Development of a Duplex dPCR Assay for Detecting Palm Lethal Yellowing Phytoplasmas in Africa and Madagascar and Separation of Regional Species by High-Resolution Melt Curve Analysis (HRMA) Based on the secA Gene
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phytoplasma Isolates, DNA Extraction, and Verification of Identity
2.2. Assay Design and Optimization
2.2.1. Oligonucleotides
2.2.2. Gradient PCR for Optimal Annealing Temperature
2.2.3. Cloning for Standard Generation
2.2.4. TaqMan Assay Optimization
2.2.5. HRMA Assay Optimization
3. Results
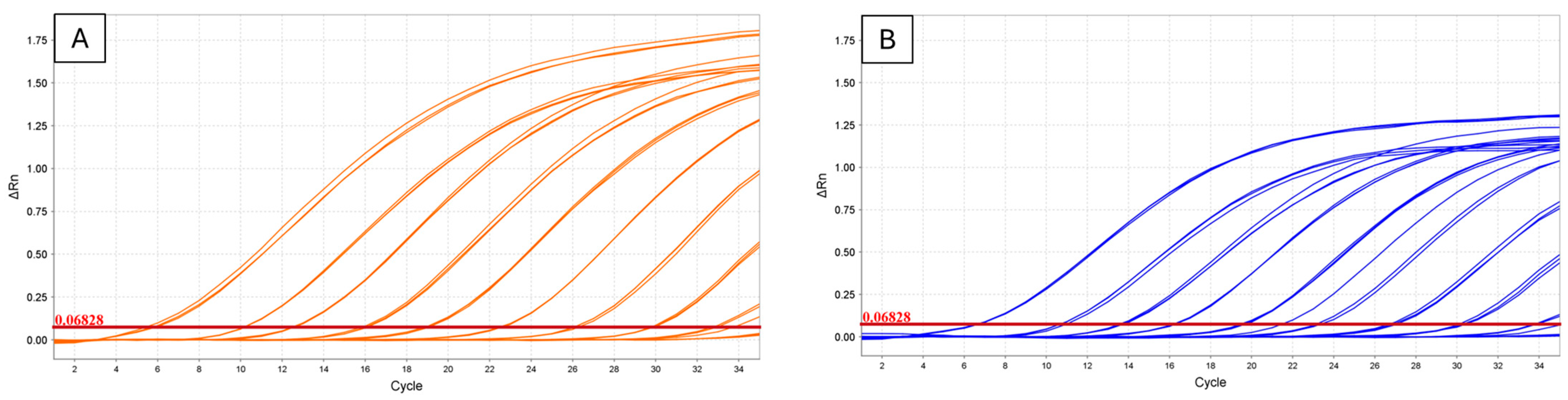
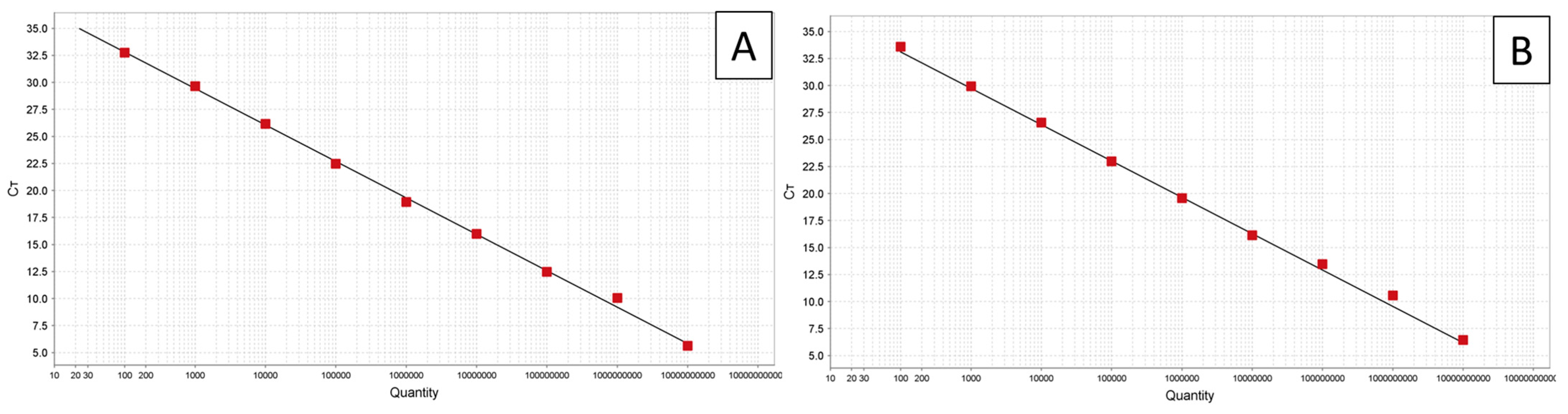
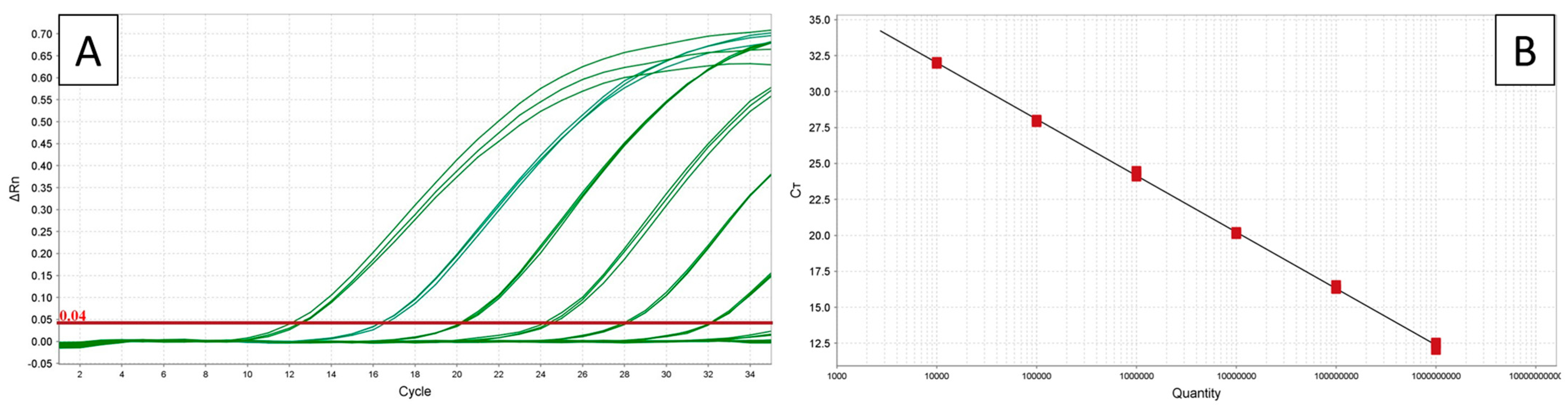
3.1. TaqMan Assays
3.2. HRMA Assays
| Species Mixture | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target | C+PA 1 | C+PB 2 | M+PA 3 | M+PB 4 |
| Total Wells | 20,473 | 20,465 | 20,465 | 20,457 |
| FAM (C/M) | ||||
| Positive Wells | 1750 | 1754 | 323 | 396 |
| % Positive | 8.6% | 8.6% | 1.6% | 1.9% |
| Conc. (cp/µL) | 206.84 | 207.42 | 36.83 | 45.25 |
| 95% C.I. | 9.471, 9.925 | 9.487, 9.941 | 3.805, 4.243 | 4.244, 4.684 |
| Precision % | 4.798 | 4.793 | 11.523 | 10.351 |
| VIC (A/B) | ||||
| Positive Wells | 3063 | 430 | 2962 | 381 |
| % Positive | 15.0% | 2.1% | 14.5% | 1.9% |
| Conc. (copies/µL) | 375.14 | 49.16 | 361.91 | 43.52 |
| 95% C.I. | 13.067, 13.539 | 4.433, 4.873 | 12.814, 13.285 | 4.158, 4, 597 |
| Precision % | 3.609 | 9.913 | 3.671 | 10.563 |
| HRMA Assay | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Ca. P. Palmicola’ | ‘Ca. P. Cocostanzaniae’/Malagasy Isolate | |||||||
| Conc. (copies/µL) | Subgroup A | Subgroup B | ‘Ca. P. Cocostanzaniae’ | Malagasy Isolate | ||||
| Avg. Ct (±SE) | Avg. Tm (±SE) | Avg. Ct (±SE) | Avg. Tm (±SE) | Avg. Ct (±SE) | Avg. Tm (±SE) | Avg. Ct (±SE) | Avg. Tm (±SE) | |
| 1010 | 6 ± 0.1 | 69.6 ± 0.01 | 4.9 ± 0.1 | 68.6 ± 0.00 | 5.8 ± 0.3 | 72.4 ± 0.05 | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 73.2 ± 0.05 |
| 109 | 9.3 ± 0.0 | 69.5 ± 0.02 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 68.6 ± 0.02 | 8.5 ± 0.2 | 72.4 ± 0.02 | 9.1 ± 0.4 | 73.3 ± 0.02 |
| 108 | 12.3 ± 0.1 | 69.5 ± 0.03 | 9.8 ± 0.0 | 68.6 ± 0.02 | 11.1 ± 0.2 | 72.4 ± 0.04 | 11.6 ± 0.3 | 73.2 ± 0.04 |
| 107 | 15.5 ± 0.0 | 69.7 ± 0.01 | 13.6 ± 0.1 | 68.7 ± 0.01 | 14.6 ± 0.1 | 72.4 ± 0.04 | 15.0 ± 0.2 | 73.2 ± 0.04 |
| 106 | 19.1 ± 0.0 | 69.6 ± 0.02 | 17.2 ± 0.1 | 68.6 ± 0.02 | 18.4 ± 0.2 | 72.3 ± 0.03 | 18.9 ± 0.2 | 73.2 ± 0.03 |
| 105 | 22.7 ± 0.0 | 69.4 ± 0.06 | 20.5 ± 0.1 | 68.6 ± 0.01 | 21.8 ± 0.1 | 72.3 ± 0.02 | 22.1 ± 0.2 | 73.1 ± 0.02 |
| 104 | 26.1 ± 0.1 | 69.5 ± 0.01 | 23.9 ± 0.1 | 68.6 ± 0.02 | 25.7 ± 0.1 | 72.4 ± 0.04 | 25.8 ± 0.3 | 73.1 ± 0.04 |
| 103 | 29.3 ± 0.3 | 69.5 ± 0.02 | 27.2 ± 0.0 | 68.6 ± 0.00 | 29.7 ± 0.9 | 72.8 ± 0.09 | 31.7 ± 1.2 | 73.7 ± 0.09 |
| 102 | 33.1 ± 0.0 | 69.5 ± 0.03 | 30.9 ± 0.1 | 68.5 ± 0.00 | 32 ± 0.1 | 72.9 ± 0.05 | 32.2 ± 0.4 | 73.8 ± 0.05 |
| 101 | - | 69.4 ± 0.08 | 34.1 ± 0.2 | 68.6 ± 0.00 | - | 73 ± 0.22 | 31.5 ± 2.1 | 73.2 ± 0.22 |
| HRMA Assay | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Ca. P. Palmicola’ | secA614F/secA759R | |||
| Avg. Ct (±SE) | Avg. Tm (±SE) | Avg. Ct (±SE) | Avg. Tm (±SE) | |
| ‘Ca. P. palmicola’ A | ||||
| Awka | 27.5 ± 0.1 | 69.6 ± 0.02 | No Ct | 87.7 ± 6.82 |
| Nig 1 | 26.7 | 69.6 | No Ct | 87.2 |
| Nig 2 | 24.6 | 69.6 | No Ct | 73.7 |
| 185 | 21.4 | 69.6 | No Ct | 73.1 |
| ‘Ca. P. palmicola’ B | ||||
| ADN 22 | 27.7 ± 0.6 | 68.7 ± 0.02 | No Ct | 80.8 ± 7.92 |
| ADN 19 | 28.5 | 68.7 | No Ct | 65.3 |
| ADN 36 | 34.9 | 68.6 | No Ct | 63.7 |
| ‘Ca. P. cocostanzaniae’ | ||||
| TT tall | No Ct | 74.4 ± 4.73 | 26.8 ± 0.2 | 72.6 ± 0.05 |
| EAT LY PS | No Ct | 64.1 | 28.3 | 72.7 |
| PB 121A | No Ct | 65.3 | 34.2 | 73.0 |
| Malagasy Isolates | ||||
| MG24−009 | No Ct | 78.2 ± 8.81 | 30.3 ± 0.2 | 73.7 ± 0.05 |
| MG24−002 | No Ct | 68.7 | 28.4 | 73.2 |
| MG24−005 | No Ct | 87.9 | 31.3 | 74.2 |
| MG24−006 | No Ct | 63.2 | 28.8 | 73.4 |
| MG24−007 | No Ct | 69.6 | 33.7 | 74.2 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PLYP | Palm lethal yellow phytoplasmas |
| LYTS | Lethal yellowing type syndrome |
| dPCR | Digital PCR |
| qPCR | Quantitative PCR |
| HRMA | High-resolution melt curve analysis |
| LY | Lethal yellowing |
| LB | Lethal bronzing |
References
- Dollet, M.; Quaicoe, R.; Pilet, F. Review of Coconut “Lethal Yellowing” type diseases Diversity, variability and diagnosis. Oléagineux Corps Gras Lipides 2009, 16, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahder, B.W.; Bloch, M.; Lane, J.; Helmick, E.E.; Jimenez Madrid, A.M. Multi-Locus Analysis Confirms Identity of Lethal Bronzing Phytoplasma for the First Time in Declining Wild Date Palms (Phoenix sylvestris) from Georgia, U.S.A. Plant Health Prog. 2025, 26, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.A.; Womack, M.; Carpio, M.L. Detection and characterization of a lethal yellowing (16SrIV) group phytoplasma in Canary Island date palms affected by lethal decline in Texas. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilet, F.; Loiseau, M.; Boyer, C.; Cavalier, A.; Diman, C. First report of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma palmae’ (16SrIV-A subgroup) associated with palm lethal yellowing disease on Cocos nucifera and Pritchardia sp. In Guadeloupe, French West Indies. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrie, W.; Ortíz, C.F.; Narvaez, M.; Oropeza, C. Distribution of lethal yellowing and associated phytoplasma strains in Jamaica, Mexico and other countries in the region. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 2019, 9, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahder, B.W.; Soto, N.; Helmick, E.E.; Dey, K.K.; Komondy, L.; Humphries, A.R.; Mou, D.F.; Bailey, R.; Ascunce, M.S.; Goss, E.M. A survey of declining palms (Arecaceae) with 16SrIV-D phytoplasma to evaluate the distribution and host range in Florida. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2512–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Euán, R.; Harrison, N.; Narvaez, M.; Oropeza, C. Occurrence of a 16SrIV group phytoplasma not previously associated with palm species in Yucatan, Mexico. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.T.; Narvaez, M.; Fabre, S.; Harrison, N.; Oropeza, C.; Dollet, M.; Hichez, E. Coconut lethal yellowing on the southern coast of the Dominican Republic is associated with a new 16SrIV group phytoplasma. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova, I.; Oropeza, C.; Puch-Hau, C.; Harrison, N.; Collí-Rodríguez, A.; Narvaez, M.; Nic-Matos, G.; Reyes, C.; Sáenz, L. A real-time PCR assay for detection of coconut lethal yellowing phytoplasmas of group 16SrIV subgroups a, D and E found in the Americas. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 96, 343–352. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, N.A.; Davis, R.E.; Oropeza, C.; Helmick, E.E.; Narvaez, M.; Eden-Green, S.; Dollet, M.; Dickinson, M. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma palmicola’, associated with a lethal yellowing-type disease of coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) in Mozambique. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64 Pt 6, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilet, F.; Quaicoe, R.N.; Osagie, I.J.; Freire, M.; Foissac, X. Multilocus sequence analysis reveals three distinct populations of “Candidatus Phytoplasma palmicola” with a specific geographical distribution on the African continent. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02716-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpunami, A.; Tymon, A.; Jones, P.; Dickinson, M. Genetic diversity in the coconut lethal yellowing disease phytoplasmas of East Africa. Plant Pathol. 1999, 48, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpunami, A.; Pilet, F.; Fabre, S.; Kullaya, A.; Dickinson, M.; Dollet, M. Spatial distribution of the different strains of the distinct coconut lethal yellowing-type phytoplasma species associated with the syndrome in Tanzania. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2021, 46, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilet, F.; Rakotoarisoa, E.; Rakotomalala, M.; Sisteron, S.; Razakamanana, H.N.; Rabemiafara, L. First report of strains related to the phytoplasma associated with Tanzanian Lethal Decline on Cocos nucifera on the Western coast of Madagascar. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, A.; Shigaki, T.; Koinuma, H.; Iwabuchi, N.; Rauka, G.B.; Kembu, A.; Saul, J.; Watanabe, K.; Nijo, T.; Maejima, K.; et al. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma noviguineense’, a novel taxon associated with Bogia coconut syndrome and banana wilt disease on the island of New Guinea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.M.; Pease, B.; Perkins, S.L.; Constable, F.E.; Kinoti, W.M.; Warmington, D.; Allgood, B.; Powell, S.; Taylor, P.; Pearce, C.; et al. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma dypsidis’, a novel taxon associated with a lethal wilt disease of palms in Australia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, D.F.; Helmick, E.E.; Bahder, B.W. Multilocus sequence analysis reveals new hosts of palm lethal decline phytoplasmas in Florida, USA. Plant Health Prog. 2021, 23, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahder, B.W.; Helmick, E.E.; Chakrabarti, S.; Osorio, S.; Soto, N.; Chouvenc, T.; Harrison, N.A. Disease progression of a lethal decline caused by the 16SrIV-D phytoplasma in Florida palms. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahder, B.W.; Soto, N.; Komondy, L.; Mou, D.F.; Humphries, A.R.; Helmick, E.E. Detection and quantification of the 16SrIV-D phytoplasma in leaf tissue of common ornamental palm species in Florida using qPCR and dPCR. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1918–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahder, B.W.; Soto, N.; Mou, D.F.; Humphries, A.R.; Helmick, E.E. Quantification and distribution of the 16SrIV-D phytoplasma in the wild date palm, Phoenix sylvestris, at different stages of decline using quantitative PCR (qPCR) Analysis. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, D.F.; Di Lella, B.; Halbert, S.E.; Bextine, B.; Helmick, E.E.; Bahder, B.W. Acquisition and transmission of the lethal bronzing phytoplasma by Haplaxius crudus using infected palm spear leaves and artificial feeding media. Phytopathology 2022, 112, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, M.; Helmick, E.E.; Bahder, B.W. Differentiation of palm-infecting phytoplasmas in the Caribbean basin using high resolution melt curve analysis of the secA gene. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 2480–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, N.; Helmick, E.E.; Harrison, N.A.; Bahder, B.W. Genetic variability of palm lethal decline phytoplasmas in the Caribbean Basin and Florida, USA, based on a multilocus analysis. Phytopathology 2021, 111, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis version 12 for adaptive and green computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpunami, A.; Tymon, A.; Jones, P.; Dickinson, M.J. Identification of potential vectors of the coconut lethal disease phytoplasma. Plant Pathol. 2000, 49, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilet, F.; Philippe, R.; Reignard, S.; Descamps, S.; Quaicoe, R.N.; Nkansah Poku, J.; Fabre, S.; Dollet, M. Identification of potential insect vectors of the Cape Saint Paul Wilt Disease of coconut in Ghana by PCR. Agron.–Environ. 2009, 16, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilet, F.; Mendes, C.D.; Yankey, E.N.; Lopes Parruque, M.; Attivor, I.N.; Nkansah-Poku, J.; Vaz, A. Genetic diversity of ’Candidatus Phytoplasma palmicola’ in Ghana and Mozambique. Phytopathenogenic Mollicutes 2022, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilet, F.; Boyer, C.; Brière, G.; Rakotomalala, M.R.; Mbanzibwa, D.; Pruvost, O. Average nucleotide identity suggests the presence of a new species of phytoplasma responsible for lethal decline of palms in Madagascar. In Proceedings of the XXIII Bienniel Congress of the International Organization for Mycoplasmology: Congress Program (IOM 2021), Tel Aviv, Israel, 1–4 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
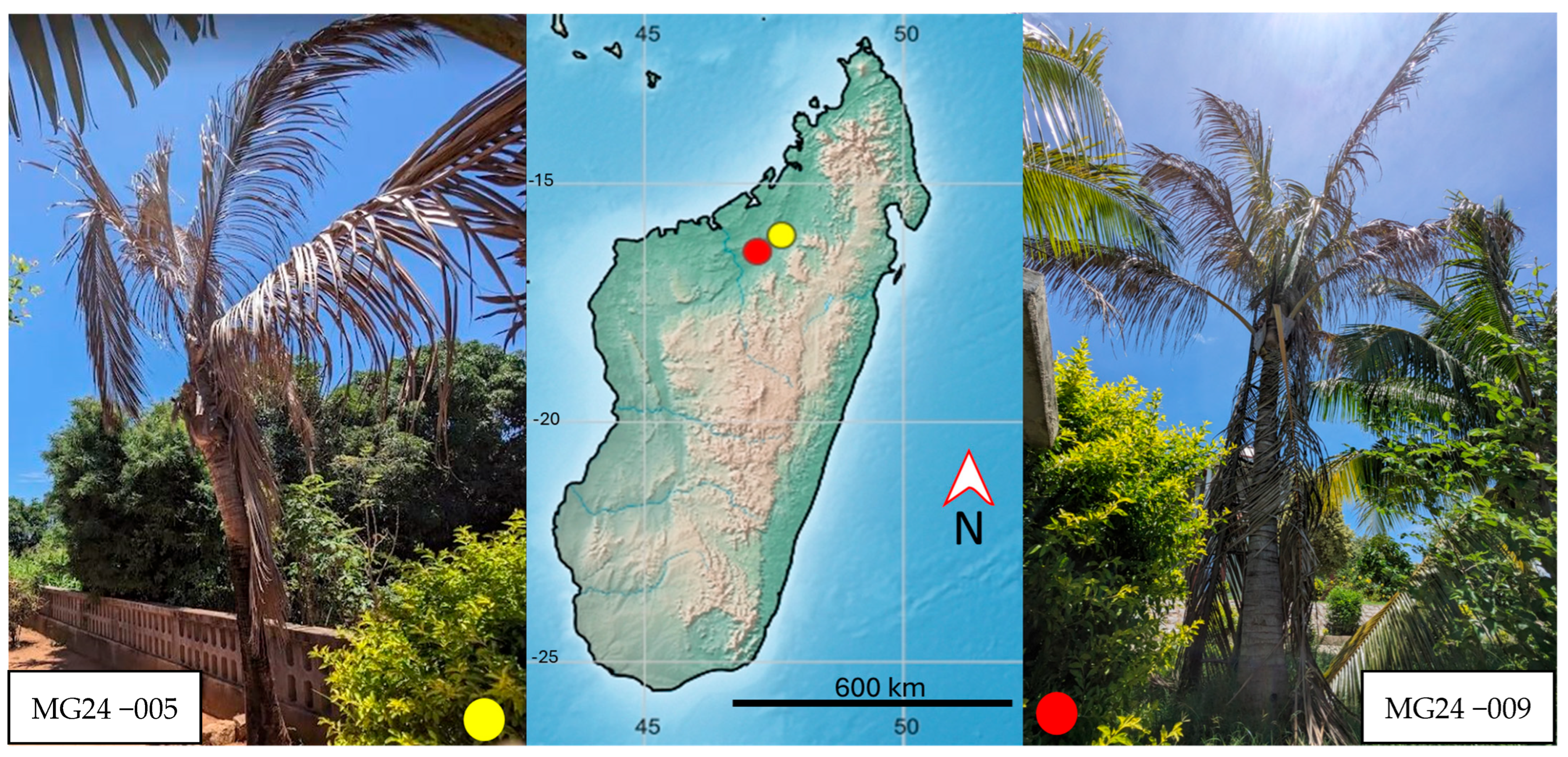
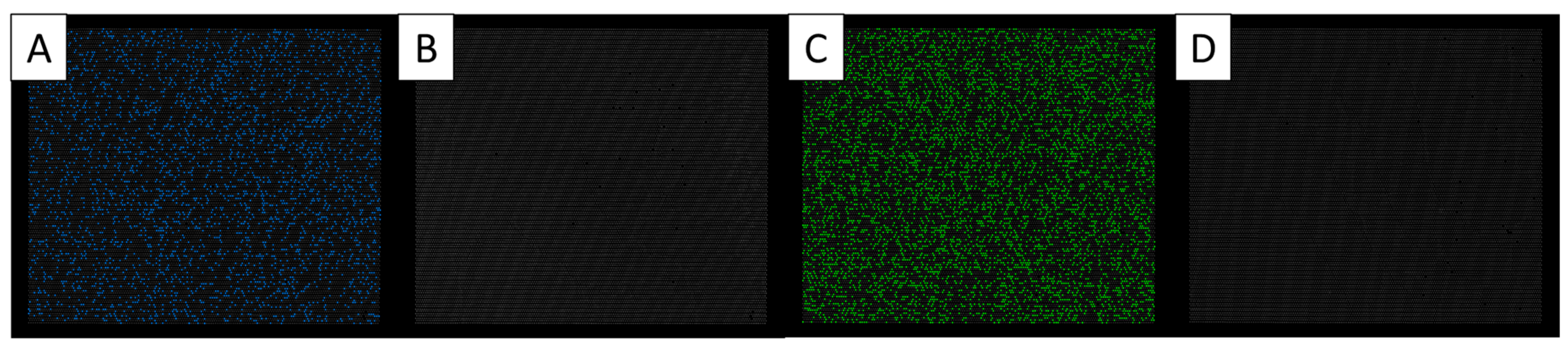
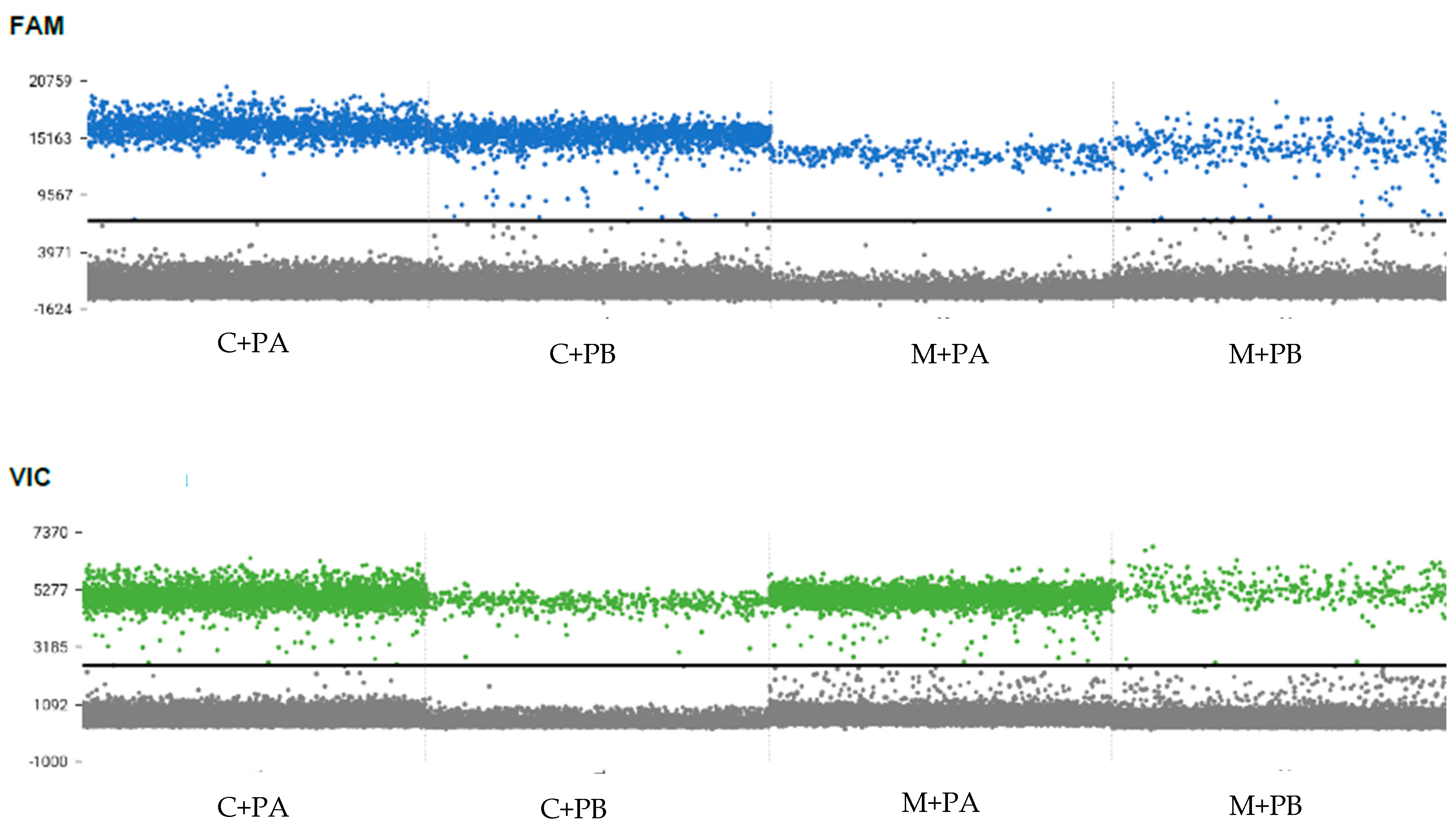
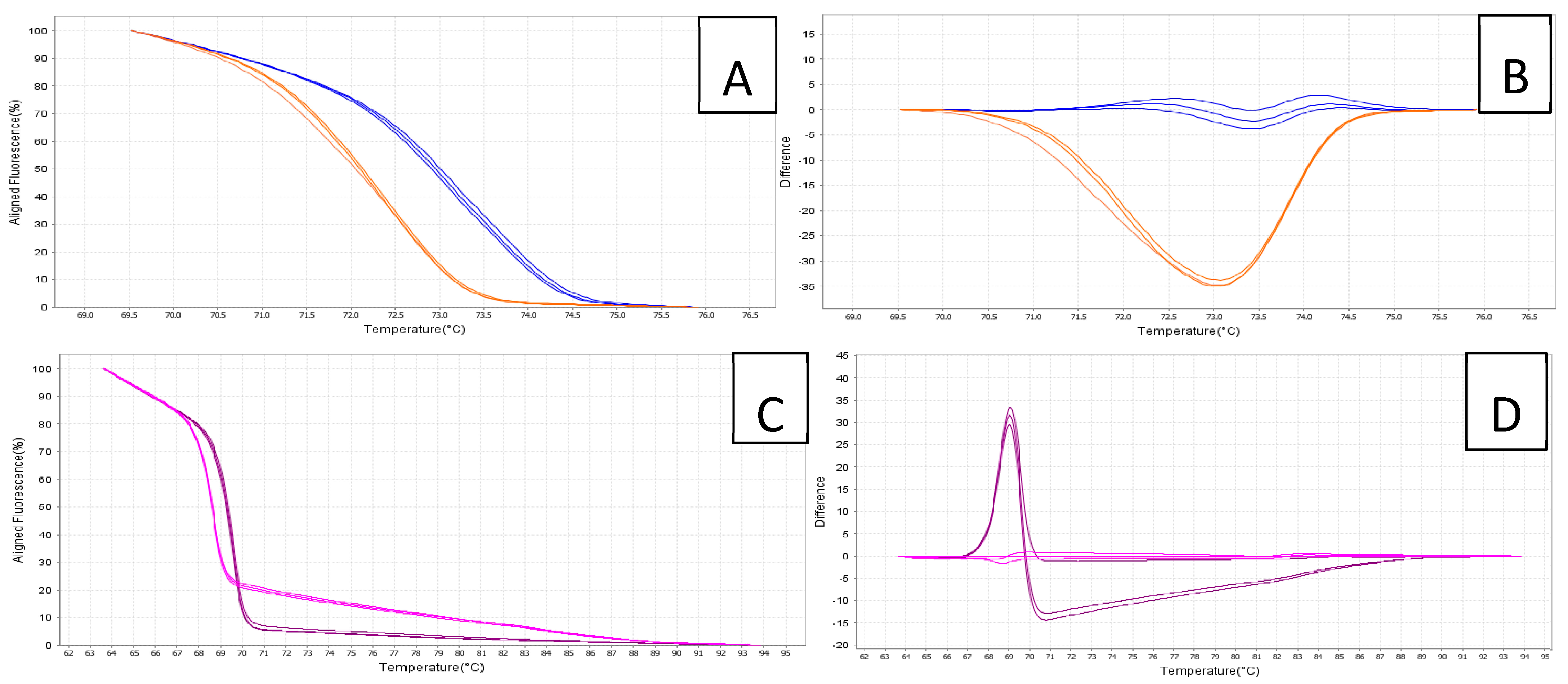
| Species | Isolate | Locality | GenBank Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Ca. P. palmicola’ (16SrXXII-A) | Awka | Nigeria | PX136635 |
| Nig1 | Nigeria | PX136636 | |
| Nig2 | Nigeria | PX136637 | |
| 185 | Nigeria | PX136638 | |
| ‘Ca. P. palmicola’ (16SrXXII-B) | ADN22 | Côte d’Ivoire | PX136639 |
| ADN19 | Côte d’Ivoire | PX136640 | |
| ADN36 | Côte d’Ivoire | PX136641 | |
| ‘Ca. P. cocostanzaniae’ | TanzTagTall | Tanzania | PX136643 |
| EAT LY PS | Tanzania | PX136644 | |
| PB 121A | Tanzania | PX136642 | |
| Malagasy isolates | MG24-002 | Madagascar | PX136646 |
| MG24-005 | Madagascar | PX136645 | |
| MG24-006 | Madagascar | PX136647 | |
| MG24-007 | Madagascar | PX136648 | |
| MG24-009 | Madagascar | PX136649 |
| Assay Type | Species | Orientation | Sequence (5′-3′) | Annealing Temp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TaqMan | ‘Ca. P. cocostanzaniae’/ Malagasy isolate | Sense | CAGGAAGAATTTTGCATG | |
| Antisense | CATCCTTCTTTAGCTTCTAA | 54 °C | ||
| Probe -Sense | FAM-ATGTAAACCATCGCTAAATTGACG-NFQ-MGB | |||
| ‘Ca. P. palmicola’ | Sense | CTCCTGATTTGATATTTGTTAA | ||
| Antisense | GCTGTACCAATTAAAATAGG | 54 °C | ||
| Probe—Antisense | VIC-TTGATGTCGGTCTTCTTATCTTCTAA-NFQ-MGB | |||
| HRMA | ‘Ca. P. palmicola’ | Sense | TAGCCCTCAAAATTGTAA | 54 °C |
| Antisense | ACCAGTAAATTGATCTACA | |||
| ‘Ca. P. cocostanzaniae’/Malagasy | Sense | GGWCGTCAATTTAGTGAWGG [22] | 55 °C | |
| Antisense | GCMGTTCCTGTCATTCCTGA [22] |
| ‘Ca. P. Cocostanzaniae’ | Malagasy Isolate MG24-009 | ‘Ca. P. Palmicola’ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conc. (copies/µL) | Avg. Ct (±SE) | Avg. Ct (±SE) | Avg. Ct (±SE) |
| 1010 | 5.6 ± 0.1 | 6.5 ± 0.0 | Not assessed |
| 109 | 10.1 ± 0.0 | 10.7 ± 0.1 | 12.3 ± 0.2 |
| 108 | 12.4 ± 0.0 | 13.5 ± 0.0 | 16.4 ± 0.1 |
| 107 | 15.9 ± 0.1 | 16.1 ± 0.0 | 20.2 ± 0.0 |
| 106 | 18.8 ± 0.1 | 19.5 ± 0.1 | 24.3 ± 0.1 |
| 105 | 22.4 ± 0.0 | 22.5 ± 0.6 | 28.0 ± 0.1 |
| 104 | 26 ± 0.1 | 26.8 ± 0.1 | 32.0 ± 0.0 |
| 103 | 29.7 ± 0.0 | 30.1 ± 0.1 | - |
| 102 | 33 ± 0.3 | 34.1 ± 0.4 | - |
| 101 | - | - | - |
| FAM (C/M) | VIC (PA/PB) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Isolate | Avg. Ct (±SE) | Qty. (copies/µL) | Avg. Ct (±SE) | Qty. (copies/µL) |
| ‘Ca. P. palmicola’ subgroup A | Awka | No Ct | 0.0 | 31.5 ± 0.0 | 13,080 ± 294 |
| Nig 1 | No Ct | 0.0 | 29.7 ± 0.0 | 38,075 ± 1018 | |
| Nig 2 | No Ct | 0.0 | 28.9 ± 0.7 | 74,829 ± 33,145 | |
| 185 | No Ct | 0.0 | 23.1 ± 0.1 | 1,848,754 ± 130,683 | |
| ‘Ca. P. palmicola’ subgroup B | ADN 22 | No Ct | 0.0 | 34.1 ± 0.1 | 2881 ± 105 |
| ADN 19 | No Ct | 0.0 | 33.1 ± 0.1 | 5189 ± 319 | |
| ADN 32 | No Ct | 0.0 | 32.4 ± 0.1 | 7745 ± 309 | |
| ‘Ca. P. cocostanzaniae’ | TT tall | 26.7 ± 0.5 | 9002 ± 3760 | No Ct | 0.0 |
| EAT LY PS | 26.7 ± 0.1 | 8069 ± 632 | No Ct | 0.0 | |
| PB 121A | 32.1 ± 0.3 | 325 ± 43 | No Ct | 0.0 | |
| Malagasy isolates | MG24-002 | 25.03± 0.2 | 26137 ± 2249 | No Ct | 0.0 |
| MG24-005 | 29.2 ± 0.0 | 1468 ± 22 | No Ct | 0.0 | |
| MG24-006 | 26.4 ± 0.1 | 15710 ± 517 | No Ct | 0.0 | |
| MG24-007 | 30.7 ± 0.3 | 650 ± 87 | No Ct | 0.0 | |
| MG24-009 | 30.4 ± 0.0 | 597 ± 51 | No Ct | 0.0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bloch, M.; Pilet, F.; Helmick, E.E.; Rakotomalala, M.R.; Bahder, B.W. Development of a Duplex dPCR Assay for Detecting Palm Lethal Yellowing Phytoplasmas in Africa and Madagascar and Separation of Regional Species by High-Resolution Melt Curve Analysis (HRMA) Based on the secA Gene. Biology 2025, 14, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091175
Bloch M, Pilet F, Helmick EE, Rakotomalala MR, Bahder BW. Development of a Duplex dPCR Assay for Detecting Palm Lethal Yellowing Phytoplasmas in Africa and Madagascar and Separation of Regional Species by High-Resolution Melt Curve Analysis (HRMA) Based on the secA Gene. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091175
Chicago/Turabian StyleBloch, Melody, Fabian Pilet, Ericka E. Helmick, Mbolarinosy R. Rakotomalala, and Brian W. Bahder. 2025. "Development of a Duplex dPCR Assay for Detecting Palm Lethal Yellowing Phytoplasmas in Africa and Madagascar and Separation of Regional Species by High-Resolution Melt Curve Analysis (HRMA) Based on the secA Gene" Biology 14, no. 9: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091175
APA StyleBloch, M., Pilet, F., Helmick, E. E., Rakotomalala, M. R., & Bahder, B. W. (2025). Development of a Duplex dPCR Assay for Detecting Palm Lethal Yellowing Phytoplasmas in Africa and Madagascar and Separation of Regional Species by High-Resolution Melt Curve Analysis (HRMA) Based on the secA Gene. Biology, 14(9), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091175







