Distribution Characteristics of Suspended Macroalgae in the Southern Yellow Sea Before the Green Tide Outbreak
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Station Setup
2.2. Environmental Parameter Measurement
2.3. Suspended Macroalgae Sampling
2.4. Suspended Macroalgae Counting and Processing
3. Results
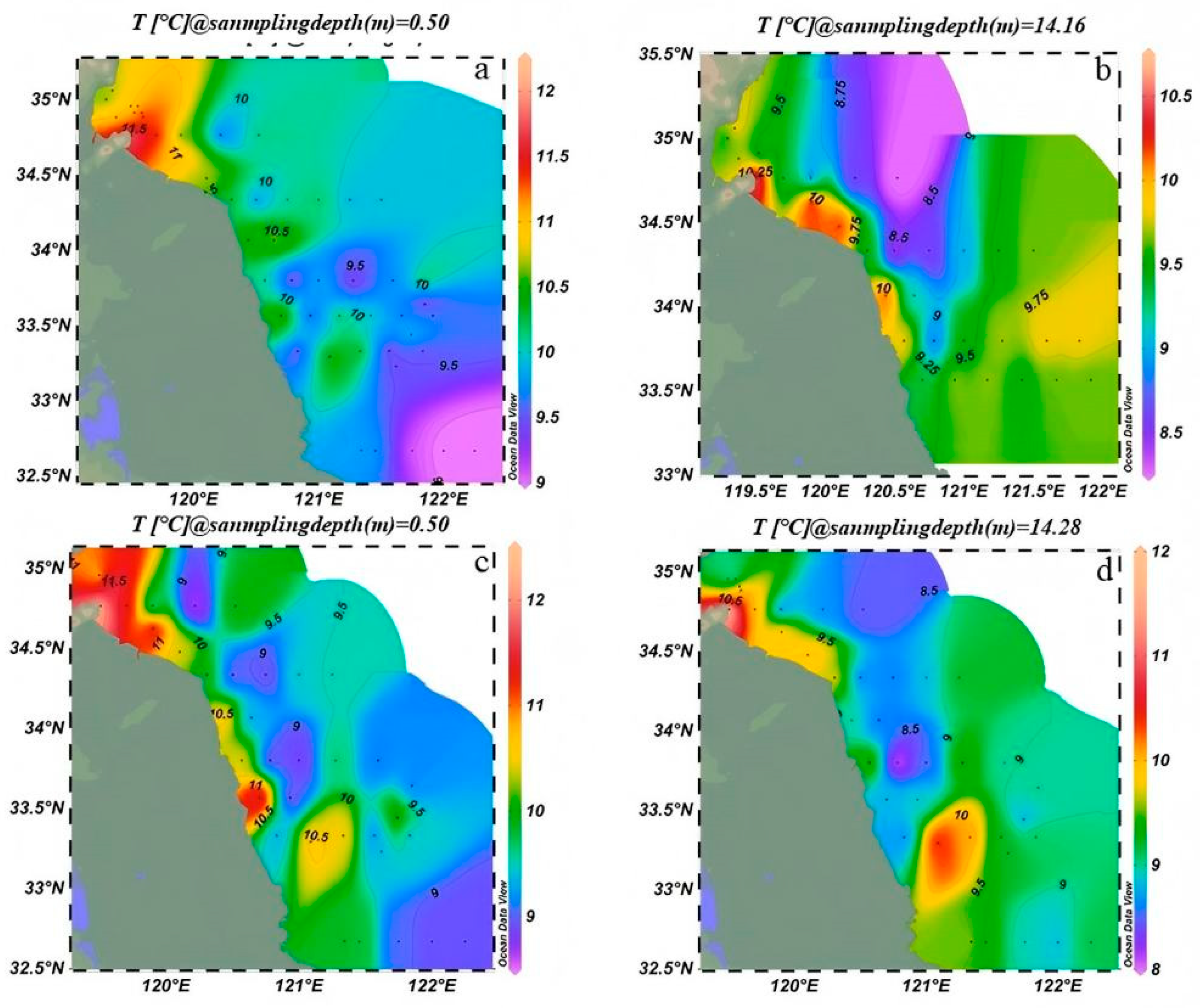
3.1. Changes in Environmental Factors
3.1.1. Changes in Physical and Chemical Parameters
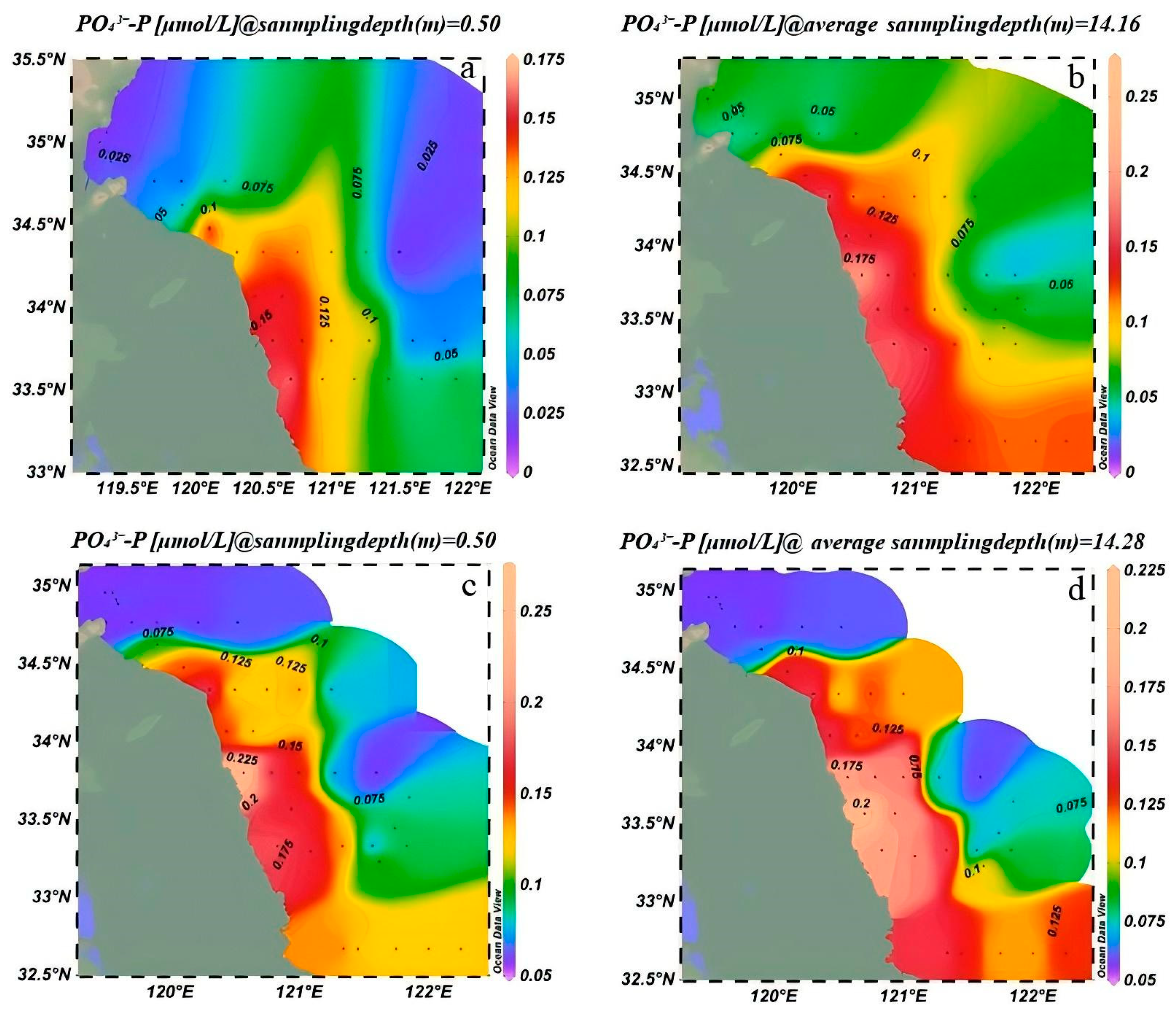
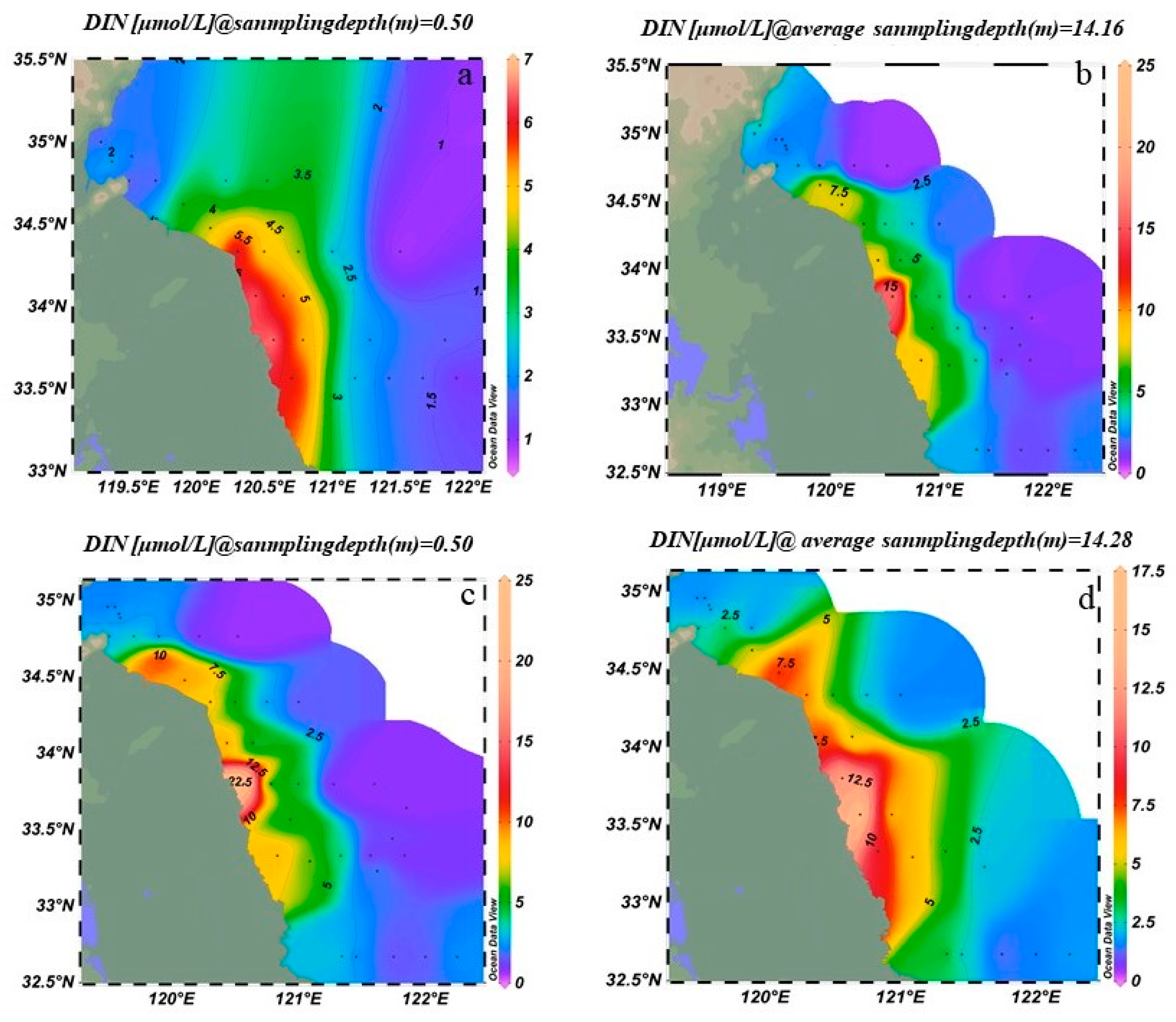
3.1.2. Interannual Variation of Nutrients in the Southern Yellow Sea
3.1.3. Spatial Distribution of Phosphate and Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen in the Southern Yellow Sea
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variation in Suspended Macroalgae Abundance in the Southern Yellow Sea
3.2.1. Variation in Suspended Macroalgae Abundance
3.2.2. Variation in Suspended Macroalgae Abundance in the Radial Sand Ridges During 2024
3.3. Changes in the Spatiotemporal Distribution and Species Composition of Suspended Macroalgae in the Southern Yellow Sea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, D.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Cochlan, W.P.; Glibert, P.M.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Kudela, R.M.; Parsons, M.L.; Rensel, J.E.J.; Townsend, D.W.; et al. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Examining linkages from selected coastal regions of the United States. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiela, I.; McClelland, J.; Hauxwell, J.; Behr, P.J.; Hersh, D.; Foreman, K. Macroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: Controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellner, K.G.; Doucette, G.J.; Kirkpatrick, G.J. Harmful algal blooms: Causes, impacts, and detection. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. The complex relationships between increases in fertilization of the earth, coastal eutrophication and proliferation of harmful algal blooms. In Ecology of Harmful Algae; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 189, pp. 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, J.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.C.; Dortch, Q.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende, J.F.D.; Bezerra, J.N.D.; Borburema, H.D.S.; de Oliveira, V.P. Future environmental scenarios favor the performance of Ulva lactuca—Implications for the intensification of green tides. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 210, 107262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, R.L. The British Isles. In Marine Benthic Vegetation: Recent Changes, the Effects of Eutrophication; Schramm, W., Nienhuis, P.H., Eds.; Marine Benthic Vegetation 123; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996; pp. 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, R.L. The occurrence of ‘green tides’: A review. In Marine Benthic Vegetation: Recent Changes and the Effects of Eutrophication; Schramm, W., Nienhuis, P.H., Eds.; Marine Benthic Vegetation 123; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996; pp. 7–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenstein, G. Blooms of Ulvoids in Puget Sound; Puget Sound water quality action team, Office of the Governor: Olympia, WA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.Y.; Keesing, J.K.; Xing, Q.U.; Shi, P. World’s largest macroalgal bloom caused by expansion of seaweed aquaculture in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gower, J.F.R.; King, S.A. Distribution of floating Sargassum in the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean mapped using MERIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 1917–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.H.; Zhang, X.W.; Mao, Y.Z.; Liang, C.W.; Xu, D.; Zou, J.; Zhuang, Z.M.; Wang, Q.Y. ‘Green tides’ are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: Taking the world’s largest example. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Y.; Keesing, J.K.; He, P.M.; Wang, Z.L.; Shi, Y.J.; Wang, Y.J. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: Formation and implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.Y.; Liu, J.L.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y.Q.; Cui, Q.W.; Wu, L.J.; Gao, S.; Zhang, J.H.; He, P.M. Review of the development of the green tide and the process of control in the southern Yellow Sea in 2022. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 302, 108772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, N.; Shao, K.; Shen, L.; Wang, Z.; Han, X.; Zhou, K.; Kong, D.; Pan, X. How did the floating Ulva prolifera develop into the world’s largest green tide? Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 202, 106763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, Y.; Fang, S.; Wang, Z.L.; Xiao, J.; Li, R.X.; Fu, M.Z.; Zhu, M.Y.; Zhang, X.L. Temporal and spatial distributions of green algae micro-propagules in the coastal waters of the Subei Shoal, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; He, L.W.; Ma, Y.C.; Huan, L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xia, B.M.; Wang, G.C. Economically important red algae resources along the Chinese coast: History, status, and prospects for their utilization. Algal Res. 2020, 46, 101817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Xia, J.; Zhuang, M.M.; Zhang, J.H.; Yu, K.F.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y.Q.; Tong, Y.C.; Xia, L.H.; Qin, Y.T.; et al. Controlling the source of green tides in the Yellow Sea: NaClO treatment of Ulva attached on Pyropia aquaculture rafts. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.Y.; Cao, X.L.; Li, S.; Cao, J.X.; Tong, Y.C.; Sun, Y.Q.; Liu, J.L.; Zhao, S.; Cui, Q.W.; Zeng, Y.Q.; et al. Distribution of Ulva prolifera, the dominant species in green tides along the Jiangsu Province coast in the Southern Yellow Sea, China. J. Sea Res. 2023, 196, 102436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Miyamura, S.; Hiraoka, M.; Kawano, S. Asexual thalli originated from sporophytic thalli via apomeiosis in the green seaweed Ulva. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.Z.; Kim, K.J.; Yarish, C.; Augyte, S.; He, P.M. Responses of the germination and growth of Ulva prolifera parthenogametes, the causative species of green tides, to gradients of temperature and light. Aquat. Bot. 2021, 170, 103343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.Z.; Fan, S.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Song, W.; Sun, K.M.; Han, H.B.; Xiao, J.; Shen, S.D. Buoyancy potential of dominant green macroalgal species in the Yellow Sea’s green tides, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Xu, D.; Mao, Y.Z.; Li, Y.X.; Xue, S.Y.; Zou, J.; Lian, W.; Liang, C.W.; Zhuang, Z.M.; Wang, Q.Y.; et al. Settlement of vegetative fragments of Ulva prolifera confirmed as an important seed source for succession of a large-scale green tide bloom. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Pang, S.J.; Zhao, X.B.; Hu, C.M. Quantitative, molecular and growth analyses of Ulva microscopic propagules in the coastal sediment of Jiangsu province where green tides initially occurred. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 74, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.X.; Liu, J.L.; Zhao, S.; Tong, Y.C.; Li, S.; Xia, Z.Y.; Hu, M.J.; Sun, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.H.; He, P.M. Advances in the research on micropropagules and their role in green tide outbreaks in the Southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.S.; Gong, N.; Shen, L.Y.; Han, X.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhou, K.; Pan, X.S.; Cong, P.F. Why did the world’s largest green tides occur exclusively in the southern Yellow Sea? Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 200, 106671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.C.; Liu, Q.; Kang, Z.J.; Yu, R.C.; Yan, T.; Zhou, M.J. Development of a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) method for rapid detection of Ulva prolifera. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Huo, Y.Z.; Wu, H.L.; Yu, K.F.; Kim, J.K.; Yarish, C.; Qin, Y.T.; Liu, C.C.; Xu, R.; He, P.M. The origin of the Ulva macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea in 2013. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Hu, C.Y.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.H.; Xu, N.J. Dynamic metabolic profiles of the marine macroalga Ulva prolifera during fragmentation-induced proliferation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, L.; Gu, W.H.; Wang, X.L.; Yan, Y.R.; Tang, Q.; Han, X.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhou, K.; Qiu, Q.; Xu, J.T.; et al. Reproductive traits of floating Ulva prolifera sporophytes and gametophytes and their contribution to the Yellow Sea green tide. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 214, 117752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Yarish, C.; He, P.M. The expansion of Ulva prolifera O.F. Müller macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea, PR China, through asexual reproduction. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasshoff, K.; Ehrhardt, M.; Kremling, K. Methods of Seawater Analysis, 2nd ed.; Verlag Chemie GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 1983; p. 419. [Google Scholar]
- Grasshoff, K.; Kremling, K.; Ehrhardt, M. Methods of Seawater Analysis, 3rd ed.; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999; p. 600. [Google Scholar]
- GB 17378-2007; Marine Monitoring Specification. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 12763.6-2007; Supervision Specifications for Oceanographic Survey. State Bureau of Quality and Technical. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Hayden, H.S.; Blomster, J.; Maggs, C.A.; Silva, P.C.; Stanhope, M.J.; Waaland, J.R. Linnaeus was right all along: Ulva and Enteromorpha are not distinct genera. Eur. J. Phycol. 2003, 38, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomster, J.; Maggs, C.A.; Stanhope, M.J. Molecular and morphological analysis of Enteromorpha intestinalis and E. compressa (Chlorophyta) in the British Isles. Phycologia 1998, 34, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Yokoyama, N.; Arai, S.; Hiraoka, M. Phylogeography of the genus Ulva (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta), with special reference to the Japanese freshwater and brackish taxa. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.C.; Xia, L.H.; Liu, J.L.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y.Q.; Wu, T.J.; Xia, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Cao, J.X.; Zhang, J.H. Distribution and identification of Ulva aragoensis (Ulvaceae, Chlorophyta), a constituent species of green tides in the Southern Yellow Sea, based on molecular data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Fu, M.Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Song, W. Progress on the study of the Yellow Sea green tides caused by Ulva prolifera. Hai Yang Xue Bao 2018, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Zhou, F.; Meng, Q.; Ma, X.; Bao, M. Exploring the potential of cold patches as an indicator for algal bloom occurrence and migration. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2026, 222, 118588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, P.; Sun, J.; Liu, S.; Xing, L.; Yu, D.; Feng, Q. Potential impact of sea surface temperature variability on the 2007 sudden bloom of Ulva prolifera in the Southern Yellow Sea. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, R.X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Microscopic observation on population growth and reproduction of Enteromorpha prolifera under different temperature and salinity. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2012, 30, 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.L.; Fu, M.Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Song, W.; Liu, G.X.; Shi, X.Y.; Wang, X.N.; Zhu, M.Y. Temporal variation of green macroalgal assemblage on Porphyra aquaculture rafts in the Subei Shoal, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.T.; Yang, G.P.; Yu, J.; Wu, G.W. Distributional characteristics of nutrients in the sea-surface microlayer and subsurface water of the Bohai and Yellow Sea in summer. Environ. Sci. 2013, 34, 2983–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Zhang, C.S.; Han, X.R.; Shi, X.Y. Changes in concentrations of oxygen, dissolved nitrogen, phosphate, and silicate in the southern Yellow Sea, 1980–2012: Sources and seaward gradients. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.A.; Liu, D.Y.; Du, J.Z. Radium-traced nutrient outwelling from the Subei Shoal to the Yellow Sea: Fluxes and environmental implication. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Tang, H.J.; Shi, X.Y.; Rivkin, R.B.; Legendre, L. Spatiotemporal variations of inorganic nutrients along the Jiangsu coast, China, and the occurrence of macroalgal blooms (green tides) in the southern Yellow Sea. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.N.; Wei, Q.S.; Jian, H.M.; Li, D.D.; Yu, Z.G.; Yao, Q.Z. Long-term variation in nutrients in the Southern Yellow Sea in response to anthropogenic inputs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, L.; Dai, W.; Gao, J.; Zhang, F.; Jin, Y. Environmental factors affecting Ulva prolifera blooms in the South Yellow Sea: Insights from deep learning models with attention mechanisms. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2025, 89, 104304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Kong, F.Z.; Liu, Q.C.; Li, F.J.; Wei, X.; Yan, T.; Jiang, P. Tempo-spatial distribution of Ulva spp. micro-propagules in the Yellow Sea during and after green tide in 2019. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 2462–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, Y.; Fu, M.Z.; Fan, S.L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.H. The dynamics of micropropagules before the Green tide (Ulva prolifera) outbreak in the southern Huanghai Sea and Changjiang (Yangtze) River Estuary area. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 34, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.; Kong, F.Z.; Yan, T.; Jiang, P. Morphological discrimination of fouling Ulva and Blidingia species on Pyropia rafts in Rudong, China: An in-field protocol for early monitoring of algae forming the Yellow Sea green tide. Bot. Mar. 2025, 68, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.J.; Miao, X.X.; Fan, S.L.; Zang, Y.; Zhang, B.T.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.L.; Fu, M.Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Xiao, J. Dynamics of green macroalgal micro-propagules and the influencing factors in the southern Yellow Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 940, 173658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Zhang, X.T.; Zhu, M.X.; Li, T.; Cao, X.Y. Experimental degradation of Ulva prolifera in sand sediments: Implications for dissolved carbon and alkalinity export from green-tide macroalgae buried in sandy intertidal zones. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 209, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.; Fu, J.; Shi, X.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, G.; Sha, Z.; Cui, H.; Wu, J. Dissipation of Ulva prolifera green tides across various spatial and temporal scales and the short-term effects on marine environments. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 207, 107082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Li, H.Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Liu, J.S.; Yang, W.D. Molecular identification of green algae from the rafts based infrastructure of Porphyra yezoensis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2077–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.X.; Zeng, Y.Q.; Xia, Z.Y.; Li, S.; He, P.M.; Zhang, J.H. Spatio-temporal distribution of micropropagules of green algae along the Jiangsu coast. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 198, 106533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.C.; Kong, F.Z.; Yan, T.; Yu, R.C.; Hu, X.K.; Miao, H.; Zhou, M.J. Green algae detachen from aquaculture rafts into seawater resultted in green tide occurrence in the yellow sea. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 49, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Geng, H.X.; Hong, X.; Kong, F.Z.; Yu, R.C. Strong interannual variation of green tides in the southern Yellow Sea: Crucial factors and implications on management strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 216, 117989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Year | Station | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | T3-3 | 121°54′49.80″ | 33°33′53.34″ |
| SE5 | 121°39′57.00″ | 33°33′53.34″ | |
| SE4 | 121°25′04.80″ | 33°33′53.34″ | |
| SE3 | 121°10′02.40″ | 33°33′53.34″ | |
| T2-1 | 120°56′02.10″ | 33°33′53.34″ | |
| T1-1 | 120°42′03.48″ | 33°33′53.34″ | |
| SY0 | 120°34′08.70″ | 33°47′48.48″ | |
| SY1 | 120°47′04.38″ | 33°47′48.48″ | |
| SY2 | 121°00′00.00″ | 33°47′48.48″ | |
| SY3 | 121°16′37.20″ | 33°47′48.48″ | |
| SY4 | 121°35′45.60″ | 33°47′48.48″ | |
| SF6 | 121°49′48.00″ | 33°47′48.48″ | |
| SH5 | 121°30′00.00″ | 34°20′00.00″ | |
| BH5 | 121°15′00.00″ | 34°20′00.00″ | |
| BH4 | 121°00′00.00″ | 34°20′00.00″ | |
| BH3 | 120°45′00.00″ | 34°20′00.00″ | |
| BH2 | 120°30′00.00″ | 34°20′00.00″ | |
| LYG5 | 120°31′16.02″ | 34°45′50.10″ | |
| LYG4 | 120°13′05.94″ | 34°45′50.10″ | |
| LYG3 | 119°53′56.22″ | 34°45′50.10″ | |
| LYG2 | 119°42′05.76″ | 34°45′50.10″ | |
| LYG1 | 119°30′17.16″ | 34°45′50.10″ | |
| HZW2 | 119°22′48.00″ | 34°52′48.00″ | |
| HZW4 | 119°31′32.88″ | 34°54′43.20″ | |
| HZW1 | 119°18′00.00″ | 35°00′00.00″ | |
| HZW3 | 119°21′00.00″ | 35°03′36.00″ | |
| T4-2 | 119°54′10.26″ | 34°37′13.38″ | |
| T4-1 | 120°06′14.76″ | 34°28′36.72″ | |
| BH1 | 120°18′19.26″ | 34°20′00.00″ | |
| T1-2 | 120°26′13.98″ | 34°03′54.24″ | |
| T2-2 | 120°38′32.16″ | 34°03′54.24″ | |
| 2024 | LYG5 | 120°31′15.60″ | 34°45′46.80″ |
| HZW1 | 119°33′14.40″ | 34°57′21.60″ | |
| HZW2 | 119°35′42.00″ | 34°52′58.80″ | |
| HZW3 | 119°29′45.60″ | 34°57′21.60″ | |
| HZW4 | 119°35′02.40″ | 34°54′36.00″ | |
| T1-1 | 120°42′03.60″ | 33°33′54.00″ | |
| T1-2 | 120°26′09.60″ | 34°03′54.00″ | |
| T2-1 | 120°56′06.00″ | 33°33′54.00″ | |
| T2-2 | 120°38′31.20″ | 34°03′54.00″ | |
| T3-1 | 121°37′12.00″ | 33°13′40.80″ | |
| T3-2 | 121°44′24.00″ | 33°26′24.00″ | |
| T3-3 | 121°51′00.00″ | 33°38′24.00″ | |
| T4-1 | 120°06′10.80″ | 34°28′33.60″ | |
| T4-2 | 119°54′10.80″ | 34°37′15.60″ | |
| RD1 | 121°20′31.20″ | 32°40′08.40″ | |
| RD2 | 121°27′10.80″ | 32°39′57.60″ | |
| RD3 | 121°45′00.00″ | 32°40′01.20″ | |
| RD4 | 122°00′00.00″ | 32°39′57.60″ | |
| RD5 | 122°15′00.00″ | 32°39′57.60″ | |
| DF1 | 120°50′00.00″ | 33°19′40.80″ | |
| DF2 | 121°05′20.40″ | 33°17′27.60″ | |
| DF3 | 121°20′00.00″ | 33°19′40.80″ | |
| DF4 | 121°34′01.20″ | 33°19′44.40″ | |
| DF5 | 121°49′58.80″ | 33°19′44.40″ | |
| SY0 | 120°34′08.40″ | 33°47′52.80″ | |
| SY1 | 120°47′02.40″ | 33°47′52.80″ | |
| SY2 | 121°00′00.00″ | 33°47′52.80″ | |
| SY3 | 121°16′37.20″ | 33°47′49.20″ | |
| SY4 | 121°35′45.60″ | 33°47′52.80″ | |
| BH1 | 120°18′19.80″ | 34°20′02.40″ | |
| BH2 | 120°30′03.60″ | 34°20′00.00″ | |
| BH3 | 120°45′00.00″ | 34°20′02.40″ | |
| BH4 | 121°00′00.00″ | 34°20′02.40″ | |
| BH5 | 121°15′00.00″ | 34°20′02.40″ | |
| LYG1 | 119°30′17.00″ | 34°45′47.00″ | |
| LYG2 | 119°42′07.20″ | 34°45′50.40″ | |
| LYG3 | 119°53′56.40″ | 34°45′50.40″ | |
| LYG4 | 120°13′03.00″ | 34°45′50.40″ |
| Primer | Primer Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| ITS-F | 5′-TCTTTGAAACCGTATCGTGA-3′ | [36] |
| ITS-R | 5′-GCTTATTGATATGCTTAAGTTCAGCGGGT-3′ | [37] |
| 5S-F | 5′-GGTTGGGCAGGATTAGTA-3′ | [38] |
| 5S-R | 5′-AGGCTTAAGTTGCGAGTT-3′ |
| Year | Station | Salinity | PH | DO (μmol/L) | COD-Mn (μmol/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value | Range of Change | Average Value | Range of Change | Average Value | Range of Change | Average Value | Range of Change | ||
| 2023 | Surface layer | 30.42 ± 1.12 | 27.69~32.13 | 8.14 ± 0.05 | 8.06~8.22 | 280.84 ± 8.47 | 257.19~295.00 | 16.14 ± 7.91 | 7.81~47.50 |
| Bottom layer | 30.41 ± 1.09 | 27.69~32.09 | 8.15 ± 0.05 | 8.06~8.23 | 295.18 ± 6.91 | 285.63~315.63 | 23.36 ± 16.74 | 8.44~78.75 | |
| 2024 | Surface layer | 29.54 ± 1.99 | 23.49~31.65 | 8.07 ± 0.06 | 7.97~8.20 | 292.48 ± 5.32 | 278.44~300.94 | 29.38 ± 11.60 | 17.19~69.06 |
| Bottom layer | 29.89 ± 1.40 | 26.53~31.87 | 8.08 ± 0.06 | 7.98~8.20 | 296.46 ± 4.84 | 280.94~305.63 | 34.93 ± 15.76 | 20.94~86.56 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, W.; Lei, Y.; Tan, S.; Qin, Y.; Ji, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Distribution Characteristics of Suspended Macroalgae in the Southern Yellow Sea Before the Green Tide Outbreak. Biology 2025, 14, 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101347
Yao W, Lei Y, Tan S, Qin Y, Ji H, Sun Y, Zhang J, Liu J. Distribution Characteristics of Suspended Macroalgae in the Southern Yellow Sea Before the Green Tide Outbreak. Biology. 2025; 14(10):1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101347
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Weimin, Yaoyao Lei, Shulin Tan, Yutao Qin, Huanhong Ji, Yuqing Sun, Jianheng Zhang, and Jinlin Liu. 2025. "Distribution Characteristics of Suspended Macroalgae in the Southern Yellow Sea Before the Green Tide Outbreak" Biology 14, no. 10: 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101347
APA StyleYao, W., Lei, Y., Tan, S., Qin, Y., Ji, H., Sun, Y., Zhang, J., & Liu, J. (2025). Distribution Characteristics of Suspended Macroalgae in the Southern Yellow Sea Before the Green Tide Outbreak. Biology, 14(10), 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101347








