Germplasm Resources and Genetic Breeding of Huang-Qi (Astragali Radix): A Systematic Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Germplasm Resources
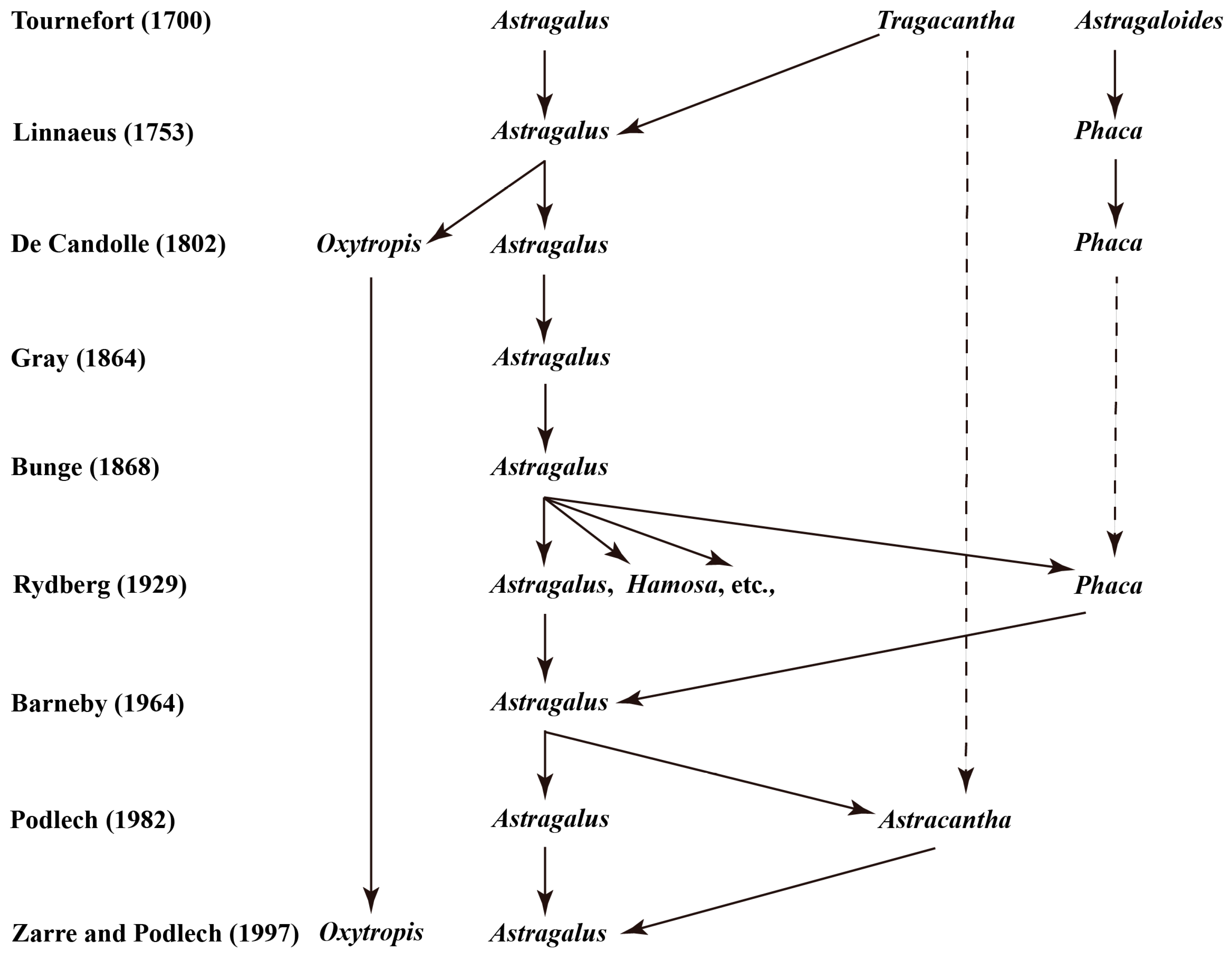
2.1. Astragalus Species Resources and Morphological Classification
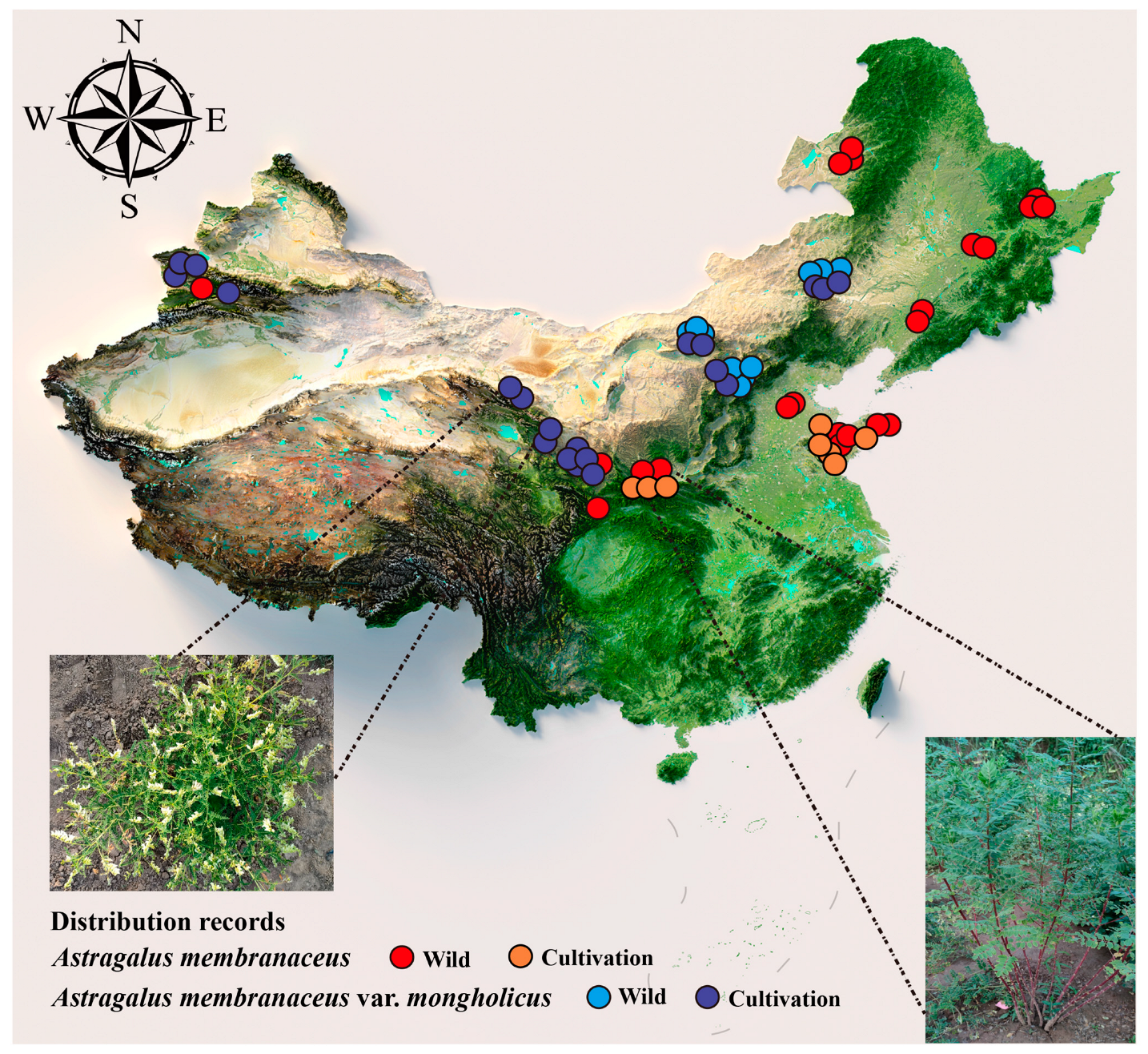
2.2. Geographic Distribution of Huang-Qi
2.3. Status of Huang-Qi Resources
2.4. Huang-Qi Substitutes of Different Origins
3. Genetic Diversity of Huang-Qi Germplasm Resources
3.1. Species Diversity
3.2. Morphological Diversity
3.3. Genetic Diversity of Cytological Markers
3.4. Molecular Genetic Diversity
4. Genetic Breeding
4.1. Genetic Research
4.2. Trait Inheritance
4.3. Classical Cytogenetics and Molecular Markers
4.4. Biochemical Marker
4.5. Traditional Breeding
4.6. Selective Breeding
4.7. Molecular Breeding
4.8. Flower and Leaf Color
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
5.1. Germplasm Diversity
5.2. Breed Authenticity Protection
5.3. Breeding of Superior Seeds
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Podlech, D. The genus Astragalus L. (Fabaceae) in Europe with exclusion of the former Soviet Union. Feddes Repert. 2008, 119, 310–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchadi, W.; Haba, H.; Lavaud, C.; Harakat, D.; Benkhaled, M. Secondary metabolites of Astragalus cruciatus Link and their chemotaxonomic significance. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2013, 7, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, M.S.; Joharchi, M.R.; Nadaf, M.; Nasseh, Y. Ethnobotanical knowledge of Astragalus spp.: The world’s largest genus of vascular plants. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2020, 10, 128–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Duan, J.A.; Huang, W.Z. Current status and analysis of medicinal plant resources of Astragalus Linn. in China. Chin. Wild Pl. Resour. 2000, 6, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, H.; Luo, Y. Anti-aging implications of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi): A well-known Chinese tonic. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zheng, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Yang, S. Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi). Phytother Res. 2014, 28, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Pan, Q.; Ji, K.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, S. Review on the protective mechanism of astragaloside IV against cardiovascular diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1187910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Sheng, W.; Zhou, Q. Astragalus–scorpion drug pair inhibits the development of prostate cancer by regulating GDPD4-2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and Autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 895696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. Astragalus polysaccharide promotes sheep satellite cell differentiation by regulating miR-133a through the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, N.; Yu, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M. Allelopathy and Identification of Volatile Components from the Roots and Aerial Parts of Astragalus mongholicus Bunge. Plants 2024, 13, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Huang, P.; Jin, W.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Wan, H.; He, Y. Optimization of extraction or purification process of multiple components from natural products: Entropy Weight Method Combined with Plackett-Burman Design and Central Composite Design. Molecules 2021, 26, 5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Sun, H.F. Status and analysis of Huang-Qi medicinal resources in China. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 3234–3238. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Geng, Y.P.; Xie, X.D.; Wang, F. Genetic diversity and genetic structure analysis of Astragalus based on SSR molecular marker. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2019, 27, 1154. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Jin, X.; Zhao, L. Rare and endangered plants in China. In Conservation and Reintroduction of Rare and Endangered Plants in China; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.M.; Wu, W.G.; Guo, L.; Yang, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhi, H.; Liu, Z.D.; Yang, X. Changes of Astragali Radix producing regions and development process of cultivation industry in China. Mod. Chin. Med. 2023, 25, 2428–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Deng, S.; Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Hua, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y. Identify production area, growth mode, species, and grade of Astragali radix using metabolomics “big data” and machine learning. Phytomedicine 2024, 123, 155201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, L.B.; Rana, T.S.; Anand, K.K. Current status of the systematics of Astragalus L. (Fabaceae) with special reference to the Himalayan species in India. Taiwania 2008, 53, 338–355. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C. Phylogenetics and Evolutionary History of Eastern Asian Astragalus L. (Fabaceae). Ph.D. Thesis, North West Agriculture and Forestry University, Xianyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.L.; Kang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Podlech, D. Phylogenetic origin of Phyllolobium with a further implication for diversification of Astragalus in China. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2009, 51, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M. Taxonomic Note and Floristic Geographical Study of astragalus L. in Mongoliian plateau. Master’s Thesis, North West Agriculture and Forestry University, Xianyang, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Linnaeus, C. Species Plantarum; Impensis GC Nauk: Stockholm, Sweden, 1753; pp. 755–762. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, G.D.J. Synopsis Florae Germanicae et Helveticae; Sumptibus Gebhardt et Reisland: Lipsiae, Germany, 1857; Volume III. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, A. A revision and arrangement (mainly by the fruit) of the North American species of Astragalus and Oxytropis. Proc. Amer. Acad. Arts. 1864, 6, 188–236. [Google Scholar]
- Bunge, A. Generis Astragali species gerontogeae. Mem. Acad. Imp. Sci. Saint Petersbourg. 1868, 11, 1–140. [Google Scholar]
- Boissier, E. Flora Orientalis 2; H. Georg: Geneva, Switzerland, 1872; pp. 205–498. [Google Scholar]
- Rygdberg, P.A. Astragalanae. North Am. Flora 1929, 24, 251–462. [Google Scholar]
- Barneby, R.C. Atlas of North American Astragalus. Mem. N. Y. Bot. 1964, 13, 1–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlech, D. Zur taxonomie und nomenclatur de tragacanthoiden Astragali. Mitt. Bot. Staatss. Munch. 1983, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Podlech, D. Revision der altweltlichen annuellen Arten der Gattung Astragalus L. (Leguminosae). Sendtnera 1994, 2, 39–170. [Google Scholar]
- Osaloo, S.K.; Maassoumi, A.A.; Murakami, N. Molecular systematics of the genus Astragalus L. (Fabaceae): Phylogenetic analyses of nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacers and chloroplast gene ndh F sequences. Plant Syst. Evol. 2003, 242, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, M.F.; Sanderson, M.J.; Hu, J.M. Evidence on the monophyly of Astragalus (Fabaceae) and its major subgroups based on nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS and chloroplast DNA trnL intron data. Syst. Bot. 1999, 24, 409–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Q.; Duan, J.; Zhu, D.; Dong, T.X.; Tsim, K.W.K. Chemical comparison of Astragali Radix (Huangqi) from different regions of China. Nat. Med. 2000, 54, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.Z. Correlation on quality and ecotype of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2014, 24, 2395–2399. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, R.J.; Xi, X.Q.; Zhang, X.L. Research and utilisation of Astragalus germplasm resources. Anhui Agronomy Bulletin. 2020, 26, 34–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Xiong, F.; Nie, X.; Li, C.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, G. Nitrogen fertilizer levels affect the growth and quality parameters of Astragalus mongolica. Molecules 2020, 25, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.L.; Deng, A.P.; Peng, H.S.; Zhang, X.B.; Guo, L.P.; Huang, L.Q. Study of genuineness based on changes of ancient herbal origin--taking Astragalus membranaceus and Salvia miltiorrhiza as examples. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2016, 41, 3202–3208. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhang, C.; Yao, R.; Li, M. Quality control of Radix astragali (the root of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus) along its value chains. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 562376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Cheng, X.L.; Jing, W.G.; Chen, J.; Yu, K.Z.; Zhang, P.; Yan, H.; Li, M.H.; Yang, J.B.; Ma, S.C. Some Concerns About the Standard Establishment of Chinese Medicinal Medicines and Decoction Pieces. Chin. Pharm. J. 2020, 57, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.C. Report on the Selection and Breeding of a New Line of Astragalus 94-01. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2005, 7, 535–536. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.J.; Gou, Y.P. High yielding and high quality Astragalus new variety-9118. Agric. Sci. Technol. Newsl. 2000, 2000, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.P.; Li, W.Q.; Jia, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.P. Transcriptome sequencing and characterization of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus root reveals key genes involved in flavonoids biosynthesis. Genes Genom. 2020, 42, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.T.; Xu, Y.Q.; Zhong, Y.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, J.K.; Li, X.; Nan, P. Global transcriptome analysis profiles metabolic pathways intraditional herb Astragalus membranaceus Bge. var. mongolicus (Bge.) Hsiao. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Du, Q.; Shen, Y.H. Research Progress on Chemical Constituents and Pharmacology of B10 Kinds Medicinal Plants of Astragalus. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2017, 23, 222–234. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.G.; Jia, X.Y.; Dai, R.; Gu, D.S.; Pi, W.L. Studies on the species diversity of medicinal plants of Astragalus membranaceus in Yunnan Province, China. J. Yunnan Coll. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1997, 20, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Gang, J.; Guo, P.J. Medicinal resources of Astragalus spp. in Qinghai and its commercial herbs. Chin. Herb. Med. 1993, 16, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.Q. Collation and Quality Study of Commonly Used Chinese Herbal Medicines Varieties; Fujian Science and Technology Press: Fuzhou, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Li, L. DT-PICS: An efficient and cost-effective SNP selection method for the germplasm identification of Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.H.; Li, H.L.; Hou, J.L.; Wang, W.Q. Research Progress on Germplasm Resources of Huangqi (Radix astragali). Guid. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2016, 22, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Q.; Yao, J.; Xu, C. Effect of simulated warming on leaf functional traits of urban greening plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, R.P.; Fornel, R.; Kasper, C.B. Geographic variation in the skull morphology of the lesser grison (Galictis cuja: Carnivora, Mustelidae) from two Brazilian ecoregions. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.L.; Wang, X.S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. Morphotype Diversity of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. Var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2004, 6, 1203–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.Y. Talking about Astragalus at the onset of SARS. Plant J. 2003, 3, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.J. Studies on Idioplasm Resource of Chinese Troditional Medicine Astragalus and on Effects of Environmental Factors on Quality. Master’s Thesis, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, Xianyang, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.P.; Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.E. Studies on the seed esterase isoenzymes of A. membranaceus or A. membranaceus var. mongholicus. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2006, 3, 1534–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.S. Correlation analysis between effective components and genetic diversity of ISSR and ITS markers in Astragalus membranaceus. Master’s. Thesis, Ningxia University, Yinchuan, Chian, 2018; pp. 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.P. Preliminary construction and genetic diversity analysis of core collection of Astragalus. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi Agricultural University, Taiyuan, Chian, 2020; pp. 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.Q. Study of Different Sources Astragalus with AFLP and Metabolic Profiling. Ph.D. Thesis, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.R. Cluster analysis for karyotype of Astragalus penduliflorus Lam. Complex (Leguminosae). Bull. Bot. Res. 2003, 23, 220–223. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, D.; Maurya, A.K.; Abdi, G.; Majeed, M.; Agarwal, R.; Mukherjee, R.; Ganguly, S.; Aziz, R.; Bhatia, M.; Majgaonkar, A.; et al. Integrated Genomic Selection for Accelerating Breeding Programs of Climate-Smart Cereals. Genes 2023, 14, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chen, P.; Hou, X.R.; Ma, J.; Yang, N.; Lu, Y.; Huang, H. rDNA and mtDNA analysis for the identification of genetic characters in the hybrid grouper derived from hybridization of Cromileptes altivelis (female) × Epinephelus lanceolatus (male). BMC Genom Data 2024, 25, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Wan, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.R.; Sun, W.B. Analysis on botanical characters of Astragalus membranacens Bunge. and A. membranacens var. mongolicus (Bunge) Hsiao. Neimenggu Nongye Daxue Xuebao 2001, 22, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Abudirehemu, R.; Ren, X. Karyotype and banding pattern analysis of somatic cell chromosome in Astragalus mongolicus. North. Hortic. 2015, 39, 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.G.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Liang, J.P.; Feng, Q.J.; Wang, J.S. The chromosome number and karyotype of two Astragalus species. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2016, 24, 699–702. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, C.; Hou, D.; Li, T.; Li, Z. Detection of CNV in the SH3RF2 gene and its effects on growth and carcass traits in chickens. BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Gao, X.; Yu, X.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, G.; Liu, C.; Liu, X. Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Meconopsis (Papaveraceae) provides insights into their genomic evolution and adaptation to high elevation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.J.; Um, J.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Koh, K.H.; Hwang, W.J.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, H.M. Molecular discrimination of medicinal Astragali radix by RAPD analysis. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2004, 26, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, P.Y.; Kwan, H.S. Molecular identification of Astragalus membranaceus at the species and locality levels. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, F.S.; Qin, X.M. Comparison between Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus and Hedysarum polybotrys based on ITS sequences and metabolomics. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2015, 50, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Xu, Z.M.; Chen, J.Y. Genetic diversity analysis of Scutellaria baicalensis by RAPD. J. Sichuan Tradit. Chin. Med. 2010, 28, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.F. Study on RAPD Analysis of Genetic Relationship and Comparison of Effective Component for Astragalus membranaceus. Master’s Thesis, Yanbian University, Yanji, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R. Analysis on Genetic Diversity of Radix Astragalus by ISSR Marker. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi Agricultural University, Jinzhong, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, R.L.; Fan, J.; Ping, L.L.; Wen, X.D.; Di, J.L. Transferability of soybean gemonic-SSR and EST-SSR markers in Astragalus. Mol. Plant Breed. 2015, 13, 994–998. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Yang, Q.W.; Zhang, J.P.; Zhang, J.M.; Qiu, L.J.; Wang, T.Y. Genomics-based crop germplasm research: Advances and perspectives. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 3333–3353. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Tan, B.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Kang, H. Genetic diversity and population structure of Asian and European common wheat accessions based on genotyping-by-sequencing. Front Genet. 2020, 11, 580782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.J. Studies on the pollination characteristics of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus. Mod. Chin. Med. 2011, 13, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.F.; Li, M.H.; Yi, L.T.; Hou, X.K.; Wei, Z.Q. Planting techniques of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao: A Review. J. Agric. 2019, 9, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.Y.; Chen, G.L. Current situation, problems and countermeasures of Radix astragali industrialization in Inner Mongolia. Mol. Breed. 2018, 16, 5126–5133. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.Q.; Shi, Q.; Duan, J.A.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W. Chemical analysis of Radix astragali (Huangqi) in China: A comparison with its adulterants and seasonal variations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4861–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Gao, X.X.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Bai, Z.Q. Establishment of callus induction and regeneration toxin system of Astragalus mongolica and Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus. Mol. Breed. 2022, 20, 5080–5087. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.L.; Guo, S.H.; Zhang, L.J.; Wu, C.J.; Pei, S.S. Study on flowering habits and sexual hybridization of Astragalusmem branaceus var. mongholicus. Seed 2022, 41, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.; Guo, F.X.; Dong, L.L.; Liu, L.L.; Sun, Y.P.; Xu, H.L.; Li, H.L. Genetic Variation of SP2 Biennial Population from Astragalus membranaceus Seeds Carried in Space. Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 24, 687–695. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.M. Karyotype analysis of wild and cultivated Astragalus membranaceus. Chin. Herb. Med. 1988, 19, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, M.; Shrivastava, N.; Padh, H. Advances in molecular marker techniques and their applications in plant sciences. Plant Cell Rep. 2008, 27, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; He, R.L.; Han, Y.L.; Wang, F.; Li, H.F. Identification of Astragalus membranaceus and Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus based on SSR marker. J. Chin. Med. Mat. 2018, 41, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, F.S.; Geng, Y.P.; Zhang, P.F.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X.F.; Liu, Y.L. Genetic diversity and structure of a core collection of Huangqi (Astragalus ssp.) developed using genomic simple sequence repeat markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2021, 70, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Park, S.J. Development of genetic marker specific for Korean Hwanggi medicine (Radix astragali). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 1561–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, D.W.; Yang, J.Y.; Jian, Y.; Hu, Z.L. Genetic Diversity of Cultivated and Wild Mongolian Astragalus in Inner Mongolia Area. Chin. J. Grassland. 2018, 40, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.Q.; Shi, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.P.; Liu, X.X.; Chen, Y.L. Astragali Radix and Hedysari Radix molecular identification of SSR primers screening and fingerprints code. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2016, 41, 1819–1822. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, D.; Huang, L.Q.; Cui, G.H.; Chen, M. Study on genetic relationship of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus in different producing area using SRAP. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2009, 34, 382–385. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.Y. Study on Drought Resistance and Diversity of Astragali radix Germplasm Resources. Ph.D. Thesis, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot, China, 2017; pp. 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Hou, X.; Xu, R.; Liu, C.; Tu, M. Research review on the pharmacological effects of astragaloside IV. Fundam Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 31, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.P.; Shi, Z.Y.; Tian, H.L.; Guo, S.H.; Song, S.J.; Wang, B.H.; Guo, X.; Liang, J.P. Genetic diversity analysis of different Astragalus membranaceus germplasm resources by genotyping-by-sequencing technology. Mol. Plant Breed. 2022, 20, 8291–8298. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.Y.; Wei, L.; Qiao, Y.X.; Gao, P.P. On the ultrastructure of Mongolian milkvetch (Astragalus mongholicus) and a comparison of their isozymes and lipase. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 1994, 504, 479–481. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.L.; Li, Y. Studies on esterase isozymic differences between two phenotypes of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus seeds. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2013, 42, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.X.; Wang, G.X.; Cai, Z.P.; Wang, Y.L.; Jin, L. Establishment of high-frequency regeneration system of Astragalus membranaceus in Mongolia. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2017, 40, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Shen, T.; Li, X.; Lin, H.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Zhong, Y. Genome-wide characterization and analysis of bHLH transcription factors related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in Cinnamomum camphora (‘Gantong 1’). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Zheng, M.J.; Yu, H.J.; Rong, F.L.; Cui, A.N. Astragalus membranaceus new variety—Wenhuang11. China Agric. Technol. Ext. 2001, 3, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.H.; Liu, X.R.; Song, Z.H.; Shang, H.S.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, X.Z. Research on the selection and breeding of the new variety of Astragalus membranaceus Longqi 3 and standardised cultivation techniques. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2013, 36, 1392–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. Integrating multi-omics analysis reveals the regulatory mechanisms of white–violet mutant flowers in grape Hyacinth (Muscari latifolium). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Liao, J.; He, Z.; Khurshid, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, Y. Effects of peanut rust disease (Puccinia arachidis Speg.) on agricultural production: Current control strategies and progress in breeding for resistance. Genes 2024, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.B.; Thwe, A.A.; Li, X.; Tuan, P.A.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.W.; Park, S.U. Accumulation of astragalosides and related gene expression in different organs of Astragalus membranaceus Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.). Molecules 2014, 19, 10922–10935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Shan, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, M.; Li, X. Integrated metabolomics and transcriptomics study of traditional herb Astragalus membranaceus Bge. var. mongolicus (Bge.) Hsiao reveals global metabolic profile and novel phytochemical ingredients. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, X.; Peng, G.; Liu, M.; Zhang, S.; Chen, M.; Zhou, H. Methylesterification of cell-wall pectin controls the diurnal flower-opening times in rice. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 956–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, L.; Zou, H.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Y. PsGSTF3, an anthocyanin-related glutathione S-transferase gene, is essential for petal coloration in tree peony. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiong, L.; Luo, Y.; Wen, B.; Wang, K.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Identification, molecular characteristic, and expression analysis of PIFs related to chlorophyll metabolism in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roguz, K.; Hill, L.; Koethe, S.; Lunau, K.; Roguz, A.; Zych, M. Visibility and attractiveness of Fritillaria (Liliaceae) flowers to potential pollinators. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, X.; Zhao, M.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Han, X. RrGT2, a key gene associated with anthocyanin biosynthesis in Rosa rugosa, was identified via virus-induced gene silencing and overexpression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Liu, S.; Hu, L.; Shi, J.; Chen, J. Transcriptome analysis and metabolic profiling reveal the key role of carotenoids in the petal coloration of Liriodendron tulipifera. Hort. Res. 2020, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Suriguga; Zhao, M.; Chen, S.; Wu, X.; Wan, Q. Transcriptional regulation mechanism of flavonoids biosynthesis gene during fruit development in Astragalus membranaceus. Front Genet. 2022, 13, 972990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Piero, A.R. The state of the art in biosynthesis of anthocyanins and its regulation in pigmented sweet oranges (Citrus sinensis) L. Osbeck. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4031–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, A. Tetrapyrrole biosynthesis in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khusnutdinov, E.; Sukhareva, A.; Panfilova, M.; Mikhaylova, E. Anthocyanin biosynthesis genes as model genes for genome editing in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strygina, K.V.; Kochetov, A.V.; Khlestkina, E.K. Genetic control of anthocyanin pigmentation of potato tissues. BMC Genet. 2019, 20, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Zhi, J.W.; Liu, M.X.; Zhang, J.W.; Guo, W.J.; Sun, Y.; Kong, J.J.; Sun, J.X. Study on the quantitative analysis of 11 key genes expression of flower color in different color system of Rosa. Mol. Breed. 2022, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Jiang, Y.; Ning, C.; Meng, J.; Lin, S.; Ding, W.; Tao, J. Transcriptome sequencing of a chimaera reveals coordinated expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes mediating yellow formation in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China, 1st ed. China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 191. (In Chinese)
- Wu, S.Q.; Zu, Y.G.; Guan, Q.J.; Wu, J.R. Cloning and sequence analysis of a novel phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene from Astragalus membranaceus. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2010, 41, 456–460. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Fang, T.; Su, H.; Duan, S.; Ma, R.; Wang, P.; Dong, X. A reference-grade genome assembly for Astragalus mongholicus and insights into the biosynthesis and high accumulation of triterpenoids and flavonoids in its roots. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Bunge (1868/9) | Boissier (1872) | Bunge (1880) | Podlech (1983) | Zhang (2009) | New Worlds “Phalanxes” Barneby (1964) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basifixed hair | Phaca | Phaca | Phaca | Astragalus | Phaca | Phacoid (6 sections, 13 species) |
| Caprinus | Caprinus | |||||
| Calycophysa | Calycophysa | Calycophysa | Calycophysa | |||
| Hypoglottis | Hypoglottis | Hypoglottis | Hypoglottis | Hypoglottis (1 section, 2 species) | ||
| Tragacantha | Tragacantha | Tragacantha | Tragacantha | |||
| Pogonophace | Pogonophace | Pogonophace | ||||
| Trimeniaeus | Trimeniaeus | Trimeniaeus | Trimeniaeus (1 section, 1 species) | |||
| Medifixed hair | Cercidothrix | Cercidothrix | Cercidothrix | Cercidothrix | Cercidothrix | Cercidothrix (2 sections, 4 species) |
| Calycocystis | Calycocystis | Calycocystis | Calycocystis | |||
| Epiglottis | Epiglottis | Epiglottis | ||||
| Others | Trimeniaeus (basifixed hair and medifixed hair) | gen Astracantha | gen Pogonophace | Homoloboid * (46 sections, 194 species) Piptolobid * (35 sections, 192 species) Orophaca * (2 sections, 7 species) |
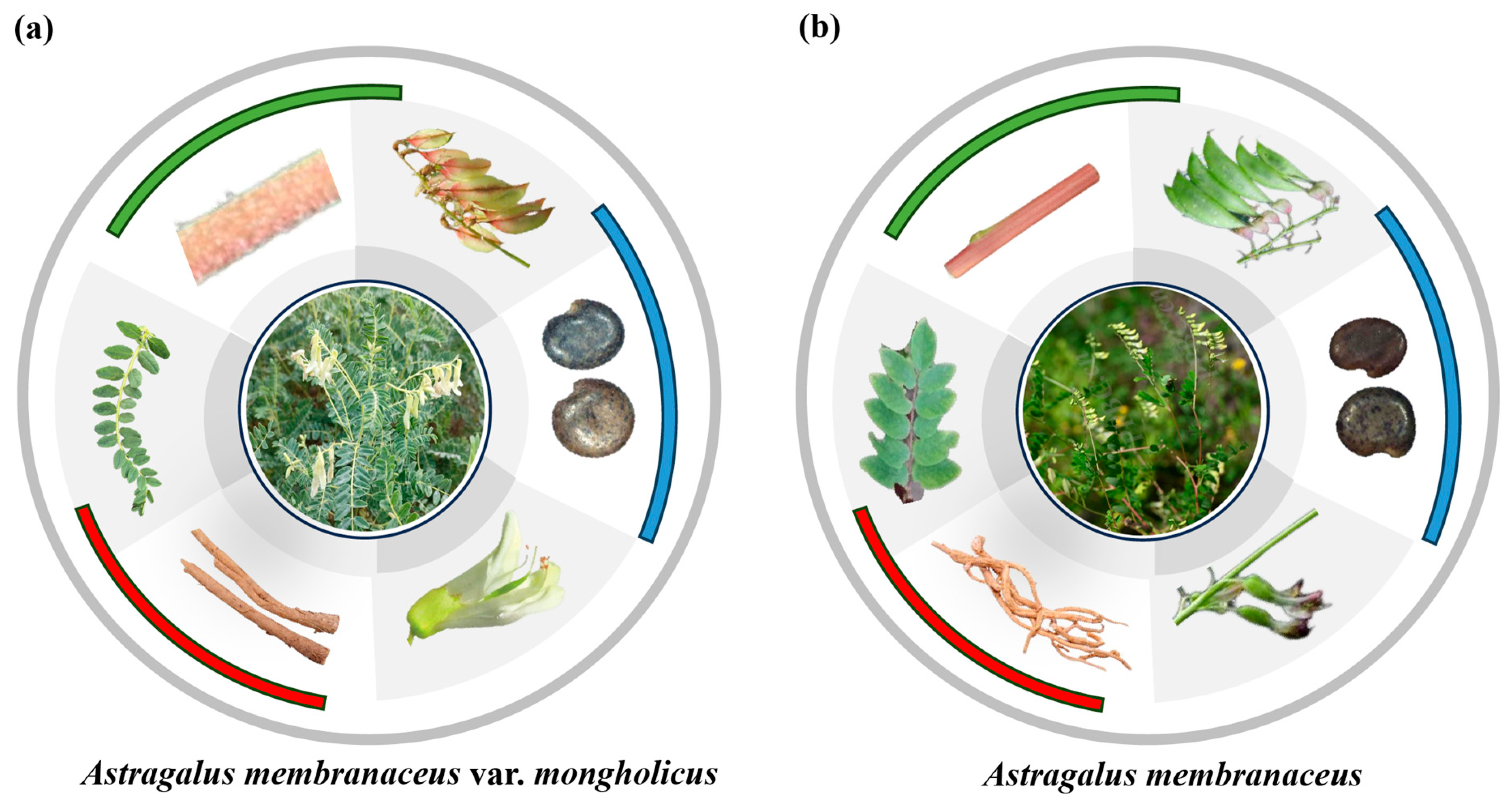
| Plant Morphology | Astragalus membranaceus | Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height | 50–100 cm | 40–80 cm | [54] |
| Stem | Upright stem and sparsely branched | Repent stem and much branched | [55] |
| Leaf | The number of leaves is small, generally 5–8 pairs, and the leaflets are long oval | The number of leaves is more, generally 9–11 pairs, and the leaflets are wide elliptic | [56] |
| Root | Most of them are chicken feet | Most of them are whiplash | [56] |
| Legume | There are bristles on the surface | The surface is setae-free | [57] |
| Seed | The seed umbilicus is heart-shaped with no obvious lines on the outer edge, and the germination pore is relatively wide | The seed umbilicus is oblong, the outer edge has obvious lines, and the germination pore is narrow | [48] |
| Flowering phase | July–August | May–June | [55] |
| Lavender flower variation | The variation rate is 50% | The variation rate is 59.3% | [58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, W.; Wang, H.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Guo, F. Germplasm Resources and Genetic Breeding of Huang-Qi (Astragali Radix): A Systematic Review. Biology 2024, 13, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080625
Dong P, Wang L, Chen Y, Wang L, Liang W, Wang H, Cheng J, Chen Y, Guo F. Germplasm Resources and Genetic Breeding of Huang-Qi (Astragali Radix): A Systematic Review. Biology. 2024; 13(8):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080625
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Pengbin, Lingjuan Wang, Yong Chen, Liyang Wang, Wei Liang, Hongyan Wang, Jiali Cheng, Yuan Chen, and Fengxia Guo. 2024. "Germplasm Resources and Genetic Breeding of Huang-Qi (Astragali Radix): A Systematic Review" Biology 13, no. 8: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080625
APA StyleDong, P., Wang, L., Chen, Y., Wang, L., Liang, W., Wang, H., Cheng, J., Chen, Y., & Guo, F. (2024). Germplasm Resources and Genetic Breeding of Huang-Qi (Astragali Radix): A Systematic Review. Biology, 13(8), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080625






