Photosynthesis and Spatial Distribution of Surface Phytoplankton in the Yangtze Estuary and Adjacent Waters During Spring
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
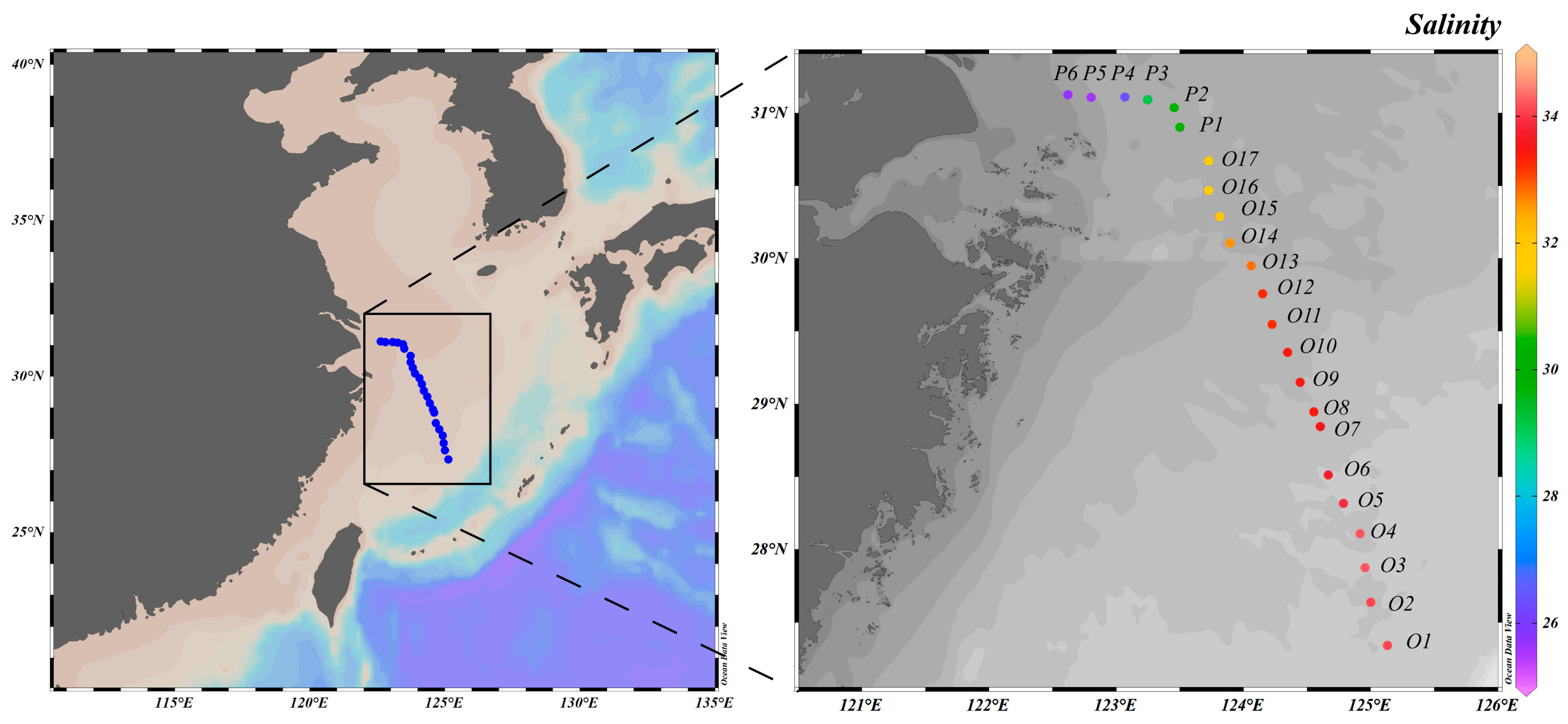
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Environmental Parameters Determination
2.3. In Situ Quantification of Photosynthetic Characteristics
2.4. Phytoplankton Community Composition Based on Pigment Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Basic Environmental Parameters in the YRE and the Adjacent East China Sea
3.2. Distribution of Phytoplankton Photosynthetic Parameters in the YRE and the Adjacent East China Sea
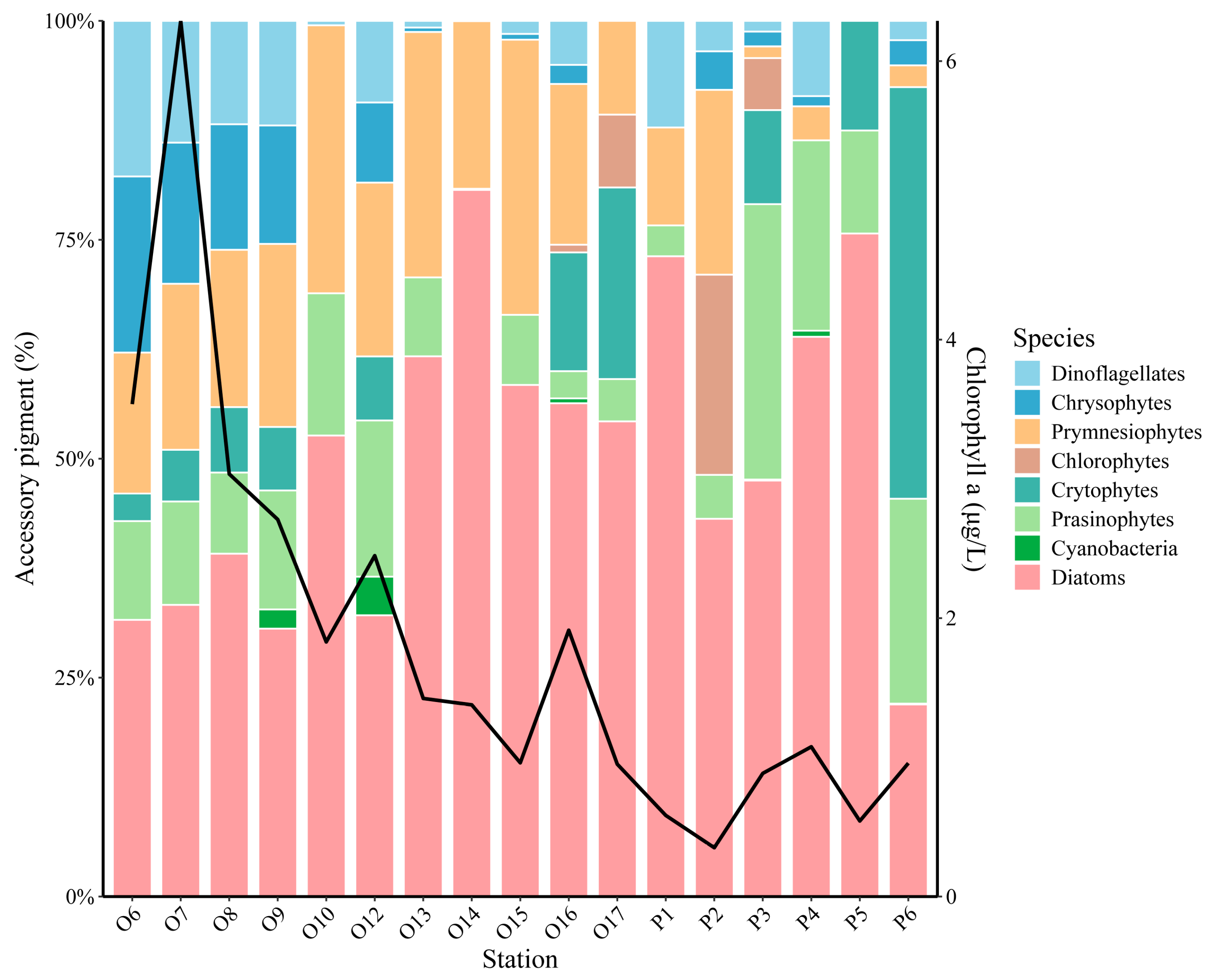
3.3. Phytoplankton Community Composition in Representative Areas
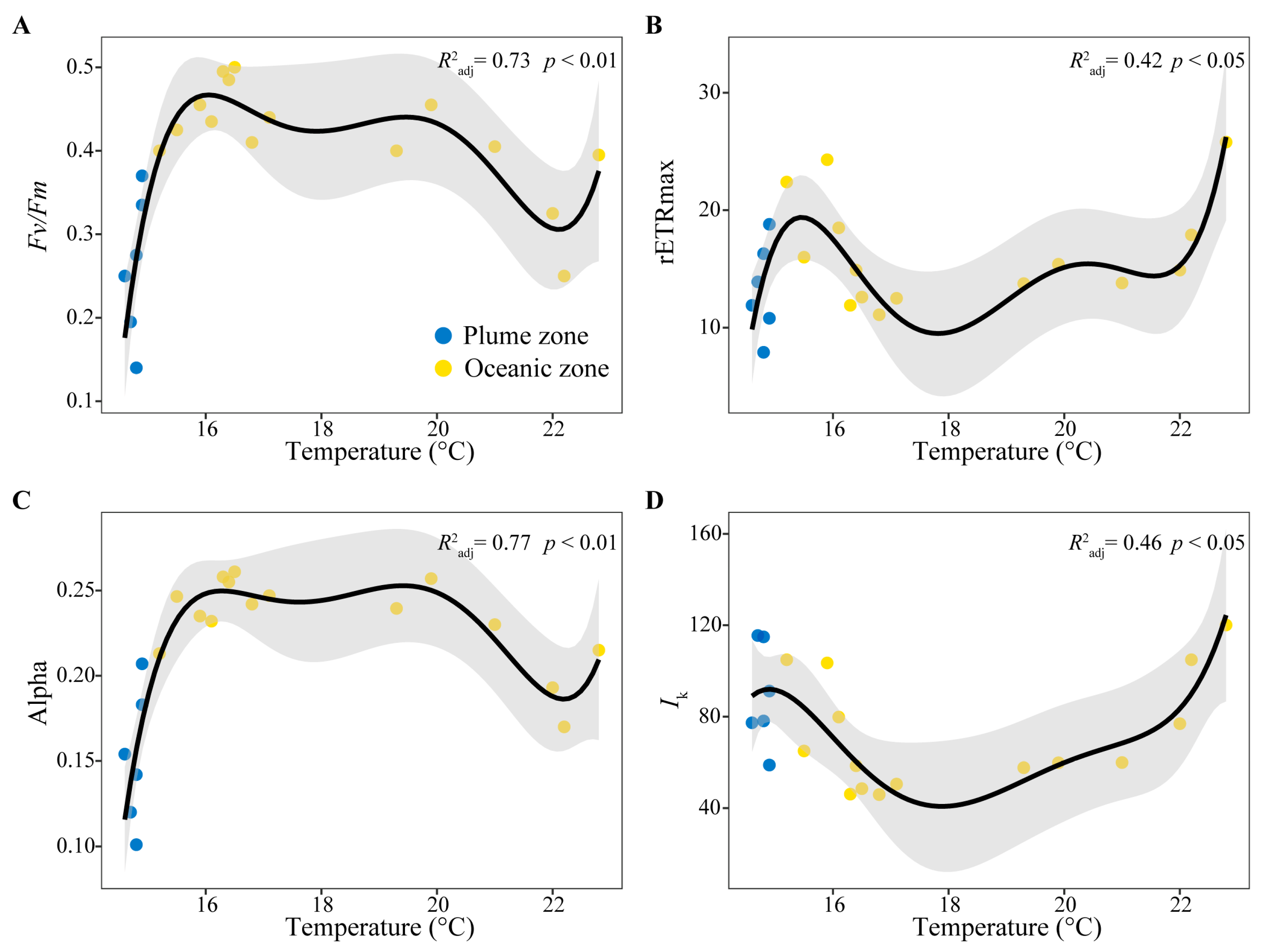
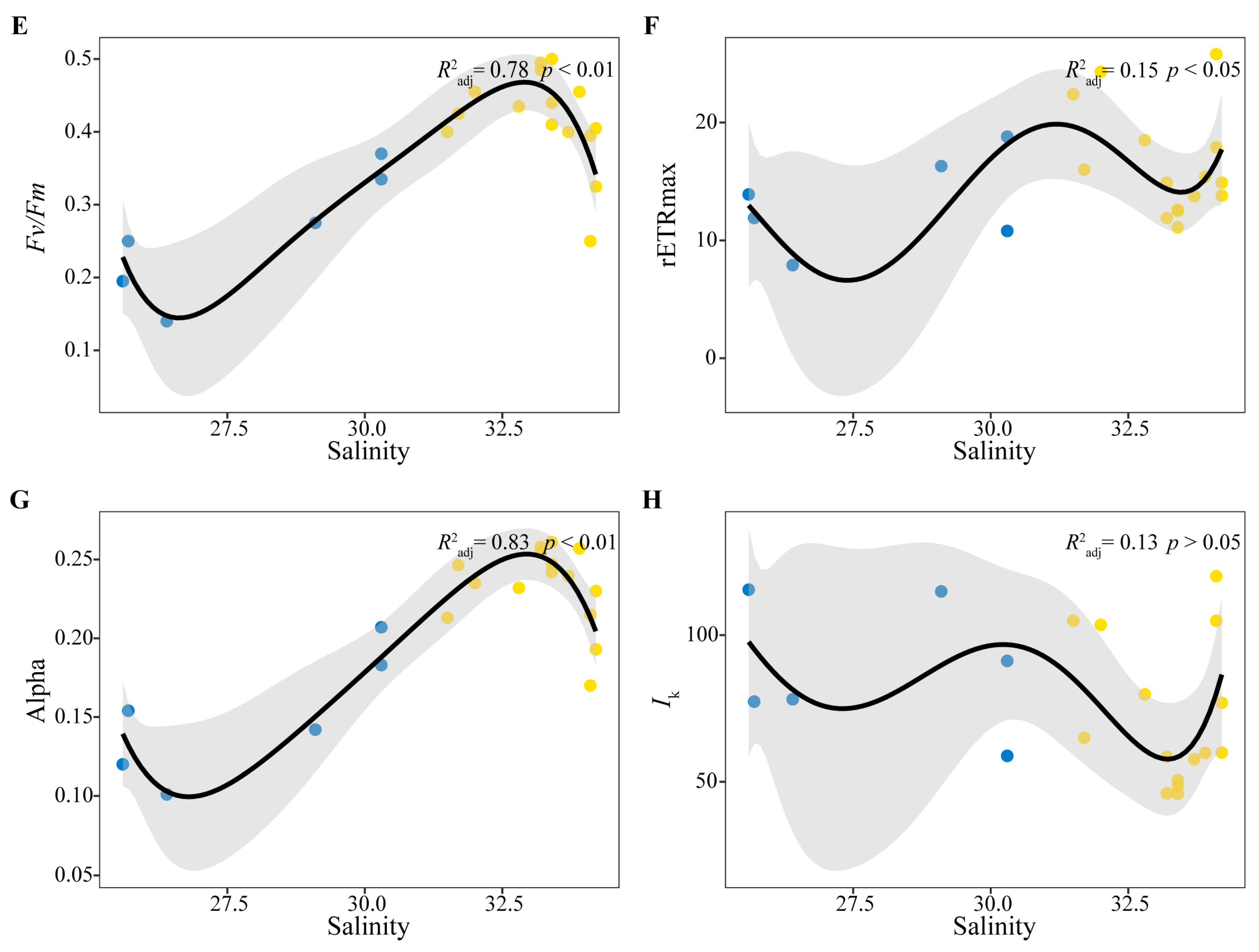
3.4. Correlation Analysis Between Phytoplankton Photosynthetic Characteristics and Environmental Factors
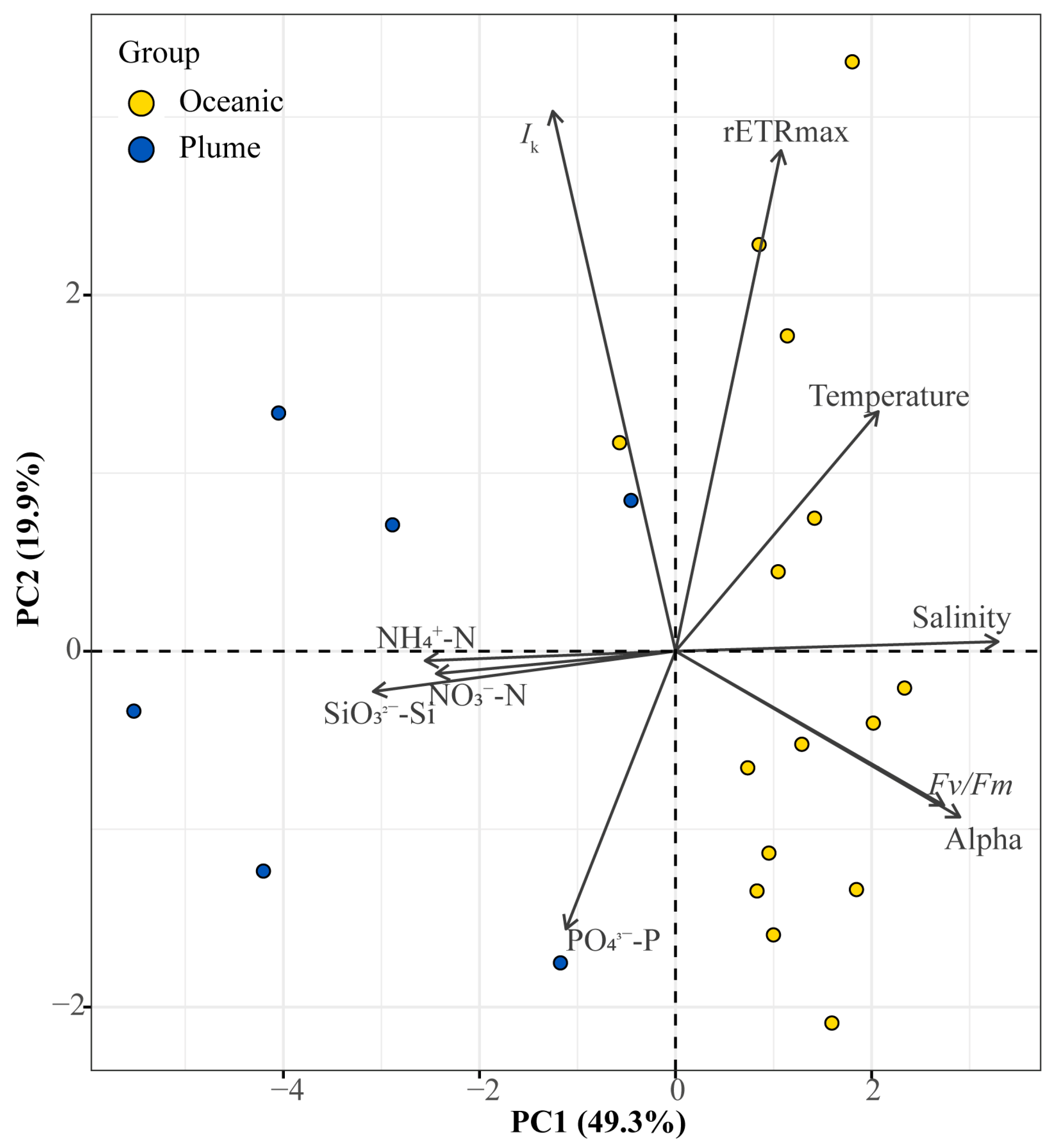
3.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Phytoplankton Communities Shaped by Environmental Gradients
4.2. Factors Influencing the Distribution of Phytoplankton Photosynthetic Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lotze, H.K.; Lenihan, H.S.; Bourque, B.J.; Bradbury, R.H.; Cooke, R.G.; Kay, M.C.; Kidwell, S.M.; Kirby, M.X.; Peterson, C.H.; Jackson, J.B.C. Depletion, degradation, and recovery potential of estuaries and coastal seas. Science 2006, 312, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Xu, X.-R.; Sun, Y.-X.; Liu, J.-L.; Li, H.-B. Heavy metal pollution in coastal areas of South China: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloern, J.E.; Abreu, P.C.; Carstensen, J.; Chauvaud, L.; Elmgren, R.; Grall, J.; Greening, H.; Johansson, J.O.R.; Kahru, M.; Sherwood, E.T.; et al. Human activities and climate variability drive fast-paced change across the world’s estuarine-coastal ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agardy, T.A.J.; Dayton, P.; Curran, S.; Vrsmarty, C. Coastal systems and coastal communities. In Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Current State and Trends; Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, Ed.; Findings of the Condition and Trends Working Group; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 513–549. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Hu, H.J.; Gao, X.; Kan, J.J.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, J. Phytoplankton diversity, spatial patterns, and photosynthetic characteristics under environmental gradients and anthropogenic influence in the Pearl River Estuary. Biology 2024, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Chen, F.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, M.; Kan, J.J. Estuarine gradients dictate spatiotemporal variations of microbiome networks in the Chesapeake Bay. Environ. Microbiome 2021, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Heil, C.A.; Glibert, P.M.; Solomon, C.M.; Greenwood, J.; Greenwood, J.G. Plankton Community Changes and Nutrient Dynamics Associated with Blooms of the Pelagic Cyanobacterium Trichodesmium in the Gulf of Mexico and the Great Barrier Reef. Water 2024, 16, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.R.; Yates, K.K.; Hubbard, K.A.; Garrett, M.J.; Frankle, J.D. Nutrient and carbonate chemistry patterns associated with Karenia brevis blooms in three West Florida Shelf estuaries 2020–2023. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1331285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.T.; Li, S.Y.; Geng, B.X. Modeling the mass flux budgets of water and suspended sediments for the river network and estuary in the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Mar. Syst. 2011, 88, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Xu, J.; Huang, X.P.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.J.; Ye, F.; Liang, X.M. Relationship between nutrients and plankton biomass in the turbidity maximum zone of the Pearl River Estuary. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloern, J.E.; Jassby, A.D.; Schraga, T.S.; Nejad, E.; Martin, C. Ecosystem variability along the estuarine salinity gradient: Examples from long-term study of San Francisco Bay. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, S272–S291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changjiang Water Resources Commission. Changjiang Sediment Bulletin 2023; Ministry of Water Resources: Wuhan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Lin, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, C. Phytoplankton Blooms off a High Turbidity Estuary: A Case Study in the Changjiang River Estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2019, 124, 8036–8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wu, H. Rapid variations of phytoplankton blooms and their dynamics off the Changjiang River Estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1345940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.-J.; Shen, Z.-L.; Yu, R.-C. Responses of a coastal phytoplankton community to increased nutrient input from the Changjiang (Yangtze) River. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhong, X.; Lv, Z.; Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Song, Z.; Ran, X. Tracking phosphorus dynamics in the Changjiang Estuary: Causes and implications. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, R.-C.; Kong, F.-Z.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-X. Seasonal impacts of Kuroshio intrusion on pico-phytoplankton dynamics near the Changjiang River estuary. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 202, 106789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Xu, M.; Zou, X.; Wang, C. The changing Changjiang River estuarine-coastal ocean continuum in the anthropocene. Catena 2024, 238, 107904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, M. Long-term changes in phytoplankton communities in China’s Yangtze Estuary driven by altered riverine fluxes and rising sea surface temperature. Geomorphology 2021, 376, 107566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yao, Q.; Yu, Z.; Ran, X. Trends in nutrients in the Changjiang River. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Shi, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Bellerby, R.; Ding, P. Interannual variabilities of nutrients and phytoplankton off the changjiang estuary in response to Changing River inputs. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2020, 125, e2019JC015595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Song, X.; Cao, X.; Yuan, Y. The Seasonal Characteristics of Dissolved Oxygen Distribution and Hypoxia in the Changjiang Estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.T.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Ge, J.Z.; Deng, B.; Du, J.Z.; Zhang, J. Reconstruction of the main phytoplankton population off the Changjiang Estuary in the East China Sea and its assemblage shift in recent decades: From observations to simulation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, C.; Sun, B.; Wang, X.; Shi, X. Seasonal changes in phytoplankton biomass and dominant species in the Changjiang River Estuary and adjacent seas: General trends based on field survey data 1959–2009. J. Ocean Univ. China 2014, 13, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gao, Y.H.; Zhu, T.M.; Li, J. Application comparison of two marine primary production models inthe adjacent sea area of the Changjiang River Estuary. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2023, 53, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Tan, L. Variation in photosynthetic activity of phytoplankton during the spring algal blooms in the adjacent area of Changjiang River estuary. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Cao, L. The linkage between phytoplankton productivity and photosynthetic electron transport in the summer from the Changjiang River to the East China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1383988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guo, S.J.; Liang, J.H.; Sun, X.X. In situ phytoplankton photosynthetic characteristics and their controlling factors in the eastern Indian Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 198, 115869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.L.; Sun, X.X.; Zheng, S. In situ study on photosynthetic characteristics of phytoplankton in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea in summer 2013. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 160, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Li, J. Photosynthetic characteristics of phytoplankton in the surface water of Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent sea area in summer. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2023, 41, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Bao, Y.L.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, J. The effects of temperature and sulfamethoxazole on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanelt, D. Photosynthesis assessed by chlorophyll fluorescence. In Bioassays; Häder, D.-P., Erzinger, G.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 169–198. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.H.; Bao, Y.L.; Gao, X.; Glibert, P.M. Summer phytoplankton photosynthetic characteristics in the Changjiang River Estuary and the adjacent East China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1111557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiao, W.; Landry, M.R.; Chiang, K.-P.; Wang, L.; Huang, B. Responses of Phytoplankton Communities to Environmental Variability in the East China Sea. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 832–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Pan, D.; Mao, Z.; Zhu, Q. The study on the inversing model of water transparency using the SeaWiFS data. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2004, 26, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Van Heukelem, L.; Thomas, C.S. Computer-assisted high-performance liquid chromatography method development with applications to the isolation and analysis of phytoplankton pigments. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 910, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wei, H.; Li, C.; Huang, Q. High-resolution phytoplankton diel variations in the summer stratified central Yellow Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2012, 68, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlitzer, R. Ocean Data View (ODV). Available online: https://odv.awi.de/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Mackey, M.D.; Mackey, D.J.; Higgins, H.W.; Wright, S.W. CHEMTAX—A program for estimating class abundances from chemical markers: Application to HPLC measurements of phytoplankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 144, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.; Whitfield, A.K. Challenging paradigms in estuarine ecology and management. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 94, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Gao, L.; Shen, F.; Liang, X.S. Spatial Distribution and Physical Controls of the Spring Algal Blooming Off the Changjiang River Estuary. Estuar. Coast. 2019, 42, 1066–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ors, A.; Bartolomé, M.C.; Sánchez-Fortún, S. Repercussions of salinity changes and osmotic stress in marine phytoplankton species. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 175, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lin, Q.; Lin, J.; Song, X.; Tan, Y.; Huang, L. Environmental gradients regulate the spatial variations of phytoplankton biomass and community structure in surface water of the Pearl River estuary. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Su, S.; Li, H.; Kang, W.; Jia, R. Spatio-temporal variability of surface phytoplankton community structure in relation to different water systems in the east China sea coast. Cont. Shelf Res. 2025, 287, 105426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Xu, Q.; Gibson, K.; Liu, S.; Chen, N. Metabarcoding analysis of harmful algal bloom species in the Changjiang Estuary, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Xu, Z.; Yu, R.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, M. Distribution patterns of phytoplankton in the Changjiang River estuary and adjacent waters in spring 2009. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Yu, Z. The response of spring phytoplankton assemblage to diluted water and upwelling in the eutrophic Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-M.; Tang, H.-J.; Shi, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.-S.; Wang, X.-L. Increased nutrient loads from the Changjiang (Yangtze) River have led to increased Harmful Algal Blooms. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.; Gowen, R.J.; Harrison, P.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Hoagland, P.; Moschonas, G. Anthropogenic nutrients and harmful algae in coastal waters. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.J.; Liu, D.F.; Yang, Z.J.; Tian, Z.B. Effects of water temperature on the phytoplankton community structure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Ou, L.; Dai, X.; Cui, L.; Dong, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Lu, D. An overview of Prorocentrum donghaiense blooms in China: Species identification, occurrences, ecological consequences, and factors regulating prevalence. Harmful Algae 2022, 114, 102207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.H.; Li, Z.; Seo, M.H.; Soh, H.Y.; Lim, W.A.; Park, J.W. Harmful Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu is widely distributed along the East China Sea and Korean Coastal Area. Ocean Sci. J. 2019, 54, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-X.; Yu, R.-C.; Zhou, M.-J. Seasonal succession of microalgal blooms from diatoms to dinoflagellates in the East China Sea: A numerical simulation study. Ecol. Model. 2017, 360, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Li, D.; Wang, B.; Jin, H.; Ye, R.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Tao, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, Q.; et al. Influences of nutrients on summer algal bloom in the Changjiang plume revealed by high-resolution profiles. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 210, 107318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, M.J.; Won, J.; Choi, D.H.; Lee, H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, C.M.; Park, C.H.; Noh, J.H. A CHEMTAX Study Based on Picoeukaryotic Phytoplankton Pigments and Next-Generation Sequencing Data from the Ulleungdo-Dokdo Marine System of the East Sea (Japan Sea): Improvement of Long-Unresolved Underdetermined Bias. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, M.J.; Choi, D.H.; Lee, H.; Won, J.; Kim, G.-U.; Lee, Y.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Ra, K.; Yang, W.; Lee, J.; et al. Phytoplankton spring succession pattern in the Yellow Sea surveyed at Socheongcho Ocean Research Station. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1280612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latasa, M. Improving estimations of phytoplankton class abundances using CHEMTAX. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 329, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.M.; Li, G.H.; He, C.; Huang, Y.; Yu, D.; Deng, H.W.; Tong, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Dupuy, C.; Huang, B.Q.; et al. Diversity, community structure, and quantity of eukaryotic phytoplankton revealed using 18S rRNA and plastid 16S rRNA genes and pigment markers: A case study of the Pearl River Estuary. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2023, 5, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Song, S.; Chen, T.; Li, C. The diversity and structure of marine protists in the coastal waters of China revealed by morphological observation and 454 pyrosequencing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 189, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Environment Factors | Oceanic | Plume | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | Range | |
| Salinity | 33.25 ± 0.89 | 31.50–34.10 | 27.90 ± 2.25 | 25.70–30.30 |
| Temperature (°C) | 18.20 ± 2.71 | 15.20–22.80 | 14.78 ± 0.12 | 14.60–14.90 |
| NH4+-N (μM) | 1.42 ± 0.28 | 1.08–1.93 | 1.92 ± 0.30 | 1.58–2.27 |
| PO43−-P (μM) | 0.02 ± 0.02 | <LD–0.06 | 0.04 ± 0.05 | <LD–0.11 |
| SiO32−-Si (μM) | 3.24 ± 1.97 | 1.01–7.93 | 14.61 ± 9.66 | 5.17–31.11 |
| NO3−-N (μM) | 1.02 ± 1.13 | <LD–4.04 | 6.06 ± 8.00 | 1.40–21.30 |
| SSC (mg/L) | 3.43 ± 8.72 | 0.50–29.70 | 3.62 ± 6.54 | 0.60–16.9 |
| Chlorophyll Fluorescence | Fv/Fm | Alpha | rETRmax | Ik |
|---|---|---|---|---|
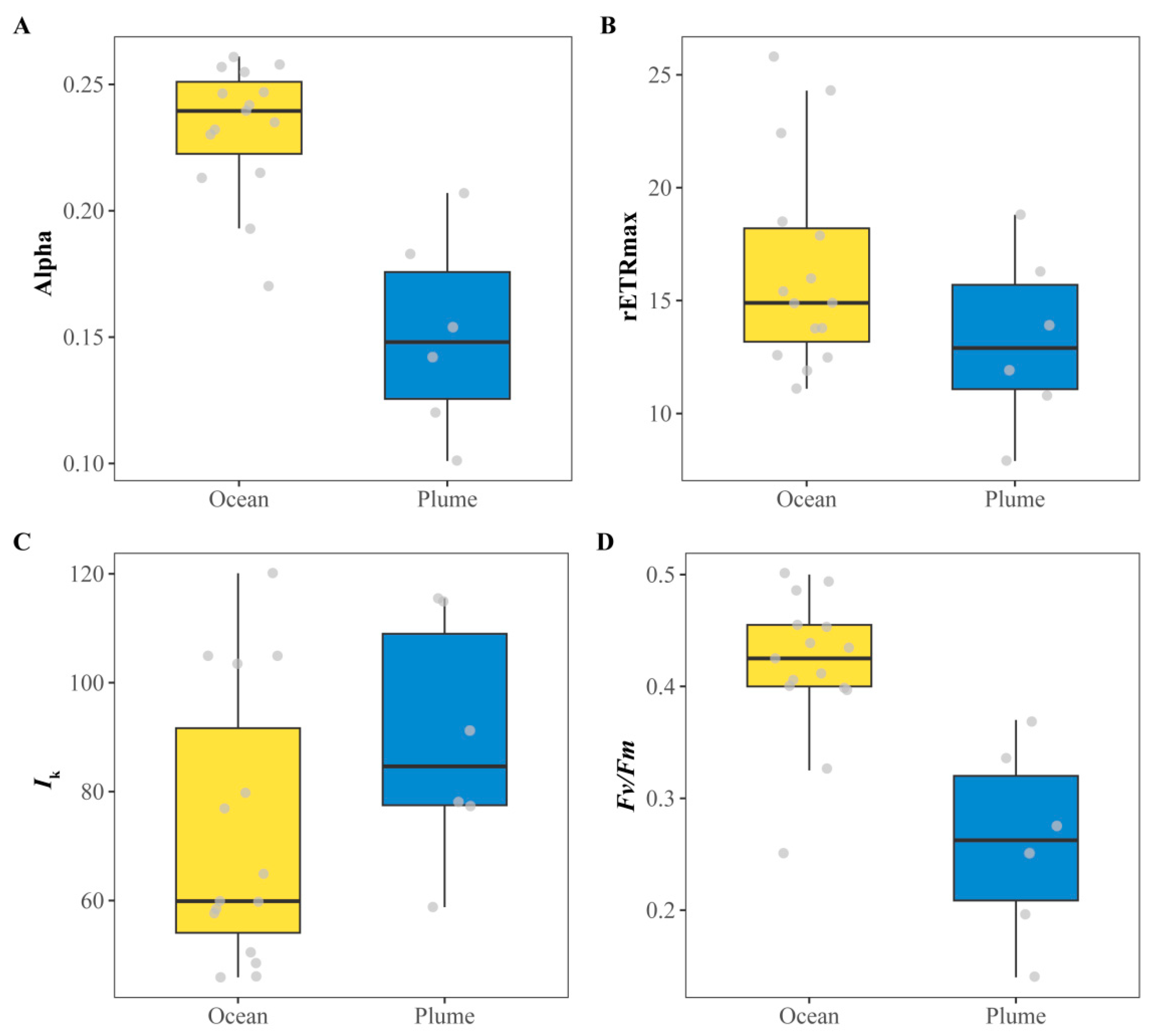
| Oceanic | 0.42 ± 0.06 | 0.23 ± 0.03 | 16.38 ± 4.56 | 72.13 ± 24.86 |
| Plume | 0.26 ± 0.09 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 13.27 ± 3.92 | 89.30 ± 22.56 |
| Factors | Salinity | Temperature | NH4+-N | PO43−-P | SiO32−-Si | NO3−-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fv/Fm | 0.37 | 0.34 | −0.47 * | −0.09 | −0.33 | −0.16 |
| Alpha | 0.47 * | 0.45 * | −0.52 * | −0.11 | −0.38 | −0.14 |
| rETRmax | 0.14 | 0.19 | −0.14 | −0.34 | −0.39 | −0.15 |
| Ik | −0.30 | −0.24 | 0.22 | −0.15 | 0.06 | 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, H.; Xia, J.; Gao, X.; Huang, W.; Pan, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, J. Photosynthesis and Spatial Distribution of Surface Phytoplankton in the Yangtze Estuary and Adjacent Waters During Spring. Biology 2025, 14, 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111628
Hu H, Xia J, Gao X, Huang W, Pan J, Chen Z, Li J. Photosynthesis and Spatial Distribution of Surface Phytoplankton in the Yangtze Estuary and Adjacent Waters During Spring. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111628
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Haojie, Jing Xia, Xiu Gao, Wenlian Huang, Jiuyi Pan, Zhi Chen, and Ji Li. 2025. "Photosynthesis and Spatial Distribution of Surface Phytoplankton in the Yangtze Estuary and Adjacent Waters During Spring" Biology 14, no. 11: 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111628
APA StyleHu, H., Xia, J., Gao, X., Huang, W., Pan, J., Chen, Z., & Li, J. (2025). Photosynthesis and Spatial Distribution of Surface Phytoplankton in the Yangtze Estuary and Adjacent Waters During Spring. Biology, 14(11), 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111628






