolphins (Sousa chinensis), from Queensland. Aust. Vet.J. 2003, 81, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezón, O.; Resendes, A.R.; Domingo, M.; Raga, J.A.; Agustí, C.; Alegre, F.; Mons, J.L.; Dubey, J.P.; Almería, S. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in wild dolphins from the Spanish Mediterranean coast. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 643–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, P.S.; Albuquerque, G.R.; da Silva, V.M.; Martin, A.R.; Marvulo, M.F.; Souza, S.L.; Ragozo, A.M.; Nascimento, C.C.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in free-living Amazon River dolphins (Inia geoffrensis) from central Amazon, Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 183, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaelian, I.; Boisclair, J.; Dubey, J.P.; Kennedy, S.; Martineau, D. Toxoplasmosis in beluga whales from the St. Lawrence estuary: Two case reports and a serological survey. J. Comp. Pathol. 2000, 122, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, R.A.; Lindsay, D.S.; Howe, D.K.; Roderick, C.L.; Dubey, J.P.; Thomas, N.J.; Baeten, L.A. Biological and molecular characterizations of Toxoplasma gondii strains obtained from southern sea otters (Enhydra lutris nereis). J. Parasitol. 2000, 86, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.D.; Reese, E.; Reif, J.S.; Varela, R.A.; McCulloch, S.D.; Dfran, R.H.; Fair, P.A.; Bossart, G.D. Hematologic, biochemical, and cytologic findings from apparently healthy Atlantic bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) inhabiting the India River Lagoon, Florida, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.J.; Wells, R.S.; Sweeney, J.C.; Townsend, F.I.; Balmer, B.C.; Hohn, A.A.; Rhinehart, H.L. Annual, seasonal and individual variation in hematology and clinical blood chemistry profiles in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Sarasota Bay, Florida. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2007, 148, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venn-Watson, S.; Jensen, E.D.; Ridgway, S.H. Effects of age and sex on clinic-pathologic reference ranges in a healthy managed Atlantic bottlenose dolphin population. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2007, 231, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwacke, L.H.; Hall, A.J.; Townsend, F.I.; Wells, R.S.; Hansen, L.J.; Hohn, A.A.; Bossart, G.D.; Fair, P.A.; Rowles, T.K. Hematologic and serum biochemical reference intervals for free-ranging common bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) and variation in the distributions of clinicopathologic values related to geographic sampling site. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 70, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asper, E.D.; Cornell, L.; Duffield, D.A.; Odell, D.K.; Joseph, B.E.; Stark, B.I.; Perry, C.A. Hematology and serum chemistry values in bottlenose dolphins. In The Bottlenose Dolphin; Leatherwood, S., Reeves, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 479–485. ISBN 9780323139618. [Google Scholar]
- Woolford, L.; Wong, A.; Sneath, H.L.; Long, T.; Boyd, S.P.; Lanyon, J.M. Hematology of dugongs (Dugong dugon) in southern Queensland. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 44, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossart, G.D. Immunocytes of the Atlantic Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) and West Indian Manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris): Morphologic Characterizations and Correlations Between Healthy and Disease States and under Free-Ranging and Captive Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, Florida International University, Miami, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Reidarson, T.H.; Duffield, D.; McBain, J. Normal hematology of marine mammals. In Schalm’s Veterinary Hematology, 5th ed.; Feldman, B.F., Zinkl, J.G., Jain, N.C., Eds.; Lippincott Williams& Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 1164–1173. ISBN 978-0683306927. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, A.S.; Foster, D.N.; Troedsson, M.H. Equine seminal plasma reduces sperm binding to polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) and improves the fertility of fresh semen inseminated into inflamed uteri. Reproduction 2004, 127, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.M.R.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Rüdiger, G.; Vila-Viçosa, M.J.M.; Cortes, H.C.E.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. The apicomplexan parasite Eimeria arloingi induces caprine neutrophil extracellular traps. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2797–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Caro, T.; Conejeros, I.; Zhou, E.; Pikhovych, A.; Gärtner, U.; Hermosilla, C.; Kulke, D.; Taubert, A. Dirofiliaria immitis microfilariae and third-stage larvae induce canine NETosis resulting in different types of neutrophil extracellular traps. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiehl, A.R.; Schiller, C.A. A study of manatee leukocytes using peroxidase stain. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 1994, 23, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Caro, T.; Silva, L.M.R.; Rentería-Solís, Z.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Neutrophil extracellular traps in the intestinal mucosa of Eimeria-infected animals. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.J.; Harvey, J.W. Veterinary Laboratory Medicine: Interpretation and Diagnosis; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998; p. 350. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, J.A.; Kaeberle, M.L. Isolation of neutrophils and eosinophils from the peripheral blood of cattle and comparison of functional activities. J. Immunol. Methods 1981, 45, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, A.D.; Jacobsen, E.A.; Ochkur, S.I.; McGarry, M.P.; Shim, K.G.; Nguyen, D.T.; Protheroe, C.; Colbert, D.; Kloeber, J.; Neely, J.; et al. Expression of the secondary granule proteins major basic protein 1 (MBP-1) and eosinophil peroxidase (EPX) is required for eosinophilopoiesis in mice. Blood 2013, 122, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, J.P.W.; Sonne, C.; Levin, M.; Siebert, U.; de Guise, S.; Dietz, R. Immunotoxic effects of environmental pollutants in marine mammals. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Swart, R.L.; Kluten, R.M.G.; Huizing, C.J.; Vedder, L.J.; Reijnders, P.J.H.; Visser, I.K.G.; UytdeHaag, F.G.C.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. Mitogen and antigen induced B and T cell responses of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from the harbour seal (Phoca vitulina). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1993, 37, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Swart, R.; Ross, P.S.; Vedder, L.J.; Boink, F.B.T.J.; Reijnders, P.J.H.; Mulduer, P.G.H.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. Haematology and clinical chemistry values for harbour seals (Phoca vitulina) fed environmentally contaminated herring remain within normal ranges. Can. J. Zool. 1995, 73, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, K.; Schwanke, E.; Hahnb, K.; Wohlsein, P.; Siebert, U. Heartworm (Acanthocheilonema spirocauda) and seal louse (Echinophthirius horridus) infections in harbour seals (Phoca vitulina) from the North and Baltic Seas. J. Sea Res. 2015, 113, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmeier, I.; Fonfara, S.; Driver, J.; Siebert, U. Differential hematology profiles of free-ranging, rehabilitated, and captive harbor seals (Phoca vitulina) of the German North Sea. Aquat. Mammals 2008, 34, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Hasler, P.; Holzgreve, W.; Gebhardt, S.; Hahn, S. Induction of neutrophil extracellular DNA lattices by placental microparticles and IL-8 and their presence in preeclampsia. Hum. Immunol. 2005, 66, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, S.; Giaglis, S.; Hoesli, I.; Hasler, P. Neutrophil NETs in reproduction: From infertility to preeclampsia and the possibility of fetal loss. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, S.; Giaglis, S.; Chowdhury, C.S.; Hösli, I.; Hasler, P. Modulation of neutrophil NETosis: Interplay between infectious agents and underlying host physiology. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, O.Z.; Palaniyar, N. NET Balancing: A problem in inflammatory lung diseases. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, F.; Carrau, T.; Gärtner, U.; Seipp, A.; Taubert, A.; Felmer, R.; Sánchez, R.; Hermosilla, C. Leukocytes co-incubated with human sperm trigger classic neutrophil extracellular traps formation, reducing sperm motility. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 18, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Goldmann, O.; Thulin, P.; Heinemann, K.; Norrby-Teglund, A.; Rohde, M.; Medina, E. Phagocytosis-independent antimicrobial activity of mast cells by means of extracellular trap formation. Blood 2008, 111, 3070–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.M.; Rubin, C.J.; Khandpur, R.; Wang, J.Y.; Riblett, M.; Yalavarthi, S.; Villanueva, E.C.; Shah, P.; Kaplan, M.J.; Bruce, A.T. Mast cells and neutrophils release IL-17 through extracellular trap formation in psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möllerherm, H.; von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Branitzki-Heinemann, K. Antimicrobial activityof mast cells: Role and relevance of extracellular DNA traps. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, S.; Gold, J.A.; Andina, N.; Lee, J.J.; Kelly, A.M.; Kozlowski, E.; Schmid, I.; Straumann, A.; Reichenbach, J.; Gleich, G.J.; et al. Catapult-like release of mitochondrial DNA by eosinophils contributes to antibacterial defense. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulik, N.A.; Hellenbrand, K.M.; Czuprynski, C.J. Mannheimia haemolytica and its leukotoxin cause macrophage extracellular trap formation by bovine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2010, 80, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenbrand, K.M.; Forsythe, K.M.; Rivera-Rivas, J.J.; Czuprynski, C.J.; Aulik, N.A. Histophilus somni causes extracellular trap formation by bovine neutrophils and macrophages. Microb. Pathog. 2013, 54, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boe, D.M.; Curtis, B.J.; Chen, M.M.; Ippolito, J.A.; Kovacs, E.J. Extracellular traps and macrophages: New roles for the versatile phagocyte. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doster, R.S.; Rogers, L.M.; Gaddy, J.A.; Aronoff, D.M. Macrophage extracellular traps: A scoping review. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorn, C.; Janko, C.; Latzko, M.; Chaurio, R.; Schett, G.; Herrmann, M. Monosodium urate crystals induce extracellular DNA traps in neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils but not in mononuclear cells. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, M.; Hlushchuk, R.; Simon, D.; Walls, A.F.; Obata-Ninomiya, K.; Karasuyama, H.; Djonov, V.; Eggel, A.; Kaufmann, T.; Simon, H.U.; et al. NADPH oxidase-independent formation of extracellular DNA traps by basophils. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5314–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taubert, A.; Behrendt, J.H.; Sühwold, A.; Zahner, H.; Hermosilla, C. Monocyte- and macrophage-mediated immune reactions against Eimeria bovis. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 164, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Caro, T.; Hermosilla, C.; Silva, L.M.R.; Cortes, H.; Taubert, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps as innate immune reaction against the emerging apicomplexan parasite Besnoitia besnoiti. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91415. [Google Scholar]
- Halder, L.D.; Abdelfatah, M.A.; Jo, E.A.; Jacobsen, I.D.; Westermann, M.; Beyersdorf, N.; Lorkowski, S.; Zipfel, P.F.; Skerka, C. Factor H binds to extracellular DNA traps released from human blood monocytes in response to Candida albicans. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Hurwitz, R.; Schulze, I.; Wahn, V.; Weinrauch, Y.; Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, S.; Urosevic, M.; Daryadel, A.; Oberholzer, P.A.; Baumann, C.; Fey, M.F.; Dummer, R.; Simon, H.U.; Yousefi, S. Induction of genes mediating interferon dependent extracellular trap formation during neutrophil differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44123–44132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães-Costa, A.B.; Rochael, N.C.; Oliveira, F.; Echevarria-Lima, J.; Saraiva, E.M. Neutrophil extracellular traps reprogram IL-4/GM-CSF-induced monocyte differentiation to anti-inflammatory macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudrillier, A.; Kessenbrock, K.; Gilliss, B.M.; Nguyen, J.X.; Marques, M.B.; Monestier, M.; Toy, P.; Werb, Z.; Looney, M.R. Platelets induce neutrophil extracellular traps in transfusion-related acute lung injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2661–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.R.; Ma, A.C.; Tavener, S.A.; McDonald, B.; Goodarzi, Z.; Kelly, M.M.; Patel, K.D.; Chakrabarti, S.; McAvoy, E.; Sinclair, G.D.; et al. Platelet TLR4 activates neutrophil extracellular traps to ensnare bacteria in septic blood. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijanowski, L.; Golbach, L.; Kolaczkowska, E.; Scheer, M.; Verburg-van Kemenade, B.M.L.; Chadzinska, M. Carp neutrophilic granulocytes form extracellular traps via ROS-dependent and independent pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, J.; Kumar, S.V.; Mulay, S.R.; Konrad, L.; Romoli, S.; Schauer, C.; Herrmann, M.; Bilyy, R.; Müller, S.; Popper, B.; et al. PMA and crystal-induced neutrophil extracellular trap formation involves RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL signaling. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, E.F.; Herzig, A.; Krüger, R.; Muth, A.; Mondal, S.; Thompson, P.R.; Brinkmann, V.; Bernuth, H.V.; Zychlinsky, A. Diverse stimuli engage different neutrophil extracellular trap pathways. eLife 2017, 6, e24437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishinaka, Y.; Arai, T.; Adachi, S.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Yamashita, K. Singlet oxygen is essential for neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res.Commun. 2011, 413, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, C.F.; Reichard, U.; Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps capture and kill Candida albicans yeast and hyphal forms. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, C.F.; Ermert, D.; Schmid, M.; Abu-Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Nacken, W.; Brinkmann, V.; Jungblut, P.R.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps contain calprotectin, a cytosolic protein complex involved in host defense against Candida albicans. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemán, O.R.; Mora, N.; Cortes-Vieyra, R.; Uribe-Querol, E.; Rosales, C. Differential use of human neutrophil Fcγ receptors for inducing neutrophil extracellular trap formation. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 2908034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Shi, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Jiang, M.; Liu, M.; Yu, L. Aflatoxin B1 induces reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagy and extracellular trap formation in macrophages. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilsczek, F.H.; Salina, D.; Poon, K.K.H.; Fahey, C.; Yipp, B.G.; Sibley, C.D.; Robbins, S.M.; Green, F.H.Y.; Surette, M.G.; Sugai, M. A novel mechanism of rapid nuclear neutrophil extracellular trap formation in response to Staphylococcus aureus. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7413–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.J.; Davis, J.M.; Huttenlocher, A.; Kernien, J.F.; Nett, J.E. Emerging fungal pathogen Candida auris evades neutrophil attack. mBio 2018, 9, e01403-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenne, C.N.; Kubes, P. NETs tangle with HIV. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenne, C.N.; Kubes, P. Virus-induced NETs-critical component of host defense or pathogenic mediator? PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães-Costa, A.B.; Nascimento, M.T.; Froment, G.S.; Soares, R.P.; Morgado, F.N.; Conceição-Silva, F.; Saraiva, E.M. Leishmania amazonensis promastigotes induce and are killed by neutrophil extracellular traps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6748–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abi Abdallah, D.S.; Lin, C.; Ball, C.J.; King, M.R.; Duhamel, G.E.; Denkers, E.Y. Toxoplasma gondii triggers release of human and mouse neutrophil extracellular traps. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermosilla, C.; Ruiz, A.; Taubert, A. Eimeria bovis: An update on parasite-host interactions. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 302, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xin, L.; Beverley, S.M.; Carlsen, E.D.; Popov, V.; Chang, K.P.; Wang, M.; Soong, L. Differential microbicidal effects of human histone proteins H2A and H2B on Leishmania promastigotes and amastigotes. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papayannopoulos, V.; Metzler, K.D.; Hakkim, A.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase regulate the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leshner, M.; Wang, S.; Lewis, C.; Zheng, H.; Chen, X.A.; Santy, L.; Wang, Y. PAD4 mediated histone hypercitrullination induces heterochromatin decondensation and chromatin unfolding to form neutrophil extracellular trap like structures. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Caro, T.; Mena Huertas, J.S.; Conejeros, I.; Alarcón, P.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Burgos, R.A.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. CD11b-, ERK/MAP kinase- and SOCE-dependent Eimeria bovis-triggered neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Caro, T.; Lendner, M.; Daugschies, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. NADPH oxidase, MPO, NE, ERK1/2, p38 MAPK and Ca2+ influx are essential for Cryptosporidium parvum-induced NET formation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 52, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, M.; Lindberg, M.R.; Kennett, M.J.; Xiong, N.; Wang, Y. PAD4 is essential for antibacterial innate immunity mediated by neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yipp, B.G.; Kubes, P. NETosis: How vital is it? Blood 2013, 122, 2784–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Guise, S.; Flipo, D.; Boehm, J.; Martineau, D.; Béland, P.; Fournier, M. Immune functions in beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas): Evaluation of phagocytosis and respiratory burst with peripheral blood using flow cytometry. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1995, 47, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkim, A.; Fuchs, T.A.; Martinez, N.E.; Hess, S.; Prinz, H.; Zychlinsky, A.; Waldmann, H. Activation of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway is required for neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, R.A.; Conejeros, I.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Werling, D.; Hermosilla, C. Calcium influx, a new potential therapeutic target in the control of neutrophil- dependent inflammatory diseases in bovines. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejeros, I.; Jara, E.; Carretta, M.D.; Alarcón, P.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Burgos, R.A. 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) reduces respiratory burst, MMP-9 release and CD11b expression, and increases l-selectin shedding in bovine neutrophils. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 92, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villagra-Blanco, R.; Silva, L.M.R.; Gärtner, U.; Wagner, H.; Failing, K.; Wehrend, A.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Molecular analyses on Neospora caninum-triggered NETosis in the caprine system. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 72, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douda, D.N.; Khan, M.A.; Grasemann, H.; Palaniyar, N. SK3 channel and mitochondrial ROS mediate NADPH oxidase-independent NETosis induced by calcium influx. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2817–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochael, N.C.; Guimarães-Costa, A.B.; Nascimento, M.T.C.; De Souza-Vieira, T.S.; Oliveira, M.P.; Garcia e Souza, L.F.; Oliveira, M.F.; Saraiva, E.M. Classical ROS-dependent and early/rapid ROS-independent release of neutrophil extracellular traps triggered by Leishmania parasites. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoiber, W.; Obermayer, A.; Steinbacher, P.; Krautgartner, W.D. The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the formation of extracellular traps (ETs) in humans. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 702–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malawista, S.E.; Van Blaricom, G.; Breitenstein, M.G. Cryopreservable neutrophil surrogates. Stored cytoplasts from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes retain chemotactic, phagocytic, and microbicidal function. J. Clin.Investig. 1989, 83, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Mihalache, C.; Kozlowski, E.; Schmid, I.; Simon, H.U. Viable neutrophils release mitochondrial DNA to form neutrophil extracellular traps. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yipp, B.G.; Petri, B.; Salina, D.; Jenne, C.N.; Scott, B.N.V.; Zbytnuik, L.D.; Pittman, K.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Wu, K.; Meijndert, H.C.; et al. Infection-induced NETosis is a dynamicprocess involving neutrophil multitasking in vivo. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, C.; Janko, C.; Munoz, L.E.; Zhao, Y.; Kienhöfer, D.; Frey, B.; Lell, M.; Manger, B.; Rech, J.; Naschberger, E.; et al. Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppens, I.; Dunn, J.D.; Romano, J.D.; Pypaert, M.; Zhang, H.; Boothroyd, J.C.; Joiner, K.A. Toxoplasma gondii sequesters lysosomes from mammalian hosts in the vacuolar space. Cell 2006, 125, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.M.; Jones, A.R.; Carmen, J.C.; Sinai, A.P.; Burchmore, R.; Wastling, J.M. Modulation of the host cell proteome by the intracellular apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Infect. Immun. 2007, 76, 828–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, P.H.; Hirzmann, J.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Differential inhibition of host cell cholesterol de novo biosynthesis and processing abrogates Eimeria bovis intracellular development. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 4165–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, P.H.; Hirzmann, J.; Kerner, K.; Gimpl, G.; Lochnit, G.; Hermosilla, C.R.; Taubert, A. Eimeria bovis infection modulates endothelial host cell cholesterol metabolism for successful replication. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Silva, L.M.R.; Wieck, A.; Failing, K.; Mazurek, S. Metabolic signatures of Besnoitia besnoiti-infected endothelial host cells and blockage of key metabolic pathways indicate high glycolytic and glutaminolytic needs of the parasite. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2023–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A.; He, X.; Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X. Canine neutrophil extracellular traps release induced by the apicomplexan parasite Neospora caninum in vitro. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, J.H.; Ruiz, A.; Zahner, H.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Neutrophil extracellular trap formation as innate immune reactions against the apicomplexan parasite Eimeria bovis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 133, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagra-Blanco, R.; Silva, L.M.R.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Gärtner, U.; Taubert, A.; Zhang, X.; Hermosilla, C. Bovine PMN cast neutrophil extracellular traps against the abortive parasite Neospora caninum. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A.; He, X.; Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Li, J.; Zhang, X. Caprine monocytes release extracellular traps against Neospora caninum in vitro. Front. Immunol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, K.; Gokpinar, S.; Gazyagci, A.N.; Babur, C.; Sursal, N.; Azkur, A.K. Role of NETs in the difference in host susceptibility to Toxoplasma gondii between sheep and cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017, 189, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wormer, E.; Conrad, P.A.; Miller, M.A.; Melli, A.C.; Carpenter, T.E.; Mazet, J. Toxoplasma gondii, source to sea: Higher contribution of domestic felids to terrestrial parasite loading despite lower infection prevalence. EcoHealth 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begde, D.; Bundale, S.; Mashitha, P.; Rudra, J.; Nashikkar, N.; Upadhyay, A. Immunomodulatory efficacy of nisin—A bacterial lantibiotic peptide. J. Pept. Sci. 2011, 17, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullar, J.M.; Vissers, M.C.; Winterbourn, C.C. Living with a killer: The effects of hypochlorous acid on mammalian cells. IUBMB Life 2000, 50, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebanoff, S.J. Myeloperoxidase: Friend and foe. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 598–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Buhr, N.; von Köckritz-Blickwede, M. How Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Become Visible. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 4604713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itou, T.; Sugisawa, H.; Inoue, Y.; Jinbo, T.; Sakai, T. Oxygen radical generationand expression of NADPH oxidase genes in bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) neutrophils. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Chow, O.; Ghochani, M.; Nizet, V. Visualization and functional evaluation of phagocyte extracellular traps. Methods Microbiol. 2010, 37, 139–160. [Google Scholar]
- Von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Nizet, V. Innate immunity turned inside-out: Antimicrobial defense by phagocyte extracellular traps. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).