Riociguat Alleviates Cisplatin-Caused Kidney Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Simple Summary
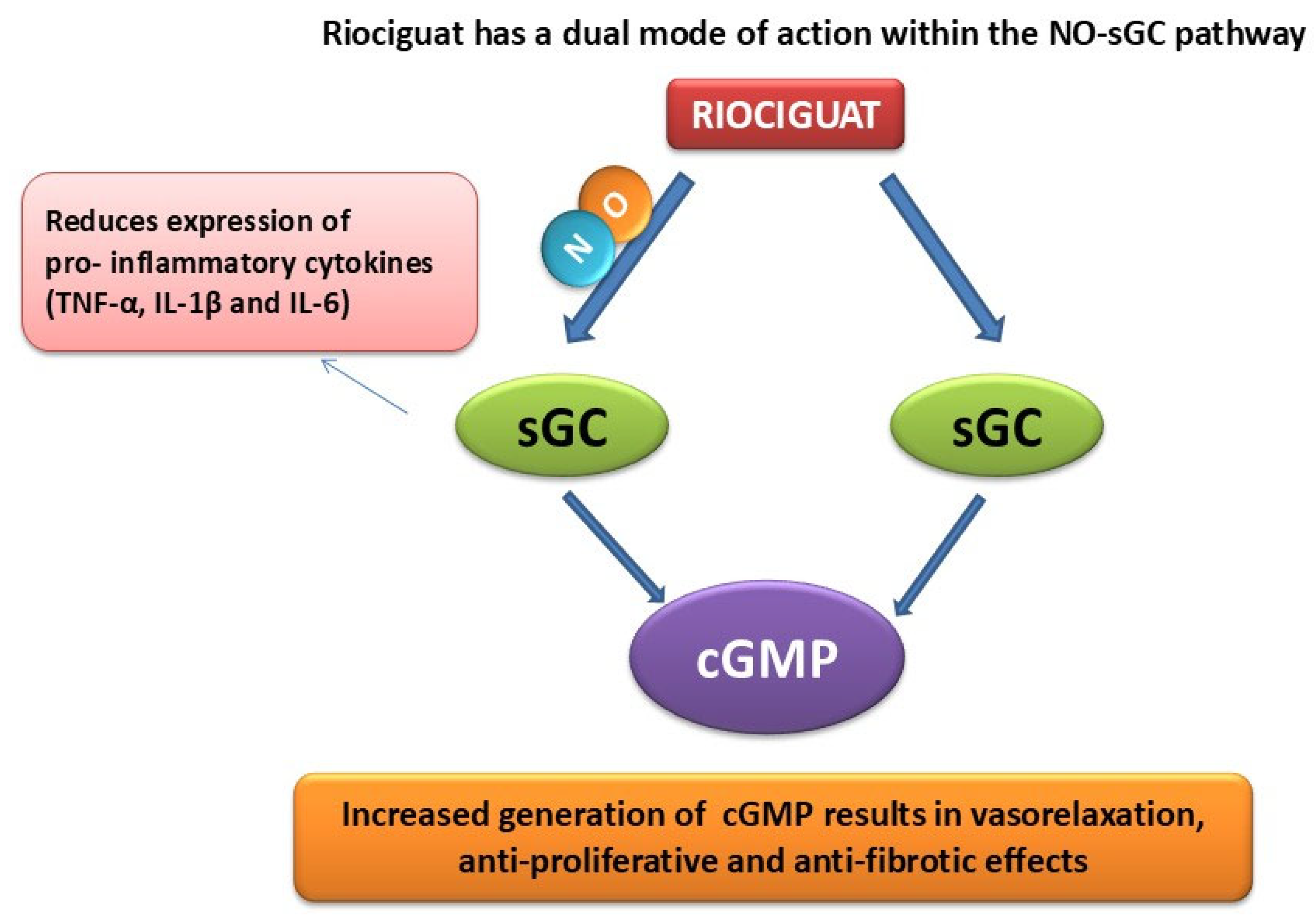
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs, Chemicals, and Biochemical Analysis
2.2. Animals
2.3. Animal Grouping
2.4. Experimental Protocol
2.5. Preparation of Tissue Homogenates
2.6. Kidney Function Markers
2.7. Oxidative Stress Parameters
2.8. Inflammatory Markers
2.9. Histopathological Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect on Physiological Parameters
3.2. Effect on the Renal Biomarkers
3.3. Effect on Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress
3.4. Effect on Inflammatory Cytokines
3.5. Effect on Kidney Morphology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gameiro, J.; Fonseca, J.A.; Outerelo, C.; Lopes, J.A. Acute Kidney Injury: From Diagnosis to Prevention and Treatment Strategies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Kellum, J.A. Defining Acute Kidney Injury. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, F.; Awad, A.S.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M. Acute Kidney Injury: Medical Causes and Pathogenesis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomsa, A.M.; Alexa, A.L.; Junie, M.L.; Rachisan, A.L.; Ciumarnean, L. Oxidative Stress as a Potential Target in Acute Kidney Injury. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, S.; Becker, C.; Frey, R.; Mück, W. Population Pharmacokinetics of Single-Dose Riociguat in Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment. Pulm. Circ. 2016, 6, S75–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, B.H.; Al-Salam, S.; Al Husseini, I.S.; Al-Lawati, I.; Waly, M.; Yasin, J.; Fahim, M.; Nemmar, A. Abrogation of Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Emodin in Rats. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 27, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSweeney, K.R.; Gadanec, L.K.; Qaradakhi, T.; Ali, B.A.; Zulli, A.; Apostolopoulos, V. Mechanisms of Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: Pathological Mechanisms, Pharmacological Interventions, and Genetic Mitigations. Cancers 2021, 13, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorsy, E.A.; Saber, S.; Hamad, R.S.; Abdel-Reheim, M.A.; El-Kott, A.F.; AlShehri, M.A.; Morsy, K.; Salama, S.A.; Youssef, M.E. Advances in Understanding Cisplatin-Induced Toxicity: Molecular Mechanisms and Protective Strategies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 203, 106939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.L.C.; de Brito, B.B.; da Silva, F.A.F.; Botelho, A.C.D.S.; de Melo, F.F. Nephrotoxicity in Cancer Treatment: An Overview. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 11, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xie, D.; Gewirtz, D.A.; Li, N. Nephrotoxicity in Cancer Treatment: An Update. Adv. Cancer Res. 2022, 155, 77–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perše, M.; Večerić-Haler, Ž. Cisplatin-Induced Rodent Model of Kidney Injury: Characteristics and Challenges. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 1462802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conole, D.; Scott, L.J. Riociguat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2013, 73, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, M.; Clarke, M.M.; Pogue, K.T. Overview of Riociguat and Its Role in the Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Pharm. Pract. 2022, 35, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, R.; Becker, C.; Saleh, S.; Unger, S.; van der Mey, D.; Mück, W. Clinical Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Profile of Riociguat. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Suleimani, Y.M.; Ali, B.H.; Ali, H.; Manoj, P.; Almashaiki, K.S.; Abdelrahman, A.M. The Salutary Effects of Diminazene, Lisinopril or Valsartan on Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats: A Comparative Study. Physiol. Res. 2024, 73, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geschka, S.; Kretschmer, A.; Sharkovska, Y.; Evgenov, O.V.; Lawrenz, B.; Hucke, A.; Hocher, B.; Stasch, J.P. Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Stimulation Prevents Fibrotic Tissue Remodeling and Improves Survival in Salt-Sensitive Dahl Rats. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upreti, G.C.; Davis, C.; Oliver, J. Preparation of Representative Homogenates of Biological Tissues: Effect of Salt on Protein Extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 198, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.H.; Al-Salam, S.; Al Za’abi, M.; Al Balushi, K.A.; Ramkumar, A.; Waly, M.I.; Yasin, J.; Adham, S.A.; Nemmar, A. Does Swimming Exercise Affect Experimental Chronic Kidney Disease in Rats Treated with Gum Acacia? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volarevic, V.; Djokovic, B.; Jankovic, M.G.; Harrell, C.R.; Fellabaum, C.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N. Molecular Mechanisms of Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabla, N.; Dong, Z. Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity: Mechanisms and Renoprotective Strategies. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.P.; Tadagavadi, R.K.; Ramesh, G.; Reeves, W.B. Mechanisms of Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Toxins 2010, 2, 2490–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, A.M.; Al Suleimani, Y.; Shalaby, A.; Ashique, M.; Manoj, P.; Al-Saadi, H.; Ali, B.H. Effect of Levosimendan, a Calcium Sensitizer, on Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, F.; Kothiyal, P.; Alshehri, S.; Afzal, M.; Iqbal, M.; Khan, M.R.; Alanazi, A.A.H.; Anwer, M.K. Hirsutidin Prevents Cisplatin-Evoked Renal Toxicity by Reducing Oxidative Stress/Inflammation and Restoring the Endogenous Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Level. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, T.; Alshahrani, S.; Somaili, A.M.H.; Khubrani, A.H.; Ahmed, R.A.; Jali, A.M.; Alshamrani, A.; Rashid, H.; Nomeir, Y.; Khalid, M.; et al. Nephroprotective Effect of Diosmin against Cisplatin-Induced Kidney Damage by Modulating IL-1β, IL-6, TNFα and Renal Oxidative Damage. Molecules 2023, 28, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, R.; Devrim, E.; Kiliçoğlu, B.; Avci, A.; Candir, O.; Durak, I. Cisplatin Impairs Antioxidant System and Causes Oxidation in Rat Kidney Tissues: Possible Protective Roles of Natural Antioxidant Foods. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2006, 26, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurászová, M.; Gurecká, R.; Bábíčková, J.; Tóthová, Ľ. Oxidative Stress in the Pathophysiology of Kidney Disease: Implications for Noninvasive Monitoring and Identification of Biomarkers. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5478708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, L.; Ardaillou, R. Reactive Oxygen Species: Production and Role in the Kidney. Am. J. Physiol. 1986, 251, F765–F776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Wei, W.; Fan, X.; Ci, X. Farrerol Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Inhibiting the Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Oxidation, Inflammation, and Apoptotic Signaling Pathways. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Gomez, H.; Murugan, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Z.Y. Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5080843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, N.; Wood, J.; Barber, J. The Role of Glutathione Reductase and Related Enzymes on Cellular Redox Homoeostasis Network. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 95, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi Sadeer, N.; Montesano, D.; Albrizio, S.; Zengin, G.; Mahomoodally, M.F. The Versatility of Antioxidant Assays in Food Science and Safety—Chemistry, Applications, Strengths, and Limitations. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vašková, J.; Kočan, L.; Vaško, L.; Perjési, P. Glutathione-Related Enzymes and Proteins: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safhi, M.M.; Qumayri, H.M.; Masmali, A.U.M.; Siddiqui, R.; Alam, M.F.; Khan, G.; Anwer, T. Thymoquinone and Fluoxetine Alleviate Depression via Attenuating Oxidative Damage and Inflammatory Markers in Type-2 Diabetic Rats. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 125, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Maskari, R.; Abdelrahman, A.M.; Ali, H.; Manoj, P.; Al Suleimani, Y. Nephroprotective Effects of the Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase Stimulator, Riociguat, in Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2024, 13, 101800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sravani, S.; Saifi, M.A.; Godugu, C. Riociguat Ameliorates Kidney Injury and Fibrosis in an Animal Model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 530, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xiong, Y.; Zeng, S.; Delić, D.; Gaballa, M.; Kalk, P.; Klein, T.; Krämer, B.K.; Hocher, B. Comparison of sGC Activator and sGC Stimulator in 5/6 Nephrectomized Rats on High-Salt Diet. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1480186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, M.S.; Pavkovic, M.; Frederick, J.; Abedini, A.; Freyberger, A.; Vienenkötter, J.; Mathar, I.; Siudak, K.; Eitner, F.; Sandner, P.; et al. Treatment Effects of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Modulation on Diabetic Kidney Disease at Single-Cell Resolution. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 100999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasch, J.P.; Schlossmann, J.; Hocher, B. Renal Effects of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Stimulators and Activators: A Review of the Preclinical Evidence. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 21, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandner, P.; Follmann, M.; Becker-Pelster, E.; Hahn, M.G.; Meier, C.; Freitas, C.; Roessig, L.; Stasch, J.P. Soluble GC Stimulators and Activators: Past, Present and Future. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 4130–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Liu, W.; Tsai, X.Q.; Wang, Z.; Outtrim, C.; Tang, A.; Pieper, M.P.; Reinhart, G.A.; Huang, Y. A Novel Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activator, Avenciguat, in Combination with Empagliflozin, Protects against Renal and Hepatic Injury in Diabetic db/db Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 328, E362–E376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, G.; Reeves, W.B. Cisplatin Increases TNF-Alpha mRNA Stability in Kidney Proximal Tubule Cells. Ren. Fail. 2006, 28, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, H.A.; Humbert, M.; Langleben, D.; Schermuly, R.; Stasch, J.P.; Wilkins, M.R.; Klinger, J.R. Riociguat: Mode of action and clinical development in pulmonary hypertension. Chest 2017, 151, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabl, P.; Brusilovskaya, K.; Supper, P.; Bauer, D.; Königshofer, P.; Riedl, F.; Hayden, H.; Fuchs, C.D.; Stift, J.; Oberhuber, G.; et al. The soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator riociguat reduces fibrogenesis and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
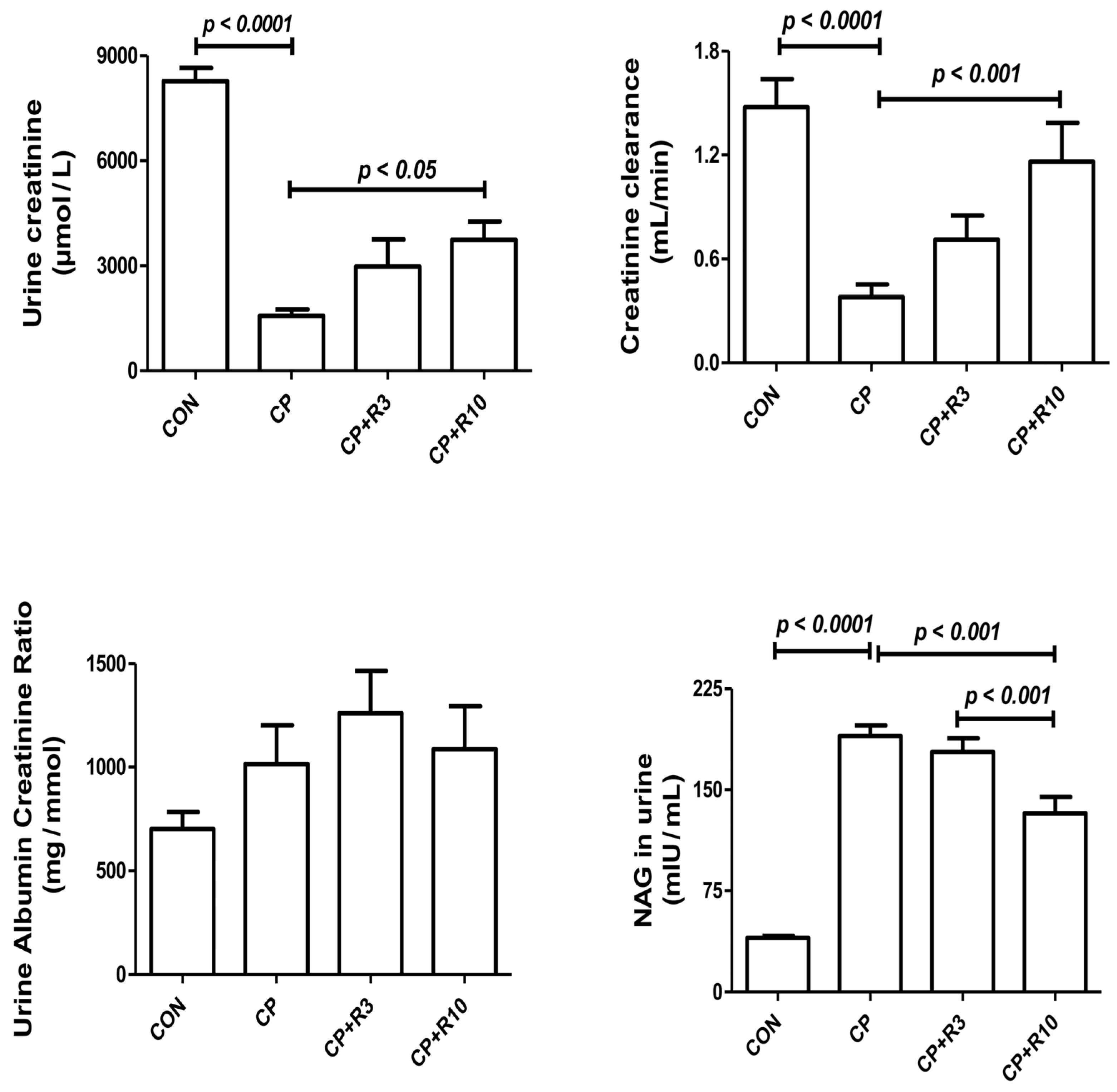
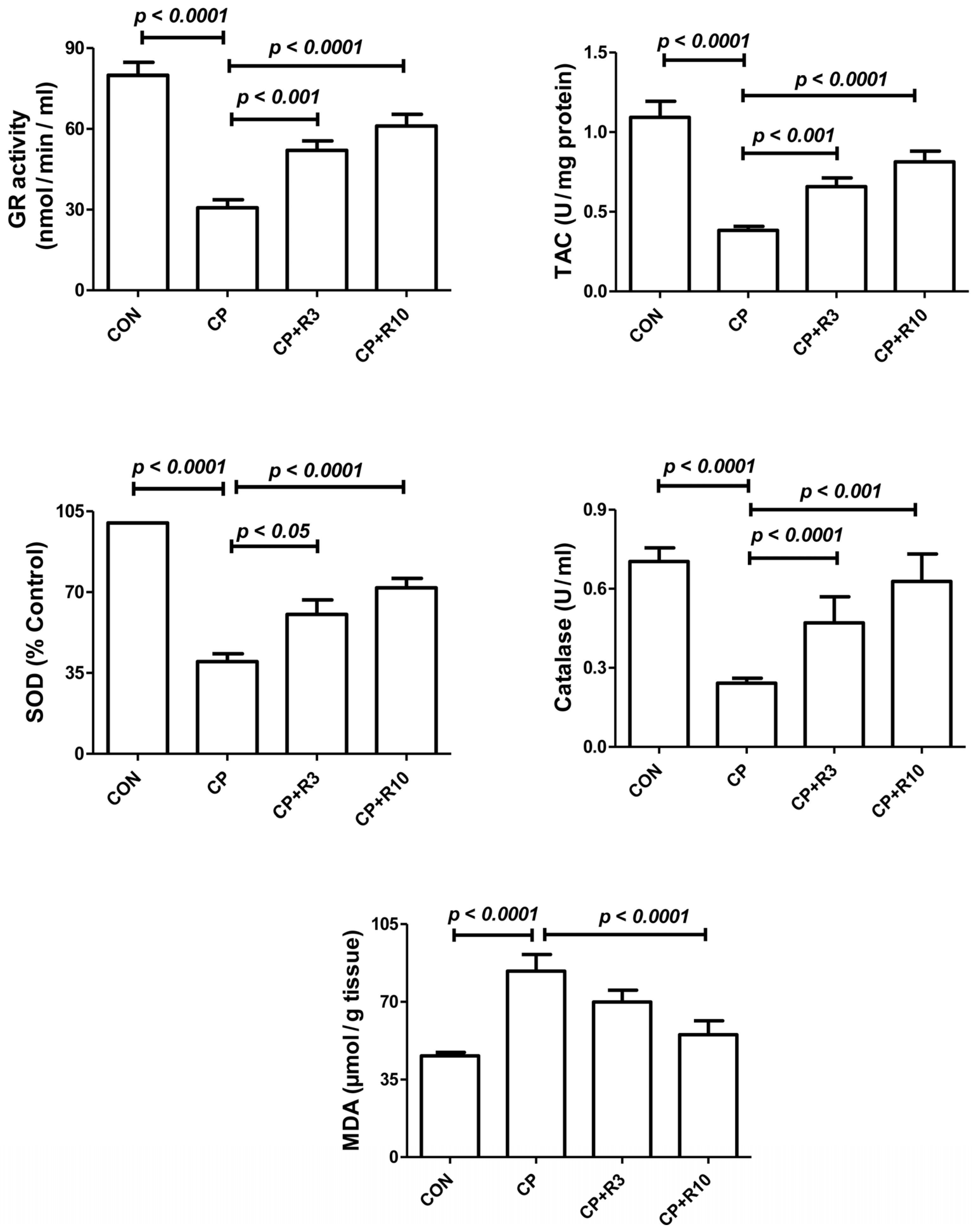
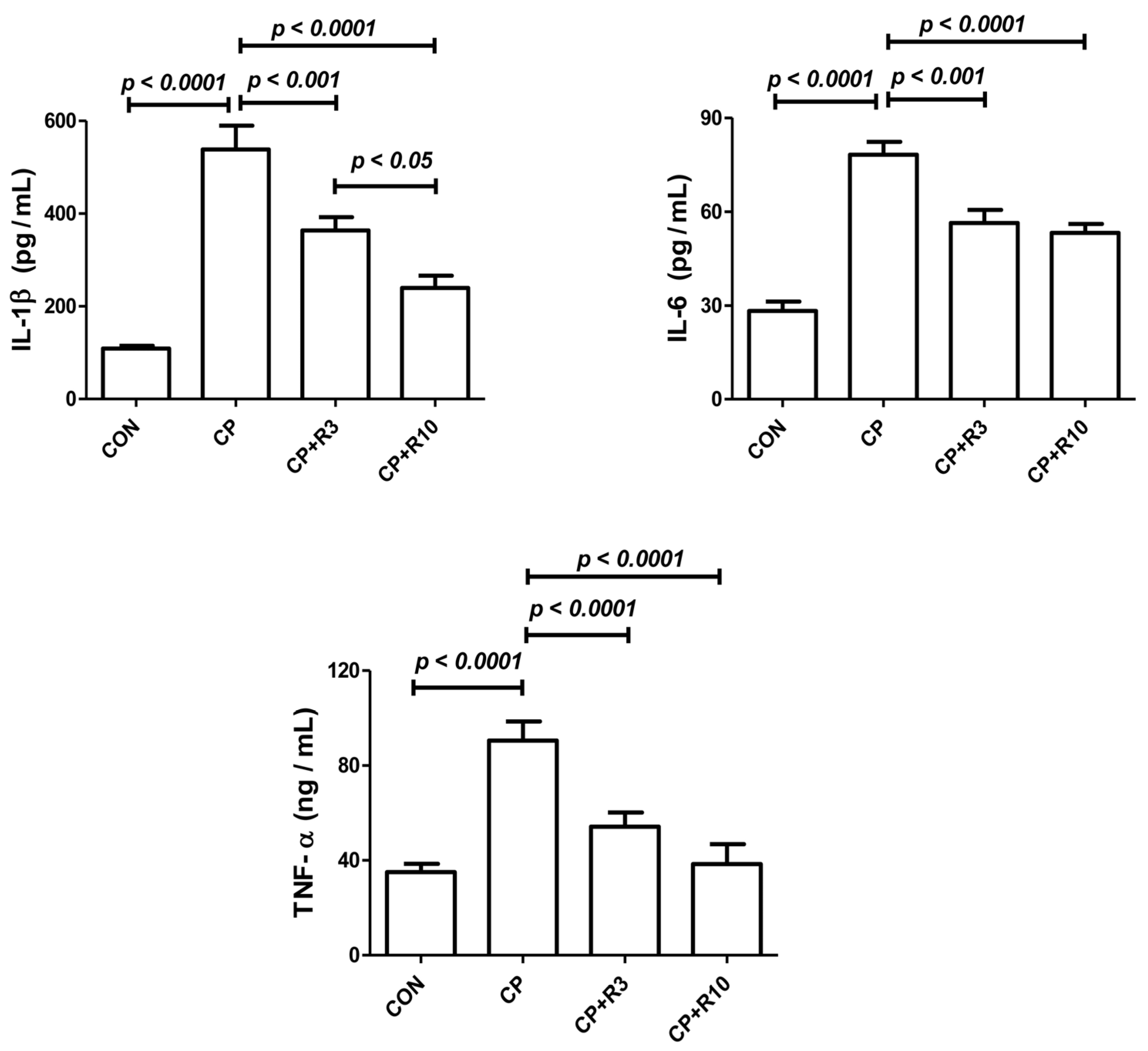
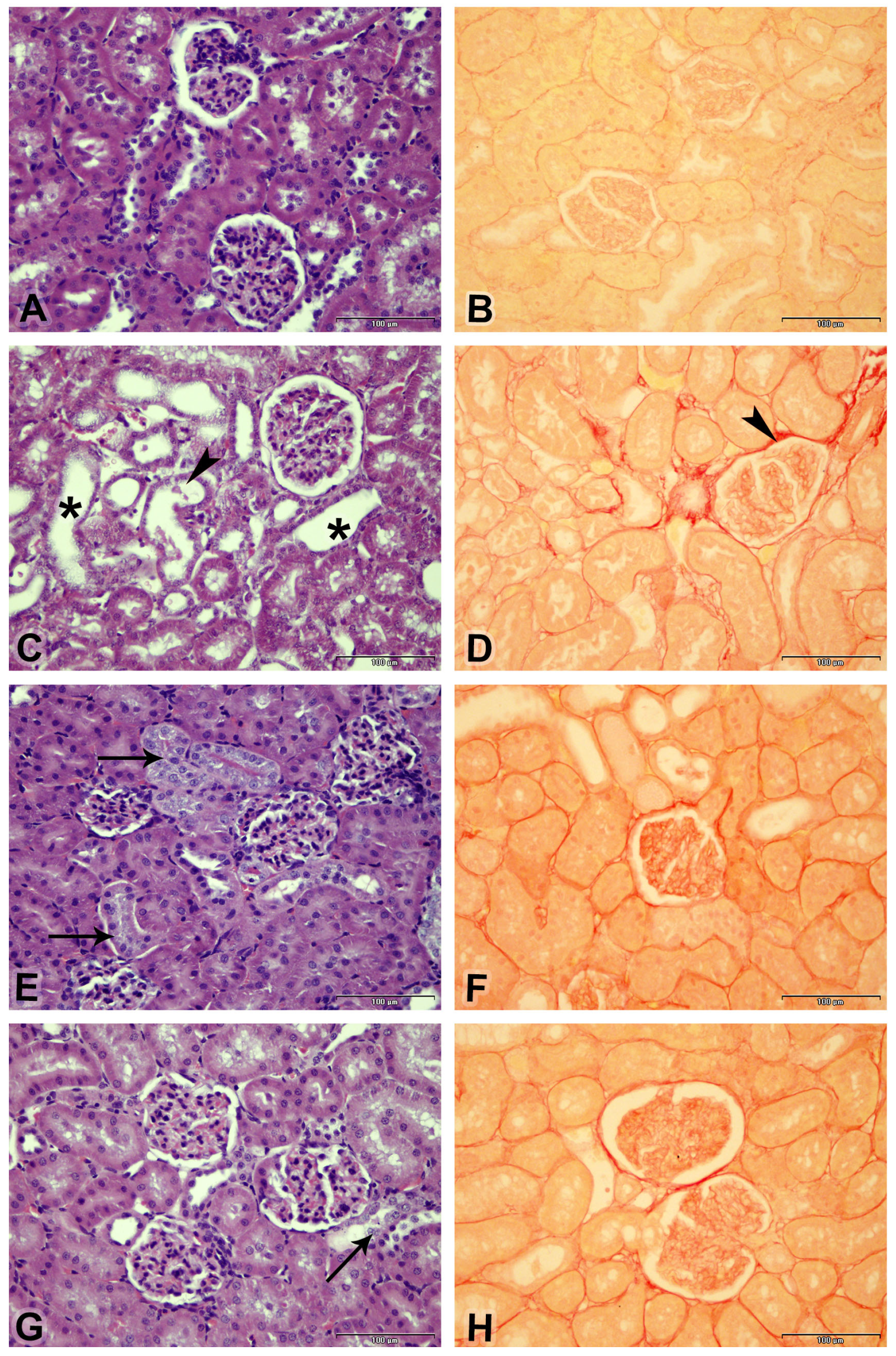
| Parameters/Treatment | Control | CP | CP + R3 | CP + R10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline body weight (g) | 282.0 ± 10.21 | 282.0 ± 9.55 | 281.3 ± 11.75 | 282.0 ± 10.01 |
| Final body weight (g) taken on day 10 | 300.0 ± 8.80 | 268.8 ± 8.73 | 271.2 ± 9.90 | 278.3 ± 10.81 |
| Body weight change (%) | 6.55 ± 1.45 | −4.59 ± 1.49 a | −3.40 ± 1.41 | −1.33 ± 0.97 |
| Total kidney weight (g) | 1.87 ± 0.08 | 1.96 ± 0.06 | 1.85 ± 0.05 | 1.67 ± 0.06 b |
| Relative kidney weight (%) | 0.62 ± 0.02 | 0.73 ± 0.02 a | 0.68 ± 0.02 | 0.60 ± 0.01 b |
| Water intake (mL) | 21.83 ± 0.79 | 46.50 ± 1.73 a | 40.67 ± 3.73 | 39.50 ± 2.08 |
| Urine output (mL) | 6.00 ± 0.73 | 41.67 ±1.05 a | 36.83 ± 2.71 | 33.33 ± 3.29 b |
| Urine osmolality (mOsm/Kg) | 2063.7 ± 179.9 | 510 ± 84.9 a | 789.3 ± 178.6 | 942.3 ± 70.1 b |
| CP + R10 | CP + R3 | CP | Control | Parameters/ Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12.12 ± 1.36 b | 19.53 ± 3.06 | 20.06 ± 2.39 a | 3.58 ± 0.46 | Urea (mmol/L) |
| 85.3 ± 8.1 b | 116.9 ± 19.6 b | 127.6 ± 11.4 a | 23.2 ± 0.7 | Creatinine (μmol/L) |
| 24.53 ± 2.52 | 23.78 ± 4.04 b | 31.22 ± 2.27 a | 17.35 ± 1.43 | Uric acid (μmol/L) |
| 77.65 ± 3.00 b | 91.32 ± 7.45 b | 125.23 ± 4.56 a | 34.32 ± 3.26 | NGAL (ng/mL) |
| Assessment/Treatment | Acute Tubular Necrosis | Fibrosis Index | |
|---|---|---|---|
| % | Lesion Score | % | |
| Control | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0 | 5.1 ± 0.17 |
| CP | 27.8 ± 2.38 a | 3 | 12.05 ± 0.29 a |
| CP + R3 | 19.4 ± 3.37 b | 2 | 9.24 ± 0.27 b |
| CP + R10 | 7.2 ± 1.8 b | 1 | 8.07 ± 0.21 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Suleimani, Y.M.; Nomeir, Y.; Al Maskari, R.; Ali, H.; Manoj, P.; Abdelrahman, A.M. Riociguat Alleviates Cisplatin-Caused Kidney Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Biology 2025, 14, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101346
Al Suleimani YM, Nomeir Y, Al Maskari R, Ali H, Manoj P, Abdelrahman AM. Riociguat Alleviates Cisplatin-Caused Kidney Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Biology. 2025; 14(10):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101346
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Suleimani, Yousuf M., Yousra Nomeir, Raya Al Maskari, Haytham Ali, Priyadarsini Manoj, and Aly M. Abdelrahman. 2025. "Riociguat Alleviates Cisplatin-Caused Kidney Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation" Biology 14, no. 10: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101346
APA StyleAl Suleimani, Y. M., Nomeir, Y., Al Maskari, R., Ali, H., Manoj, P., & Abdelrahman, A. M. (2025). Riociguat Alleviates Cisplatin-Caused Kidney Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Biology, 14(10), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101346







