Effects of Salinity, Temperature, and Diet on the Biological Characteristics of Brachionus plicatilis Müller, 1786
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. B. plicatilis Culturing
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Culture Conditions According to Salinity, Temperature, and Diet
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
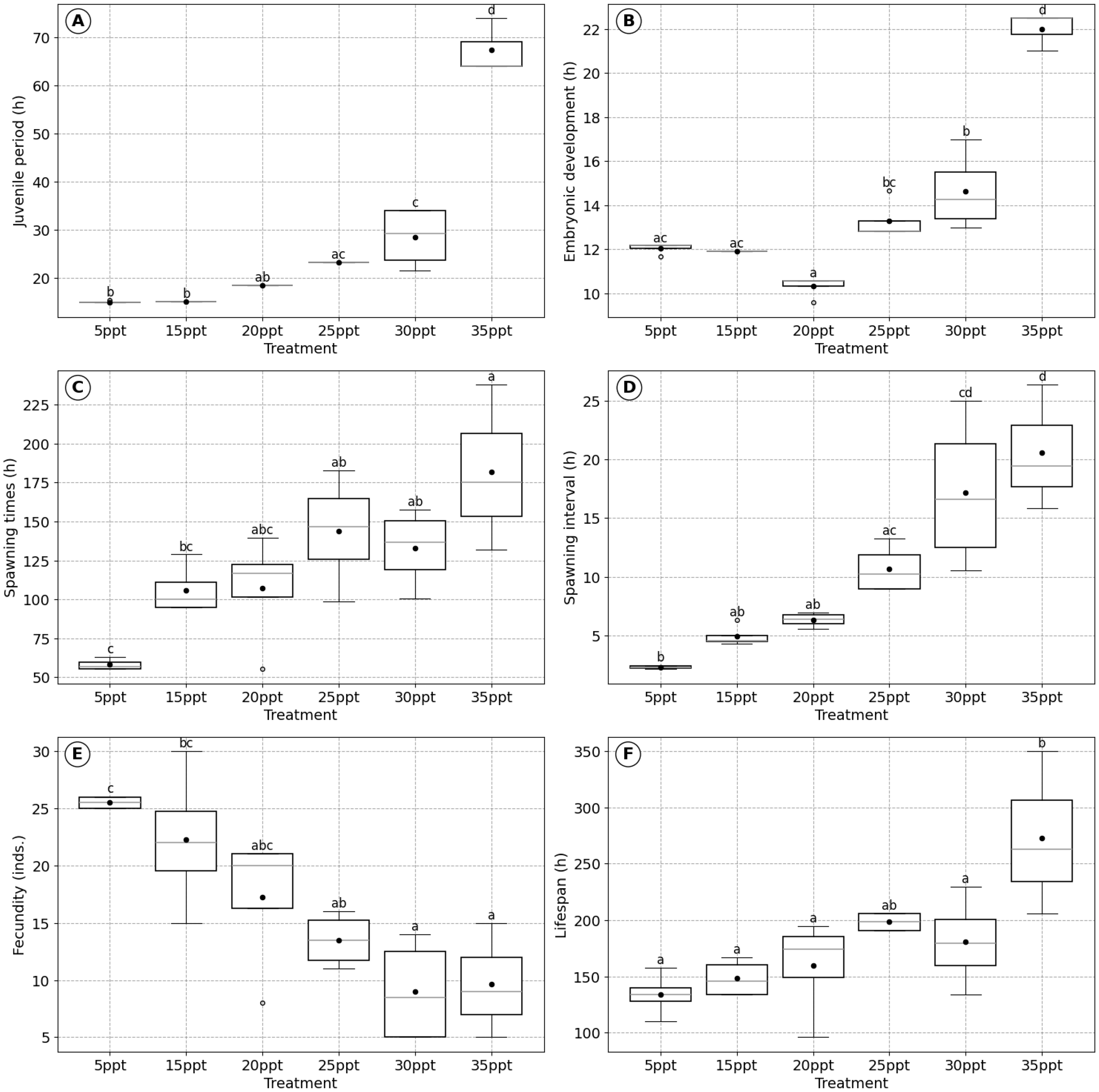
3.1. Effects of Salinity on B. plicatilis
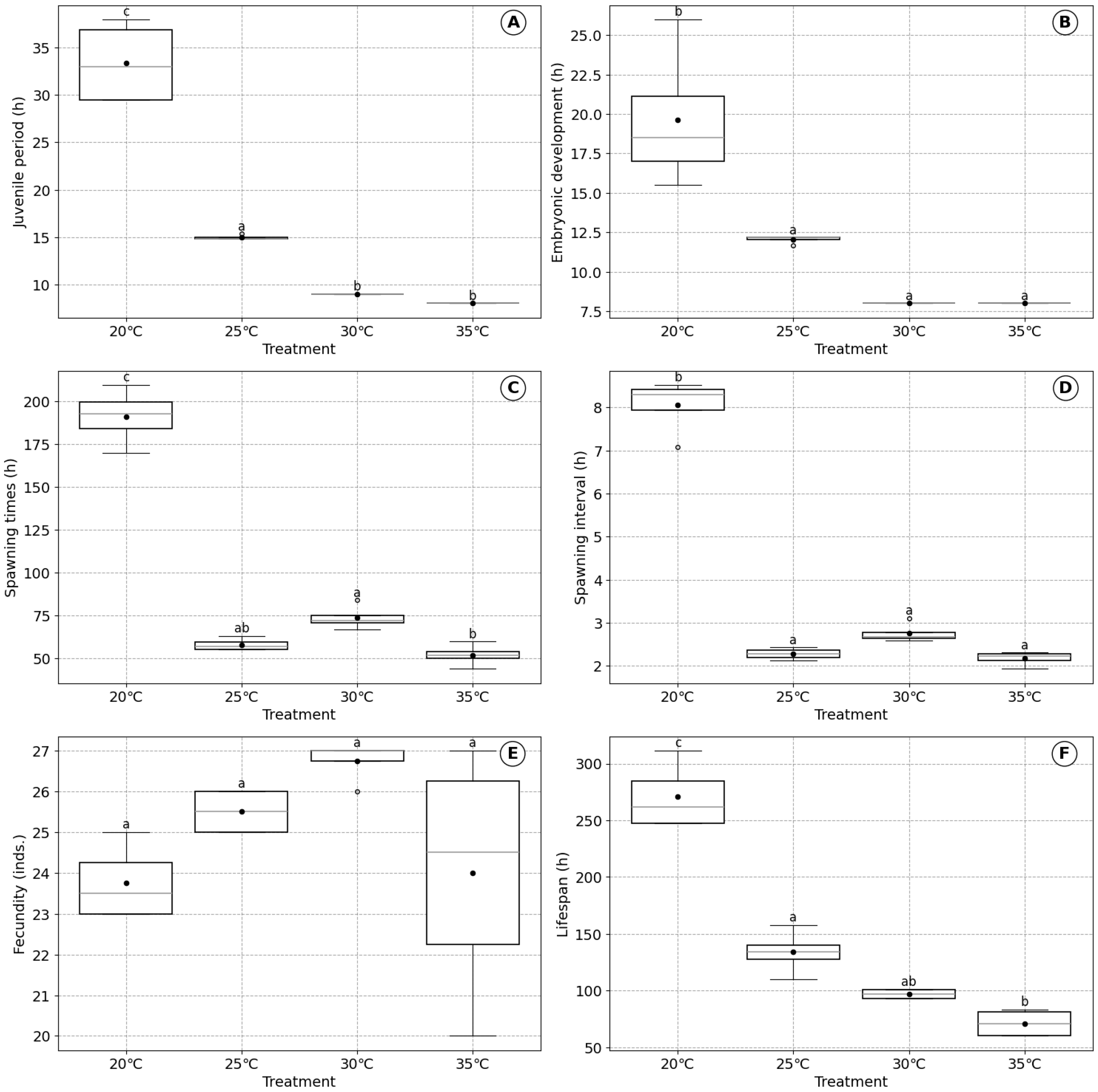
3.2. Effects of Temperature on B. plicatilis
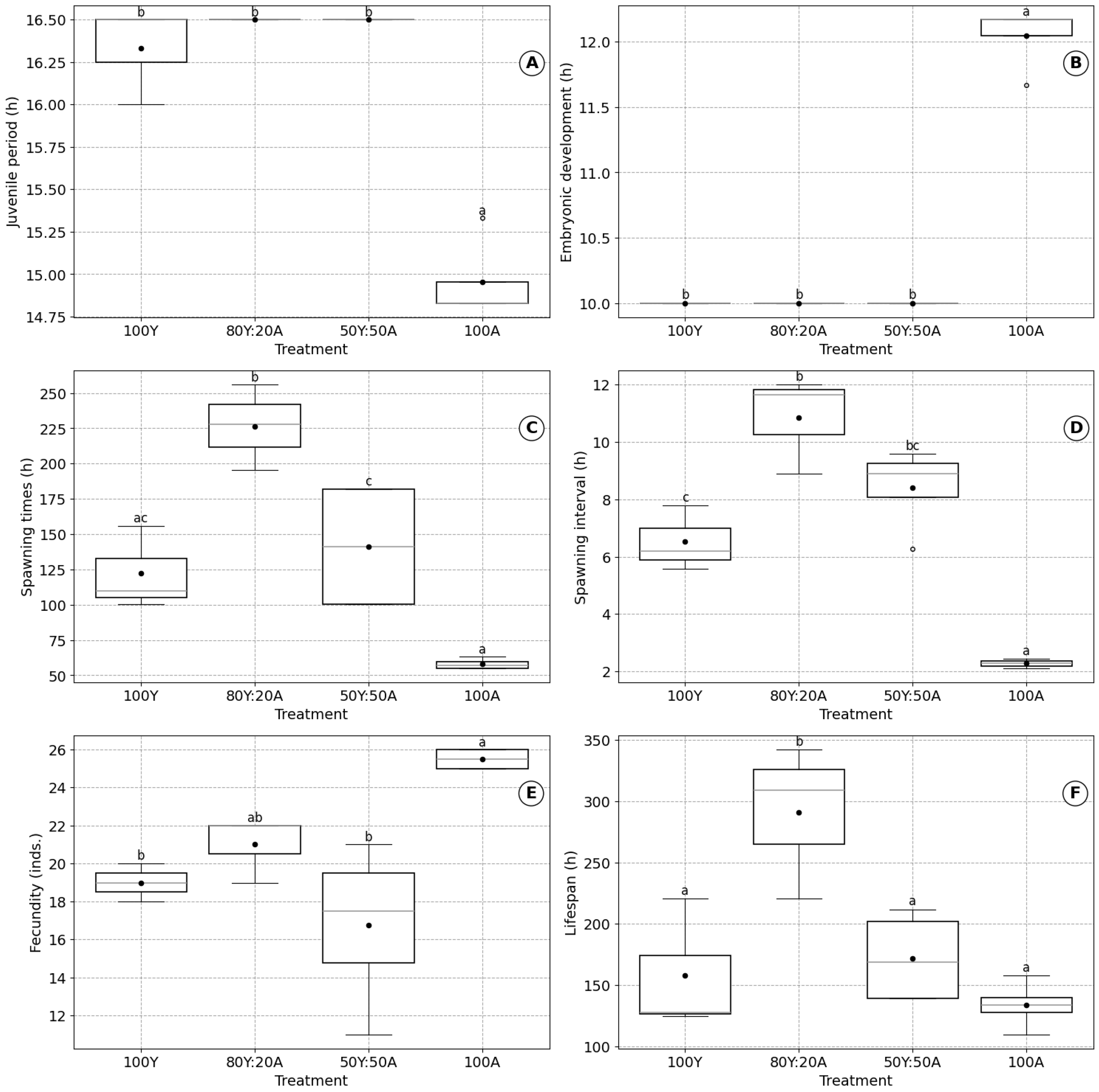
3.3. Effects of Diet on B. plicatilis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Salinity on Physiological Mechanisms
4.2. Effects of Temperature on Physiological Mechanisms
4.3. Effects of Diet on Physiological Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmid-Araya, J.R.B. Rotifera. Volume 1: Biology, Ecology and Systematics. Second Edition. Guides to the Identification of the Microinvertebrates of the Continental Waters of the World, Volume 23; Wallace, R.L., Snell, T.W., Ricci, C., Nogrady, T.Q., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers and Ghent: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 82, pp. 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, V.; Carmona, M.J.; Divanach, P. The rotifer Brachionus plicatilis: An emerging bio-tool for numerous applications. J. Biol. Res. 2012, 17, 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Lubzens, E.; Zmora, O.; Barr, Y. Biotechnology and Aquaculture of Rotifers. Hydrobiologia 2001, 446, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhert, P.; Rombaut, G.; Suantika, G.; Sorgeloos, P. Advancement of rotifer culture and manipulation techniques in Europe. Aquaculture 2001, 200, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailasam, M.; Thirunavukkarasu, A.R.; Ponniah, A.G.; Selvaraj, S.; Stalin, P. Recent Advances in Rotifer Culture and Its Application for Larviculture of Finfishes. In Advances in Marine and Brackishwater Aquaculture; Perumal, S., Thirunavukkarasu, A.R., Pachiappan, P., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.W.; Zhao, W. Studies on life history characteristics of Brachionus plicatilis O.F. Müller (Rotifera) in relation to temperature, salinity and food algae. Aquat. Ecol. 2008, 42, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, T.W. Effect of Temperature, Salinity and Food Level on Sexual and Asexual Reproduction in Brachionus plicatilis (Rotifera). Mar. Biol. 1986, 92, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.-K.; Kim, S.-S.; Lee, K.-W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Jung, M.-M.; Woo, S.-J. Determination of the Optimal Conditions for the Mass Culture of Large-Type Rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis) at Low Temperatures. Water 2023, 15, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubzens, E.; Hamo, R.; Blais, I.; Jeries, S.; Almog-Gabai, O.; Assaraf, Y.G. Rotifer Resting Eggs: An Alternative for Rotifer Mass Cultures in Fish Farms—Lessons from a Comprehensive Study on Production, Storage and Hatching of Resting Eggs. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lee, J.-S.; Park, J.C.; Hagiwara, A.; Lee, K.-W.; Lee, J.-S. Effects of Temperature Changes on Life Parameters, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidant Defense System in the Monogonont Marine Rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 155, 111062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauler, P.; Enesco, H.E. The Effect of Temperature on Life History Parameters and Cost of Reproduction in the Rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2011, 26, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sayegh, F.A.Q.; Radi, N.; Montagnes, D.J.S. Do Strain Differences in Microalgae Alter Their Relative Quality as a Food for the Rotifer Brachionus plicatilis? Aquaculture 2007, 273, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eryalçın, K.M. Nutritional value and production performance of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Müller, 1786 cultured with different feeds at commercial scale. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, M.; Estévez, A. Effects of diet on population development of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis in culture. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1989, 43, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo, S.; García-Roger, E.M.; Carmona, M.J.; Serra, M. Local adaptation in rotifer populations. Evol. Ecol. 2011, 25, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavens, P.; Sorgeloos, P. (Eds.) Manual on the Production and Use of Live Food for Aquaculture; FAO Fisheries Technical Paper No. 361; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1996; 295p. [Google Scholar]
- Peltier, W.H.; Weber, C.I. (Eds.) Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents to Freshwater and Marine Organisms; EPA 600/4-85/013; Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1985; pp. 126–137.
- Alalayah, W.M.; Alhamed, Y.A.; Al-Zahrani, A.; Edris, G. Experimental investigation parameters of hydrogen production by algae Chlorella vulgaris. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Chemical, Environment & Biological Sciences (CEBS-2014), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–18 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D. Life History Patterns in Zooplankton. Am. Nat. 1976, 110, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Walz, N. Life History Strategies of Rotifers. In Plankton Regulation Dynamics: Experiments and Models in Rotifer Continuous Cultures; Walz, N., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, R.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Lv, C.; Xu, J. Response of Planktonic Diversity and Stability to Environmental Drivers in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, M.R.; Serra, M. Salinity and Temperature Influence in Rotifer Life History Characteristics. Hydrobiologia 1989, 186, 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chong, L.; Chen, L. Rotifer Community Structure and Its Response to Environmental Factors in the Backshore Wetland of Expo Garden, Shanghai. Aquac. Fish. 2018, 3, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, C.-P. Evolution of Rotifer Life Histories. Hydrobiologia 2005, 546, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, G.D. The meanings of r- and K-selection. Oecologia 1981, 48, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, S.A.L.M.; Troost, T.A. Quantitative Steps in the Evolution of Metabolic Organisation as Specified by the Dynamic Energy Budget Theory. Biol. Rev. 2007, 82, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applebaum, S.L.; Pan, T.-C.F.; Hedgecock, D.; Manahan, D.T. Separating the nature and nurture of the allocation of energy in response to global change. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2014, 54, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.-C.F.; Applebaum, S.L.; Manahan, D.T. Experimental ocean acidification alters the allocation of metabolic energy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4696–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenjie, L.; Binxia, L.; Cuijuan, N. Effects of Temperature on Life History Strategy of the Rotifer Euchlanis dilatata. Zoolog. Sci. 2019, 36, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, B. Dynamic Energy Budget Theory for Metabolic Organisation, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debelgarric, M.; Récapet, C. Exploring Physiological Constraints on Life-History Traits Using Dynamic Energy Budgets. Ecol. Model. 2025, 501, 110993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Jiang, B.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Z. Application of a Dynamic Energy Budget Model to the Blood Clam, Tegillarca granosa, Reared in Culture Pond. Aquac. Rep. 2025, 40, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, S.A.L.M. Dynamic Energy and Mass Budgets in Biological Systems, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.S.; Jin, X.; Yang, T.; Kooijman, S.A.L.M.; Shan, X. A Dynamic Energy Budget Model for Small Yellow Croaker Larimichthys polyactis: Parameterisation and Application in Its Main Geographic Distribution Waters. Ecol. Model. 2020, 427, 109051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speakman, J.R.; Colin, S.; McLaren, J.S.; Harper, E.J. Living Fast, Dying When? The Link between Aging and Energetics. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 1583S–1597S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaldón, C.; Montero-Pau, J.; Carmona, M.J.; Serra, M. Life-history variation, environmental fluctuations and competition in ecologically similar species: Modeling the case of rotifers. J. Plankton Res. 2015, 37, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.F. 13. A Synopsis of Ecological Information on the Saline Lake Rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Müller 1786. Hydrobiologia 1981, 81, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, C.D.; Kemp, S.J.; Bates, A.D.; Montagnes, D.J.S. Evidence That the Rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Is Not an Osmoconformer. Mar. Biol. 2005, 146, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.-N.; Wang, A.-L.; Wang, J.-M.; Sun, R.-Y. Effects of Dietary Vitamin E Supplementation on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) Exposed to Acute Salinity Changes. Aquaculture 2007, 265, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchman, E.; Ohman, M.D.; Kiørboe, T. Trait-based approaches to zooplankton communities. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntley, M.E.; Lopez, M.D.G. Temperature-Dependent Production of Marine Copepods: A Global Synthesis. Am. Nat. 1992, 140, 201–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.J. Morphological variation and its significance in a polymorphic rotifer: Environmental, endogenous, and genetic controls. BioScience 2018, 68, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Ohtani, M.; Kakumu, A.; Sakakura, Y.; Hagiwara, A. External Factors That Regulate Movement in the Marine Rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Hagiwara, A. Effect of Salinity during Resting Egg Formation and Hatching on Descendent Reproduction in the Rotifer Brachionus rotundiformis Tschugunoff. J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gabaldón, C.; Serra, M.; Carmona, M.J.; Montero-Pau, J. Life-History Traits, Abiotic Environment and Coexistence: The Case of Two Cryptic Rotifer Species. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 465, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.S. Influence of Salinity on Population Growth of a Rotifer, Brachionus plicatilis (Mullen). J. Indian Fish. Assoc. 1988, 18, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, D.-H.; Kang, H.-M.; Wang, M.; Jeong, C.-B.; Lee, J.-S. Adverse Effects of Methylmercury (MeHg) on Life Parameters, Antioxidant Systems, and MAPK Signaling Pathways in the Rotifer Brachionus koreanus and the Copepod Paracyclopina nana. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-C.; Park, J.C.; Kim, D.-H.; Kang, S.; Shin, K.-H.; Park, H.G.; Han, J.; Lee, J.-S. Interrelationship of Salinity Shift with Oxidative Stress and Lipid Metabolism in the Monogonont Rotifer Brachionus koreanus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 214, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosque, T.; Hernández, R.; Pérez, R.; Todolí, R.; Oltra, R. Effects of Salinity, Temperature and Food Level on the Demographic Characteristics of the Seawater Rotifer Synchaeta littoralis Rousselet. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2001, 258, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, M.E.; Hofmann, G.E. Heat-shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: Evolutionary and Ecological Physiology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1999, 61, 243–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, J.G.; Kristensen, T.N.; Loeschcke, V. The evolutionary and ecological role of heat shock proteins. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Shin, Y.; Han, S.; Ha, J.; Tiwari, P.K.; Kim, S.S.; Kang, I. Molecular Chaperonin HSP60: Current Understanding and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Han, S.; Ju, S.; Ranbhise, J.S.; Ha, J.; Yeo, S.G.; Kim, S.S.; Kang, I. Hsp70: A Multifunctional Chaperone in Maintaining Proteostasis and Its Implications in Human Disease. Cells 2025, 14, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yúfera, M. Effect of Algal Diet and Temperature on the Embryonic Development Time of the Rotifer Brachionus plicatilis in Culture. Hydrobiologia 1987, 147, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhert, P.; Lim, L.C.; Candreva, P.; Van Duffel, H.; Sorgeloos, P. Possible Applications of Modern Fish Larviculture Technology to Ornamental Fish Production. Aquar. Sci. Conserv. 1997, 1, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, S.; Jiang, Q.; Si, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, J. Characterization and expression of cytoplasmic Copper/Zinc superoxide dismutase (CuZn SOD) gene under temperature and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in Rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. Gene 2013, 518, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kültz, D. Molecular and evolutionary basis of the cellular stress response. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2005, 67, 225–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevopoulou, S.; Dennis, A.B.; Weithoff, G.; Tiedemann, R. Temperature-dependent life history and transcriptomic responses in heat-tolerant versus heat-sensitive Brachionus rotifers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczyńska, A.; Serra, M. Inter- and intraspecific relationships between performance and temperature in a cryptic species complex of the Rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Hydrobiologia 2014, 734, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, L.; Xu, D. Survival strategies of Phytoplankton functional groups to environmental factors in a drinking water reservoir, Central China. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol. 2021, 57, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadstein, O.; Attramadal, K.J.K.; Bakke, I.; Olsen, Y. K-selection as microbial community management strategy: A method for improved viability of larvae in aquaculture. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hou, X.; Xue, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z. Trade-off between Reproduction and Lifespan of the Rotifer Brachionus plicatilis under Different Food Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Raptova, R.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Chronic diseases and aging. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2499–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, C.; Castro, B.B.; Cuco, A.P.; Pedrosa, M.A.; Gonçalves, F. Life-History responses of salinity-tolerant and salinity-sensitive lineages of a stenohaline Cladoceran do not confirm clonal differentiation. Hydrobiologia 2013, 702, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Beladjal, L.; Nandini, S.; Cerón-Martínez, G.; Tavera-Briseño, K. Effect of salinity stress on the life history variables of Branchipus schaefferi Fisher, 1834 (Crustacea: Anostraca). Saline Syst. 2005, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Snell, T.W.; Janssen, C.R. Rotifers in ecotoxicology: A review. Hydrobiologia 1995, 313, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.A.; Burns, A.R.; Shearer, T.L.; Snell, T.W. Three heat shock proteins are essential for rotifer thermotolerance. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 413, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Byeon, E.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.S.; Sayed, A.E.-D.H.; Bo, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.-Z.; Park, H.G.; Lee, J.-S. Single and combined effects of increased temperature and methylmercury on different stages of the marine rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezeq, T.A.; James, C.M. Production and nutritional quality of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis fed marine Chlorella sp. at different cell densities. Hydrobiologia 1987, 147, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z. Changes in key life-history traits and transcriptome regulations of marine rotifer Brachionus plicatilis in eliminating harmful algae Phaeocystis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, K.; Nakamura, K. Fundamental studies on the physiology of Rotifers in mass culture—V. Dry Chlorella powder as a food for Rotifers. Aquaculture 1976, 8, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latta, L.C.; Tucker, K.N.; Haney, R.A. The relationship between oxidative stress, reproduction, and survival in a bdelloid rotifer. BMC Ecol. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
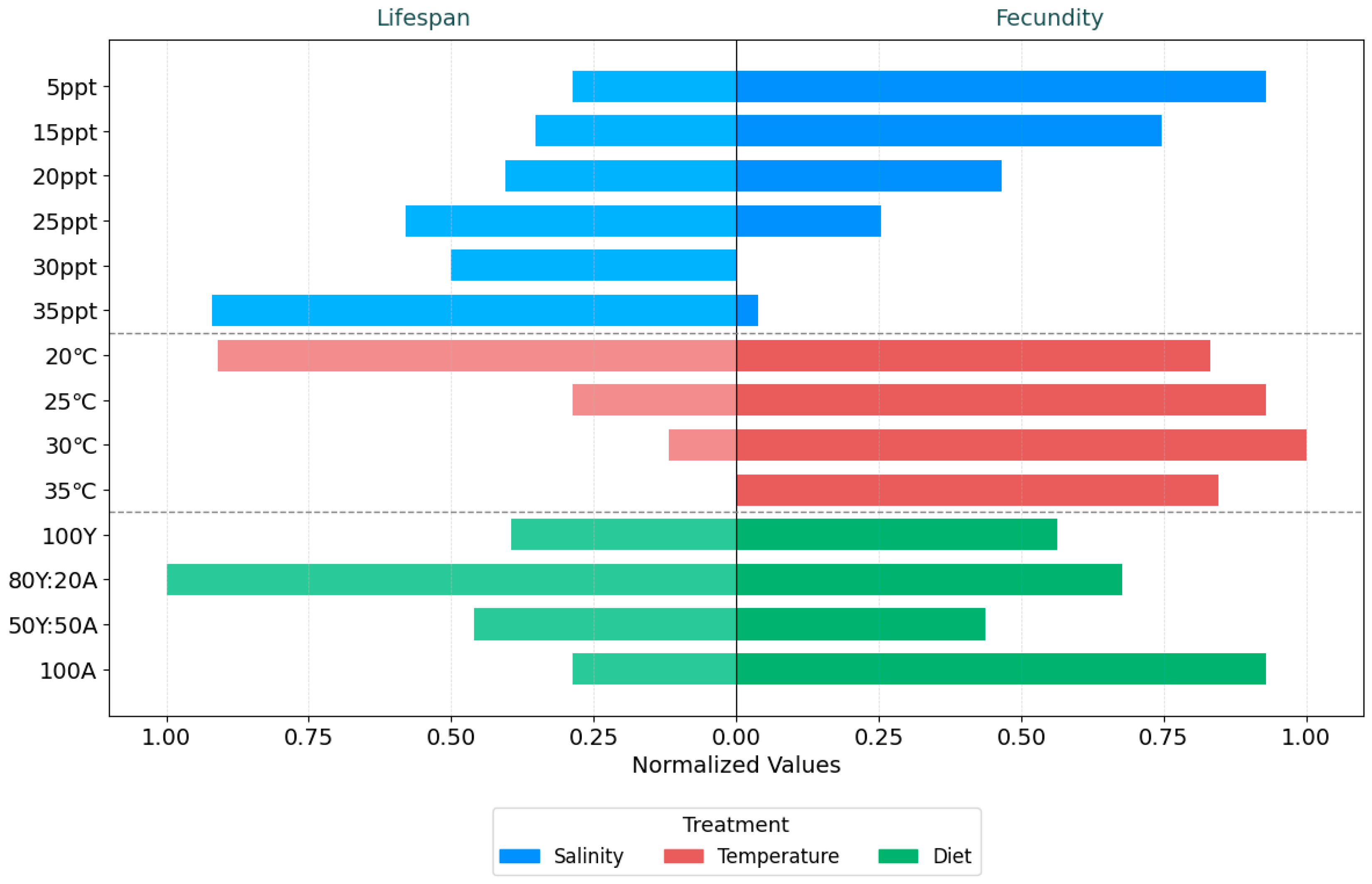
| Environmental Factor | Sub-Optimal Condition | Optimal Condition | Adverse Condition | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | Low salinity (5 ppt) | Moderate salinity (10–20 ppt) | High salinity (25–35 ppt) | Figure 1 |
| Temperature | High temperature (30–35 °C) | Moderate temperature (20–25 °C) | Low temperature (<20 °C) | Figure 2 |
| Nutritional Conditions | 80% baker’s yeast–20% C. vulgaris (80Y:20A) | 50% baker’s yeast–50% C. vulgaris (50Y:50A) | 100% C. vulgaris (100A) | Figure 3 |
| DEB Strategy | Optimal energy uptake → high reproductive potential | Balanced energy allocation | Energy redirection to survival | [32] |
| r/K selection | r-selection dominance | Intermediate r/K strategy | K selection prominence | [27,31] |
| Biological Performance | Accelerated reproduction | Balanced growth and reproduction | Reduced reproduction, extended survival | [22] |
| Environmental Factor | Metabolic Processes | Cellular Responses | Gene Expression | Physiological Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity |
|
|
|
| [39,65,66] [22,67] [15,45] |
| Temperature |
|
|
|
| [21,23,68] [69] [10,30] |
| Diet |
|
|
|
| [70,71] [14] [72,73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran-Nguyen, Q.-A.; Phan, T.N.; Tran, Q.-A.; Mai, H.T.; Thi, T.L.P.; Phan, D.D.; Trinh-Dang, M. Effects of Salinity, Temperature, and Diet on the Biological Characteristics of Brachionus plicatilis Müller, 1786. Biology 2025, 14, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070878
Tran-Nguyen Q-A, Phan TN, Tran Q-A, Mai HT, Thi TLP, Phan DD, Trinh-Dang M. Effects of Salinity, Temperature, and Diet on the Biological Characteristics of Brachionus plicatilis Müller, 1786. Biology. 2025; 14(7):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070878
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran-Nguyen, Quynh-Anh, Truong Nhat Phan, Quang-Anh Tran, Hong Thi Mai, Thao Linh Phan Thi, Dang Doan Phan, and Mau Trinh-Dang. 2025. "Effects of Salinity, Temperature, and Diet on the Biological Characteristics of Brachionus plicatilis Müller, 1786" Biology 14, no. 7: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070878
APA StyleTran-Nguyen, Q.-A., Phan, T. N., Tran, Q.-A., Mai, H. T., Thi, T. L. P., Phan, D. D., & Trinh-Dang, M. (2025). Effects of Salinity, Temperature, and Diet on the Biological Characteristics of Brachionus plicatilis Müller, 1786. Biology, 14(7), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070878





