Recent Progress in Rice–Xanthomonas oryzae Interactions
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
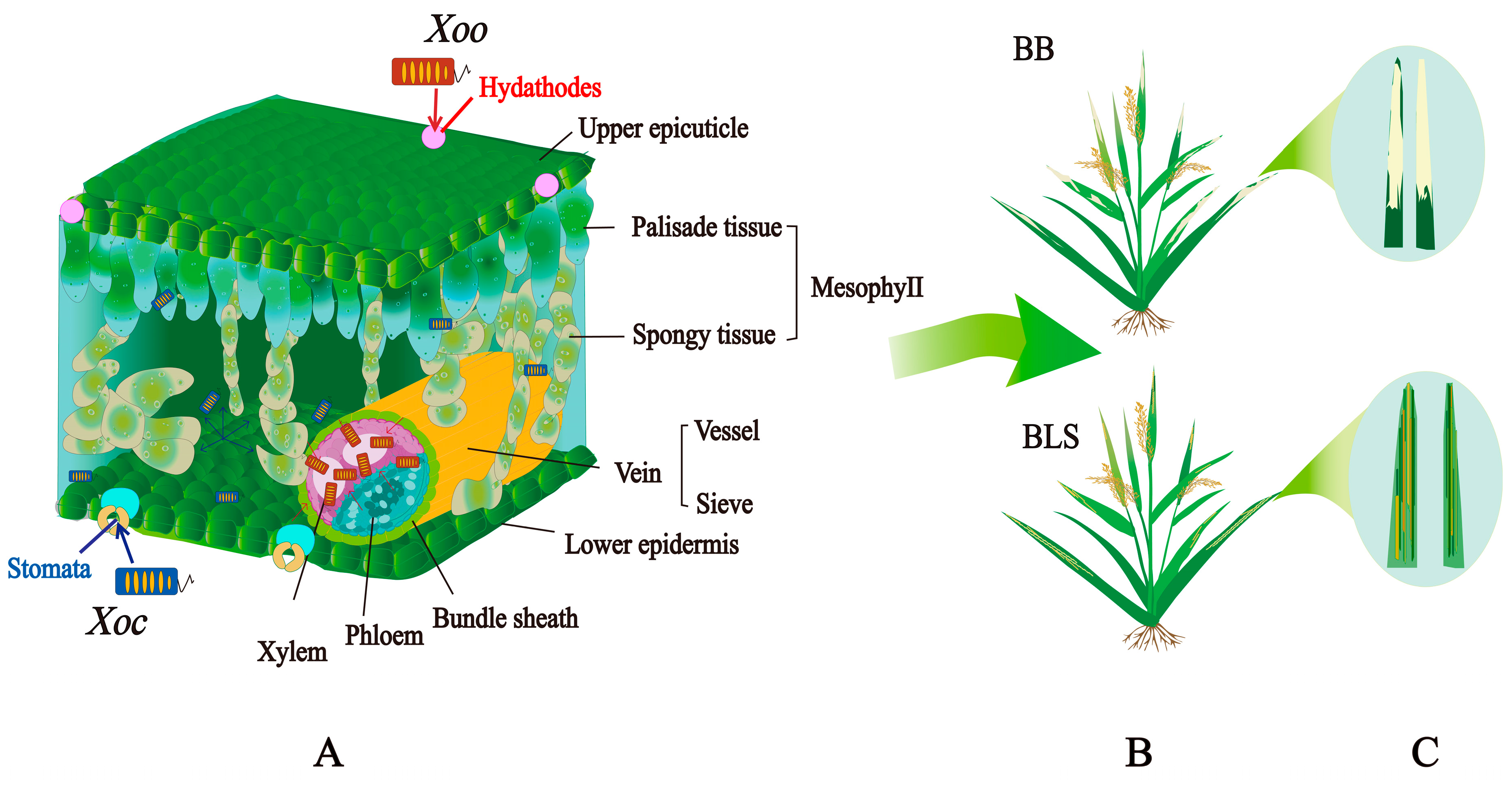
2. Xanthomonas oryzae Infection Models
3. Type III Secreted Effectors of Xanthomonas—TALEs
4. Type III Secreted Effectors of Xanthomonas—Non-TALEs
5. TALEs-Induced Rice Immunity to Xanthomonas oryzae
6. Non-TALE-Induced Rice Immunity to Xanthomonas oryzae
7. Whole Picture of Rice–Xanthomonas oryzae Interaction Mechanisms from Multi-Omics View
8. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryan, R.P.; Vorhölter, F.J.; Potnis, N.; Jones, J.B.; Van Sluys, M.A.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Dow, J.M. Pathogenomics of Xanthomonas: Understanding bacterium-plant interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niño-Liu, D.O.; Ronald, P.C.; Bogdanove, A.J. Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars: Model pathogens of a model crop. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2006, 7, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.B.; Arul, L.; Ramalingam, J.; Uthandi, S. Advances in the Xoo-rice pathosystem interaction and its exploitation in disease management. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Yap, R.; Tseng, Y.C.; Wu, Y.P. Pyramiding Bacterial Blight Resistance Genes in Tainung82 for Broad-Spectrum Resistance Using Marker-Assisted Selection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Triplett, L.; Leach, J.E.; Wang, G.L. Novel insights into rice innate immunity against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mew, T.W.; Alvarez, A.M.; Leach, J.E.; Swings, J. Focus on bacterial blight of rice. Plant Dis. 1993, 77, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Makino, S.; Subedee, A.; Bogdanove, A.J. Novel candidate virulence factors in rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola as revealed by mutational analysis. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 8023–8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yan, J.; Liang, Y.; Shi, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Peng, J. Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)-an Updated Review. Rice 2020, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsina, S.; Potnis, N.; Newberry, E.A.; Liyanapathiranage, P.; Iruegas-Bocardo, F.; White, F.F.; Goss, E.M.; Jones, J.B. Xanthomonas diversity, virulence and plant-pathogen interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Zou, L.; Chen, G. TALE-induced immunity against the bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice. Phytopathol. Res. 2022, 4, 1434–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boch, J.; Bonas, U. Xanthomonas AvrBs3 family-type III effectors: Discovery and function. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2010, 48, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonas, U.; Stall, R.E.; Staskawicz, B. Genetic and structural characterization of the avirulence gene avrBs3 from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1989, 218, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarup, S. Isolation of pathogenicity genes from Xanthomonas species and study of their regulation; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Swarup, S.; Yang, Y.; Kingsley, M.T.; Gabriel, D.W. An Xanthomonas citri pathogenicity gene, pthA, pleiotropically encodes gratuitous avirulence on nonhosts. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1992, 5, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.M.; White, F.F.; Choi, S.H.; Guo, A.; Leach, J.E. Identification of a family of avirulence genes from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1992, 5, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; White, F.F. Diverse members of the AvrBs3/PthA family of type III effectors are major virulence determinants in bacterial blight disease of rice. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholze, H.; Boch, J. TAL effectors are remote controls for gene activation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, F.F.; Potnis, N.; Jones, J.B.; Koebnik, R. The type III effectors of Xanthomonas. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 749–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Ji, C.; Liu, B.; Zou, L.; Chen, G.; Yang, B. Interfering TAL effectors of Xanthomonas oryzae neutralize R-gene-mediated plant disease resistance. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.G.; Suh, J.W.; Lee, C.H. Metabolomics-Based Chemotaxonomic Classification of Streptomyces spp. and Its Correlation with Antibacterial Activity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg, S.L.; Sommer, D.D.; Schatz, M.C.; Phillippy, A.M.; Rabinowicz, P.D.; Tsuge, S.; Furutani, A.; Ochiai, H.; Delcher, A.L.; Kelley, D.; et al. Erratum to: Genome sequence and rapid evolution of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, H.; Inoue, Y.; Takeya, M.; Sasaki, A.; Kaku, H. Genome Sequence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Suggests Contribution of Large Numbers of Effector Genes and Insertion Sequences to Its Race Diversity. Jarq-Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2005, 39, 275–287. [Google Scholar]
- White, F.F.; Yang, B. Host and pathogen factors controlling the rice-Xanthomonas oryzae interaction. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Yang, B. Mutagenesis of 18 type III effectors reveals virulence function of XopZ(PXO99) in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, B.; Staskawicz, B.J. Widespread distribution and fitness contribution of Xanthomonas campestris avirulence gene avrBs2. Nature 1990, 346, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swords, K.M.; Dahlbeck, D.; Kearney, B.; Roy, M.; Staskawicz, B.J. Spontaneous and induced mutations in a single open reading frame alter both virulence and avirulence in Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria avrBs2. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 4661–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Song, C.; Yan, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, H.; Yang, B. Non-TAL Effectors From Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Suppress Peptidoglycan-Triggered MAPK Activation in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, P.N.; Rathjen, J.P. Plant immunity: Towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Bao, J.; Li, H.; Hu, W.; Kong, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Fu, Q.; Xu, G.; Liu, F.; Jiao, X.; et al. Structural and biochemical basis of FLS2-mediated signal activation and transduction in rice. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S.; Yamanouchi, U.; Katayose, Y.; Toki, S.; Wang, Z.X.; Kono, I.; Kurata, N.; Yano, M.; Iwata, N.; Sasaki, T. Expression of Xa1, a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, R.; Sengupta, D.; Das, S.N.; Pandey, M.K.; Bohra, A.; Sharma, N.K.; Sinha, P.; Sk, H.; Ghazi, I.A.; et al. Deployment of Genetic and Genomic Tools Toward Gaining a Better Understanding of Rice-Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Interactions for Development of Durable Bacterial Blight Resistant Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Ji, Z.; Liu, B.; Cheng, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Chen, G. Xa1 Allelic R Genes Activate Rice Blight Resistance Suppressed by Interfering TAL Effectors. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Han, X.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, H. TALEs as double-edged swords in plant-pathogen interactions: Progress, challenges, and perspectives. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, K.; Yang, B.; Tian, D.; Wu, L.; Wang, D.; Sreekala, C.; Yang, F.; Chu, Z.; Wang, G.L.; White, F.F.; et al. R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 2005, 435, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.; Gu, K.; Qiu, C.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Goh, M.; Luo, Y.; Murata-Hori, M.; et al. The rice TAL effector-dependent resistance protein XA10 triggers cell death and calcium depletion in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zheng, C.; Qin, T.; Li, Y.; Che, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Mol. Plant 2014, ssu132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, P.; Mei, L.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Shen, S.; Ji, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Xa7, a new executor R gene that confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ma, W.; Zakria, M.; Zou, L.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, G. A Transcription Activator-Like Effector Tal7 of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola Activates Rice Gene Os09g29100 to Suppress Rice Immunity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscou, M.J.; Bogdanove, A.J. A simple cipher governs DNA recognition by TAL effectors. Science 2009, 326, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Ouyang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. Multiple Alleles Encoding Atypical NLRs with Unique Central Tandem Repeats in Rice Confer Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Huguet-Tapia, J.C.; Raborn, R.T.; White, F.F.; Brendel, V.P.; Yang, B. The Xa7 resistance gene guards the rice susceptibility gene SWEET14 against exploitation by the bacterial blight pathogen. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zheng, C.; Qin, T.; Li, Y.; Che, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Fu, B.; Yang, H.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Sanchez, A.; Park, Y.J.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. Targeting xa13, a recessive gene for bacterial blight resistance in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, Z.; Long, J.; Sosso, D.; Liu, B.; Eom, J.S.; Huang, S.; Liu, S.; Vera Cruz, C.; Frommer, W.B.; et al. Gene targeting by the TAL effector PthXo2 reveals cryptic resistance gene for bacterial blight of rice. Plant J. 2015, 82, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutin, M.; Sabot, F.; Ghesquière, A.; Koebnik, R.; Szurek, B. A knowledge-based molecular screen uncovers a broad-spectrum OsSWEET14 resistance allele to bacterial blight from wild rice. Plant J. 2015, 84, 694–703. [Google Scholar]
- Sugio, A.; Yang, B.; Zhu, T.; White, F.F. Two type III effector genes of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae control the induction of the host genes OsTFIIAgamma1 and OsTFX1 during bacterial blight of rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10720–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Zou, L.; Chen, G. Identification of an avirulence gene, avrxa5, from the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Sci. China Life Sci. 2010, 53, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.H.; Xia, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.L.; Wan, J.; Li, D.Y.; Chen, R.S.; Zhai, W.X.; Zhu, L.H. Testifying the rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5 by genetic complementation and further analyzing xa5 (Xa5) in comparison with its homolog TFIIAgamma1. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2006, 275, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Sugio, A.; White, F.F. Os8N3 is a host disease-susceptibility gene for bacterial blight of rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2006, 103, 10503–10508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, G.; Zhou, J.; Huang, S.; Li, T.; Liu, B.; White, F.; Yang, B. Rice xa13 recessive resistance to bacterial blight is defeated by induction of the disease susceptibility gene Os-11N3. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3864–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Streubel, J.; Balzergue, S.; Champion, A.; Boch, J.; Koebnik, R.; Feng, J.; Verdier, V.; Szurek, B. Colonization of rice leaf blades by an African strain of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae depends on a new TAL effector that induces the rice nodulin-3 Os11N3 gene. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streubel, J.; Pesce, C.; Hutin, M.; Koebnik, R.; Boch, J.; Szurek, B. Five phylogenetically close rice SWEET genes confer TAL effector-mediated susceptibility to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Xu, X.; Gong, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, L.; Zhu, B.; et al. Engineering Broad-Spectrum Bacterial Blight Resistance by Simultaneously Disrupting Variable TALE-Binding Elements of Multiple Susceptibility Genes in Rice. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1434–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Ke, Y.; Huang, R.; Ma, L.; Yang, Z.; Chu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, S. A host basal transcription factor is a key component for infection of rice by TALE-carrying bacteria. Elife 2016, 5, e19605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Pérez-Quintero, A.L.; Wonni, I.; Carpenter, S.C.D.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Leach, J.E.; Verdier, V.; Cunnac, S.; Bogdanove, A.J.; et al. Functional analysis of African Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae TALomes reveals a new susceptibility gene in bacterial leaf blight of rice. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernadas, R.A.; Doyle, E.L.; Niño-Liu, D.O.; Wilkins, K.E.; Bancroft, T.; Wang, L.; Schmidt, C.L.; Caldo, R.; Yang, B.; White, F.F.; et al. Code-assisted discovery of TAL effector targets in bacterial leaf streak of rice reveals contrast with bacterial blight and a novel susceptibility gene. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Lin, X.; Poland, J.; Trick, H.; Leach, J.; Hulbert, S. A maize resistance gene functions against bacterial streak disease in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2005, 102, 15383–15388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Xu, M.R.; Zhao, M.F.; Xie, X.W.; Zhu, L.H.; Fu, B.Y.; Li, Z.K. Genome-wide gene responses in a transgenic rice line carrying the maize resistance gene Rxo1 to the rice bacterial streak pathogen, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, A.C.; Rinaldi, F.C.; Hutin, M.; He, Y.Q.; Triplett, L.R.; Bogdanove, A.J. Suppression of Xo1-Mediated Disease Resistance in Rice by a Truncated, Non-DNA-Binding TAL Effector of Xanthomonas oryzae. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triplett, L.R.; Cohen, S.P.; Heffelfinger, C.; Schmidt, C.L.; Huerta, A.I.; Tekete, C.; Verdier, V.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Leach, J.E. A resistance locus in the American heirloom rice variety Carolina Gold Select is triggered by TAL effectors with diverse predicted targets and is effective against African strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Plant J. 2016, 87, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, A.C.; Hutin, M.; Moscou, M.J.; Rinaldi, F.C.; Bogdanove, A.J. Cloning of the Rice Xo1 Resistance Gene and Interaction of the Xo1 Protein with the Defense-Suppressing Xanthomonas Effector Tal2h. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Q.; Hou, B.H.; Lalonde, S.; Takanaga, H.; Hartung, M.L.; Qu, X.Q.; Guo, W.J.; Kim, J.G.; Underwood, W.; Chaudhuri, B.; et al. Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 2010, 468, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. Characterization of Xanthomonas oryzae-responsive cis-acting element in the promoter of rice race-specific susceptibility gene Xa13. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanvillain-Baufumé, S.; Reschke, M.; Solé, M.; Auguy, F.; Doucoure, H.; Szurek, B.; Meynard, D.; Portefaix, M.; Cunnac, S.; Guiderdoni, E.; et al. Targeted promoter editing for rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae reveals differential activities for SWEET14-inducing TAL effectors. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. A paralog of the MtN3/saliva family recessively confers race-specific resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. Plant Cell Env. 2011, 34, 1958–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Yuan, M.; Yao, J.; Ge, X.; Yuan, B.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Fu, B.; Li, Z.; Bennetzen, J.L.; et al. Promoter mutations of an essential gene for pollen development result in disease resistance in rice. Genes. Dev. 2006, 20, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zou, L.; Zhiyuan, J.I.; Xiameng, X.U.; Zhengyin, X.U.; Yang, Y.; Alfano, J.R.; Chen, G. Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae TALE proteins recruit OsTFIIAγ1 to compensate for the absence of OsTFIIAγ5 in bacterial blight in rice. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 2248–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, Z.; Ma, W.; Haq, F.; Li, Y.; Shah, S.M.A.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, C.; Zou, L.; Chen, G. TALE-triggered and iTALE-suppressed Xa1-mediated resistance to bacterial blight is independent of rice transcription factor subunits OsTFIIAγ1 or OsTFIIAγ5. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 3249–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Chen, Z.; Cao, J.; Guan, H.; Lin, D.; Li, C.; Lan, T.; Duan, Y.; Mao, D.; Wu, W. Toward the positional cloning of qBlsr5a, a QTL underlying resistance to bacterial leaf streak, using overlapping sub-CSSLs in rice. PLoS One 2014, 9, e95751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, H.; Kim, C.Y.; Jeon, J.S.; Lee, B.M.; Sun Moon, J.; Hwang, I. Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae type III effector XopN targets OsVOZ2 and a putative thiamine synthase as a virulence factor in rice. PLoS One 2013, 8, e73346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.-X.; Li, J.-Y.; Mo, X.-Y.; Ni, Z.; Jiang, W.; He, Y.-Q.; Huang, S. Type III effectors xopN and avrBS2 contribute to the virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola strain GX01. Res. Microbiol. 2020, 171, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Fan, F.; Tan, Z.; Zou, Y.; Lu, D. A Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae effector, XopR, associates with receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases and suppresses PAMP-triggered stomatal closure. Sci. China Life Sci. 2016, 59, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Yamada, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Yoshimura, S.; Hayashi, N.; Uchihashi, K.; Ishihama, N.; Kishi-Kaboshi, M.; Takahashi, A.; Tsuge, S.; et al. A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase targeted by a plant pathogen effector is directly phosphorylated by the chitin receptor and mediates rice immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Ishikawa, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Tsuge, S.; Kawasaki, T. Suppression of rice immunity by Xanthomonas oryzae type III effector Xoo2875. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Zhou, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, K.; Yang, F.; Liao, H.; Rong, W.; Yin, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; et al. The Xanthomonas effector XopK harbours E3 ubiquitin-ligase activity that is required for virulence. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sakamoto, K.; Yoshimura, S.; Inoue, K.; Tsuge, S.; Kojima, C.; Kawasaki, T. Bacterial effector modulation of host E3 ligase activity suppresses PAMP-triggered immunity in rice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Xu, X.; Cai, L.; Cao, Y.; Haq, F.; Alfano, J.R.; Zhu, B.; Zou, L.; Chen, G. A Xanthomonas oryzae type III effector XopL causes cell death through mediating ferredoxin degradation in Nicotiana benthamiana. Phytopathol. Res. 2020, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D. XopZ and ORP1C cooperate to regulate the virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae on Nipponbare. Plant Signal Behav. 2022, 17, 2035126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O.; Kopka, J.; Dörmann, P.; Altmann, T.; Trethewey, R.N.; Willmitzer, L. Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, D.; Ewing, R.; Gollub, J.; Sterky, F.; Cherry, J.M.; Somerville, S. Microarray data quality analysis: Lessons from the AFGC project. Arabidopsis Functional Genomics Consortium. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henikoff, S.; Comai, L. Single-nucleotide mutations for plant functional genomics. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 375–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, T.R.; Fischer, S.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Katrekar, A.; Jung, K.H.; Ronald, P.C.; Fiehn, O. Metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis of the rice response to the bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Fu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Liang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Long, Y.; et al. Genome-wide association mapping for resistance to bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak in rice. Planta 2021, 253, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wang, C.; Zeng, D.; Li, J.; Shi, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, Y. Genome-Wide Association Study Dissects Resistance Loci against Bacterial Blight in a Diverse Rice Panel from the 3000 Rice Genomes Project. Rice 2021, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wu, Z.C.; Wang, M.M.; Zhang, F.; Dingkuhn, M.; Xu, J.L.; Zhou, Y.L.; Li, Z.K. Genome-wide association analysis identifies resistance loci for bacterial blight in a diverse collection of indica rice germplasm. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0174598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, K.; Lou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, F. Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Provide Novel Insights into the Crucial Roles of Host-Induced Carbohydrate Metabolism Enzymes in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Virulence and Rice-Xoo Interaction. Rice 2021, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qian, G.; Yin, F.; Fan, J.; Zhai, Z.; Liu, C.; Hu, B.; Liu, F. Proteomic analysis of the regulatory function of DSF-dependent quorum sensing in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Microb. Pathog. 2011, 50, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, F.; Huang, L.; Zeng, D.; Cruz, C.V.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y. Comparative proteomic analysis reveals novel insights into the interaction between rice and Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Mao, S.; Wu, T.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Chu, Z. Comparative transcriptomic profiling of the two-stage response of rice to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola interaction with two different pathogenic strains. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Das, A.; Saikia, K.; Barah, P. Temperature differentially modulates the transcriptome response in Oryza sativa to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae infection. Genomics 2020, 112, 4842–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.P.; Kumar, A.; Mohammed, M.; Bhati, K.; Babu, K.R.; Bhandari, K.P.; Sundaram, R.M.; Ghazi, I.A. Comparative metabolites analysis of resistant, susceptible and wild rice species in response to bacterial blight disease. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Mo, Q.; Sun, B.; Mao, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Lv, S.; et al. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Rice Cultivar CBB23 after Inoculation by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Strains AH28 and PXO99(A). Plants 2024, 13, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, K.T.X.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Trinh, K.T.T.; Kim, S.T.; Jeon, J.S. Proteomics and Metabolomics Studies on the Biotic Stress Responses of Rice: An Update. Rice 2021, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, M.; Kliebenstein, D.J. Plant Secondary Metabolites as Defenses, Regulators, and Primary Metabolites: The Blurred Functional Trichotomy. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, M. Volatiles as inducers and suppressors of plant defense and immunity-origins, specificity, perception and signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 44, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwmeester, H.; Schuurink, R.C.; Bleeker, P.M.; Schiestl, F. The role of volatiles in plant communication. Plant J. 2019, 100, 892–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, H.; Yang, P. Plant secondary metabolites-mediated plant defense against bacteria and fungi pathogens. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 217, 109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, J.; Liang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; et al. Research Progress on Cloning and Function of Xa Genes Against Rice Bacterial Blight. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 847199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yang, C.; Ji, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Li, G.; E, Z. Complete Genomic Sequence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Strain, LA20, for Studying Resurgence of Rice Bacterial Blight in the Yangtze River Region, China. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q.J.; Yang, B. High-efficiency prime editing enables new strategies for broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight of rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Liu, B.; Raza, S.; Chen, Q.-J.; Yang, B. Modularly assembled multiplex prime editors for simultaneous editing of agronomically important genes in rice. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Cao, Y.; Jin, X.; Fu, Z.; Li, J.; Mo, X.; He, Y.; Tang, J.; Huang, S. Engineering Resistance to Bacterial Blight and Bacterial Leaf Streak in Rice. Rice 2021, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duy, P.N.; Lan, D.T.; Pham Thu, H.; Thi Thu, H.P.; Nguyen Thanh, H.; Pham, N.P.; Auguy, F.; Bui Thi Thu, H.; Manh, T.B.; Cunnac, S.; et al. Improved bacterial leaf blight disease resistance in the major elite Vietnamese rice cultivar TBR225 via editing of the OsSWEET14 promoter. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0255470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Römer, P.; Jordan, T.; Lahaye, T. Identification and application of a DNA-based marker that is diagnostic for the pepper (Capsicum annuum) bacterial spot resistance gene Bs3. Plant Breed. 2010, 129, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; He, N.; Yu, M.; Li, D.; Yang, D. Identification and fine mapping of a new bacterial blight resistance gene, Xa43(t), in Zhangpu wild rice (Oryza rufipogon). Plant Biol. 2023, 25, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, A.W.; Doyle, E.L.; Bogdanove, A.J. Addition of transcription activator-like effector binding sites to a pathogen strain-specific rice bacterial blight resistance gene makes it effective against additional strains and against bacterial leaf streak. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Tian, D.; Gu, K.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, X.; Luo, Y.; White, F.F.; Yin, Z. Genetic engineering of the Xa10 promoter for broad-spectrum and durable resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; He, F.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, Y.L. Prediction of protein-protein interactions between Ralstonia solanacearum and Arabidopsis thaliana. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L. Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions Between Rice and Blast Fungus Using Structure-Based Approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 690124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, M.S.; Carvunis, A.R.; Dreze, M.; Epple, P.; Steinbrenner, J.; Moore, J.; Tasan, M.; Galli, M.; Hao, T.; Nishimura, M.T.; et al. Independently evolved virulence effectors converge onto hubs in a plant immune system network. Science 2011, 333, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weßling, R.; Epple, P.; Altmann, S.; He, Y.; Yang, L.; Henz, S.R.; McDonald, N.; Wiley, K.; Bader, K.C.; Gläßer, C.; et al. Convergent targeting of a common host protein-network by pathogen effectors from three kingdoms of life. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.Y.; Khan, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Mirmiran, A.; Moeder, W.; Lumba, S.; Yoshioka, K.; Desveaux, D. A host-pathogen interactome uncovers phytopathogenic strategies to manipulate plant ABA responses. Plant J. 2019, 100, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Tale-Targeted (R/S Gene) | Encoding Products | Matched TALEs | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Xa1 Xo1 Xa2/31 Xa14 Xa45 | NLR | Multiple TALEs, iTALEs/truncTALE | [19,30,33,40] |
| Xa7 | Executor | AvrXa7, PthXo3 | [37,41] | |
| Xa10 | Executor | AvrXa10 | [35] | |
| Xa23 | Executor | AvrXa23 | [42] | |
| Xa27 | executor | AvrXa27 | [34] | |
| xa13 | Sweet transporter | PthXo1 | [43] | |
| xa25 | Sweet transporter | PthXo2 | [44] | |
| xa41 | Sweet transporter | AvrXa7, PthXo3, Tal5, TalC | [45] | |
| xa5 | TFIIA transcription factor | AvrXa5, PthXo7 | [46,47,48] | |
| Susceptibility | OsSWEET11(Xa13/Os8N3) | Sweet transporter | PthXo1 | [49] |
| OsSWEET14(Xa41/Os11N3) | Sweet transporter | AvrXa7, PthXo3, TalC, Tal5 | [50,51,52] | |
| OsSWEET13(Xa25/Os12N3) | Sweet transporter | PthXo2 | [44,53] | |
| OsSWEET12 | Sweet transporter | ArtTAL12 | [52] | |
| OsSWEET15 | Sweet transporter | ArtTAL15 | [52] | |
| OsTFIIAγ5 | Gamma subunit of rice basal transcription factor | Multiple TALEs | [54] | |
| OsTFIIAγ1 | Gamma subunit of rice basal transcription factor | PthXo7 | [46] | |
| OsTFX1 | bZIP transcription factor | PthXo6 TalBMAl1 | [46,55] | |
| OsERF#123 | AP2/ERF transcription factor | TalBMAl1 | [55] | |
| OsSULTR3;6 | Sulfate transporter | Tal2g | [56] | |
| Rice Genes (Interaction Genes) | Encoding Products | Matched TALEs | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| OsVOZ2, OsXNP |
Vascular plant one zinc finger protein 2, putative thiamine synthase | XopN | [27,70,71] |
| OsBIK1 | Receptor-like kinases | XopR | [72] |
| OsRLCK185 | Receptor-like kinase | XopY | [73] |
| OsBAK1 | Receptor-like kinase | XopAA | [74] |
| OsSERK2 | Somatic embryogenic receptor kinase 2 | XopK | [75] |
| OsPUB44 | Ubiquitin E3 ligase | XopP | [76] |
| NbFd | Ferredoxin protein | XopL | [77] |
| OsORP1C | Oxysterol-binding related protein | XopZ | [78] |
| Omics | Rice Varieties | Xanthomonas oryzae | Main Conclusion | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genomics | 895 accessions from the 3K RGP | Xoo Xoc | 7 and 77 loci linked to resistance for Xoo and Xoc, respectively, were identified | [83] |
| Genomics | 340 accessions from the 3K RGP | Xoo | 11 loci linked to resistance against Xoo were identified | [84] |
| Genomics | 172 indica rice | Xoo | Chromosomes 11 and 12 were important for the evolution of rice resistance for Xoo | [85] |
| Proteomics | IR24 | Xoo | Carbohydrate-metabolizing enzymes play a key roles in rice–Xoo interactions | [86] |
| Proteomics | Shanyou63 | Xoc | DSF may play an important role in Xoc virulence and growth | [87] |
| Proteomics | H471 and HHZ | Xoo | Phytoalexin and SA signaling pathways were activated faster in the incompatible interaction than in the compatible interaction | [88] |
| Transcriptomics | ZH11 | Xoc | Early PTI: conserved DEGs drive basal defense; Late ETI/ETS: TALE targets and specialized DR genes prevail | [89] |
| Transcriptomics | IR24 | Xoo | The ΔxanA and Δimp mutants dysregulated photosynthesis, redox balance, and secondary metabolism | [86] |
| Transcriptomics | IR24 | Xoo | Rice plants tend to shift their focus from defensive responses to growth and reproduction at high temperatures | [90] |
| Metabolomics | IRBB27, Oryza minuta - CG154 , IR24 | Xoo | Key metabolites such as flavonoids, terpenes, and phenolic compounds showed significantly higher levels in resistant varieties | [91] |
| Metabolomics | CBB23 | Xoo | Metabolites such as alkaloids and amino acid were involved in rice defense against Xoo | [92] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Rao, Q.; Lu, C.; Gong, J.; Hou, Y. Recent Progress in Rice–Xanthomonas oryzae Interactions. Biology 2025, 14, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050471
Qi Y, Rao Q, Lu C, Gong J, Hou Y. Recent Progress in Rice–Xanthomonas oryzae Interactions. Biology. 2025; 14(5):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050471
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yuting, Qiong Rao, Chenglong Lu, Junyi Gong, and Yuxuan Hou. 2025. "Recent Progress in Rice–Xanthomonas oryzae Interactions" Biology 14, no. 5: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050471
APA StyleQi, Y., Rao, Q., Lu, C., Gong, J., & Hou, Y. (2025). Recent Progress in Rice–Xanthomonas oryzae Interactions. Biology, 14(5), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050471







