Small Extracellular Vesicles with a High Sphingomyelin Content Isolated from Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice Inhibits Calcium Mobilization and Augments Amiloride-Sensitive Epithelial Sodium Channel Activity
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Animal Studies
2.3. uEV Isolation
2.4. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis of uEVs
2.6. Patch Clamping
2.7. Transient Transfection of siRNA
2.8. SDS PAGE and Western Blotting
2.9. Transepithelial Measurements
2.10. Microscopy
2.11. Measurement of Sphingomyelins
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Increased Release of Small uEVs in Salt-Loaded Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice
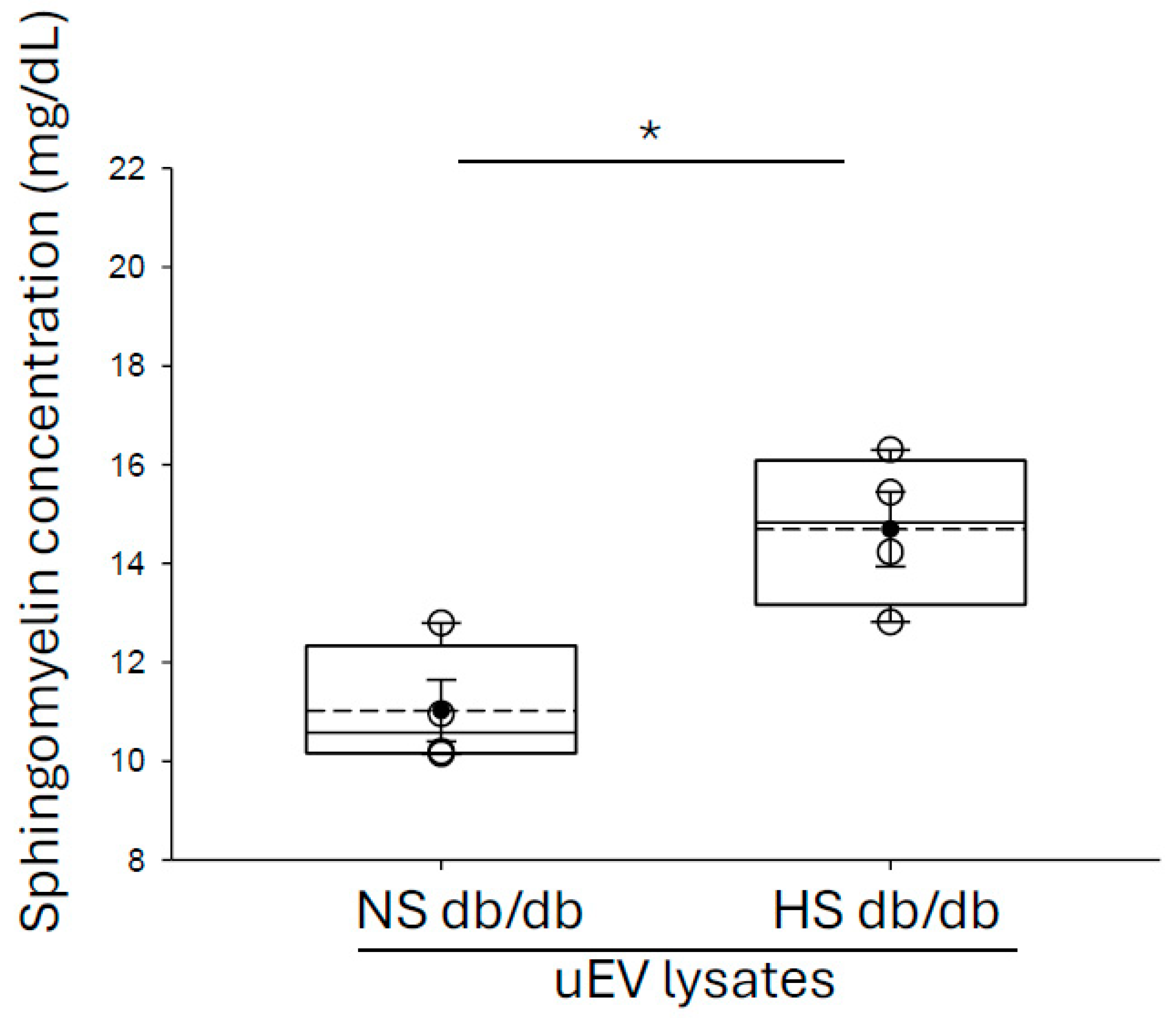
3.2. Enrichment of Sphingomyelins in Small uEVs from Salt-Loaded Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice Compared to Diabetic db/db Mice
3.3. Increased Sphingomyelins Content in Small uEVs from Salt-Loaded Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice Inhibit Calcium Mobilization in mpkCCD Cells
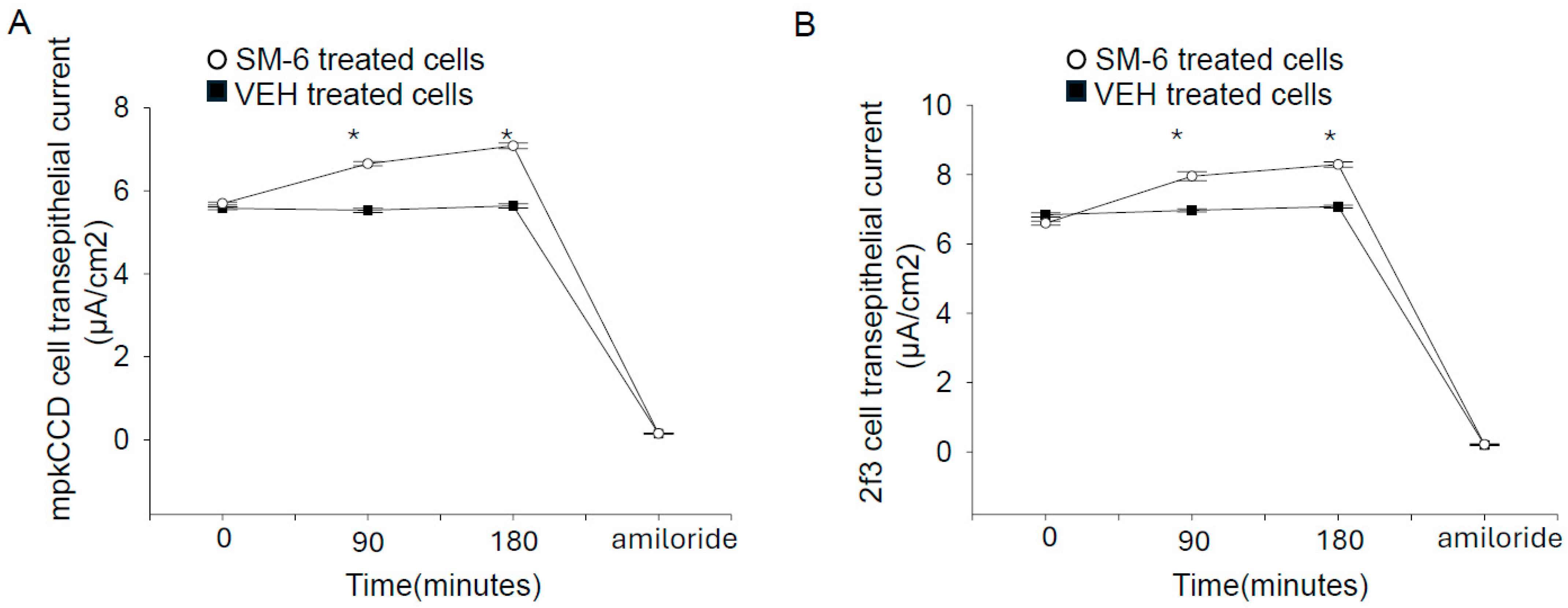
3.4. Exogenous Sphingomyelin Augments Amiloride-Sensitive Transepithelial Current in Mouse mpkCCD Cells and in Xenopus 2f3 Cells
3.5. ENaC Protein Expression Is Comparable in mpkCCD Cells Treated with uEVs from Salt-Loaded and Non-Salt Loaded db/db Mice
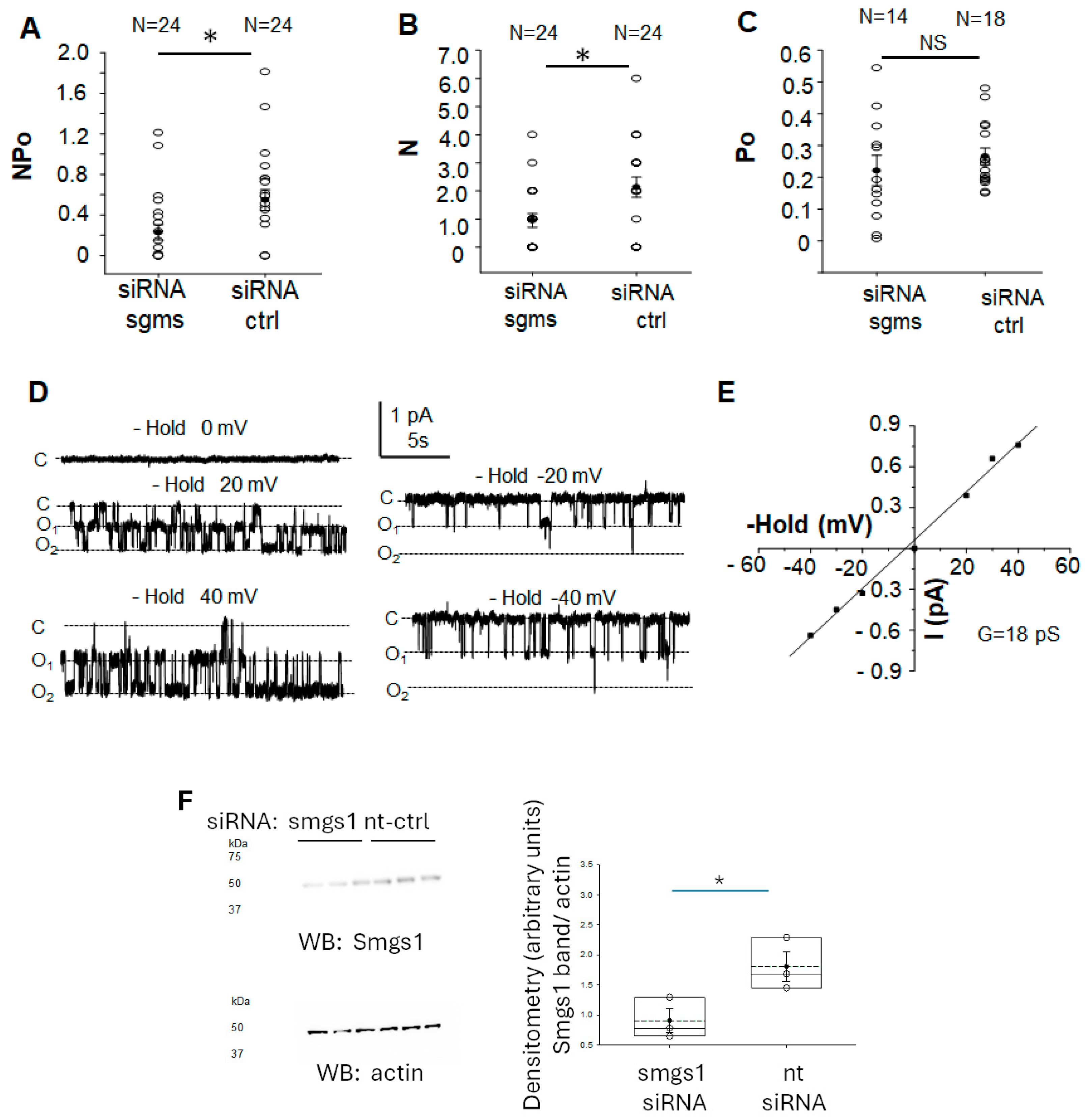
3.6. siRNA Mediated Knockdown of Sphingomyelin Synthase 1 and 2 Attenuates ENaC Activity in mpkCCD Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konstas, A.A.; Korbmacher, C. The gamma-subunit of ENaC is more important for channel surface expression than the beta-subunit. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2003, 284, C447–C456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yue, G.; Malik, B.; Yue, G.; Eaton, D.C. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) stimulates epithelial sodium channel activity in A6 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11965–11969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, M.N.; Liu, L.; Liang, Y.Y.; Al-Khalili, O.; Vandewalle, A.; Saxena, S.; Eaton, D.C.; Ma, H.P. Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate mediates aldosterone stimulation of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) and interacts with gamma-ENaC. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40885–40891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, A.A.; Bao, H.F.; Alli, A.A.; Aldrugh, Y.; Song, J.Z.; Ma, H.P.; Yu, L.; Al-Khalili, O.; Eaton, D.C. Phosphatidylinositol phosphate-dependent regulation of Xenopus ENaC by MARCKS protein. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2012, 303, F800–F811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, R.; Ogawa, K.; Matsumoto, S.I.; Satou, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Sakamoto, J.; Nakahata, T.; Okamoto, R.; Kamaura, M.; Kawamoto, T. Discovery and characterization of selective human sphingomyelin synthase 2 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hailemariam, T.K.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Duckworth, D.C.; Peake, D.A.; Zhang, Y.; Kuo, M.S.; Cao, G.; Jiang, X.C. Inhibition of sphingomyelin synthase (SMS) affects intracellular sphingomyelin accumulation and plasma membrane lipid organization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1771, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulli, I.; Asghar, M.Y.; Kemppainen, K.; Tornquist, K. Sphingolipid-mediated calcium signaling and its pathological effects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, A.A.; Bao, H.F.; Liu, B.C.; Yu, L.; Aldrugh, S.; Montgomery, D.S.; Ma, H.P.; Eaton, D.C. Calmodulin and CaMKII modulate ENaC activity by regulating the association of MARCKS and the cytoskeleton with the apical membrane. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2015, 309, F456–F463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, W.C.; Bala, N.; Arekar, T.; Malik, Z.; Chacko, K.M.; Lewis, R.L.; Denslow, N.D.; Scindia, Y.; Alli, A.A. Enrichment of Bioactive Lipids in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles and Evidence of Apoptosis in Kidneys of Hypertensive Diabetic Cathepsin B Knockout Mice after Streptozotocin Treatment. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Verdera, H.; Gitz-Francois, J.J.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Vader, P. Cellular uptake of extracellular vesicles is mediated by clathrin-independent endocytosis and macropinocytosis. J. Control Release 2017, 266, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jella, K.K.; Yu, L.; Yue, Q.; Friedman, D.; Duke, B.J.; Alli, A.A. Exosomal GAPDH from Proximal Tubule Cells Regulate ENaC Activity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekkucuksen, N.T.; Liu, L.P.; Aly, R.; Shoemaker, L.R.; Alli, A.A. Extracellular vesicles from focal segmental glomerulosclerosis pediatric patients induce STAT3 activation and mesangial cell proliferation. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, M.Z.; Yu, L.; Liu, L.P.; Chacko, K.M.; Denslow, N.D.; LaDisa, J.F., Jr.; Alli, A.A. Increased endothelial sodium channel activity by extracellular vesicles in human aortic endothelial cells: Putative role of MLP1 and bioactive lipids. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2021, 321, C535–C548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongrac Barlovic, D.; Harjutsalo, V.; Sandholm, N.; Forsblom, C.; Groop, P.H.; FinnDiane Study, G. Sphingomyelin and progression of renal and coronary heart disease in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, S.; Bruschi, M.; Deiana, M.; Petretto, A.; Lombardi, G.; Verlato, A.; Elia, R.; Candiano, G.; Malerba, G.; Gambaro, G.; et al. Sphingomyelin and Medullary Sponge Kidney Disease: A Biological Link Identified by Omics Approach. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 671798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, A.; Ma, C.; Xu, Y.; Ye, T.; Su, W.; Zhou, P.; Gao, W.Q.; Li, L.; et al. SETD2 deficiency accelerates sphingomyelin accumulation and promotes the development of renal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Hsu, C.C.; Hamm, G.; Darshi, M.; Diamond-Stanic, M.; Decleves, A.E.; Slater, L.; Pennathur, S.; Stauber, J.; Dorrestein, P.C.; et al. Mass Spectrometry Imaging Reveals Elevated Glomerular ATP/AMP in Diabetes/obesity and Identifies Sphingomyelin as a Possible Mediator. EBioMedicine 2016, 7, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo, C.I.; Liu, L.P.; Bala, N.; Morales, A.G.; Gholam, M.F.; Abchee, J.C.; Elmoujahid, N.; Elshikha, A.S.; Avdiaj, R.; Searcy, L.A.; et al. Human Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Attenuates ENaC and MARCKS and Lowers Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice. Biomolecules 2022, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senador, D.; Kanakamedala, K.; Irigoyen, M.C.; Morris, M.; Elased, K.M. Cardiovascular and autonomic phenotype of db/db diabetic mice. Exp. Physiol. 2009, 94, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, O.I.; Karkischenko, N.N.; Baranova, O.V.; Galahova, T.V.; Semenov, X.X.; Beskova, T.B.; Stepanova, E.A.; Zakir’yanov, A.R.; Onischenko, N.A. Mutant C57Bl/Kslepr(db/+) mice as a genetic model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 144, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scindia, Y.M.; Gholam, M.F.; Waleed, A.; Liu, L.P.; Chacko, K.M.; Desai, D.; Lopez, J.P.; Malik, Z.; Schramm, W.C.; Morales, A.G.; et al. Metformin Alleviates Diabetes-Associated Hypertension by Attenuating the Renal Epithelial Sodium Channel. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholam, M.F.; Liu, L.P.; Searcy, L.A.; Denslow, N.D.; Alli, A.A. Dapagliflozin Treatment Augments Bioactive Phosphatidylethanolamine Concentrations in Kidney Cortex Membrane Fractions of Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice and Alters the Density of Lipid Rafts in Mouse Proximal Tubule Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorrance, A.M.; Graham, D.; Webb, R.C.; Fraser, R.; Dominiczak, A. Increased membrane sphingomyelin and arachidonic acid in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zager, R.A.; Burkhart, K.M.; Johnson, A. Sphingomyelinase and membrane sphingomyelin content: Determinants ofProximal tubule cell susceptibility to injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, D.S.; Yu, L.; Ghazi, Z.M.; Thai, T.L.; Al-Khalili, O.; Ma, H.P.; Eaton, D.C.; Alli, A.A. ENaC activity is regulated by calpain-2 proteolysis of MARCKS proteins. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2017, 313, C42–C53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, J.H.; Thelen, M.; Rosen, A.; Janmey, P.A.; Nairn, A.C.; Aderem, A. MARCKS is an actin filament crosslinking protein regulated by protein kinase C and calcium-calmodulin. Nature 1992, 356, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, N.; Catarino, S.; Cristovao, B.; Rodrigues, L.; Carvalho, F.A.; Sarmento, M.J.; Zuzarte, M.; Almeida, J.; Ribeiro-Rodrigues, T.; Correia-Rodrigues, A.; et al. Connexin43 promotes exocytosis of damaged lysosomes through actin remodelling. EMBO J. 2024, 43, 3627–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, M.E.; Dykens, J.A.; Wright, C.D. Regulation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte membrane fluidity: Effect of cytoskeletal modification. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1994, 56, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.D.; Jella, K.K.; Ragheb, R.R.T.; Denslow, N.D.; Alli, A.A. Lipidomic and proteomic analysis of exosomes from mouse cortical collecting duct cells. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 5399–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Pillot, T.; Chambaz, J.; Drouet, B. Determination of plasma membrane fluidity with a fluorescent analogue of sphingomyelin by FRAP measurement using a standard confocal microscope. Brain Res. Brain Res. Protoc. 2003, 11, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorska, M.; Baranczuk, E.; Dobrzyn, A. Secretory Zn2+-dependent sphingomyelinase activity in the serum of patients with type 2 diabetes is elevated. Horm. Metab. Res. 2003, 35, 506–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kady, N.; Yan, Y.; Salazar, T.; Wang, Q.; Chakravarthy, H.; Huang, C.; Beli, E.; Navitskaya, S.; Grant, M.; Busik, J. Increase in acid sphingomyelinase level in human retinal endothelial cells and CD34(+) circulating angiogenic cells isolated from diabetic individuals is associated with dysfunctional retinal vasculature and vascular repair process in diabetes. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2017, 11, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Huang, S.; Duan, W.; Liu, Q.; Lei, M. Inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase activity ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in db/db mice. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20182144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antibody | Size (kDa) | Company | Catalog Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-CD9 | 25 kDa | abcam (Waltham, MA, USA) | ab223052 |
| Anti-Caveolin-1 | 21 kDa | Cell Signaling Tech (Danvers, MA, USA) | 3267 |
| Anti-syntenin | 32 kDa | abcam | ab19903 |
| Anti-flotillin | 47 kDa | abcam | ab41927 |
| Anti-sphingomyeiln synthase | 49 kDa | Proteintech (Rosemont, IL, USA) | 19050-1-AP |
| Anti-Beta actin HRP | 42 kDa | Sigma | A3854 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramsay, H.; Yu, L.; Alousi, F.F.; Alli, A.A. Small Extracellular Vesicles with a High Sphingomyelin Content Isolated from Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice Inhibits Calcium Mobilization and Augments Amiloride-Sensitive Epithelial Sodium Channel Activity. Biology 2025, 14, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030252
Ramsay H, Yu L, Alousi FF, Alli AA. Small Extracellular Vesicles with a High Sphingomyelin Content Isolated from Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice Inhibits Calcium Mobilization and Augments Amiloride-Sensitive Epithelial Sodium Channel Activity. Biology. 2025; 14(3):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030252
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamsay, Hunter, Ling Yu, Faisal F. Alousi, and Abdel A. Alli. 2025. "Small Extracellular Vesicles with a High Sphingomyelin Content Isolated from Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice Inhibits Calcium Mobilization and Augments Amiloride-Sensitive Epithelial Sodium Channel Activity" Biology 14, no. 3: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030252
APA StyleRamsay, H., Yu, L., Alousi, F. F., & Alli, A. A. (2025). Small Extracellular Vesicles with a High Sphingomyelin Content Isolated from Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice Inhibits Calcium Mobilization and Augments Amiloride-Sensitive Epithelial Sodium Channel Activity. Biology, 14(3), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030252







