Simple Summary
Three inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria strains were inoculated individually and in combination into the planting soil of the traditional Chinese medicinal herb Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis, to find out the suitable strain or combination to improve the phosphorus utilization efficiency and medicinal quality of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. The results showed that inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria inoculation increased the inorganic phosphorus content and proportion in the soil; the single-strain inoculation increased the effective phosphorus content in soil and the phosphorus content in the plant; there is an antagonistic effect when different strains are mixed for inoculation; the treatments of B. aryabhattai inoculation significantly increased the contents of total steroidal saponins in the plant. In summary, inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria inoculation improved the planting soil phosphorus form structure and medicinal quality of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. These findings provide a basis for efficient phosphorus resource utilization and sustainable cultivation to enhance medicinal plant quality.
Abstract
To improve the phosphorus utilization efficiency and medicinal quality of the traditional Chinese medicinal herb Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis, three inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria strains (Bacillus cereus Y1-1, Bacillus aryabhattai Z6-1, and Bacillus aryabhattai Z3-4) were inoculated individually and in combination into the rhizosphere soil of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis in a greenhouse pot experiment. At the late growth stage, the contents of total and inorganic phosphorus in the rhizosphere soils, as well as the total phosphorus and six steroidal saponins in the plants, were measured. The proportion of inorganic phosphorus in rhizosphere soils of treatment groups increased by 9.83~30.43%. The content of effective phosphorus form Ca2-P in the rhizosphere soils of treatment groups increased by 50.81~328.37%. Inoculation with B. aryabhattai (S2, S3, and S6) significantly increased total steroidal saponin content in plants by 9.14%, 10.64%, and 16.58%, respectively. An antagonistic effect was observed when multiple bacterial strains were inoculated together. Thus, mixed inoculation was less effective than single-strain inoculation in improving rhizosphere soil phosphorus structure. In conclusion, inoculation with inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria could enhance phosphorus availability in rhizosphere soil and improve medicinal quality of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. These findings provide a basis for efficient phosphorus resource utilization and sustainable cultivation to enhance medicinal plant quality.
1. Introduction
Phosphorus is not only an indispensable nutrient for plant growth but also enhances the medicinal quality of numerous medicinal plants [1]. Plants primarily obtain phosphorus from the soil during their growth period. Soil phosphorus exists in two distinct forms: inorganic and organic. Inorganic phosphorus comprises about 60–80% of total phosphorus content in soils [2], making it the predominant phosphorus type. Traditionally, inorganic phosphorus has been categorized into aluminum phosphate (Al-P), iron phosphate (Fe-P), occluded phosphate (O-P), and calcium phosphate (Ca-P) [3,4]. Among these, Ca2-P, being water-soluble, is the most bioavailable phosphorus, making it easily assimilated by plants. Ca8-P, Al-P, and Fe-P are considered slow-release phosphorus sources that modulate soil phosphorus availability. In contrast, O-P and Ca10-P exist as insoluble compounds and serve as potential phosphorus reserves, making it difficult for plants to absorb directly. Applying phosphorus fertilizers can effectively address phosphorus deficiencies in soils. However, excessive phosphorus fertilizer application causes nutrient loss, disrupts soil nutrient balance, induces soil degradation and crusting, and damages the ecological environment [5,6]. Through mineral decomposition, inorganic phosphorus and other insoluble elements can be transformed into soluble forms, which plants can then absorb, thus promoting plant growth [7].
Phosphorus-solubilizing microorganisms (PSMs) represent a naturally abundant class of rhizosphere microorganisms beneficial to plant growth, significantly influencing the soil phosphorus cycle [8]. By releasing organic ions or protons, PSMs convert insoluble phosphorus into accessible forms, creating phosphorus-rich microenvironments within the rhizosphere and thereby improving phosphorus utilization efficiency in plants [9]. Among these microorganisms, phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria account for about half of the population, predominantly including the genera Pseudomonas and Bacillus [10].
Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis, a perennial medicinal herb from the family Liliaceae (now classified as Melanthiaceae), mainly thrives in the Dali and Lijiang regions of Yunnan Province, China. The rhizome of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis has been officially recognized in the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China due to its significant medicinal properties [11]. Characterized by bitter and cooling properties, this traditional Chinese medicine is utilized for heat-clearing, detoxification, hemostasis, cooling the liver, and immune regulation. Clinically, it has been extensively applied in treating conditions such as sore throat, bruises, abscesses, carbuncles, epidemic encephalitis B, lymph node tuberculosis, tonsillitis, and appendicitis. The herb contains diverse bioactive substances, notably polysaccharides and steroidal saponins [12,13,14]. According to the Pharmacopoeia standards, the rhizome’s quality is evaluated based on the content of four active saponins: polyphyllin I, polyphyllin II, polyphyllin VII, and dioscin [11]. Saponins isolated from Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis exhibit potent anticancer effects, regulate protein and gene expression in humans, and possess antibacterial and hemostatic properties. Moreover, for the plant itself, saponins confer antioxidant, insecticidal, antifungal, antiparasitic, and antibacterial activities, enhancing plant resilience [15]. Previous studies have shown that inoculation with mycorrhizal fungi notably increases the total saponin content in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis, thereby boosting its medicinal quality [16]. Furthermore, the medicinal properties of this plant closely correlate with environmental factors [17], and reduced soil pH or organic matter can negatively impact its medicinal value [18]. Application of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria significantly elevates phosphorus levels in plant tissues and enhances leaf protective enzyme activity [19]. The above results indicate that the application of inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria could enhance the medicinal quality of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis and merits further investigation.
In this study, three inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacterial strains were inoculated individually and in combination into the rhizosphere soil of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Measurements included phosphorus concentrations in the rhizosphere soil and plants. Relationships between soil and plant phosphorus contents were analyzed to evaluate whether phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria positively influence soil phosphorus composition. Additionally, steroidal saponin contents under various treatments were measured to determine if inoculation with inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria enhances the medicinal quality of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis, aiming to identify the most effective bacterial combination for its cultivation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objects and Experimental Design
The pot experiment was conducted in a greenhouse at Chongqing Three Gorges University, Chongqing, China. Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis was planted from December 2023 to November 2024. Pots used for planting were 30 cm high, 28 cm top inner diameter, and 22 cm bottom inner diameter, each with a bottom tray. Each pot contained 5 kg of soil. Four-year-old dormant rhizomes with high uniformity and stable quality were obtained from a cultivation base in Baoshan, Yunnan, China (25°4′ N, 99°10′ E), ensuring consistent germplasm resources. The planting medium consisted of organic fertilizer, garden soil, and river sand mixed in a 1:1:2 ratio (pH 6.72, organic matter 21.2 mg·g−1, tototal N 1.83 mg·g−1, available N 10.64 mg·kg−1, total P 315 mg·g−1, available P 104.66 mg·kg−1, total K 8.83 mg·g−1, available K 28.64 mg·kg−1). Before planting, the soil was sieved through an 8 mm mesh, sterilized at 121 °C for 120 min, and subsequently incubated for one week. This study utilized three prominent inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria strains isolated from the rhizosphere of wild Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis plants in Baoshan, Yunnan: Bacillus cereus strain Y1-1, and two Bacillus aryabhattai strains, Z6-1 and Z3-4.
In this experiment, seven treatment groups (S1–S7) and one control group (CK) were established, with ten pots per group and five seedlings per pot. Pre-cultured bacterial strains were prepared in physiological saline solution at a concentration of 106 CFU·mL−1. Each treatment pot received 300 mL bacterial suspension with different combinations of strains, while the CK group received 300 mL sterile physiological saline solution. The specific inoculation details are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Treatment groups and their inoculated bacterial strains.
2.2. Sampling
In November 2024, at the late stage of the annual growth cycle, three pots from each group were randomly selected for phosphorus and saponin determination. Rhizosphere soil from each of the five plants in a pot was collected by the shaking-root method, from 6 to 10 cm below the surface [20]. Rhizosphere soil samples from five plants per pot were pooled, air-dried, and sieved through an 80-mesh screen. The rhizomes collected from each pot were oven-dried at 35 °C (HGZF-II-101-0, Shanghai Yuejin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) until reaching a stable weight. Afterward, they were combined, ground, and passed through an 80-mesh sieve. Each pot’s resulting rhizosphere soil and rhizome powders served as three biological replicates for the determination of phosphorus and saponin contents.
2.3. Determination of Steroid Saponins by UPLC
2.3.1. Preparation of Standard Reference Solutions
Standard reference materials of polyphyllin I (CAS: 50773-41-6), polyphyllin II (CAS: 76296-72-5), polyphyllin VII (CAS: 68124-04-9), polyphyllin H (CAS: 81917-50-2), dioscin (CAS: 19057-60-4), and pseudoprotodioscin (CAS: 102115-79-7) were obtained from Chengdu Pusi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China, 2023). These compounds were individually dissolved in methanol (CAS: 67-56-1, Merck & Co., Inc., Shanghai, China, 2023) to prepare standard stock solutions with concentrations of 4.165, 3.245, 3.870, 2.975, 4.830, and 3.045 mg·mL−1, respectively, and stored at 4 °C [17].
2.3.2. Preparation of Sample Solutions
Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis rhizome powder samples (0.5 g) were extracted with 10 mL methanol in a conical flask via ultrasonication (SB-5200DTN ultrasonic cleaner, Ningbo Xinzhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China) for 30 min at room temperature, and the volume was adjusted to the required level with additional methanol. Subsequently, the extracts were centrifuged at 4000 r·min−1 for 15 min using a TDZ5-WS automatic balancing centrifuge (Hunan Saite Xiangyi Centrifuge Instrument Co., Ltd., Changsha, China). The resulting supernatants were filtered using a 0.22-µm microporous membrane (Guangdong huankai Microbial Technology Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China), discarding the precipitates [17].
2.3.3. Chromatographic Conditions
Steroidal saponin concentrations in rhizome samples were measured using an H-Class ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) system (Waters Inc., Milford, MA, USA) equipped with an Accucore PFP chromatographic column (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Shanghai, China). Acetonitrile (CAS: 75-05-8, Merck & Co., Inc., Shanghai, China, 2023) (mobile phase A) and water (mobile phase B) constituted the mobile phase. The gradient elution was as follows: 0–5 min, 20–45% A; 5–9 min, 45–55% A; 9–18 min, 55–20% A; and 18–20 min, 20% A. A methanol-water solution was employed as the cleaning solvent. Chromatographic analysis conditions included a column temperature of 30 °C, a flow rate of 0.2 mL·min−1, a sample injection volume of 5 µL, and detection at a wavelength of 203 nm [17].
2.3.4. Sample Determination
Rhizome powders from different treatment groups were prepared as described above, and steroidal saponin contents were determined according to the chromatographic conditions (Figures S1–S8). The chromatographic profile is shown in Figure 1.
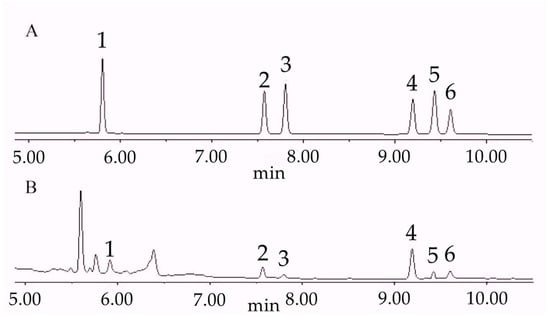
Figure 1.
Chromatogram of steroid saponins. (A): chromatogram of standard reference; (B): chromatogram of sample (S6). 1: pseudoprotodioscin; 2: polyphyllin VII; 3: polyphyllin H; 4: polyphyllin II; 5: dioscin; 6: polyphyllin I.
Six samples from the S6 group were tested using the above method. Peak areas were recorded, and the relative standard deviation (RSD, n = 6) of steroidal saponin peak areas ranged from 0.87% to 1.62%, indicating good repeatability.
The S6 sample solution was analyzed after storage periods of 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 h. The recorded peak areas showed RSD (n = 6) ranging from 0.77% to 2.57%, indicating sample solution stability for 24 h.
Known amounts of standard compounds were added to six S6 samples (0.25 g each) and analyzed according to the method described. Steroidal saponin recovery ranged from 96.8% to 102.35%, and RSD (n = 6) ranged from 1.19% to 2.52%, indicating good accuracy of the method.
2.4. Phosphorus Determination
Total phosphorus was quantified using the H2SO4-HClO4 digestion technique as previously reported [4]. The inorganic phosphorus levels were assessed following the method detailed by Koistinen [2].
2.5. Data Analysis
Statistical analyses were carried out using Excel 2010 for one-way ANOVA with a significance level set at p < 0.05. Correlation analyses and principal component analyses (PCA) were conducted using SPSS 22.0. Graphs and figures were created using Origin 2020 software.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Inorganic Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria on Phosphorus Fractions in the Rhizosphere Soil of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis
Figure 2 illustrates that single-strain inoculations (S1, S2, S3) significantly elevated Ca2-P levels (p < 0.05) in rhizosphere soil compared to multi-strain inoculations (S4, S5, S6, S7). A comparable trend was detected for Ca8-P concentrations. The highest Al-P levels were recorded in treatments inoculated with dual Bacillus aryabhattai strains (S6, S7). The Fe-P content exhibited no significant variation (p > 0.05) across most treatment conditions compared with the control (CK). Treatments S5, S6, and S7 exhibited significantly higher Ca10-P levels compared to CK, whereas Ca10-P in S2 showed no significant difference (p > 0.05) from CK. In contrast, S1, S3, and S4 had significantly lower Ca10-P concentrations (p < 0.05). The O-P content was higher (p < 0.05) in treatments S3, S4, and S6 compared to CK, while S1 presented a lower O-P level than CK. No significant differences (p > 0.05) in O-P were found among treatments S2, S5, S7, and CK.
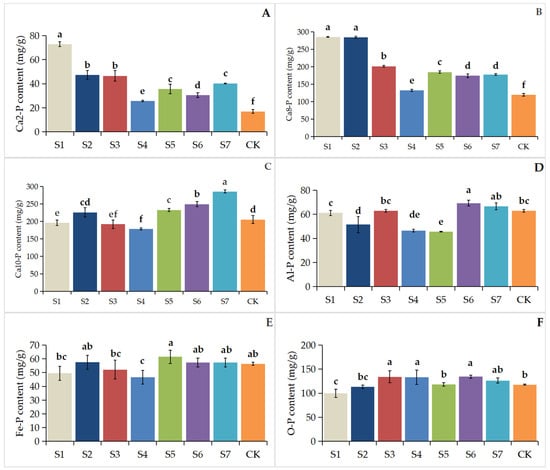
Figure 2.
Contents of different inorganic phosphorus forms in the rhizosphere soil of Paris polyphylla var. Yunnanensis. (A): Ca2-P content; (B): Ca8-P content; (C): Ca10-P content; (D): Al-P content; (E): Fe-P content; (F): O-P content. S1: B. cereus Y1-1; S2: B. aryabhattai Z6-1; S3: B. aryabhattai Z3-4; S4: B. cereus Y1-1 + B. aryabhattai Z6-1; S5: B. cereus Y1-1 + B. aryabhattai Z3-4; S6: B. aryabhattai Z6-1 + B. aryabhattai Z3-4; S7: B. cereus Y1-1 + B. aryabhattai Z6-1 + B. aryabhattai Z3-4; CK: saline solution. Different letters indicate significant differences at p < 0.05 levels.
Table 2 indicates that, apart from S4, the inorganic phosphorus contents in rhizosphere soils of all treatments were significantly greater (p < 0.05) than CK. Additionally, the proportion of inorganic phosphorus relative to total phosphorus was consistently higher in treatment groups compared to CK. Total phosphorus contents in the rhizosphere soils of treatments S1, S2, S3, and S6 were increased (p < 0.05) relative to CK. Notably, plant total phosphorus levels were significantly greater in single-strain inoculation treatments (S1, S2) compared with CK. Interestingly, dual-strain inoculation groups (S4 and S5) demonstrated relatively lower levels of soil inorganic phosphorus, total soil phosphorus, and plant total phosphorus compared to other groups.

Table 2.
Phosphorus contents (mg·g−1) in rhizosphere soils and plants of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
3.2. Effect of Inorganic Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria on Steroidal Saponin Content in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis
Figure 3 demonstrates that polyphyllin VII and total saponin contents in plants from most treatment groups, except S4 and S5, were increased (p < 0.05). Treatments S4 and S5 displayed relatively lower total saponin contents, aligning with the observed trends in soil and plant phosphorus content. Polyphyllin I, polyphyllin H, and dioscin concentrations were enhanced (p < 0.05) in most treatments. Conversely, pseudoprotodioscin concentrations across all treatment groups were lower (p < 0.05). Polyphyllin II contents were notably higher in treatments S3 and S6 (p < 0.05), while other treatments exhibited no significant variations (p > 0.05).
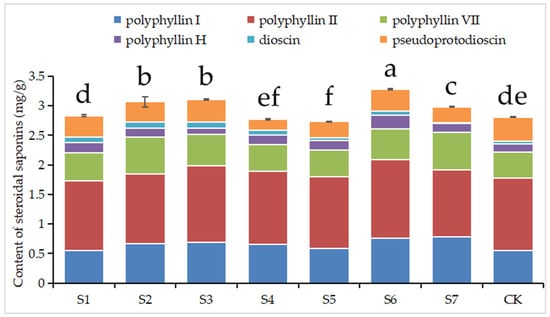
Figure 3.
Contents of six steroidal saponins in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis plants under different treatments. Different letters indicate significant differences at p < 0.05 levels.
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of Six Steroidal Saponins in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis Plants
PCA of steroidal saponin contents in plants from seven treatment groups and CK was conducted using SPSS software. As shown in Table 3, three principal components (PCs) with eigenvalues > 1.000 were extracted. PC1 had an eigenvalue of 1.791 and explained 29.848% of the variance, primarily representing polyphyllin I and polyphyllin VII. PC2 had an eigenvalue of 1.649 and explained 27.487% of the variance, mainly representing polyphyllin II and polyphyllin H. PC3 had an eigenvalue of 1.363 and explained 22.724% of the variance, primarily representing dioscin and pseudoprotodioscin. The cumulative variance explained by the three PCs was 80.058%.

Table 3.
Principal component analysis matrix of steroidal saponins.
The principal component scores for steroidal saponins in the treatment groups and CK group were calculated and ranked (Table 4) using the following formulas:
F1 = 0.513X1 + 0.037X2 + 0.061X3 − 0.106X4 + 0.554X5 − 0.033X6
F2 = 0.184X1 + 0.074X2 + 0.510X3 + 0.523X4 − 0.228X5 − 0.152X6
F3 = −0.064X1 + 0.561X2 + 0.249X3 − 0.232X4 + 0.058X5 + 0.472X6
Fcomprehensive = 0.373F1 + 0.343F2 + 0.284F3

Table 4.
Principal component scores and rankings of steroidal saponins in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis plants among different groups.
In the above formulas, F1, F2, and F3 are scores for PC1, PC2, and PC3, respectively. X1–X6 represent standardized data for the six steroidal saponins. The comprehensive score (Fcomprehensive) was calculated using the ratios of variance contributions of the three PCs to the cumulative variance contribution as weights. As shown in Table 4, the treatment groups with the highest scores for PC1, PC2, and PC3 were S7, S6, and S5, respectively. Group S6 had the highest comprehensive score. The PC1, PC2, and comprehensive scores of all treatment groups were higher than those of CK.
3.4. Correlation Analysis Between Saponin Contents in Plants and Phosphorus in Rhizosphere Soils
As presented in Table 5, the concentration of polyphyllin I in plants exhibited a highly significant positive correlation with the contents of Ca10-P and O-P in rhizosphere soils (p < 0.01). A significant positive correlation was also observed between polyphyllin II concentration and O-P content (p < 0.05). Polyphyllin VII concentrations showed highly significant positive correlations with Ca10-P and soil inorganic phosphorus (p < 0.01), and a significant positive correlation with total soil phosphorus (p < 0.05). Dioscin levels were significantly positively associated with Ca2-P and total soil phosphorus (p < 0.05), highly positively associated with Ca8-P (p < 0.01), and exhibited a highly significant negative correlation with Ca10-P content (p < 0.01). Pseudoprotodioscin concentrations displayed highly significant positive correlations with Al-P and total soil phosphorus (p < 0.01). Total plant saponin content had significant positive correlations with soil inorganic and total phosphorus contents (p < 0.05), and a highly significant positive correlation with Al-P content (p < 0.01). Generally, most plant saponin contents were positively correlated with rhizosphere soil phosphorus contents, although polyphyllin II showed a negative correlation with most phosphorus forms in rhizosphere soils. Plant phosphorus content demonstrated highly significant positive correlations with Ca8-P, inorganic soil phosphorus, total soil phosphorus, pseudoprotodioscin, and total plant saponins (p < 0.01). Additionally, it was positively correlated with polyphyllin VII and polyphyllin H contents (p < 0.05) and significantly negatively correlated with O-P content (p < 0.05).

Table 5.
Correlation analysis between saponin contents in plants and phosphorus contents in rhizospheric soils.
4. Discussion
Previous studies have reported that the utilization rate of phosphorus absorbed by plants is only 15–25% in soils receiving long-term large-scale chemical fertilizer application [21]. The low phosphorus utilization rate leads to the accumulation of various phosphorus forms in soils. Certain Bacillus isolates can mineralize organic phosphorus, an ability associated with genes encoding phytase [22]. Moreover, Bacillus can secrete various organic acids, thus dissolving insoluble phosphorus [23]. In this study, the rhizosphere soils of all treatment groups showed significantly higher Ca2-P (water-soluble phosphorus and the most plant-available form) compared to CK. Ca2-P content in single-strain inoculation groups (S1, S2, and S3) was significantly higher than that in mixed-strain groups. Previous studies indicated that the order of phosphorus contents in soils is typically Ca10-P > Ca8-P > O-P > Al-P > Fe-P > Ca2-P [3,4], with Ca10-P (a potential phosphorus source difficult for plants to absorb directly) accounting for a large proportion. In contrast, this study showed that Ca10-P contents in S1, S2, and S3 were lower than Ca8-P contents (a slow-acting form convertible to available phosphorus). These results suggest that inoculation with the three Bacillus strains effectively improves soil phosphorus structure and increases available phosphorus content. Previous studies reported interspecific antagonism in co-cultures of different Bacillus strains [24]. When multiple Bacillus species establish molecular interactions with plants, their quorum-sensing signals can interfere with each other, weakening their respective interactions with the plants. Compared to single-strain cultures, mixed-strain inoculations showed significantly lower relative abundance, propagation rates, metabolite production, and beneficial effects on plant growth. Similarly, Wang [25] reported significantly lower alkane degradation rates by mixed Bacillus strains compared to single strains, likely due to resource competition. Therefore, the significantly higher contents of effective phosphorus (Ca2-P) and slow-acting phosphorus (Ca8-P) in single-strain groups (S1, S2, S3) compared to mixed groups observed in this study could also be explained by interspecific antagonism among different Bacillus strains.
In this study, soil inorganic phosphorus proportions in treatment groups were significantly higher. This result indicates that the bacterial strains effectively converted soil organic phosphorus into inorganic forms. Plant total phosphorus contents in single-strain groups (S1, S2) were significantly higher than CK. However, no significant differences or significantly lower contents occurred in the plant total phosphorus of mixed-strain groups (S3–S7) compared to CK. This result may also be due to interspecific antagonism among Bacillus strains. For groups S1 and S2, inoculated individually with B. cereus and B. aryabhattai, respectively, the plant total phosphorus content was significantly higher than in CK. B. cereus not only dissolves inorganic phosphorus but also organic phosphorus. It produces oxalic, malonic, and succinic acids, secretes acidic, neutral, and alkaline phosphatases, and produces IAA, thereby promoting plant growth [26]. Additionally, B. cereus can enhance plant integration with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), significantly increasing plant biomass when co-inoculated with AMF [27]. Interestingly, despite significantly lower total soil phosphorus contents in groups S3, S5, and S7 compared to CK, their inorganic phosphorus contents were significantly higher. Each of these groups contained at least one strain of B. aryabhattai, which functions as both a soil phosphorus-solubilizing bacterium and an endophyte [28]. B. aryabhattai can collaborate with AMF, promoting conversion of soil organic phosphorus into inorganic forms [29]. As an endophytic bacterium with plant growth-promoting properties, B. aryabhattai can solubilize inorganic and organic phosphorus, as well as potassium, and produce IAA, thereby enhancing plant growth and phosphorus absorption [30]. The highly significant positive correlation between soil inorganic phosphorus, plant phosphorus, and total saponin content observed in this study further indicates that B. aryabhattai plays an essential role in enhancing the medicinal quality of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
Total Paris saponins can inhibit cell proliferation in lung cancer, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and gastric cancer [31]. Polyphyllin I inhibits lung and colon cancer cells [32]. Polyphyllin VI and polyphyllin VII inhibit liver cancer cell growth [33]. Polyphyllin I, polyphyllin II, polyphyllin VI, and polyphyllin VII significantly inactivate influenza virus type A by blocking viral adsorption, invasion, and proliferation in target cells [34]. Polyphyllin H exhibits anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and anticoagulant activities [13]. Through the A1 and A3 adenosine receptor pathways, it inhibits glioma U251 cell proliferation, exerts anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects [35], and increases serum SOD activity [36]. Dioscin has anti-inflammatory effects, inhibits multiple cancer cell types, and alleviates Alzheimer’s disease [37]. Pseudoprotodioscin inhibits endometrial cancer cell growth, repairs heart damage, and improves liver fat metabolism and antioxidant function in rats [38,39,40]. In this study, plants inoculated with B. aryabhattai (groups S2, S3, S6) had significantly higher total steroidal saponin contents and comprehensive principal component scores compared to other groups. Bacillus species are well-known as plant probiotics or pathogens; however, their primary agricultural role is as producers of biological control agents (fungicides, bactericides, fertilizers) [20]. Beyond phosphorus solubilization, previous studies have reported that inoculation with B. aryabhattai alters the microbial community structure within the plant rhizosphere. Such inoculation significantly elevates the abundance of beneficial rhizobacteria, fostering positive interactions between the rhizosphere microbiome and plants, consequently promoting plant growth and improving quality [28]. Furthermore, B. cereus produces the enzyme ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid) deaminase, which breaks down the ethylene precursor ACC into α-ketobutyric acid and ammonia. This enzymatic activity lowers ethylene levels in plants under stress, enhancing plant resistance to adverse conditions [41]. However, ethylene directly affects saponin accumulation and expression of squalene synthase and squalene cyclooxygenase genes during saponin biosynthesis [42]. For instance, treating cultured ginseng cells (Panax ginseng) with ethylene precursor ACC induces transcriptional expression of squalene synthase and squalene cyclooxygenase, increasing saponin content [43]. Therefore, ACC deaminase produced by B. cereus in this study could explain the relatively low saponin contents observed in groups inoculated with B. cereus (S1, S4, S5).
5. Conclusions
In this study, three inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacterial strains (Bacillus cereus Y1-1, Bacillus aryabhattai Z6-1, and Bacillus aryabhattai Z3-4) were inoculated individually and in combination into the rhizosphere soil of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Results showed that inoculation with inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria improved the phosphorus structure in soil and increased the available phosphorus content. Single-strain inoculations (S1, S2, and S3) significantly enhanced the effective phosphorus (Ca2-P) content in rhizosphere soil. Antagonism among different strains was indicated by the lower Ca2-P and Ca8-P contents in mixed-strain groups compared to single-strain groups, reflecting competition for resources or production of inhibitory substances. Inoculation with B. aryabhattai (S2, S3, and S6) significantly increased total steroidal saponin contents in plants. The relatively lower saponin contents in groups S1, S4, and S5 may be due to ACC deaminase production by B. cereus. In summary, inoculating inorganic phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria markedly improved phosphorus bioavailability in the rhizosphere soil and enhanced the medicinal quality of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. The results presented here support the efficient utilization of phosphorus resources and sustainable agricultural practices aimed at optimizing medicinal plant quality. Subsequent studies will further explore the impact of phosphorus-solubilizing bacterial inoculation on the rhizosphere microbiome, transcriptomic and metabolomic profiles, and the biosynthesis pathway of saponins, to elucidate the underlying mechanisms through which these microorganisms enhance yield and medicinal properties in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology14091284/s1, Figure S1: Chromatogram of steroid saponins in sample S1; Figure S2: Chromatogram of steroid saponins in sample S2; Figure S3: Chromatogram of steroid saponins in sample S3; Figure S4: Chromatogram of steroid saponins in sample S4; Figure S5: Chromatogram of steroid saponins in sample S5; Figure S6: Chromatogram of steroid saponins in sample S6; Figure S7: Chromatogram of steroid saponins in sample S7; Figure S8: Chromatogram of steroid saponins in sample CK.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.Z., D.G. and H.Z.; methodology, N.Z., Y.Z. and Y.W.; software, Y.Z., Y.W. and L.X.; validation, Y.Z., Y.W. and G.L.; formal analysis, Y.Z. and Y.W.; investigation, Y.Z. and Y.W.; resources, H.Z.; data curation, N.Z., Y.Z. and Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z. and Y.W.; writing—review and editing, D.G., N.Z., Y.Z. and Y.W.; visualization, Y.Z. and Y.W.; supervision, G.L.; project administration, N.Z., Y.Z., D.G., G.L. and H.Z.; funding acquisition, N.Z., Y.Z., D.G., G.L. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82460749) and the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (KJZD-M202401201).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available at reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sun, H.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Y.Y. Response of root morphogenesis of medicinal plants to low phosphorus stress and molecular mechanism. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2022, 47, 6573–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koistinen, J.; Sjöblom, M.; Spilling, K. Determining inorganic and organic phosphorus. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 1890, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Ren, R.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, G.X.; He, Q.S.; Han, Z.W.; Meng, S.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, X.H. Factors regulating interaction among inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus species, plant uptake, and relevant cycling genes in a weakly alkaline soil treated with biochar and inorganic fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, R.; Ma, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, J.; Weng, L.; Li, Y. Retardation factors in controlling the transport of inorganic, organic, and particulate phosphorus in fluvo-aquic soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.I.A.; Castro, P.M.L. Phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria enhance Zea mays growth in agricultural P-deficient soils. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, R.E.; Nelson, N.O.; Roozeboom, K.L.; Kluitenberg, G.J.; Tomlinson, P.J.; Kang, Q.; Abel, D.S. Cover crop and phosphorus fertilizer management impacts on surface water quality from a no-till corn-soybean rotation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikuvire, T.J.; Muchaonyerwa, P.; Zengeni, R. Decomposition of Wolffia arrhiza residues rapidly increases mineral nitrogen and decreases extractable phosphorus in acidic soils. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, P.; Das, S.; Shankhdhar, D.; Shankhdhar, S.C. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms: Mechanism and their role in phosphate solubilization and uptake. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 21, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yao, P.; Cai, C.; Xie, Z.; Luo, L.; Li, T.; Wang, Z. Effects of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria and biochar application on phosphorus availability and tomato growth under phosphorus stress. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Xie, J.; Xue, X.; Jiang, Y. Screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and their abilities of phosphorus solubilization and wheat growth promotion. BMC Biol. 2022, 22, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 1st ed.; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 271–272. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.H.; Liang, M.Y.; Wen, X.D.; Yang, J. Research progress in chemical constituents in the aerial parts of Paris L. and their pharmacological effects. Chin. Wild Plant Res. 2018, 1, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, W.; Di, F.; Wang, C.; An, Q. Saponins of Paris polyphylla for the improvement of acne: Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects. Molecules 2024, 29, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, F.R.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.Y. Rapid and simple determination of polyphyllin I, II, VI, and VII in different harvest times of cultivated Paris polyphylla Smith var. yunnanensis (Franch.) Hand.-Mazz by UPLC-MS/MS and FT-IR. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, C.B.; Paudel, M.R.; Bhattarai, H.D.; Pant, K.K.; Devkota, H.P.; Adhikari, Y.P.; Pant, B. Bioactive secondary metabolites in Paris polyphylla Sm. and their biological activities: A review. Heliyon 2022, 17, e08982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.F.; Gu, W.C.; Li, Z.W.; Du, H.H.; Guo, D.Q.; Zhou, N. Comparative study on the contents of 15 amino acids in wild and cultivated Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis from different producing areas. Tradit. Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 33, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Z.; Wen, F.Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.X.; Fang, Q.M.; Zhang, H.; Xue, D. Evaluation of saponins in Paris polyphylla var. chinensis from twenty-one growing areas. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2017, 39, 2345–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Dai, L.J.; He, K.H.; Wei, J.R.; Zhao, T.Z.; Su, B.; Wang, M.H. Relation between soil nutrient of artificially cultivated area and rhizome quality of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2012, 35, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, Z. Phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria improve the growth of Nicotiana benthamiana on lunar regolith simulant by dissociating insoluble inorganic phosphorus. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.Y.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Y.F.; Li, H.; Yang, S.N. Different rhizosphere soil microbes are recruited by tomatoes with different fruit color phenotypes. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Yu, H.; Jiao, X.G.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.M.; Sui, Y.Y. Effects of reducing irrigation and chemical fertilizers on forms and distribution of inorganic phosphorus in facility vegetable field of black soil. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2021, 37, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemneh, A.A.; Zhou, Y.; Ryder, M.H.; Denton, M.D. Mechanisms in plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria that enhance legume-rhizobial symbioses. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1133–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnieszka, S.; Ewelina, P.; Justyna, D.-I. Phosphorus solubilization by Bacillus species. Molecules 2018, 23, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, L.-M.; María, G.C.-C.; Thelma, C.; Angélica, L.-C.; Trinidad, A.-D.; Aarón, B. Growth effects in oregano plants (Origanum vulgare L.) assessment through inoculation of bacteria isolated from crop fields located on desert soils. Can. J. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Shi, Y.Y.; Zheng, L.Y.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Liu, J. Isolation and identification of petroleum degradation bacteria and interspecific interactions among four Bacillus strains. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 2245–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.; Xu, G.; Tian, X.; Xie, H.; Yang, X.; Cao, C. Root colonization and growth promotion of soybean, wheat and Chinese cabbage by Bacillus cereus YL6. PLoS ONE. 2018, 13, e0200181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Hao, R.; Gui, F. Effects of Septoglomus constrictum and Bacillus cereus on the competitive growth of Ageratina adenophora. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 2, 1131797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, N.; Liang, X.; Huang, T.; Li, B. Bacillus aryabhattai LAD impacts rhizosphere bacterial community structure and promotes maize plant growth. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 6650–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S. Effects of interaction between Claroideogolmus etuicatum and Bacillus aryabhattai on the utilization of organic phosphorus in Camellia oleifera Abel. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, L.; He, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Deng, N.; Chen, Y. Integration and potential application ability of culturable functional microorganism in oil tea Camellia. Indian J. Microbiol. 2021, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Paridis saponins inhibiting carcinoma growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, J.; Zheng, F.; Tang, Q.; Wu, W.; Hann, S.S. Inhibition of EZH2 via activation of SAPK/JNK and reduction of p65 and DNMT1 as a novel mechanism in inhibition of human lung cancer cells by polyphyllin I. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jia, X.; Bao, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Wan, J.-B.; Su, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Polyphyllin VII induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells through ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and MAPK pathways. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Preparation of polyphylla saponins and their antiviral effect on influenza A virus. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 27, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Tang, H. Paris saponin H inhibits the proliferation of glioma cells through the A1 and A3 adenosine receptor-mediated pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Tang, D.X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, T.Z. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory eeffects of Chonglou saponin VII, H and total saponins. J. Sichuan Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 39, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, L.; Mao, Z.; Yang, S.; Wu, G.; Chen, Y.; Yin, L.; Qi, Y.; Han, L.; Xu, L. Dioscin alleviates Alzheimer’s disease through regulating RAGE/NOX4 mediated oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.X.; Gao, R.R.; Gao, Z.H.; Qiao, Y.; Dong, X.R.; Ding, G.; Sun, D.A. Microbial transformation of pseudoprotodioscin by Gibberella fujikuroi. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 20, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Y.N.; Li, Y.S.; Xu, Z.L.; Chen, J. Pseudoprotodioscin inhibits SREBPs and microRNA 33a/b levels and reduces the gene expression regarding the synthesis of cholesterol and triglycerides. Fitoterapia 2019, 139, 104393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Yang, D.; Yin, Y.Z.; Xiao, J. Estrogenic and anti-inflammatory effects of pseudoprotodioscin in atherosclerosis-prone mice: Insights into endothelial cells and perivascular adipose tissues. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 869, 172887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, B.R. Plant growth-promoting bacteria: Mechanisms and applications. Scientifica 2012, 2012, 963401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.H.; Choi, Y.E.; Shin, C.G.; Kim, Y.Y.; Kim, Y.S. Enhanced ginsenoside productivity by combination of ethephon and methyl jasmoante in ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) adventitious root cultures. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.J.; Hu, X.Y.; Neill, S.J.; Fang, J.Y.; Cai, W.M. Fungal elicitor induces singlet oxygen generation, ethylene release and saponin synthesis in cultured cells of Panax ginseng CA Meyer. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).