Bactericidal Effect and Mechanism of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB) on Pathogenic Bacteria in Marine Aquaculture
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Bacteria
2.3. Bacterial Solution Preparation
2.4. Determination of MIC and MBC
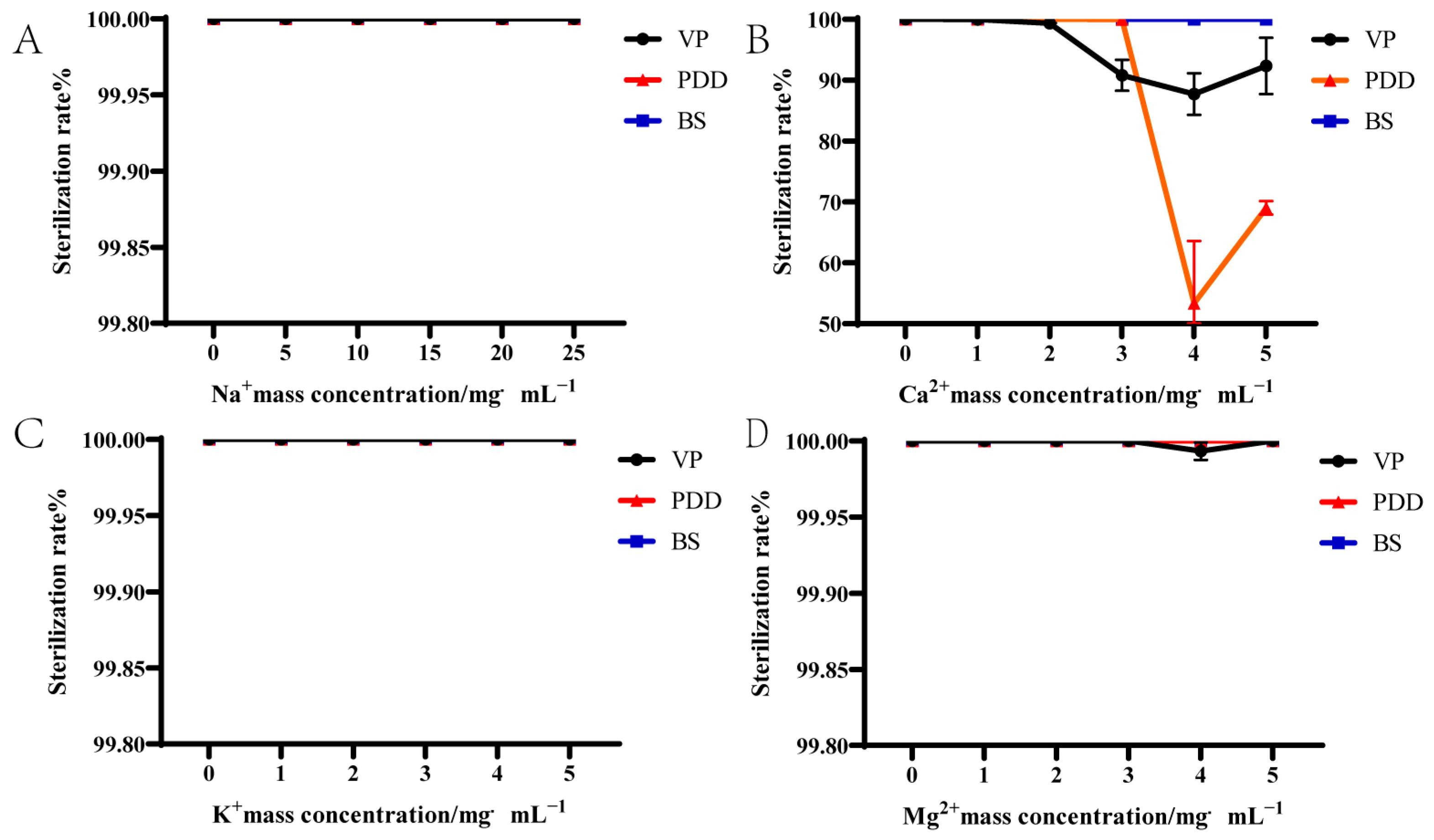
2.5. The Effect of Metal Ion Concentrations on the Bactericidal Activity of PHMB
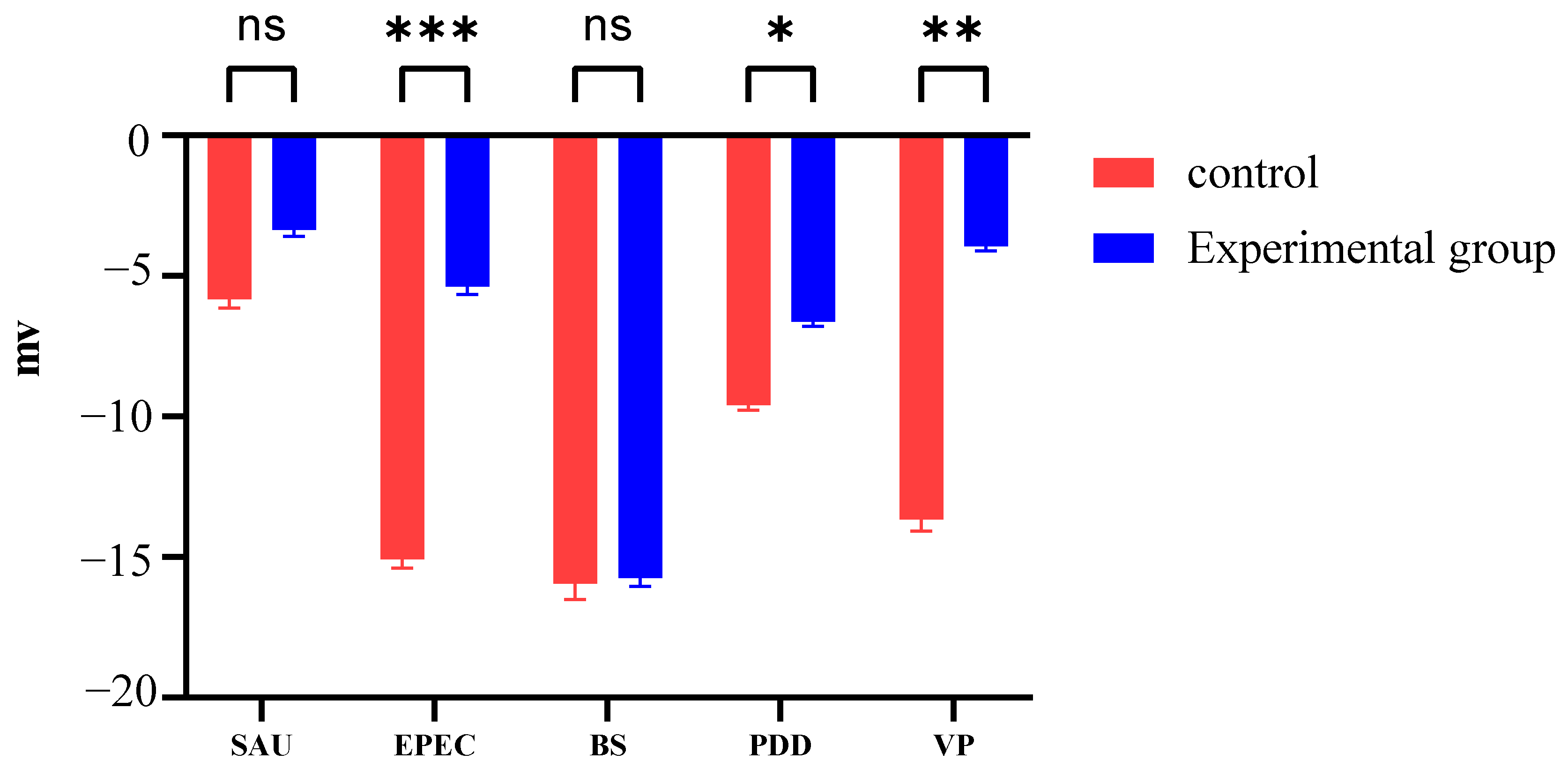
2.6. Zeta Potential Measurement
2.7. Propidium Iodide (PI) Staining Experiments
2.8. SEM Observation
2.9. Effect of PHMB on DNA and RNA Leakage
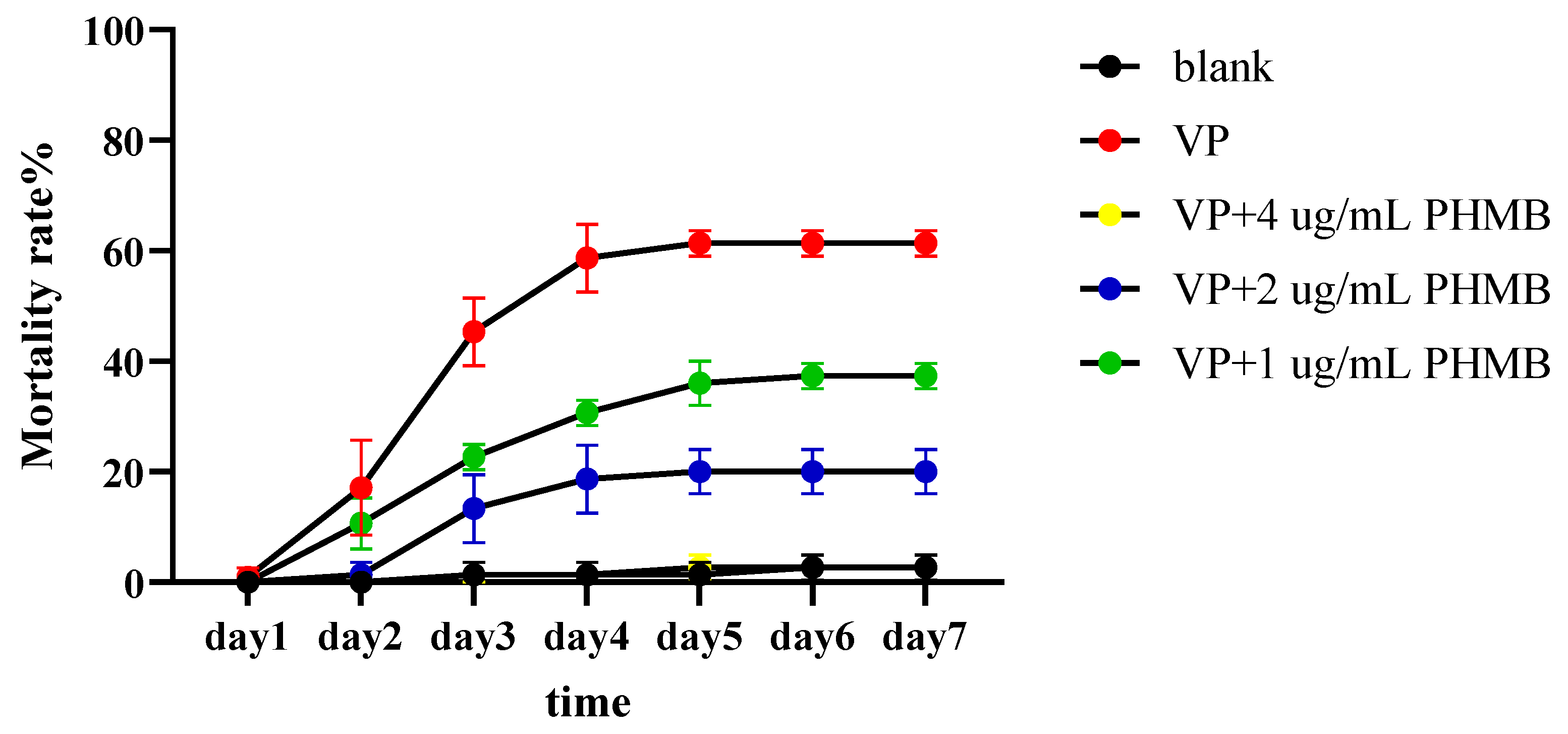
2.10. The Prevention Effect of PHMB on Litopenaeus vannamei
3. Results
3.1. Determination of MIC and MBC for Different Bacteria
3.2. Effect of Ions on the Bactericidal Activity of PHMB
3.3. Zeta Potential Changes Induced by PHMB
3.4. PI Staining
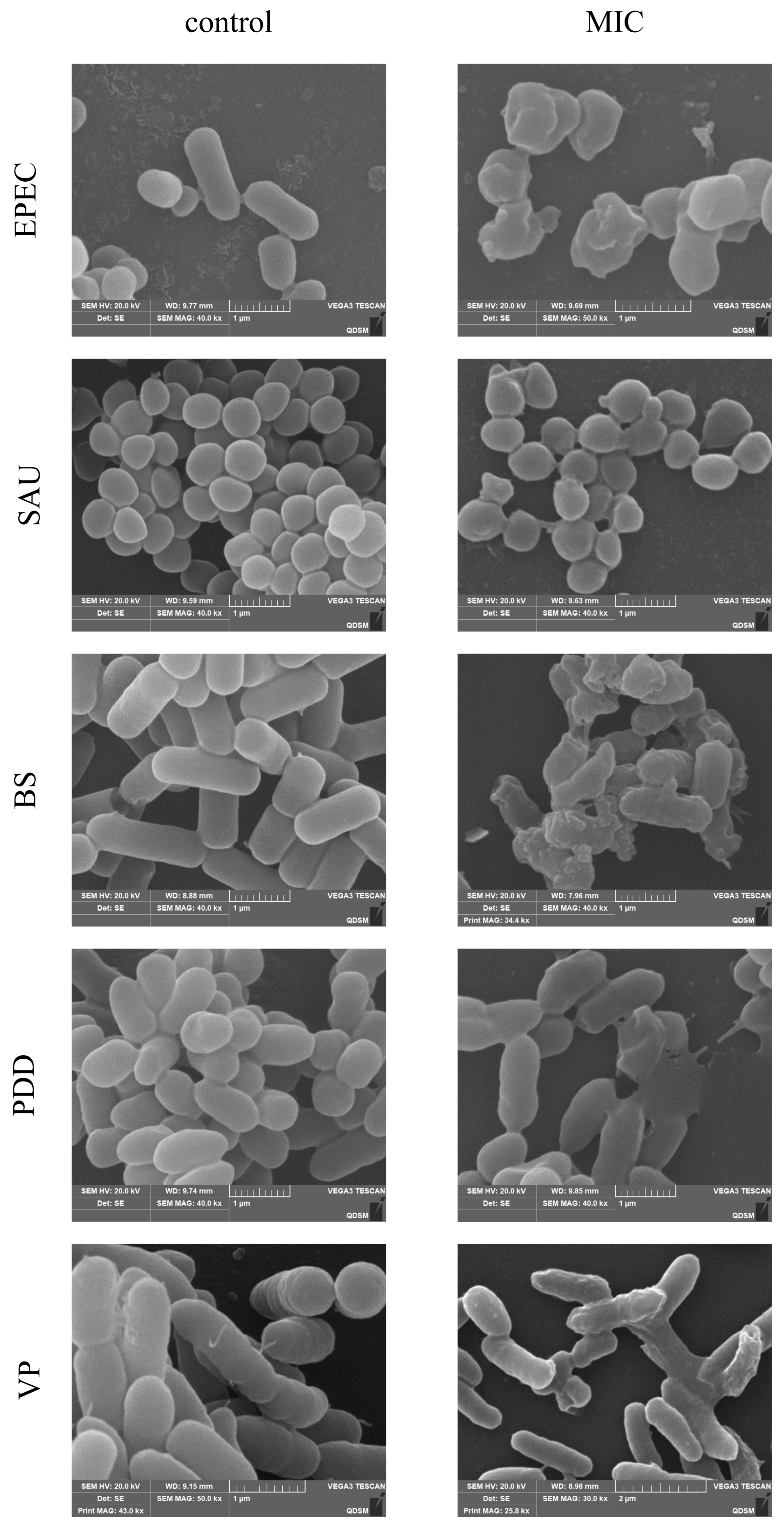
3.5. SEM Observation of Cell Morphology
3.6. DNA and RNA Leakage
3.7. The Prevention Experiment of PHMB on L. vannamei
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, K.; Xie, F.; Zhao, Q. Screening and identification of lactic acid bacteria with antimicrobial abilities for aquaculture pathogens in vitro. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 0302–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laktuka, K.; Kalnbalkite, A.; Sniega, L.; Logins, K.; Lauka, D. Towards the Sustainable Intensification of Aquaculture: Exploring Possible Ways Forward. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Soliman, A.A.; Sewilam, H.; Almeer, R.; Van Doan, H.; Alagawany, M.; Dawood, M.A.O. The influence of raffinose on the growth performance, oxidative status, and immunity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Jung, K.J.; Yoon, S.-j.; Lee, K.; Kim, B. Polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate induces cytotoxicity through disruption of membrane integrity. Toxicology 2019, 414, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, S. Sixty years from the discovery of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and some recollections. Biocontrol Sci. 2011, 16, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroyanagi, Y.; Tsuchiya, J.; Jiang, C.; Mino, S.; Kasai, H.; Motooka, D.; Iida, T.; Satomi, M.; Sawabe, T. Light response of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1037594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, X.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zu, Y.; Li, W. Zebrafish as a useful model for zoonotic Vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenicity in fish and human. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 55, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, A.J.; Lemos, M.L.; Osorio, C.R. Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae, a bacterium pathogenic for marine animals and humans. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Multifaceted applications of probiotic Bacillus species in aquaculture with special reference to Bacillus subtilis. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 13, 862–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, S.; Hill, C.; Johansen, E.; Obis, D.; Pot, B.; Sanders, M.E.; Tremblay, A.; Ouwehand, A.C. Criteria to Qualify Microorganisms as “Probiotic” in Foods and Dietary Supplements. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.; Caudal, F.; Taupin, L.; Dufour, A.; Le Ker, C.; Giudicelli, F.; Rodrigues, S.; Bazire, A. Antibiofilm Activity of the Marine Probiotic Bacillus subtilis C3 Against the Aquaculture-Relevant Pathogen Vibrio harveyi. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 11, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.-Z.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Probiotics as Means of Diseases Control in Aquaculture, a Review of Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Ma, L.Z. Effect of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide in Combination with Undecylenamidopropyl Betaine or PslG on Biofilm Clearance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Yang, Q.; Wang, H.; Xie, G.; Cao, Z.; Chen, X.; Gao, W.; Huang, J. In vitro disinfection efficacy and clinical protective effects of common disinfectants against acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND)-causing Vibrio isolates in Pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei. J. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, L.; Matrella, S.; Mella, M.; Benvenuto, G.; Vigliotta, G. Escherichia coli as a Model for the Description of the Antimicrobial Mechanism of a Cationic Polymer Surface: Cellular Target and Bacterial Contrast Response. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15332–15343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, A.; Weeks, R.M.; Chikindas, M.; Uhrich, K.E. Cationic Amphiphiles with Specificity against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria: Chemical Composition and Architecture Combat Bacterial Membranes. Langmuir 2019, 35, 5557–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.-X.; Ooi, C.W.; Liu, B.-L.; Song, C.P.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-K. Antibacterial efficacy of poly(hexamethylene biguanide) immobilized on chitosan/dye-modified nanofiber membranes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowlati-Hashjin, S.; Carbone, P.; Karttunen, M. Insights into the Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB) Mechanism of Action on Bacterial Membrane and DNA: A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 4487–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liao, M.; Li, B.; Rong, X.; Wang, C.; Ge, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. The Genetic and Phenotypic Diversity of Bacillus spp. from the Mariculture System in China and Their Potential Function against Pathogenic. Vibrio. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Sun, Q.; Meng, J.; Xu, J.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, O.; Liu, S.; Sun, Q. Mechanism of inactivation of Pseudomonas fluorescens by plasma-activated water based on active substances. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 96, 103764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Abreu, A.C.; Ferreira, C.; Saavedra, M.J.; Simões, L.C.; Simões, M. Antibacterial activity and mode of action of selected glucosinolate hydrolysis products against bacterial pathogens. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 52, 4737–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S. Potent in vitro and in vivo antimicrobial activity of semisynthetic amphiphilic γ-mangostin derivative LS02 against Gram-positive bacteria with destructive effect on bacterial membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Ye, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, D. Exploring the antibacterial mechanism of essential oils by membrane permeability, apoptosis and biofilm formation combination with proteomics analysis against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 310, 151435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.; De Melo Carrasco, L. Cationic Antimicrobial Polymers and Their Assemblies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9906–9946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiwala, R.; Sharma, P.; Ganapathy Ayappa, K. Differentiating interactions of antimicrobials with Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cell walls using molecular dynamics simulations. Biointerphases 2022, 17, 061008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-J. Assessment of sulfonation in cornstalk for adsorption of metal-ions from seawater. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischler, A.H.; Vanek, M.E.; Peterson, N.; Visick, K.L. Calcium-Responsive Diguanylate Cyclase CasA Drives Cellulose-Dependent Biofilm Formation and Inhibits Motility in Vibrio fischeri. mBio 2021, 12, e0257321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, R. The effect of environmental calcium on gene expression, biofilm formation and virulence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Le, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Ren, L.; Lin, L.; Cui, S.; Hu, J.J.; Hu, Y.; et al. Targeting Negative Surface Charges of Cancer Cells by Multifunctional Nanoprobes. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulrajah, B.; Qoms, M.S.; Muhialdin, B.J.; Meor Hussin, A.S.; Hasan, H.; Zarei, M.; Chau, D.-M.; Ramasamy, R.; Saari, N. Elucidating the mechanisms underlying the action of kenaf seed peptides mixture against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and its efficacy in whole milk preservation. LWT 2023, 181, 114757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.-Q.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.-X. Synergistic effects of endolysin Lysqdvp001 and ε-poly-lysine in controlling Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its biofilms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 343, 109112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkowski, A.; Kowalczyk, P.; Czerwonka, G.; Cieśla, J.; Cłapa, T.; Misiewicz, A.; Szala, M.; Drabik, M. Interaction of quaternary ammonium ionic liquids with bacterial membranes—Studies with Escherichia coli R1–R4-type lipopolysaccharides. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 246, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Azevedo, N.F.; Ivask, A. Propidium iodide staining underestimates viability of adherent bacterial cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2045–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitina, E.V.; Zeldi, M.I.; Pugachev, M.V.; Sapozhnikov, S.V.; Shtyrlin, N.V.; Kuznetsova, S.V.; Evtygin, V.E.; Bogachev, M.I.; Kayumov, A.R.; Shtyrlin, Y.G. Antibacterial effects of quaternary bis-phosphonium and ammonium salts of pyridoxine on Staphylococcus aureus cells: A single base hitting two distinct targets? World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Berditsch, M.; Hawecker, J.; Ardakani, M.F.; Gerthsen, D.; Ulrich, A.S. Damage of the Bacterial Cell Envelope by Antimicrobial Peptides Gramicidin S and PGLa as Revealed by Transmission and Scanning Electron Microscopy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3132–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam-Koong, H.; Schroeder, J.P.; Petrick, G.; Schulz, C. Preliminary test of ultrasonically disinfection efficacy towards selected aquaculture pathogens. Aquaculture 2020, 515, 734592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, T.G.; Kamilya, D. Paraprobiotics: An aquaculture perspective. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 11, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; White, G.F.; Morby, A.P. The response of Escherichia coli to exposure to the biocide polyhexamethylene biguanide. Microbiology 2006, 152, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; Morby, A.P.; White, G.F. Cooperativity in the binding of the cationic biocide polyhexamethylene biguanide to nucleic acids. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 318, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawęda, S.; Morán, M.C.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Dias, R.S.; Schillén, K.; Lindman, B.; Miguel, M.G. Cationic agents for DNA compaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Bloomfield, V.A. Condensation of supercoiled DNA induced by MnCl2. Biophys. J. 1994, 67, 1678–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, L.J.C.; Annes, K.; Milazzotto, M.P.; Mattei, B.; Riske, K.A.; Jäger, E.; Pánek, J.; Štěpánek, P.; Kapusta, P.; Muraro, P.I.R.; et al. Efficient Condensation of DNA into Environmentally Responsive Polyplexes Produced from Block Catiomers Carrying Amine or Diamine Groups. Langmuir 2016, 32, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, L.; van Eijk, M.C.P.; Söderman, O. Compaction of DNA by Gemini Surfactants: Effects of Surfactant Architecture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 252, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, M.; López-Cornejo, P.; Martín, V.I.; Ostos, F.J.; Checa-Rodríguez, C.; Prados-Carvajal, R.; Lebrón, J.A.; Huertas, P.; Moyá, M.L. Importance of hydrophobic interactions in the single-chained cationic surfactant-DNA complexation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 521, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, W.; Boyer, I.; Zhu, J.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; et al. Safety Assessment of Polyaminopropyl Biguanide (Polyhexamethylene Biguanide Hydrochloride) as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2020, 39, 26S–73S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippon, M.G.; Daly, K.; Rogers, A.A.; Westgate, S. Safety and effectiveness of an antiseptic wound cleansing and irrigation solution containing polyhexamethylene biguanide. J. Wound Care 2024, 33, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, F.; Li, J. Safety studies of polyhexamethylenebiguanide on shrimp Penaeus vannamei at different growth stages and bait algae. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2009, 28, 597–601. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sengar, A.; Vijayanandan, A. Comprehensive review on iodinated X-ray contrast media: Complete fate, occurrence, and formation of disinfection byproducts. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Chen, Z.; Yao, M.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Ma, L.; Mo, J.; Lin, L.; Qin, Z. Effects of glutaraldehyde and povidone-iodine on apoptosis of grass carp liver and hepatocytes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 272, 116078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougin, J.; Midelet, G.; Leterme, S.; Best, G.; Ells, T.; Joyce, A.; Whiley, H.; Brauge, T. Benzalkonium chloride disinfectant residues stimulate biofilm formation and increase survival of Vibrio bacterial pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1309032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, P.A.; Machado, I.; Meireles, A.; Leiknes, T.; Mergulhão, F.; Melo, L.F.; Simões, M. Combination of selected enzymes with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide in biofilm inactivation, removal and regrowth. Food Res. Int. 2017, 95, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Bacteria † | MIC (µg/mL) | MBC (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| EPEC | 31.25 | 31.25 |
| SAU | 125.00 | 250.00 |
| BS ‡ | 7.81 | 62.50 |
| PDD ± | 3.91 | 15.63 |
| VP ± | 7.81 | 15.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, C.; Rong, X.; Chen, L.; Liao, M.; Yang, Y. Bactericidal Effect and Mechanism of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB) on Pathogenic Bacteria in Marine Aquaculture. Biology 2025, 14, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050470
Wu L, Wang C, Wang Y, Yu Y, Zhang Z, Ma C, Rong X, Chen L, Liao M, Yang Y. Bactericidal Effect and Mechanism of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB) on Pathogenic Bacteria in Marine Aquaculture. Biology. 2025; 14(5):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050470
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Lanting, Chunyuan Wang, Yingeng Wang, Yongxiang Yu, Zheng Zhang, Cuiping Ma, Xiaojun Rong, Ling Chen, Meijie Liao, and Yapeng Yang. 2025. "Bactericidal Effect and Mechanism of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB) on Pathogenic Bacteria in Marine Aquaculture" Biology 14, no. 5: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050470
APA StyleWu, L., Wang, C., Wang, Y., Yu, Y., Zhang, Z., Ma, C., Rong, X., Chen, L., Liao, M., & Yang, Y. (2025). Bactericidal Effect and Mechanism of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB) on Pathogenic Bacteria in Marine Aquaculture. Biology, 14(5), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050470





