High-Abundance Heterotrophic Bacteria Inhabit the 85° E Hydrothermal Plume of the Explosive Volcanic Zone at Gakkel Ridge, Arctic Ocean
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hydrothermal Plume Detection and Near-Bottom Optical Survey
2.2. Sampling and Physicochemical Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction, 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Analysis
2.4. Metagenomic Sequencing and Analysis
2.5. Metagenomic Binning and Metagenome-Assembled Genome (MAG) Classification
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Water Column and Sediments
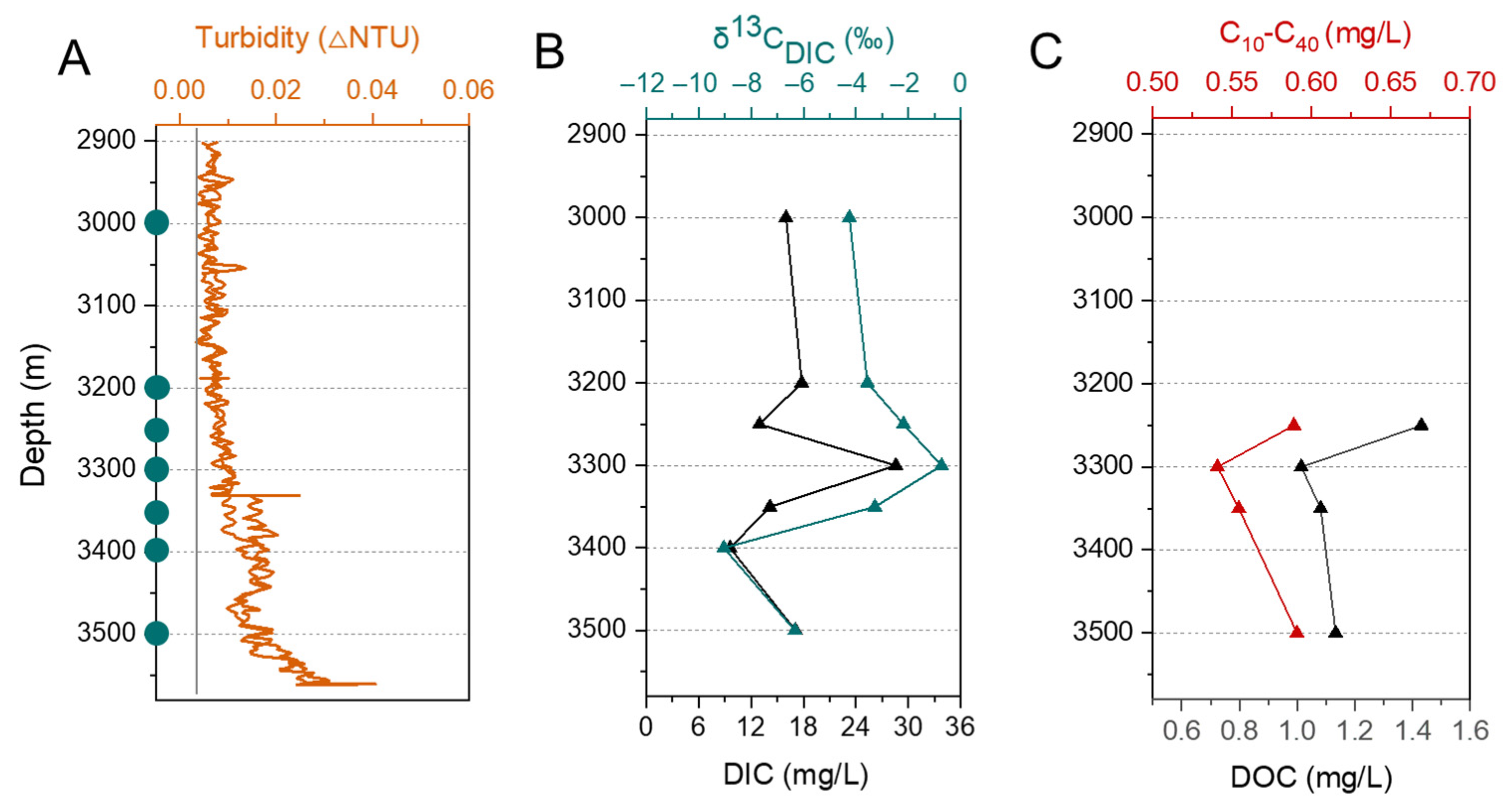
3.2. Microbial Diversity and Its Correlation with Environmental Factors
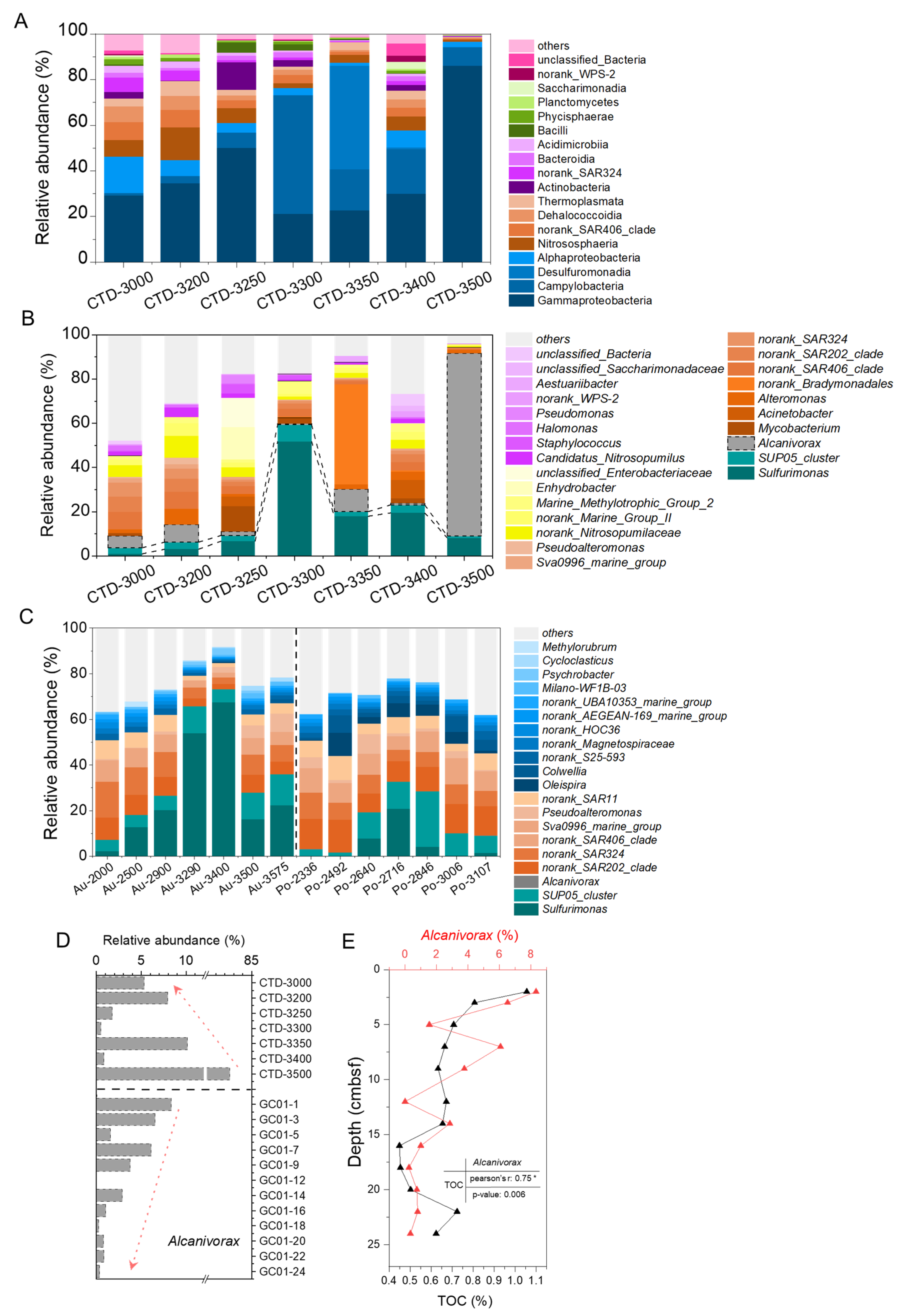
3.3. Carbon Fixation and Sulfur Oxidation Potential
3.4. Organic Carbon Degradation Potential and Alcanivorax-Associated MAGs
4. Discussion
4.1. Chemosynthetic Taxa and Energy Metabolism Potential
4.2. Explosive Volcanism as a Potential Driver of Heterotrophic Bacteria Bloom Represented by Alcanivorax
4.3. Effects on Carbon Cycling in the Deep Ocean
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rantanen, M.; Karpechko, A.Y.; Lipponen, A.; Nordling, K.; Hyvärinen, O.; Ruosteenoja, K.; Vihma, T.; Laaksonen, A. The Arctic has warmed nearly four times faster than the globe since 1979. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemke, R.; Polvani, L.M.; Kay, J.E.; Orbe, C. Quantifying the role of ocean coupling in Arctic amplification and sea-ice loss over the 21st century. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, J.R.; Kelley, D.S.; Lilley, M.D.; Butterfield, D.A.; Baross, J.A.; Wilcock, W.S.D.; Embley, R.W.; Summit, M. The quantum event of oceanic crustal accretion: Impacts of diking at mid-ocean ridges. Science 1998, 281, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannat, M.; Daniel, S.; Luc, L.; Manon, B.; Ekéabino, M.; Sylvie, L. On spreading modes and magma supply at slow and ultraslow mid-ocean ridges. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 519, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, G.J. The microbiomes of deep-sea hydrothermal vents: Distributed globally, shaped locally. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, J.B.; Niu, X.W.; Ding, W.W.; Fang, Y.X.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Zha, C.C.; Tan, P.C.; Kong, F.S.; et al. Highly variable magmatic accretion at the ultraslow-spreading Gakkel Ridge. Nature 2024, 633, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubseid, H.H.; Bjerga, A.; Haflidason, H.; Pedersen, L.E.R.; Pedersen, R.B. Volcanic evolution of an ultraslow-spreading ridge. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, H.N.; Michael, P.J.; Baker, E.T.; Connelly, D.P.; Snow, J.E.; Langmuir, C.H.; Dick, H.J.B.; Mühe, R.; German, C.R.; Graham, D.W. Discovery of abundant hydrothermal venting on the ultraslow-spreading Gakkel Ridge in the Arctic Ocean. Nature 2003, 421, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, P.J.; Thiede, J.; Dick, H.J.; Goldstein, S.L.; Graham, D.; Jokat, W.; Langmuir, C.H.; Muhe, R.; Snow, J.E. The Arctic Mid-Ocean Ridge Expedition-AMORE 2001: Seafloor spreading at the top of the world. EOS 2001, 82, F1097. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, P.J.; Langmuir, C.H.; Dick, H.J.B.; Snow, J.E.; Goldstein, S.L.; Graham, D.W.; Lehnert, K.; Kurras, G.; Jokat, W.; Mühe, R.; et al. Magmatic and amagmatic seafloor generation at the ultraslow-spreading Gakkel Ridge, Arctic Ocean. Nature 2003, 423, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Llodra, E.; Argentino, C.; Baker, M.C.; Boetius, A.; Costa, C.; Dahle, H.; Denny, E.; Dessandier, P.-A.; Eilertsen, M.; Ferre, B.; et al. Hot vents beneath an icy ocean: The Aurora Vent Field, Gakkel Ridge, revealed. Oceanography 2022, 36, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.R.; Reeves, E.P.; Türke, A.; Diehl, A.; Albers, E.; Bach, W.; Purser, A.; Ramalho, S.P.; Stefano, S.; Mertens, C.; et al. Volcanically hosted venting with indications of ultramafic influence at Aurora hydrothermal field on Gakkel Ridge. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.W.; Postberg, F.; Sekine, Y.; Shibuya, T.; Kempf, S.; Horányi, M.; Juhász, A.; Altobelli, N.; Suzuki, K.; Masaki, Y.; et al. Ongoing hydrothermal activities within Enceladus. Nature 2015, 519, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, J.H.; Glein, C.R.; Perryman, R.S.; Teolis, B.D.; Magee, B.A.; Miller, G.; Grimes, J.; Perry, M.E.; Miller, K.E.; Bouquet, A.; et al. Cassini finds molecular hydrogen in the Enceladus plume: Evidence for hydrothermal processes. Science 2017, 356, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.C.; Breier, J.A.; Jiang, H.S.; Anantharaman, K.; Klausmeier, C.A.; Toner, B.M.; Hancock, C.; Speer, K.; Thurnherr, A.M.; Dick, G.J. Predicting the response of the deep-ocean microbiome to geochemical perturbations by hydrothermal vents. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1857–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Alain, K.; Shao, Z.Z. Microorganisms from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 204–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, K.; Breier, J.A.; Sheik, C.S.; Dick, G.J. Evidence for hydrogen oxidation and metabolic plasticity in widespread deep-sea sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, K.; Breier, J.A.; Dick, G.J. Metagenomic resolution of microbial functions in deep-sea hydrothermal plumes across the Eastern Lau Spreading Center. ISME J. 2016, 10, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik, C.S.; Jain, S.; Dick, G.J. Metabolic flexibility of enigmatic SAR324 revealed through metagenomics and meta transcriptomics. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik, C.S.; Anantharaman, K.; Breier, J.A.; Sylvan, J.B.; Edwards, K.J.; Dick, G.J. Spatially resolved sampling reveals dynamic microbial communities in rising hydrothermal plumes across a back-arc basin. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Zhou, H.Y.; Fang, J.S.; Wu, Z.J.; Peng, X.T. Microbial distribution in a hydrothermal plume of the Southwest Indian Ridge. Geomicrobiol. J. 2016, 33, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Yang, J.Y.; Sun, M.X.; Su, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, J.Q.; Bai, S.J. Distribution and Succession of Microbial Communities Along the Dispersal Pathway of Hydrothermal Plumes on the Southwest Indian Ridge. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 581381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, S.S.; Schultz, J.; Lauersen, K.J.; Rosado, A.S. Natural carbon fixation and advances in synthetic engineering for redesigning and creating new fixation pathways. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 47, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molari, M.; Hassenrueck, C.; Laso-Pérez, R.; Wegener, G.; Offre, P.; Scilipoti, S.; Boetius, S. A hydrogenotrophic Sulfurimonas is globally abundant in deep-sea oxygen-saturated hydrothermal plumes. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amend, J.P.; McCollom, T.M.; Hentscher, M.; Bach, W. Catabolic and anabolic energy for chemolithoautotrophs in deep-sea hydrothermal systems hosted in different rock types. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 5736–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Früh-Green, G.L.; Kelley, D.S.; Lilley, M.D.; Lilley, M.D.; Cannat, M.; Chavagnac, V.; Baross, J.A. Diversity of magmatism, hydrothermal processes and microbial interactions at mid-ocean ridges. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathalot, C.; Roussel, E.G.; Perhirin, A.; Creff, V.; Donval, J.P.; Guyader, V.; Roullet, G.; Gula, J.; Tamburini, C.; Garel, M.; et al. Hydrothermal plumes as hotspots for deep-ocean heterotrophic microbial biomass production. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.P.; Li, Z.Y.; Zeng, L.Y.; Dong, C.M.; Shao, Z.Z. The oxidation of hydrocarbons by diverse heterotrophic and mixotrophic bacteria that inhabit deep-sea hydrothermal ecosystems. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1994–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jain, S.; Dick, G.J. Genomic and transcriptomic resolution of organic matter utilization among deep-sea bacteria in Guaymas Basin hydrothermal plumes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.R.; Takai, K.; Bris, N. Hydrothermal vent ecosystems. Oceanography 2007, 20, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoy, M.; Bohnenstiehl, D.R.; Edwards, M.H.; Kurras, G.J. Seismic character of volcanic activity at the ultraslow-spreading Gakkel Ridge. Geology 2001, 29, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.H.; Kurras, G.J.; Tolstoy, M.; Bohnenstiehl, D.R.; Coakley, B.J.; Cochran, J.R. Evidence of recent volcanic activity on the ultraslow-spreading Gakkel ridge. Nature 2001, 409, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, R.A.; Willis, C.; Humphris, S.; Shank, T.M.; Singh, H.; Edmonds, H.N.; Kunz, C.; Hedman, U.; Helmke, E.; Jakuba, M.; et al. Explosive volcanism on the ultraslow-spreading Gakkel Ridge, Arctic Ocean. Nature 2008, 453, 1236–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Deng, Y.; Shen, L.N.; Wen, C.Q.; Yan, Q.Y.; Ning, D.L.; Qin, Y.J.; Xue, K.; Wu, L.Y.; He, Z.L.; et al. Temperature mediates continental-scale diversity of microbes in forest soils. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.H.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.B.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.L.; Li, X.F.; Jiang, L.J.; Gong, L.F.; Geslin, C.; Shao, Z.Z. Virus diversity and interactions with hosts in deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Microbiome 2022, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.J.; Li, Y.R.; Cai, Z.M.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.D.; Li, F.; Kirton, E.; Thomas, A.; Egan, R.; An, H.; Wang, Z. MetaBAT 2: An adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ 2019, 7, 7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzer, M. POCP-nf: An automatic Next flow pipeline for calculating the percentage of conserved proteins in bacterial taxonomy. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, P.A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk: A toolkit to classify genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Shi, C.P.; Liu, L.M.; Han, J.C.; Yang, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.D.; Fu, W.Y.; Gao, H.; Huang, H.S.; et al. Majorbio Cloud 2024: Update single-cell and multiomics workflows. iMeta 2024, 3, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.M.; Spietz, R.L. The Physiology and Biogeochemistry of SUP05. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2022, 14, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dede, B.; Hansen, C.T.; Neuholz, R.; Schnetger, B.; Kleint, C.; Walker, S.; Bach, W.; Amann, R.; Meyerdierks, A. Niche differentiation of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SUP05) in submarine hydrothermal plumes. ISME J. 2022, 16, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.T.; Luo, C.L.; Ren, P.; Zhang, H.M.; Fan, D.; Chen, H.T.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.C. Stable carbon isotopes of dissolved inorganic carbon in the Western North Pacific Ocean: Proxy for water mixing and dynamics. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 998437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.T.; Wang, X.C.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.C.; Xue, Y.J. Dissolved Inorganic Radiocarbon in the Northwest Pacific Continental Margin. Radiocarbon 2016, 58, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNichol, A.P.; Druffel, E.R. Variability of the δ13C of dissolved inorganic carbon at a site in the North Pacific Ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 3589–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takai, K. Sulfur metabolisms in epsilon- and gamma-proteobacteria in deep-sea hydrothermal fields. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A. Ecological aspects of the distribution of different autotrophic CO2 fixation pathways. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.J.; Engel, A.S.; Porter, M.L.; Takai, K. The versatile ε-proteobacteria: Key players in sulphidic habitats. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Takai, K. Deep-sea vent chemoautotrophs: Diversity, biochemistry, and ecological significance. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hügler, M.; Sievert, S.M. Beyond the Calvin cycle: Autotrophic carbon fixation in the ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 3, 261–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooijmans, R.J.W.; Pastink, M.I.; Siezen, R.J. Hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria: The oil-spill clean-up crew. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, A.; Syutsubo, K.; Harayama, S. Alcanivorax which prevails in oil-contaminated seawater exhibits broad substrate specificity for alkane degradation. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneiker, S.; Santos, V.; Bartels, D.; Bekel, T.; Brecht, M.; Buhrmester, J.; Chernikova, T.N.; Denaro, R.; Ferrer, M.; Gertler, C.; et al. Genome sequence of the ubiquitous hydrocarbon-degrading marine bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.E.; Bird, K.J.; Pitman, J.K. Geology and Assessment of Undiscovered Oil and Gas Resources of the Lomonosov-Makarov Province, 2008, Chap. CC. In The 2008 Circum-Arctic Resource Appraisal: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1824; Moore, T.E., Gautier, D.L., Eds.; United States Geological Survey, USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2019; 43p. [Google Scholar]
- Tennyson, M.E.; Pitman, J.K. Geology and Assessment of Undiscovered Oil and Gas Resources of the Sverdrup Basin Province, Arctic Canada, 2008, Chap. I. In The 2008 Circum-Arctic Resource Appraisal: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1824; Moore, T.E., Gautier, D.L., Eds.; United States Geological Survey, USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; 21p. [Google Scholar]
- Houseknecht, D.W.; Bird, K.J.; Garrity, C.P. Geology and Assessment of Undiscovered Oil and Gas Resources of the Arctic Alaska Province, 2008, Chap. E. In The 2008 Circum-Arctic Resource Appraisal: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1824; Moore, T.E., Gautier, D.L., Eds.; United States Geological Survey, USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2019; 25p. [Google Scholar]
- Rusakov, V.Y.; Levitan, M.A.; Roshchina, I.A.; Spielhagen, R.F.; Gebhardt, K. Chemical composition of late Pleistocene-Holocene pelagic sediments in Gakkel Ridge, Arctic Ocean. Geochem. Int. 2010, 48, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekant, P.V.; Gusev, E.A. Sediments in the Gakkel Ridge rift zone (Arctic Ocean): Structure and history. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 57, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekant, P.V.; Petrov, O.V.; Gusev, E.A. Model of Formation of the Sedimentary System of the Eurasian Basin, the Arctic Ocean, as a Basis for Reconstructing Its Tectonic Evolution. Geotectonics 2021, 55, 676–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.T.; Edmonds, H.N.; Michael, P.J.; Bach, W.; Dick, H.J.B.; Snow, J.E.; Walker, S.L.; Banerjee, N.R.; Langmuir, C.H. Hydrothermal venting in magma deserts: The ultraslow-spreading Gakkel and Southwest Indian Ridges. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2004, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, K.H.; Chadwick, W.; Fornari, D.; Clague, D.; Embley, R.; Baker, E.; Perfit, M.; Caress, D.; Dziak, R. Volcanic Eruptions in the Deep Sea. Oceanography 2012, 25, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dede, B.; Priest, T.; Bach, W.; Walter, M.; Amann, R.; Meyerdierks, A. High abundance of hydrocarbon-degrading Alcanivorax in plumes of hydrothermally active volcanoes in the South Pacific Ocean. ISME J. 2023, 17, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truskewycz, A.; Gundry, T.D.; Khudur, L.S.; Kolobaric, A.; Taha, M.; Aburto-Medina, A.; Ball, A.S.; Shahsavari, E. Petroleum Hydrocarbons Contamination in Terrestrial Ecosystem- Fate and Microbial Responses. Molecules 2019, 24, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, J.X.; Han, L.; Lee, J.; Williams, S.C.; Forsberg, A.; Xu, Y.; Austin, R.N.; Feng, L. Structure and mechanism of the alkane-oxidizing enzyme AlkB. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minerdi, D.; Zgrablic, I.; Sadeghi, S.J.; Gilardi, G. Identification of a novel Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase from Acinetobacter radioresistens: Close relationship to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis prodrug activator EtaA. Microb. Biotechnol. 2012, 5, 700–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y. High hydrostatic pressure stimulates n-C16 mineralization to CO2 by deep-ocean bacterium Alcanivorax xenomutans A28. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.B.; Ding, W.W. How does Carbon Cycle in the Mid-Ocean Ridge Deep? Earth Sci. 2022, 47, 3924–3925. [Google Scholar]
- Clague, D.A.; Paduan, J.B.; Davis, A.S. Widespread strombolian eruptions of mid-ocean ridge basalt. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2009, 180, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spotlight on deep carbon research. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4800. [CrossRef]
- Foley, S.F.; Fischer, T.P. An essential role for continental rifts and lithosphere in the deep carbon cycle. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hondt, S.; Pockalny, R.; Fulfer, V.M.; Spivack, A.J. Subseafloor life and its biogeochemical impacts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Xu, S.; Sano, Y.J. Deep carbon recycling viewed from global plate tectonics. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, 089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Ding, W.; Yang, C.; Fang, Y.; Li, J. High-Abundance Heterotrophic Bacteria Inhabit the 85° E Hydrothermal Plume of the Explosive Volcanic Zone at Gakkel Ridge, Arctic Ocean. Biology 2025, 14, 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081036
Yu J, Wang Y, Han X, Wang H, Zhang T, Ding W, Yang C, Fang Y, Li J. High-Abundance Heterotrophic Bacteria Inhabit the 85° E Hydrothermal Plume of the Explosive Volcanic Zone at Gakkel Ridge, Arctic Ocean. Biology. 2025; 14(8):1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081036
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Juan, Yejian Wang, Xiqiu Han, Hanlin Wang, Tao Zhang, Weiwei Ding, Chi Yang, Yinxia Fang, and Jiabiao Li. 2025. "High-Abundance Heterotrophic Bacteria Inhabit the 85° E Hydrothermal Plume of the Explosive Volcanic Zone at Gakkel Ridge, Arctic Ocean" Biology 14, no. 8: 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081036
APA StyleYu, J., Wang, Y., Han, X., Wang, H., Zhang, T., Ding, W., Yang, C., Fang, Y., & Li, J. (2025). High-Abundance Heterotrophic Bacteria Inhabit the 85° E Hydrothermal Plume of the Explosive Volcanic Zone at Gakkel Ridge, Arctic Ocean. Biology, 14(8), 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081036





