Effect of Probiotic Fermented Milk Supplementation on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Parameters and Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Eligibility Criteria and Study Selection
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Assessment of Risk of Bias in Included Studies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
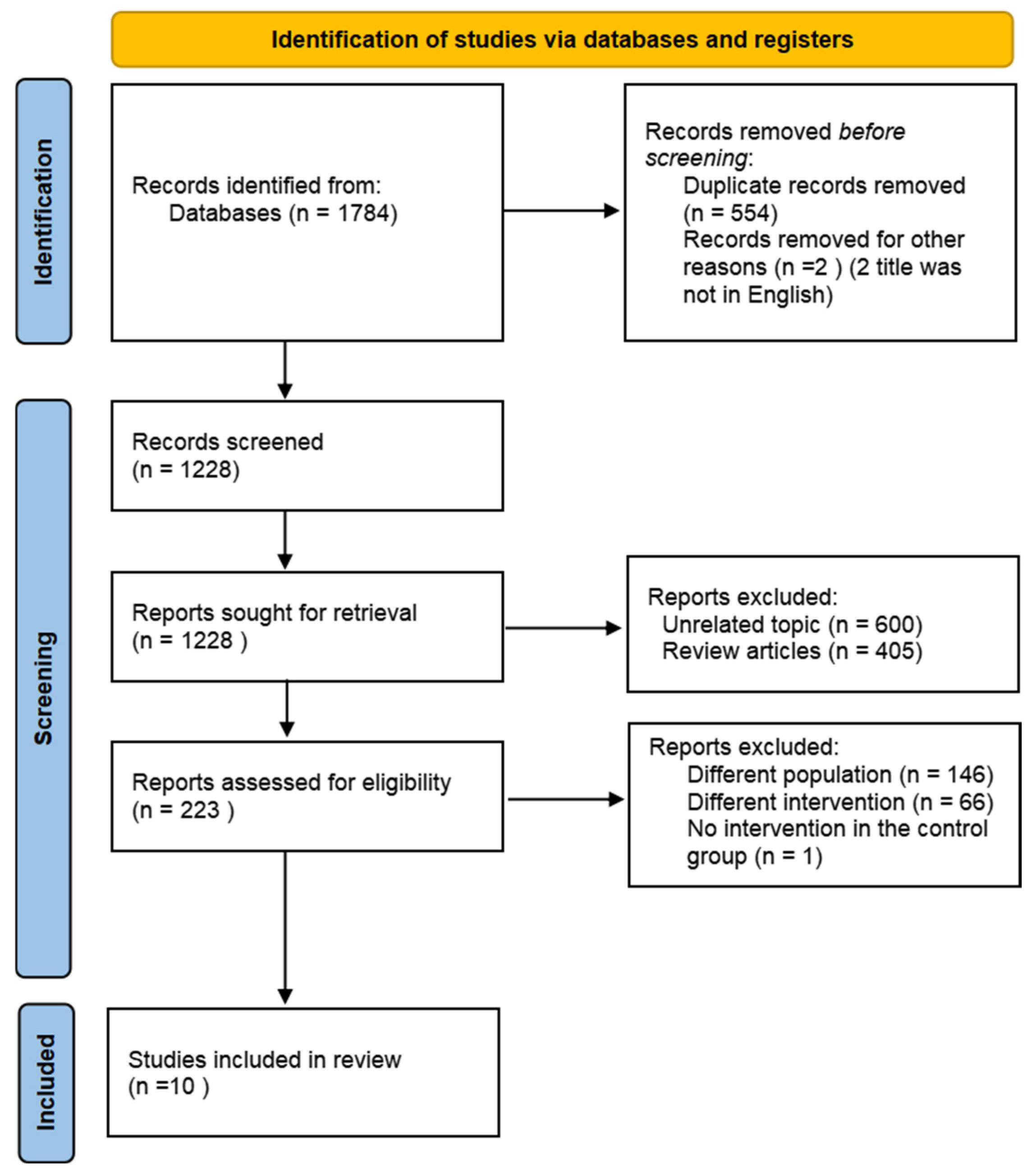
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Characteristics of Included Trials
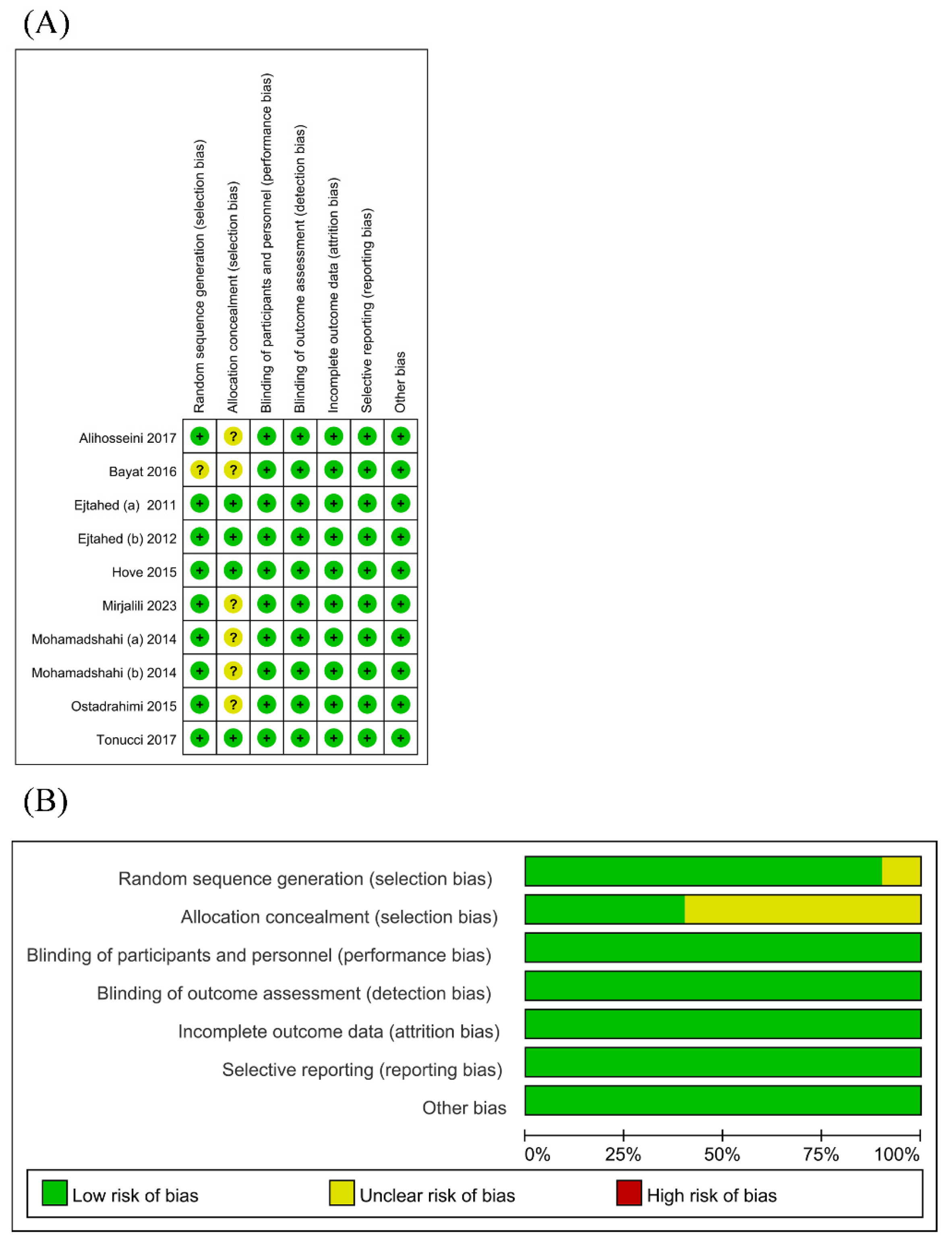
3.3. Risk of Bias
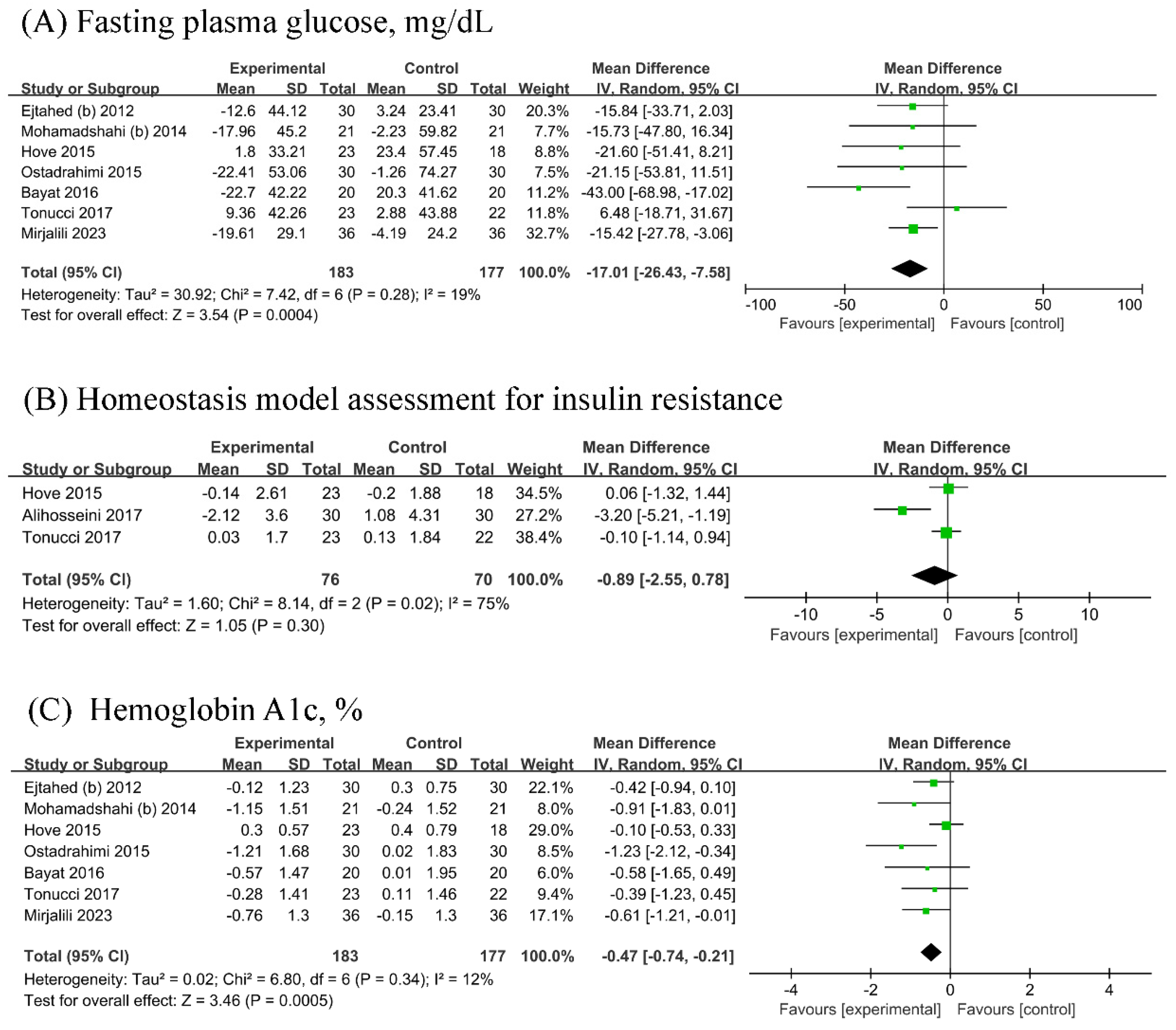
3.4. Glucose Metabolism Parameters
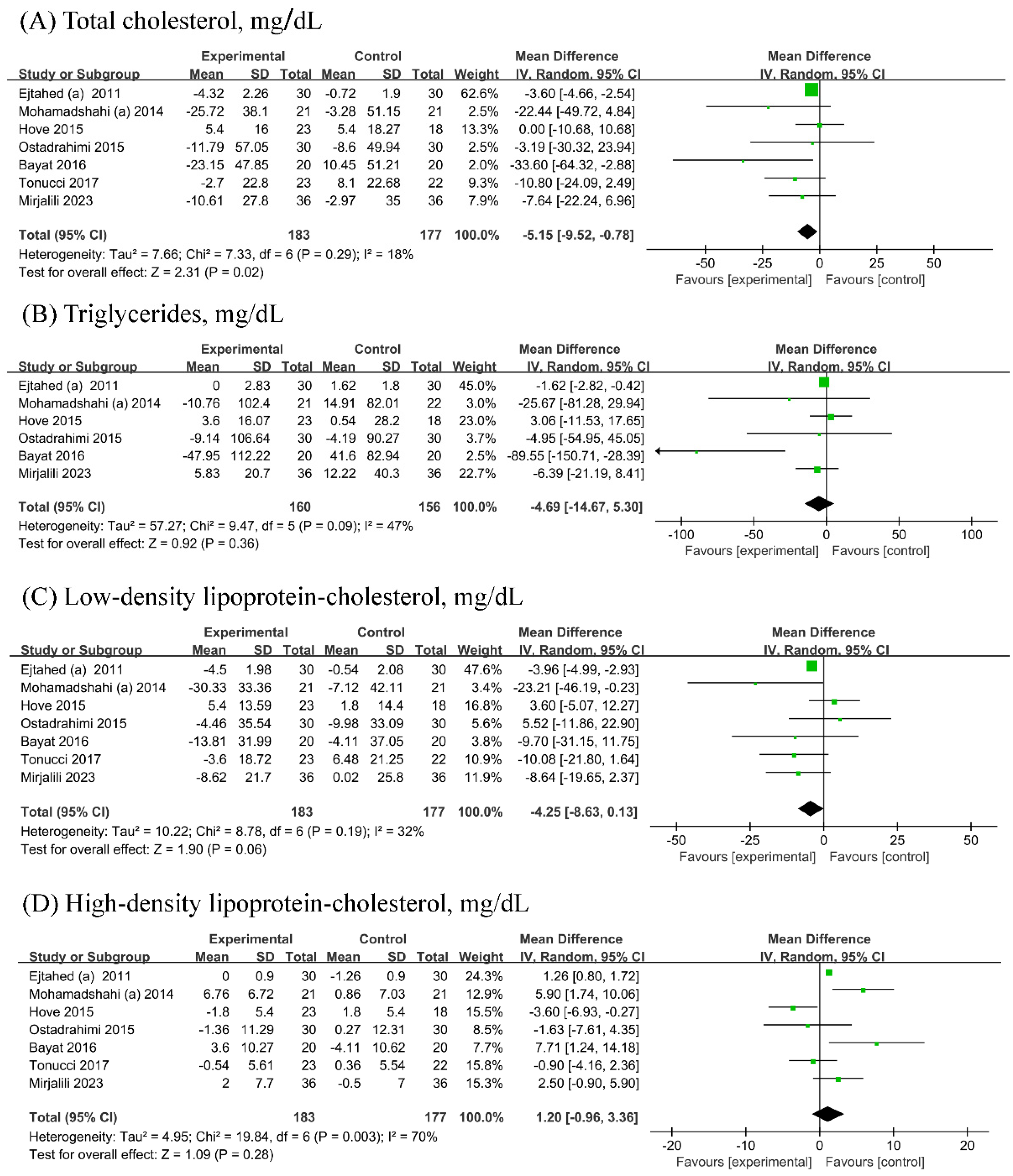
3.5. Lipid Metabolism Parameters
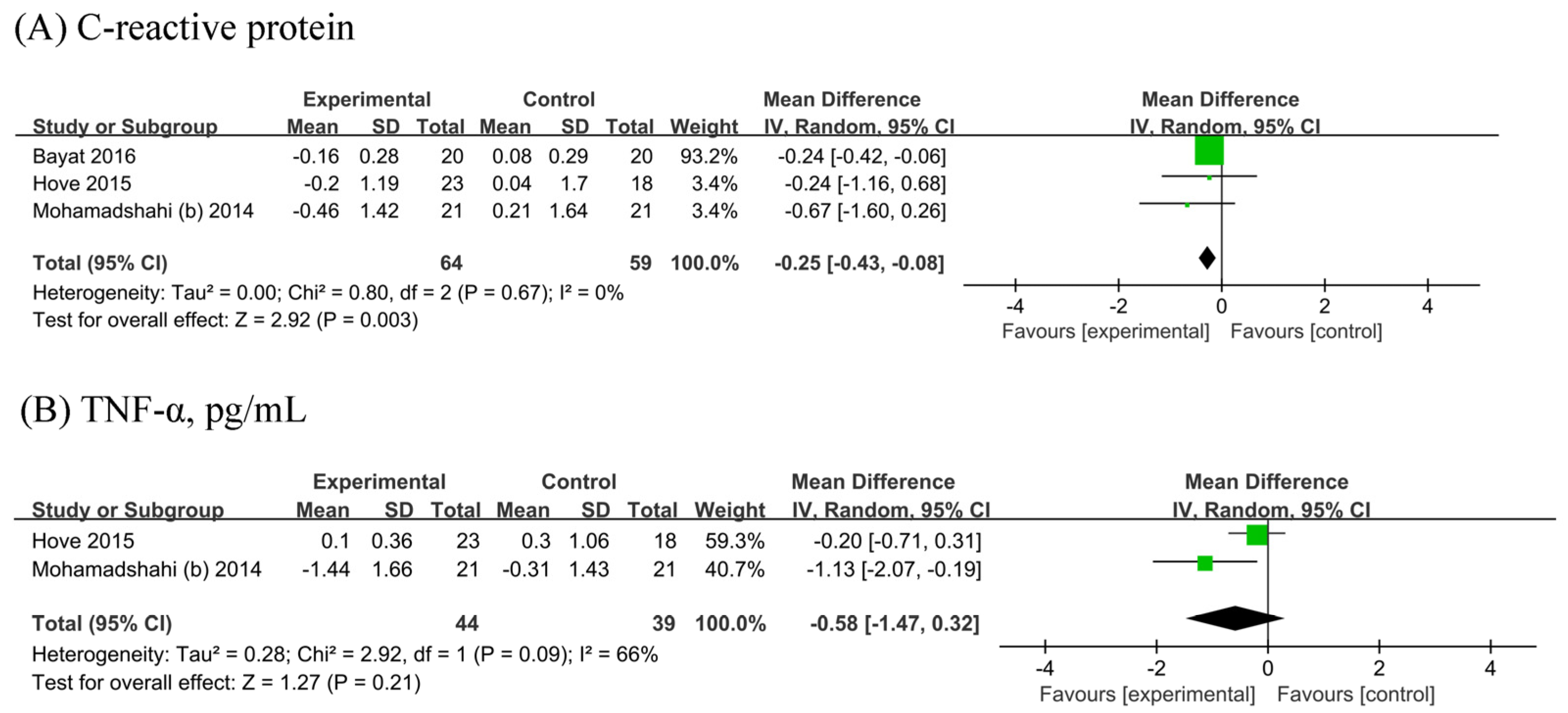
3.6. Inflammatory Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, S81–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, K.; Świtalski, J.; Tatara, T.; Miazga, W.; Jopek, S.; Augustynowicz, A.; Religioni, U.; Gujski, M. Workplace Interventions for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Prevention-an Umbrella Review. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2023, 23, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athyros, V.G.; Doumas, M.; Imprialos, K.P.; Stavropoulos, K.; Georgianou, E.; Katsimardou, A.; Karagiannis, A. Diabetes and lipid metabolism. Hormones 2018, 17, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidayat, K.; Du, X.; Shi, B.M. Milk in the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: The potential role of milk proteins. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, R.B. Cytokine and cytokine-like inflammation markers, endothelial dysfunction, and imbalanced coagulation in development of diabetes and its complications. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3171–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, M.; Li, Z.; You, H.; Rodrigues, R.; Jump, D.B.; Morgun, A.; Shulzhenko, N. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, B.; Yu, D.; Zhu, C. Gut Microbiota: An Important Player in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 834485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidian, N.; Yousefi, M.; Mortazavian, A.M. Fermented milk: The most popular probiotic food carrier. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 94, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, T.A.; Mainville, I.; Arcand, Y. The impact of meals on a probiotic during transit through a model of the human upper gastrointestinal tract. Benef. Microbes 2011, 2, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Tachon, S.; Eigenheer, R.A.; Phinney, B.S.; Marco, M.L. Lactobacillus casei Low-Temperature, Dairy-Associated Proteome Promotes Persistence in the Mammalian Digestive Tract. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3136–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranadheera, C.S.; Vidanarachchi, J.K.; Rocha, R.S.; Cruz, A.G.; Ajlouni, S. Probiotic Delivery through Fermentation: Dairy vs. Non-Dairy Beverages. Fermentation 2017, 3, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barengolts, E.; Smith, E.D.; Reutrakul, S.; Tonucci, L.; Anothaisintawee, T. The Effect of Probiotic Yogurt on Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes or Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of Nine Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. Bmj 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alihosseini, N.; Moahboob, S.A.; Farrin, N.; Mobasseri, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Ostadrahimi, A.R. Effect of probiotic fermented milk (kefir) on serum level of insulin and homocysteine in type 2 diabetes patients. Acta Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.; Azizi-Soleiman, F.; Heidari-Beni, M.; Feizi, A.; Iraj, B.; Ghiasvand, R.; Askari, G. Effect of Cucurbita ficifolia and Probiotic Yogurt Consumption on Blood Glucose, Lipid Profile, and Inflammatory Marker in Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejtahed, H.S.; Mohtadi-Nia, J.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Niafar, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Mofid, V. Probiotic yogurt improves antioxidant status in type 2 diabetic patients. Nutrition 2012, 28, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejtahed, H.S.; Mohtadi-Nia, J.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Niafar, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Mofid, V.; Akbarian-Moghari, A. Effect of probiotic yogurt containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium lactis on lipid profile in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3288–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hove, K.D.; Brons, C.; Faerch, K.; Lund, S.S.; Rossing, P.; Vaag, A. Effects of 12 weeks of treatment with fermented milk on blood pressure, glucose metabolism and markers of cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 172, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirjalili, M.; Salari Sharif, A.; Sangouni, A.A.; Emtiazi, H.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H. Effect of probiotic yogurt consumption on glycemic control and lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 54, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadshahi, M.; Veissi, M.; Haidari, F.; Javid, A.Z.; Mohammadi, F.; Shirbeigi, E. Effects of probiotic yogurt consumption on lipid profile in type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohamadshahi, M.; Veissi, M.; Haidari, F.; Shahbazian, H.; Kaydani, G.-A.; Mohammadi, F. Effects of probiotic yogurt consumption on inflammatory biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes. BioImpacts BI 2014, 4, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostadrahimi, A.; Taghizadeh, A.; Mobasseri, M.; Farrin, N.; Payahoo, L.; Gheshlaghi, Z.B.; Vahedjabbari, M. Effect of Probiotic Fermented Milk (Kefir) on Glycemic Control and Lipid Profile In Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Iran. J. Public Health 2015, 44, 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- Tonucci, L.B.; dos Santos, K.M.O.; de Oliveira, L.L.; Ribeiro, S.M.R.; Martino, H.S.D. Clinical application of probiotics in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.N.; Saboori, S.; Asbaghi, O. Effect of daily probiotic yogurt consumption on inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized Controlled Clinical trials. Obes. Med. 2020, 18, 10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaei, R.; Ghavami, A.; Khalesi, S.; Ghiasvand, R.; Mokari Yamchi, A. The effect of probiotic fermented milk products on blood lipid concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 997–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dilidaxi, D.; Wu, Y.; Sailike, J.; Sun, X.; Nabi, X.H. Composite probiotics alleviate type 2 diabetes by regulating intestinal microbiota and inducing GLP-1 secretion in db/db mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak-Kopeć, P.; Śliżewska, K. The Effect of Probiotics on the Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids by Human Intestinal Microbiome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sailike, J.; Sun, X.; Abuduwaili, N.; Tuoliuhan, H.; Yusufu, M.; Nabi, X.-h. Fourteen composite probiotics alleviate type 2 diabetes through modulating gut microbiota and modifying M1/M2 phenotype macrophage in db/db mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.A.; Keogh, J.B.; Clifton, P.M. Probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics and insulin sensitivity. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2018, 31, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintarič, M.; Langerholc, T. Probiotic Mechanisms Affecting Glucose Homeostasis: A Scoping Review. Life 2022, 12, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria | |
|---|---|---|
| Participants | Adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus patients | Patients with other types of diabetes mellitus |
| Intervention or exposure | Probiotics-enriched fermented milk | Conventional fermented milk |
| Comparison | Conventional fermented milk or non-dairy controls/placebos | |
| Outcome | Glucose metabolism parameters (fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance) Lipid metabolism parameters (total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein) Inflammatory markers (tumor necrosis factor-alpha and C-reactive protein) | |
| Study design | Parallel or cross-over randomized controlled trial | Non-randomized study (i.e., observational study) |
| Author Year | Country | No.of Participants in the Probiotics Group/No. of Participants in the Placebo Group | Age in Intervention Group (mean ± SD) | Age in Control Group (mean ± SD) | Treatment (Bacteria) | Control (Bacteria) | Duration (Weeks) | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ejtahed(a). 2011 [21] | Iran | 30/30 | 50.87 ± 1.40 | 51.00 ± 1.34 | 300 g/d probiotic-enriched yogurt (original culture: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus; additional culture (3.98 × 109 cfu/d): Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 (7.23 × 106 cfu/g on day 1) and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 (6.04 × 106 cfu/g on day 1)) | 300 g/d conventional yogurt (original culture: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus) | 6 | TC, TG, HDL-C, LDC-C |
| Ejtahed(b). 2012 [20] | Iran | 30/30 | 50.87 ± 7.68 | 51.00 ± 7.32 | 300 g/d of probiotic-enriched yogurt (original culture: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus; additional culture (3.98 × 109 cfu/d): Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 (7.23 × 106 cfu/g on day 1) and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 (6.04 × 106 cfu/g on day 1)) | 300 g/d of conventional yogurt (original culture: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus) | 6 | FPG, HbA1c |
| Mohamadshahi(a), 2014 [24] | Iran | 22/22 | 51 | 51 | 300 g/d probiotic-enriched yogurt (original culture: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus; additional culture (2.22 × 109 cfu/d): Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 (3.7 × 106 cfu/d on day 1) and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 (3.7 × 106 cfu/d on day 1)) | 300g/d of conventional yogurt (original culture: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus) | 8 | TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C |
| Mohamadshahi(b), 2014 [25] | Iran | 22/21 | 53.00 ± 5.9 | 49.00 ± 7.08 | Probiotic-enriched yogurt (original culture: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus; additional culture (2.22 × 109 cfu/d): Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 (3.7 × 106 cfu/d on day 1) and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 (3.7 × 106 cfu/d on day 1)) | Conventional yogurt (original culture: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus) | 8 | FPG, HbA1c, CRP, TNF-α, IL-6 |
| Hove, 2015 [22] | Denmark | 23/18 | 58.5 ± 7.7 | 60.6 ± 5.2 | 300 g/d of Commercial probiotic yogurt ‘Cardi04’ (Lactobacillus helveticus Cardi04) | 300 g/d of probiotics-free acidified milk | 12 | FPG, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, CRP, TNF-α |
| Ostadrahimi, 2015 [26] | Iran | 30/30 | no | no | 600 g/d of probiotic-enriched kefir (original cultures: Streptococcus thermophilus; additional cultures (2.88 × 1010 cfu/d): Lactobacillus casei (1.5 × 107 cfu/g on day 1), Lactobacillus acidophilus (2.5 × 107 cfu/g on day 1), and bifidobacterium lactis (8 × 106 cfu/g on day 1)) | 600 g/d of conventional fermented milk (original cultures: Streptococcus thermophilus) | 8 | FPG, HbA1c, TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, |
| Bayat, 2016 [19] | Iran | 20/20 | 54.1 ± 9.54 | 46.95 ± 9.34 | 150 g/d of probiotic yogurt (not reported) | Dietary advice (not applicable) | 8 | FPG, HbA1c, TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C, CRP |
| Alihosseini, 2017 [18] | Iran | 30/30 | Not reported | Not reported | 600 g/d of probiotic-enriched kefir (original cultures: Streptococcus thermophilus; additional cultures (2.88 × 1010 cfu/d): Lactobacillus casei (1.5 × 107 cfu/g on day 1), Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 (2.5 × 107 cfu/g on day 1), and bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 (8 × 106 cfu/g on day 1)) | 600 g/d of conventional fermented milk (original cultures: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus) | 8 | HOMA-IR |
| Tonucci, 2017 [27] | Brazil | 23/22 | 51.83 ± 6.64 | 50.95 ± 7.20 | 120 g/d of probiotic fermented goat milk (original culture (6.26 × 1010 cfu/d): Streptococcus thermophilus; Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 (7.72 × 107 cfu/g on day 1) and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 (4.45 × 108 cfu/g on day 1)) | 120 g/d of conventional fermented goat milk (original culture: Streptococcus thermophilus) | 6 | FPG, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, TC, HDL-C, LDL-C |
| Mirjalili, 2023 [23] | Iran | 36/36 | 54.5 ± 8.0 | 58.1 ± 9.8 | 100 g/d of probiotic-enriched yogurt (original culture: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus; additional culture (7.3 × 108 cfu/d): Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 (7.3 × 106 cfu/d on day 1)) | 100 g/d of conventional yogurt (original culture: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus) | 12 | FPG, HbA1c, TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, H.; Wang, L.; Jia, F.; Yan, Y.; Xiong, F.; Hidayat, K.; Li, Y. Effect of Probiotic Fermented Milk Supplementation on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Parameters and Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biology 2024, 13, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080641
Zhong H, Wang L, Jia F, Yan Y, Xiong F, Hidayat K, Li Y. Effect of Probiotic Fermented Milk Supplementation on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Parameters and Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biology. 2024; 13(8):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080641
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Hao, Lingmiao Wang, Fuhuai Jia, Yongqiu Yan, Feifei Xiong, Khemayanto Hidayat, and Yunhong Li. 2024. "Effect of Probiotic Fermented Milk Supplementation on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Parameters and Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Biology 13, no. 8: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080641
APA StyleZhong, H., Wang, L., Jia, F., Yan, Y., Xiong, F., Hidayat, K., & Li, Y. (2024). Effect of Probiotic Fermented Milk Supplementation on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Parameters and Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biology, 13(8), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080641






