Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism Prediction of Sinomenine Based on Network Pharmacology and Its Biological Activity Verification
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Targets Collection for Disease and Sinomenine
2.2. PPI Network Construction
2.3. GO Enrichment and KEGG Analysis
2.4. RAW264.7 Cell Culture
2.5. RAW264.7 Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Inflammatory Factor Inhibition Assay
2.7. RT-qPCR Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Molecular Docking
3. Results
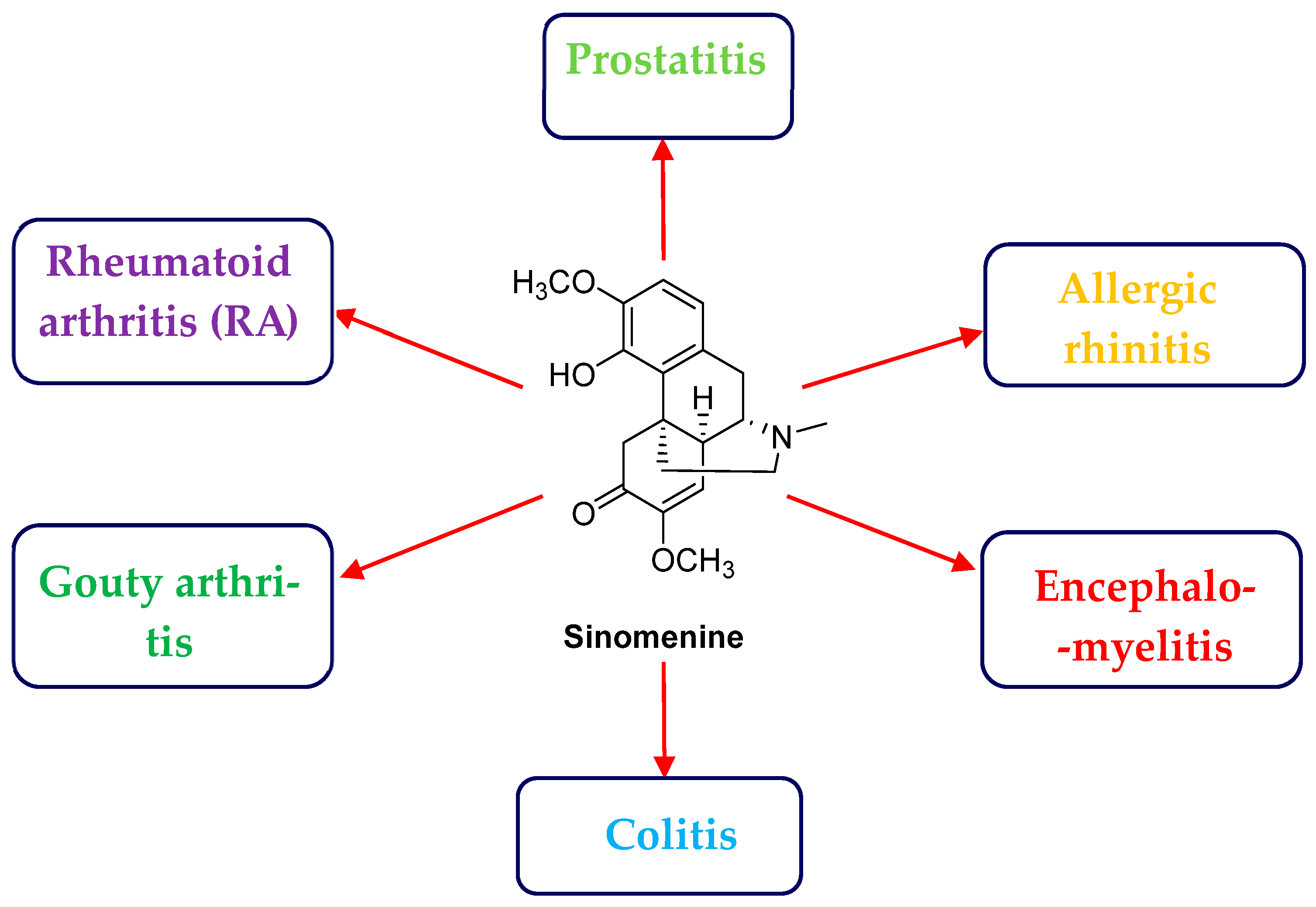
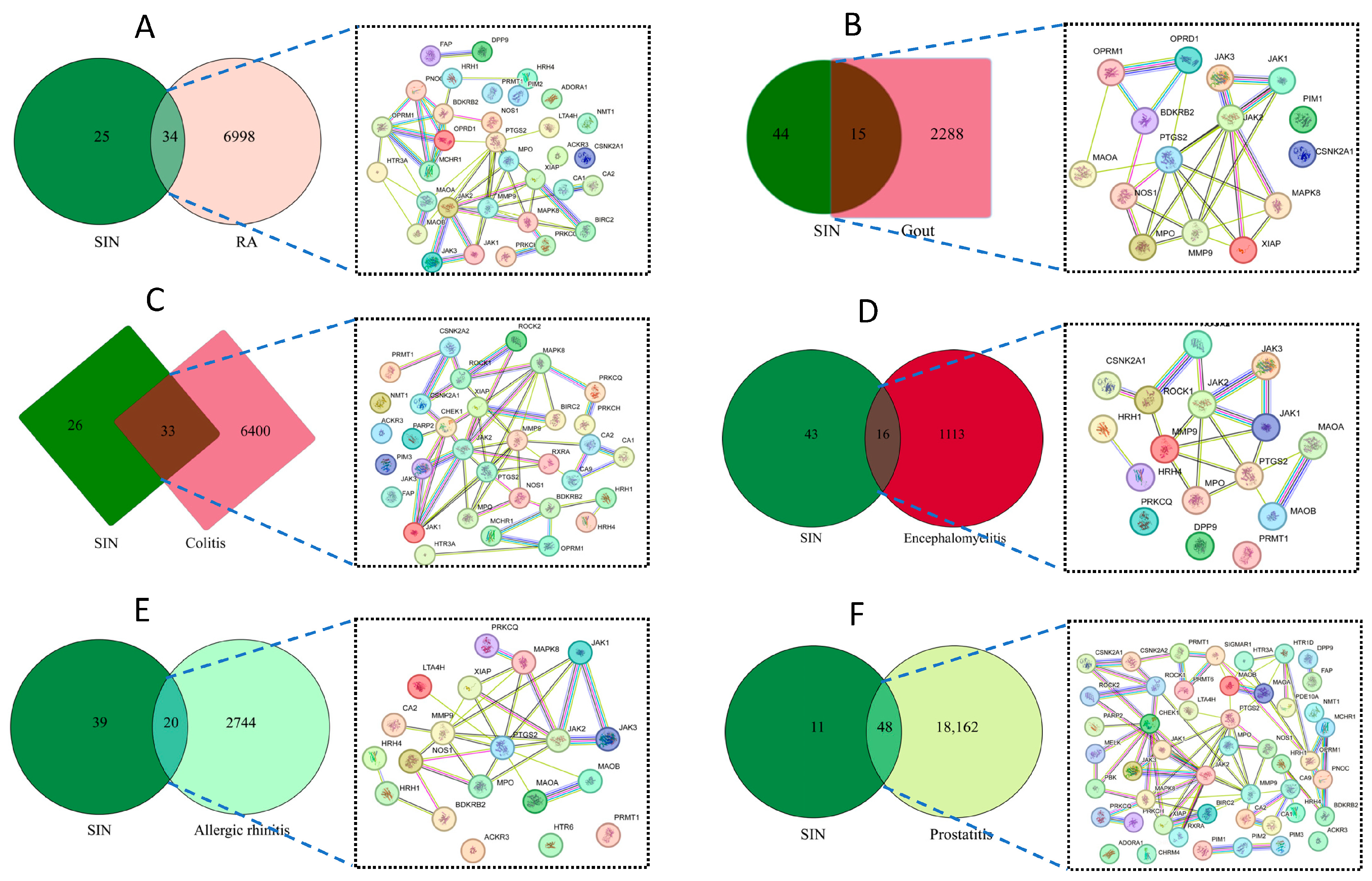
3.1. Disease and Sinomenine Targets Analysis
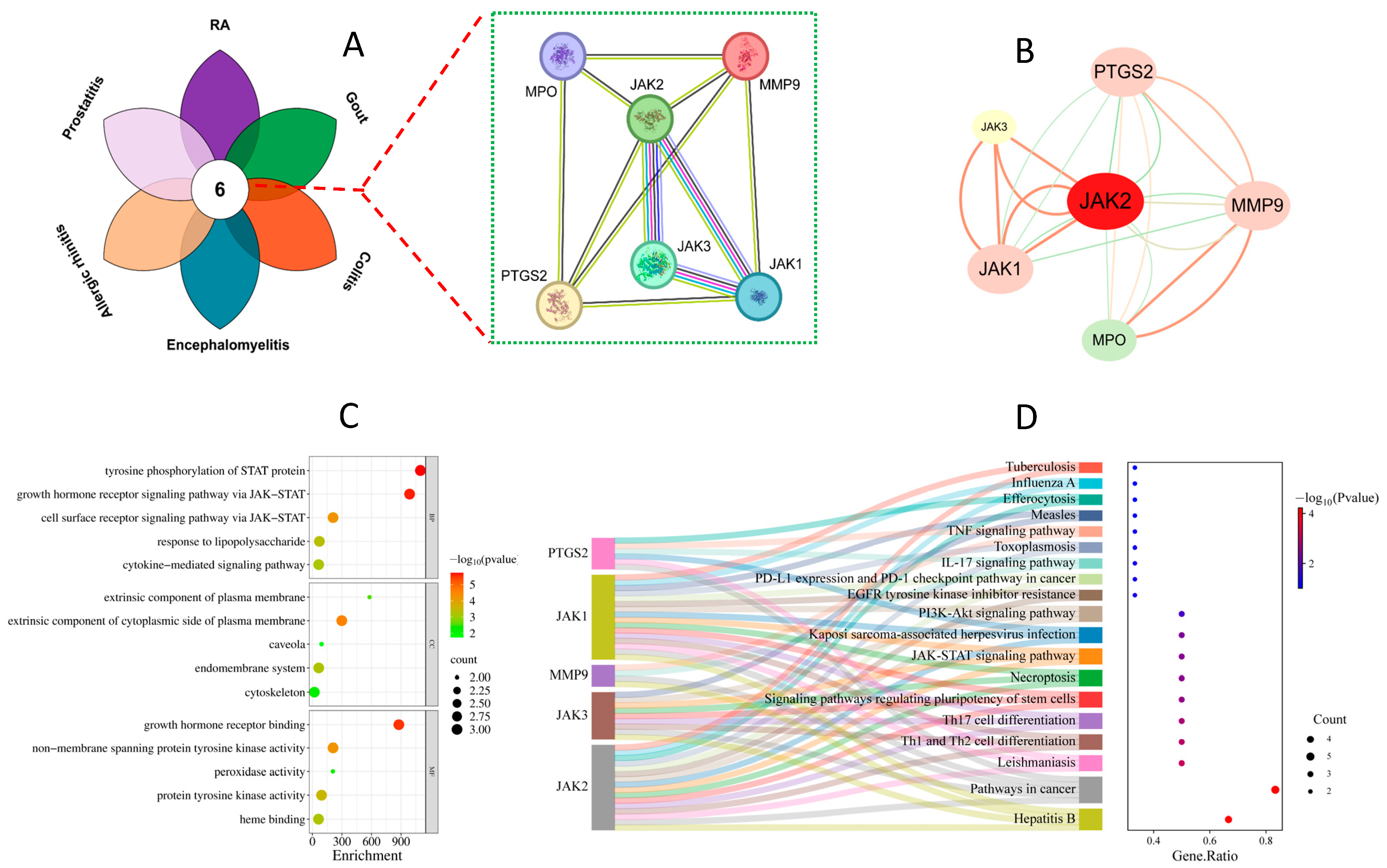
3.2. The PPI Network Construction, GO Enrichment, and KEGG Analysis
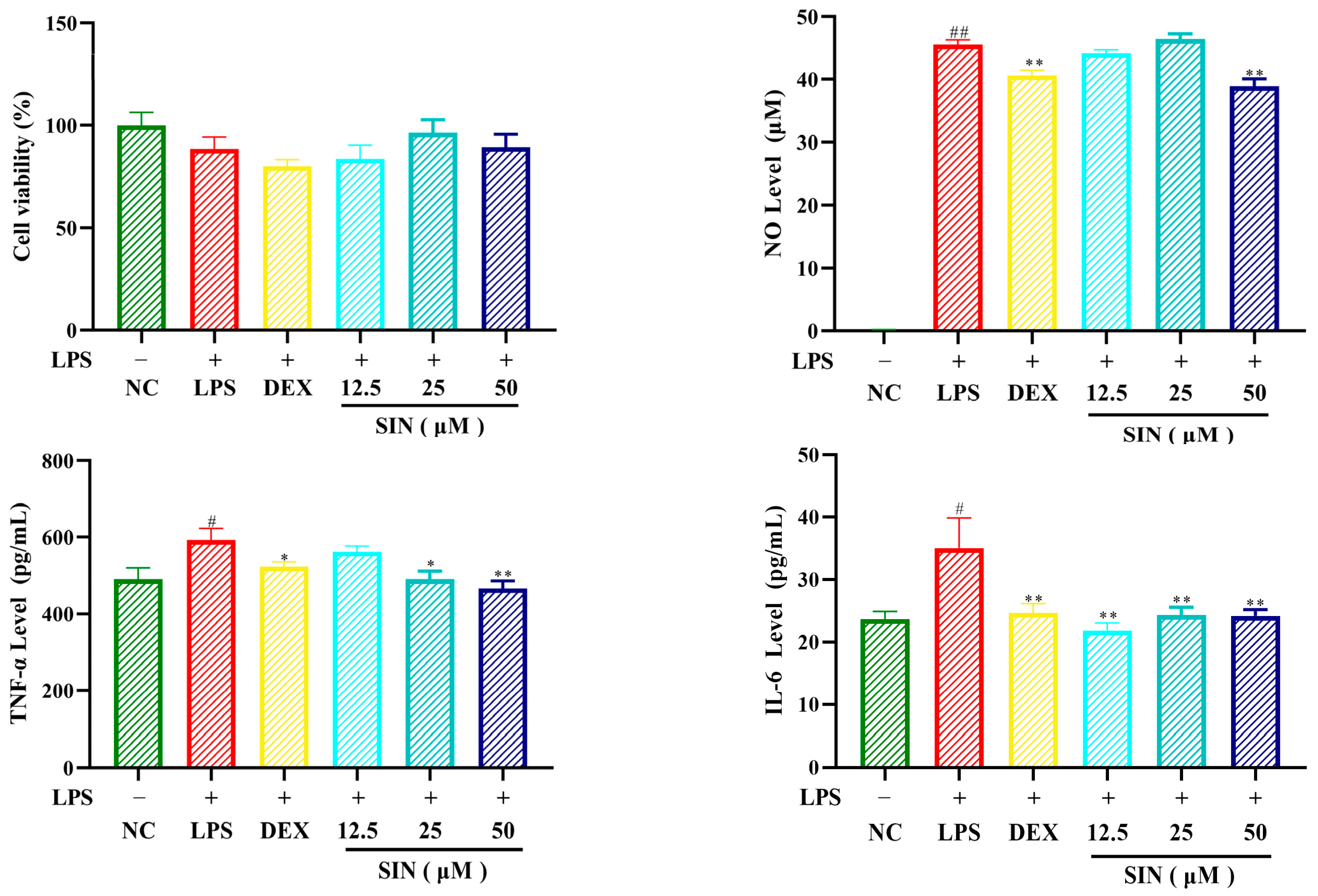
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity Evaluation of Sinomenine
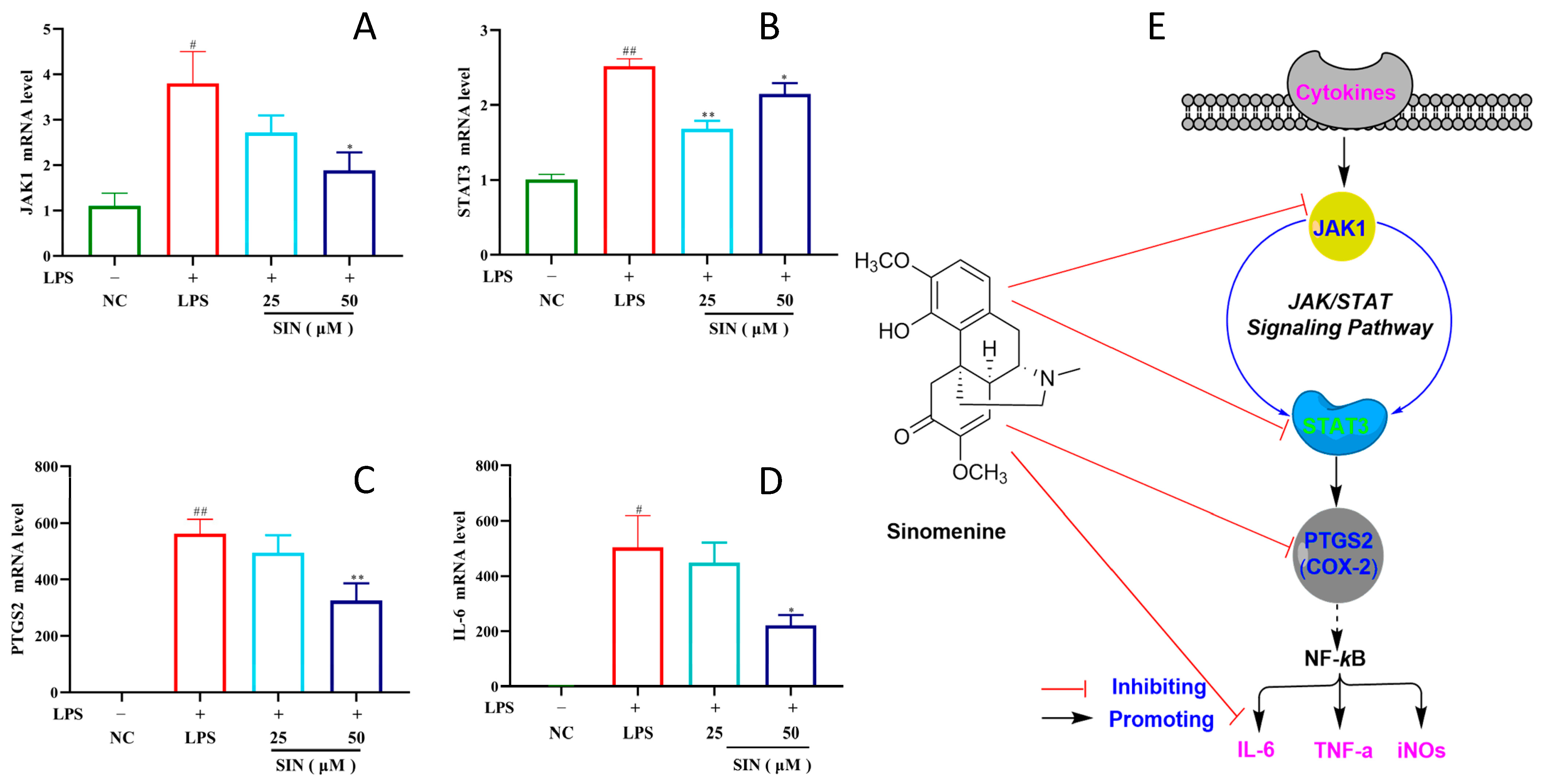
3.4. PCR Analysis and Pathway Confirmation
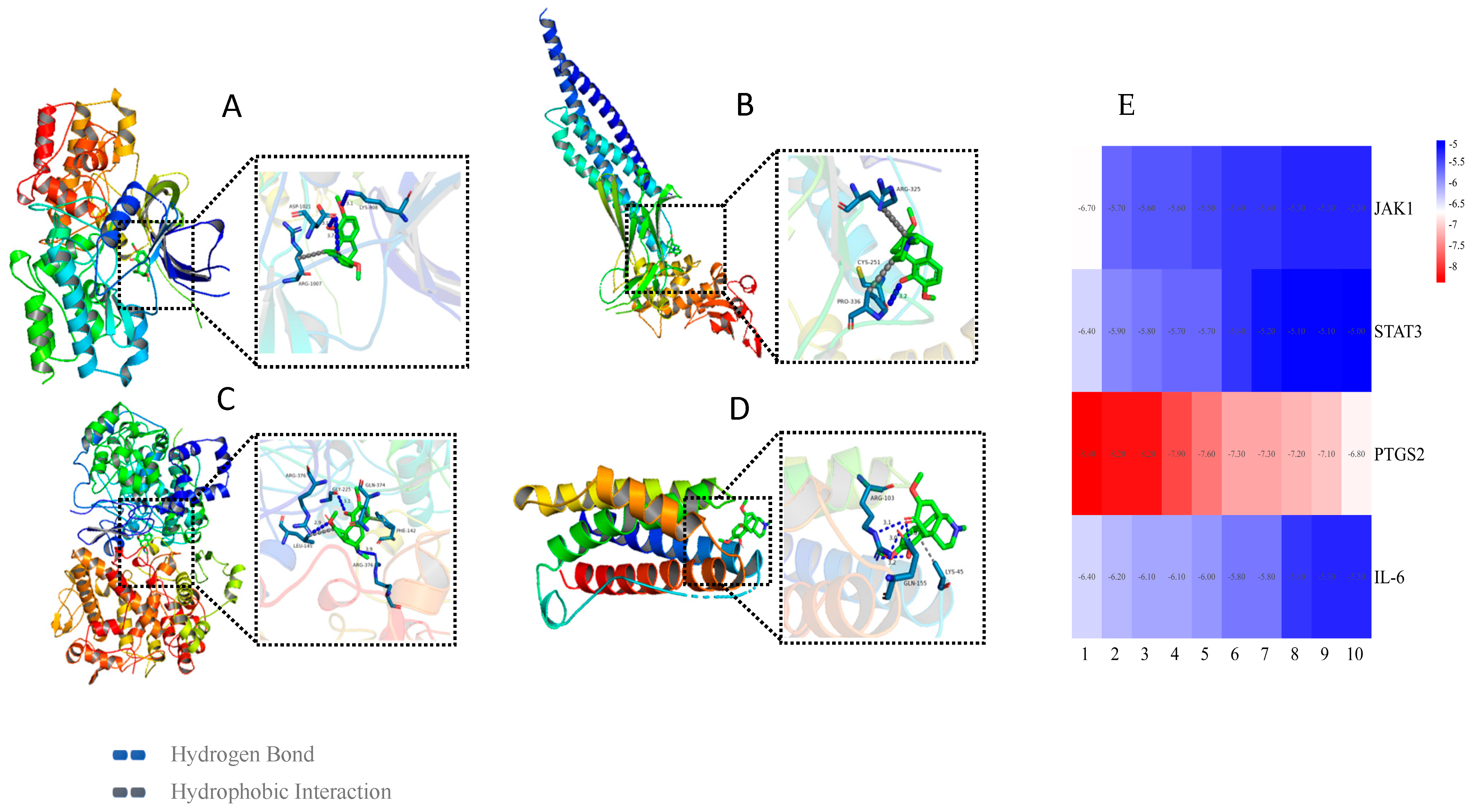
3.5. Molecular Docking
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| BP | Biological process |
| CC | Cellular component |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| COX 2 | Cyclooxygenase 2 |
| DEX | Dexamethasone |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| JAK | Janus activated kinase |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| MF | Molecular function |
| MMP 9 | Matrix Metalloproteinases 9 |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PLIP | Protein Ligand Interaction Profiler |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| PTGS 2 | Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| RT-qPCR | Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| SIN | Sinomenine |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese medicine |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
References
- Editorial. A current view on inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L.; Deng, H.D.; Cui, H.M.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.C.; Deng, J.L.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.H.; Chiou, Y.S.; Tsai, M.L.; Ho, C.T. Anti-Inflammatory Anti-inflammatory activity of traditional Chinese medicinal herbs. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2011, 1, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Huang, L.J.; Huang, H.; Liu, S.L.; Dai, W.; Tang, J.H.; Chen, X.Z.; Lu, X.L.; Zheng, Q.S.; Zhou, Z.N.; et al. Bioactivities and mechanisms of action of sinomenine and its derivatives: A comprehensive review. Molecules 2024, 29, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, E.T.; Hu, S.S.; Geng, H.L.; Zhu, H.Q.; Xie, J.J.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.B.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, J.Y. Zhengqing fengtongning sustained-release tablets prevents gout flares in the process of ULT. Medicine 2022, 101, e29199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.B.; Wu, P.; Zhang, J.H. Identification of potential targets and mechanisms of sinomenine in allergic rhinitis treatment based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.N.; Zhang, W.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, R.Q.; Xu, G.Y.; Zhang, R.G.; Guo, Y.Q. Clinical study on sinomenine combined with ultrasound physical in the treatment of III chronic prostatitis pain symptoms. Chin. J. Androl. 2011, 25, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, F.Q.; Chen, X.D.; Wang, H.J.; Zhou, J.Y.; Chai, K.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Lei, H.L.; Lu, P.; et al. Network pharmacology: A crucial approach in traditional Chinese medicine research. Chin. Med. 2025, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.L.; Song, D.; Xue, Y.; Han, W.; Liu, X.; Feng, T.T.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, X. Chemical information network and molecular docking inspire the novel indole discovery against glioma from Tabernaemontana corymbosa. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 22, e202402586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.J.; Yin, J.; Chen, J.Y.; Ma, J.; Si, H.B.; Xia, D.Q. Inhibition of inflammation by berberine: Molecular mechanism and network pharmacology analysis. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.T.; Yu, Q.X. Research progress in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Clin. Med. 2024, 14, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Deng, H.S.; Yao, Y.; Wang, W.T.; Hu, J.Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, P.X.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Xie, Y.; et al. Sinomenine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by targeting GBP5 and regulating the P2X7 receptor to suppress NLRP3-related signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 2504–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.T.; Yang, T.; Hou, X.Q.; Wu, H.Y.; Feng, J.T.; Ou, B.J.; Cai, S.J.; Li, J.; Mei, Z.G. Sinomenine mitigates collagen-induced arthritis mice by inhibiting angiogenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 113, 108759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdiana, Y.; Wardhana, Y.W.; Kurniawansyah, I.S.; Gozali, D.; Wathoni, N.; Sofian, F.F. Current status of gout arthritis: Current approaches to gout arthritis treatment: Nanoparticles delivery systems approach. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, E.T.; He, S.H.; Huang, J.J.; Zhang, J.Y. Research status of sinomenine for treatment of gouty arthritis. J. Guizhou Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 44, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Feng, S.Y.; Li, K.Y.; Liang, J.; Meng, J.Y.; Huang, Z.X.; Zhang, G.F.; Yin, Z.G. Experimental study on the effect of sinomenine on interleukin-6 in synovial tissue of rat model with gouty arthritis. J. Liaoning Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 20, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; He, Z.M.; Zong, Y.; Shi, K.; Chen, W.J.; Du, R. Excretion kinetics of sinomenine hydrochloride in acute gout rats in vivo. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2021, 43, 3275–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, X.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, M.; Ma, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xu, Q.R.; Tu, K.S.; Zhang, M.Z. Oral administration of turmeric-derived exosome-like nanovesicles with anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving bioactions for murine colitis therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.B.; Li, X.H.; Yang, X.H.; Sun, Z.W. Protective effects of sinomenine against dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats via alteration of HO-1/Nrf2 and inflammatory pathway. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 2007–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, Y.H.; Ji, X.H.; Li, J.; Que, L.L.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.D. Sinomenine inhibits brain nuclear factor-κB activity in rat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunol. J. 2005, 21, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tao, Z.Z.; Zhang, N.N.; Ren, J.; Deng, Y.Q.; Xiao, B.K. The role of sinomenine in treatment of allergic rhinitis mice model and its mechanism. J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 27, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Huang, B.; Wu, W.Q.; Pu, S.N.; Zhang, R.G. The effect of sinomenin on chronic prostategland inflammation in rats. Progress. Mod. Biomed. 2011, 11, 4244–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Y.; Li, J.; Fu, M.R.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: From bench to clinic. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koon, H.W.; Zhao, D.Z.; Zhan, Y.N.; Rhee, S.H.; Moyer, M.P.; Pothoulakis, C. Substance P stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 expression through JAK-STAT activation in human colonic epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 5050–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthian, G.; Raikwar, H.P.; Johnson, C.; Rajasingh, J.; Kalgutkar, A.; Marnett, L.J.; Bright, J.J. COX-2 inhibitors modulate IL-12 signaling through JAK-STAT pathway leading to Th1 response in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 26, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.Z.; Xie, Q.; Huang, T.; Ou, Y.B.; Xiao, Z.Q. Study on anti-inflammatory effects of serum containing ampelopsis grossedentata alcohol extract on LPS induced RAW264.7 inflammation model. Guid. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2024, 30, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.; Jeoung, D.; Kim, Y.M.; Choe, J. Interferon-γ stimulates human follicular dendritic cell-like cells to produce prostaglandins via the JAK-STAT pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 66, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddhadeb, D.; Xuan, Y.T.; Guo, Y.; Rezazadeh, A.; Stein, A.B.; Hunt, G.; Wu, W.J.; Tan, W.; Bolli, R. IL-6 plays an obligatory role in late preconditioning via JAK–STAT signaling and upregulation of iNOS and COX-2. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 64, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Song, D.; Liu, S.R.; Lei, C.W.; Shi, H.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, T.T.; Wei, X. Discovery, characterization, and anti-XOD activity of calcium metallophore from Coix lacryma-jobi. Org. Lett. 2025, 27, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeberle, A.; Werz, O. Multi-target approach for natural products in inflammation. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, J.M.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.J.; Liang, Q.Q. Network pharmacology, a promising approach to reveal the pharmacology mechanism of Chinese medicine formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 309, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhou, W.A.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Li, S. Network pharmacology: Towards the artificial intelligence-based precision traditional Chinese medicine. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 25, bbad518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Dong, J.X.; Xu, X.D. New research progress on the anti-inflammatory analgesic effects of sinomenine and its action mechanism. Hebei Med. J. 2020, 42, 3148–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | FORWARD | REVERSE |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | CTTCTTGGGACTGATGCTGGTGAC | AGGTCTGTTGGGAGTGGTATCCTC |
| JAK1 | CCCACTCCTTGATGCCAGTTCAC | CATGTCCGTCTTGCTCCGTCTTG |
| STAT3 | GCAGAAGACACTGACTGATGAAGAG | AGACGGTCCAGGCAGATGTTG |
| PTGS2 | GGTGCCTGGTCTGATGATGTATGC | GATGCTCCTGCTTGAGTATGTCG |
| GAPDH | CGATGCCCCCATGTTTGTGA | GAGCCCTTCCACAATGCCAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, D.; Khan, A.; Dong, M.-H.; Lei, C.-W.; Feng, T.-T.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, X. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism Prediction of Sinomenine Based on Network Pharmacology and Its Biological Activity Verification. Biology 2025, 14, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050543
Song D, Khan A, Dong M-H, Lei C-W, Feng T-T, Zhou Y, Wei X. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism Prediction of Sinomenine Based on Network Pharmacology and Its Biological Activity Verification. Biology. 2025; 14(5):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050543
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Da, Afsar Khan, Ming-Hong Dong, Chuan-Wen Lei, Ting-Ting Feng, Ying Zhou, and Xin Wei. 2025. "Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism Prediction of Sinomenine Based on Network Pharmacology and Its Biological Activity Verification" Biology 14, no. 5: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050543
APA StyleSong, D., Khan, A., Dong, M.-H., Lei, C.-W., Feng, T.-T., Zhou, Y., & Wei, X. (2025). Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism Prediction of Sinomenine Based on Network Pharmacology and Its Biological Activity Verification. Biology, 14(5), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050543







