Environmental Hazards and Chemoresistance in OTSCC: Molecular Docking and Prediction of Paclitaxel and Imatinib as BCL2 and EGFR Inhibitors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microarray Data
2.2. Identification of DEGs
2.2.1. OTSCC-Related DEGs
2.2.2. Irinotecan-Related DEGs
2.3. Filtration of Common DEGs Between OTSCC and Irinotecan
2.4. An Examination of Functional and Pathway Enrichment
2.5. PPI Networks to Select Potential Key Genes
2.6. Identification for Drugs Related to Key Genes and Molecular Docking Analysis
2.7. Molecular Dynamics Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Irinotecan and OTSCC Target Determination
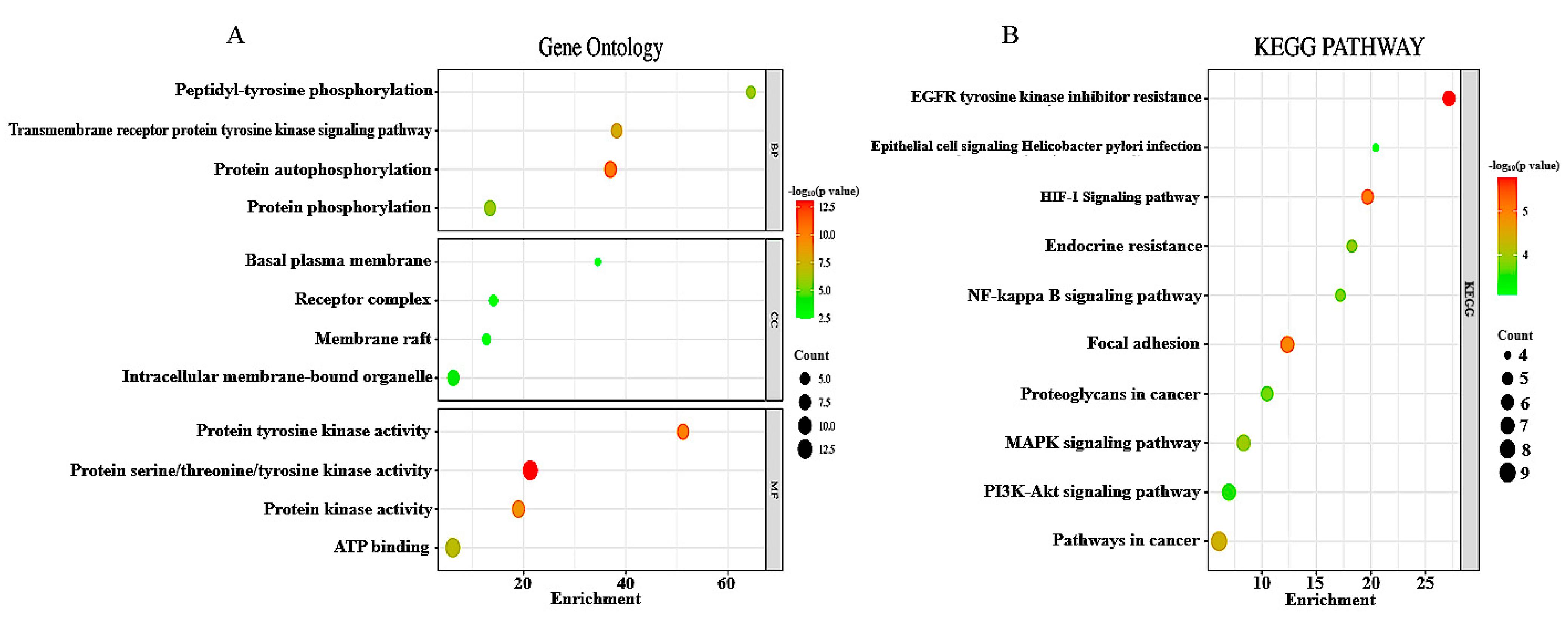
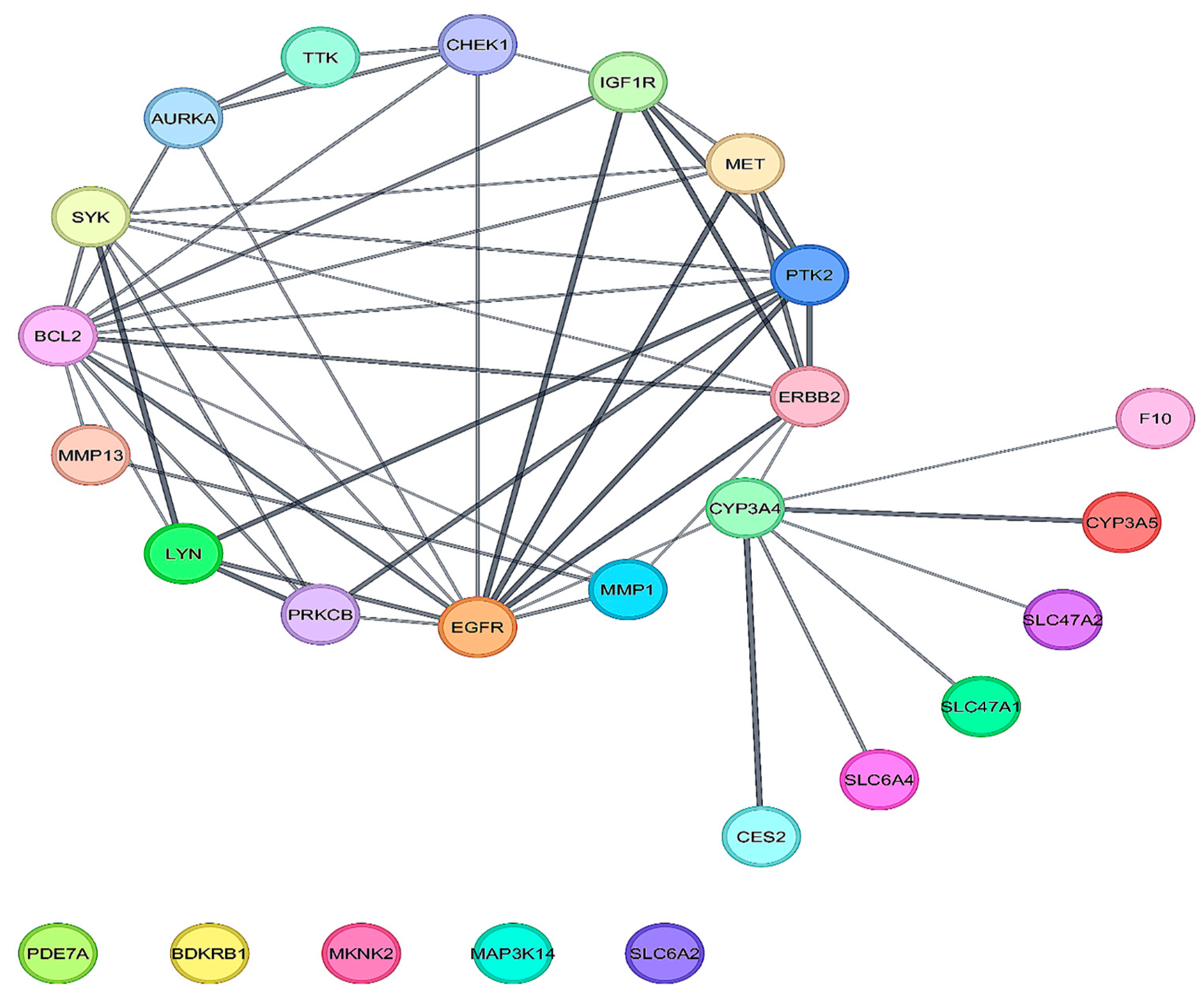
3.2. Analysis of DEGs for Functional and Pathway Enrichment and Selection of Hub Protein from PPI
3.3. Validation of Results via Molecular Docking
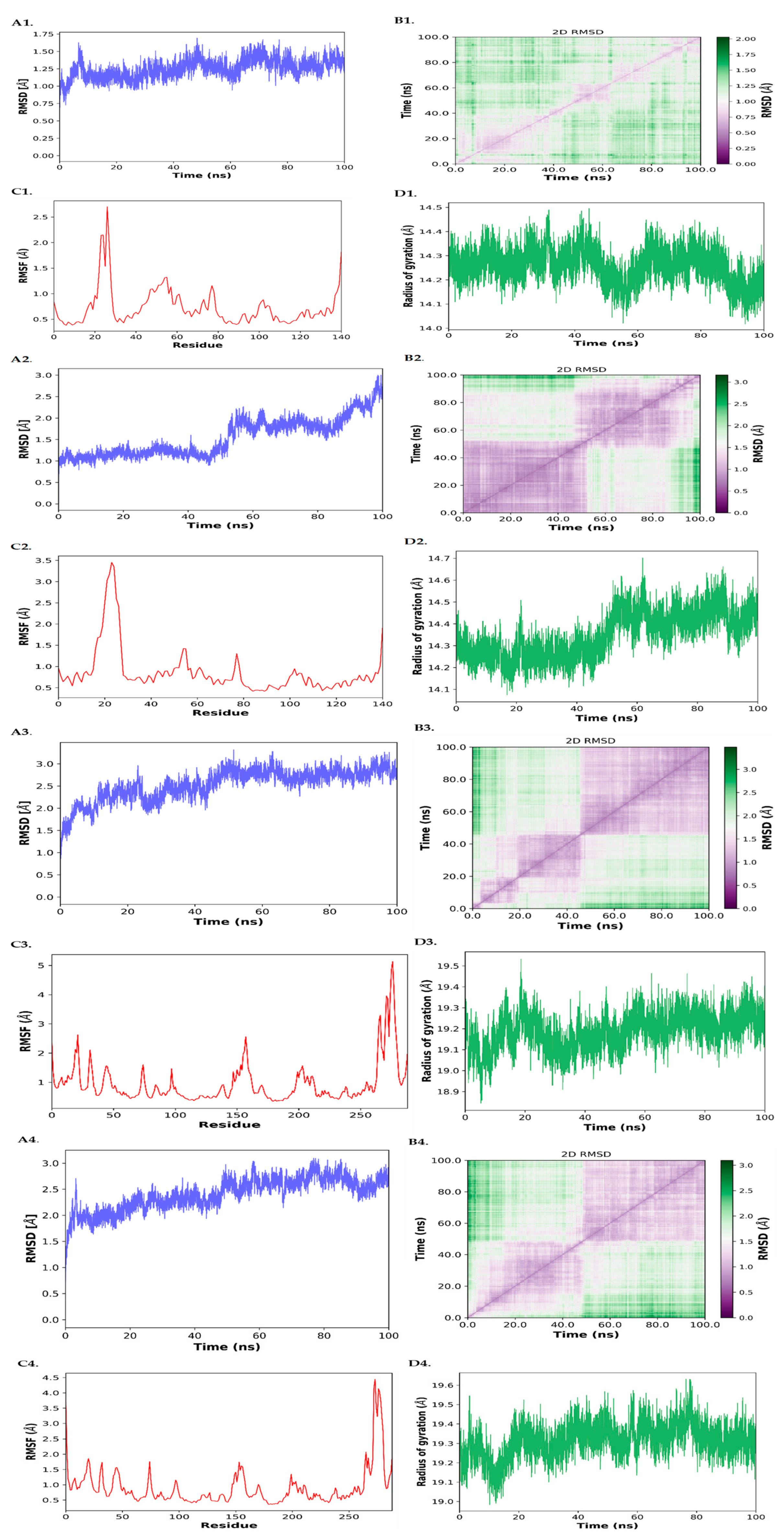
3.4. MD Simulation
3.4.1. RMSD (Root Mean Square Deviation)
3.4.2. RMSF (Root Mean Square Fluctuation)
3.4.3. Radius of Gyration (Rg)
3.4.4. D RMSD Maps
3.4.5. MM/GBSA Binding Free Energy Calculations
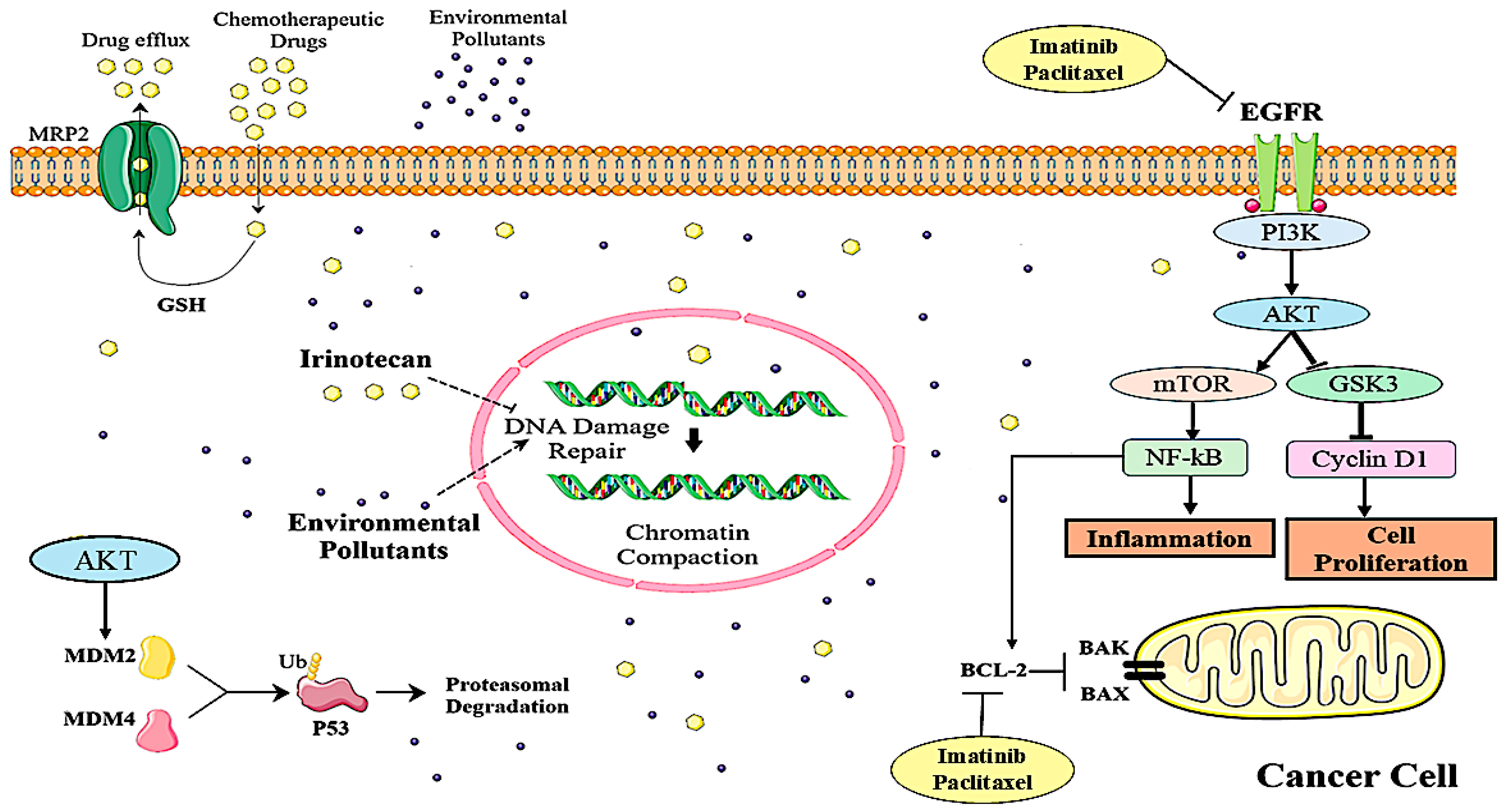
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarode, S.C.; Sarode, G.S.; Sharma, N. Outdoor air pollution and oral cancer: Critical viewpoints and future prospects. Future Oncol. 2023, 19, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Guerra, M.; Zheng, Y.; Osorio-Yanez, C.; Zhong, J.; Chervona, Y.; Wang, S.; Chang, D.; McCracken, J.P.; Díaz, A.; Bertazzi, P.A.; et al. Effects of particulate matter exposure on blood 5-hydroxymethylation: Results from the Beijing truck driver air pollution study. Epigenetics 2015, 10, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.I.; Shin, D.M. Recent Advances in Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Lin, Y.P.; Wang, Y.C.; Chang, T.K.; Chiang, L.C. Assessing and Mapping Spatial Associations among Oral Cancer Mortality Rates, Concentrations of Heavy Metals in Soil, and Land Use Types Based on Multiple Scale Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2148–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roi, A.; Roi, C.I.; Andreescu, N.I.; Riviş, M.; Badea, I.D.; Meszaros, N.; Rusu, L.C.; Iurciuc, S. Oral cancer histopathological subtypes in association with risk factors: A 5-year retrospective study. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2020, 61, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, P.W.; Lam, K.Y.; Chan, A.C.L.; Wei, W.I.; Lam, L.K. Clinicopathological Analysis of Local Spread of Carcinoma of the Tongue. Am. J. Surg. 1998, 175, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.S.; Clark, J.R.; Dirven, R.; Wyten, R.; Gao, K.; O’Brien, C.J. Prognostic factors in the surgical treatment of patients with oral carcinoma. ANZ J. Surg. 2009, 79, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.H.; Iyer, N.G.; Tan, M.H.; Edgren, G. Changing epidemiology of oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: A global study. Head Neck 2017, 39, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcangi, G.; Patano, A.; Guglielmo, M.; Sardano, R.; Palmieri, G.; Pede, C.D.; de Ruvo, E.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Mancini, A.; Inchingolo, F.; et al. Precision Medicine in Oral Health and Diseases: A Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Mesia, R.; Rivera, F.; Remenar, E.; Kawecki, A.; Rottey, S.; Erfan, J.; Zabolotnyy, D.; Kienzer, H.R.; Cupissol, D.; et al. Platinum-Based Chemotherapy plus Cetuximab in Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagunas-Rangel, F.A.; Liu, W.; Schiöth, H.B. Can Exposure to Environmental Pollutants Be Associated with Less Effective Chemotherapy in Cancer Patients? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Liang, L. Identification Hub Genes in Colorectal Cancer by Integrating Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis and Clinical Validation in vivo and vitro. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Xu, C.; Yu, D. Mechanisms correlated with chemotherapy resistance in tongue cancers. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Hua, L.; Huang, H.; Li, G. Expression of Topoisomerase 1 and carboxylesterase 2 correlates with irinotecan treatment response in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kciuk, M.; Marciniak, B.; Kontek, R. Irinotecan—Still an Important Player in Cancer Chemotherapy: A Comprehensive Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.; Cmelak, A.; Shyr, Y.; Netterville, J.; Burkey, B.B.; Sinard, R.J.; Yarbrough, W.G.; Chung, C.H.; Aulino, J.M.; Murphy, B.A. Phase II trial of irinotecan plus cisplatin in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer 2008, 113, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-C.; Chang, P.M.-H.; Yang, M.-H. Cisplatin/Tegafur/Uracil/Irinotecan Triple Combination Therapy for Recurrent/Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Phase I/II Clinical Study. Oncologist 2016, 21, 537–538h. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enokida, T.; Fujii, S.; Takahashi, M.; Higuchi, Y.; Nomura, S.; Wakasugi, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Hayashi, R.; Ohtsu, A.; Tahara, M. Gene expression profiling to predict recurrence of advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: Discovery and external validation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 61786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.; Wu, Y. The prognostic and clinical significance of IFI44L aberrant downregulation in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, M.; Griffith, O.L.; Coffman, A.C.; Weible, J.V.; McMichael, J.F.; Spies, N.C.; Koval, J.; Das, I.; Callaway, M.B.; Eldred, J.M.; et al. DGIdb: Mining the druggable genome. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, F.; Giangreco, I.; Cole, J.C. Use of molecular docking computational tools in drug discovery. Prog. Med. Chem. 2021, 60, 273–343. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Bolton, E.E.; Chen, J.; Fu, G.; Gindulyte, A.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Shoemaker, B.A.; et al. PubChem Substance and Compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1202–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.C.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. LIGPLOT: A program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1995, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gopi, P.; Pandya, P. Structural aspects of formetanate hydrochloride binding with human serum albumin using spectroscopic and molecular modeling techniques. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 281, 121618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, P.R.; Polêto, M.D.; Pedebos, C.; Ligabue-Braun, R. Making it Rain: Cloud-Based Molecular Simulations for Everyone. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 4852–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-L.; Wang, X.K.; Wu, W. Identification of ITGA3 as an Oncogene in Human Tongue Cancer via Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Curr. Med. Sci. 2018, 38, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Sabiha, B.; Jan, H.U.; Haider, S.A.; Khan, A.A.; Ali, S.S. Genetic etiology of oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2017, 70, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Bao, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, H.; Jiao, K. MicroRNA-378-3p/5p represses proliferation and induces apoptosis of oral squamous carcinoma cells via targeting KLK4. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, I.; Kitahara, H.; Ooi, K.; Kato, K.; Noguchi, N.; Yoshizawa, K.; Nakamura, H.; Kawashiri, S. Loss of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma is associated with invasiveness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Li, N.; Guo, F.; Jian, X.C.; Jiang, C.H.; Yin, P.; Min, A.J.; Huang, L. Twist-related protein 1 enhances oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell invasion through β-catenin signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Ni, Y.; Han, W.; Wang, J. PTK7 is a molecular marker for metastasis, TNM stage, and prognosis in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Pol. J. Pathol. 2017, 68, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeldag, G.; Rice, A.; Del Río Hernández, A. Chemoresistance and the Self-Maintaining Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2018, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffetta, P. Human cancer from environmental pollutants: The epidemiological evidence. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2006, 608, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibáñez-Andrade, M.; Chirino, Y.I.; González-Ramírez, I.; Sánchez-Pérez, Y.; García-Cuellar, C.M. Deciphering the Code between Air Pollution and Disease: The Effect of Particulate Matter on Cancer Hallmarks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, T.F.; Hornik, C.P.; Segev, L.; Shostak, G.A.; Sugimoto, C. PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: Size matters. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8983–8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Yokota, T.; Arai, K.; Miyajima, A. Regulation of Bcl-2 expression by oncogenic Ras protein in hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 1995, 10, 2207–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Dai, J.; Wang, X. BCL-2 inhibition impairs mitochondrial function and targets oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPensee, E.W.; Tuttle, T.R.; Fox, S.R. Ben-Jonathan N Bisphenol A at Low Nanomolar Doses Confers Chemoresistance in Estrogen Receptor-α–Positive and –Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPensee, E.W.; LaPensee, C.R.; Fox, S.; Schwemberger, S.; Afton, S. Ben-Jonathan N Bisphenol A and estradiol are equipotent in antagonizing cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 290, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesterer, O.; Milas, L.; Ang, K.K. Combining molecular therapeutics with radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 97, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, J.; Baselga, J. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Targeting in Cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; McKenna, W.G.; Weber, C.N.; Feldman, M.D.; Goldsmith, J.D.; Mick, R.; Machtay, M.; I Rosenthal, D.; Bakanauskas, V.J.; Cerniglia, G.J.; et al. Local recurrence in head and neck cancer: Relationship to radiation resistance and signal transduction. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 885–892. [Google Scholar]
- Bentzen, S.M.; Atasoy, B.M.; Daley, F.M.; Dische, S.; Richman, P.I.; Saunders, M.I.; Trott, K.R.; Wilson, G.D. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in pretreatment biopsies from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma as a predictive factor for a benefit from accelerated radiation therapy in a randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5560–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryott, M.; Wangsa, D.; Heselmeyer-Haddad, K.; Lindholm, J.; Elmberger, G.; Auer, G.; Lundqvist, E.Å.; Ried, T.; Munck-Wikland, E. EGFR protein overexpression and gene copy number increases in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.D.; Rotunno, S.; Erben, P.; Sommer, J.U.; Anders, C.; Stern-Straeter, J.; Hofheinz, R.D.; Hörmann, K.; Sauter, A. Down-regulation of MMP-2 expression due to inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinases by imatinib and carboplatin in HNSCC. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.; Tsukuda, M.; Ishiguro, Y.; Kimura, M.; Fujita, K.; Sakakibara, A.; Takahashi, H.; Toth, G.; Matsuda, H. Antitumor effects of lapatinib (GW572016), a dual inhibitor of EGFR and HER-2, in combination with cisplatin or paclitaxel on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bruce, I.A.; Sleving, N.J.; Homer, J.J.; McGown, A.T.; Ward, T.H. Synergistic effects of imatinib (STI 571) in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs in head and neck cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2005, 16, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, A.C.; Bauer, T.M.; Aggarwal, C.; Lee, C.B.; Harvey, R.D.; Cohen, R.B.; Sedarati, F.; Nip, T.K.; Faessel, H.; Dash, A.B.; et al. Phase Ib study of pevonedistat, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, in combination with docetaxel, carboplatin and paclitaxel, or gemcitabine, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pêtre, A.; Dalban, C.; Karabajakian, A.; Neidhardt, E.-M.; Roux, P.E.; Poupart, M.; Deneuve, S.; Zrounba, P.; Fayette, J. Carboplatin in combination with weekly Paclitaxel as first-line therapy in patients with recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma unfit to EXTREME schedule. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22038–22046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampaki, E.C.; Tampakis, A.; Alifieris, C.E.; Krikelis, D.; Pazaiti, A.; Kontos, M.; Trafalis, D.T. Efficacy and Safety of Neoadjuvant Treatment with Bevacizumab, Liposomal Doxorubicin, Cyclophosphamide and Paclitaxel Combination in Locally/Regionally Advanced, HER2-Negative, Grade III at Premenopausal Status Breast Cancer: A Phase II Study. Clin. Drug Investig. 2018, 38, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dataset | Sample Type | Number of Samples | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria | Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE78060 | OTSCC Tissue | 26 Tumor, 4 Normal | Histologically confirmed OTSCC, untreated patients, transcriptomic data of GPL570 | Incomplete data; less than 10 samples | GPL 570, [HG-U133_Plus_2] Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array |
| GSE138206 | OTSCC Tissue | 5 Tumor, 5 Normal | Histologically confirmed OTSCC, untreated patients, transcriptomic data of GPL570 | Incomplete data; less than 10 samples | GPL 570, [HG-U133_Plus_2] Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array |
| Topology | Occurrence | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| BottleNeck, Betweenness, Degree, Closeness, EcCentricity, EPC, Radiality, MCC, MNC, Stress | 2 | BCL2, EGFR |
| Closeness, Betweenness, EcCentricity, Degree, MCC, EPC, MNC, Radiality, Stress | 1 | ERBB2 |
| DMNC, Closeness, EPC, Degree, MCC, Radiality, MNC | 1 | PTK2 |
| EPC, BottleNeck, DMNC, EcCentricity, MNC, MCC | 1 | SYK |
| BottleNeck, Betweenness, Degree, Closeness, Stress, Radiality | 1 | CYP3A4 |
| Clustering Coefficient, DMNC, EcCentricity | 1 | MET |
| Betweenness, BottleNeck, Stress | 1 | CHEK1 |
| Clustering Coefficient, DMNC | 2 | PRKCB, LYN |
| Clustering Coefficient | 2 | MMP13, TTK |
| Drugs | BCL2 | EGFR |
|---|---|---|
| Docetaxel | −10.5 | −8.6 |
| Paclitaxel | −10.3 | −11.4 |
| Imatinib | −9.9 | −10.4 |
| Irinotecan | −9.8 | −9.6 |
| Ponatinib | −9.6 | −10.2 |
| Ibrutinib | −9.1 | −11 |
| Teniposide | −9 | −8.4 |
| Sorafenib | −8.7 | −9.9 |
| Epirubicin | −8.7 | −8.9 |
| Temsirolimus | −8.6 | −9.3 |
| Pemetrexed | −8.5 | −9.3 |
| Doxorubicin | −8.3 | −8.9 |
| Dasatinib | −8.1 | −8.8 |
| Everolimus | −8.1 | −7.9 |
| Raltitrexed | −8.1 | −7.6 |
| Etoposide | −7.9 | −9.7 |
| Methylprednisolone | −7.7 | −7.9 |
| Sirolimus | −7.5 | −7.1 |
| Sunitinib | −7.3 | −8.8 |
| Bortezomib | −7.3 | −8.3 |
| Bosutinib | −7.3 | −7.5 |
| Vincristine | −7.3 | −6.9 |
| Tretinoin | −7 | −8.7 |
| Mitoxantrone | −6.5 | −8.5 |
| Floxuridine | −6.2 | −6.3 |
| Streptozocin | −6.1 | −6.1 |
| Gemcitabine | −6 | −6.5 |
| Temozolomide | −6 | −5.7 |
| Decitabine | −5.6 | −6.1 |
| CARBOPLATIN | −5.5 | −5.1 |
| Fluorouracil | −4.9 | −5.3 |
| Sr. No. | Protein–Ligand | Van der Waals Energy (kcal/mol) | Electrostatic Energy (kcal/mol) | Polar Solvation Energy (kcal/mol) | Non-polar Solvation Energy (kcal/mol) | Estimated Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BCL2–Imatinib | −44.15 ± 5.73 | −119.29 ± 14.24 | 142.17 ± 14.74 | −5.62 ± 0.63 | −26.90 ± 5.41 |
| 2 | BCL2-Paclitaxel | −59.96 ± 5.90 | −14.33 ± 6.45 | 42.42 ± 6.48 | −7.86 ± 0.75 | −39.74 ± 5.68 |
| 3 | EGFR-Imatinib | −53.52 ± 3.83 | −20.97 ± 9.63 | 47.51 ± 8.03 | −6.97 ± 0.26 | −33.95 ± 6.63 |
| 4 | EGFR-Paclitaxel1 | −36.05 ± 2.52 | −21.55 ± 15.62 | 42.07 ± 13.66 | −4.71 ± 0.64 | −20.23 ± 3.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, N.K.; Awasthi, P.; Gupta, A.; Anand, N.; Giri, B.S.; Hasan, S. Environmental Hazards and Chemoresistance in OTSCC: Molecular Docking and Prediction of Paclitaxel and Imatinib as BCL2 and EGFR Inhibitors. Biology 2025, 14, 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091174
Singh NK, Awasthi P, Gupta A, Anand N, Giri BS, Hasan S. Environmental Hazards and Chemoresistance in OTSCC: Molecular Docking and Prediction of Paclitaxel and Imatinib as BCL2 and EGFR Inhibitors. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091174
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Nishant Kumar, Prankur Awasthi, Agrika Gupta, Nidhi Anand, Balendu Shekher Giri, and Saba Hasan. 2025. "Environmental Hazards and Chemoresistance in OTSCC: Molecular Docking and Prediction of Paclitaxel and Imatinib as BCL2 and EGFR Inhibitors" Biology 14, no. 9: 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091174
APA StyleSingh, N. K., Awasthi, P., Gupta, A., Anand, N., Giri, B. S., & Hasan, S. (2025). Environmental Hazards and Chemoresistance in OTSCC: Molecular Docking and Prediction of Paclitaxel and Imatinib as BCL2 and EGFR Inhibitors. Biology, 14(9), 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091174








