African Cultivated, Wild and Weedy Rice (Oryza spp.): Anticipating Further Genomic Studies
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of African Cultivated and Wild Rice
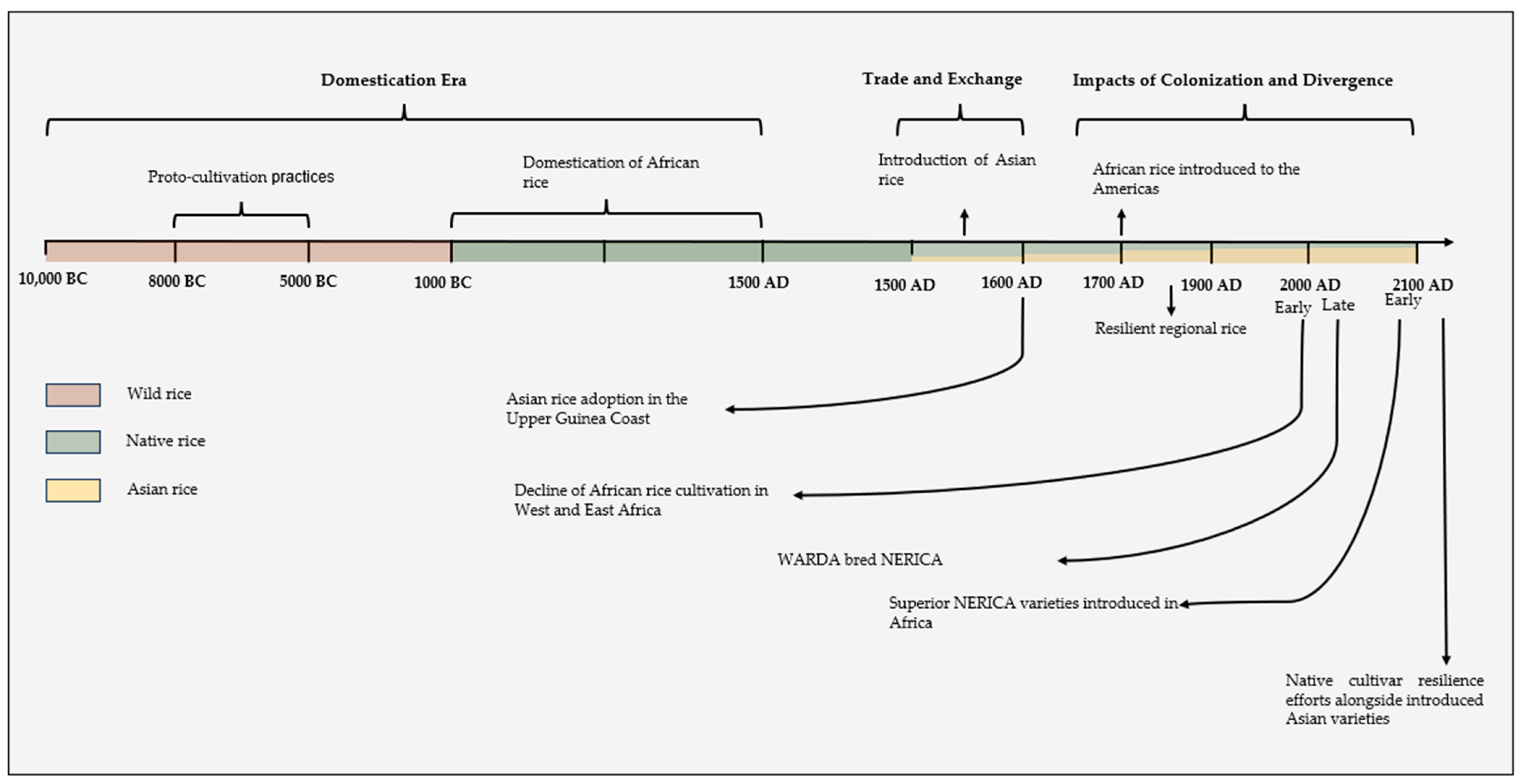
2.1. The Introduction of Asian Rice (O. sativa)
2.2. African Cultivated and Wild Rice
| Country | Total Production (Thousand ton) | Harvested Area (Thousand ha) | Average Yield (t/ha) | Rainfed Rice (as % of Total Rice Area) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nigeria | 8080 | 5409 | 1.50 | 99 |
| Tanzania | 3220 | 1162 | 2.77 | 93 |
| Mali | 2972 | 879 | 3.39 | 37 |
| Ghana | 815 | 285 | 2.85 | 82 |
| Burkina Faso | 367 | 171 | 2.14 | 92 |
| Uganda | 212 | 77 | 2.76 | 42 |
| Ethiopia | 164 | 57 | 2.87 | 99 |
| Kenya | 127 | 28 | 4.66 | <1 |
| Niger | 124 | 28 | 4.37 | 100 |
| Zambia | 34 | 26 | 1.31 | 62 |
2.3. Interspecific Hybridization: The New Rice for Africa (NERICA) Varieties
3. African Weedy Rice
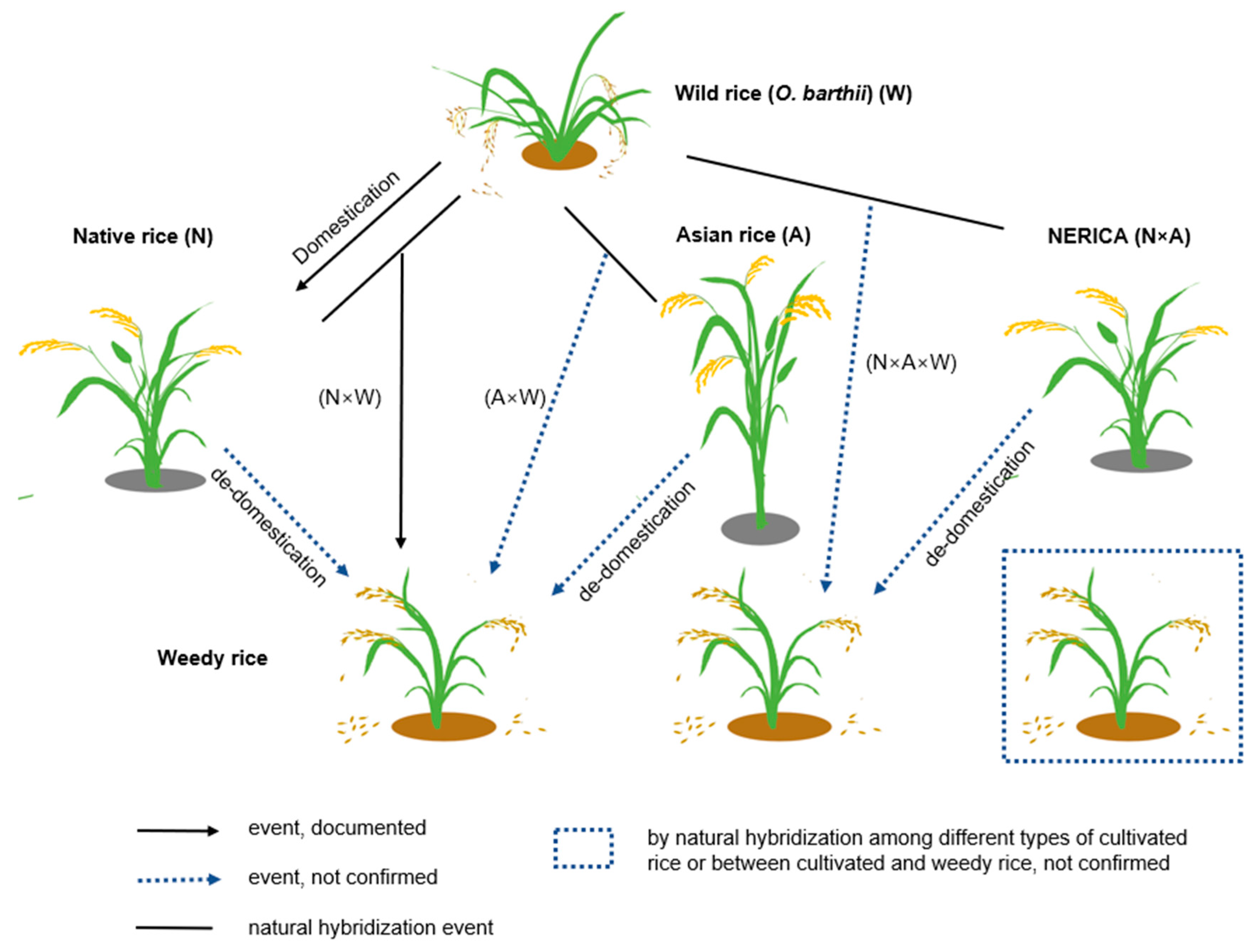
3.1. Weedy Rice: Origins and Traits
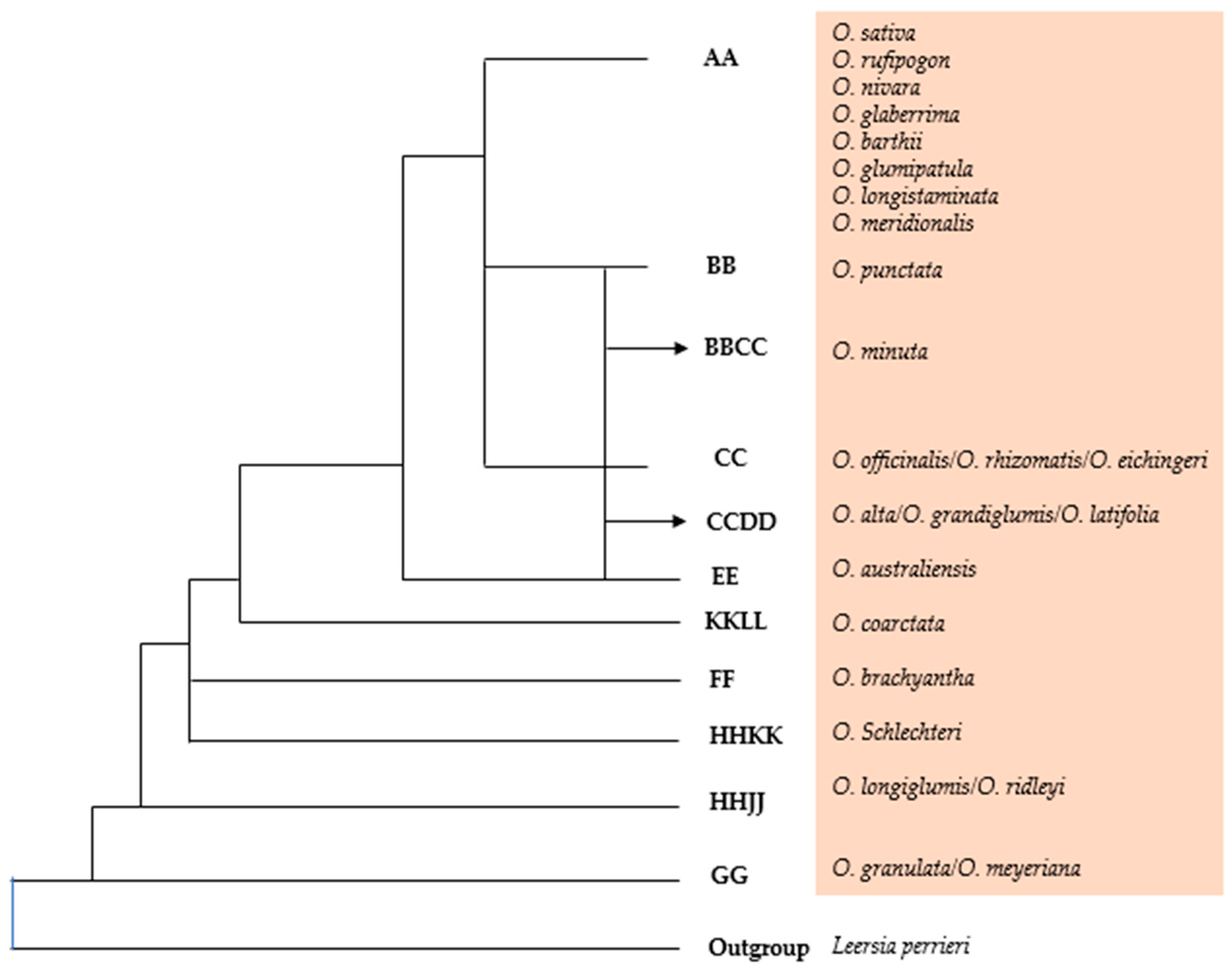
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationships: Connecting Weedy, Cultivated, and Wild Rice
3.3. Genetics and Adaptation of African Weedy Rice
3.4. Genomic Studies on African Native Rice
4. Challenges and Future Directions
4.1. Mystery of African Weedy Rice
4.2. Africa Needs More Genomic Studies on Local Rice
4.3. Challenges of Genomic Studies in Africa
5. Ethical and Social Implications of Rice Genomics in Africa
5.1. Current State of Rice Genomics in Africa
5.2. Ethical and Social Considerations
5.3. Responsible Research and Innovation Framework
5.4. Strategies for Implementing RRI in African Rice Genomics
5.5. Challenges and Opportunities
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Futakuchi, K.; Senthilkumar, K.; Arouna, A.; Vandamme, E.; Diagne, M.; Zhao, D.; Manneh, B.; Saito, K. History and progress in genetic improvement for enhancing rice yield in sub-Saharan Africa. Field Crops Res. 2021, 267, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.; Hegde, V. Assessment of global rice production and export opportunity for economic development in Ethiopia. Int. J. Res. 2013, 2, 2319–7064. [Google Scholar]
- Tadesse, Z.; Tadesse, T.; Habtamu, A. Effect of seed rate and row spacing on yield and yield components of rain fed lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.) variety. Int. J. Res. Stud. Agric. Sci. 2019, 5, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Stallworth, S.; Tseng, T.M. Weedy Rice: Competitive Ability, Evolution, and Diversity; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Qiu, J.; Sun, J.; Song, B.K.; Olsen, K.M.; Fan, L. Weedy rice, a hidden gold mine in the paddy field. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, S.A.; Ricke, D.; Lan, T.H.; Presting, G.; Wang, R.; Dunn, M.; Glazebrook, J.; Sessions, A.; Oeller, P.; Varma, H.; et al. A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science 2002, 296, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Wong, G.K.; Li, S.; Liu, B.; Deng, Y.; Dai, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science 2002, 296, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Mauleon, R.; Hu, Z.; Chebotarov, D.; Tai, S.; Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Zheng, T.; Fuentes, R.R.; Zhang, F.; et al. Genomic variation in 3,010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice. Nature 2018, 557, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, A.; Tian, Q.; Zhan, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, T.; et al. Pan-genome analysis highlights the extent of genomic variation in cultivated and wild rice. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wu, Z.; Sun, C.; Li, M.; Lu, J.; Fu, B.; Shi, J.; Xu, J.; Ruan, J.; et al. Novel sequences, structural variations and gene presence variations of Asian cultivated rice. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutaker, R.M.; Groen, S.C.; Bellis, E.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Pires, I.S.; Bocinsky, R.K.; Slayton, E.R.; Wilkins, O.; Castillo, C.C.; Negrão, S.; et al. Genomic history and ecology of the geographic spread of rice. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kurata, N.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, A.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, K.; Lu, H.; Li, W.; et al. A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice. Nature 2012, 490, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chebotarov, D.; Kudrna, D.; Llaca, V.; Lee, S.; Rajasekar, S.; Mohammed, N.; Al-Bader, N.; Sobel-Sorenson, C.; Parakkal, P.; et al. A platinum standard pan-genome resource that represents the population structure of Asian rice. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civáň, P.; Craig, H.; Cox, C.J.; Brown, T.A. Three geographically separate domestications of Asian rice. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 15164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, L.; Ye, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Fu, F.; Wang, Y.; Qian, F.; et al. Genomic variation associated with local adaptation of weedy rice during de-domestication. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.F.; Li, Y.L.; Jia, Y.; Caicedo, A.L.; Olsen, K.M. Signatures of adaptation in the weedy rice genome. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Jia, L.; Wu, D.; Weng, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, M.; Mao, L.; Jiang, B.; Ye, C.; et al. Diverse genetic mechanisms underlie worldwide convergent rice feralization. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Han, Z.; Qiao, W.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; Ge, J.; Lou, D.; Fan, W.; et al. High-quality genomes and high-density genetic map facilitate the identification of genes from a weedy rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 775051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portères, R. Berceaux agricoles primaires sur le continent Africain. J. Afr. Hist. 1962, 3, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, M.; Boivin, N.; Crowther, A. Eastern Africa and the early Indian Ocean: Understanding mobility in a globalising world. J. Egypt Hist. 2021, 13, 380–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, E. Asian Rice in Africa: Plant Genetics and Crop History; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, O.F. African rice (Oryza glaberrima): History and future potential. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16360–16365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beye, A.; Billot, C.; Ronfort, J.; McNally, K.L.; Diouf, D.; Glaszmann, J.C. Traces of introgression from cAus into tropical Japonica observed in African upland rice varieties. Rice 2023, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezançon, G. Riziculture traditionnelle en Afrique de l’Ouest: Valorisation et conservation des ressources génétiques. J. Agric. Tradit. Bot. Appliquée 1995, 37, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Zaidem, M.; Gutaker, R.; Dorph, K.; Singh, R.K.; Purugganan, M.D. The complex geography of domestication of the African rice Oryza glaberrima. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Andel, T. African Rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud.): Lost crop of the enslaved Africans discovered in Suriname. Econ. Bot. 2010, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, C. Breeding and dissemination efforts of “NERICA” (1) breeding of upland rice. J. Jpn. Trop. Agr. 2007, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britwum, K.; Owusu, E.S.; Demont, M. Confronting genetic gains with markets: Retrospective lessons from new rice for Africa (NERICA) in Uganda. Outlook Agric. 2020, 49, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubry, P.; Tranchant-Dubreuil, C.; Thuillet, A.C.; Monat, C.; Ndjiondjop, M.N.; Labadie, K.; Cruaud, C.; Engelen, S.; Scarcelli, N.; Rhoné, B.; et al. The rise and fall of African rice cultivation revealed by analysis of 246 new genomes. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghesquière, A.; Séquier, J.; Second, G.; Lorieux, M. First steps towards a rational use of African rice, Oryza glaberrima, in rice breeding through a “contig line” concept. Euphytica 1997, 96, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, Y.; Haberer, G.; Marri, P.R.; Fan, C.; Goicoechea, J.L.; Zuccolo, A.; Song, X.; Kudrna, D.; Ammiraju, J.S.; et al. The genome sequence of African rice (Oryza glaberrima) and evidence for independent domestication. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeken, B. African Rice (Oryza glaberrima) Cultivation in the Togo Hills: Ecological and Socio-Cultural Cues in Farmer Seed Selection and Development. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University & Research, Centre for Crop Systems Analysis, Wageningen School of Social Sciences (WASS), Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad, K.B.; Singh, N.; Kaur, P.; Rani, S.; Babu, H.P.; Singh, K. Deployment of wild relatives for genetic improvement in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Breed. 2021, 40, 23–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.A.; Morishima, H.; Kadowaki, K. Diversity in the Oryza genus. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.A. The Wild Relatives of Rice: A Genetic Resources Handbook; International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- You, L.; Wood, S.; Wood-Sichra, U.; Wu, W. Generating global crop distribution maps: From census to grid. Agric. Syst. 2014, 127, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedger, M.J.; Roma-Burgos, N.; Olsen, K.M. Genomic revolution of US weedy rice in response to 21st century agricultural technologies. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; He, W.; Nassirou, T.Y.; Zhou, W.; Yin, Y.; Dong, X.; Rao, Q.; Shi, H.; Zhao, W.; Efisue, A.; et al. Genetic diversity and phenotypic variation in an introgression line population derived from an interspecific cross between Oryza glaberrima and Oryza sativa. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedze, Y.; He, W.; Samoura, A.; Huang, F.; Nassirou, T.; Efisue, A.; Zhang, S.; Xie, G.; Jin, A. Genomic composition and yield heterosis of the partial interspecific hybrid rice between Oryza sativa L. and Oryza glaberrima Steud. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 154, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndjiondjop, M.N.; Semagn, K.; Zhang, J.; Gouda, A.C.; Kpeki, S.B.; Goungoulou, A.; Wambugu, P.; Dramé, K.N.; Bimpong, I.K.; Zhao, D. Development of species diagnostic SNP markers for quality control genotyping in four rice (Oryza L.) species. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwakyusa, L.; Dixit, S.; Herzog, M.; Heredia, M.C.; Madege, R.R.; Kilasi, N.L. Flood-tolerant rice for enhanced production and livelihood of smallholder farmers of Africa. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1244460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRRI. Adhunik Dhaner Chash (In Bengali). Bangladesh Rice Research Institute, Gazipur. 2020, Volume 1701, p. 12.e390. Available online: http://knowledgebank-brri.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/ADC.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2024).
- Nadir, S.; Xiong, H.B.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Xu, H.Y.; Li, J.; Dongchen, W.; Henry, D.; Guo, X.Q.; Khan, S.; et al. Weedy rice in sustainable rice production. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma-Burgos, N.; Sudo, M.; Olsen, K.; Werle, I.; Song, B.K. Weedy Rice (Oryza spp.): What’s In a Name? Weed Sci. 2021, 69, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellstrand, N.C.; Heredia, S.M.; Leak-Garcia, J.A.; Heraty, J.M.; Burger, J.C.; Yao, L.; Nohzadeh-Malakshah, S.; Ridley, C.E. Crops gone wild: Evolution of weeds and invasives from domesticated ancestors. Evol. Appl. 2010, 3, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Patra, B.; Munda, S.; Mohapatra, T. Weedy rice: Problems and its management. Indian J. Weed 2014, 46, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Orjuela, J.; Sabot, F.; Chéron, S.; Vigouroux, Y.; Adam, H.; Chrestin, H.; Sanni, K.; Lorieux, M.; Ghesquière, A. An extensive analysis of the African rice genetic diversity through a global genotyping. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 2211–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuijten, E.; van Treuren, R.; Struik, P.C.; Mokuwa, A.; Okry, F.; Teeken, B.; Richards, P. Evidence for the emergence of new rice types of interspecific hybrid origin in West African farmers’ fields. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Peng, Y.; Qiao, J.; Henry, R.; Qian, Q. Wild rice: Unlocking the future of rice breeding. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanapeckas, K.L.; Vigueira, C.C.; Ortiz, A.; Gettler, K.A.; Burgos, N.R.; Fischer, A.J.; Lawton-Rauh, A.L. Escape to ferality: The endoferal origin of weedy rice from crop rice through de-domestication. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Sharma, G.; Stallworth, S.; Redona, E.D.; Tseng, T.M. Exploring the genetic diversity among weedy rice accessions differing in herbicide tolerance and allelopathic potential. Diversity 2022, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jia, Y.; Jia, M.; Gealy, D.R.; Olsen, K.M.; Caicedo, A.L. Molecular evolution of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta in invasive weedy rice in the USA. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurber, C.S.; Hepler, P.K.; Caicedo, A.L. Timing is everything: Early degradation of abscission layer is associated with increased seed shattering in U.S. weedy rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S. Evaluation of Herbicide Tolerance and Interference Potential among Weedy Rice Germplasm; Mississippi State University: Mississippi State, MS, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Diallo, S. Problème posé par le riz rouge en riziculture au Sénégal. In Global Workshop on Red Rice Control; FAO Plant Production and Protection Division: Rome, Italy, 1999; pp. 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero, A. Weedy Rice, Biological Features, and Control; FAO Plant Production and Protection Division: Rome, Italy, 2003; pp. 89–107. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, J.C.; Yu, Y.; Copetti, D.; Zwickl, D.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Chougule, K.; Gao, D.; Iwata, A.; Goicoechea, J.L.; et al. Genomes of 13 domesticated and wild rice relatives highlight genetic conservation, turnover and innovation across the genus Oryza. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambugu, P.W.; Henry, R.J. Oryza barthii a. Chev. In The wild Oryza Genomes; Mondal, T.K., Henry, R.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizerland, 2018; pp. 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wambugu, P.W.; Ndjiondjop, M.-N.; Henry, R. Advances in molecular genetics and genomics of African Rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud). Plants 2019, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubry, P.; Pidon, H.; Ta, K.N.; Tranchant-Dubreuil, C.; Thuillet, A.C.; Holzinger, M.; Adam, H.; Kam, H.; Chrestin, H.; Ghesquière, A.; et al. Genome wide association study pinpoints key agronomic QTLs in African rice Oryza glaberrima. Rice 2020, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veltman, M.A.; Flowers, J.M.; van Andel, T.R.; Schranz, M.E. Origins and geographic diversification of African rice (Oryza glaberrima). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0203508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.; Huang, X.; Tian, Z.; Wing, R.A.; Han, B. The genomics of Oryza species provides insights into rice domestication and heterosis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 639–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Han, B. Comparative population genomics reveals strong divergence and infrequent introgression between Asian and African rice. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 958–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wei, H.; Yu, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Q.; Shang, L.; Guo, L. Compared analysis with a high-quality genome of weedy rice reveals the evolutionary game of de-domestication. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1065449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roffler, S.; Wicker, T. Genome-wide comparison of Asian and African rice reveals high recent activity of DNA transposons. Mob. DNA 2015, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Zheng, X.M.; Ge, S. Genetic diversity and domestication history of African rice (Oryza glaberrima) as inferred from multiple gene sequences. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 123, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabholz, B.; Sarah, G.; Sabot, F.; Ruiz, M.; Adam, H.; Nidelet, S.; Ghesquière, A.; Santoni, S.; David, J.; Glémin, S. Transcriptome population genomics reveals severe bottleneck and domestication cost in the African rice (Oryza glaberrima). Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 2210–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndjiondjop, M.N.; Semagn, K.; Gouda, A.C.; Kpeki, S.B.; Dro, T.D.; Sow, M.; Goungoulou, A.; Sie, M.; Perrier, X.; Ghesquiere, A.; et al. Genetic variation and population structure of Oryza glaberrima and development of a mini-core collection using DArTseq. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semon, M.; Nielsen, R.; Jones, M.P.; McCouch, S.R. The population structure of African cultivated rice Oryza glaberrima (Steud.): Evidence for elevated levels of linkage disequilibrium caused by admixture with O. sativa and ecological adaptation. Genetics 2005, 169, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambugu, P.W.; Ndjiondjop, M.N.; Henry, R. Genetics and genomics of African rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud) domestication. Rice 2021, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajiya-Kanegae, H.; Ohyanagi, H.; Ebata, T.; Tanizawa, Y.; Onogi, A.; Sawada, Y.; Hirai, M.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Han, B.; Toyoda, A.; et al. OryzaGenome2.1: Database of diverse genotypes in wild Oryza species. Rice 2021, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q.J.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, C.; Liu, Y.L.; Xia, E.H.; Jiang, J.J.; Shi, C.; et al. Improved hybrid de novo genome assembly and annotation of African wild rice, Oryza longistaminata, from Illumina and PacBio sequencing reads. Plant Genome 2020, 13, e20001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, M.; Huang, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, G.; Zhang, J.; Kassahun, T.; Teklehaimanot, H.; Hu, F. Genetic relatedness among Ethiopian Oryza longistaminata populations and other AA genome Oryza species. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 91, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.E.; Oka, H.I. The genetic basis of crossing barriers between Oryza perennis Subsp. barthii and its related taxa. Evolution 1970, 24, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Ge, S.; Lu, B.; Hong, D. Identification of genome constitution of Oryza malampuzhaensis, O. minuta, and O. punctata by multicolor genomic in situ hybridization. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambugu, P.W.; Brozynska, M.; Furtado, A.; Waters, D.L.; Henry, R.J. Relationships of wild and domesticated rices (Oryza AA genome species) based upon whole chloroplast genome sequences. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Lu, B.R.; Ge, S. Identification of genomic constitutions of Oryza species with the B and C genomes by the PCR-RFLP method. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2005, 52, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.L.; Zou, X.H.; Zhang, F.M.; Yang, Z.; Ge, S. Phylogeny and species delimitation of the c-genome diploid species in Oryza. J. Syst. Evol. 2011, 49, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuscher, S.; Furuta, T.; Bessho-Uehara, K.; Cosi, M.; Jena, K.K.; Toyoda, A.; Fujiyama, A.; Kurata, N.; Ashikari, M. Assembling the genome of the African wild rice Oryza longistaminata by exploiting synteny in closely related Oryza species. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, T.; Vaughan, D.A.; Kadowaki, K. Phylogenetic analysis of Oryza species, based on simple sequence repeats and their flanking nucleotide sequences from the mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 110, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Fu, B.; Li, L.; Xie, M.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Cai, J.; Wan, W.; et al. Genome and comparative transcriptomics of African wild rice Oryza longistaminata provide insights into molecular mechanism of rhizomatousness and self-incompatibility. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1683–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Lu, B.; Li, Z.; Tong, J.; Kong, J.; Yao, W.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y. Phylogenetic analysis of AA-genome Oryza species (Poaceae) based on chloroplast, mitochondrial, and nuclear DNA sequences. Biochem. Genet. 2007, 45, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Fan, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, X.; Sun, C.; Tan, L. Whole-genome de novo assemblies reveal extensive structural variations and dynamic organelle-to-nucleus DNA transfers in African and Asian rice. Plant J. 2020, 104, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monat, C.; Pera, B.; Ndjiondjop, M.N.; Sow, M.; Tranchant-Dubreuil, C.; Bastianelli, L.; Ghesquière, A.; Sabot, F. De novo assemblies of three Oryza glaberrima accessions provide first insights about pan-genome of African rices. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, H.; Ikawa, H.; Tanaka, T.; Numa, H.; Minami, H.; Fujisawa, M.; Shibata, M.; Kurita, K.; Kikuta, A.; Hamada, M.; et al. Distinct evolutionary patterns of Oryza glaberrima deciphered by genome sequencing and comparative analysis. Plant J. 2011, 66, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svizzero, S. Weedy rice and the sustainability of alternative establishment methods. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 23, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, M.; Singh, R.; Kumar, B.; Chauhan, B.S. Characterization of functional trait diversity among Indian cultivated and weedy rice populations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, H.; Adam, Y.; Idrissi Azami, A.; Sehli, S.; Nyarko, H.N.; Chaouni, B.; Olasehinde, G.; Isewon, I.; Adebiyi, M.; Ajani, O.; et al. Plant genomics in Africa: Present and prospects. Plant J. 2021, 107, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryee, S.N.D.; Owusu-Adjei, D.; Osei-Amponsah, R.; Skinner, B.; Sowatey, E.; Sargent, C. Sustainable genomic research for food security in Sub-Saharan Africa. Agric. Food Secur. 2021, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, Z.D.; Lee, S.Y.; Faghri, F.; Campbell, R.H.; Zhai, C.; Efron, M.J.; Iyer, R.; Schatz, M.C.; Sinha, S.; Robinson, G.E. Big data: Astronomical or genomical? PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwood, D.; Ranganathan, S. Genome databases and browsers. In Encycl Bioinform Comput Biol: ABC of Bioinformatics; Ranganathan, S., Gribskov, M., Nakai, K., Schönbach, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- FAO: Second Report on the World’s Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/013/i1500e/i1500e.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2013).
- Khoury, C.; Laliberté, B.; Guarino, L. Trends in ex situ conservation of plant genetic resources: A review of global crop and regional conservation strategies. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2010, 57, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambugu, P.W.; Furtado, A.; Waters, D.L.; Nyamongo, D.O.; Henry, R.J. Conservation and utilization of African Oryza genetic resources. Rice 2013, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCouch, S.; Wing, R.A.; Semon, M.; Ramaiah, V.R.V.; Atlin, G.; Sorrells, M.E.; Jannink, J.L. Making Rice Genomics Work for Africa; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2013; pp. 108–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, M.N. Origin of African rice from Asian rice. In Innovation and Partnerships to Realize Africa’s Rice Potential, Proceedings of the Second Africa Rice Congress, Africa Rice Center, Cotonou, Benin, 22–26 March 2010; AfricaRice: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2010; pp. 1.18.1–1.18.13. [Google Scholar]
- Yamano, T.; Arouna, A.; Labarta, R.A.; Huelgas, Z.A.; Mohanty, S. Adoption and impacts of international rice research technologies. Glob. Food Secur. 2016, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilomboleni, H.; Ismail, A. Gene-editing technologies for developing climate resilient rice crops in sub-Saharan Africa: Political priorities and space for responsible innovation. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2023, 11, 00145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pixley, K.; Falck-Zepeda, J.; Paarlberg, R.; Phillips, P.; Slamet-Loedin, I.; Dhugga, K.S.; Campos, H.; Gutterson, N. Genome-edited crops for improved food security of smallholder farmers. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasti, R.A.; Voytas, D.F. Attaining the promise of plant gene editing at scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2004846117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Republic of Nigeria. National Biosafety Guidelines on Gene Editing. 2020. Available online: https://africenter.isaaa.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/From-Our-NewsRoom_2-Nigeria-Releases-National-Guidelines-on-Gene-Editing-Main-website-article.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Republic of Kenya. National Rice Development Strategy-2 (2019–2030). Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock, Fisheries and Cooperatives (MoALF&C), State Department for Crop Development and Agricultural Research. 2020. Available online: https://kilimo.go.ke/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/NRDS-2-2019-2020-14-July.pdf (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Tripathi, L.; Dhugga, K.S.; Ntui, V.O.; Runo, S.; Syombua, E.D.; Muiruri, S.; Wen, Z.; Tripathi, J.N. Genome editing for sustainable agriculture in Africa. Front. Genome Ed. 2022, 4, 876697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komen, J.; Tripathi, L.; Mkoko, B.; Ofosu, D.; Olok, H.; Wangari, D. Biosafety regulatory reviews and leeway to operate: Case studies from sub-Sahara Africa. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paarlberg, R. The trans-Atlantic conflict over “Green” farming. Food Policy 2022, 108, 102229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassoued, R.; Macall, D.M.; Smyth, S.J.; Phillips, P.W.; Hesseln, H. Risk and safety considerations of genome edited crops: Expert opinion. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2019, 1, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro de Wit, M. Democratizing CRISPR? Stories, practices, and politics of science and governance on the agricultural gene editing frontier. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Est, R. Responsible innovation as a source of inspiration for technology assessment, and vice versa: The common challenge of responsibility, representation, issue identification, and orientation. J. Responsib. Innov. 2017, 4, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lente, H.; Swierstra, T.; Joly, P.B. Responsible innovation as a critique of technology assessment. J. Responsib. Innov. 2017, 4, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, C.; Klerkx, L.; Ayre, M.; Rue, B.D. Managing socio-ethical challenges in the development of smart farming: From a fragmented to a comprehensive approach for responsible research and innovation. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2019, 32, 741–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCampbell, M.; Schumann, C.; Klerkx, L. Good intentions in complex realities: Challenges for designing responsibly in digital agriculture in lowincome countries. Sociol. Rural. 2021, 62, 279–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Sheng, Z.; Jalal, R.S.; Tabassum, J.; Ahmed, F.K.; Hu, S.; Shao, G.; Wei, X.; Abd-Elsalam, K.; Hu, P.; et al. CRISPR–Cas technology towards improvement of abiotic stress tolerance in plants. In CRISPR and RNAi Systems: Nanobiotechnology Approaches to Plant Breeding and Protection; Abd-Elsalam, K., Lim, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 755–772. [Google Scholar]
- Ayanoğlu, F.B.; Elçin, A.E.; Elçin, Y.M. Bioethical issues in genome editing by CRISPR-Cas9 technology. Turk. J. Biol. 2020, 44, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wadvalla, B.-A. Advancing biotechnology to solve Africa’s food challenges. Natl. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 904–907. [Google Scholar]
- Abigarl, N.; Angela, S.M.; Sizo, M.; Enetia, D.B. CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in crop breeding for climate change resilience: Implications for smallholder farmers in Africa. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nlend Nkott, A.L.; Temple, L. Societal acceptability conditions of genome editing for upland rice in Madagascar. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 167, 120720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakunuma, K.; de Castro, F.; Jiya, T.; Inigo, E.; Blok, V.; Bryce, V. Reconceptualising responsible research and innovation from a Global South perspective. J. Responsib. Innov. 2021, 8, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beumer, K.; de Roji, S. Inclusive innovation in crop gene editing for smallholder farmers: Status and approaches. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2023, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Methodology | References |
|---|---|---|
| O. longistaminata | Using a hybrid Illumina and PacBio sequencing approach, a high-quality assembly of African wild rice genome was generated, resulting in a 363.5 Mb assembly with long scaffolds that were anchored into 12 pseudo-chromosomes. | [72] |
| O. glaberrima | A total of 163 resequenced O. glaberrima accessions were used for a genome-wide association study utilizing complementary statistical association methods to examine traits such as flowering time, panicle architecture, Rice Yellow Mottle Virus resistance, and climatic adaptation. | [60] |
| O. barthii, O. glaberrima, O. rufipogon, O. nivara | Four Oryza species were sequenced via PacBio and next-generation sequencing, assembled, and compared to identify organelle-to-nucleus DNA transfers, detect structural variations, and analyze the distribution of giant nuclear integrants in various rice populations. | [83] |
| O. glaberrima | Whole-genome resequencing involved analyzing 282 individuals with ~16.5× for both domesticated and wild African rice samples. Estimating genetic diversity, population structure, phylogenetic linkages, and admixture were all included in the analyses of population genetics. | [25] |
| O. glaberrima | Using phylogenetics, geographic modeling, and selective sweep detection, population genetics analysis enabled the whole-genome sequencing of 100 O. glaberrima accessions at ~10× coverage. | [61] |
| O. longistaminata | By utilizing synteny with O. sativa and a high-density linkage map, the genome of O. longistaminata was assembled into chromosomes after being sequenced using SMRT sequencing. A reference genome of high quality was validated using gene annotation and quality assessment. | [79] |
| O. glaberrima | Sequencing 246 genomes covering a wide geographic range across Africa, with ~37× coverage. Population genetics analyses were performed to assess genetic diversity, population structure, linkage disequilibrium, etc. | [29] |
| O. glaberrima, O. longistaminata, O. punctata, O. glumaepatula, O. barthii, etc. | The 13-genome dataset was generated using either long-read or short-read technologies, with robust scaffold support derived from long-insert library reads, including BAC-ends. | [57] |
| O. glaberrima | Whole-genome sequencing of three O. glaberrima accessions (CG14, Tog5680, and IRGC100991) at ~10× coverage, followed by de novo assembly. | [84] |
| O. glaberrima | Analyses of conserved 2179 O. glaberrima accessions using 27,560 DArTseq-based SNPs. Principal component analysis and model-based structural analysis to analyze population structure, a mini-core collection. | [68] |
| O. glaberrima | Genome sequencing and assembly of O. glaberrima accessions. Population structure, genetic diversity, selective sweeps, domestication genes, and evidence of the independent domestication of African rice were analyzed using the genome and SNP data. | [31] |
| O. glaberrima | The genome of O. glaberrima ~220 Mb was generated by shotgun sequencing utilizing subtractive hybridization and methylation filtration for gene enrichment. African and Asian rice were found to have different SSR marker polymorphisms, splice site substitutions, and species-specific genes when compared to O. sativa. | [85] |
| O. glaberrima, O. barthii | Sequencing of 14 unlinked nuclear genes in 20 cultivated and 20 wild rice accessions, with analyses of nucleotide diversity, neutrality, and population structure. Coalescent simulations were performed to model domestication bottlenecks. | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kehinde, B.O.; Xie, L.; Song, B.-K.; Zheng, X.; Fan, L. African Cultivated, Wild and Weedy Rice (Oryza spp.): Anticipating Further Genomic Studies. Biology 2024, 13, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090697
Kehinde BO, Xie L, Song B-K, Zheng X, Fan L. African Cultivated, Wild and Weedy Rice (Oryza spp.): Anticipating Further Genomic Studies. Biology. 2024; 13(9):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090697
Chicago/Turabian StyleKehinde, Babatunde O., Lingjuan Xie, Beng-Kah Song, Xiaoming Zheng, and Longjiang Fan. 2024. "African Cultivated, Wild and Weedy Rice (Oryza spp.): Anticipating Further Genomic Studies" Biology 13, no. 9: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090697
APA StyleKehinde, B. O., Xie, L., Song, B.-K., Zheng, X., & Fan, L. (2024). African Cultivated, Wild and Weedy Rice (Oryza spp.): Anticipating Further Genomic Studies. Biology, 13(9), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090697






