Teleost Chemokines and Their Receptors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Identification, Transcriptional Regulation and Functionality of Teleost CC Chemokine Genes
2.1. Zebrafish CC Chemokines
2.2. Rainbow Trout CC Chemokines
2.3. Catfish CC Chemokines
2.4. CC Chemokines in Other Fish Species
2.5. Classification of Teleost CC Chemokines
3. Identification, Transcriptional Regulation and Functionality of Teleost CXC Chemokine Genes
3.1. Zebrafish and Carp CXC Genes
3.2. Rainbow Trout CXC Chemokines
3.3. Catfish CXC Chemokines
3.4. CXC Chemokines in Other Species
3.5. Classification of CXC Chemokines in Fish
4. Identification of Teleost C and Fish-Specific CX Chemokine Genes
5. Teleost Chemokine Receptors
| Receptor | Ligand (Agonist) | Ligand (Antagonist) |
|---|---|---|
| CXCL6, CXCL7, CXCL8 | ||
| CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL5, CXCL6, CXCL7, CXCL8 | ||
| CXCR3 | CXCL4, CXCL4L1, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, CXCL13 | CCL11 |
| CXCR4 | CXCL12, CXCL14 | |
| CXCR5 | CXCL13 | |
| CXCL16 | ||
| CXCR8 (GPR35) | CXCL17 | |
| CCL3, CCL3L1, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13, CCL14, CCL15, CCL16, CCL23 | CCL26 | |
| CCL2, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13, CCL16 | CCL11, CCL26 | |
| CCL3L1, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL11, CCL13, CCL14, CCL15, CCL24, CCL26, CCL28 | CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, CCL18 | |
| CCL17, CCL22 | ||
| CCL3, CCL3L1, CCL4, CCL5, CCL8, CCL11, CCL13, CCL14, CCL16 | CCL7, CCL26, CXCL11 | |
| CCR6 | CCL20, CCL21 | |
| CCR7 | CCL19, CCL21 | |
| CCL1, CCL16, CCL18 | ||
| CCR9 | CCL25 | |
| CCR10 | CCL27, CCL28 | |
| CCL1, CCL2, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL11, CCL13, CCL14, CCL16, CCL17, CCL18, CCL22, CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL4, CXCL5, CXCL6, CXCL7, CXCL8, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, CXCL13 | ||
| ACKR2 (CCBP2) | CCL2, CCL3, CCL3L1, CCL4, CCL4L1, CCL5, CCL6, CCL7, CCL8, CCL11, CCL12, CCL13, CCL14, CCL17, CCL22, CCL23, CCL24, CCL26 | |
| ACKR3 (CXCR7) | CXCL11, CXCL12 | |
| ACKR4 (CCR11) | CCL19, CCL21, CCL25, CXCL13 | |
| CCL19 | ||
| ACKR6 (PITPNM3) | CCL18 | |
| XCR1 | XCL1, XCL2 | |
| CCL26, CX3CL1 |
5.1. CCR Subfamily
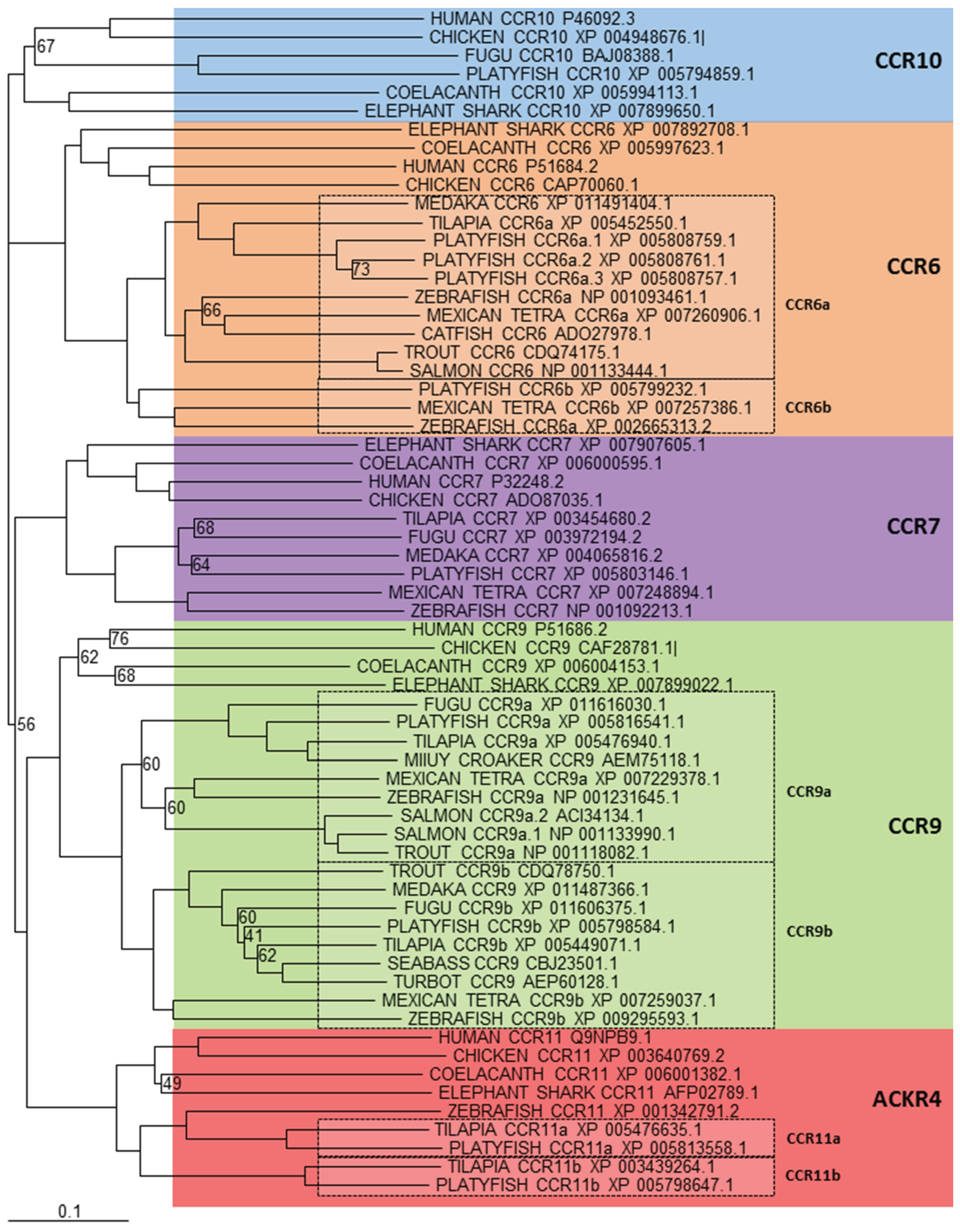
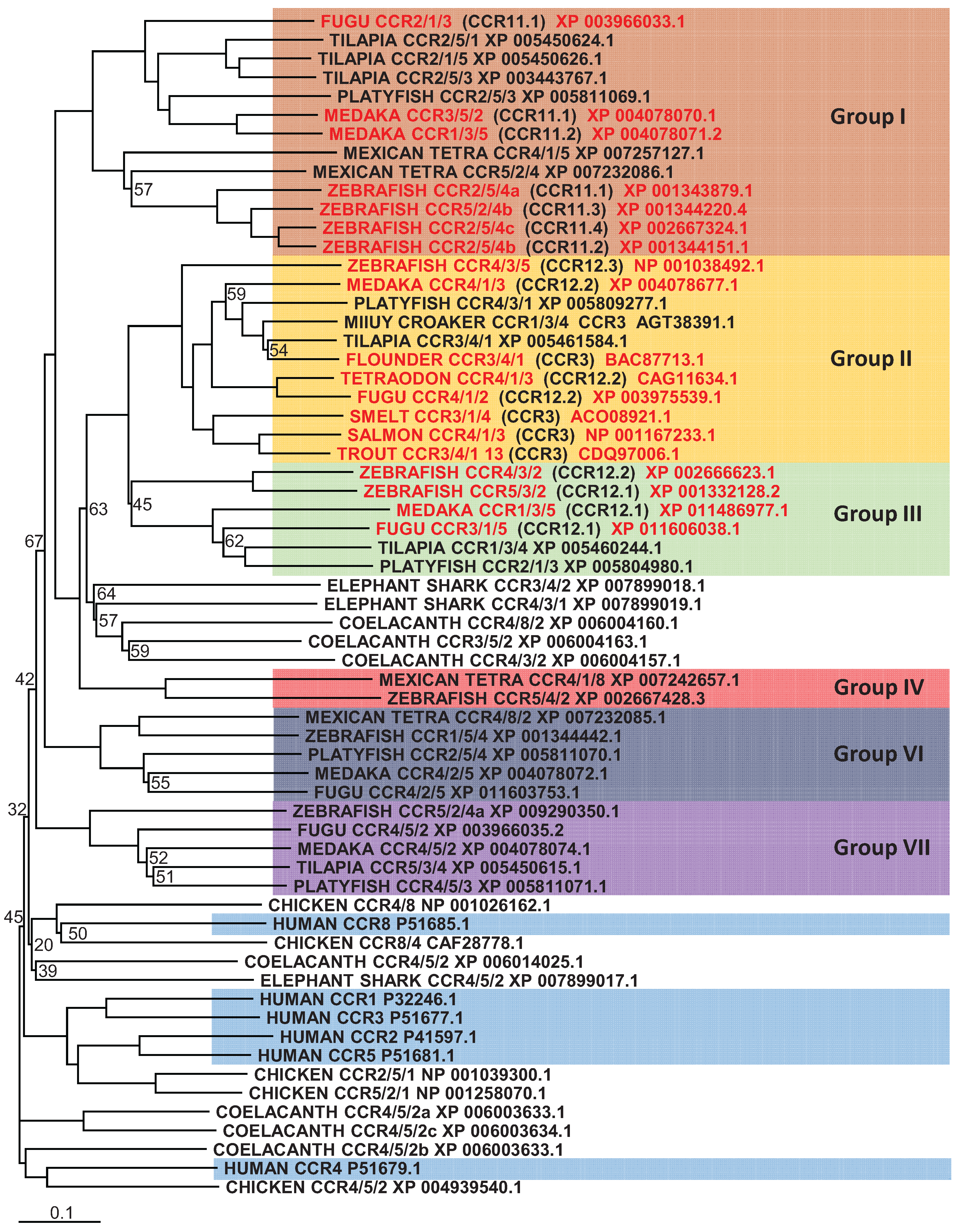
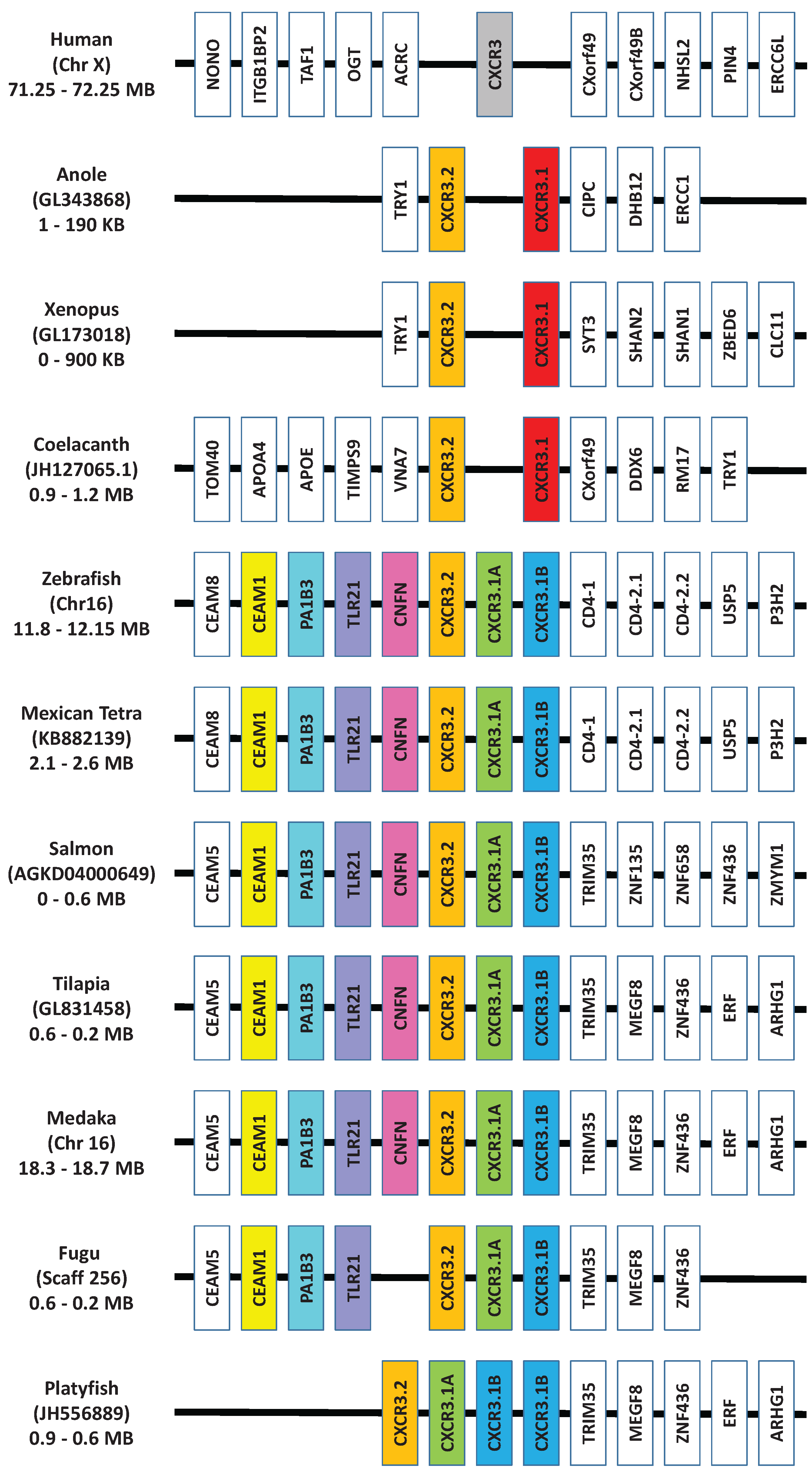
5.2. CXCR Subfamily
5.3. Other Subfamily Members

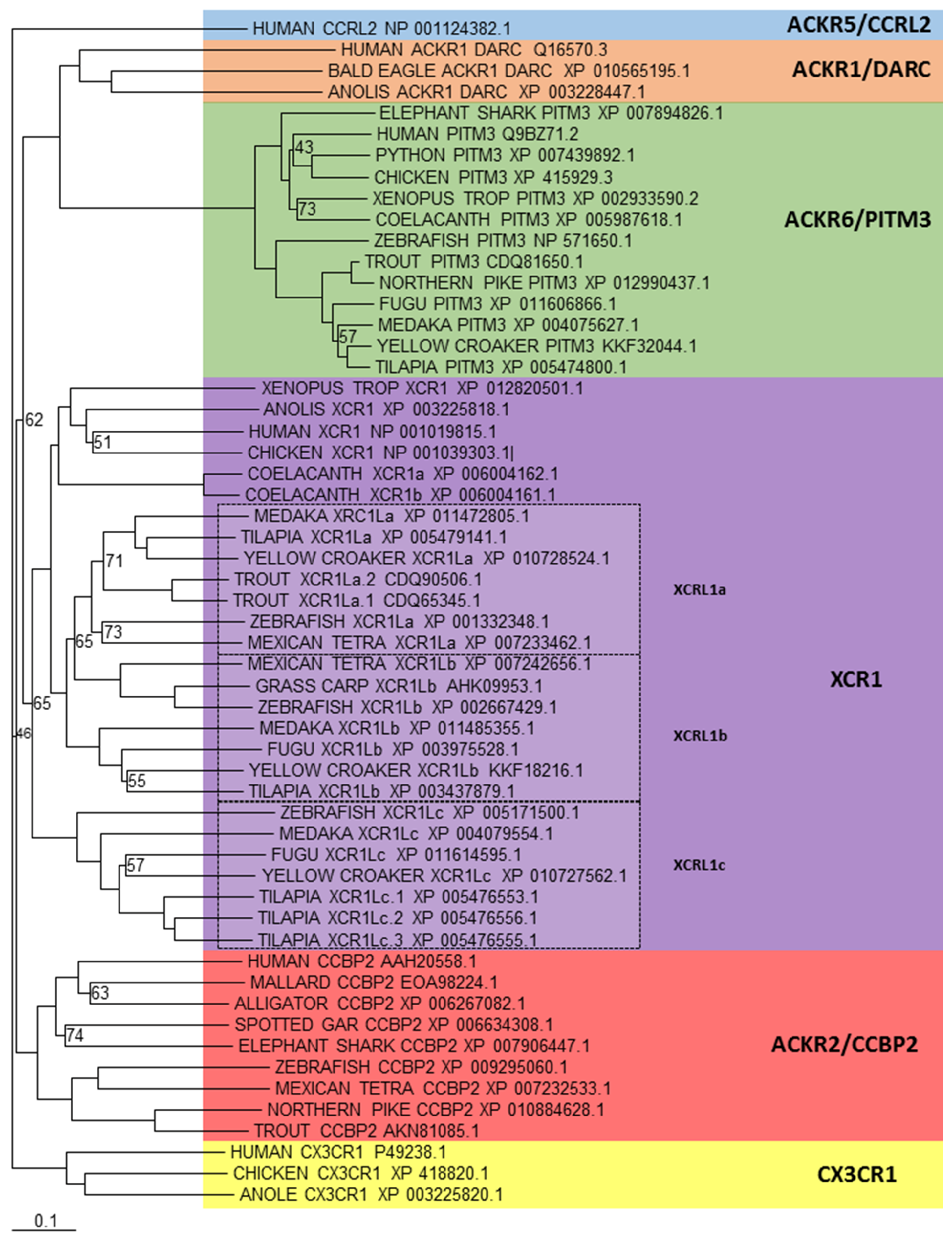
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cyster, J.G.; Ngo, V.N.; Ekland, E.H.; Gunn, M.D.; Sedgwick, J.D.; Ansel, K.M. Chemokines and B-cell homing to follicles. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1999, 246, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warnock, R.A.; Campbell, J.J.; Dorf, M.E.; Matsuzawa, A.; McEvoy, L.M.; Butcher, E.C. The role of chemokines in the microenvironmental control of T versus B-cell arrest in peyer’s patch high endothelial venules. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenberg, D.A.; Polverini, P.J.; Kunkel, S.L.; Shanafelt, A.; Strieter, R.M. In vitro and in vivo systems to assess role of CXC chemokines in regulation of angiogenesis. Methods Enzymol. 1997, 288, 190–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keane, M.P.; Arenberg, D.A.; Moore, B.B.; Addison, C.L.; Strieter, R.M. CXC chemokines and angiogenesis/angiostasis. Proc. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1998, 110, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gordon, R.J.; McGregor, A.L.; Connor, B. Chemokines direct neural progenitor cell migration following striatal cell loss. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2009, 41, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmadani, A.; Tran, P.B.; Ren, D.; Miller, R.J. Chemokines regulate the migration of neural progenitors to sites of neuroinflammation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 3182–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doitsidou, M.; Reichman-Fried, M.; Stebler, J.; Koprunner, M.; Dorries, J.; Meyer, D.; Esguerra, C.V.; Leung, T.; Raz, E. Guidance of primordial germ cell migration by the chemokine SDF-1. Cell 2002, 111, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaut, H.; Werz, C.; Geisler, R.; Nusslein-Volhard, C. A zebrafish homologue of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a germ-cell guidance receptor. Nature 2003, 421, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVries, M.E.; Kelvin, A.A.; Xu, L.; Ran, L.; Robinson, J.; Kelvin, D.J. Defining the origins and evolution of the chemokine/chemokine receptor system. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esche, C.; Stellato, C.; Beck, L.A. Chemokines: Key players in innate and adaptive immunity. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunkel, S.L.; Strieter, R.M.; Lindley, I.J.; Westwick, J. Chemokines: New ligands, receptors and activities. Immunol. Today 1995, 16, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, K.; Baggiolini, M.; Broxmeyer, H.; Horuk, R.; Lindley, I.; Mantovani, A.; Maysushima, K.; Murphy, P.; Nomiyama, H.; Oppenheim, J.; et al. Chemokine/chemokine receptor nomenclature. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002, 22, 1067–1068. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nomiyama, H.; Hieshima, K.; Osada, N.; Kato-Unoki, Y.; Otsuka-Ono, K.; Takegawa, S.; Izawa, T.; Yoshizawa, A.; Kikuchi, Y.; Tanase, S.; et al. Extensive expansion and diversification of the chemokine gene family in zebrafish: Identification of a novel chemokine subfamily CX. BMC Genomics 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson, R.; Lagerstrom, M.C.; Lundin, L.G.; Schioth, H.B. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotnik, A.; Yoshie, O. The chemokine superfamily revisited. Immunity 2012, 36, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, J.W.; Sokol, C.L.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: Positioning cells for host defense and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 659–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, G.J.; Locati, M.; Mantovani, A.; Rot, A.; Thelen, M. The biochemistry and biology of the atypical chemokine receptors. Immunol. Lett. 2012, 145, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nibbs, R.J.; Graham, G.J. Immune regulation by atypical chemokine receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark-Lewis, I.; Schumacher, C.; Baggiolini, M.; Moser, B. Structure-activity relationships of interleukin-8 determined using chemically synthesized analogs. Critical role of NH2-terminal residues and evidence for uncoupling of neutrophil chemotaxis, exocytosis, and receptor binding activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 23128–23134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark-Lewis, I.; Dewald, B.; Geiser, T.; Moser, B.; Baggiolini, M. Platelet factor 4 binds to interleukin 8 receptors and activates neutrophils when its n terminus is modified with Glu-Leu-Arg. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3574–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, C.R. Chemokines: What chemokine is that? Curr. Biol. 1997, 7, R384–R386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnik, A. Chemokines and cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2026–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, C.A.; Vitangcol, R.V.; Baker, J.B. Scanning mutagenesis of interleukin-8 identifies a cluster of residues required for receptor binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 18989–18994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, K. Functional characterization of the ELR motif in piscine ELR+ CXC-like chemokine. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, B.; Shum, B.; Adams, E.J.; Magor, K.E.; Hedrick, R.P.; Muir, D.G.; Parham, P. CK-1, a putative chemokine of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Immunol. Rev. 1998, 166, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterston, R.H.; Lander, E.S.; Sulston, J.E. On the sequencing of the human genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3712–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peatman, E.; Liu, Z. Evolution of CC chemokines in teleost fish: A case study in gene duplication and implications for immune diversity. Immunogenetics 2007, 59, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peatman, E.; Bao, B.; Peng, X.; Baoprasertkul, P.; Brady, Y.; Liu, Z. Catfish CC chemokines: Genomic clustering, duplications, and expression after bacterial infection with Edwardsiella ictaluri. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2006, 275, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotman, J.; van Gils, W.; Butler, D.; Spaink, H.P.; Meijer, A.H. Rapid screening of innate immune gene expression in zebrafish using reverse transcription—Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. BMC Res. Notes 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, I.N.; Chiang, B.L.; Lou, K.L.; Huang, P.T.; Yao, C.C.; Wang, J.S.; Lin, L.D.; Jeng, J.H.; Chang, B.E. Cloning, expression and characterization of CCL21 and CCL25 chemokines in zebrafish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomiyama, H.; Osada, N.; Yoshie, O. Systematic classification of vertebrate chemokines based on conserved synteny and evolutionary history. Genes Cells 2013, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, I.; Boehm, T. Intravital imaging of thymopoiesis reveals dynamic lympho-epithelial interactions. Immunity 2012, 36, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajoghli, B.; Aghaallaei, N.; Hess, I.; Rode, I.; Netuschil, N.; Tay, B.H.; Venkatesh, B.; Yu, J.K.; Kaltenbach, S.L.; Holland, N.D.; et al. Evolution of genetic networks underlying the emergence of thymopoiesis in vertebrates. Cell 2009, 138, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, K.J.; Secombes, C.J. Trout CC chemokines: Comparison of their sequences and expression patterns. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 41, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Fujiki, K.; Dixon, B.; Sundick, R.S. Cloning of a novel rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) CC chemokine with a fractalkine-like stalk and a TNF decoy receptor using cDNA fragments containing au-rich elements. Cytokine 2002, 17, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, S.; Liarte, C.; Iliev, D.; Planas, J.V.; Tort, L.; Goetz, F.W. Characterization of a highly inducible novel CC chemokine from differentiated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) macrophages. Immunogenetics 2004, 56, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, E.; Coll, J.; Tafalla, C. Expression of inducible CC chemokines in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in response to a viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) DNA vaccine and interleukin 8. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2007, 31, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, J.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Cuesta, A.; Tafalla, C. Chemokine transcription in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) is differently modulated in response to viral hemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHSV) or infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Montero, J.; Cuesta, A.; Tafalla, C. Viral hemorrhagic septicemia and infectious pancreatic necrosis viruses replicate differently in rainbow trout gonad and induce different chemokine transcription profiles. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, J.; Garcia, J.; Ordas, M.C.; Casanova, I.; Gonzalez, A.; Villena, A.; Coll, J.; Tafalla, C. Specific regulation of the chemokine response to viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus at the entry site. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4046–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros, N.A.; Rodriguez Saint-Jean, S.; Perez-Prieto, S.I.; Aquilino, C.; Tafalla, C. Modulation of genes related to the recruitment of immune cells in the digestive tract of trout experimentally infected with infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) or orally vaccinated. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 44, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.; Martinez-Alonso, S.; Fischer, U.; Haro, N.A.; Soto-Lampe, V.; Wang, T.; Secombes, C.J.; Lorenzen, N.; Lorenzen, E.; Tafalla, C. DNA vaccination against a fish rhabdovirus promotes an early chemokine-related recruitment of B-cells to the muscle. Vaccine 2014, 32, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, J.; Coll, J.; Sevilla, N.; Cuesta, A.; Bols, N.C.; Tafalla, C. Interleukin 8 and CK-6 chemokines specifically attract rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) RTS11 monocyte-macrophage cells and have variable effects on their immune functions. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, J.; Ordas, M.C.; Alejo, A.; Gonzalez-Torres, L.; Sevilla, N.; Tafalla, C. CK12, a rainbow trout chemokine with lymphocyte chemo-attractant capacity associated to mucosal tissues. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Peatman, E.; Baoprasertkul, P.; Kucuktas, H.; Liu, Z. Multiple CC chemokines in channel catfish and blue catfish as revealed by analysis of expressed sequence tags. Immunogenetics 2004, 56, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, B.; Peatman, E.; Peng, X.; Baoprasertkul, P.; Wang, G.; Liu, Z. Characterization of 23 CC chemokine genes and analysis of their expression in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Dev. Comp. Immunol 2006, 30, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nibbs, R.J.; Graham, G.J. CCL27/pesky: A novel paradigm for chemokine function. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2003, 3, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta, A.; Dios, S.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B.; Esteban, M.A.; Meseguer, J.; Tafalla, C. Identification of six novel CC chemokines in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) implicated in the antiviral immune response. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, T.; Kusuda, R.; Kawahara, E.; Sakai, M. The analysis of immune responses of a novel CC-chemokine gene from japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Vaccine 2003, 21, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattiya, R.; Ohira, T.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T. Identification of a novel japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) CC chemokine gene and an analysis of its function. Immunogenetics 2004, 55, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattiya, R.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T. Cloning, expression and functional analysis of a novel-chemokine gene of japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus, containing two additional cysteines and an extra fourth exon. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, G.G.; Nozaki, R.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I. Cloning and expression analysis of three novel CC chemokine genes from japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.J.; Hou, C.Y.; Lin, S.J.; Kuo, W.C.; Lin, H.T.; Lin, J.H. The biofunction of orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) CC chemokine ligand 4 (CCL4) in innate and adaptive immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, E.G.; Kim, D.H.; Shim, S.H.; Park, C.I. Molecular identification and expression analysis of the CC chemokine gene in rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus) and the biological activity of the recombinant protein. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, K.J.; Secombes, C.J. Chemokines. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Hour, A.L.; Shiau, C.Y.; Hui, C.F.; Wu, J.L. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of zebrafish (Danio rerio) chemokine genes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2008, 151, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarris, M.; Masson, J.B.; Maurin, D.; van der Aa, L.M.; Boudinot, P.; Lortat-Jacob, H.; Herbomel, P. Inflammatory chemokines direct and restrict leukocyte migration within live tissues as glycan-bound gradients. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, S.; Reyes-Aldasoro, C.C.; Candel, S.; Renshaw, S.A.; Mulero, V.; Calado, A. CXCL8 (IL-8) mediates neutrophil recruitment and behavior in the zebrafish inflammatory response. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4349–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, S.; Lopez-Munoz, A.; Martinez-Navarro, F.J.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Mulero, V.; Calado, A. CXCL8-L1 and CXCL8-L2 are required in the zebrafish defense against Salmonella typhimurium. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 49, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugman, S.; Witte, M.; Scholman, R.C.; Klein, M.R.; Boes, M.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E. T lymphocyte-dependent and -independent regulation of CXCL8 expression in zebrafish intestines. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Aa, L.M.; Chadzinska, M.; Tijhaar, E.; Boudinot, P.; van Kemenade, B.M. CXCL8 chemokines in teleost fish: Two lineages with distinct expression profiles during early phases of inflammation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y. Neutrophil infiltration and chemokines. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 26, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Aa, L.M.; Chadzinska, M.; Golbach, L.A.; Ribeiro, C.M.; van Kemenade, B.M. Pro-inflammatory functions of carp CXCL8-like and CXCb chemokines. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Raemdonck, K.; van den Steen, P.E.; Liekens, S.; van Damme, J.; Struyf, S. CXCR3 ligands in disease and therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Aa, L.M.; Chadzinska, M.; Derks, W.; Scheer, M.; Levraud, J.P.; Boudinot, P.; van Kemenade, B.M. Diversification of IFNγ-inducible CXCb chemokines in cyprinid fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torraca, V.; Cui, C.; Boland, R.; Bebelman, J.P.; van der Sar, A.M.; Smit, M.J.; Siderius, M.; Spaink, H.P.; Meijer, A.H. The CXCR3–CXCL11 signaling axis mediates macrophage recruitment and dissemination of mycobacterial infection. Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadzinska, M.; Golbach, L.; Pijanowski, L.; Scheer, M.; van Kemenade, B.M. Characterization and expression analysis of an interferon-γ2 induced chemokine receptor CXCR3 in common CARP (Cyprinus carpio L.). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 47, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, M.R.; Bussmann, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Osorio, A.; Burns, C.G.; Burns, C.E.; Sucov, H.M.; Siekmann, A.F.; Lien, C.L. Chemokine-guided angiogenesis directs coronary vasculature formation in zebrafish. Dev. Cell 2015, 33, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huising, M.O.; van der Meulen, T.; Flik, G.; Kemenade, B.M. Three novel carp CXC chemokines are expressed early in ontogeny and at nonimmune sites. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 4094–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, P.; Gilmour, D. Chemokine signaling mediates self-organizing tissue migration in the zebrafish lateral line. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diotel, N.; Vaillant, C.; Gueguen, M.M.; Mironov, S.; Anglade, I.; Servili, A.; Pellegrini, E.; Kah, O. CXCR4 and CXCL12 expression in radial glial cells of the brain of adult zebrafish. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 518, 4855–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle Nogare, D.; Somers, K.; Rao, S.; Matsuda, M.; Reichman-Fried, M.; Raz, E.; Chitnis, A.B. Leading and trailing cells cooperate in collective migration of the zebrafish posterior lateral line primordium. Development 2014, 141, 3188–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyon, A. CXCL12 chemokine and its receptors as major players in the interactions between immune and nervous systems. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augsten, M.; Hagglof, C.; Olsson, E.; Stolz, C.; Tsagozis, P.; Levchenko, T.; Frederick, M.J.; Borg, A.; Micke, P.; Egevad, L.; et al. CXCL14 is an autocrine growth factor for fibroblasts and acts as a multi-modal stimulator of prostate tumor growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3414–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebl, A.; Rebl, H.; Korytar, T.; Goldammer, T.; Seyfert, H.M. The proximal promoter of a novel interleukin-8-encoding gene in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) is strongly induced by CEBPA, but not NF-κB p65. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 46, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, K.J.; Zou, J.J.; Wang, T.; Bols, N.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T.; Secombes, C.J. Identification and analysis of an interleukin 8-like molecule in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2002, 26, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafalla, C.; Coll, J.; Secombes, C.J. Expression of genes related to the early immune response in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, M.K.; Kurath, G.; Garver, K.A.; Herwig, R.P.; Winton, J.R. Quantitative expression profiling of imune response genes in rainbow trout following infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) infection or DNA vaccination. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 17, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harun, N.O.; Zou, J.; Zhang, Y.A.; Nie, P.; Secombes, C.J. The biological effects of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) recombinant interleukin-8. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, K.J.; Bols, N.; Secombes, C.J. A CXC chemokine sequence isolated from the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss resembles the closely related interferon-γ-inducible chemokines CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2002, 13, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Carrington, A.; Collet, B.; Dijkstra, J.M.; Yoshiura, Y.; Bols, N.; Secombes, C. Identification and bioactivities of IFN-γ in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: The first Th1-type cytokine characterized functionally in fish. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2484–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, T.; Collet, B.; Corripio-Miyar, Y.; Bird, S.; Xie, P.; Nie, P.; Secombes, C.J.; Zou, J. Phylogenetic analysis of vertebrate CXC chemokines reveals novel lineage specific groups in teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiens, G.D.; Glenney, G.W.; Lapatra, S.E.; Welch, T.J. Identification of novel rainbow trout (Onchorynchus mykiss) chemokines, CXCd1 and CXCd2: mRNA expression after Yersinia ruckeri vaccination and challenge. Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobe, J.; Montfort, J.; Nguyen, T.; Fostier, A. Identification of new participants in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) oocyte maturation and ovulation processes using cDNA microarrays. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baoprasertkul, P.; He, C.; Peatman, E.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Liu, Z. Constitutive expression of three novel catfish CXC chemokines: Homeostatic chemokines in teleost fish. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; He, C.; Baoprasertkul, P.; Xu, P.; Li, P.; Serapion, J.; Waldbieser, G.; Wolters, W.; Liu, Z. Analysis of a catfish gene resembling interleukin-8: cDNA cloning, gene structure, and expression after infection with Edwardsiella ictaluri. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baoprasertkul, P.; Peatman, E.; Chen, L.; He, C.; Kucuktas, H.; Li, P.; Simmons, M.; Liu, Z. Sequence analysis and expression of a CXC chemokine in resistant and susceptible catfish after infection of Edwardsiella ictaluri. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.P.; Kelly, L.M.; Cyster, J.G. Finding the right niche: B-cell migration in the early phases of T-dependent antibody responses. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Yasuike, M.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T. Molecular characterization and gene expression of a CXC chemokine gene from japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Ao, J.; Chen, X. Molecular characterization and bioactivity of a CXCl13 chemokine in large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.Y.; Hikima, J.; Ohtani, M.; Jang, H.B.; del Castillo, C.S.; Nho, S.W.; Cha, I.S.; Park, S.B.; Aoki, T.; Jung, T.S. Recombinant interferon-γ activates immune responses against Edwardsiella tarda infection in the olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corripio-Miyar, Y.; Bird, S.; Tsamopoulos, K.; Secombes, C.J. Cloning and expression analysis of two pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and IL-8, in haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus). Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppola, M.; Larsen, A.N.; Steiro, K.; Robertsen, B.; Jensen, I. Characterisation and expression analysis of the interleukin genes, IL-1β, IL-8 and IL-10, in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.Q.; Lu, X.J.; Li, C.H.; Chen, J. Molecular characterization of a CXCL8-like protein from ayu and its effect on chemotaxis of neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages. Gene 2014, 548, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thulasitha, W.S.; Umasuthan, N.; Whang, I.; Lim, B.S.; Jung, H.B.; Noh, J.K.; Lee, J. A CXC chemokine gene, CXCL12, from rock bream, Oplegnathus fasciatus: Molecular characterization and transcriptional profile. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huising, M.O.; Stet, R.J.; Kruiswijk, C.P.; Savelkoul, H.F.; van Kemenade, B.M. Molecular evolution of CXC chemokines: Extant CXC chemokines originate from the CNS. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, M.X.; Wu, S.G.; Nie, P. Characterization of CC chemokine receptor subfamily in teleost fish. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghaallaei, N.; Bajoghli, B.; Schwarz, H.; Schorpp, M.; Boehm, T. Characterization of mononuclear phagocytic cells in medaka fish transgenic for a CXCR3A: GFP reporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18079–18084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomiyama, H.; Osada, N.; Yoshie, O. A family tree of vertebrate chemokine receptors for a unified nomenclature. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajoghli, B. Evolution and function of chemokine receptors in the immune system of lower vertebrates. Eur J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Redmond, A.K.; Qi, Z.; Dooley, H.; Secombes, C.J. The CXC chemokine receptors of fish: Insights into CXCR evolution in the vertebrates. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 215, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanegashima, K.; Suzuki, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Tsuji, K.; Shigenaga, A.; Otaka, A.; Hara, T. CXCL14 is a natural inhibitor of the CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling axis. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1731–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maravillas-Montero, J.L.; Burkhardt, A.M.; Hevezi, P.A.; Carnevale, C.D.; Smit, M.J.; Zlotnik, A. Cutting edge: GPR35/CXCR8 is the receptor of the mucosal chemokine CXCL17. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, G.D.; Zou, J.; Charlemagne, J.; Partula, S.; Cunningham, C.; Secombes, C.J. Cloning of two chemokine receptor homologs (CXC-R4 and CC-R7) in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 65, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dixon, B.; Luque, A.; Abos, B.; Castro, R.; Gonzalez-Torres, L.; Tafalla, C. Molecular characterization of three novel chemokine receptors in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, R.; Ren, L.; Xu, T. Characterization of the CCR3 and CCR9 genes in miiuy croaker and different selection pressures imposed on different domains between mammals and teleosts. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Villegas, J.; Mulero, I.; Garcia-Alcazar, A.; Munoz, I.; Penalver-Mellado, M.; Streitenberger, S.; Scapigliati, G.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V. Recombinant TNFα as oral vaccine adjuvant protects european sea bass against vibriosis: Insights into the role of the CCL25/CCR9 axis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, W.R.; Lipman, D.J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2444–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Page, R.D. Treeview: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1996, 12, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leick, M.; Catusse, J.; Follo, M.; Nibbs, R.J.; Hartmann, T.N.; Veelken, H.; Burger, M. CCL19 is a specific ligand of the constitutively recycling atypical human chemokine receptor Cram-B. Immunology 2010, 129, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maho, A.; Bensimon, A.; Vassart, G.; Parmentier, M. Mapping of the CCXCR1, CX3CR1, CCBP2 and CCR9 genes to the CCR cluster within the 3p21.3 region of the human genome. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1999, 87, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lio, P.; Vannucci, M. Investigating the evolution and structure of chemokine receptors. Gene 2003, 317, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, R.; Monte, M.M.; Jiang, Y.; Nie, P.; Holland, J.W.; Secombes, C.J.; Wang, T. Sequence and expression analysis of rainbow trout CXCR2, CXCR3A and CXCR3B aids interpretation of lineage-specific conversion, loss and expansion of these receptors during vertebrate evolution. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 45, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelerie, F.; Graham, G.J.; Locati, M.; Mantovani, A.; Murphy, P.M.; Nibbs, R.; Rot, A.; Sozzani, S.; Thelen, M. New nomenclature for atypical chemokine receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelerie, F.; Graham, G.J.; Locati, M.; Mantovani, A.; Murphy, P.M.; Nibbs, R.; Rot, A.; Sozzani, S.; Thelen, M. An atypical addition to the chemokine receptor nomenclature: IUPHAR Review 15. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3945–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yao, Y.; Gong, C.; Yu, F.; Su, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Deng, H.; Wang, F.; Lin, L. CCL18 from tumor-associated macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via PITPNM3. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Holland, J.W.; Nie, P.; Secombes, C.J.; Wang, T. Identification and expression analysis of an atypical chemokine receptor-2 (ACKR2)/CC chemokine binding protein-2 (CCBP2) in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burge, C.B.; Karlin, S. Finding the genes in genomic DNA. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1998, 8, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bird, S.; Tafalla, C. Teleost Chemokines and Their Receptors. Biology 2015, 4, 756-784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040756
Bird S, Tafalla C. Teleost Chemokines and Their Receptors. Biology. 2015; 4(4):756-784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040756
Chicago/Turabian StyleBird, Steve, and Carolina Tafalla. 2015. "Teleost Chemokines and Their Receptors" Biology 4, no. 4: 756-784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040756
APA StyleBird, S., & Tafalla, C. (2015). Teleost Chemokines and Their Receptors. Biology, 4(4), 756-784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040756





