The Mechanisms of Soil Conditioner and Switchgrass in Improving Saline–Alkali Soil: A Field Study in a Semi-Arid Area
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
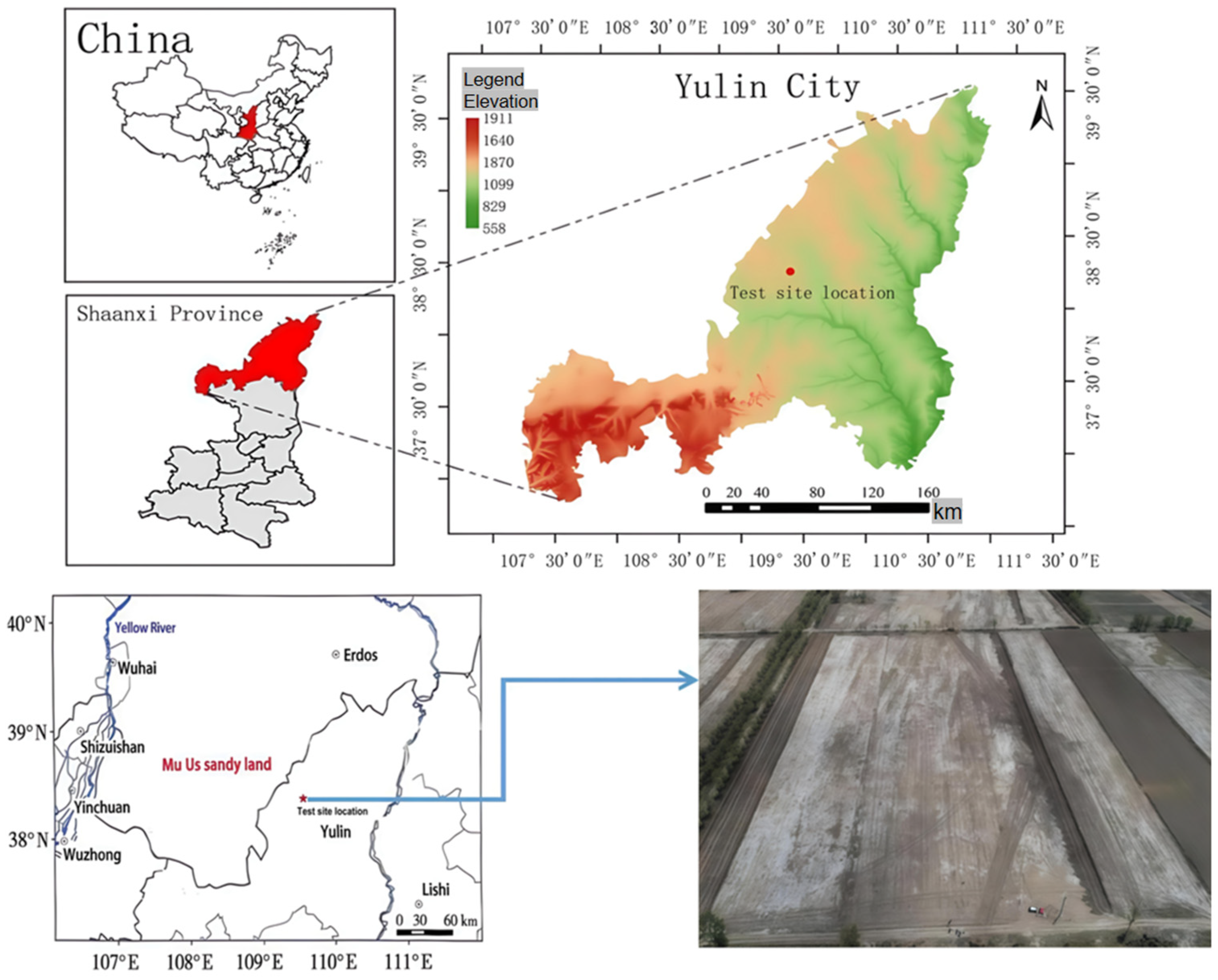
2.1. Study Site Description
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Soil Conditioner Composition and Panicum virgatum L. Cultivation
2.5. Sample Collection
2.6. Analytical Methods
2.7. Data Processing
3. Results and Analysis
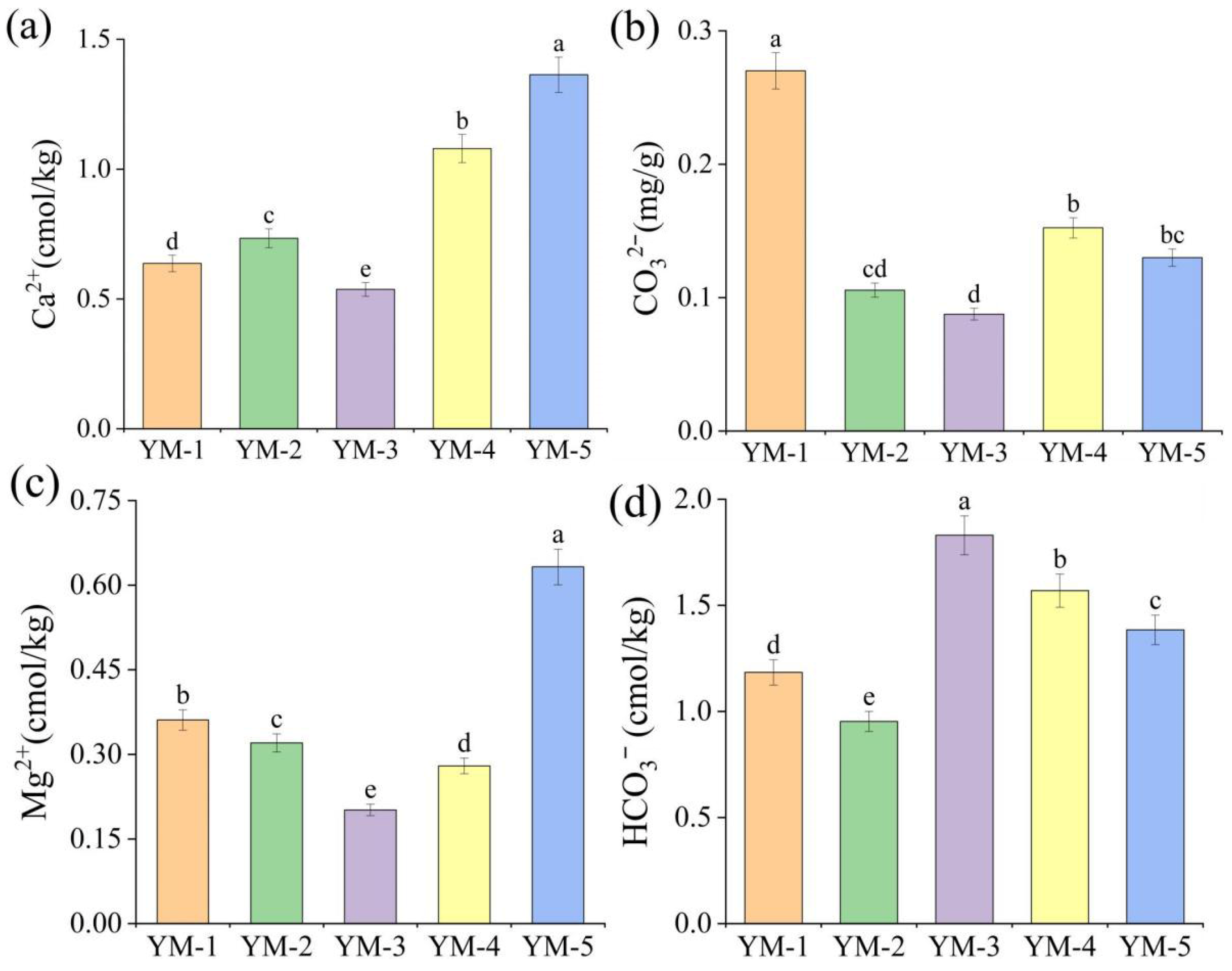
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties
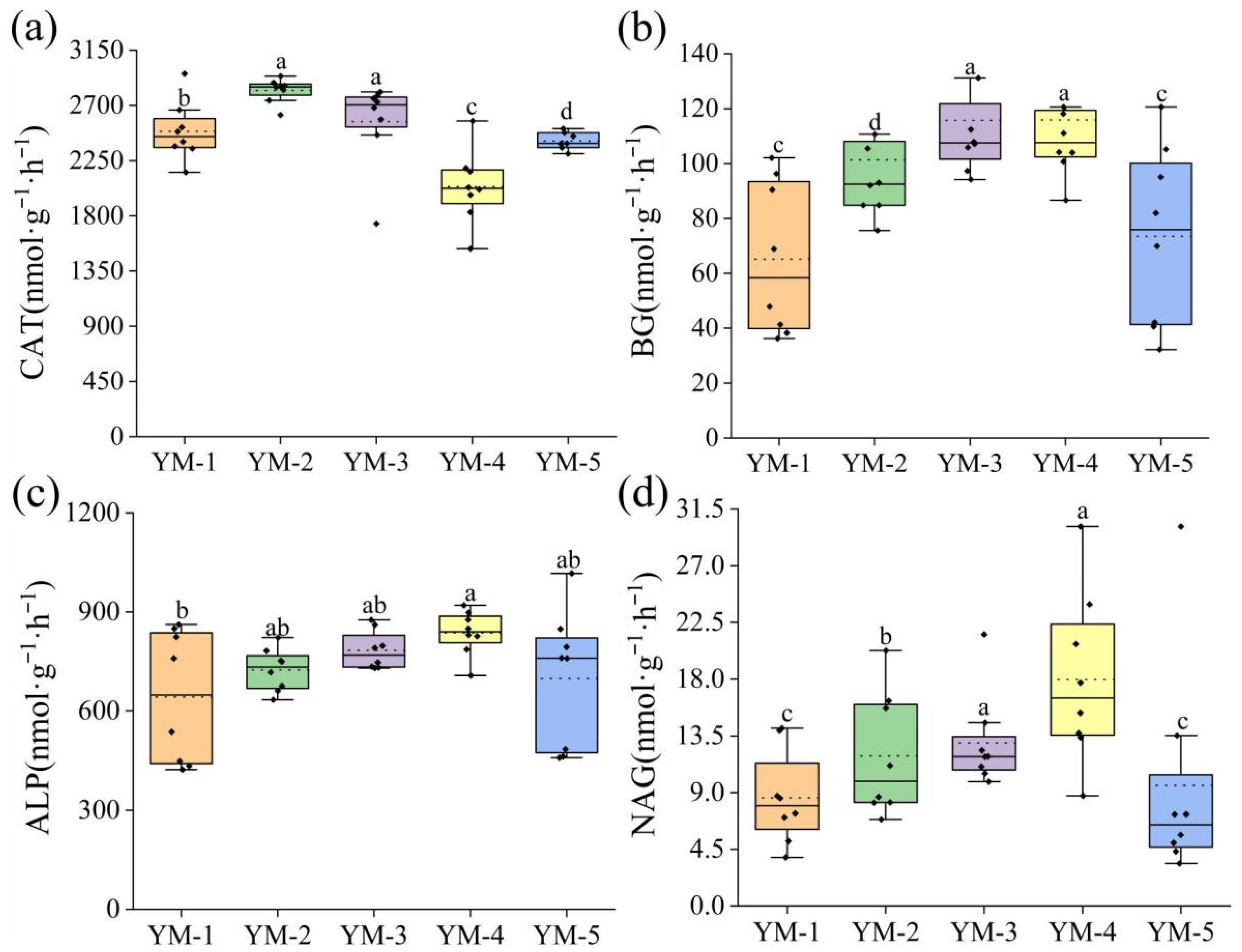
3.2. Soil Enzyme Activities
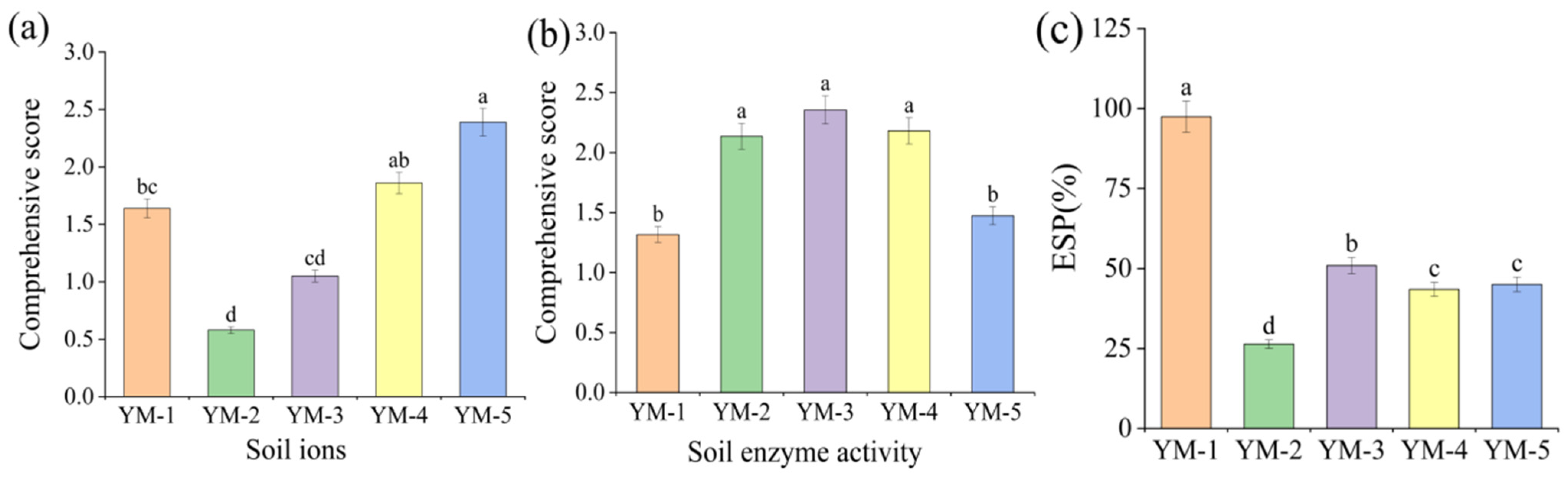
3.3. Comprehensive Evaluation of Soil Properties
3.4. Soil Microbial Communities
3.5. Biological and Non-Biological Factors Contributing to Changes in Soil Quality
4. Discussion
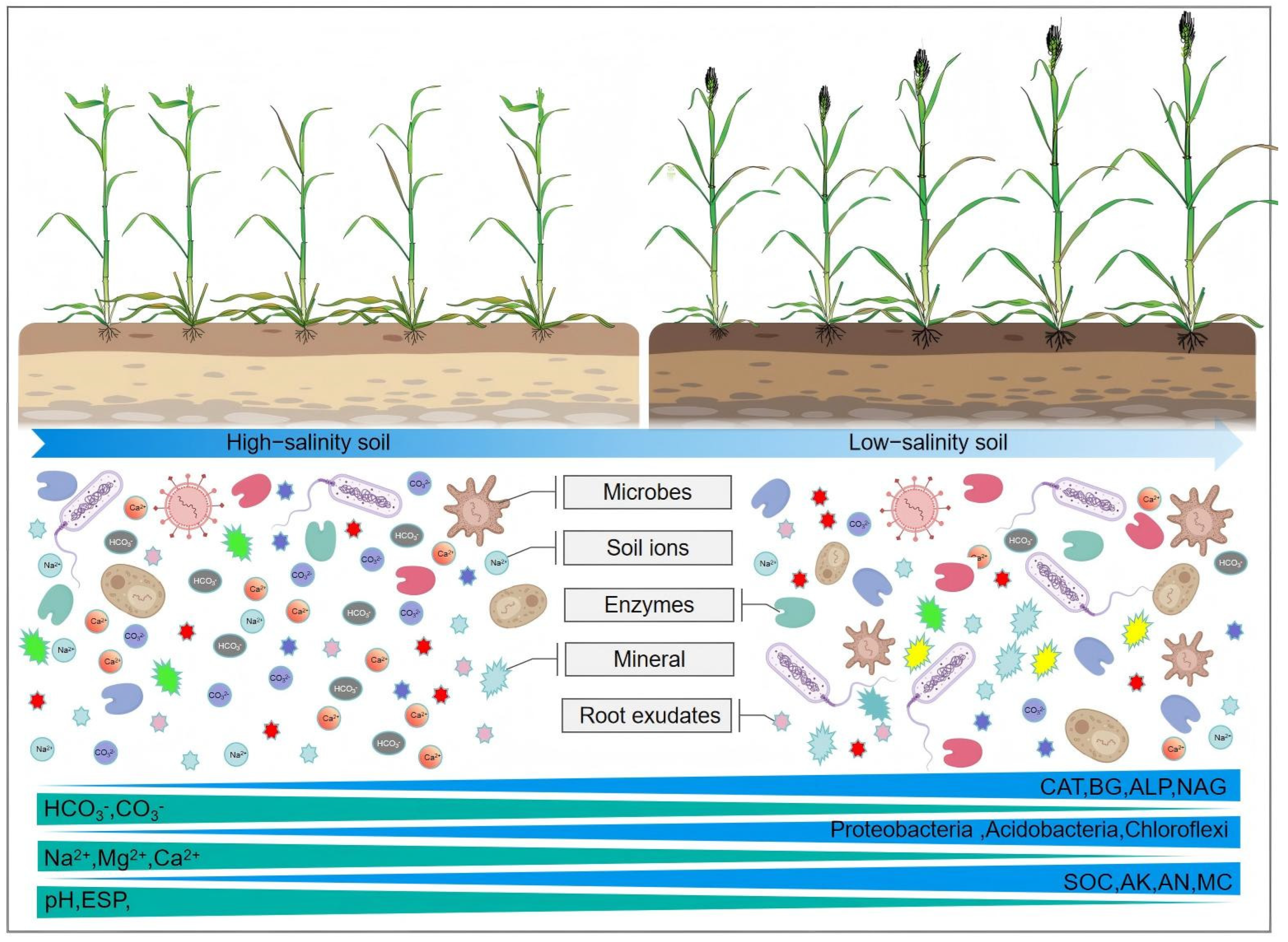
4.1. Effect of Switchgrass Combined with Coal-Based Conditioner on Soil Properties
4.2. Response of Switchgrass Synergistic Conditioner to Soil Microbial Communities
5. Limitations and Implications
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, C.; Tian, H.; Wang, X.; Song, X.; Ju, R.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Bacillus subtilis HG-15, a halotolerant rhizoplane bacterium, promotes growth and salinity tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum). BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9506227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Ren, M.; Zhao, P.; Lin, A. Effective strategies for reclamation of saline-alkali soil and response mechanisms of the soil-plant system. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.U.; Fan, Y.A.N.G.; Ning, Y.A.N.G.; Wei, J.I.A.; Yong, C.U.I. Analysis and prospects of saline-alkali land in China from the perspective of utilization. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 54, 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Fan, Y.; Li, J.; Ke, X.M. Analysis of Precipitation Characteristics and Precipitation Forecast in the Yulin Area. People’s Yellow River 2022, 44, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Gu, W.Z.; Liu, X.M.; Li, Q.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, X.F.; Liu, J.T. The effect of coal gangue soil conditioner on the growth of Salix babylonica in the Maowusu sandy land. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2024, 52, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Jin, S. Effects of the lignite bioorganic fertilizer on greenhouse gas emissions and pathways of nitrogen and carbon cycling in saline-sodic farmlands at Northwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, L.; Chu, Y.; Ye, X.; Chen, L. Effects of lignite based organic fertilizer combining straw application on soil fertility and oil sunflower growth. Soils Crops 2021, 10, 440–448. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Liu, S.; Ma, C.; Liu, Z. Effects of microbial communities during the cultivation of three salt-tolerant plants in saline-alkali land improvement. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1470081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, G.; Feng, B.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, J. Saline-alkali land reclamation boosts topsoil carbon storage by preferentially accumulating plant-derived carbon. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 2948–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Xie, L.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Yu, Q. Combined microbe-plant remediation of cadmium in saline-alkali soil assisted by fungal mycelium-derived biochar. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, X.L.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, S.Q. Construction of phosphate-solubilizing microbial consortium and its effect on the remediation of saline-alkali soil. Microb. Ecol. 2025, 88, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Tian, H.; Dong, B.; Xu, Z. Mechanism of stabilized sludge-driven remediation in saline-alkali soil: New insights from salt-discharge capacity and microbially mediated carbon/nitrogen cycles. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, L.; Du, H.; Lin, X.; Hu, W.; Li, Y. Soil conditioners promote the formation of Fe-bound organic carbon and its stability. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengasamy, P. Transient salinity and subsoil constraints to dryland farming in Australian sodic soils: An overview. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2002, 42, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Hou, N.; Li, D. Remediation of soda-saline-alkali soil through soil amendments: Microbially mediated carbon and nitrogen cycles and remediation mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Li, B.; Zhang, D.; Xu, H.; Zhang, G. Supply and demand of agricultural water resources under future saline-alkali land improvement. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 314, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QU, X.; Wu, N.; Zhao, C.; Chen, J.; LIU, J. Effects of Phosphorus Supply Level on Dry Matter Weight and Phosphorus Uptake and Utilization Characteristics of Switchgrass. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2023, 52, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Fike, J.H.; Parrish, D.J.; Wolf, D.D.; Balasko, J.A.; Green Jr, J.T.; Rasnake, M.; Reynolds, J.H. Long-term yield potential of switchgrass-for-biofuel systems. Biomass Bioenergy 2006, 30, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, F.; He, L.; Li, Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C. Vermicompost combined with soil conditioner improves the ecosystem multifunctionality in saline-alkali land. Water 2023, 15, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Guo, Q.; Cao, S.; Zhan, Z. Diversity of bacterium communities in saline-alkali soil in arid regions of Northwest China. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilibio, C.; Weber, T.K.D.; Hammer-Weis, M.; Junge, S.M.; Leisch-Waskoenig, S.; Wack, J.; Peth, S. Changes in soil mechanical and hydraulic properties through regenerative cultivation measures in long-term and farm experiments in Germany. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 246, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wenbiao, W.; Hou, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Yuan, H.; Li, Y. Effect of combined nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on summer maize yield and soil fertility in coastal saline-alkali land. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 309, 109277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Ding, H.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Feng, L. Comparative effects of humic acid biostimulation on soil properties, growth, and fragrance of Rosa rugosa. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 225, 120444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.R.; Ma, Y.B.; Bian, J.D.; Zhang, Z.; Ai, F.; Yang, H.; Li, Q. The effect of decarbonized gasification ash-based soil conditioners on soil nutrients and the growth of sheepgrass. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2024, 52, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Xu, Z.; Ren, M.; Li, S.; Xie, Z.; Luo, Y.; Tian, Y. Identification of microbial diversity in buried ivory soil at the Sanxingdui site in Guanghan City, China, using high-throughput sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1384650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huang, L.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, G.; Yang, C.; Kong, Q. Quantitative evaluation and mechanism analysis of soil chemical factors affecting rice yield in saline-sodic paddy fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.M.; Wang, X.Q.; Qu, Z.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J. Study on the effects of different amendments on soil salinity and alkalinity indicators and crop yield in the Hetao irrigation area. Soil Bull. 2020, 51, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Guo, B.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Xu, R.; Zhang, H. Comprehensive Evaluation of Nutritional Quality of Foxtail Millet Based on Principal Component Analysis and Membership Function Method. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2025, 54, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, G.C.; Saha, S.; Ghosh, K.G. Assessing the soil quality of Bansloi river basin, eastern India using soil-quality indices (SQIs) and Random Forest machine learning technique. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Li, X.; Smyth, E.M.; Yannarell, A.C.; Mackie, R.I. Enrichment of specific bacterial and eukaryotic microbes in the rhizosphere of switchgrass (P anicum virgatum L.) through root exudates. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, N.; Liu, J.L.; Chen, J.; Yan, C.H. The effects of different phosphorus supply levels on the root morphology of Salix matsudana and the physicochemical properties of saline-alkali soil. Chin. Soil Fertil. 2022, 120–126, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Xu, H.; Shen, G.; Chen, Q. Optimizing Biochar Application Rates to improve soil properties and crop growth in saline–alkali soil. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Hu, C.; Wu, S.; Sun, X.; Tan, Q. Molybdenum regulates phosphorus cycling species diversity and improves soil phosphorus availability through key flavonoids in the soybean (Glycine max). Geoderma 2025, 456, 117242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idress, M.; Khan, P.; Nawab, J.; Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Ali, R.; Bayabil, H. Improving phosphorus availability in saline-alkaline agricultural soils through biochar and phosphorus solubilizing bacteria (PSB) inoculation: A greenhouse experiment. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2025, 27, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Dong, H.; Dai, S.; Ma, X. Trade-offs of organic amendment input on soil quality and crop productivity in saline-alkali land globally: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Li, L.; Friman, V.P.; Guo, J.; Guo, S.; Shen, Q.; Ling, N. Organic amendments increase crop yields by improving microbe-mediated soil functioning of agroecosystems: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniji, A.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Lu, X.; Guo, R. Hot viewpoint on how soil texture, soil nutrient availability, and root exudates interact to shape microbial dynamics and plant health. Plant Soil 2025, 511, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.F.; Jiang, F.; Liu, X.S.; Sun, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.X.; Yu, F.H. Biochar-amended coastal wetland soil enhances growth of Suaeda salsa and alters rhizosphere soil nutrients and microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Noya, Y.E.; Gómez-Acata, S.; Montoya-Ciriaco, N.; Rojas-Valdez, A.; Suárez-Arriaga, M.C.; Valenzuela-Encinas, C.; Dendooven, L. Relative impacts of tillage, residue management and crop-rotation on soil bacterial communities in a semi-arid agroecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrune, F.; Dufrêne, M.; Colinet, G.; Massart, S.; Taminiau, B.; Bodson, B.; Vandenbol, M. A novel sub-phylum method discriminates better the impact of crop management on soil microbial community. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lareen, A.; Burton, F.; Schäfer, P. Plant root-microbe communication in shaping root microbiomes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, F.T.; Griffiths, R.I.; Knight, C.G.; Nicolitch, O.; Williams, A. Harnessing rhizosphere microbiomes for drought-resilient crop production. Science 2020, 368, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Yang, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.M.; Luo, Z.M.; Yang, T.; Gao, L. Research on the adaptability of different Salix branches in saline-alkali land. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2025, 53, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Hualpa-Ramirez, E.; Carrasco-Lozano, E.C.; Madrid-Espinoza, J.; Tejos, R.; Ruiz-Lara, S.; Stange, C.; Norambuena, L. Stress salinity in plants: New strategies to cope with in the foreseeable scenario. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 208, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Ye, F.; Ding, Z.J.; Zheng, S.J.; Qiao, S.; Su, N. Structures and ion transport mechanisms of plant high-affinity potassium transporters. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, B.R.; Dou, Y.X.; Xue, Z.J.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liang, C.; An, S.S. Advances in the research of transformation and stabilization of soil organic carbon from plant and microbe. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol./Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2024, 35, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich, T.A.; Sachs, G.; Padan, E. Molecular aspects of bacterial pH sensing and homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil organic matter priming: The pH effects. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Vijver, M.G.; Peijnenburg, W.J. Impacts of major cations (K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+) and protons on toxicity predictions of nickel and cadmium to lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) using exposure models. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Xie, W. Short-term effects of biochar and gypsum on soil hydraulic properties and sodicity in a saline-alkali soil. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; He, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Lv, G. Root exudates facilitate the regulation of soil microbial community function in the genus Haloxylon. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1461893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Hina, K.; Hussain, Q.; Qiu, T.; Zhu, J. Revitalizing coastal saline-alkali soil with biochar application for improved crop growth. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 179, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Wei, S.; Ji, L.; Yan, S. A potential CO2 carrier to improve the utilization of HCO3–by plant-soil ecosystem for carbon sink enhancement. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 73, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.M.; Martínez, V.; Carvajal, M. Ammonium, bicarbonate and calcium effects on tomato plants grown under saline conditions. Plant Sci. 2000, 157, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hou, Y.; Zang, J. Salinity survival: Molecular mechanisms and adaptive strategies in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1527952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.; Greenberg, I.; Ludwig, B.; Hippich, L.; Fischer, D.; Glaser, B.; Kaiser, M. Effect of biochar and compost on soil properties and organic matter in aggregate size fractions under field conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 295, 106882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Wang, Y.; Ning, S.; Mao, J.; Sheng, J.; Jiang, P. Assessment of the effects of biochar on the physicochemical properties of saline–alkali soil based on meta-analysis. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, M.S.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Pan, W.; Fu, J.; Pan, G.; Yu, X. Effects of amendment of biochar-manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution on soil quality and wheat yield of a salt-stressed cropland from Central China Great Plain. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Abrar, M.M.; Naeem, M.A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Ali, H.M.; Li, Y.; Xu, M. Biochar increases salt tolerance and grain yield of quinoa on saline-sodic soil: Multivariate comparison of physiological and oxidative stress attributes. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 1446–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescimanno, G.; Iovino, M.; Provenzano, G. Influence of salinity and sodicity on soil structural and hydraulic characteristics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Wei, H.; Huang, F.; Li, Z.; Li, F.M.; Zhang, F. Fungal community composition changes and reduced bacterial diversity drive improvements in the soil quality index during arable land restoration. Environ. Res. 2024, 244, 117931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
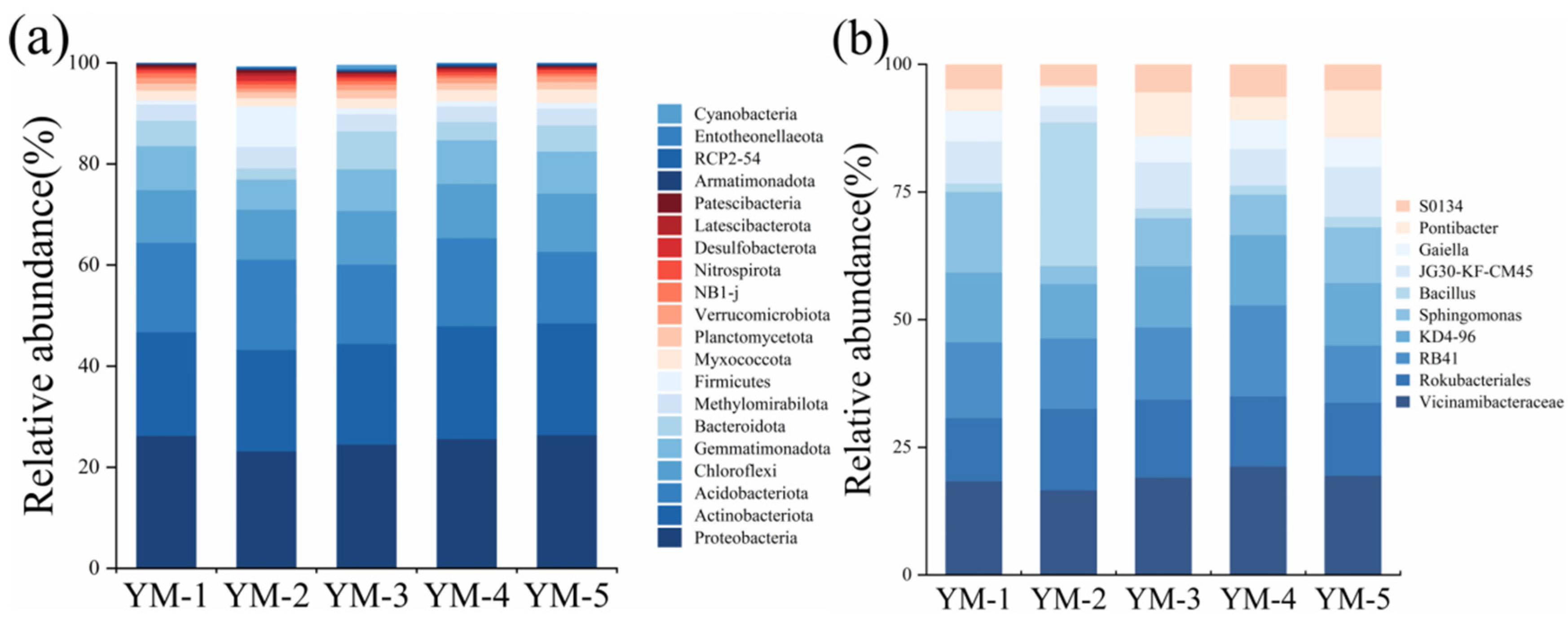
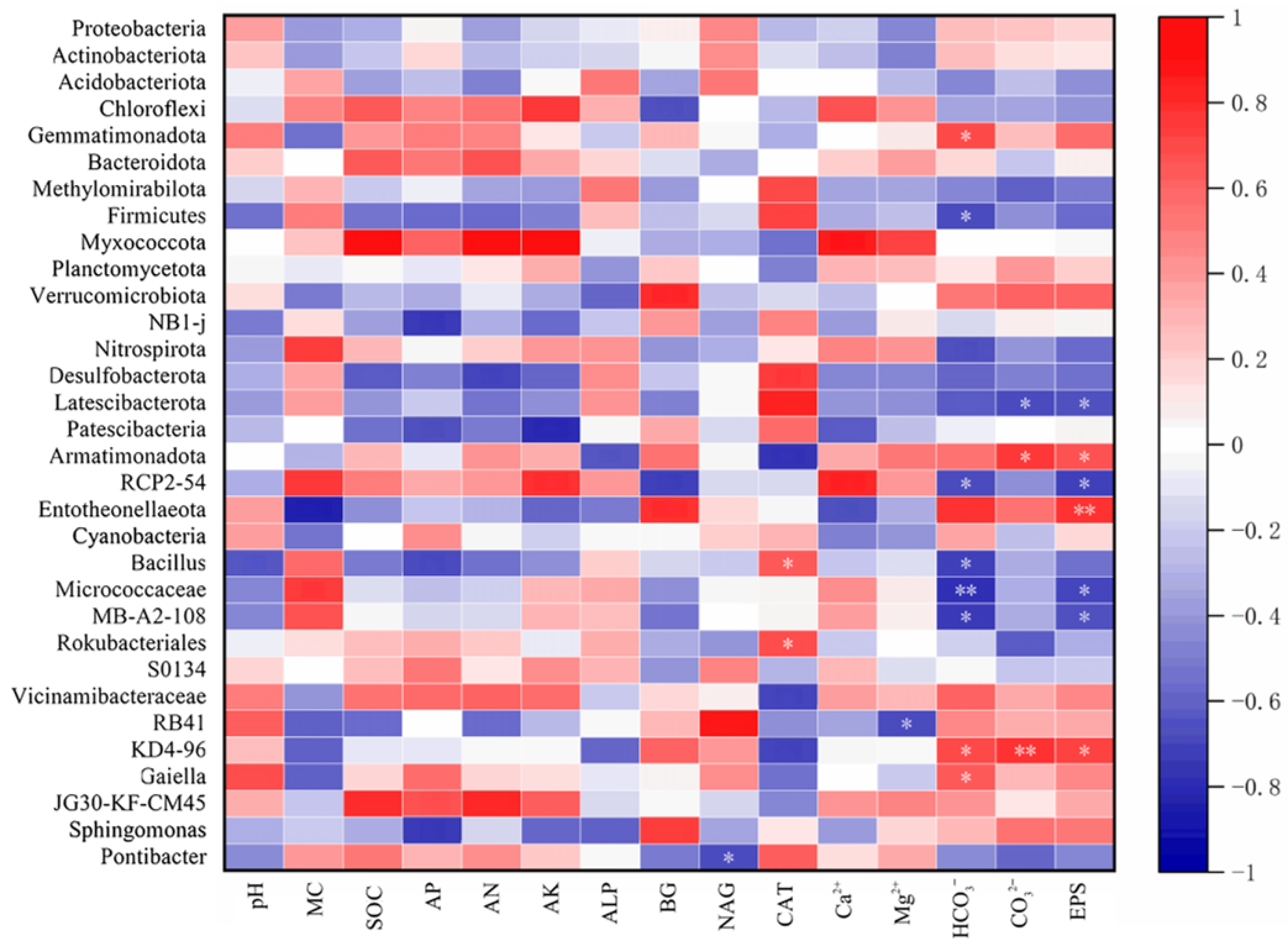
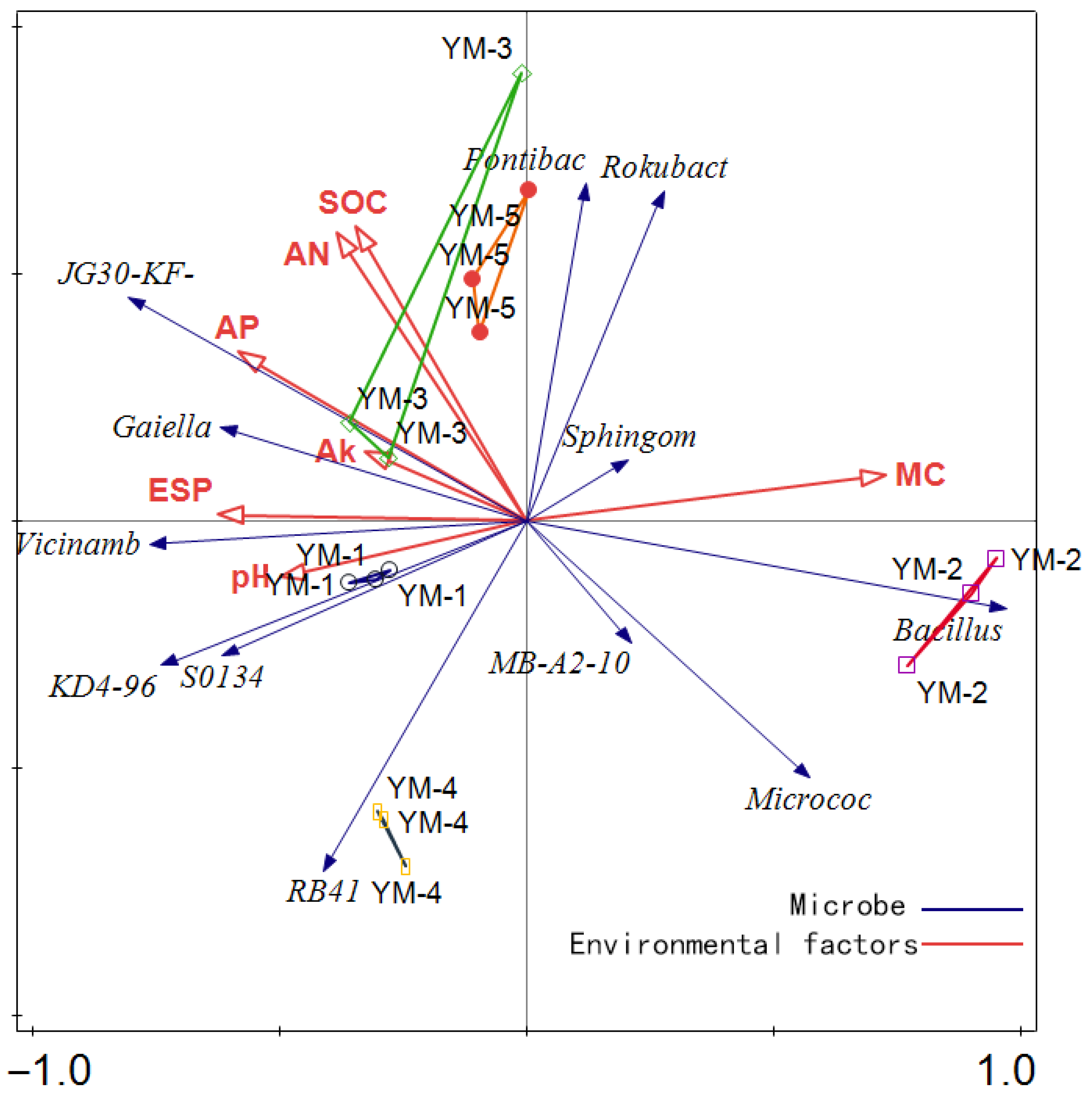
| Soil Indicators | YM-1 | YM-2 | YM-3 | YM-4 | YM-5 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.13 ± 0.05 a | 7.62 ± 0.11 b | 8.10 ± 0.13 a | 8.11 ± 0.12 a | 7.75 ± 0.09 b | 0.047 * |
| AN (mg/kg) | 38.3 ± 0.37 c | 44.5 ± 0.34 d | 42.1 ± 0.34 b | 39.6 ± 0.34 c | 59.2 ± 0.72 a | 0.015 * |
| AK (mg/kg) | 44.4 ± 0.31 d | 65.5 ± 0.28 d | 50.5 ± 2.58 c | 63.1 ± 0.11 b | 72.5 ± 0.86 a | 0.023 * |
| AP (mg/kg) | 17.1 ± 0.13 c | 24.1 ± 0.32 d | 28.7 ± 0.68 a | 23.2 ± 0.28 b | 23.5 ± 0.32 b | 0.026 * |
| MC (%) | 4.25 ± 0.19 e | 9.12 ± 0.08 a | 5.41 ± 0.18 d | 6.72 ± 0.13 c | 8.58 ± 0.23 b | 0.039 * |
| SOC (g/kg) | 7.63 ± 0.25 d | 6.40 ± 0.25 e | 10.7 ± 0.17 b | 9.67 ± 0.06 c | 11.4 ± 0.09 a | 0.008 ** |
| Na+ (cmol/kg) | 0.287 ± 0.66 c | 0.254 ± 0.27 c | 1.01 ± 0.46 b | 1.44 ± 85.9 a | 1.14 ± 1.57 b | 0.042 * |
| Dispose | pH | MC | SOM | AP | AN | Ak | ALP | BG | NAG | CAT | Ca2+ | Mg | HCO3− | CO32− | Soil Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YM-1 | 0.922 | 0.000 | 0.112 | 0.125 | 0.787 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.376 | 0.401 | 0.121 | 0.370 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 2.702 |
| YM-2 | 0.084 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.031 | 0.745 | 0.089 | 0.512 | 1.000 | 0.239 | 0.276 | 0.000 | 0.111 | 2.245 |
| YM-3 | 1.000 | 0.237 | 0.387 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.21 | 0.931 | 0.059 | 0.560 | 0.933 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.632 | 0.000 | 4.018 |
| YM-4 | 0.922 | 0.506 | 0.297 | 0.778 | 0.857 | 0.666 | 1.00 | 0.142 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.656 | 0.182 | 0.448 | 0.370 | 4.214 |
| YM-5 | 0.000 | 0.887 | 1.000 | 0.787 | 3.107 | 1.000 | 0.293 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.481 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.322 | 0.259 | 5.477 |
| Weight | 0.854 | 1.000 | 0.904 | 0.531 | 0.611 | 0.576 | 0.601 | 0.535 | 0.320 | 0.407 | 0.236 | 0.065 | 0.261 | 0.137 | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Kang, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, Q.; Ai, F. The Mechanisms of Soil Conditioner and Switchgrass in Improving Saline–Alkali Soil: A Field Study in a Semi-Arid Area. Biology 2025, 14, 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121788
Li Y, Liu Q, Kang L, Zhang K, Li Q, Ai F. The Mechanisms of Soil Conditioner and Switchgrass in Improving Saline–Alkali Soil: A Field Study in a Semi-Arid Area. Biology. 2025; 14(12):1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121788
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yixuan, Qing Liu, Longfei Kang, Kaiyu Zhang, Qiang Li, and Feng Ai. 2025. "The Mechanisms of Soil Conditioner and Switchgrass in Improving Saline–Alkali Soil: A Field Study in a Semi-Arid Area" Biology 14, no. 12: 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121788
APA StyleLi, Y., Liu, Q., Kang, L., Zhang, K., Li, Q., & Ai, F. (2025). The Mechanisms of Soil Conditioner and Switchgrass in Improving Saline–Alkali Soil: A Field Study in a Semi-Arid Area. Biology, 14(12), 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121788





