Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics and Adaptive Strategies of Herbaceous Plants in the Yellow River Delta Wetland, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
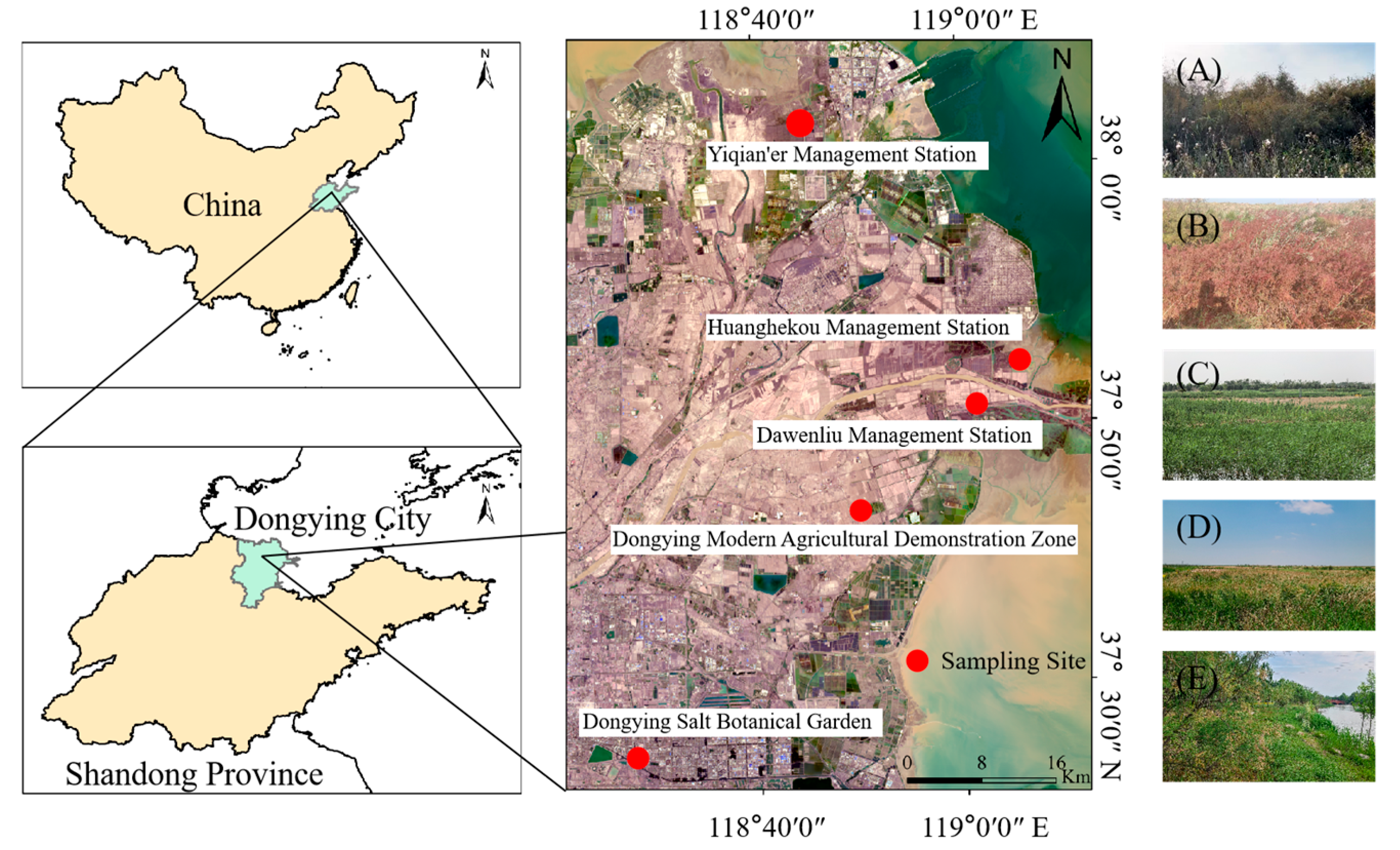
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Design and Vegetation Survey
2.3. Sample Collection and Determination
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
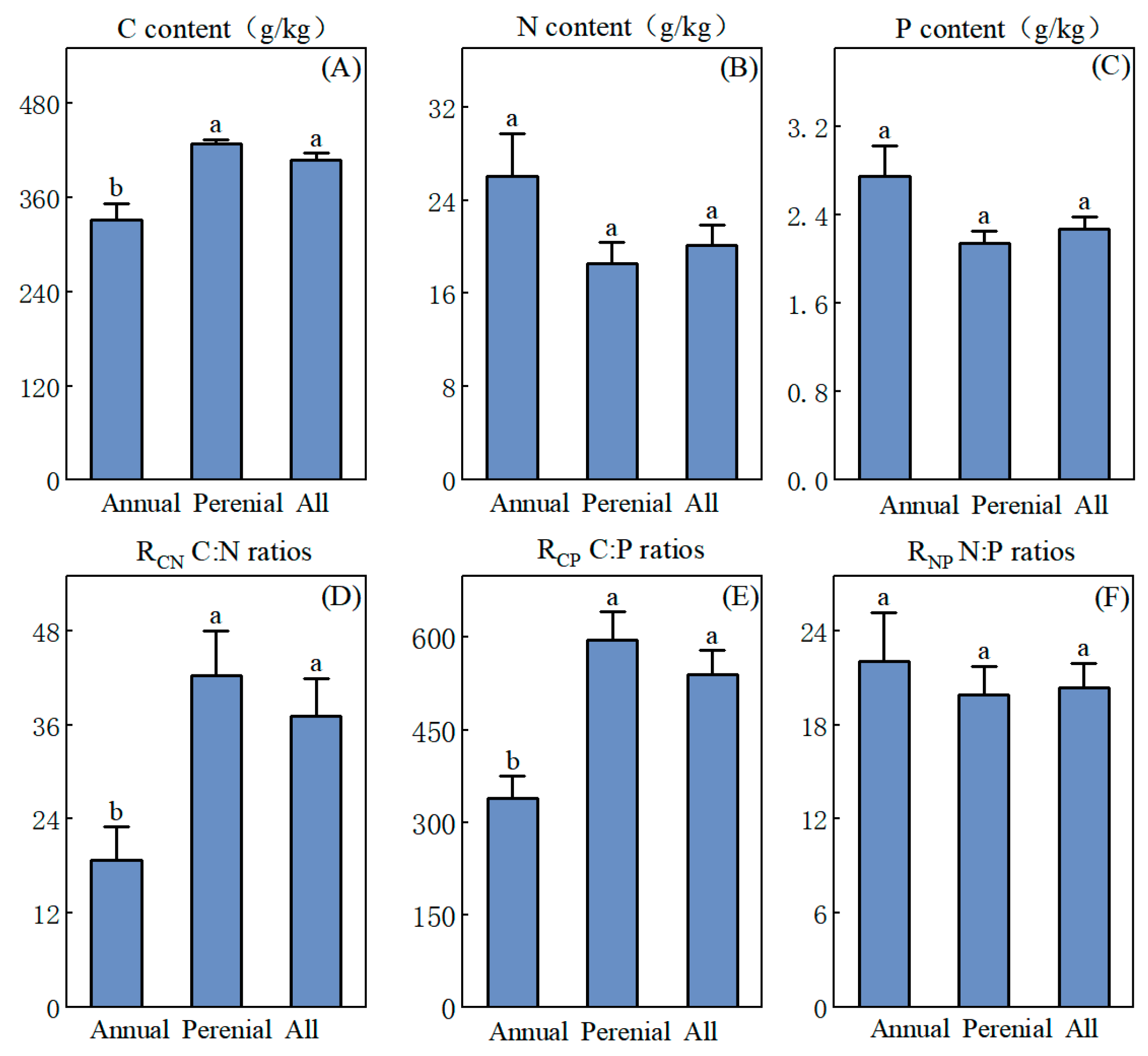
3.1. Characterization of C, N, and P Stoichiometry in Herbs of Different Life Forms
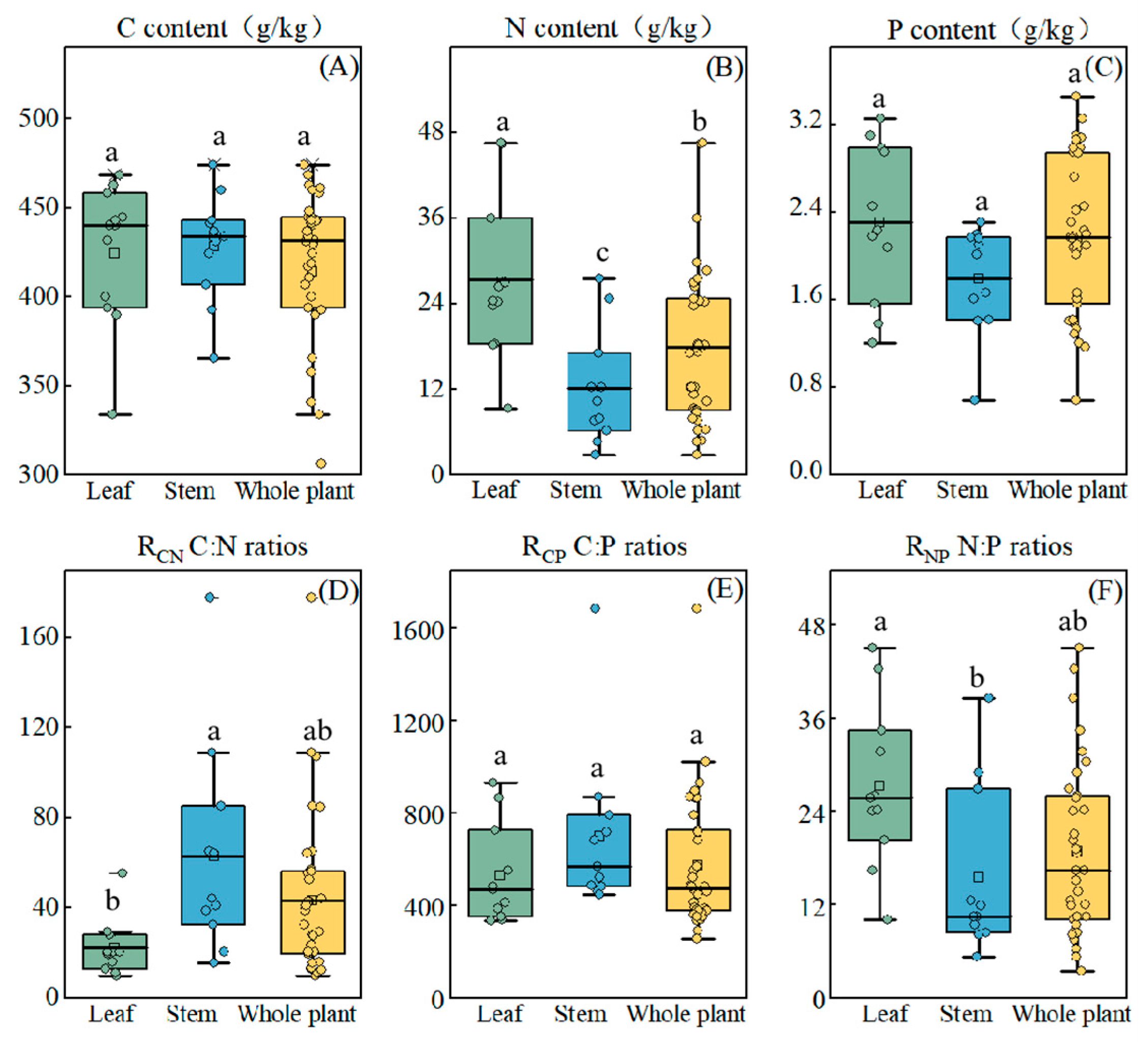
3.2. Characterization of C, N, and P Content and Distribution in Stem and Leaf Organs
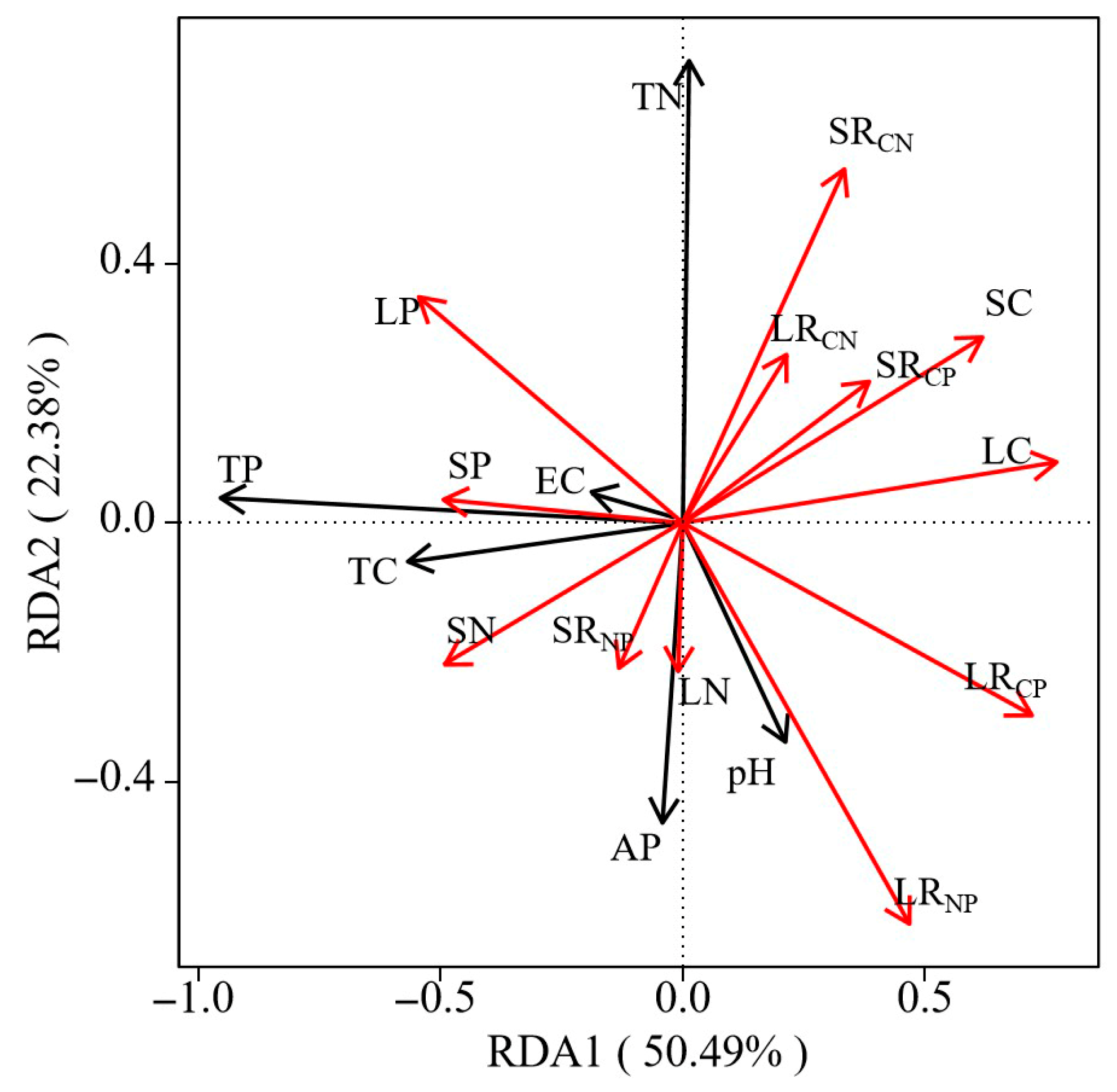
3.3. Correlation of Soil Physicochemical Factors with Plant C, N, and P Stoichiometric Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutrient Characteristics and Adaptive Strategies of Herbaceous Plants of Different Life Forms in the YRD
4.2. Organ-Specific Nutrient Allocation Strategies and Their Role in Environmental Adaptation
4.3. Soil Physicochemical Properties and Their Impact on C, N, and P Allocation in Plant Organs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sampling Point | Family | Species |
|---|---|---|
| Yiqian’er Management Stations | Poaceae | Phragmites australis |
| Poaceae | Cynodon dactylon | |
| Poaceae | Eleusine indica | |
| Poaceae | Setaria viridis | |
| Asteraceae | Sonchubrachyotus | |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia annua | |
| Asteraceae | Anthemis cotula | |
| Asteraceae | Cirsium setosum | |
| Fabaceae | Medicago sativa | |
| Fabaceae | Medicago lupulina | |
| Amaranthaceae | Suaeda glauca | |
| Plumbaginaceae | Limonium gmelinii | |
| Asclepiadaceae | Cynanchum chinense | |
| Huanghekou Management Stations | Poaceae | Phragmites australis |
| Poaceae | Imperata cylindrica | |
| Poaceae | Setaria viridis | |
| Poaceae | Deyeuxia pyramidalis | |
| Asteraceae | Cirsium setosum | |
| Asteraceae | Sonchubrachyotus | |
| anthaceae | Suaeda glauca | |
| Amaranthaceae | Salicornia europaea | |
| Dawenliu Management Stations | Poaceae | Eragrostis minor |
| Poaceae | Digitaria sanguinali | |
| Poaceae | Eleusine indica | |
| Poaceae | Setaria viridis | |
| Poaceae | Imperata cylindrica | |
| Poaceae | Phragmites australis | |
| Asteraceae | Conyza canadensis | |
| Asteraceae | Sonchubrachyotus | |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia annua | |
| Asteracea | Anthemis cotula | |
| Asteraceae | Cirsium setosum | |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia scoparia | |
| Asteraceae | Sonchus arvensis | |
| Fabaceae | Sesbania cannabina | |
| Fabaceae | Medicago sativa | |
| Fabaceae | Medicago lupulina | |
| Cannabaceae | Humulus scandens | |
| Portulacaceae | Portulaca oleracea | |
| Cucurbitaceae | Cucumis melo var. Agrestis | |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia hypericifolia | |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago major | |
| Apocynaceae | Apocynum venetum | |
| Malvaceae | Alcea rosea | |
| Plumbaginaceae | Limonium gmelinii | |
| Asclepiadaceae | Cynanchum chinense | |
| Asparagaceae | Asparagus officinalis | |
| Iridaceae | Iris lactea var. chinensis | |
| Dongying Modern Agricultural Demonstration Zone | Poaceae | Imperata cylindrica |
| Poaceae | Phragmites australis | |
| Poaceae | Deyeuxia pyramidalis | |
| Poaceae | Cynodon dactylon | |
| Poaceae | Echinochloa crus-galli | |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia mongolica | |
| Asteraceae | Lactuca tatarica | |
| Asteraceae | Sonchus arvensis | |
| Asteraceae | Achillea millefolium | |
| Asteraceae | Cirsium setosum | |
| Fabaceae | Medicago sativa | |
| Fabaceae | Sesbania cannabina | |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago major | |
| Cannabaceae | Humulus scandens | |
| Oleaceae | Syringa oblata Lindl | |
| Typhaceae | Typha orientalis | |
| Cyperaceae | Bolboschoenus maritimus | |
| Linaceae | Linum usitatissimum | |
| Portulacaceae | Portulaca oleracea | |
| Apocynaceae | Apocynum venetum | |
| Iridaceae | Iris lactea var. Chinensis | |
| Iridaceae | Iris tectorum | |
| Asphodelaceae | Hemerocallis fulva | |
| Plumbaginaceae | Limonium gmelinii | |
| Dongying Salt Botanical Garden | Poaceae | Digitaria sanguinali |
| Poaceae | Imperata cylindrica | |
| Poaceae | Phragmites australis | |
| Poaceae | Deyeuxia pyramidalis | |
| Poaceae | Cynodon dactylon | |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia mongolica | |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia scoparia | |
| Asteraceae | Mulgedium tataricum | |
| Asteraceae | Sonchus arvensis | |
| Asteraceae | Achillea millefolium | |
| Asteraceae | Cirsium setosum | |
| Fabaceae | Medicago sativa | |
| Fabaceae | Sphaerophysa salsula | |
| Amaranthaceae | Suaeda glauca | |
| Amaranthaceae | Kochia scoparia var. sieversiana | |
| Linaceae | Linum usitatissimum | |
| Portulacaceae | Portulaca oleracea | |
| Apocynaceae | Apocynum venetum | |
| ridaceae | Iris lactea var. Chinensis | |
| Iridaceae | Iris tectorum | |
| Asphodelaceae | Hemerocallis fulva | |
| Lamiaceae | Scutellaria baicalensis | |
| Plumbaginaceae | Limonium gmelinii | |
| Asclepiadaceae | Cynanchum chinense | |
| Asparagaceae | Asparagus officinalis | |
| Caprifoliaceae | Lonicera japonica | |
| Lamiaceae | Salvia miltiorrhiza |
References
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Denno, R.F.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.; Interlandi, S.; Kilham, S.S.; McCauley, E.; Schulz, K.L.; et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 2000, 408, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ågren, G.I. The C:N:P stoichiometry of autotrophs—Theory and observations. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Peñuelas, J. The C:N:P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 14, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gong, Y.; Lafleur, P.; Wu, Y. Patterns and drivers of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry in Southern China’s grasslands. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhou, G.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Tang, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, Q.; Ma, W.; Xiong, G.; et al. Patterns of plant carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentration in relation to productivity in China’s terrestrial ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4033–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Adamowski, J.F.; Biswas, A.; Liu, C.; Chang, Z.; Feng, Q. Response of leaf stoichiometry of Oxytropis ochrocephala to elevation and slope aspect. Catena 2020, 194, 104772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Fang, J.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Y. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGroddy, M.E.; Daufresne, T.; Hedin, L.O. Scaling of C: N: P stoichiometry in forests worldwide: Implications of terrestrial redfield-type ratios. Ecology 2004, 85, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, M.C.; Seehausen, O.; Matthews, B. The Ecology and Evolution of Stoichiometric Phenotypes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, J.T.; Raynal, D.J. Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessen, D.; Kylet, T.; Elser, J. RNA responses to N- and P-limitation; reciprocal regulation of stoichiometry and growth rate in Brachionus. Funct. Ecol. 2007, 21, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; O’brien, W.J.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Dowling, T.E. The evolution of ecosystem processes: Growth rate and elemental stoichiometry of a key herbivore in temperate and arctic habitats. J. Evol. Biol. 2000, 13, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrede, T.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Kooijman, S.; Elser, J.J. Fundamental connections among organism C: N: P stoichiometry, macromolecular composition, and growth. Ecology 2004, 85, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Sterner, R.W.; Gorokhova, E.a.; Fagan, W.F.; Markow, T.A.; Cotner, J.B.; Harrison, J.F.; Hobbie, S.E.; Odell, G.M.; Weider, L. Biological stoichiometry from genes to ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Reich, P.B.; Ian Woodward, F.; Wang, Z.H. Biogeography and variability of eleven mineral elements in plant leaves across gradients of climate, soil and plant functional type in China. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Fu, Z. Study on ecological stoichiometry homeostasis characteristics of different halophytes in the Yellow River Delta. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L.; Fan, Z.; Deng, Y.; Feng, T. Influence of Functional Traits of Dominant Species of Different Life Forms and Plant Communities on Ecological Stoichiometric Traits in Karst Landscapes. Plants 2024, 13, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, P.B.; Oleksyn, J. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11001–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Ji, Z.; Fan, B.; Wang, X.; He, G.; Shi, L.; Liu, G. Plants adapted to nutrient limitation allocate less biomass into stems in an arid-hot grassland. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Lv, T.; Liu, C.; Yu, D. Variation in resource allocation strategies and environmental driving factors for different life-forms of aquatic plants in cold temperate zones. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 3046–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseman-Valtierra, S.; Gonzalez, R.; Kroeger, K.D.; Tang, J.; Chao, W.C.; Crusius, J.; Bratton, J.; Green, A.; Shelton, J. Short-term nitrogen additions can shift a coastal wetland from a sink to a source of N2O. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4390–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Song, X.L.; Lu, X.G.; Xue, Z.-S. Ecological stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in estuarine wetland soils: Influences of vegetation coverage, plant communities, geomorphology, and seawalls. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Han, G.; Zhang, Q. China promotes coastal wetland restoration to protect wetland ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2025, 37, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Qu, F.; Bi, X.; Xia, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, J. Elemental stoichiometry (C, N, P) of soil in the Yellow River Delta nature reserve: Understanding N and P status of soil in the coastal estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Han, B. Spatiotemporal Changes of Soil Salinization in the Yellow River Delta of China from 2015 to 2019. Sustainability 2021, 13, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Luo, Y. An overview of ecohydrology of the Yellow River delta wetland. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2016, 16, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Lin, W.; Zeng, C.; Tong, C. Stoichiometric characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in major wetland vegetation of China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 38, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, L.; Qu, Q.; Yao, B.; Fu, S.; Hu, Q. Leaf litter and soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry of dominant plant specues in the Poyang Lake wetland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Abliz, A.; Lyu, G.; Zhang, X.; Gong, Y. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of photosynthetic organs across Ebinur Lake Wetland Natural Reserve of Xinjiang, Northwest China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 34, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; He, F.; Tian, D.; Zou, D.; Yan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Huang, K.; Shen, H.; Fang, J. Variations and determinants of carbon content in plants: A global synthesis. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.; Ehsanzadeh, P. Photosynthetic pigments, ionic and antioxidative behaviour of hulled tetraploid wheat in response to NaCl. Photosynthetica 2016, 54, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Arif, M.; Zheng, J.; Li, C. Patterns and drivers of plant carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry in a novel riparian ecosystem. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1354222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güsewell, S.; Koerselman, W. Variation in nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations of wetland plants. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2002, 5, 37–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Peng, Q.; Li, K.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, W. Patterns of nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry among leaf, stem and root of desert plants and responses to climate and soil factors in Xinjiang, China. Catena 2021, 199, 105100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppenwimer, T.; Mayrose, I.; DeMalach, N. Revising the global biogeography of annual and perennial plants. Nature 2023, 624, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Han, D.; Zhan, J. Comparison of Leaf and Fine Root Traits Between Annuals and Perennials, Implicating the Mechanism of Species Changes in Desertified Grasslands. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 778547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, M.R.; Jonckheere, W.; Knegt, B.; Lemos, F.; Liu, J.; Schimmel, B.C.J.; Villarroel, C.A.; Ataide, L.M.S.; Dermauw, W.; Glas, J.J.; et al. Mechanisms and ecological consequences of plant defence induction and suppression in herbivore communities. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 1015–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endara, M.J.; Coley, P.D. The resource availability hypothesis revisited: A meta-analysis. Funct. Ecol. 2011, 25, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingestad, T.; Ågren, G.I. Nutrient uptake and allocation at steady-state nutrition. Physiol. Plant. 1988, 72, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Cheng, X.; Kang, F.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Han, H. The patterns of N/P/K stoichiometry in the Quercus wutaishanica community among different life forms and organs and their responses to environmental factors in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, N.; Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Yu, G.; Wilcox, K.; Yu, Q.; He, N. C:N:P stoichiometry in China’s forests: From organs to ecosystems. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhang, K.; Tan, H.; Hu, R.; Su, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Nutrient levels within leaves, stems, and roots of the xeric species Reaumuria soongorica in relation to geographical, climatic, and soil conditions. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Song, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Mao, P.; Zhang, H. Seasonal variations of C: N: P stoichiometry and their trade-offs in different organs of Suaeda salsa in coastal wetland of Yellow River Delta, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minden, V.; Kleyer, M. Internal and external regulation of plant organ stoichiometry. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.J.; Reich, P.B.; Westoby, M.; Ackerly, D.D.; Baruch, Z.; Bongers, F.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Chapin, T.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Diemer, M.; et al. The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 2004, 428, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschet, G.T.; Cornelissen, J.H.; Van Logtestijn, R.S.; Aerts, R. Evidence of the ‘plant economics spectrum’ in a subarctic flora. J. Ecol. 2010, 98, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.L.; Wang, J.J.; Kardol, P.; Wu, H.F.; Zeng, H.; Deng, X.B.; Deng, Y. Economic strategies of plant absorptive roots vary with root diameter. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, A.; Mommer, L.; Andraczek, K.; Iversen, C.M.; Bergmann, J.; Bruelheide, H.; Fan, Y.; Freschet, G.T.; Guerrero-Ramírez, N.R.; Kattge, J. An integrated framework of plant form and function: The belowground perspective. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorey, T.; Frachon, L.; Rieseberg, L.H.; Kreiner, J.M.; Schiestl, F.P. Biotic interactions promote local adaptation to soil in plants. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fang, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, G.; Xu, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, G.; Yan, J.; Ma, K. Patterns and controlling factors of plant nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across China’s forests. Biogeochemistry 2019, 143, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. The Nature and Properties of Soils; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Fan, S.; Zhang, X. C:N:P stoichiometric variations of herbs and its relationships with soil properties and species relative abundance along the Xiaokai River irrigation in the Yellow River Delta, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1130477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.A.; Puissant, J.; Buckeridge, K.M.; Goodall, T.; Jehmlich, N.; Chowdhury, S.; Gweon, H.S.; Peyton, J.M.; Mason, K.E.; van Agtmaal, M.; et al. Land use driven change in soil pH affects microbial carbon cycling processes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, R.A.; Grundon, N.J.; Rayment, G.E.; Probert, M.E. Plant-soil interactions at low pH: Principles and management. In Proceedings of the Third Intenational Symposium on Plant-Soil Interactions at Low pH, Brisbane, Australia, 12–16 September 1993; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Neina, D. The Role of Soil pH in Plant Nutrition and Soil Remediation. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2019, 2019, 5794869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneklaas, E.J.; Lambers, H.; Bragg, J.; Finnegan, P.M.; Lovelock, C.E.; Plaxton, W.C.; Price, C.A.; Scheible, W.R.; Shane, M.W.; White, P.J. Opportunities for improving phosphorus-use efficiency in crop plants. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hou, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yu, T. Nitrogen isotope fractionation mechanism, analysis measurement tracer technology and its application in ecological environment. Geol. China 2024, 51, 1617–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Arif, M.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Ding, D.; Li, C. Dam inundation simplifies the plant community composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Siddique, A.; Shabala, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, C. Phosphorus plays key roles in regulating plants’ physiological responses to abiotic stresses. Plants 2023, 12, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate phosphorus limitation by reducing plant N: P ratios under warming and nitrogen addition in a temperate meadow ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, F.; Yu, J.; Du, S.; Li, Y.; Lv, X.; Ning, K.; Wu, H.; Meng, L. Influences of anthropogenic cultivation on C, N and P stoichiometry of reed-dominated coastal wetlands in the Yellow River Delta. Geoderma 2014, 235, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Life Form | Family | Species |
|---|---|---|
| Annual herbaceous plant | Asteraceae | Conyza canadensis |
| Asteraceae | Sonchubrachyotus | |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia annua | |
| Asteraceae | Anthemis cotula | |
| Poaceae | Eragrostis minor | |
| Poaceae | Digitaria sanguinali | |
| Poaceae | Echinochloa crus-galli | |
| Poaceae | Eleusine indica | |
| Poaceae | Setaria viridis | |
| Amaranthaceae | Suaeda salsa | |
| Amaranthaceae | Salicornia europaea | |
| Cannabaceae | Humulus scandens | |
| Linaceae | Linum usitatissimum | |
| Portulacaceae | Portulaca oleracea | |
| Cucurbitaceae | Cucumis melo var. agrestis | |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia hypericifolia | |
| Fabaceae | Sesbania cannabina | |
| Perennial herbaceous plant | Poaceae | Imperata cylindrica |
| Poaceae | Phragmites australis | |
| Poaceae | Deyeuxia pyramidalis | |
| Poaceae | Cynodon dactylon | |
| Poaceae | Phalaris arundinacea | |
| Fabaceae | Sphaerophysa salsula | |
| Fabaceae | Medicago sativa | |
| Fabaceae | Medicago lupulina | |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia mongolica | |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia scoparia | |
| Asteraceae | Lactuca tatarica | |
| Asteraceae | Sonchus arvensis | |
| Asteraceae | Achillea millefolium | |
| Asteraceae | Cirsium setosum | |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago major | |
| Apocynaceae | Apocynum venetum | |
| Malvaceae | Alcea rosea | |
| Iridaceae | Iris lactea var. chinensis | |
| Iridaceae | Iris tectorum | |
| Asphodelaceae | Hemerocallis fulva | |
| Lamiaceae | Scutellaria baicalensis | |
| Plumbaginaceae | Limonium gmelinii | |
| Oleaceae | Syringa oblata Lindl | |
| Typhaceae | Typha orientalis | |
| Cyperaceae | Bolboschoenus maritimus | |
| Asclepiadaceae | Cynanchum chinense | |
| Asparagaceae | Asparagus officinalis | |
| Amaranthaceae | Kochia scoparia var. sieversiana | |
| Caprifoliaceae | Lonicera japonica | |
| Lamiaceae | Salvia miltiorrhiza |
| Plant | Organ | Intercept | Exponent | 95%CI | r2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Species | Leaf | 1.174 | 0.618 | (0.03–1.28) | 0.169 | 0.02 |
| Stem | 0.96 | 0.35 | (−1.12–2.1) | 0.014 | 0.3 | |
| Annual Species | Leaf | 1.242 | 0.541 | (−2.23–5.57) | 0.16 | 0.28 |
| Stem | 1.067 | 0.524 | — | 0.006 | 0.44 | |
| Perennial Species | Leaf | 1.183 | 0.566 | (−0.18–1.38) | 0.14 | 0.04 |
| Stem | 1.517 | 1.388 | (−1.51–1.19) | 0.003 | 0.47 |
| Index | Soil | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | EC | TC | TN | TP | AP | ||
| Annual plants | LC | −0.265 | 0.277 | −0.023 | −0.223 | −0.75 | 0.549 |
| LN | −0.572 | 0.519 | −0.781 | −0.879 * | −0.284 | 0.072 | |
| LP | −0.662 | 0.73 | −0.164 | −0.365 | 0.582 | −0.926 * | |
| LCN | 0.686 | −0.613 | 0.888 * | 0.944 * | −0.104 | 0.443 | |
| LCP | 0.642 | −0.676 | 0.343 | 0.483 | −0.598 | 0.910 * | |
| LNP | 0.007 | −0.142 | −0.682 | −0.555 | −0.614 | 0.646 | |
| SC | 0.919 * | −0.950 * | 0.317 | 0.661 | 0.217 | 0.404 | |
| SN | −0.333 | 0.357 | −0.542 | −0.526 | 0.696 | −0.569 | |
| SP | 0.289 | −0.263 | 0.286 | 0.427 | 0.738 | −0.567 | |
| SCN | 0.764 | −0.746 | 0.712 | 0.848 | −0.248 | 0.601 | |
| SCP | 0.652 | −0.713 | −0.057 | 0.178 | −0.454 | 0.976 ** | |
| SNP | −0.409 | 0.428 | −0.647 | −0.695 | 0.282 | −0.166 | |
| Perennial plants | LC | −0.024 | 0.162 | 0.104 | 0.377 | −0.09 | 0.298 |
| LN | 0.096 | −0.319 | −0.276 | −0.189 | −0.159 | −0.105 | |
| LP | −0.154 | −0.095 | −0.402 | −0.532 * | 0.003 | −0.24 | |
| LCN | −0.086 | 0.31 | 0.091 | 0.041 | −0.058 | 0.031 | |
| LCP | 0.108 | 0.043 | 0.276 | 0.565 * | −0.106 | 0.278 | |
| LNP | 0.201 | −0.311 | 0.023 | 0.288 | −0.125 | 0.092 | |
| SC | 0.163 | 0.117 | 0.222 | 0.369 | −0.12 | 0.341 | |
| SN | −0.178 | −0.17 | −0.253 | −0.293 | −0.139 | −0.088 | |
| SP | −0.099 | −0.164 | −0.053 | −0.31 | 0.447 | −0.387 | |
| SCN | −0.083 | 0.566 * | 0.132 | 0.269 | −0.144 | 0.116 | |
| SCP | −0.03 | 0.466 | 0.253 | 0.41 | −0.318 | 0.418 | |
| SNP | −0.002 | −0.117 | −0.17 | −0.129 | −0.293 | 0.053 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, M.; Liu, J.; Qu, F.; Sun, B.; Yu, Y.; Guan, B. Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics and Adaptive Strategies of Herbaceous Plants in the Yellow River Delta Wetland, China. Biology 2025, 14, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091132
Luo M, Liu J, Qu F, Sun B, Yu Y, Guan B. Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics and Adaptive Strategies of Herbaceous Plants in the Yellow River Delta Wetland, China. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091132
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Mengjiao, Jiaxuan Liu, Fanzhu Qu, Bowen Sun, Yang Yu, and Bo Guan. 2025. "Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics and Adaptive Strategies of Herbaceous Plants in the Yellow River Delta Wetland, China" Biology 14, no. 9: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091132
APA StyleLuo, M., Liu, J., Qu, F., Sun, B., Yu, Y., & Guan, B. (2025). Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics and Adaptive Strategies of Herbaceous Plants in the Yellow River Delta Wetland, China. Biology, 14(9), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091132







