Simple Summary
Borrelia infections, caused by bacteria of the genus Borrelia, are transmitted by ticks and lice and affect human and animals across Eurasia. This review outlines the geographic distribution and ecological dynamics of Lyme borreliosis and relapsing fever, emphasizing the role of tick species, wildlife reservoirs, and environmental factors. It highlights how climate change and human activity are expanding tick habitats, increasing disease risk in new regions. The emergence of novel Borrelia species and the complexity of transmission cycles underscore the need of improved surveillance and diagnostic tools. Understanding these patterns is essential for developing effective public health strategies and anticipating future outbreaks.
Abstract
This comprehensive review explores the distribution, diversity, and epidemiology of tick-borne borrelioses across Eurasia, focusing on Lyme borreliosis (LB) and other Borrelia-related infections. The genus Borrelia is categorized into three major groups, the Lyme Group (LG), the Relapsing Fever Group (RFG), and the Echidna–Reptile Group (REPG), each with distinct vectors, reservoirs, and pathogenic profiles. LB, caused by Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, is highly endemic in Europe and is increasingly reported in Asia, although it is underdiagnosed in Southeast Asia due to limited surveillance. This review details the ecological dynamics of tick vectors—primarily Ixodes spp.—and their vertebrate hosts, emphasizing the role of migratory birds and climate change in disease spread. It also highlights the presence of relapsing fever Borrelia species transmitted by soft ticks (Ornithodoros spp.) and the emergence of novel species such as Borrelia miyamotoi (RFG) and Borrelia turcica (REPG). This study underscores the need for harmonized surveillance systems, improved diagnostic tools, and integrated public health strategies to address the growing threat of borreliosis in Eurasia.
1. Introduction
Borreliae, members of the Spirochaetaceae family, are characterized by their distinctive spiral morphology. Currently, molecular techniques represent the cornerstone of Borrelia identification, with sequence-based approaches gaining increasing relevance in microbial research [1].
The genus Borrelia encompasses a diverse group of spirochetes, broadly classified as three major phylogenetic clades: the Borrelia Lyme Group (LG), the Borrelia Echidna-Reptile Group (REPG), and the Borrelia Relapsing Fever Group (RFG) [2]. While most species fall within these categories, several remain unclassified due to difficulties in cultivation and limited genomic data [3]. Borreliosis is usually transmitted by hard and soft ticks, except for Louse-Borne Relapsing Fever (LBRF) caused by Borrelia recurrentis, transmitted by the human body louse (Pediculus humanus corporis), a vector largely absent from Eurasia since World War II, and in some cases by B. theileri, which has been detected in the head lice of African pygmies [4]. Hard ticks (family Ixodidae) exhibit relatively long feeding durations—often several days—compared to soft ticks (family Argasidae) and the more recently described Nuttalliellidae [5].
Climate change has significantly altered the ecology of ticks and the epidemiology of tick-borne diseases (TBDs) through several interconnected mechanisms. Rising temperatures have enabled ticks like I. scapularis (vector of LB) and I. ricinus to expand into higher latitudes and altitudes, leading to the emergence of TBDs in previously unaffected regions, such as parts of Canada and Northern Europe [6]. Warmer winters and earlier springs have prolonged the active season of ticks, increasing the duration of host-seeking behavior and the risk of disease transmission [7]. Climate conditions such as higher humidity and milder winters have improved tick survival and reproduction with denser tick populations and a higher likelihood of human–tick encounters [8]. Climate change also impacts the establishment of invasive tick species such as Hyalomma marginatum and Haemaphysalis longicornis, which can carry novel pathogens. These species are now being reported in areas where they were previously absent [8]. These findings underscore the complexity of Borrelia ecology and raise important questions about the future distribution of borrelioses.
1.1. LG
To date, 24 species have been identified within the LG, 9 of which are known to be pathogenic to humans. Clinically, B. afzelii is predominantly associated with dermatological manifestations, whereas B. garinii and B. bavariensis are linked to neurological involvement. Lyme arthritis is most commonly attributed to B. burgdorferi sensu stricto (Bbss) [9]. Other pathogenic LG species include B. spielmanii, B. lusitaniae, B. valaisiana, B. bissettii, and B. mayonii, the latter being notable for its association with spirochetemia [10].
A recent addition to this group is B. maritima, isolated from coastal California, expanding the previously recognized diversity [3]. The identification of LG Borreliae can be performed through whole-genome sequencing and/or multi-locus sequence typing (MLST), based on eight genes, which enables unique genotyping and improves phylogenetic analysis [11].
Diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis (LB) typically relies on serological detection of anti-Borrelia antibodies via immunofluorescence assay (IFA), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), chemiluminescent immunoassay (CLIA), or Western Blot (WB). Direct detection methods include culture in Barbour–Stoenner–Kelly H (BSK-H) medium and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of DNA extracted from skin biopsies or body fluids such as blood, cerebrospinal fluid, or synovial fluid [9].
LB is endemic throughout the Northern Hemisphere, with a particularly high incidence in North America and Europe. Its distribution is tightly linked to the presence of hard ticks of the genus Ixodes, including I. ricinus in Europe and North Africa (also I. inopinatus), I. persulcatus in Asia and Eastern Europe, and I. scapularis and I. pacificus in North America. Conversely, LB is rarely reported in the Southern Hemisphere [3].
Ticks of the genus Ixodes acquire Borrelia from reservoirs of Borrelia-infected vertebrate hosts. The composition of local wildlife and the dynamics of tick–host interactions are critical to the persistence and spread of LB in natural ecosystems. Ixodes spp. ticks thrive in humid environments (>80% relative humidity) and can colonize a wide range of habitats, such as woodlands, grassy meadows, broad-leaved forests, and pastures. Their abundance is influenced by vegetation and host density, particularly domestic animals (e.g., sheep and cattle) and wild fauna.
Vertebrates play dual ecological roles:
- As tick hosts, wild species such as roe deer, red deer, foxes, and hares facilitate tick dispersal.
- As reservoir hosts, small mammals (e.g., rodents) and birds maintain and transmit B. burgdorferi sensu lato (Bbsl) in nature.
Migratory birds are particularly important in the long-distance dissemination of infected ticks, potentially bridging endemic and non-endemic regions, including intercontinental spread—although LB remains rare in the Southern Hemisphere [12]. In Southeast Asia, LB is likely underreported due to limited diagnostic infrastructure and surveillance [13].
1.2. REPG
The REPG was established following the identification of B. turcica in Hyalomma aegyptium ticks from tortoises in Türkiye [14]. This group currently includes B. turcica and B. tachyglossi, expanding the ecological and evolutionary scope of Borrelia.
1.3. RFG
Relapsing fever Borrelia species are also present in Eurasia, typically transmitted by soft ticks of the genus Ornithodoros. The epidemiological distinction between the vectors of LB and Tick-borne Relapsing fever (TBRF) is significant:
- LG Borreliae exhibit limited vertical transmission in Ixodes spp.
- RFG Borreliae are efficiently transmitted vertically in Ornithodoros spp., which may also act as reservoirs, as seen with O. moubata [15].
Some RFG species are also transmitted by hard ticks, a condition termed Hard Tick-Borne Relapsing Fever (HTBRF). B. miyamotoi, a notable HTBRF agent, is transmitted by Ixodes spp. (I. ricinus, I. scapularis, and I. persulcatus) [16], capable of vertical transmission [17], and has been detected in various wildlife reservoirs [18]. B. theileri, another HTBRF Borrelia, is transmitted by Rhipicephalus spp. and Margaropus australis and affects primarily livestock, but is not known to infect humans, although it causes significant economic losses in the agricultural sector [19,20]. B. lonestari, transmitted by the Lone Star tick (Amblyomma americanum), has been associated with human illness, but its pathogenic role remains uncertain [21].
2. Borreliosis in Eurasia
Europe lies entirely within the Northern Hemisphere, whereas parts of Asia—specifically Indonesia, East Timor, and Brunei— are located in the Southern Hemisphere. Additionally, the southernmost regions of Malaysia, Singapore, the Philippines, Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam—extend into the Southern Hemisphere. This geographical diversity contributes to varying ecological and disease dynamics across the continent.
This review provides an overview of the distribution of borreliosis in Europe, where Lyme borreliosis is highly endemic, followed by a more detailed analysis of its presence in Asia. The Asian region encompasses countries in both hemispheres and is characterized by limited and heterogeneous epidemiological data. Several areas may be considered transitional zones, situated between regions where LB is well documented and those where it is either non-endemic or remains unreported. In addition to LB, other Borrelia-associated diseases are discussed, including those caused by species within the RFG and the REPG.
Overall, several Borrelia species are pathogenic to both humans and other mammals, while others infect animals or are not pathogenic. Vector ecology plays a crucial role in the transmission dynamics of Borrelia infections. In Eurasia, human infections are primarily transmitted by hard ticks of the genus Ixodes and soft ticks of the genus Ornithodoros, as summarized in Table 1. Animal borreliosis (see Table 2) is vectored by hard ticks belonging to the genera Ixodes, Rhipicephalus, Haemaphysalis, Hyalomma, and Amblyomma. Soft ticks, mainly of the genus Ornithodoros, are responsible for transmitting Soft Tick-Borne Relapsing Fever (STBRF). Additionally, ticks of the genus Argas can transmit relapsing fever to birds, while Carios spp. are associated with transmission in bats.

Table 1.
Hard and soft ticks and transmitted Borreliae to humans in Europe and Asia.

Table 2.
Hard and soft ticks and transmitted Borreliae to animals in Europe and Asia.
Some species primarily infect animals, which has important implications for both public health and the economy. For instance, B. theileri and B. persica can cause disease and abortion in livestock, resulting in significant economic losses.
Other species, such as B. hispanica, B. duttoni, and members of the B. burgdorferi sensu lato complex, are capable of infecting domestic animals and may pose a zoonotic risk, potentially facilitating transmission to humans.
2.1. Europe
In the Northern Hemisphere, Ixodes spp. ticks are more abundant in cool, humid microclimates. Their activity peaks during spring and autumn in temperate regions, while high summer temperatures often drive them to adopt an endophilic (indoor or sheltered) lifestyle. Rainy climates with high humidity levels (90–95%) further facilitate their proliferation.
In Europe, the primary vector of LB is I. ricinus, whose distribution has expanded significantly in recent decades. This expansion is attributed to a combination of climatic, ecological, landscape, and anthropogenic factors [42]. Ixodes ricinus exhibits high ecological plasticity, enabling it to survive in suboptimal climatic conditions and colonize high-altitude environments, reaching elevations up to 1800 m above sea level. These adaptive traits, coupled with land-use changes and biotope transformation, influence tick habitat availability and increase the likelihood of host–tick–pathogen interactions, thereby elevating the risk of tick-borne pathogens transmission [43]. Moreover, I. ricinus exhibits low host specificity, parasitizing a broad range of vertebrates, including mammals (humans included) and birds [44].
The distribution of tick-borne pathogens is primarily governed by tick population density and the presence of competent reservoir hosts. Figure 1 illustrates the distribution of Borreliae across Europe. In this region, primary reservoirs for Lyme Group Borrelia species include small- to medium-sized rodents, such as Clethrionomys glareolus [45], alongside various bird species, especially passerines like Turdus merula (the common blackbird) [33]. Transmission among ticks can also occur via co-feeding, a mechanism whereby multiple ticks feed in close proximity on the same host, facilitating pathogen exchange even in the absence of systemic infection [46].
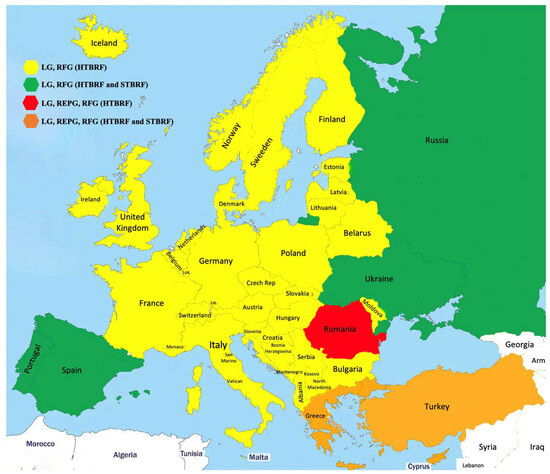
Figure 1.
Borreliae distribution in Europe.
Estimating the true incidence of Lyme borreliosis in Europe is challenging due to substantial heterogeneity in surveillance systems. These range from passive to mandatory reporting and from sentinel site monitoring to nationwide data collection. Variations in case definitions (clinical, laboratory-based, or both) and diagnostic methodologies further contribute to underreporting, particularly in countries where notification is not mandatory.
The average population-weighted incidence across Europe is estimated at 22 cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year [47], with at least 200,000 new cases annually [48]. Approximately 24% of the European population resides in regions classified as high-incidence areas. To improve the comparability and understanding of LB incidence across countries, standardized surveillance systems and harmonized case definitions are urgently needed [49].
Documented cases of LB have been reported in numerous European countries, including Austria, Belgium, Bosnia, Bulgaria, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Norway, Poland, Russia, Slovakia, Sweden, and the United Kingdom [49].
In 2016, approximately 85,000 clinically manifest LB cases were reported across Europe, with the highest frequency observed in temperate regions. However, this figure likely underrepresents the true burden due to underreporting and variability in surveillance practices [49]. Notably, Iceland—previously considered a low-incidence country (2 cases per 100,000 inhabitants/year)—has experienced a significant rise in incidence, averaging a 21% increase over the past 12 years [50].
Population-based LB incidence is typically expressed as cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year. Regions with incidence rates exceeding 10 cases per 100,000 are considered high-risk. The highest national incidence rates have been reported in Estonia, Lithuania, Slovenia, and Switzerland, each exceeding 100 cases per 100,000 population per year. France and Poland report intermediate rates (40–80/100,000), followed by Finland and Latvia (20–40/100,000). The lowest incidence rates (<20/100,000) are observed in Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, England, Hungary, Ireland, Norway, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Scotland, and Serbia [49]. Nevertheless, epidemiological data should be evaluated with care because they do not always reflect the real situation. This is the case in Serbia, where reporting has not been obligatory since 2016. In Italy, LB is present nationwide, with a particularly endemic patterns in Alpine regions [51].
In European Russia, the southern forested regions have experienced both an extension of the tick activity season and an increase in LB incidence rates. The primary vector in these areas is I. persulcatus, capable of transmitting B. garinii, B. afzelii, and B. bavariensis [52]. In Europe, the following pathogenic Borrelia LG genospecies have been identified: B. afzelii, B. garinii, B. bavarensis, B. burgdorferi sensu stricto (Bbss), B. lusitaniae, B. valaisiana, B. spielmani. B. garini is most prevalent in Central Europe, whereas B. afzelii predominates in Northern and Southern Europe. Notably, Fratercula arctica birds (Atlantic puffins) have been reported to carry I. uriae ticks infected with B. garinii to the Faroe Islands [22].
Tick-borne relapsing fever borreliosis is also present in Europe, particularly in the form of Hard Tick-Borne Relapsing Fever, caused by B. miyamotoi. This species shares the same tick vectors as B. burgdorferi sensu lato, primarily Ixodes spp., and has been detected in nearly all European countries [53].
Additionally, several European countries report cases of Soft Tick-Borne Relapsing Fever. For example,
- B. caucasica is transmitted by O. verrucosus in Ukraine and parts of European Russia [54,55].
- B. hispanica is transmitted by O. erraticus in Spain, Portugal, and Greece [56]. This species can infect both humans and domestic animals, including dogs and cats, with cases reported in Córdoba, Valencia, and Seville [57].
Ticks carrying Borrelia species responsible for relapsing fever have been reported on all continents except Antarctica and Australia. While molecular diagnostic techniques (e.g., PCR and sequencing) are required for precise species identification, microscopy remains the gold standard in many clinical settings, particularly in resource-limited areas.
The hallmark clinical feature of tick-borne relapsing fever is its recurrent febrile episodes, which give the disease its name. These episodes are typically separated by afebrile intervals and are caused by waves of spirochetemia. A notable complication during treatment is the Jarisch–Herxheimer reaction, an acute inflammatory response that may occur shortly after the initiation of antibiotic therapy. It is characterized by fever, chills, hypotension, and worsening symptoms, and is thought to result from the rapid lysis of spirochetes and the release of endotoxin-like substances [58].
2.2. Asia
In Southeast Asia, a total of 97 tick species have been documented, including 42 species of Haemaphysalis and 14 species of Ixodes.
Borrelia species have been detected in both hard and soft ticks in the region. Potential reservoir hosts include rodents, birds, lizards, and snakes. Individuals engaged in agricultural activities near forested areas are at increased risk of tick exposure. Moreover, anthropogenic factors such as deforestation and urbanization can disrupt natural habitats, potentially expanding the geographic range of tick-borne and zoonotic diseases by increasing human–animal contact [59].
In Asian countries, the distribution of ticks and their associated pathogens is influenced by a combination of climatic, environmental, and ecological factors. Studies analyzing ticks collected in China, Japan, Malaysia, Mongolia, Pakistan, Asian Russia, South Korea, Thailand, and Turkey have confirmed the presence of B. burgdorferi sensu lato in ticks of the genera Ixodes and Haemaphysalis [60].
In northern Mongolia, China, and Japan, the predominant vector is I. persulcatus, which is capable of transmitting B. afzelii and B. garinii (Asian variant NT29), but not B. burgdorferi sensu stricto. The most frequently identified reservoir hosts include Apodemus ainu in Japan and Niviventer confucianus in China, Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia [61].
In China and Thailand, I. granulatus and Ixodes columnae are important vectors, whereas in Japan and Korea, Ixodes nipponensis is responsible for the transmission of B. valaisiana (strain Am 501) [62].
Clinical cases of LB have also been reported in several Asian countries (see Table 3), including Korea, Nepal, China, and Japan. In Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore, LB has been identified in human serum, primarily through IgG and IgM ELISA testing. Borrelia of the Lyme group has been detected by PCR in ticks collected from host animals such as Sundamys muelleri and Python species in Malaysia, Thailand, and Laos. These findings confirm the presence of Bbsl infections in Southeast Asia, although the actual number of cases is likely underestimated [63].

Table 3.
Lyme group Borrelia distribution in Asian countries.
Soft ticks of the genus Ornithodoros, vectors of STBRF, are also widespread in Asia, as reported in Table 4. B. persica, transmitted by O. tholozani, is prevalent in the region. Other STBRF-associated Borrelia species reported in Asia include B. baltazardii, B. graingeri, and B. microti [94].

Table 4.
Soft tick-borne relapsing fever in Asian countries.
In some Asian countries, however, data remain scarce. No cases have been reported in the literature for Brunei and Vietnam [63]. In Bhutan [108] and Myanmar [109], a study aimed at identifying zoonotic pathogens in rodents and ticks yielded negative results for Borrelia spp. A summary of the distribution of different Borrelia groups across the region is provided in Figure 2 [63]. In the following sections, countries where Borreliae have been documented are listed in alphabetic order.
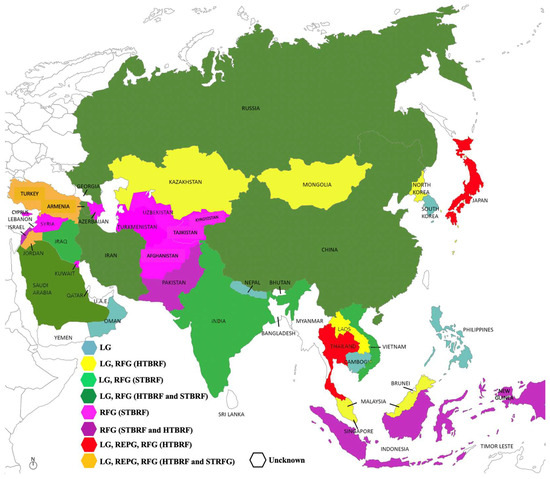
Figure 2.
Borreliae distribution in Asia.
2.2.1. Asian Russia
In Eastern Russia, I. persulcatus is the vector of LG Borrelia species, but not of Bbss. This pattern mirrors findings from wild rodent hosts such as Clethrionomys rufocanus and Apodemus peninsulae, and aligns with results from studies conducted on I. persulcatus and wild rodents in Hokkaido, Japan [110]. The tick I. pavlovskyi has been found to be exclusively infected by B. garinii [64].
In Eastern Russia, B. afzelii, B. garinii, B. bavariensis (LG), and B. miyamotoi (HTBRF) have been identified [111]. The B. garinii NT29 group, transmitted by I. persulcatus, is present in both Asian Russia and northern China. This strain has been successfully cultured and sequenced [112].
In Moscow region, the predominant tick species are I. ricinus and Dermacentor reticulatus, which carry B. afzelii and B. garinii. The infection rate is approximately 30% in ticks, with peak activity observed from early spring to mid-autumn, when temperatures range between 20 and 25 °C and relative humidity is 50% or higher [113].
In the Russian Far East—specifically in Khabarovsk, Vladivostok, and Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk—B. garinii and B. afzelii have been isolated from I. persulcatus ticks and wild rodents [65,66].
Borrelia miyamotoi, the agent of HTBRF, has been identified in I. persulcatus using molecular methods [114].
2.2.2. Afghanistan
Currently, there are no documented cases of LB in Afghanistan. However, STBRF, caused by B. microti and transmitted by O. erraticus, has been reported [115].
2.2.3. Armenia
The first cases of LB were documented in 2010, based on clinical presentation and serological confirmation [67]. STBRF has been described in the country, caused by B. caucasica and transmitted by O. verrucosus [96,116].
2.2.4. Azerbaijan
In eastern Azerbaijan and northwestern Iran, B. caucasica, transmitted by O. verrucosus, has been identified. Additionally, Meriones persicus rodents have been recognized as reservoirs of a B. duttonii-like strain, confirmed through Multilocus sequence analysis [97].
2.2.5. Cambodia (South Hemisphere)
In Cambodia, reports on Borrelia infections are limited. A case of tick-borne relapsing fever has been documented [117]. Moreover, a tourist developed LB caused by B. valaisiana after being bitten by an I. persulcatus tick during a trip to Cambodia [68].
Cases of louse-borne relapsing fever have also been reported in the country [116].
2.2.6. China
China is home to more than 100 tick species. The most representative species in the continental region include I. granulatus, Dermacentor marginatus, Dermacentor silvarum, and Haemaphysalis longicornis. Environmental factors influencing tick presence and distribution include urbanization, agricultural land-use, forest cover, annual temperature range, and precipitation. Under climate warming scenarios, tick distributions have shifted northward, while deforestation has contributed to population declines in central and southern China [118].
Borrelia species identified in China include members of the LG, the RFG, and species outside these classifications. The first documented case of LB occurred in 1986 in Heilongjiang Province, northeastern China, in a patient presenting with erythema migrans following a tick bite. Since then, hundreds of EM cases have been reported in the region. Molecular analyses have confirmed the presence of B. garinii, B. afzelii, and B. valaisiana, with at least one case demonstrating human pathogenicity [119].
A novel LG species, B. sinica, was identified through molecular methods in ticks and rodents. This species was cultured from I. granulatus and rodents such as Apodemus agrarius and Niviventer confucianus, collected along the Yangtze River valley. Transmission electron microscopy revealed four periplasmic flagella inserted at each end of the spirochete [120,121]. Genetic and amino acid diversity in the p66 gene have been observed among Chinese strains of B. garinii and B. afzelii [122]. In northeastern provinces such as Jilin and Heilongjiang, I. persulcatus ticks have tested positive for Borrelia DNA. Phylogenetic analysis confirmed the presence of B. garinii, B. afzelii, B. bavariensis, and B. bissettii [69].
Borreliae of the RFG, including both hard tick-borne relapsing fever and soft tick-borne relapsing fever, have also been identified. HTBRF includes B. miyamotoi (vector: I. persulcatus; reservoir: Apodemus agrarius), which is pathogenic to humans [123]. B. theileri, pathogenic to livestock, has been found in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Apodemus agrarius.
B. persica, a member of the STBRF group (vector: Ornithodoros tholozani), is pathogenic to humans and dogs [98] and has been detected in wild small mammals such as Rhombomys opimus and Meriones libycus [98].
In Hubei province, Candidatus B. fainii, a novel species pathogenic to humans, was identified in two bats. This species belongs to the RFG and shows sequence similarity to New World STBRF species [40,124].
Unclassified Borrelia species have been detected in Haemophysalis concinna and Niviventer confucianus. The wide distribution and diversity of RFG Borrelia in China pose a significant public health concern [98].
A new species, Candidatus B. javanense, has been isolated from Amblyomma javanense ticks infesting Manis javanica pangolins. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that this species does not belong to either the LG or RFG, suggesting a distinct lineage. Its pathogenicity to humans remains unknown [125].
2.2.7. Cyprus
Relapsing fever was first diagnosed in Cyprus in 1939, primarily in rural areas around Kyrenia, Famagusta, Nicosia, and Larnaca. Several cases were reported among British soldiers in 1945. The vector, O. tholozani, inhabits caves, holes, and rodent burrows. The causative agent has not been definitively identified, with B. persica and B. hispanica both considered potential pathogens [101].
2.2.8. India
In Arunachal Pradesh, ticks collected from mithun (Bos frontalis) and the Tibetan yak (B. grunniens), include I. acutitarsus, I. ricinus and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) geigy, Rhipicephalus sanguineus, Haemaphysalis davisi, Haemaphysalis darjeeling, Haemaphysalis longicornis, and Haemaphysalis bispinosa [126]. Evidence of LB in Arunachal Pradesh includes seroprevalence of anti-Bbsl antibodies and the presence of I. ricinus, the primary vector of LB in Europe [70]. LB cases have been indeed reported in northern India, frequently involving the nervous system. Articular and cardiac involvement occurred in 27% and 16% of cases, respectively [127]. Diagnosis was based on ELISA and Western Blot detection of anti-Bbsl antibodies in serum and cerebrospinal fluid [128].
Patients with EM and anti-Borrelia antibodies have been observed in Haryana [129]. LB is also known to occur in southern India, particularly in the forested areas of Nagarahole and Bandipur, near Rajiv Gandhi National Park [71].
STBRF has been documented in Kashmir, primarily caused by B. persica, transmitted by O. tholozani, which inhabits caves, ruins, and rodents dens [100].
2.2.9. Indonesia
On Sulawesi island, several hard tick species have been collected, including Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, a livestock parasite and vector of Borrelia theileri, and I. granulatus, a vector of LG spirochetes [20,72]. In the Bogor district, a novel Borrelia species was detected in Amblyomma varanense, which parasitizes the lizard Varanus salvator, common in urban areas of Indonesia and other Asian countries. Phylogenetic analysis revealed a monophyletic group within the REPG. This study highlights the potential public health risks posed by reptile-associated ticks, especially given the increasing global trade in reptiles as pets [130].
2.2.10. Iran
On the Iranian Caspian Sea coast, several hard tick species, including I. ricinus, have been found feeding on various mammals, such as sheep, goats, cattle, camels, horses, dogs, donkeys, rodents, and small mammals. PCR analyses have identified B. bavariensis, B. garinii, B. afzelii, B. valaisiana (agents of LB), and B. miyamotoi (HTBRF agent) [73].
B. microti, transmitted by O. erraticus is endemic in East Azerbaijan province in Iran and causes STBRF [97]. In northwestern Iran, B. persica and B. balthazardi, transmitted by O. tholozani, have been identified in rodents such as Meriones persicus and other small mammals. B. latyschewii, transmitted by O. tartakovsky, has also been reported [97].
2.2.11. Iraq
Serological evidence has documented LB in humans [131], while molecular methods have detected Borrelia infection in stray dogs in Nineveh Province [74]. The geographic distribution of O. tholozani closely mirrors the occurrence of clinical relapsing fever caused by B. persica. This tick species is extensively distributed across Iraq [100].
2.2.12. Israel
Isolated cases of LB have been reported in humans [75] and in dogs [76], although further studies are needed to confirm these findings. B. persica has been isolated in culture from humans and in ticks. Its infection [99] transmitted by O. tholozani has been documented in humans [100,102], as well as in dogs and cats [132]. Rock hyrax (Procavia capensis) has been identified as a reservoir host for B. persica [133].
2.2.13. Japan
The first case of Lyme disease in Japan dates back to 1987. Isolations from erythema migrans lesions [77] and from I. persulcatus confirmed the presence of B. garinii and B. afzelii. Japanese strains of B. garinii differ immunologically and genetically from European strains in their outer surface protein A, while B. afzelii isolates from Japan and Europe are identical. B. japonica, a novel LG species, with unknown human pathogenicity, was isolated from I. ovatus [134].
In eastern Hokkaido, B. lonestari-like organisms have been detected in wild deer (Cervus nippon yesoensis) [135] and in Haemaphysalis flava and Haemaphysalis megaspinosa ticks [136].
A novel HTBRF agent, B. miyamotoi sp. nov. (strain HT31T) was identified in I. persulcatus [137]. Retrospective serological surveillance revealed high anti-GlpQ seroprevalence in the Chubu region, where B. miyamotoi was found in I. persulcatus ticks, marking the first such report in Japan [138].
Imported cases of relapsing fever due to B. persica have been described in Japan, although no native cases have been documented [139].
Borrelia spp. have also been reported in reptiles and Amblyomma ticks, which are suspected vectors of REP-group Borreliae [140].
2.2.14. Jordan
In southeastern Jordan, I. ricinus ticks and anti-Bbsl antibodies in humans have been documented [78]. Borrelia turcica (REPG) has also been found in blood and organs of Testudo graeca exported from Jordan [36].
B. persica, the agent of the STBRF, transmitted by O. tholozani, has also been identified. Diagnosis is primarily based on blood smear microscopy [100].
2.2.15. Kazakhstan
The prevalence of Borrelia spp. in Ixodid ticks collected from southeastern Kazakhstan (Almaty Oblast) was studied using conventional PCR targeting the 16S rRNA gene to differentiate Bbsl genospecies. LB agents were detected exclusively in I. persulcatus, while Bbss was not found in any tick pools. Partial sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene revealed the presence of B. miyamotoi, B. afzelii, and B. garinii, with B. afzelii being the dominant genospecies in the Zailiyskiy Alatau, Dzungarian Alatau, and Yenbekshikazakh districts [79].
Almaty Oblast is considered endemic for LB, transmitted by I. persulcatus in Almaty city and the Talgar and Karasay districts [141]. In the Zhambyl region, a case of meningoencephalitis with co-infection by B. burgdorferi and tick-borne encephalitis virus has been reported [142].
2.2.16. Korea
LB is endemic in the northeastern alpine region of Korea. Clinical manifestations include EM in 55% of patients and neurological symptoms in 36%. A case of acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans has also been reported [80].
B. burgdorferi sensu lato has been isolated from I. persulcatus, and EM cases with anti-Borrelia antibodies have been documented [143]. LB is particularly prevalent among forest workers in national parks [144].
In the Chungbuk and Kangwon provinces, B. afzelii and B. garinii have been identified and characterized in Ixodes ticks and in Apodemus agrarius mice [81]. B. garinii, B. bissettii (LG), and B. miyamotoi (RFG) have also been detected in I. nipponensis ticks [145].
The raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides), a wild canid native of East Asia and Europe, is a potential reservoir for zoonotic pathogens. Haemaphysalis flava and Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks collected from raccoon dogs have tested positive for B. theileri and other pathogens [146]. A study conducted at the United States Army Garrison Humphreys (Republic of Korea), used molecular and genotypic analyses to detect Borrelia spp. in hard ticks collected from Korean water deer (Hydropotes inermis argyropus) between January 2018 and December 2019. B. afzelii and B. miyamotoi were identified in I. nipponensis [147,148].
2.2.17. Kuwait
In 1996, a 25-year-old woman who tended sheep developed relapsing fever caused by B. duttoni. However, reports of STBRF in the Arabian Gulf region remain rare [103].
2.2.18. Kyrgyzstan
In Kyrgyzstan, borreliosis is represented by STBRF, caused by B. microti, transmitted by O. erraticus [104].
2.2.19. Laos (Southern Hemisphere)
Cases of LB have been documented in Laos, primarily caused by B. afzelii [63]. In the Nakai District, Khammouan province, a B. lonestari-like spirochete (RFG) was isolated from Amblyomma spp. and Haemaphysalis spp. ticks collected from the wild deer, Cervus nippon yesoensis [63].
2.2.20. Malaysia (Southern Hemisphere)
Two patients with LB and erythema migrans have been reported, and B. afzelii has been identified in blood donors [149]. A serological survey for anti-Borrelia burgdorferi antibodies in Orang Asli, the indigenous people of Peninsular Malaysia, indicated a positivity rate of 8% (73 out of 904 volunteers), although human LB cases in rural Malaysian communities remain poorly documented [82].
In I. granulatus ticks collected from the forests of Gunung Gading National Park and Kubah (Sarawak), and from small mammals (especially in Rattus tanezumi) on oil palm plantations in Sarawak (Malaysian Borneo), Borrelia yangtzensis (an LB agent) was detected. B. miyamotoi (HTBRF agent) was found in Sundamys muelleri [150,151] and identified in Haemaphysalis hystricis ticks, collected from wild boars in the Orang Asli community [59,152].
2.2.21. Mongolia
The first LB cases were detected in 2007 in the Zavkhan and Selenge Provinces through serological testing for anti-Bbsl antibodies [83]. In 2009, B. bavarensis (was identified in ticks and rodents [84].
The primary vector is I. persulcatus. Molecular analyses of ticks collected in the Selenge and Bulgan Provinces revealed the presence of B. afzelii, B. bavariensis, and B. garinii (LG), as well as B. miyamotoi, belonging to the Siberian strain of the HTBRF [153,154]. B. miyamotoi has also been detected in Haemaphysalis longicornis and Dermacentor nuttalli ticks using molecular methods applied to both humans and tick samples [155].
2.2.22. Nepal
The first documented case of LB was reported in 2018 in a 32-year-old woman from Pokhara, Kaski District. The patient recalled a lesion consistent with erythema migrans on her left thigh, but did not remember a tick bite. ELISA and Western Blot tests for anti-Bbsl antibodies, along with PCR for Borrelia detection, were positive [85].
2.2.23. New Guinea
Reports have suggested the presence of anti-Bbsl antibodies in HIV-positive patients, although often cases were not confirmed by Western Blot. These may represent false positives, and the presence of borreliosis in New Guinea requires further confirmation [156].
2.2.24. Oman
The first case of LB (Lyme arthritis) in Oman was described in 2022 in a 10-year-old girl [86].
2.2.25. Pakistan
In Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, B. theileri was identified in hard ticks (Rhipicephalus microplus and R Rhipicephalus turanicus) collected from domestic animals [20]. In the same province, Amblyomma gervaisi ticks, collected from Varanus bengalensis lizards, tested positive for Borreliae of the REPG, as confirmed by PCR and phylogenetic analysis [157].
Argas persicus (vector: O. tholozani) infests domestic chickens and ducks, while Carios vespertilionis infests bats. These ticks were collected in districts including Peshawar, Mardan, Swabi, Charsadda, Chitral, Lakki Marwat, Bannu, Bajaur, and Hangu. Molecular characterization confirmed the presence of B. anserina DNA [38].
A case of louse-borne relapsing fever was reported in Karachi in 1990 [158].
2.2.26. Philippines
Equine tick-borne infections were identified using molecular methods, including the detection of B. burgdorferi sensu lato [159].
2.2.27. Saudi Arabia
A case of LB has been reported in a 30-year-old man from Dammam, Eastern Province, presenting with erythema migrans, paresthesia, myalgia, and vertigo [87,88].
Due to the economic importance of camels, tick infestations are closely monitored. B. theileri, an HTBRF agent, has been identified in Hyalomma dromedarii and Hyalomma marginatum ticks, collected in Riyadh [160].
Human cases of STRF caused by B. persica have occurred in Saudi Arabia, although their incidence is likely underestimated [105]. In 2014, a case of LBRF due to B. recurrentis was reported [161].
2.2.28. Singapore
The presence of LB is rare or uncertain. Seventy-two patients with erythema anulare, resembling EM, tested negative for anti-Bbsl antibodies. In 2012, a patient with neuroretinitis in the left eye tested positive for Bbsl IgG by Western Blot [63].
2.2.29. Syria
No cases of LB have been reported in Syria. However, STBRF caused by B. persica, transmitted by O. tholozani, has been documented [100].
2.2.30. Tajikistan
A French tourist who visited Tajikistan was diagnosed with B. persica infection upon returning to Paris. The diagnosis was confirmed through molecular methods, including sequencing. B. persica is typically transmitted by O. tholozani, a tick species that inhabits caves, soil, wall crevices, homes, and cow stables [106].
Similarly, an Italian tourist was diagnosed with B. microti infection, an agent of tick-borne relapsing fever, following travel to Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. The diagnosis was confirmed upon her return by blood smear microscopy and PCR-based methods [104].
2.2.31. Thailand (Southern Hemisphere)
LB has been reported in dogs from Chiang Mai, as confirmed by ELISA and PCR [89]. In the Phop Phra District, Tak Province, B. miyamotoi was identified in rodents and I. granulatus ticks collected from Mus caroli, Berylmys bowersi, Bandicota indica, and Leopoldamys sabanus, which inhabit cultivated areas, increasing the risk of human exposure. Anti-B. miyamotoi antibodies were also detected in both humans and rodents [162].
In Lophuri Province, Borrelia spp. were detected in Amblyomma varanense and Amblyomma helvolum ticks collected from aquatic lizards (Varanus salvator, Varanus bengalensis) and reptiles (Python reticulatus and Python bivittatus) and Amblyomma geoemydae ticks collected from a turtle (Indotestudo elongata) [63]. Molecular analyses identified Borreliae of the REPG [163].
2.2.32. Türkiye
LB was first described in Istanbul in 2010, confirmed by serological testing and isolation in Barbour–Stonner–Kelly medium from cerebrospinal fluid and skin samples [90]. Between 2009 and 2013, ten cases of LB with erythema migrans appearing 1–2 weeks after tick bites were reported [91]. A case of LB-related uveitis was also documented [93], which is notable given the high prevalence of uveitis due to Adamantiades–Behçet disease in Turkey [164]. LB cases have also been reported in Erzincan, Northeastern Turkey [92].
B. persica, an STBRF agent, is present in Turkey and transmitted by O. tholozani [100]. B. turcica, belonging to the REPG, is transmitted by Hyalomma aegyptium ticks and can infect turtles and birds. However, the only reservoir hosts are turtles of the Testudo genus [165].
2.2.33. Turkemnistan
STBRF has been documented in association with B. persica, vectored by O. tholozani, and B. latyschewii, transmitted by Ornithodoros tartakovskyi [100], which is known to inhabit rodent burrows.
2.2.34. Uzbekistan
In Gava, located in the foothills of Namangan Province, cases of B. persica infection have been reported. The vector is O. papillipes, a tick with anthropophilic behavior [107].
3. Discussion
Vector-borne pathogens maintain transmission cycles between arthropod vector and vertebrate reservoir hosts. The movement of host and vector contributes to the geographical expansion of infectious agents and the emergence of new diseases. In Eurasia, bacteria such as Borrelia spp. infect a wide range of vertebrates, including birds, rodents, and larger mammals, including humans, highlighting the critical role of host–vector associations in the northward and southward expansion of tick habitats and the spread of diseases, such as borreliosis [166].
Environmental and climatic factors, including temperature, humidity, latitude, and altitude significantly influence the tick survival and distribution, thereby reshaping their ecological niches. Additionally, increased travel involving infected animals from endemic regions, the introduction of new vectors, and anthropogenic environmental changes have contributed to the emergence and proliferation of canine vector-borne diseases, posing a growing risk to human health [167]. Ecological niche models (ENMs) can be applied, with this regard, to predict the geographic distribution of tick species and understanding the environmental factors that influence their presence and the transmission of tick-borne diseases and the transmitted pathogens [168].
Europeans are increasingly exposed not only to the direct effects of climate change, but also to its indirect consequences, such as the spread of climate-sensitive infectious diseases with epidemic potential [169]. Studies have confirmed the presence of borreliosis across Europe, Northwest Asia, and Southeast Asia, although its prevalence in Southeast Asia appears lower. This may be attributed to limited research and underreporting in countries such as Vietnam, the Philippines, Cambodia, Myanmar, Brunei, and East Timor [63].
In Eurasia, Borrelia spp. have been identified in hard ticks species, including I. granulatus, I. persulcatus, I. ricinus, Haemaphysalis spp., Amblyomma varanense, A. testudinarium, Dermacentor auratus, and Rhipicephalus spp. Members of the relapsing fever group have also been found in soft ticks of the families Asgasidae (Ornithodoros spp., Argas spp.) and the newly described family Nuttalliellidae [170].
Within the Lyme group, three major genospecies—B. afzelii, B. bavariensis, and B. garinii—likely of Asian origin, utilize distinct tick vectors in Asia (I. persulcatus, I. granulatus, I. acutitarsus) and Europe (I. ricinus). These ticks require high relative humidity (≥80%) and are typically found in forested environments [44]. The bacteria infect a wide range of vertebrates and cause Lyme borreliosis, the most prevalent vector-borne disease in the Northern Hemisphere. The geographic expansion of LB agents is facilitated by host–vector associations, reinforcing their role in the emergence and spread of vector-borne pathogens [166].
LB is present in all European countries, and has been reported in 24 Asian countries, although case numbers in some regions may be underestimated [63]. In Europe, I. ricinus is the primary vector, transmitting both Bbsl and Bbss genospecies, whereas I. persulcatus, prevalent in Asia does not transmit Bbss.
In Central Asian and Middle East, tick-borne relapsing fever is primarily caused by B. persica, although other species such as B. microti, B. latyschewii, B. baltazardi, and B. caucasica have also been described. The taxonomy of Borrelia spp. is complex and based on the co-speciation. Species-specific PCR targeting the glpQ gene is commonly used to differentiate B. persica from B. microti, the two most prevalent species in Asia [171].
The distribution of vectors and reservoirs of the three Borrelia groups—Lyme group, relapsing Fever group, and Echidna–Reptile Group—varies between the Northern and Southern Hemispheres and near the equator. This review focuses on their distribution in Eurasia. LB is associated with hard ticks (Ixodes spp.), which prefer humid environments but exhibit ecological plasticity, allowing for adaptation to suboptimal conditions. These ticks are widespread in the Northern Hemisphere and decline in prevalence toward the equator and Southern Hemisphere. In contrast, relapsing fever is more common in tropical and arid regions, favored by Ornithodoros spp. ticks. Notably, while LB has been reported in four Southern Hemisphere Asian countries (Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Thailand), STBRF has not been documented in these regions. Climate change has facilitated the emergence and geographic expansion of vector-borne diseases, including LB and other borrelioses, by altering the distribution of tick vectors [169]. RFG Borrelia spp. can be transmitted by soft ticks (STBRF), hard ticks (HTBRF), or lice (LBRF). STBRF is typically transmitted by Ornithodoros spp., which prefer dry climates [172]. HTBRF agents such as B. theileri and B. miyamotoi share vectors with LB agents. While B. theileri infects livestock, B. miyamotoi is pathogenic to both humans and animals. STBRF is also present in Central Asia and the Middle East [171].
The REPG has been documented in Indonesia, Japan, Pakistan, Thailand, Turkey, and China. Most LBRF cases are imported, particularly from African countries such as Somalia and Eritrea. In Asia, LBRF was reported during the Second World War, with sporadic cases currently documented in countries like Saudi Arabia and Pakistan [173].
B. recurrentis is not transmitted by ticks; the human body louse is its only confirmed vector, and humans are the sole known reservoir [174]. B. javanense, isolated from Amblyomma javanense ticks, does not belong to either the LG or RFG, and its pathogenicity to humans remains unknown [125].
All major Borrelia groups are present in both Europe and Asia. LB is highly endemic across Europe and is reported in 24 Asian countries. STBRF is present in five European and 20 Asian countries. B. turcica, belonging to the REPG, has been identified in Greece and Turkey, infecting tortoises (Testudo spp.), and is transmitted by Hyalomma aegyptium ticks [175].
4. Conclusions
The distribution of borreliosis across Eurasia provides a valuable model for studying the spread and evolution of tick-borne diseases in the context of climate change. The presence and prevalence of different Borrelia species are closely linked to climatic conditions that influence the life cycles and habitats of their respective vectors. Understanding these ecological and epidemiological dynamics is essential for anticipating future disease emergence and implementing effective public health strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.T. and S.B. (Serena Bergamo); methodology, S.B. (Serena Bonin); resources, G.T.; writing—original draft preparation, G.T. and S.B. (Serena Bonin); writing—review and editing, S.B. (Serena Bergamo), G.T., S.B. (Serena Bonin) and M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Nausicaa De Rosa for drawing the figures and Margherita Trevisan for the English revision of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EM | Erythema migrans |
| LB | Lyme borreliosis |
| LG | Lyme Group |
| RFG | Relapsing Fever Group |
| REPG | Echidna-Reptile Group |
| Bbss | Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto |
| Bbsl | Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato |
| STBRF | Soft Tick-Borne Relapsing Fever |
| HTBRF | Hard Tick-Borne Relapsing Fever |
| LTBRF | Louse-Borne Relapsing Fever |
| TBP | Tick-borne pathogens |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
References
- Margos, G.; Notter, I.; Fingerle, V. Species Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato Using Molecular Biological Methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1690, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margos, G.; Gofton, A.; Wibberg, D.; Dangel, A.; Marosevic, D.; Loh, S.M.; Oskam, C.; Fingerle, V. The genus Borrelia reloaded. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, G.; Cinco, M.; Trevisini, S.; di Meo, N.; Chersi, K.; Ruscio, M.; Forgione, P.; Bonin, S. Borreliae Part 1: Borrelia Lyme Group and Echidna-Reptile Group. Biology 2021, 10, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanzougaghene, N.; Akiana, J.; Mongo Ndombe, G.; Davoust, B.; Nsana, N.S.; Parra, H.J.; Fenollar, F.; Raoult, D.; Mediannikov, O. Head Lice of Pygmies Reveal the Presence of Relapsing Fever Borreliae in the Republic of Congo. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledwaba, M.B.; Malatji, D.P. Nuttalliella namaqua Bedford, 1931, a sole extant species of the genus Nuttalliella—A scoping review. Front. Parasitol. 2024, 3, 1401351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, P.A. Climate change impacts on ticks and tick-borne infections. Biologia 2022, 77, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, N.H.; Ben Beard, C.; Ginsberg, H.S.; Tsao, J.I. Possible Effects of Climate Change on Ixodid Ticks and the Pathogens They Transmit: Predictions and Observations. J. Med. Entomol. 2020, 58, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.N.; Allen, K.E.; Lineberry, M.W.; Little, S.E.; Reichard, M.V. Ticks infesting dogs and cats in North America: Biology, geographic distribution, and pathogen transmission. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 294, 109392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, G.; Bonin, S.; Ruscio, M. A Practical Approach to the Diagnosis of Lyme Borreliosis: From Clinical Heterogeneity to Laboratory Methods. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritt, B.S.; Respicio-Kingry, L.B.; Sloan, L.M.; Schriefer, M.E.; Replogle, A.J.; Bjork, J.; Liu, G.; Kingry, L.C.; Mead, P.S.; Neitzel, D.F.; et al. Borrelia mayonii sp. nov., a member of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex, detected in patients and ticks in the upper midwestern United States. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4878–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepner, S.; Jolley, K.A.; Castillo-Ramirez, S.; Mourkas, E.; Dangel, A.; Wieser, A.; Hubner, J.; Sing, A.; Fingerle, V.; Margos, G. A core genome MLST scheme for Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato improves insights into the evolutionary history of the species complex. Cell Rep. Methods 2025, 5, 100935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, H.S.; Hickling, G.J.; Burke, R.L.; Ogden, N.H.; Beati, L.; LeBrun, R.A.; Arsnoe, I.M.; Gerhold, R.; Han, S.; Jackson, K.; et al. Why Lyme disease is common in the northern US, but rare in the south: The roles of host choice, host-seeking behavior, and tick density. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Sun, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, J. Tick-borne pathogens and the vector potential of ticks in China. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guner, E.S.; Watanabe, M.; Hashimoto, N.; Kadosaka, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Ezaki, T.; Kawabata, H.; Imai, Y.; Kaneda, K.; Masuzawa, T. Borrelia turcica sp. nov., isolated from the hard tick Hyalomma aegyptium in Turkey. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, P.-C. Les Tiques d’Afrique et du Bassin Méditerranéen; CIRAD-EMVT: Montpellier, France, 2003; p. 1 Cd-Rom. [Google Scholar]
- Gugliotta, J.L.; Goethert, H.K.; Berardi, V.P.; Telford, S.R., 3rd. Meningoencephalitis from Borrelia miyamotoi in an immunocompromised patient. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, G.E.; Breuner, N.E.; Hojgaard, A.; Oliver, J.; Eisen, L.; Eisen, R.J. A comparison of horizontal and transovarial transmission efficiency of Borrelia miyamotoi by Ixodes scapularis. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinck, C.B.; Lloyd, V.K. Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia miyamotoi in Atlantic Canadian wildlife. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Robbins, R.G.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Petney, T.N.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Horak, I.G. The Hard Ticks of the World, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Nederlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Almutairi, M.M.; Alouffi, A.; Tanaka, T.; Chang, S.C.; Chen, C.C.; Ali, A. Molecular evidence of Borrelia theileri and closely related Borrelia spp. in hard ticks infesting domestic animals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1297928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez Guillamet, L.J.; Marx, G.E.; Benjamin, W.; Pappas, P.; Lieberman, N.A.P.; Bachiashvili, K.; Leal, S.; Lieberman, J.A. Relapsing Fever Caused by Borrelia lonestari after Tick Bite in Alabama, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gylfe; Olsen, B.; Strasevicius, D.; Marti Ras, N.; Weihe, P.; Noppa, L.; Ostberg, Y.; Baranton, G.; Bergstrom, S. Isolation of Lyme disease Borrelia from puffins (Fratercula arctica) and seabird ticks (Ixodes uriae) on the Faeroe Islands. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L. [Investigation of rodents and Ixodes for Lyme disease and four strains of Borrelia burgdorferi first isolated from Ixodes granulatus Supino, Rattus confucianus and R. norvegicus in Fujian province]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 1992, 13, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takano, A.; Fujita, H.; Kadosaka, T.; Takahashi, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Ishiguro, F.; Takada, N.; Yano, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; Honda, T.; et al. Construction of a DNA database for ticks collected in Japan: Application of molecular identification based on the mitochondrial 16S rDNA gene. Med. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 65, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, T.; Hashimoto, N.; Kudeken, M.; Kadosaka, T.; Nakamura, M.; Kawabata, H.; Koizumi, N.; Imai, Y. New genomospecies related to Borrelia valaisiana, isolated from mammals in Okinawa archipelago, Japan. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jung, K.D.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, W.J.; Park, K.H. Characterization of Borrelia afzelii isolated from Ixodes nipponensis and Apodemus agrarius in Chungju, Korea, by PCR-rFLP analyses of ospC gene and rrf (5S)-rrl (23S) intergenic spacer. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 46, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palma, M.; Lopes de Carvalho, I.; Osorio, H.; Ze-Ze, L.; Cutler, S.J.; Nuncio, M.S. Portuguese hosts for Ornithodoros erraticus ticks. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telmadarraiy, Z.; Kooshki, H.; Edalat, H.; Vatandoost, H.; Bakhshi, H.; Faghihi, F.; Hosseini-Chegeni, A.; Oshaghi, M.A. Study on Hard and Soft Ticks of Domestic and Wild Animals in Western Iran. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2022, 16, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinerman, G.; Eshed, T.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; King, R.; Baneth, G. Transmission of the Human Relapsing Fever Spirochete Borrelia persica by the Argasid Tick Ornithodoros tholozani Involves Blood Meals from Wildlife Animal Reservoirs and Mainly Transstadial Transfer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e03117-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi-Asl, E.; Jafari, S. The habitat suitability model for the potential distribution of Ornithodoros tholozani (Laboulbene et Megnin, 1882) and Ornithodoros lahorensis (Neumann, 1908) (Acari: Argasidae): The main vectors of tick-borne relapsing fever in Iran. Ann. Parasitol. 2020, 66, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Tan, W.; Wang, H.; Han, X.; Hornok, S.; Zhao, S.; Mi, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y. The great gerbil (Rhombomys opimus) as a host for tick species in Gurbantunggut Desert. Parasit. Vectors 2024, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balashov Iu, S. [Infestation of natural populations of Ornithodoros tartakovskyi 01., 1931 ticks with Borrelia latyshevi Sof., 1941 spirochetes in different sections of the geographic area of the vector]. Parazitologiia 1972, 6, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Norte, A.C.; Ramos, J.A.; Gern, L.; Núncio, M.S.; Lopes de Carvalho, I. Birds as reservoirs for Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. in Western Europe: Circulation of B. turdi and other genospecies in bird-tick cycles in Portugal. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneda, K.; Masuzawa, T.; Simon, M.M.; Isogai, E.; Isogai, H.; Yasugami, K.; Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Yanagihara, Y. Infectivity and arthritis induction of Borrelia japonica on SCID mice and immune competent mice: Possible role of galactosylceramide binding activity on initiation of infection. Microbiol. Immunol. 1998, 42, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, T.; Suzuki, H.; Kawabata, H.; Ishiguro, F.; Takada, N.; Yanagihara, Y. Characterization of Borrelia spp. isolated from the tick, Ixodes tanuki and small rodents in Japan. J. Wildl. Dis. 1996, 32, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmar, Z.; Cozma, V.; Sprong, H.; Jahfari, S.; D’Amico, G.; Marcutan, D.I.; Ionica, A.M.; Magdas, C.; Modry, D.; Mihalca, A.D. Transstadial transmission of Borrelia turcica in Hyalomma aegyptium ticks. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, M.; Naddaf, S.R.; Ziapour, S.P.; Sepahi, A.A.; Rohani, M. Borrelia theileri infections in Rhipicephalus annulatus ticks from the north of Iran. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2024, 93, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, H.; Alouffi, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Ateeq, M.; Tanaka, T.; Chang, S.C.; Chen, C.C.; Ali, A. Argas persicus and Carios vespertilionis Ticks Infesting Ducks, Domestic Fowls and Bats in Pakistan: First Report on Molecular Survey and Phylogenetic Position of Borrelia anserina. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yang, B.; Yuan, M.; Bao, R. Predicting the potential habitat for Argas japonicus, Argas persicus, Argas reflexus, Argas vulgaris and Carios vespertilionis tick species in China. Vet. Parasitol. 2025, 337, 110501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.M.; Xiao, X.; Zhou, C.M.; Liu, J.X.; Gu, X.L.; Fang, L.Z.; Liu, B.Y.; Wang, L.R.; Yu, X.J.; Han, H.J. Human-pathogenic relapsing fever Borrelia found in bats from Central China phylogenetically clustered together with relapsing fever borreliae reported in the New World. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenson, T.G.T.; Wilhelmsson, P. First Record of a Suspected Human-Pathogenic Borrelia Species in Populations of the Bat Tick Carios vespertilionis in Sweden. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, B.; Chatterjee, M. Lyme borreliosis and skin. Indian J. Dermatol. 2013, 58, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azagi, T.; Harms, M.; Swart, A.; Fonville, M.; Hoornstra, D.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Hovius, J.W.; Sprong, H.; van den Wijngaard, C. Self-reported symptoms and health complaints associated with exposure to Ixodes ricinus-borne pathogens. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, G.; Rais, O.; Moran Cadenas, F.; Gonseth, Y.; Bouzelboudjen, M.; Gern, L. Influence of climatic factors on Ixodes ricinus nymph abundance and phenology over a long-term monthly observation in Switzerland (2000–2014). Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassner, F.; Takken, W.; Plas, C.L.-v.d.; Kastelein, P.; Hoetmer, A.J.; Holdinga, M.; van Overbeek, L.S. Rodent species as natural reservoirs of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in different habitats of Ixodes ricinus in The Netherlands. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- States, S.L.; Huang, C.I.; Davis, S.; Tufts, D.M.; Diuk-Wasser, M.A. Co-feeding transmission facilitates strain coexistence in Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Epidemics 2017, 19, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.H.; Pilz, A.; Jodar, L.; Moïsi, J.C. The Epidemiology of Lyme Borreliosis in Europe: An Updated Review on a Growing Public Health Issue. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.R.; Strle, F.; Wormser, G.P. Comparison of Lyme Disease in the United States and Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, L.; Tran, T.M.P.; Pilz, A.; Vyse, A.; Fletcher, M.A.; Angulo, F.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Moisi, J.C.; Jodar, L.; Stark, J.H. Incidence of Lyme Borreliosis in Europe from National Surveillance Systems (2005–2020). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigfusson, H.B.; Hardarson, H.S.; Ludviksson, B.R.; Gudlaugsson, O. [Lyme disease in Iceland—Epidemiology from 2011 to 2015]. Laeknabladid 2019, 105, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, G.; Ruscio, M.; Cinco, M.; Nan, K.; Forgione, P.; Di Meo, N.; Tranchini, P.; Nacca, M.; Trincone, S.; Rimoldi, S.G.; et al. The history of Lyme disease in Italy and its spread in the Italian territory. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1128142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiades, P.; Ezhova, E.; Raty, M.; Orlov, D.; Kulmala, M.; Lelieveld, J.; Malkhazova, S.; Erguler, K.; Petaja, T. The impact of climatic factors on tick-related hospital visits and borreliosis incidence rates in European Russia. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susnjar, J.; Cerar Kisek, T.; Strasek Smrdel, K.; Ruzic-Sabljic, E.; Adam, K.; Ivovic, V. Detection, identification and genotyping of Borrelia spp. in ticks of Coastal-Karst and Littoral-Inner Carniola regions in Slovenia. Folia Parasitol. (Praha) 2023, 70, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filatov, S.; Krishnavajhala, A.; Armstrong, B.A.; Kneubehl, A.R.; Nieto, N.C.; Perez De Leon, A.A.; Lopez, J.E. Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Tick-Borne Relapsing Fever Borrelia Infecting Ornithodoros (Pavlovskyella) verrucosus Ticks Collected in Ukraine. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goubau, P.F. Relapsing fevers. A review. Ann. Soc. Belg. Med. Trop. 1984, 64, 335–364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, M.C.; Vergara, S.; Gomez, M.C.; Roldan, M.E. Epidemiology of Tick-Borne Relapsing Fever in Endemic Area, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Pantchev, N.; Globokar, M.; Lopez, J.; Rodon, J.; Hernandez, L.; Herold, H.; Salas, N.; Civit, A.; Fingerle, V. First Cases of Natural Infections with Borrelia hispanica in Two Dogs and a Cat from Europe. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakab, A.; Kahlig, P.; Kuenzli, E.; Neumayr, A. Tick borne relapsing fever—A systematic review and analysis of the literature. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, J.J.; Ishak, S.N.; Lim, F.S.; Mohd-Taib, F.S.; Khor, C.S.; Loong, S.K.; AbuBakar, S. Detection of a Borrelia sp. From Ixodes granulatus Ticks Collected From Rodents in Malaysia. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Jian, M.; Yue, P.; Cao, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, M.; et al. Prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi in Ixodidae Tick around Asia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, T.; Masuda, S.; Fukui, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Bataa, J.; Oikawa, Y.; Ishiguro, F.; Takada, N. PCR detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Borrelia burgdorferi in Ixodes persulcatus ticks in Mongolia. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 67, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, T.; Fukui, T.; Miyake, M.; Oh, H.B.; Cho, M.K.; Chang, W.H.; Imai, Y.; Yanagihara, Y. Determination of members of a Borrelia afzelii-related group isolated from Ixodes nipponensis in Korea as Borrelia valaisiana. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49 Pt. 4, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, K.J.; Tang, H.Y.; Lim, L.S.; Pung, H.S.; Gan, S.Y.; Lai, N.S. Mini review: Surveillance of Lyme borreliosis in Southeast Asia and method of diagnosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 4378–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhacheva, T.A.; Kovalev, S.Y. Borrelia spirochetes in Russia: Genospecies differentiation by real-time PCR. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Iwaki, A.; Masuzawa, T.; Yanagihara, Y.; Korenberg, E.I.; Gorelova, N.B.; Volkov, V.I.; Ivanov, L.I.; Liberova, R.N. Prevalence of Lyme disease spirochetes in Ixodes persulcatus and wild rodents in far eastern Russia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3887–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasnatinov, M.A.; Liapunov, A.V.; Manzarova, E.L.; Kulakova, N.V.; Petrova, I.V.; Danchinova, G.A. The diversity and prevalence of hard ticks attacking human hosts in Eastern Siberia (Russian Federation) with first description of invasion of non-endemic tick species. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avagyan, G.A.; Khachatryan, E.A.; Sahakyan, A.E.; Sargsyan, R.T.; Koshtoyan, H.H.; Eghoyan, K.N.; Khachatryan, L.R.; Aleksanyan, A.M.; Avetisyan, A.E.; Karapetyan, A.H.; et al. Lyme Disease: A New Healthcare Issue in Armenia. New Armen. Med. J. 2012, 7, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, K.; Ito, T.; Asashima, N.; Ohno, M.; Nagai, R.; Fujita, H.; Koizumi, N.; Takano, A.; Watanabe, H.; Kawabata, H. Case report: Borrelia valaisiana infection in a Japanese man associated with traveling to foreign countries. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Q. Prevalence and Identification of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato Genospecies in Ticks from Northeastern China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praharaj, A.K.; Jetley, S.; Kalghatgi, A.T. Seroprevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi in North Eastern India. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2008, 64, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.; Murthy, K.R.; Bhagya, M.; Murthy, P.R.; Puttamallesh, V.N.; Ravi, V. Seroprevalence of Lymes disease in the Nagarahole and Bandipur forest areas of South India. Indian. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durden, L.A.; Merker, S.; Beati, L. The tick fauna of Sulawesi, Indonesia (Acari: Ixodoidea: Argasidae and Ixodidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2008, 45, 85–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naddaf, S.R.; Mahmoudi, A.; Ghasemi, A.; Rohani, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Ziapour, S.P.; Nemati, A.H.; Mostafavi, E. Infection of hard ticks in the Caspian Sea littoral of Iran with Lyme borreliosis and relapsing fever borreliae. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaj, E.A.; Al-Jumaa, Z.M. Molecular detection of Spirochetes and Borrelia burgdorferi in stray dogs of Nineveh province, Iraq. Open Vet. J. 2023, 13, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.A.; Samish, M.; Kletter, Y.; Tinghitella, T.; Heering, S.; Edberg, S.C. Lyme disease acquired in Israel: Report of a case and studies of serological cross reactivity in relapsing fever. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1993, 29, 464–465. [Google Scholar]
- Harrus, S.; Bark, H. Canine Lyme borreliosis in Israel. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1994, 30, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Kawagishi, N.; Sakai, H.; Takahashi, H.; Matsuo, S.; Nakao, M.; Miyamoto, K.; Iizuka, H. Lyme disease in Japan. Analysis of Borrelia species using rRNA gene restriction fragment length polymorphism. Dermatology 1995, 191, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, M.M.; Alshehabat, M.A.; Hayajneh, W.A.; Roess, A.A. Seroprevalence, spatial distribution and risk factors of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Jordan. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, 101559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhigailov, A.V.; Neupokoyeva, A.S.; Maltseva, E.R.; Perfilyeva, Y.V.; Bissenbay, A.O.; Turebekov, N.A.; Frey, S.; Essbauer, S.; Abdiyeva, K.S.; Ostapchuk, Y.O.; et al. The prevalence of Borrelia in Ixodes persulcatus in southeastern Kazakhstan. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Hong, Y.; Hwang, K.J.; Kim, S.; Eom, J.; Kwon, D.; Park, J.H.; Youn, S.K.; Sohn, A. Epidemiological features and clinical manifestations of Lyme borreliosis in Korea during the period 2005–2012. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 68, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Chang, W.H.; Schwan, T.G. Identification and characterization of Lyme disease spirochetes, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, isolated in Korea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, C.S.; Hassan, H.; Mohd-Rahim, N.F.; Chandren, J.R.; Nore, S.S.; Johari, J.; Loong, S.K.; Abd-Jamil, J.; Khoo, J.J.; Lee, H.Y.; et al. Seroprevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi among the indigenous people (Orang Asli) of Peninsular Malaysia. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 13, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Fricken, M.E.; Rolomjav, L.; Illar, M.; Altantogtokh, D.; Hogan, K.M.; Uyanga, B.; Ganbold, D.; Tsogbadrakh, N. Geographic Range of Lyme Borreliosis in Mongolia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Wilske, B.; Sing, A.; Hizo-Teufel, C.; Cao, W.C.; Chu, C.; Scholz, H.; Straubinger, R.K.; Fingerle, V. Borrelia bavariensis sp. nov. is widely distributed in Europe and Asia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 4284–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, S.B.; Agrawal, S.; Jha, S.; Bhandari, L.N.; Chalise, B.S.; Mishra, A.; Shah, R. First report of Lyme disease in Nepal. JMM Case Rep. 2018, 5, e005128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mughaizwi, T.; Al Rawahi, H.; Elamin, N.; Al Hinai, Z.; Al Muharrmi, Z.; Al Yazidi, L.S. Ten-year-old Omani Girl with Lyme Arthritis. Oman Med. J. 2022, 37, e446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.M.; Elbashier, A.M.; Awad, A.I.; Borgio, F. Erythema migrans—Case report from Dammam Central Hospital. Ann. Saudi Med. 1994, 14, 521–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keung, Y.K.; Cobos, E.; Kimbrough, R.C., 3rd; Carver, R.C. Borreliosis as a cause of fever in a woman who recently returned from Saudi Arabia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sthitmatee, N.; Jinawan, W.; Jaisan, N.; Tangjitjaroen, W.; Chailangkarn, S.; Sodarat, C.; Ekgatat, M.; Padungtod, P. Genetic and Immunological Evidences of Borrelia Burgdorferi in Dog in Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2016, 47, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Polat, E.; Turhan, V.; Aslan, M.; Musellim, B.; Onem, Y.; Ertugrul, B. [First report of three culture confirmed human Lyme cases in Turkey]. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2010, 44, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akin Belli, A.; Dervis, E.; Ozbas Gok, S.; Midilli, K.; Gargili, A. [Evaluation of 10 cases of Lyme disease presenting with erythema migrans in Istanbul, Turkey]. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2015, 49, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cikman, A.; Aydin, M.; Gulhan, B.; Karakecili, F.; Demirtas, L.; Kesik, O.A. Geographical Features and Seroprevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi in Erzincan, Turkey. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2018, 12, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic Muftuoglu, I.; Aydin Akova, Y.; Gur Gungor, S. A Case of Lyme Disease Accompanied by Uveitis and White Dot Syndrome. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 46, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, G.; Cinco, M.; Trevisini, S.; di Meo, N.; Ruscio, M.; Forgione, P.; Bonin, S. Borreliae Part 2: Borrelia Relapsing Fever Group and Unclassified Borrelia. Biology 2021, 10, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltazard, M.; Pournaki, R.; Bahmanyar, M.; Chamsa, M. [Ornithodorus tartakovskyi Olenev 1931 and Borrelia (Spirochaeta) latychevii Sofiev 1941; supplementary note]. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1955, 30, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenfeld, O. Borreliae, Human Relapsing Fever, and Parasite-Vector-Host Relationships. Bacteriol. Rev. 1965, 29, 46–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Naddaf, S.R.; Mahmoudi, A.; Rohani, M.; Naeimi, S.; Mordadi, A.; Cutler, S.J.; Mostafavi, E. Borrelia duttonii-like spirochetes parasitize Meriones persicus in East Azerbaijan Province of Iran. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.A.; Tian, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Jiang, B.G.; Liu, B.C.; Zhang, J.T.; Tian, S.; Ding, H.; Li, S.; et al. Molecular detection and identification of relapsing fever Borrelia in ticks and wild small mammals in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 2632–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shwartz, D.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Ben-Shitrit, B.; Straubinger, R.K.; Baneth, G. Isolation and Genetic Characterization of the Human Relapsing Fever Spirochete Borrelia persica from a Dog with Improved Cultivation Techniques. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assous, M.V.; Wilamowski, A. Relapsing fever borreliosis in Eurasia—Forgotten, but certainly not gone! Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.W. Tick borne relapsing fever imported into the United Kingdom. J. R. Army Med. Corps 1985, 131, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneth, G.; Dvorkin, A.; Ben-Shitrit, B.; Kleinerman, G.; Salant, H.; Straubinger, R.K.; Nachum-Biala, Y. Infection and seroprevalence of Borrelia persica in domestic cats and dogs in Israel. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hira, P.R. Borreliosis in the Arabian Gulf States: Report of a case from Kuwait. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, F.; Innocenti, P.; Baumgartner, M.; Binazzi, R.; Troi, C.; Pagani, E.; Ciervo, A. Borrelia microti infection in an Italian woman returning from Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 35, 101448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gwaiz, L.A.; Al-Mashhadani, S.A.; Ayoola, E.A.; Al-Khairy, K.S.; Higgy, K.G.; Al-Omair, A.O. Relapsing fever in Saudi Arabia: Report of two cases. Ann. Saudi Med. 1995, 15, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin de Verdiere, N.; Hamane, S.; Assous, M.V.; Sertour, N.; Ferquel, E.; Cornet, M. Tickborne relapsing fever caused by Borrelia persica, Uzbekistan and Tajikistan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1325–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasil’eva, I.S.; Ershova, A.S.; Mansurov, A.A.; Andrianov, V.A.; Abidov, Z.I.; Ibragimov Iu, I.; Narmatov, N.N. [Changes in the village foci of tick-borne relapsing fever in Uzbekistan over a 10-year period]. Parazitologiia 1991, 25, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Phuentshok, Y.; Dorji, K.; Zangpo, T.; Davidson, S.A.; Takhampunya, R.; Tenzinla, T.; Dorjee, C.; Morris, R.S.; Jolly, P.D.; Dorjee, S.; et al. Survey and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rodents and Important Rodent-Borne Zoonotic Pathogens in Gedu, Bhutan. Korean J. Parasitol. 2018, 56, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hmoon, M.M.; Htun, L.L.; Thu, M.J.; Chel, H.M.; Thaw, Y.N.; Win, S.Y.; Chan Soe, N.; Khaing, Y.; Thein, S.S.; Bawm, S. Molecular Prevalence and Identification of Ehrlichia canis and Anaplasma platys from Dogs in Nay Pyi Taw Area, Myanmar. Vet. Med. Int. 2021, 2021, 8827206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuzawa, T.; Iwaki, A.; Sato, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Korenberg, E.I.; Yanagihara, Y. Genetic diversity of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolated in far eastern Russia. Microbiol. Immunol. 1997, 41, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetsveld, J.; Kolyasnikova, N.M.; Wagemakers, A.; Toporkova, M.G.; Sarksyan, D.S.; Oei, A.; Platonov, A.E.; Hovius, J.W. Development and optimization of an in vitro cultivation protocol allows for isolation of Borrelia miyamotoi from patients with hard tick-borne relapsing fever. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, E.V.; Kurilshikov, A.M.; Stronin, O.V.; Fomenko, N.V. Whole-genome sequencing of Borrelia garinii BgVir, isolated from Taiga ticks (Ixodes persulcatus). J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mukhametov, A.; Osadchuk, M.; Berechikidze, I.; Pronkin, N. Epizootiological aspects of natural nidality of Ixodes tick-borne borreliosis in the Moscow region (Russian Federation). Vet. World 2022, 15, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khasnatinov, M.A.; Danchinova, G.A.; Takano, A.; Kawabata, H.; Ohashi, N.; Masuzawa, T. Prevalence of Borrelia miyamotoi in Ixodes persulcatus in Irkutsk City and its neighboring territories, Russia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltazard, M.; Bahmanyar, M.; Chamsa, M. [Relapsing fever in Afghanistan]. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. Fil. 1955, 48, 159–161. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld, O. Borrelia: Strains, Vectors, Human and Animal Borreliosis; Warren Green: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1971; pp. xii + 180. [Google Scholar]
- Bottieau, E.; Van Duffel, L.; El Safi, S.; Koirala, K.D.; Khanal, B.; Rijal, S.; Bhattarai, N.R.; Phe, T.; Lim, K.; Mukendi, D.; et al. Etiological spectrum of persistent fever in the tropics and predictors of ubiquitous infections: A prospective four-country study with pooled analysis. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Xiao, L.; Dong, N.; Wu, H.; Li, S. Projecting the potential distribution of ticks in China under climate and land use change. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.B.; Jia, N.; Jiang, B.G.; Sun, T.; Zheng, Y.C.; Huo, Q.B.; Liu, K.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Q.M.; Yang, H.; et al. Lyme borreliosis caused by diverse genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in northeastern China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.X.; Wen, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.G.; Wang, S.S.; Qiu, Q.C.; Shi, Z.X.; Li, D.Y.; Chen, D.Q.; Liu, X.D.; Zhao, J.H. Clinical manifestations and epidemiological characteristics of Lyme disease in Hailin county, Heilongjiang Province, China. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1988, 539, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, T.; Takada, N.; Kudeken, M.; Fukui, T.; Yano, Y.; Ishiguro, F.; Kawamura, Y.; Imai, Y.; Ezaki, T. Borrelia sinica sp. nov., a lyme disease-related Borrelia species isolated in China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Liu, H.X.; Hou, X.X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.N.; Wan, K.L. Polymorphism of P66 in Borrelia Burgdorferi Strains in China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.G.; Jia, N.; Jiang, J.F.; Zheng, Y.C.; Chu, Y.L.; Jiang, R.R.; Wang, Y.W.; Liu, H.B.; Wei, R.; Zhang, W.H.; et al. Borrelia miyamotoi Infections in Humans and Ticks, Northeastern China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.J.; Liu, J.W.; Wen, H.L.; Li, Z.M.; Lei, S.C.; Qin, X.R.; Zhou, C.M.; Yu, H.; Xiao, X.; Yu, X.J. Pathogenic New World Relapsing Fever Borrelia in a Myotis Bat, Eastern China, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 3083–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.G.; Wu, A.Q.; Jiang, J.F.; Yuan, T.T.; Xu, Q.; Lv, C.L.; Chen, J.J.; Sun, Y.; Fang, L.Q.; Ruan, X.D.; et al. Molecular Detection of Novel Borrelia Species, Candidatus Borrelia javanense, in Amblyomma javanense Ticks from Pangolins. Pathogens 2021, 10, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronghang, B.; Roy, B. Status of tick infections among semi-wild cattle in Arunachal Pradesh, India. Ann. Parasitol. 2016, 62, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayaraj, E.V.; Gupta, N.; Sreenath, K.; Thakur, C.K.; Gulati, S.; Anand, V.; Tripathi, M.; Bhatia, R.; Vibha, D.; Dash, D.; et al. Clinical and laboratory evidence of Lyme disease in North India, 2016–2019. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 43, 102134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Paul, M.; Panagariya, A.; Dubey, P. Neuroborreliosis in India—A Diagnostic Challenge and a Great Mimicker: A Case Series. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2022, 70, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jairath, V.; Sehrawat, M.; Jindal, N.; Jain, V.K.; Aggarwal, P. Lyme disease in Haryana, India. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2014, 80, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriyono; Takano, A.; Kuwata, R.; Shimoda, H.; Hadi, U.K.; Setiyono, A.; Agungpriyono, S.; Maeda, K. Detection and isolation of tick-borne bacteria (Anaplasma spp., Rickettsia spp., and Borrelia spp.) in Amblyomma varanense ticks on lizard (Varanus salvator). Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 63, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, J.B.; Curtis, C.E. An unexpected case of Lyme disease in a soldier serving in northern Iraq. Mil. Med. 2010, 175, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Baneth, G.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Halperin, T.; Hershko, Y.; Kleinerman, G.; Anug, Y.; Abdeen, Z.; Lavy, E.; Aroch, I.; Straubinger, R.K. Borrelia persica infection in dogs and cats: Clinical manifestations, clinicopathological findings and genetic characterization. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinerman, G.; King, R.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Baneth, G. Borrelia persica infection in rock hyraxes. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, T. [Present status of Lyme borreliosis and characterization of Lyme disease Borrelia isolated in Japan]. Yakugaku Zasshi 1997, 117, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, K.; Takano, A.; Taylor, K.; Sashika, M.; Shimozuru, M.; Konnai, S.; Kawabata, H.; Tsubota, T. A relapsing fever group Borrelia sp. similar to Borrelia lonestari found among wild sika deer (Cervus nippon yesoensis) and Haemaphysalis spp. ticks in Hokkaido, Japan. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuno, K.; Lee, K.; Itoh, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Yonemitsu, K.; Kuwata, R.; Shimoda, H.; Watarai, M.; Maeda, K.; Takano, A. Epidemiological study of relapsing fever borreliae detected in Haemaphysalis ticks and wild animals in the western part of Japan. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Tsuruta, Y.; Matsushita, O.; Ralph, D.; McClelland, M.; Nakao, M. Genetic and phenotypic analysis of Borrelia miyamotoi sp. nov., isolated from the ixodid tick Ixodes persulcatus, the vector for Lyme disease in Japan. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Sakakibara, K.; Masuzawa, T.; Ohnishi, M.; Kawabata, H. Case control study: Serological evidence that Borrelia miyamotoi disease occurs nationwide in Japan. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsuna, S.; Kawabata, H.; Kasahara, K.; Takano, A.; Mikasa, K. The first case of imported relapsing fever in Japan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 460–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, A.; Fujita, H.; Kadosaka, T.; Konnai, S.; Tajima, T.; Watanabe, H.; Ohnishi, M.; Kawabata, H. Characterization of reptile-associated Borrelia sp. in the vector tick, Amblyomma geoemydae, and its association with Lyme disease and relapsing fever Borrelia spp. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2011, 3, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostapchuk, Y.O.; Perfilyeva, Y.V.; Zhigailov, A.V.; Maltseva, E.R.; Neupokoyeva, A.S.; Bissenbay, A.O.; Berdygulova, Z.A.; Naizabayeva, D.A.; Nizkorodova, A.S.; Shapiyeva, Z.Z.; et al. Monitoring of pathogenic Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in the Almaty oblast, Kazakhstan. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostapchuk, Y.O.; Dmitrovskiy, A.M.; Pak, E.A.; Perfilyeva, Y.V. A Case of Combined Infection with Tick-Borne Encephalitis and Lyme Borreliosis with Severe Meningoencephalitis and Complete Recovery. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2023, 15, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Choi, E.H.; Lee, M.G.; Ahn, S.K. Serologically diagnosed Lyme disease manifesting erythema migrans in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 1999, 14, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D.; Park, J.H. Seroepidemiologic Survey of Lyme Disease among Forestry Workers in National Park Offices in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Goo, Y.K.; Geraldino, P.J.L.; Kwon, O.D.; Kwak, D. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Borrelia garinii (Spirochaetales: Borreliaceae) in Ixodes nipponensis (Ixodida: Ixodidae) Parasitizing a Dog in Korea. Pathogens 2019, 8, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.G.; Chae, J.B.; Cho, Y.K.; Jo, Y.S.; Shin, N.S.; Lee, H.; Choi, K.S.; Yu, D.H.; Park, J.; Park, B.K.; et al. Molecular Detection of Anaplasma, Bartonella, and Borrelia theileri in Raccoon Dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Korea. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Chong, S.T.; Kim, H.C.; Klein, T.A.; Park, K.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, W.K.; Song, J.W. Surveillance and Molecular Identification of Borrelia Species in Ticks Collected at U.S. Army Garrison Humphreys, Republic of Korea, 2018–2019. J. Med. Entomol. 2022, 59, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.W.; Han, S.Y.; Sung, S.H.; Jung, E.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Yoo, S.S. Survey on tick distribution and tick-borne pathogens in Daejeon and adjacent areas in South Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, S.T.; Kamalanathan, M.; Rohani, M.Y. Borrelia burgdorferi (strain B. afzelii) antibodies among Malaysian blood donors and patients. Southeast. Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2002, 33, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohd-Azami, S.N.I.; Loong, S.K.; Khoo, J.J.; Husin, N.A.; Lim, F.S.; Mahfodz, N.H.; Ishak, S.N.; Mohd-Taib, F.S.; Makepeace, B.L.; AbuBakar, S. Molecular Surveillance for Vector-Borne Bacteria in Rodents and Tree Shrews of Peninsular Malaysia Oil Palm Plantations. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.C.C.; Qiu, Y.; Moustafa, M.A.M.; Nakao, R.; Shimozuru, M.; Onuma, M.; Mohd-Azlan, J.; Tsubota, T. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato and Relapsing Fever Borrelia in Feeding Ixodes Ticks and Rodents in Sarawak, Malaysia: New Geographical Records of Borrelia yangtzensis and Borrelia miyamotoi. Pathogens 2020, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, J.J.; Lim, F.S.; Tan, K.K.; Chen, F.S.; Phoon, W.H.; Khor, C.S.; Pike, B.L.; Chang, L.Y.; AbuBakar, S. Detection in Malaysia of a Borrelia sp. From Haemaphysalis hystricis (Ixodida: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagunova, E.K.; Liapunova, N.A.; Tuul, D.; Otgonsuren, G.; Nomin, D.; Erdenebat, N.; Abmed, D.; Danchinova, G.A.; Sato, K.; Kawabata, H.; et al. Co-infections with multiple pathogens in natural populations of Ixodes persulcatus ticks in Mongolia. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaowa; Wulantuya; Sato, K.; Liu, D.; Cui, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, T.; Liu, R.; et al. Surveillance of Borrelia miyamotoi-carrying ticks and genomic analysis of isolates in Inner Mongolia, China. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lv, X.L.; Han, S.Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q.; Song, M. First detection of Borrelia miyamotoi infections in ticks and humans from the northeast of Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Trop. 2021, 217, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkot, T.R.; Schriefer, M.E.; Larsen, S.A. Cross-reactivity to Borrelia burgdorferi proteins in serum samples from residents of a tropical country nonendemic for Lyme disease. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Islam, N.; Khan, A.; Islam, Z.U.; Munoz-Leal, S.; Labruna, M.B.; Ali, A. New records of Amblyomma gervaisi from Pakistan, with detection of a reptile-associated Borrelia sp. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 102047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.; Zafar, F.; Khan, K. A SURVEY OF BORRELIA-RECURRENTIS IN HUMAN BLOOD IN KARACHI PAKISTAN. Karachi Univ. J. Sci. 1990, 18, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Galon, E.M.; Macalanda, A.M.; Garcia, M.M.; Ibasco, C.J.; Garvida, A.; Ji, S.; Zafar, I.; Hasegawa, Y.; Liu, M.; Ybañez, R.H.; et al. Molecular Identification of Selected Tick-Borne Protozoan and Bacterial Pathogens in Thoroughbred Racehorses in Cavite, Philippines. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajmi, R.A.; Ayaad, T.H.; Al-Harbi, H.T.; Shaurub, E.H.; Al-Musawi, Z.M. Molecular identification of ticks infesting camels and the detection of their natural infections with Rickettsia and Borrelia in Riyadh province, Saudi Arabia. Trop. Biomed. 2019, 36, 758–765. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaifi, A.A.; Masoodi, I.; Alzaidi, O.; Hussain, S.; Khurshid, S.; Sirwal, I.A. Spirocheatal shock syndrome. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 32, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhampunya, R.; Longkunan, A.; Somchaimongkol, S.; Youngdech, N.; Chanarat, N.; Sakolvaree, J.; Tippayachai, B.; Promsathaporn, S.; Phanpheuch, B.; Poole-Smith, B.K.; et al. Borrelia miyamotoi a neglected tick-borne relapsing fever spirochete in Thailand. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaenkan, W.; Nooma, W.; Chelong, I.A.; Baimai, V.; Trinachartvanit, W.; Ahantarig, A. Reptile-associated Borrelia spp. In Amblyomma ticks, Thailand. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakar Ozdal, M.P.; Yazici, A.; Tufek, M.; Ozturk, F. Epidemiology of uveitis in a referral hospital in Turkey. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 44, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepner, S.; Fingerle, V.; Duscher, G.G.; Felsberger, G.; Marosevic, D.; Rollins, R.E.; Okeyo, M.; Sing, A.; Margos, G. Population structure of Borrelia turcica from Greece and Turkey. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 77, 104050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollins, R.E.; Sato, K.; Nakao, M.; Tawfeeq, M.T.; Herrera-Mesias, F.; Pereira, R.J.; Kovalev, S.; Margos, G.; Fingerle, V.; Kawabata, H.; et al. Out of Asia? Expansion of Eurasian Lyme borreliosis causing genospecies display unique evolutionary trajectories. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otranto, D.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Beugnet, F.; Baneth, G.; Dantas-Torres, F. New paradigms in the prevention of canine vector-borne diseases. Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Espinoza, U.M.; Santiago-Alarcon, D.; Villalobos, F.; Marques, R.; Lagunes-Quintanilla, R.; Lira-Noriega, A. Current and future applications of species distribution and ecological niche modelling for the study of ticks and tick-borne pathogens. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2025, 39, 399–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, J.C.; Paz, S. Climate change and infectious disease in Europe: Impact, projection and adaptation. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 9, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Handschuh, S.; Dunlop, J.A.; Pienaar, R.; Mans, B.J. Nuttalliellidae in Burmese amber: Implications for tick evolution. Parasitology 2024, 151, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshaghi, M.A.; Rafinejad, J.; Choubdar, N.; Piazak, N.; Vatandoost, H.; Telmadarraiy, Z.; Mohtarami, F.; Ravasan, N.M. Discrimination of relapsing fever Borrelia persica and Borrelia microtti by diagnostic species-specific primers and polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Bao, R. Predicting the potential habitat for Ornithodoros tick species in China. Vet. Parasitol. 2022, 311, 109793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlig, P.; Paris, D.H.; Neumayr, A. Louse-borne relapsing fever—A systematic review and analysis of the literature: Part 1—Epidemiology and diagnostic aspects. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0008564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, R. The non-transmission of abyssinian louse-borne relapsing fever by the tick ornithodorus savignyi and certain other blood-sucking arthropods. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1938, 32, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepner, S.; Fingerle, V.; Heylen, D.; Marosevic, D.; Ghaffari, K.; Okeyo, M.; Sing, A.; Margos, G. First investigations on serum resistance and sensitivity of Borrelia turcica. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).