Novel Insights and Genomic Characterization of Coral-Associated Microorganisms from Maldives Displaying Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and UV-Protectant Activities
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
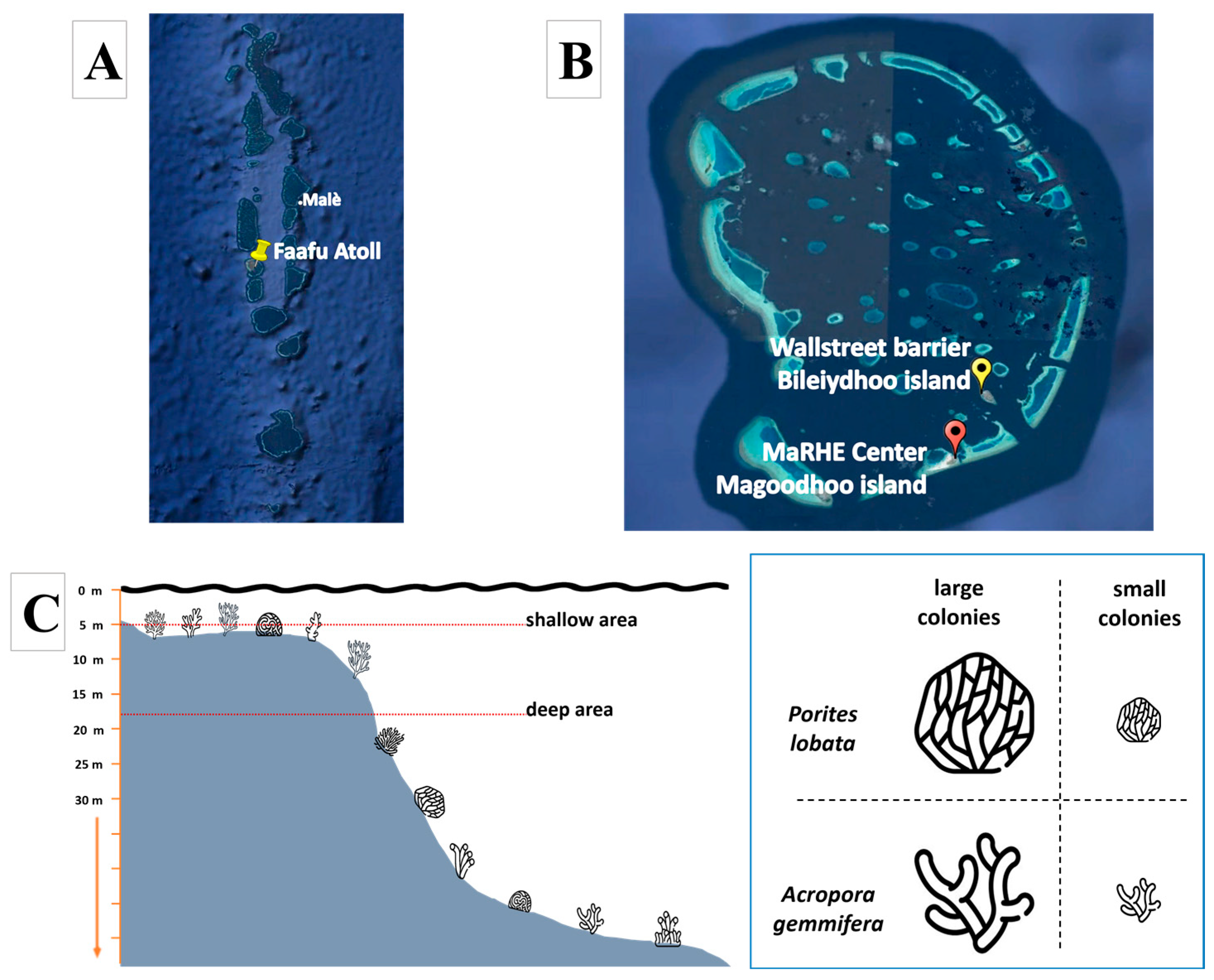
2.1. Sampling Site and Coral Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Microbial Community Characterization
2.4. Bacterial Isolation and Preliminary Molecular Identification
2.5. Bacterial Cultivation and Extraction
2.6. Functional Screening of Extracts from the Isolated Strains
2.6.1. Antimicrobial Assay
2.6.2. DPPH Assay
2.6.3. ABTS Assay
2.6.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity and UV-Screen Assay
2.6.5. Whole Genome Sequencing and Annotation
3. Results
3.1. Comparative Analysis and Isolation of Coral-Associated Microorganisms
3.2. Bioactivity Evaluation
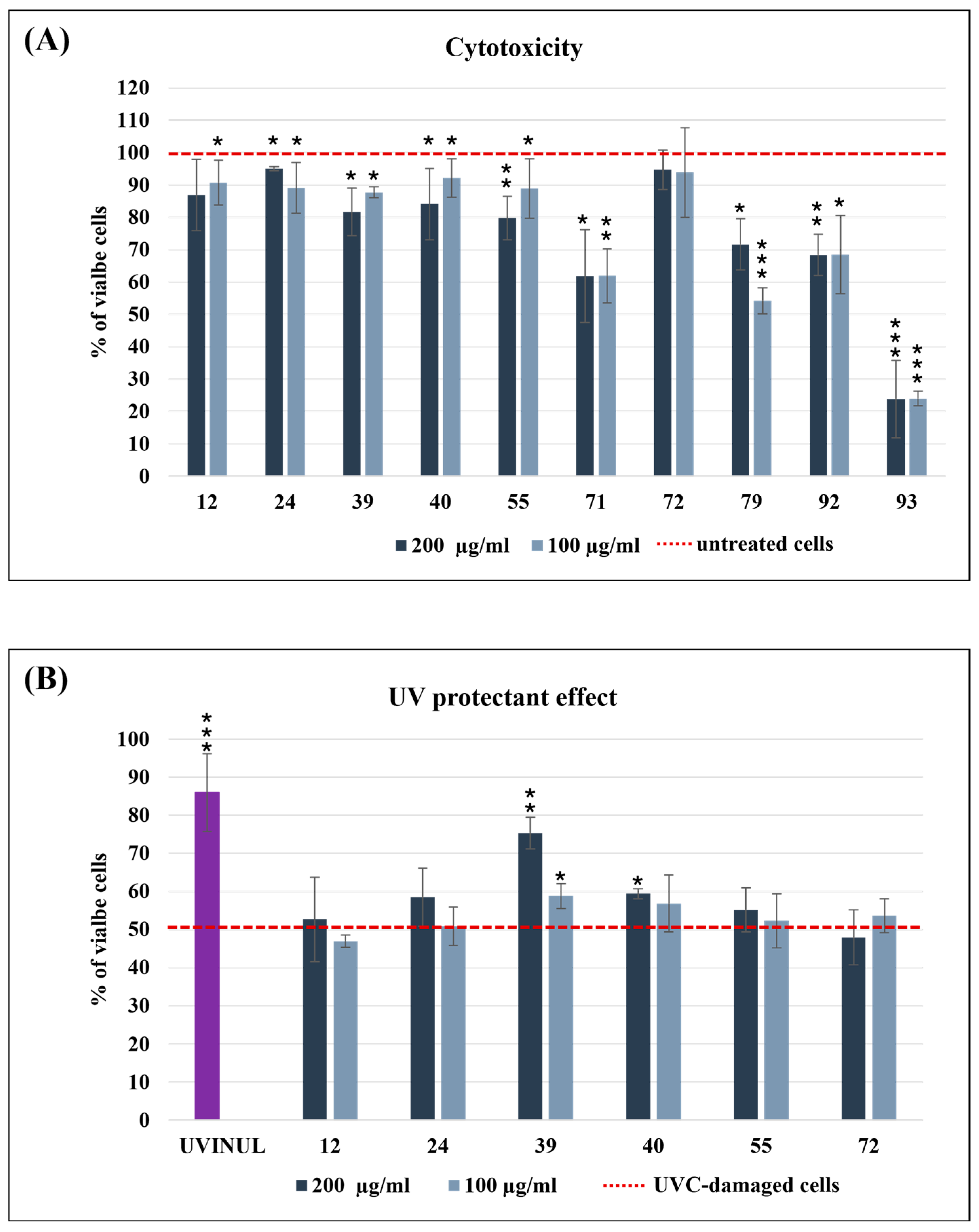
3.2.1. Antimicrobial Activity
3.2.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.2.3. UV Protectant Effect
3.3. Genome-Based Identification, Genome Annotation, and Biosynthetic Potential Analysis of Selected Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sobha, T.; Vibija, C.; Fahima, P. Coral Reef: A Hot Spot of Marine Biodiversity. In Conservation and Sustainable Utilization of Bioresources; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2023; pp. 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmi, N.; Basu, R.; Crisóstomo, M.; Lebleu, L.; Claudet, J.; Seveso, D. The pressures and opportunities for coral reef preservation and restoration in the Maldives. Front. Environ. Econ. 2023, 2, 1110214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodapp, D.; Roca, I.T.; Fiorentino, D.; Garilao, C.; Kaschner, K.; Kesner-Reyes, K.; Schneider, B.; Segschneider, J.; Kocsis, A.T.; Kiessling, W.; et al. Climate change disrupts core habitats of marine species. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 3304–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, C.; Seveso, D.; De Grandis, C.; Montalbetti, E.; Lancini, S.; Galli, P.; Villa, S. Bioconcentration and cellular effects of emerging contaminants in sponges from Maldivian coral reefs: A managing tool for sustainable tourism. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbetti, E.; Fallati, L.; Casartelli, M.; Maggioni, D.; Montano, S.; Galli, P.; Seveso, D. Reef complexity influences distribution and habitat choice of the corallivorous seastar Culcita schmideliana in the Maldives. Coral Reefs 2022, 41, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strona, G.; Lafferty, K.D.; Fattorini, S.; Beck, P.S.A.; Guilhaumon, F.; Arrigoni, R.; Montano, S.; Seveso, D.; Galli, P.; Planes, S.; et al. Global tropical reef fish richness could decline by around half if corals are lost. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20210274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isa, V.; Seveso, D.; Diamante, L.; Montalbetti, E.; Montano, S.; Gobbato, J.; Lavorano, S.; Galli, P.; Louis, Y.D. Physical and cellular impact of environmentally relevant microplastic exposure on thermally challenged Pocillopora damicornis (Cnidaria, Scleractinia). Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 918, 170651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bises, C.; Dehnert, I.; Aeby, G.; Dennis, M.; Gobbato, J.; Hodge, J.; Staiger, M.; Siena, F.; Galli, P.; Montano, S. Widespread Occurrence of Coral Growth Anomalies in the Republic of Maldives. Diversity 2024, 16, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Contardi, M.; Fadda, M.; Isa, V.; Louis, Y.D.; Madaschi, A.; Vencato, S.; Montalbetti, E.; Bertolacci, L.; Ceseracciu, L.; Seveso, D.; et al. Biodegradable Zein-Based Biocomposite Films for Underwater Delivery of Curcumin Reduce Thermal Stress Effects in Corals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 33916–33931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehnert, I.; Saponari, L.; Isa, V.; Seveso, D.; Galli, P.; Montano, S. Exploring the performance of mid-water lagoon nurseries for coral restoration in the Maldives. Restor. Ecol. 2022, 30, e13600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnert, I.; Galli, P.; Montano, S. Ecological impacts of coral gardening outplanting in the Maldives. Restor. Ecol. 2023, 31, e13783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M.J.; Bulling, M.T. On the Importance of the Microbiome and Pathobiome in Coral Health and Disease. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaJeunesse, T.C.; Parkinson, J.E.; Gabrielson, P.W.; Jeong, H.J.; Reimer, J.D.; Voolstra, C.R.; Santos, S.R. Systematic Revision of Symbiodiniaceae Highlights the Antiquity and Diversity of Coral Endosymbionts. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2570–2580.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanwonterghem, I.; Webster, N.S. Coral Reef Microorganisms in a Changing Climate. iScience 2020, 23, 100972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohwer, F.; Seguritan, V.; Azam, F.; Knowlton, N. Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 243, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, N.; Rohwer, F. Multispecies microbial mutualisms on coral reefs: The host as a habitat. Am. Nat. 2003, 162 (Suppl. S4), S51–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, N.S.; Reusch, T.B.H. Microbial contributions to the persistence of coral reefs. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggett, M.J.; Apprill, A. Coral microbiome database: Integration of sequences reveals high diversity and relatedness of coral-associated microbes. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 11, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krediet, C.J.; Ritchie, K.B.; Paul, V.J.; Teplitski, M. Coral-associated micro-organisms and their roles in promoting coral health and thwarting diseases. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20122328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.R.; Ochsenkuhn, M.A.; Kazlak, A.M.; Moustafa, A.; Amin, S.A. The coral microbiome: Towards an understanding of the molecular mechanisms of coral-microbiota interactions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Koren, O.; Reshef, L.; Efrony, R.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Morrow, K.M.; Webster, N.S. Insights into the Coral Microbiome: Underpinning the Health and Resilience of Reef Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 70, 317–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shnit-Orland, M.; Kushmaro, A. Coral mucus-associated bacteria: A possible first line of defense. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, R.S.; Rosado, P.M.; Leite, D.C.; Rosado, A.S.; Bourne, D.G. Beneficial Microorganisms for Corals (BMC): Proposed Mechanisms for Coral Health and Resilience. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, E.P.; Borges, R.M.; Espinoza, J.L.; Freire, M.; Messias, C.; Villela, H.D.M.; Pereira, L.M.; Vilela, C.L.S.; Rosado, J.G.; Cardoso, P.M.; et al. Coral microbiome manipulation elicits metabolic and genetic restructuring to mitigate heat stress and evade mortality. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörr, M.; Barno, A.; Villela, H.; García, F.; Garcias-Bonet, N.; Voolstra, C.; Peixoto, R. Microbial-Based Therapies to Restore and Rehabilitate Disrupted Coral Health. In Coral Reef Microbiome; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, C.B.; Cavalcanti, G.S.; Walter, J.M.; Silva-Lima, A.W.; Dinsdale, E.A.; Bourne, D.G.; Thompson, C.C.; Thompson, F.L. Microbial processes driving coral reef organic carbon flow. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 575–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Water, J.A.; Tignat-Perrier, R.; Allemand, D.; Ferrier-Pages, C. Coral holobionts and biotechnology: From Blue Economy to coral reef conservation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 74, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.M.; Hai, Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Chemical and Bioactive Marine Natural Products of Coral-Derived Microorganisms (2015–2017). Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6930–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, V.M. Cellular mechanisms of Cnidarian bleaching: Stress causes the collapse of symbiosis. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211 Pt 19, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, M.; Larkum, A.W.D.; Vass, I. A Review: The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Mass Coral Bleaching; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 45, pp. 459–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, M.P. Oxidative stress in marine environments: Biochemistry and physiological ecology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2006, 68, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, P.M.; Leite, D.C.A.; Duarte, G.A.S.; Chaloub, R.M.; Jospin, G.; da Rocha, U.N.; Saraiva, J.P.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Eisen, J.A.; Bourne, D.G.; et al. Marine probiotics: Increasing coral resistance to bleaching through microbiome manipulation. ISME J. 2019, 13, 921–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, V.T.; Dat, T.T.H.; Vinh, L.B.; Cuong, L.C.V.; Oanh, P.T.T.; Ha, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Anh, H.L.T.; Yang, S.Y. Coral and Coral-Associated Microorganisms: A Prolific Source of Potential Bioactive Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, J.; Kannapiran, E.; Manikandan, B.; Francis, K.; Arora, S.; Karunya, E.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S.K.; Jose, J. UV-absorbing bacteria in coral mucus and their response to simulated temperature elevations. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M.; Villela, H.; Keller-Costa, T.; Costa, R.; Romano, S.; Bourne, D.G.; Cardenas, A.; Huggett, M.J.; Kerwin, A.H.; Kuek, F.; et al. Insights into the Cultured Bacterial Fraction of Corals. mSystems 2021, 6, e0124920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowburn, B.; Moritz, C.; Grimsditch, G.; Solandt, J.L. Evidence of bleaching avoidance, resistance and recovery in the Maldives during the 2016 mass-bleaching event. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 626, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisand, V.; Cuadros, R.; Wikner, J. Phylogeny of Culturable Estuarine Bacteria Catabolizing Riverine Organic Matter in the Northern Baltic Sea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Pryer, K.M.; Miao, V.P.W.; Palmer, J.D. Investigating Deep Phylogenetic Relationships among Cyanobacteria and Plastids by Small Subunit rRNA Sequence Analysis. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahe, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Accuracy of taxonomy prediction for 16S rRNA and fungal ITS sequences. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, M. microeco: An R package for data mining in microbial community ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalita, M.; Kim, Y.O.; Park, S.; Oh, H.S.; Cho, J.H.; Moon, J.; Baek, N.; Moon, C.; Lee, K.; Yang, J.; et al. EzBioCloud: A genome-driven database and platform for microbiome identification and discovery. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 006421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska-Krochmal, B.; Dudek-Wicher, R. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Antibiotics: Methods, Interpretation, Clinical Relevance. Pathogens 2021, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedare, S.B.; Singh, R.P. Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.R.; Kumazawa, S.; Hamasaka, T.; Bang, K.S.; Nakayama, T. Antioxidant activity and constituents of propolis collected in various areas of Korea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7286–7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, A.; Kusano, M.; Sakagami, H.; Amano, S.; Inomata, M.; Abe, M.; Okazawa, M.; Ooka, T. Comparison of UVC Sensitivity and Dectin-2 Expression Between Malignant and Non-malignant Cells. In Vivo 2022, 36, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.D.; Li, F.; Kirton, E.; Thomas, A.; Egan, R.; An, H.; Wang, Z. MetaBAT 2: An adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chklovski, A.; Parks, D.H.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM2: A rapid, scalable and accurate tool for assessing microbial genome quality using machine learning. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, L.; Ruscheweyh, H.J.; Forneris, C.C.; Hubrich, F.; Kautsar, S.; Bhushan, A.; Lotti, A.; Clayssen, Q.; Salazar, G.; Milanese, A.; et al. Biosynthetic potential of the global ocean microbiome. Nature 2022, 607, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Yoshizawa, S. The OceanDNA MAG catalog contains over 50,000 prokaryotic genomes originated from various marine environments. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, M.; Borton, M.A.; McGivern, B.B.; Zayed, A.A.; La Rosa, S.L.; Solden, L.M.; Liu, P.; Narrowe, A.B.; Rodriguez-Ramos, J.; Bolduc, B.; et al. DRAM for distilling microbial metabolism to automate the curation of microbiome function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 8883–8900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkin, A.P.; Cottingham, R.W.; Henry, C.S.; Harris, N.L.; Stevens, R.L.; Maslov, S.; Dehal, P.; Ware, D.; Perez, F.; Canon, S.; et al. KBase: The United States Department of Energy Systems Biology Knowledgebase. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, P.A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk: A toolkit to classify genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, N.; Doster, E.; Worley, H.; Pinnell, L.J.; Bravo, J.E.; Ferm, P.; Marini, S.; Prosperi, M.; Noyes, N.; Morley, P.S.; et al. MEGARes and AMR++, v3.0: An updated comprehensive database of antimicrobial resistance determinants and an improved software pipeline for classification using high-throughput sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D744–D752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.D. GToTree: A user-friendly workflow for phylogenomics. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4162–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, G.A.; Coppola, D.; Palma Esposito, F.; Buonocore, C.; Ausuri, J.; Tortorella, E.; de Pascale, D. Antioxidant Molecules from Marine Fungi: Methodologies and Perspectives. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doering, T.; Wall, M.; Putchim, L.; Rattanawongwan, T.; Schroeder, R.; Hentschel, U.; Roik, A. Towards enhancing coral heat tolerance: A “microbiome transplantation” treatment using inoculations of homogenized coral tissues. Microbiome 2021, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochart, C.; Paoli, L.; Ruscheweyh, H.J.; Salazar, G.; Boissin, E.; Romac, S.; Poulain, J.; Bourdin, G.; Iwankow, G.; Moulin, C.; et al. Ecology of Endozoicomonadaceae in three coral genera across the Pacific Ocean. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fifer, J.E.; Bui, V.; Berg, J.T.; Kriefall, N.; Klepac, C.; Bentlage, B.; Davies, S.W. Microbiome Structuring Within a Coral Colony and Along a Sedimentation Gradient. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 805202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, K.; Chiou, Y.J.; Yu, S.P.; Hsieh, H.J.; Lu, C.Y.; Hsu, M.T.; Chiang, P.W.; Chen, H.J.; Wada, N.; Tang, S.L. Microbiome Restructuring: Dominant Coral Bacterium Endozoicomonas Species Respond Differentially to Environmental Changes. mSystems 2022, 7, e0035922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Zulueta, J.; Díaz-Pérez, L.; Echeverría-Vega, A.; Nava-Martínez, G.G.; García-Salgado, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A. An Update of Knowledge of the Bacterial Assemblages Associated with the Mexican Caribbean Corals Acropora palmata, Orbicella faveolata, and Porites porites. Diversity 2023, 15, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Bettarel, Y.; Chu, H.H.; Bui, V.N. An analysis of the bacterial community in and around scleractinian corals of Phu Quoc Island, Vietnam. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 60, 102817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigel, A.M.; Paz-García, D.A.; Hellberg, M.E. Microbiome of a Reef-Building Coral Displays Signs of Acclimation to a Stressful Shallow Hydrothermal Vent Habitat. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 652633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnit-Orland, M.; Sivan, A.; Kushmaro, A. Antibacterial activity of Pseudoalteromonas in the coral holobiont. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushijima, B.; Richards, G.P.; Watson, M.A.; Schubiger, C.B.; Hase, C.C. Factors affecting infection of corals and larval oysters by Vibrio coralliilyticus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Licuanan, W.Y.; Baird, A.H.; Fukami, H. Cleaning up the ‘Bigmessidae’: Molecular phylogeny of scleractinian corals from Faviidae, Merulinidae, Pectiniidae and Trachyphylliidae. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushijima, B.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Meyer, J.L.; Tittl, J.; Pitts, K.A.; Thompson, S.; Sneed, J.M.; Ding, Y.; Chen, M.; Jay Houk, L.; et al. Chemical and genomic characterization of a potential probiotic treatment for stony coral tissue loss disease. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varasteh, T.; Hamerski, L.; Tschoeke, D.; Lima, A.S.; Garcia, G.; Cosenza, C.A.N.; Thompson, C.; Thompson, F. Conserved Pigment Profiles in Phylogenetically Diverse Symbiotic Bacteria Associated with the Corals Montastraea cavernosa and Mussismilia braziliensis. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 81, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusmita, L.; Mutiara, E.V.; Nuryadi, H.; Pratama, P.A.; Wiguna, A.S.; Radjasa, O.K. Characterization of carotenoid pigments from bacterial symbionts of soft-coral Sarcophyton sp. from North Java Sea. Int. Aquat. Res. 2017, 9, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Razek, A.S.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Allam, A.; Morsy, O.M.; Othman, S.I. Microbial Natural Products in Drug Discovery. Processes 2020, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Mazumder, A.; Sikdar, S.; Zhao, Y.M.; Hao, J.; Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Sarkar, R.; Islam, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Streptomyces: The biofactory of secondary metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 968053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, H.M.; Kalendar, A.A. Coral-Associated Actinobacteria: Diversity, Abundance, and Biotechnological Potentials. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siro, G.; Pipite, A.; Christi, K.; Srinivasan, S.; Subramani, R. Marine Actinomycetes Associated with Stony Corals: A Potential Hotspot for Specialized Metabolites. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Baird, A.H.; Connolly, S.R.; Dietzel, A.; Eakin, C.M.; Heron, S.F.; Hoey, A.S.; Hoogenboom, M.O.; Liu, G.; et al. Global warming transforms coral reef assemblages. Nature 2018, 556, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Keulen, G.; Dyson, P.J. Production of specialized metabolites by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 89, 217–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.D.; Yang, H.L.; Kim, I.S. Four new Microbacterium species isolated from seaweeds and reclassification of five Microbacterium species with a proposal of Paramicrobacterium gen. nov. under a genome-based framework of the genus Microbacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1299950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, J.B.; Tapiolas, D.; Motti, C.A.; Foret, S.; Seemann, T.; Tebben, J.; Willis, B.L.; Bourne, D.G. Isolation of an antimicrobial compound produced by bacteria associated with reef-building corals. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Chuvochina, M.; Rinke, C.; Mussig, A.J.; Chaumeil, P.A.; Hugenholtz, P. GTDB: An ongoing census of bacterial and archaeal diversity through a phylogenetically consistent, rank normalized and complete genome-based taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D785–D794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zeng, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Micromonospora: A Prolific Source of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites with Therapeutic Potential. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8735–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feling, R.H.; Buchanan, G.O.; Mincer, T.J.; Kauffman, C.A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Salinosporamide A: A highly cytotoxic proteasome inhibitor from a novel microbial source, a marine bacterium of the new genus salinospora. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2003, 42, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.R.; Williams, P.G.; Oh, D.-C.; Zeigler, L.; Fenical, W. Species-Specific Secondary Metabolite Production in Marine Actinomycetes of the Genus Salinispora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril-Espinosa, A.; Hernandez-Herrera, R.M.; Meza-Canales, I.D.; Perez-Ramirez, R.; Rodriguez-Zaragoza, F.A.; Mendez-Moran, L.; Sanchez-Hernandez, C.V.; Palmeros-Suarez, P.A.; Palacios, O.A.; Choix, F.J.; et al. Habitat-adapted heterologous symbiont Salinispora arenicola promotes growth and alleviates salt stress in tomato crop plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 920881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincer, T.J.; Jensen, P.R.; Kauffman, C.A.; Fenical, W. Widespread and persistent populations of a major new marine actinomycete taxon in ocean sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5005–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couceiro, J.; Costa, R.; Keller-Costa, T. Beyond Restoration: Coral Microbiome Biotechnology. In Coral Reef Microbiome; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, L.K.; Ortiz, J.; Humanes, A.; Riginos, C.; Baums, I.; Scharfenstein, H.; Aranda, M.; Peixoto, R.; Niehaus, A.; Le Port, A.; et al. R&D Technology Roadmap for Understanding the Natural Adaptation and Assisted Evolution of Corals to Climate Change. CORDAP. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma Esposito, F.; Giugliano, R.; Della Sala, G.; Vitale, G.A.; Buonocore, C.; Ausuri, J.; Galasso, C.; Coppola, D.; Franci, G.; Galdiero, M.; et al. Combining OSMAC Approach and Untargeted Metabolomics for the Identification of New Glycolipids with Potent Antiviral Activity Produced by a Marine Rhodococcus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Pathogen Strains | Active Strains | MIC (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli ATCC 10536 | 79 | 500 |
| L. monocytogenes MB 677 | 79 | 1 |
| 92 | 1 | |
| 93 | 0.5 | |
| P. damselae subps. piscicida ATCC 51736 | 39 | 30 |
| 79 | 0.0098 | |
| 92 | 125 | |
| 93 | 125 | |
| S. aureus methicillin resistant | 39 | 500 |
| 79 | 1 | |
| 92 | 125 | |
| 93 | 31 | |
| S. aureus—quinolone resistant | 79 | 500 |
| 92 | 2 | |
| 93 | 1 | |
| S. aureus—macrolide resistant | 79 | 0.5 |
| 92 | 2 | |
| 93 | 20 | |
| S. aureus 6538p | 39 | 125 |
| 79 | 0.3 | |
| 92 | 0.313 | |
| 93 | 1.25 | |
| V. anguillarium ATCC 19264 | 39 | 0.031 |
| 92 | 20 | |
| 93 | 60 | |
| C. albicans ATCC 76485 | 79 | 0.25 |
| S. aureus—vancomycin resistant | - | - |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | - | - |
| Pseudoalteromonas piscicida 39 | Streptomyces parvus 79 | Microbacterium sp. 92 | Micromonospora arenicola 93 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Completeness (%) | 100 | 99.97 | 99.96 | 100 |
| Redundancy (%) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0,13 | 1.16 |
| Coding density | 0.88 | 0,89 | 0.92 | 0.87 |
| Genome size (bp) | 5,096,534 | 8,193,082 | 3,204,941 | 5,583,533 |
| GC content (%) | 0.43 | 0.72 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Total coding sequences | 4400 | 7126 | 3032 | 4983 |
| Total contigs | 45 | 102 | 7 | 55 |
| tRNAs | 64 | 69 | 46 | 54 |
| Pseudoalteromonas piscicida 39 | Streptomyces parvus 79 | Microbacterium sp. 92 | Micromonospora arenicola 93 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glutathione biosynthesis | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| β-carotene | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Mannitol synthesis | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| DMS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DMSP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Peroxinitrite reduction (ahpC) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nitric oxide reductase | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Lipoic acid metabolism | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Catalase-peroxidase (KatG) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Catalase (KatE) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| SOD | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Nitrosative stress | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palma Esposito, F.; López-Mobilia, A.; Tangherlini, M.; Casella, V.; Coppola, A.; Varola, G.; Vitale, L.; Della Sala, G.; Tedesco, P.; Montano, S.; et al. Novel Insights and Genomic Characterization of Coral-Associated Microorganisms from Maldives Displaying Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and UV-Protectant Activities. Biology 2025, 14, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040401
Palma Esposito F, López-Mobilia A, Tangherlini M, Casella V, Coppola A, Varola G, Vitale L, Della Sala G, Tedesco P, Montano S, et al. Novel Insights and Genomic Characterization of Coral-Associated Microorganisms from Maldives Displaying Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and UV-Protectant Activities. Biology. 2025; 14(4):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040401
Chicago/Turabian StylePalma Esposito, Fortunato, Andrea López-Mobilia, Michael Tangherlini, Vincenza Casella, Alessandro Coppola, Giulia Varola, Laura Vitale, Gerardo Della Sala, Pietro Tedesco, Simone Montano, and et al. 2025. "Novel Insights and Genomic Characterization of Coral-Associated Microorganisms from Maldives Displaying Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and UV-Protectant Activities" Biology 14, no. 4: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040401
APA StylePalma Esposito, F., López-Mobilia, A., Tangherlini, M., Casella, V., Coppola, A., Varola, G., Vitale, L., Della Sala, G., Tedesco, P., Montano, S., Seveso, D., Galli, P., Coppola, D., de Pascale, D., & Galasso, C. (2025). Novel Insights and Genomic Characterization of Coral-Associated Microorganisms from Maldives Displaying Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and UV-Protectant Activities. Biology, 14(4), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040401













