Genome-Wide Identification and Cold Stress Response Mechanism of Barley Di19 Gene Family
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Gene Family Member Identification
2.3. Protein Basic Feature Analysis
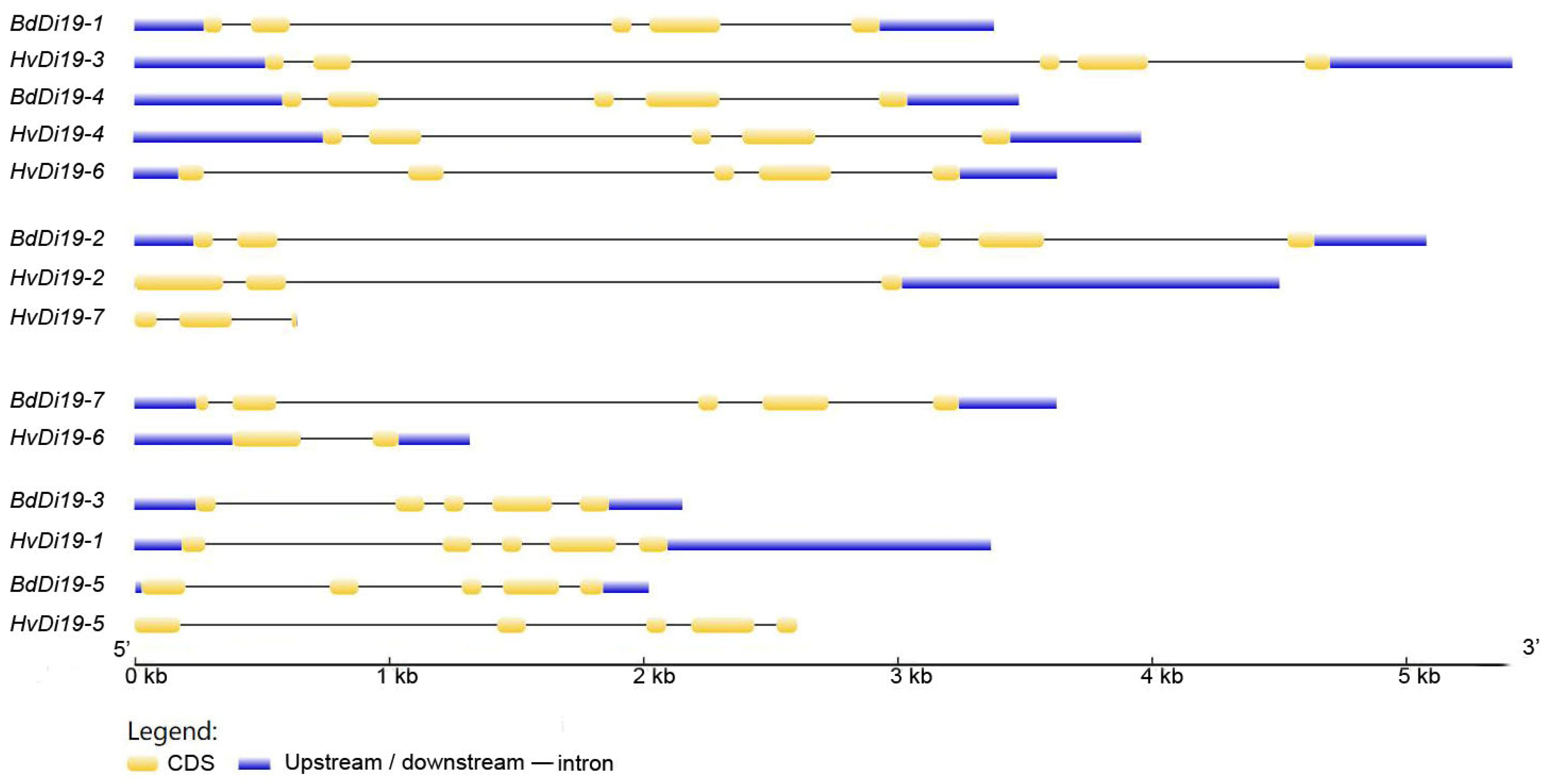
2.4. Phylogenetic Tree Construction and Gene Structure Analysis
2.5. Tissue Expression Pattern Analysis
2.6. Cold Stress Treatment
2.7. Total RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Detection
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Analysis of Di19 Gene Family Members
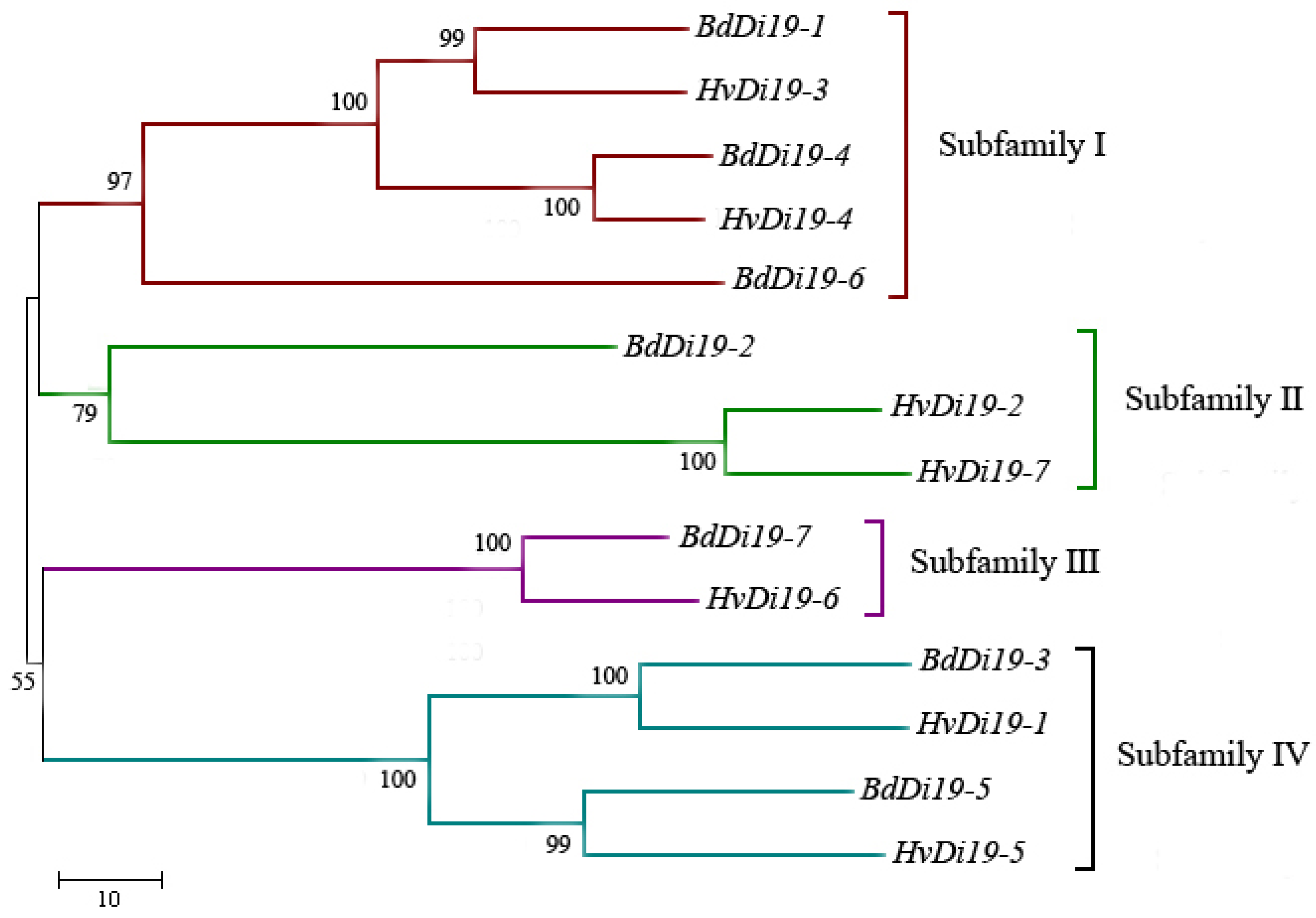
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Di19 Family Proteins in Barley and Brachypodium Distachyon
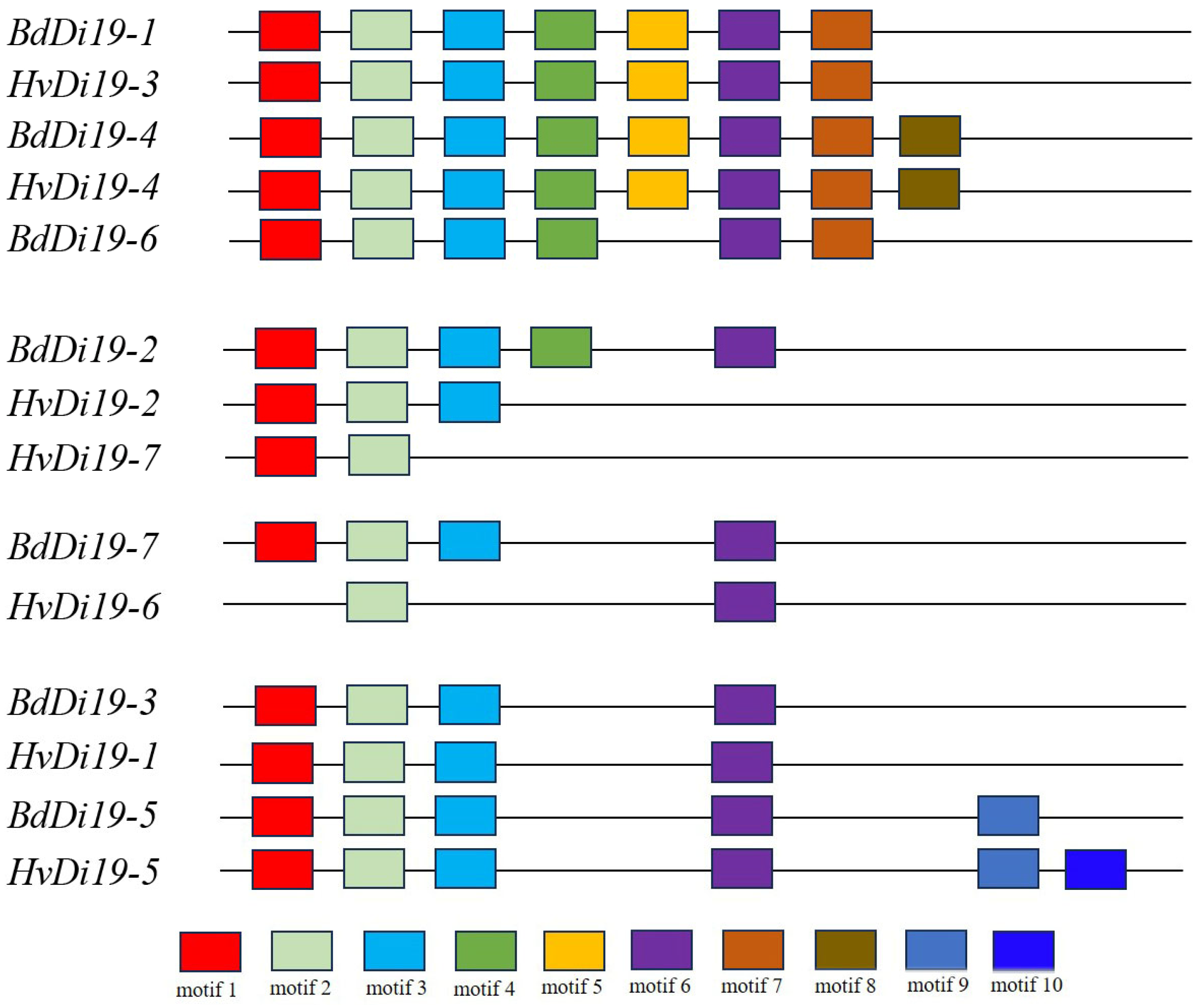
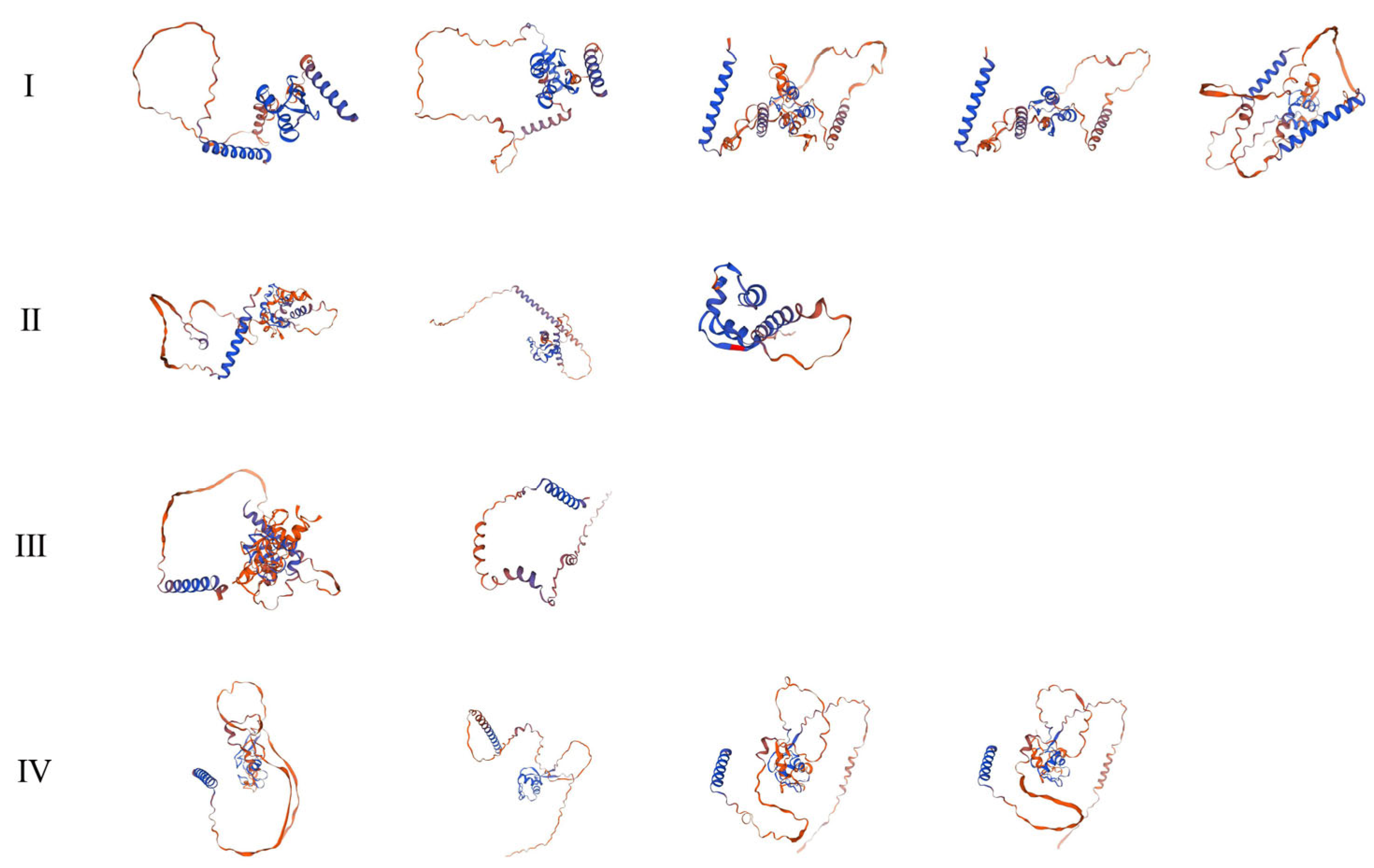
3.3. Conserved Domains and Three-Dimensional (3D) Structure Analysis of HvDi19 Gene Family
3.4. Evolutionary Selection Analysis of Genes
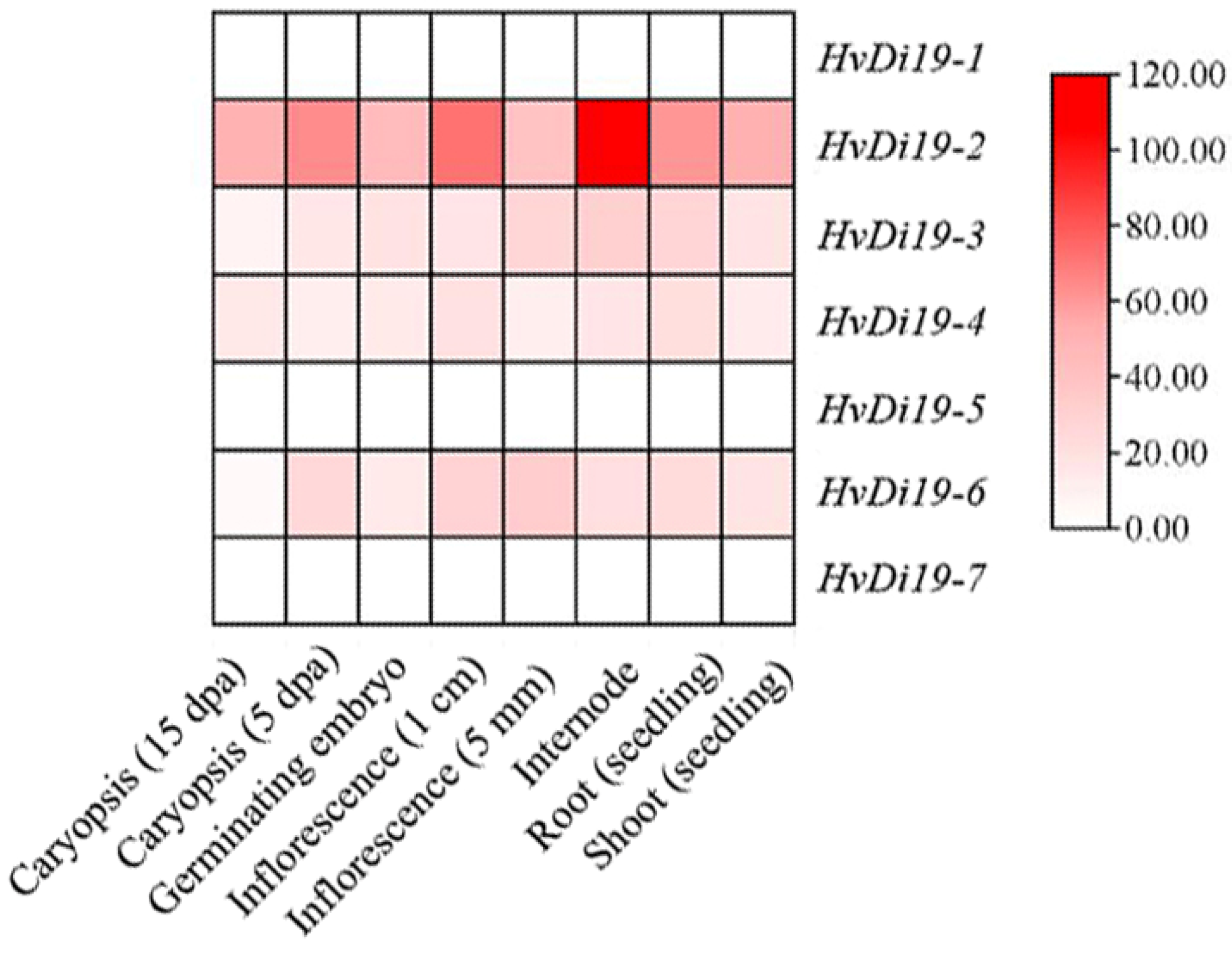
3.5. Gene Tissue Expression Pattern Analysis
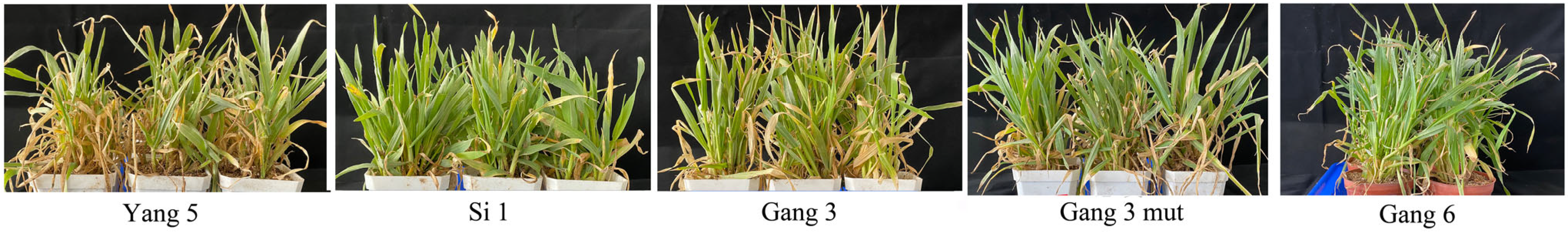
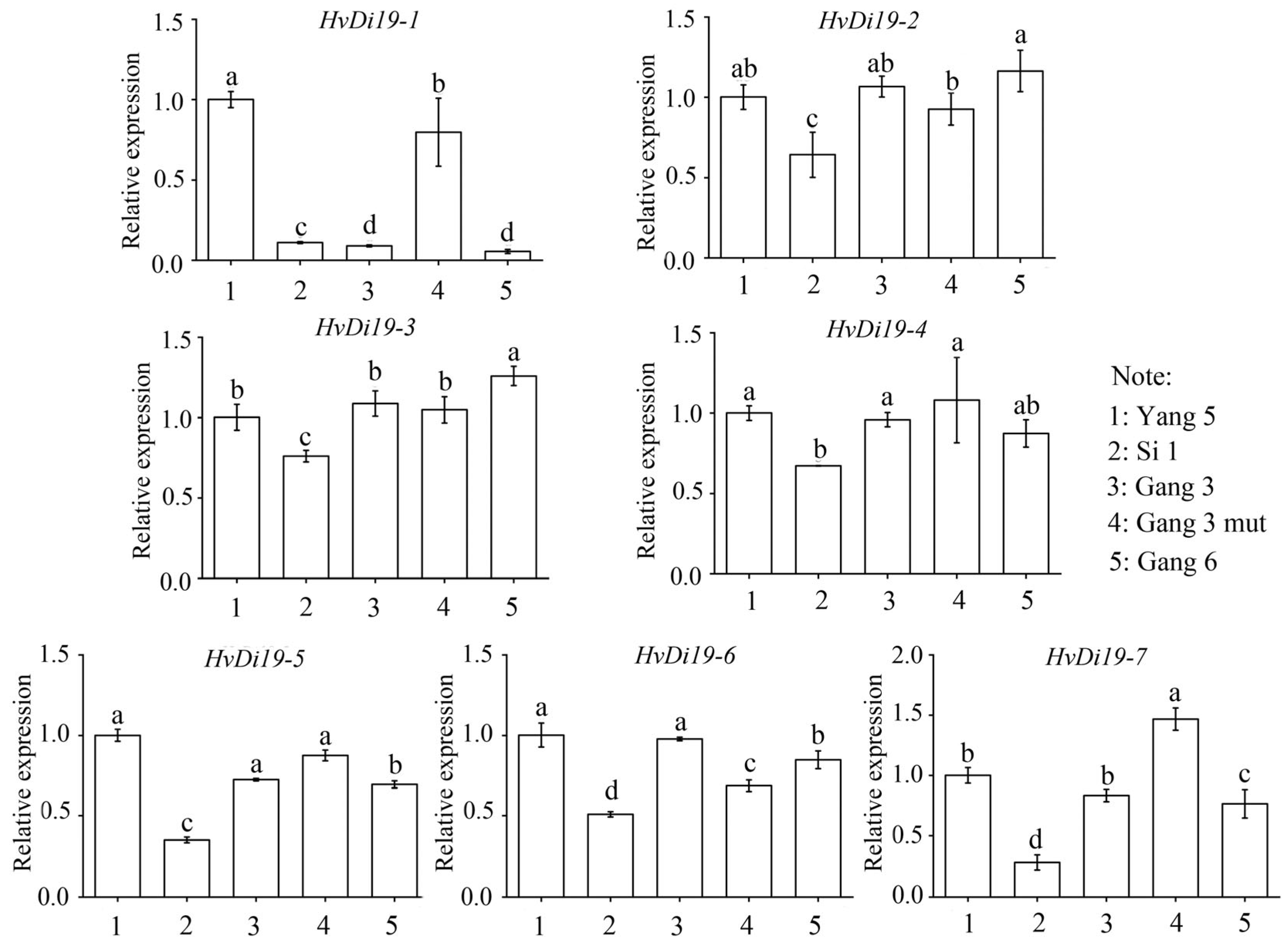
3.6. Expression of Di19 Genes in Different Varieties
4. Discussion
4.1. Conserved Features and Evolutionary Characteristics of Di19 Gene Family
4.2. Structural Diversity and Selective Pressure of Di19 Genes
4.3. Expression Patterns of Di19 Genes and Stress Responses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, W.T. Screening Barley Germplasm for Salt Tolerance and Its Associated Genetic Analyses. Ph.D. Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Castro, J.; Hill, R.D.; Stasolla, C.; Badea, A. Waterlogging Stress Physiology in Barley. Agronomy 2022, 12, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Fujita, Y.; Noutoshi, Y.; Takahashi, F.; Narusaka, Y.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Crosstalk between Abiotic and Biotic Stress Responses: A Current View from the Points of Convergence in the Stress Signaling Networks. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.Y.; Liu, Y.N.; Wang, X.Y.; Chang, C. Insight into the Role of Epigenetic Processes in Abiotic and Biotic Stress Response in Wheat and Barley. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, A.; Wen, T.; Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, G. Cotton HD-Zip I Transcription Factor GhHB4-like Regulates the Plant Response to Salt Stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278 Pt 3, 134857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W.; Gao, Y.; Xian, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Transcription Factors Dealing with Iron-Deficiency Stress in Plants: Focus on the bHLH Transcription Factor Family. Physiol. Plant. 2023, 175, e14091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Tang, X.; Zhang, N.; Si, H. Transcription Factors as Molecular Switches Regulating Plant Responses to Drought Stress. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.L.; Feng, X.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y. Effects of Drying on the Structural Characteristics and Antioxidant Activities of Polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3622–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.W.; Zhou, X.P.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, J.T.; Yu, X.Y.; Wu, W.C.; Liu, Y.Q.; Guo, L.J.; Tong, Y.Z.; Zhang, G.P.; et al. Research Progress on the Functions of Plant Transcription Factors in the Interaction between Nematodes and Hosts. Plant Prot. 2024, 50, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Qu, D.; Chen, X.; Zeng, H.; Li, X.; Hu, C.Y. Metabolomics Reveals 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Improved the Ability of Tea Leaves (Camellia sinensis L.) against Cold Stress. Metabolites 2022, 12, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Jian, S.G.; Deng, S.L. A Novel ABA-Induced Transcript Factor from Millettia pinnata, MpAITR1, Enhances Salt and Drought Tolerance through ABA Signaling in Transgenic Arabidopsis. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 288, 154060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, S.; Joshi, S.; Joshi, R. Sensing, Signalling, and Regulatory Mechanism of Cold-Stress Tolerance in Plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 197, 107646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Yao, J.; Fang, S.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S. Systematical Characterization of the Cotton Di19 Gene Family and the Role of GhDi19-3 and GhDi19-4 as Two Negative Regulators in Response to Salt Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.Y.; Ding, L.; Tang, D.L.; Zhao, H.X.; Mao, H.D. Genome-wide Analysis of Wheat Di19 Gene Family and Functional Analysis of TaDi19-7 in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 206, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, C.C.; Chen, C.; He, C.L.; Zhu, Y.G.; Huang, W.C. Identification of Rice Di19 Family Reveals OsDi19-4 Involved in Drought Resistance. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 2047–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.X.; Nie, X.Y.; Hu, R.; Li, G.; Xu, W.L.; Li, X.B. Phosphorylation of serine residue modulates cotton Di19-1 and Di19-2 activities for responding to high salinity stress and abscisic acid signaling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, G. Functional analysis of TaDi19A, a salt-responsive gene in wheat. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Lin, M.; Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Yan, H.; Xiang, Y. Homologous Drought-Induced 19 Proteins, PtDi19-2 and PtDi19-7, Enhance Drought Tolerance in Transgenic Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Gao, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, S.; Tang, W.; Li, X.; Ma, S.; Xiao, M. A novel root-specific Di19 transcription factor from Glycine max compromises drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana through suppression of auxin-related pathway. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 201, 104951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Milla, M.A.; Townsend, J.; Chang, I.-F.; Cushman, J.C. The Arabidopsis AtDi19 gene family encodes a novel type of Cys2/His2 zinc-finger protein implicated in ABA-independent dehydration, high-salinity stress and light signaling pathways. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 61, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.X.; Li, Y.; Li, D.D.; Xu, W.L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.B. Arabidopsis drought-induced protein Di19-3 participates in plant response to drought and high salinity stresses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 86, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra Majee, S.; Sharma, E.; Singh, B.; Khurana, J.P. Drought-induced protein (Di19-3) plays a role in auxin signaling by interacting with IAA14 in Arabidopsis. Plant Direct 2020, 4, e00234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, H.; Lu, M.; Wei, Q.; Xu, L.; Bo, C.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, B. A maize stress-responsive Di19 transcription factor, ZmDi19-1, confers enhanced tolerance to salt in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2019, 38, 1563–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, C.C.; Xu, S.L.; Zhu, Y.G.; Huang, W.C. OsDi19-4 acts downstream of OsCDPK14 to positively regulate ABA response in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 2740–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.X.; Zhang, F.C.; Zhang, W.Z.; Song, L.F.; Wu, W.H.; Chen, Y.F. Arabidopsis Di19 functions as a transcription factor and modulates PR1, PR2, and PR5 expression in response to drought stress. Mol. Plant 2010, 6, 1487–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, X.; Yang, T.; Huang, C.; Zhao, B.; Wang, P. Identification and expression of the Di19 gene family in response to abiotic stress in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1401011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, L.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Ma, Q. Identification and Characterization of the Core Region of ZmDi19-5 Promoter Activity and Its Upstream Regulatory Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, P. Molecular Mechanism of Calcium Signal Proteins OsClo5 and OsRbohI in Regulating Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Rice. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L. Identification of Wheat Transcription Factor TaERF87 and TaDi19-7 and Their Roles in Abiotic Stress Response. TaERF87 and TaDi19-7. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Mechanism of TaZFP21, a C2H2-Type Zinc Finger Protein, in Regulating Drought Stress in Wheat. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.T.; Cui, A.H.; Cui, Y.P.; Cui, R.F.; Han, M.G.; Zhang, Y.X.; Fan, Y.P.; Huang, H.; Feng, X.X.; Lei, Y.Q.; et al. Systematic analysis and expression of Gossypium 2ODD superfamily highlight the roles of GhLDOXs responding to alkali and other abiotic stress in cotton. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, Z.; Si, W.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Peng, H.; Mao, R.; Jiang, H.; et al. The C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factor ZmDi19-7 regulates plant height and organ size by promoting cell size in maize. Plant J. 2024, 120, 2700–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Genome-Wide Analysis of Di19 Transcription Factor Family in Poplar and Molecular Characterization of PtDi19-9. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.S.; Yang, F.; Shu, W.J.; Zhao, K.Y.; Huang, Y.Z.; Liu, Q.Q.; Yuan, Y.J. Improved qualities of cod-rice dual-protein gel as affected by rice protein: Insight into molecular flexibility, protein interaction and gel properties. Food Res. Int. 2024, 197, 115176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.H.; Yu, B. Research progress on the analysis of transcription factor and promoter interactions and their roles in plant responses to abiotic stress. China Agric. Bull. 2021, 37, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y.; Feng, S.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Q.; Feng, B. Genome-Wide Identification of DNA Binding with One Finger (Dof) Gene Family in Tartary Buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum) and Analysis of Its Expression Pattern after Exogenous Hormone Stimulation. Biology 2022, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.N.; Yu, T.F.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.B.; Ma, Y.Z.; Xu, Z.S.; Min, D.H. Response of wheat zinc finger transcription factor TaDi19A to low temperature and screening of its interacting proteins. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2017, 50, 2411–2422. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.J.; Cui, X.Y.; Cui, X.Y.; Chen, M.; Yang, G.X.; Ma, Y.Z.; He, G.Y.; Xu, Z.S. The soybean GmDi19-5 interacts with GmLEA3.1 and increases sensitivity of transgenic plants to abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Genes | Forward Primer | Downstream Primer |
|---|---|---|
| HORVU1Hr1G059310 | GCGAGGATTTCGATTTCGTAGG | GCGAGGATTTCGATTTCGTAGG |
| HORVU1Hr1G087100 | GCCTTAGCTTCCCAACATTAGA | CCTTGTGAGGGACAAGTCAATA |
| HORVU3Hr1G061690 | GGTTGCGCAGATTCGTTATTC | ATGACTATGACCGCCTCCTA |
| HORVU1Hr1G003540 | CCTCAGATGATCAAAGGCTGAA | CATGAGCATCTGCTTCACAAAC |
| HORVU5Hr1G051150 | TGTGGCGAGGATTTCGACTT | TTAGAAGATAGGGCGAGGCG |
| HORVU3Hr1G114280 | CAGGAGGAACACTGCTTTGA | GCGAGTGTTGGAATCTGAAATG |
| HORVU5Hr1G023560 | ATCCTCTACTCTCCTCCTTTGT | GCTCCTCAGCACTTTCTTCT |
| Actin | GAGAGGTTACTCCTTCACAACC | GTCTCCAGCTCCTGTTCATAAT |
| Gene Name | Gene ID | Amino Acid Number (aa) | Isoelectric Point (pI) | Molecular Weight (MW, Da) | Subcellular Localization | Chromosomal Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HvDi19-1 | HORVU1Hr1G003540 | 218 | 4.79 | 24,654.31 | Nucleus | 1H: 7841380..7844750 |
| HvDi19-2 | HORVU1Hr1G059310 | 208 | 8.87 | 22,854.45 | Nucleus | 1H: 432516342..432520847 |
| HvDi19-3 | HORVU1Hr1G087100 | 225 | 5.55 | 24,977.96 | Nucleus | 1H: 538689465..538694886 |
| HvDi19-4 | HORVU3Hr1G061690 | 252 | 4.74 | 28,414.8 | Nucleus | 3H: 469768134..469772099 |
| HvDi19-5 | HORVU3Hr1G114280 | 233 | 5.05 | 26,356.6 | Nucleus | 3H: 690566983..690569591 |
| HvDi19-6 | HORVU5Hr1G023560 | 123 | 4.84 | 13,933.46 | Nucleus | 5H: 123880698..123882018 |
| HvDi19-7 | HORVU5Hr1G051150 | 105 | 4.44 | 11,323.24 | Nucleus | 5H: 399422454..399423095 |
| BdDi19-1 | Bradi2g16670 | 230 | 5.41 | 25,672.55 | Nucleus | Bd2: 14640232..14643614 |
| BdDi19-2 | Bradi2g28040 | 228 | 5.11 | 25,078.11 | Nucleus | Bd2: 27262827..27267910 |
| BdDi19-3 | Bradi2g39370 | 206 | 4.64 | 23,343.72 | Nucleus | Bd2: 39192968..39195124 |
| BdDi19-4 | Bradi2g46240 | 251 | 4.61 | 28,396.68 | Nucleus | Bd2: 46434335..46437815 |
| BdDi19-5 | Bradi2g61990 | 224 | 5.69 | 25,592.64 | Nucleus | Bd2: 58637326..58639346 |
| BdDi19-6 | Bradi3g11400 | 236 | 6.45 | 26,711.83 | Nucleus | Bd3: 9857561..9861195 |
| BdDi19-7 | Bradi4g05020 | 220 | 4.47 | 24,890.41 | Nucleus | Bd4: 4097406..4101034 |
| Paralogous Pairs | Ks | Ka | Ka/Ks | Duplication Date (Mya) | Duplication Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HvDi19-1–HvDi19-5 | 1.5807 | 0.4730 | 0.2973 | 37.41 | segmental |
| HvDi19-2–HvDi19-7 | 0.2512 | 0.1590 | 0.6330 | 5.95 | segmental |
| HvDi19-3–HvDi19-4 | 0.5796 | 0.1744 | 0.3009 | 13.72 | segmental |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, W.; Yuan, C.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Li, H.; Ji, W.; Wang, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Cold Stress Response Mechanism of Barley Di19 Gene Family. Biology 2025, 14, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050508
Chai W, Yuan C, Li S, Xu H, Zhu Q, Li H, Ji W, Wang J. Genome-Wide Identification and Cold Stress Response Mechanism of Barley Di19 Gene Family. Biology. 2025; 14(5):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050508
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Wenbo, Chao Yuan, Shufen Li, Hanyuan Xu, Qing Zhu, Hongtao Li, Wei Ji, and Jun Wang. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Cold Stress Response Mechanism of Barley Di19 Gene Family" Biology 14, no. 5: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050508
APA StyleChai, W., Yuan, C., Li, S., Xu, H., Zhu, Q., Li, H., Ji, W., & Wang, J. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Cold Stress Response Mechanism of Barley Di19 Gene Family. Biology, 14(5), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050508






