Utilizing Mixed Cultures of Microalgae to Up-Cycle and Remove Nutrients from Dairy Wastewater
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater and Dairy Wastewater Samples Used
2.2. Isolated and Identified Microalgae
2.3. Molecular Identification of Microalgae Isolated
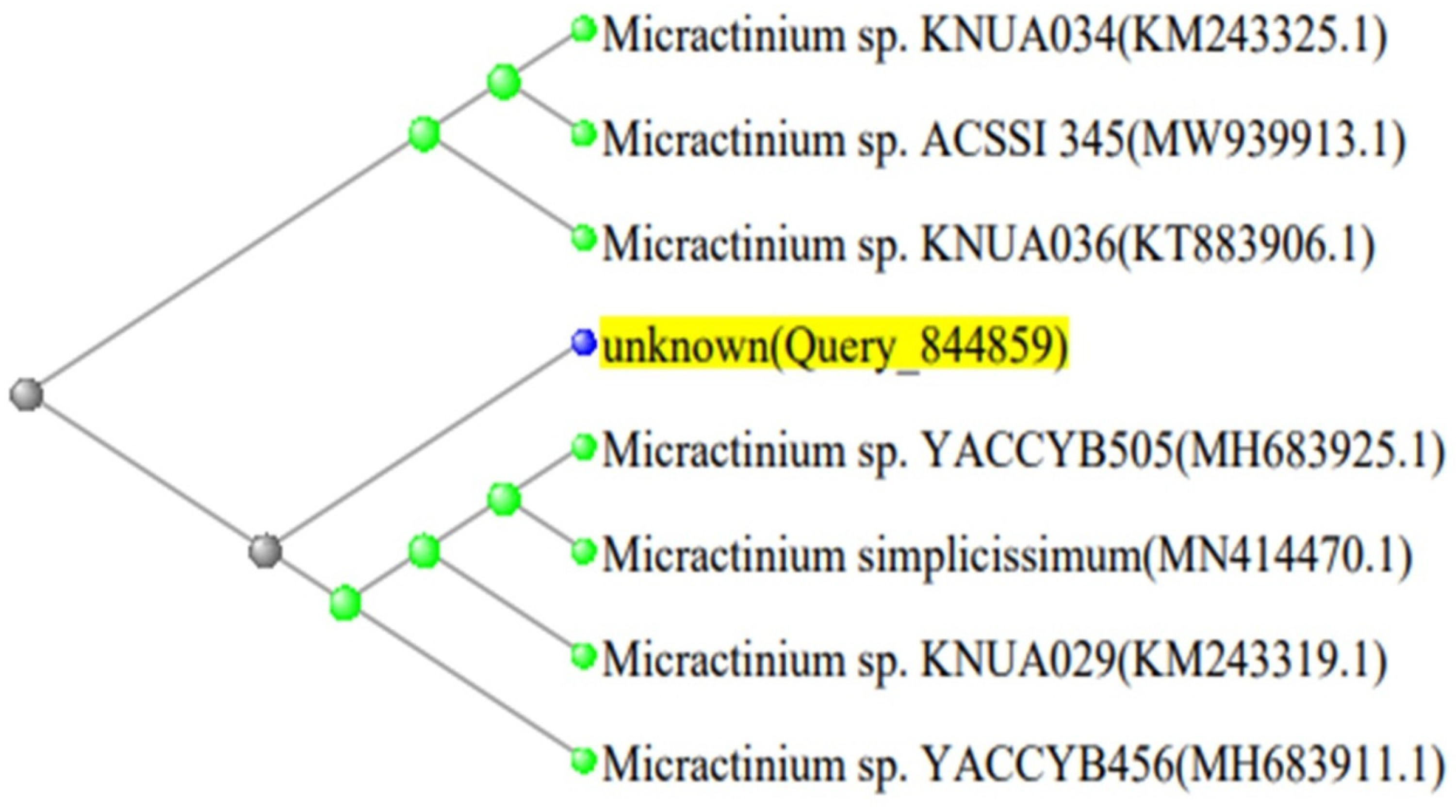
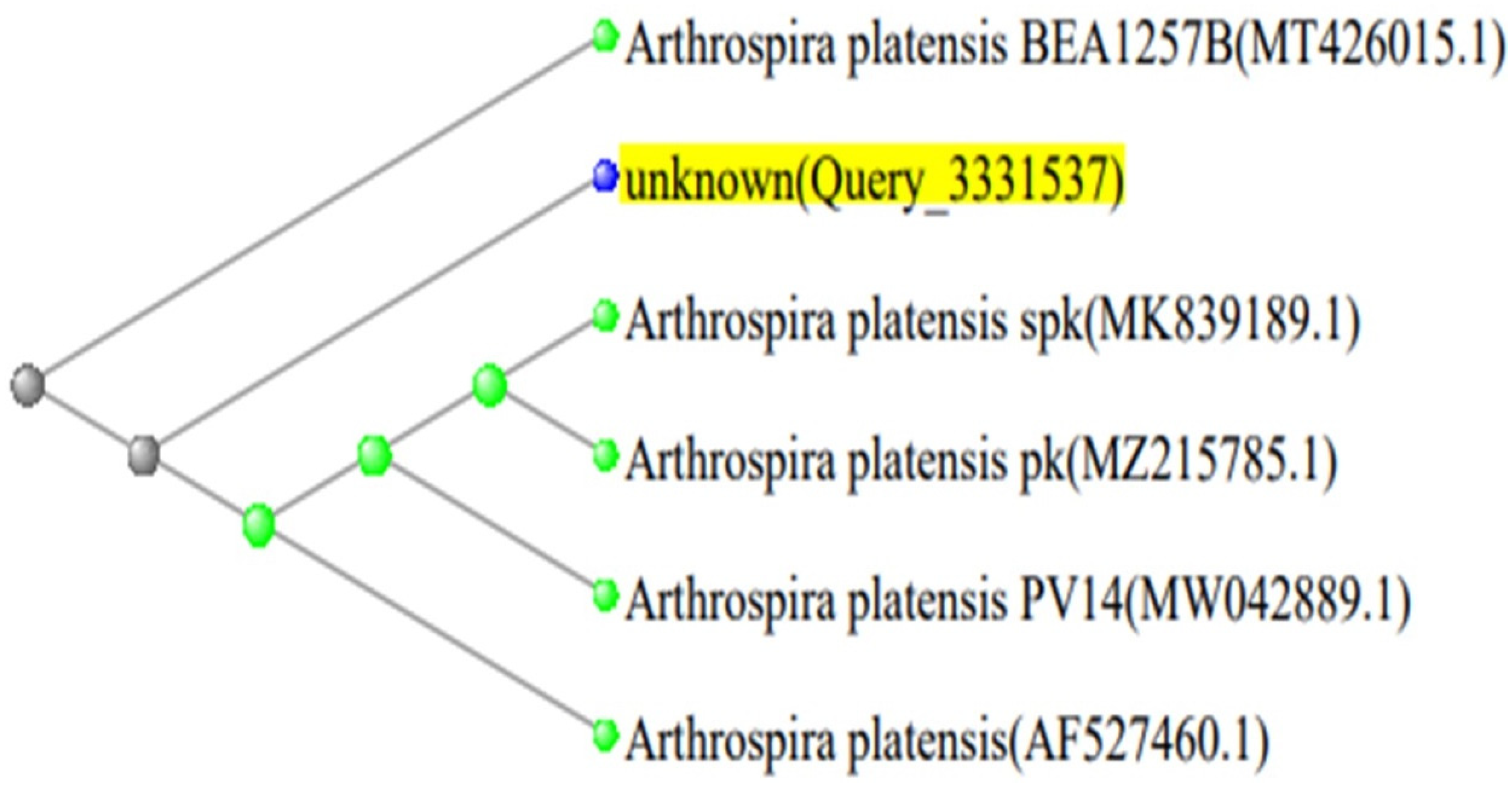
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Microalgae Cultivation in Real Dairy Wastewater
2.6. Determination of Parameters
2.7. Determination of Bacterial Indicator for the Presence of Pathogens
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
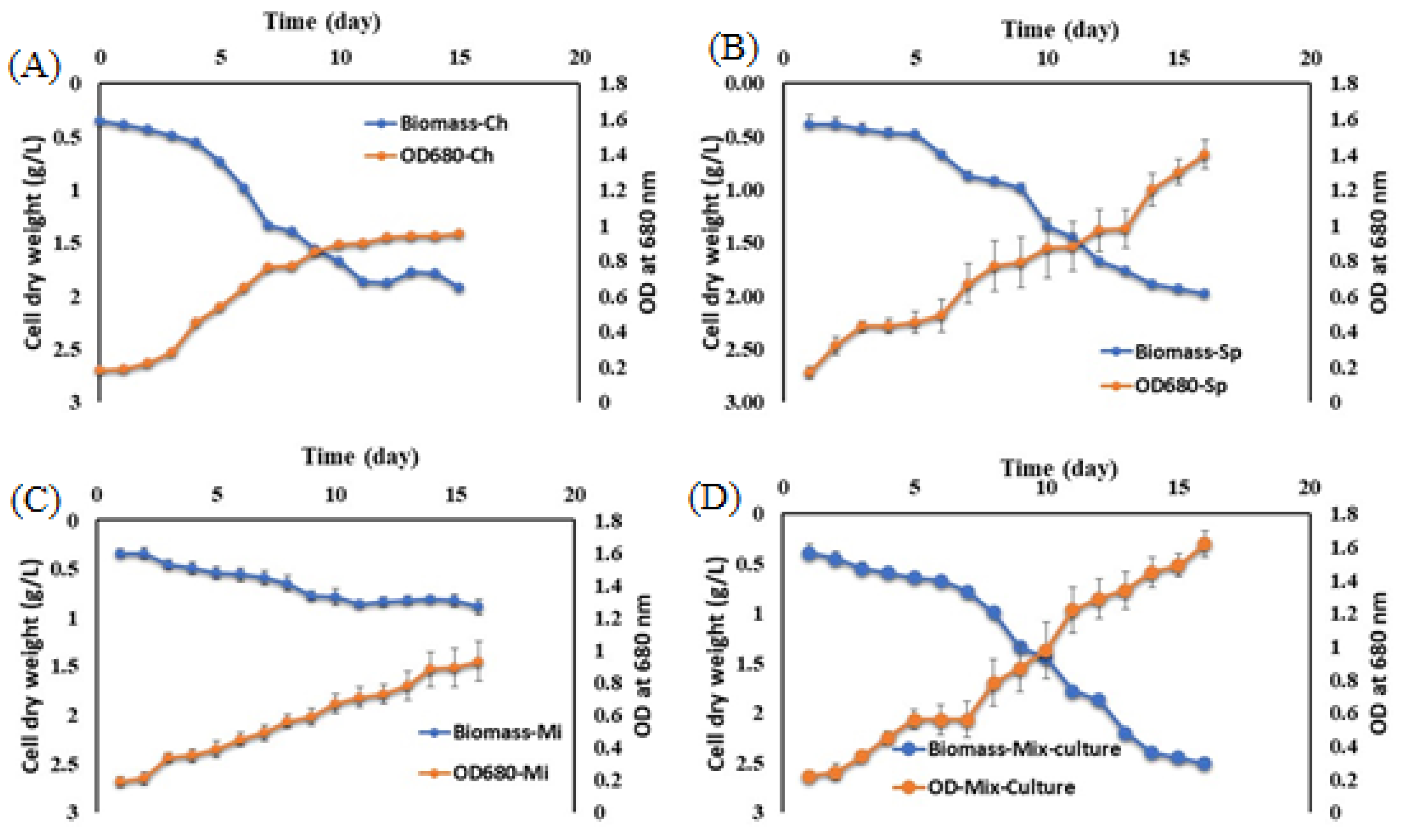
3.1. Cultivation of Microalgae in Real Dairy Wastewater
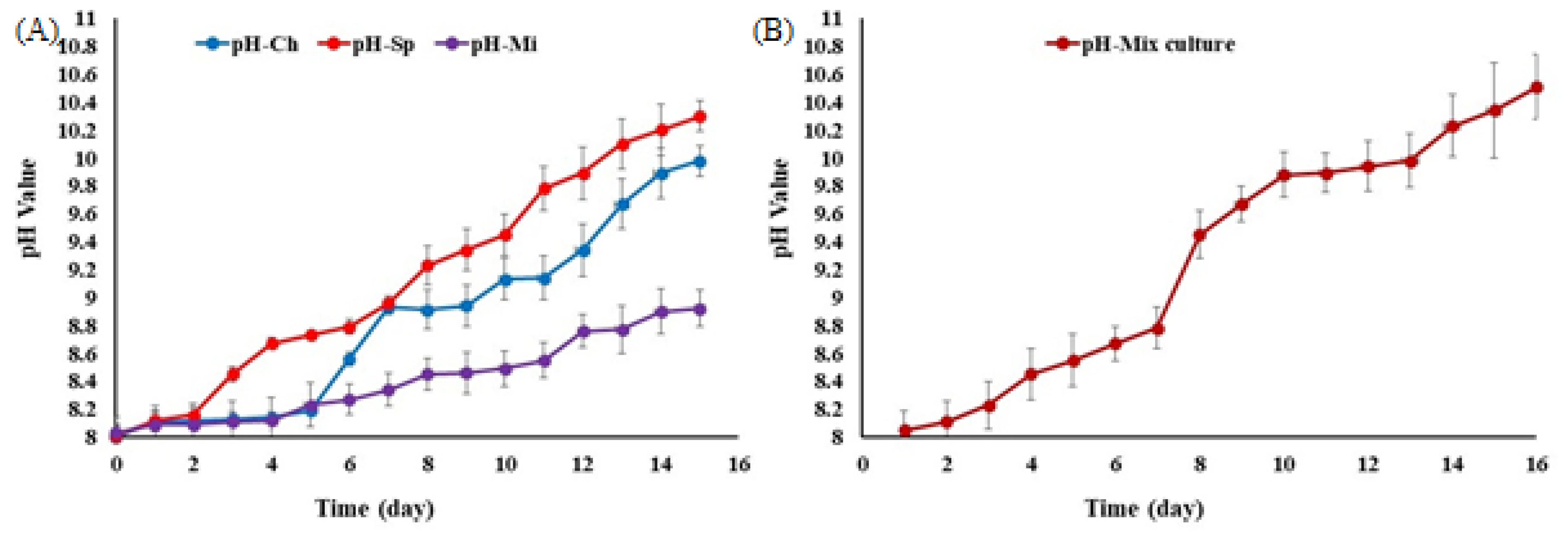
3.2. Effect of pH in Dairy Wastewater Effluent and Microalgae Biomass Production
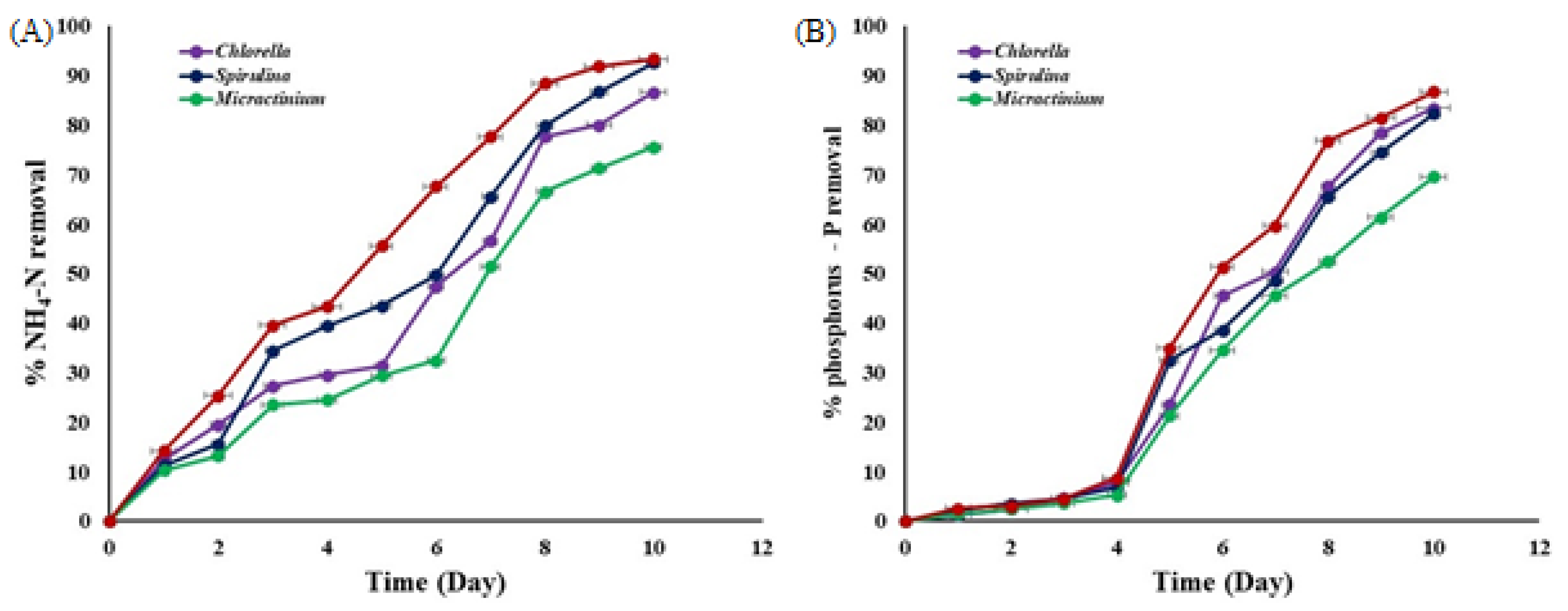
3.3. Nitrogen and Phosphorous Removal during Algae Cultivation
3.4. Microbial and Coliform Removal during Algal Cultivation
4. Discussion
4.1. Cultivation of Microalgae in Real Dairy Wastewater
4.2. Effect of pH in Dairy Wastewater Effluent and Microalgae Biomass Production
4.3. Nitrogen and Phosphorous Removal during Algae Cultivation
4.4. Microbial and Coliform Removal during Algal Cultivation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Díaz, V.; Leyva-Díaz, J.C.; Almécija, M.C.; Poyatos, J.M.; del Mar Muñío, M.; Martín-Pascual, J. Microalgae bioreactor for nutrient removal and resource recovery from wastewater in the paradigm of circular economy. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Z.-h.; Wu, G.; Zhan, X. Impact of total solids content on anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and food waste: Insights into shifting of the methanogenic pathway. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, S.; Manickam, P. Phycoremediation of industrial wastewater: Challenges and prospects. In Bioremediation for Environmental Sustainability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 99–123. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, P.A.S.; Vargas, J.V.; Mariano, A.B.; Severo, I.A. Phycoremediation: Role of microalgae in waste management and energy production. In Waste-to-Energy: Recent Developments and Future Perspectives towards Circular Economy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 511–537. [Google Scholar]
- Kusmayadi, A.; Huang, C.-Y.; Kit Leong, Y.; Lu, P.-H.; Yen, H.-W.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Integration of microalgae cultivation and anaerobic co-digestion with dairy wastewater to enhance bioenergy and biochemicals production. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mat Aron, N.S.; Khoo, K.S.; Chew, K.W.; Veeramuthu, A.; Chang, J.-S.; Show, P.L. Microalgae cultivation in wastewater and potential processing strategies using solvent and membrane separation technologies. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, Q.; Fang, F.; Luo, R.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, W.; Huo, S.; Cheng, P.; Liu, J.; Addy, M.; et al. Microalgae-based wastewater treatment for nutrients recovery: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raheem, A.; Prinsen, P.; Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Zhao, M.; Luque, R. A review on sustainable microalgae based biofuel and bioenergy production: Recent developments. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo-Mirquez, L.; Lopes, F.; Taidi, B.; Pareau, D. Nitrogen and phosphate removal from wastewater with a mixed microalgae and bacteria culture. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 11, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çakırlar, Ş.B. Integrated Nutrient Removal and Carbon Dioxide Sequestration by Using Mixed Microalgae Culture. Master’s Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Aditya, L.; Vu, H.P.; Johir, A.H.; Bennar, L.; Ralph, P.; Hoang, N.B.; Zdarta, J.; Nghiem, L.D. Nutrient Removal by Algae-Based Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2022, 8, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qv, M.; Dai, D.; Liu, D.; Wu, Q.; Tang, C.; Li, S.; Zhu, L. Towards advanced nutrient removal by microalgae-bacteria symbiosis system for wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 128574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.Y.; Patel, A.K.; Hong, M.E.; Chang, W.S.; Sim, S.J. Microalgae Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS): An emerging sustainable bioprocess for reduced CO2 emission and biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.L.; Weyers, S.L.; Goemann, H.M.; Peyton, B.M.; Gardner, R.D. Microalgae, soil and plants: A critical review of microalgae as renewable resources for agriculture. Algal Res. 2021, 54, 102200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshiba, G.J.; Kumar, P.S.; Femina, C.C.; Jayashree, E.; Racchana, R.; Sivanesan, S. Critical review on biological treatment strategies of dairy wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 160, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinna, F.; Buono, S.; Cabanelas, I.T.D.; Nascimento, I.A.; Sansone, G.; Barone, C.M.A. Wastewater treatment by microalgae can generate high quality biodiesel feedstock. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 18, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Huo, S.; Feng, F.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Cui, X.; Su, Y.; et al. Enhanced effects of symbiosis between Tribonema sp. and aerobic denitrifying phosphorus accumulating bacteria on wastewater treatment and greenhouse gas reduction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.-B.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Gong, H.; Jiang, T.; Liu, X.-P.; Liao, J.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-L. Growth of Scenedesmus obliquus in anaerobically digested swine wastewater from different cleaning processes for pollutants removal and biomass production. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parihar, R.K.; Bhandari, K.; Burnwal, P.K.; Ghosh, S.; Chaurasia, S.P.; Midda, M.O. Advancing dairy wastewater treatment: Exploring two-stage fluidized bed anaerobic membrane bioreactor for enhanced performance, fouling, and microbial community analysis. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.M.; Zimba, P.V. Minerals and Trace Elements in Microalgae. In Microalgae in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, M.; Nanda, M.; Bisht, B.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, A.; Vlaskin, M.S.; Chauhan, P.K.; Kumar, V. Heavy metal tolerance in microalgae: Detoxification mechanisms and applications. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 260, 106555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsenpour, S.F.; Hennige, S.; Willoughby, N.; Adeloye, A.; Gutierrez, T. Integrating micro-algae into wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, E.G.; Cristofoli, N.L.; Maia, I.B.; Magina, T.; Cerqueira, P.R.; Teixeira, M.R.; Varela, J.; Barreira, L.; Gouveia, L. Microalgal Systems for Wastewater Treatment: Technological Trends and Challenges towards Waste Recovery. Energies 2021, 14, 8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acién Fernández, F.G.; Gómez-Serrano, C.; Fernández-Sevilla, J.M. Recovery of Nutrients From Wastewaters Using Microalgae. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politano, A.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Alnajdi, S.; Alsaati, A.; Athanassiou, A.; Bar-Sadan, M.; Beni, A.N.; Campi, D.; Cupolillo, A.; D’Olimpio, G. 2024 roadmap on membrane desalination technology at the water-energy nexus. J. Phys. Energy 2024, 6, 021502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, E.; Calijuri, M.L.; Assemany, P. Biomass production in high rate ponds and hydrothermal liquefaction: Wastewater treatment and bioenergy integration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abinandan, S.; Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M. Nutrient removal and biomass production: Advances in microalgal biotechnology for wastewater treatment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 1244–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmayadi, A.; Lu, P.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Leong, Y.K.; Yen, H.-W.; Chang, J.-S. Integrating anaerobic digestion and microalgae cultivation for dairy wastewater treatment and potential biochemicals production from the harvested microalgal biomass. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.; Chandravanshi, P.; Chandravanshi, A.; Jaiswal, K. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on aquatic ecosystem. IOSR J. Agric. Veter. Sci. 2016, 9, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, A.; Ali, S.S.; Ramadan, H.; El-Aswar, E.I.; Eltawab, R.; Ho, S.-H.; Elsamahy, T.; Li, S.; El-Sheekh, M.M.; Schagerl, M. Microalgae-based wastewater treatment: Mechanisms, challenges, recent advances, and future prospects. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 13, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán-Rocha, J.C.; Guajardo-Barbosa, C.; Barceló-Quintal, I.D.; Reyna-Martínez, G.; Fariz-Salinas, E.; Ramírez-Castillo, A.; Rodríguez-Fuentes, H.; López-Chuken, U.J. Effect of natural increase of pH and microalgae cyclical re-cultivation on biomass production and polishing of municipal secondary effluent. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N. Different treatment techniques of dairy wastewater. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 14, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki Samani, M.S.; Mansouri, H. The novel strategy for enhancing growth and lipid accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris microalgae cultured in dairy wastewater by monochromatic LEDs and melatonin. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaji, M.; Hosseini, S.A.; Ghorbani, R.; Agh, N.; Rezaei, H.; Kornaros, M.; Koutra, E. Treatment of dairy wastewater by microalgae Chlorella vulgaris for biofuels production. Biomass Conver. Biorefinery 2021, 13, 3259–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmayadi, A.; Leong, Y.K.; Lu, P.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Yen, H.-W.; Chang, J.-S. Simultaneous nutrients removal and bio-compounds production by cultivating Chlorella sorokiniana SU-1 with unsterilized anaerobic digestate of dairy wastewater. Algal Res. 2022, 68, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein-Taylor, J.R. Handbook of Phycological Methods: Culture Methods and Growth Measurements; Stein, J.R., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1973; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, R.A. The microalgal cell. Handbook of Microalgal Culture: Applied Phycology and Biotechnology; Blackwell science: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Okoro, V.; Azimov, U.; Munoz, J.; Hernandez, H.H.; Phan, A.N. Microalgae cultivation and harvesting: Growth performance and use of flocculants—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 115, 109364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaw, Y.S.; Khong, N.M.H.; Shaharuddin, N.A.; Yusoff, F.M. A simple 18S rDNA approach for the identification of cultured eukaryotic microalgae with an emphasis on primers. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 172, 105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusmayadi, A.; Leong, Y.K.; Yen, H.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chang, J.-S. Microalgae as sustainable food and feed sources for animals and humans–Biotechnological and environmental aspects. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC. Officials Methods of Analysis, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Ge, T.; Chen, C.; O’Donnell, A.G.; Wu, J. Significant role for microbial autotrophy in the sequestration of soil carbon. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2328–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulbry, W.; Kondrad, S.; Buyer, J. Treatment of dairy and swine manure effluents using freshwater algae: Fatty acid content and composition of algal biomass at different manure loading rates. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajhaiya, A.; Mandotra, S.; Suseela, M.; Toppo, K.; Ranade, S. Algal biodiesel: The next generation biofuel for India. Asian J. Exp. Biol. Sci. 2010, 4, 728–739. [Google Scholar]
- Kothari, R.; Prasad, R.; Kumar, V.; Singh, D.P. Production of biodiesel from microalgae Chlamydomonas polypyrenoideum grown on dairy industry wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaji, M. Evaluation of fatty acid profiles of Chlorella Vulgaris microalgae grown in dairy wastewater for producing biofuel. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales Cruz, C.; Centeno da Rosa, A.P.; Strentzle, B.R.; Vieira Costa, J.A. Microalgae-based dairy effluent treatment coupled with the production of agricultural biostimulant. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 2881–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, V.C.; Velasquez-Orta, S.B.; Hernández-García, A.; Monje-Ramírez, I.; Orta-Ledesma, M.T. Kinetic modelling of microalgae cultivation for wastewater treatment and carbon dioxide sequestration. Algal Res. 2018, 32, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.; Ur Rehman, M.S.; Sadiq, M.; Mahmood, T.; Han, J.-I. Current status, issues and developments in microalgae derived biodiesel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 760–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, G.; Georgakakis, D. Cultivation of filamentous cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) in agro-industrial wastes and wastewaters: A review. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3389–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, G. Interactions between microalgae and microorganisms for wastewater remediation and biofuel production. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2019, 10, 3907–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Leng, S.; Chen, J.; Wei, L.; Peng, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Huang, H. Co-culture of fungi-microalgae consortium for wastewater treatment: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 125008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A.; Wan, C.; Tran, D.T.; Mofijur, M.; Ahmed, S.F.; Mehmood, M.A.; Shaik, F.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Xu, J. Microalgae binary culture for higher biomass production, nutrients recycling, and efficient harvesting: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Gunjyal, N.; Ojha, C.; Singh, R.P. Review of challenges for algae-based wastewater treatment: Strain selection, wastewater characteristics, abiotic, and biotic factors. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2021, 25, 03120004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.W.; Chia, S.R.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Tao, Y.; Chu, D.-T.; Show, P.L. Liquid biphasic flotation for the purification of C-phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis microalga. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iasimone, F.; Panico, A.; De Felice, V.; Fantasma, F.; Iorizzi, M.; Pirozzi, F. Effect of light intensity and nutrients supply on microalgae cultivated in urban wastewater: Biomass production, lipids accumulation and settleability characteristics. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattore, N.; Bellan, A.; Pedroletti, L.; Vitulo, N.; Morosinotto, T. Acclimation of photosynthesis and lipids biosynthesis to prolonged nitrogen and phosphorus limitation in Nannochloropsis gaditana. Algal Res. 2021, 58, 102368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.S.; Mohanty, K. Valorization of Chlorella thermophila biomass cultivated in dairy wastewater for biopesticide production against bacterial rice blight: A circular biorefinery approach. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.-J.; Lee, S.-M. Effects of microalgae on the removal of nutrients from wastewater: Various concentrations of Chlorella vulgaris. Environ. Eng. Res. 2012, 17, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Marchetti, J.M.; Wasewar, K.L. Enhancing nutrient removal, biomass production, and biochemical production by optimizing microalgae cultivation in a mixture of untreated and anaerobically digested dairy wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasauni, K.; Nailwal, T.K. Addressing the Strategies of Algal Biomass Production with Wastewater Treatment. In Phycoremediation Processes in Industrial Wastewater Treatment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Mofijur, M.; Parisa, T.A.; Islam, N.; Kusumo, F.; Inayat, A.; Badruddin, I.A.; Khan, T.Y.; Ong, H.C. Progress and challenges of contaminate removal from wastewater using microalgae biomass. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, H.A.; Muhamad, M.H.; Ji, B.; Nazairi, N.A.; Jiat, K.W.; Sim, S.I.S.W.A.; Poh, A.F.M.S. Revolutionizing wastewater treatment with microalgae: Unveiling resource recovery, mechanisms, challenges, and future possibilities. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 197, 107117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicker, R.J.; Kwon, E.; Khan, E.; Kumar, V.; Bhatnagar, A. The potential of mixed-species biofilms to address remaining challenges for economically-feasible microalgal biorefineries: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricolici, O.; Bumbac, C.; Patroescu, V.; Postolache, C. Dairy wastewater treatment using an activated sludge–microalgae system at different light intensities. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heubeck, S.; Craggs, R.J.; Shilton, A. Influence of CO2 scrubbing from biogas on the treatment performance of a high rate algal pond. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusten, B.; Sahu, A.K. Microalgae growth for nutrient recovery from sludge liquor and production of renewable bioenergy. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Chowdhury, R.; Tao, W.; Nedbalová, L. Microalga-mediated tertiary treatment of municipal wastewater: Removal of nutrients and pathogens. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayswaria, R.; Vijayan, J.; Nathan, V.K. Antimicrobial peptides derived from microalgae for combating antibiotic resistance: Current status and prospects. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2023, 41, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez-Moscoso, C.A.; Merlano, J.A.R.; Olivera Gálvez, A.; Volcan Almeida, D. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) from microalgae as an alternative to conventional antibiotics in aquaculture. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer | Sequencing (5–3′) | Primer Name | Position | Purity Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | CCTGGAAGGGGCGTATTTAT | Univ. contig,16S rRNA gene, RS_001101.5 | Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina platensis) | 98% |
| Reverse | CTTGGATGTGGTAGCCGTTT | |||
| Forward | CGACTAGCCAATGGAAGCAT | Univ. contig, 18S rRNA gene, GR_001142797.2 | Chlorella sp. Micractinium sp. | 98% |
| Reverse | GTACAAAGGGCAGGGACGTA |
| Description | Query Cover | Strain | Identity % | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorella sp. KAS007 gene for 18S rRNA gene. | 100% | Chlorella sp. | 100.00 | AB176665.1 |
| Chlorella sp. TNBR1 18S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | 99.94 | KR869729.1 | |
| Chlorella sp. KAS012 gene for 18S rRNA gene. | 100% | 99.94 | AB176666.1 | |
| Chlorella sp. KAS001 gene for 18s rRNA gene. | 100% | 99.94 | AB176663.1 | |
| Chlorella sp. WT1 18S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | 99.88 | KX109776.1 | |
| Chlorella vulgaris isolate BEA 0046B small subunit ribosomal RNA gene and internal transcribed spacer 1. | 100% | 99.88 | ON146468.1 | |
| Chlorella sp. KMMCC C-137 18S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | 99.88 | GQ122349.1 |
| Description | Query Cover | Strain | Identity % | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micractinium sp. YACCYB505 18S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | Micractinium sp. | 100.00 | MH683925.1 |
| Micractinium sp. KNUA029 18S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | 100.00 | KM243319.1 | |
| Micractinium sp. YACCYB456 18S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | 99.94 | MH683911.1 | |
| Micractinium sp. KNUA034 18S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | 99.94 | KM243325.1 | |
| Micractinium sp. KNUA036 18S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | 99.88 | KT883906.1 |
| Description | Query Cover | Stain | Identity % | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arthrospira platensis spk 16S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | Arthrospira platensis | 100.00 | MK839189.1 |
| Arthrospira platensis pk 16S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | Arthrospira platensis | 100.00 | MZ215785.1 |
| Arthrospira platensis PV14 16S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | Arthrospira platensis | 100.00 | MW042889.1 |
| Spirulina platensis 16S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | Spirulina platensis | 100.00 | AF527460.1 |
| Arthrospira platensis BEA1257B 16S ribosomal RNA gene. | 100% | Arthrospira platensis | 99.48 | MT426015.1 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| COD | 1180 ± 0.78 mg/L |
| pH | 8.11 ± 0.14 |
| EC | 450.59 ± 0.57 mS/m |
| Nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) | 19.45 ± 0.47 mg/L |
| Phosphate phosphorus (PO43−-P) | 3.83 ± 0.56 mg/L |
| Total alkalinity | 308.67 ± 0.87 mg/L as CaCO3 |
| TBC | 6.74 ± 0.45 Log10 CFU/mL |
| Total coliform | 17.56 ± 0.35 MPN/100 m |
| Escherichia coli | 15.67± MPN/100 mL |
| Elements | Amount (g/L) | Elements | Amount (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NaNO3 | 1.5 | H3BO3 | 2.8 × 10−3 |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 0.075 | MnCl2·4H2O | 1.8 × 10−3 |
| K2HPO4 | 0.04 | Na2MoO4·2H2O | 3.9 × 10−4 |
| CaCl2 | 0.036 | ZnSO4·7H2O | 2.2 × 10−4 |
| Na2CO3 | 0.02 | CuSO4·5H2O | 7.9 × 10−5 |
| Citric acid | 0.006 | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | 4.9 × 10−5 |
| Ferric (ammonium) citrate | 0.006 | EDTA·2Na | 0.001 |
| Time (day) | Chlorella | Spirulina | Micractinium | Mixed Cultures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 5.84 ± 0.19 j | 5.53 ± 0.12 k | 3.93 ± 0.43 lm | 6.17 ± 0.58 k |
| 2 | 6.15 ± 0.41 j | 5.71 ± 0.26 k | 4.85 ± 0.51 l | 7.79 ± 0.62 k |
| 3 | 10.12 ± 0.35 i | 6.78 ± 0.24 k | 5.69 ± 0.45 l | 12.15 ± 0.86 j |
| 4 | 12.31 ± 0.33 h | 9.66 ± 0.32 j | 8.81 ± 0.50 k | 14.15 ± 0.89 i |
| 5 | 25.11 ± 0.24 g | 17.78 ± 0.13 h | 14.61 ± 0.20 j | 26.64 ± 0.90 h |
| 6 | 45.61 ± 0.12 f | 51.56 ± 0.15 g | 46.53 ± 0.21 i | 52.39 ± 0.25 g |
| 7 | 73.81 ± 0.12 e | 70.78 ± 0.14 f | 54.54 ± 0.22 h | 78.72 ± 0.44 f |
| 8 | 81.62 ± 0.22 d | 74.67 ± 0.23 be | 63.61 ± 0.21 g | 83.71 ± 0.54 e |
| 9 | 83.51 ± 0.14 c | 77.67 ± 0.21 d | 68.18 ± 0.23 f | 86.48 ± 0.56 d |
| 10 | 86.54 ± 0.16 bc | 78.95 ± 0.17 d | 74.38 ± 0.19 e | 89.37 ± 0.63 c |
| 15 | 87.17 ± 0.13 bc | 81.91 ± 0.19 c | 79.55 ± 0.13 d | 90.27 ± 0.44 c |
| 20 | 89.18 ± 0.13 b | 82.33 ± 0.15 c | 81.57 ± 0.16 c | 93.47 ± 0.19 b |
| 25 | 91.71 ± 0.12 b | 84.65 ± 0.19 b | 87.23 ± 0.27 b | 94.11 ± 0.24 b |
| 30 | 93.51 ± 0.16 a | 87.83 ± 0.18 a | 90.34 ± 0.23 a | 94.41 ± 0.21 b |
| 35 | 94.15 ± 0.14 a | 88.55 ± 0.14 a | 91.47 ± 0.21 a | 96.14 ± 0.22 a |
| 40 | 95.16 ± 0.18 a | 88.33 ± 0.21 a | 91.11 ± 0.22 a | 97.21 ± 0.43 a |
| Time (day) | Chlorella | Spirulina | Micractinium | Mixed Cultures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 2.34 ± 0.13 i | 4.53 ± 0.12 h | 3.53 ± 0.23 h | 5.47 ± 0.18 g |
| 2 | 3.45 ± 0.11 h | 5.71 ± 0.16 g | 3.85 ± 0.21 h | 6.73 ± 0.12 g |
| 3 | 5.65 ± 0.12 g | 6.78 ± 0.14 g | 4.65 ± 0.15 g | 8.65 ± 0.16 f |
| 4 | 8.36 ± 0.23 f | 5.66 ± 0.12 g | 4.86 ± 0.21 h | 8.94 ± 0.14 f |
| 5 | 9.31 ± 0.14 f | 7.78 ± 0.13 f | 5.67 ± 0.27 g | 9.64 ± 0.10 f |
| 6 | 56.67 ± 0.16 e | 51.56 ± 0.15 e | 43.53 ± 0.26 e | 59.34 ± 0.15 e |
| 7 | 78.84 ± 0.15 d | 77.78 ± 0.14 d | 55.56 ± 0.12 d | 83.79 ± 0.14 d |
| 8 | 89.67 ± 0.12 c | 86.67 ± 0.13 bc | 66.67 ± 0.11 c | 89.69 ± 0.24 c |
| 9 | 95.56 ± 0.13 b | 88.67 ± 0.11 b | 69.58 ± 0.13 c | 96.68 ± 0.16 b |
| 10 | 94.56 ± 0.11 b | 89.9 ± 0.07 b | 73.78 ± 0.17 c | 95.87 ± 0.33 b |
| 15 | 94.87 ± 0.17 b | 89.97 ± 0.09 b | 88.45 ± 0.15 bc | 95.67 ± 0.14 b |
| 20 | 94.98 ± 0.17 b | 90.34 ± 0.11 ab | 89.67 ± 0.12 bc | 97.45 ± 0.13 ab |
| 25 | 95.78 ± 0.15 b | 90.67 ± 0.18 ab | 90.23 ± 0.27 ab | 97.34 ± 0.14 ab |
| 30 | 96.56 ± 0.13 ab | 90.88 ± 0.15 ab | 91.34 ± 0.23 ab | 97.45 ± 0.11 a |
| 35 | 97.45 ± 0.19 a | 93.56 ± 0.12 a | 92.47 ± 0.21 a | 98.12 ± 0.12 a |
| 40 | 97.56 ± 0.12 a | 94.34 ± 0.23 a | 93.11 ± 0.22 a | 98.23 ± 0.23 a |
| Time (day) | Chlorella | Spirulina | Micractinium | Mixed Cultures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1.31 ± 0.33 l | 1.58 ± 0.42 j | 1.51 ± 0.53 j | 3.31 ± 0.16 m |
| 2 | 1.41 ± 0.31 l | 1.76 ± 0.56 j | 1.45 ± 0.41 j | 7.78 ± 0.22 gl |
| 3 | 1.64 ± 0.22 l | 1.73 ± 0.24 j | 1.75 ± 0.35 j | 10.51 ± 0.46 f |
| 4 | 2.37 ± 0.53 k | 1.62 ± 0.32 j | 1.83 ± 0.61 j | 18.18 ± 0.54 k |
| 5 | 7.32 ± 0.24 j | 1.78 ± 0.33 j | 1.69 ± 0.37 j | 29.44 ± 0.60 j |
| 6 | 17.69 ± 0.26 i | 14.53 ± 0.55 i | 13.53 ± 0.21 i | 41.75 ± 0.85 i |
| 7 | 28.86 ± 0.25 h | 17.73 ± 0.24 h | 15.66 ± 0.22 h | 53.79 ± 0.16 h |
| 8 | 55.17 ± 0.22 g | 46.91 ± 0.23 g | 46.69 ± 0.31 g | 69.69 ± 0.22 g |
| 9 | 67.53 ± 0.23 f | 58.67 ± 0.31 f | 55.51 ± 0.33 f | 76.34 ± 0.36 f |
| 10 | 77.56 ± 0.21 de | 71.49 ± 0.17 e | 70.18 ± 0.27 e | 85.17 ± 0.43 e |
| 15 | 79.87 ± 0.27 d | 79.17 ± 0.39 d | 71.15 ± 0.19 e | 88.76 ± 0.24 cd |
| 20 | 89.91 ± 0.27 c | 83.31 ± 0.31 c | 79.17 ± 0.18 d | 91.75 ± 0.33 c |
| 25 | 91.71 ± 0.25 c | 88.64 ± 0.28 b | 85.21 ± 0.23 c | 95.97 ± 0.44 b |
| 30 | 94.55 ± 0.23 b | 89.83 ± 0.25 b | 88.35 ± 0.24 b | 96.96 ± 0.51 a |
| 35 | 95.34 ± 0.13 b | 91.51 ± 0.32 a | 90.48 ± 0.24 a | 97.95 ± 0.32 a |
| 40 | 98.59 ± 0.11 a | 92.31 ± 0.13 a | 91.19 ± 0.21 a | 97.81 ± 0.63 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hajri, A.K.; Alsharif, I.; Albalawi, M.A.; Alshareef, S.A.; Albalawi, R.K.; Jamoussi, B. Utilizing Mixed Cultures of Microalgae to Up-Cycle and Remove Nutrients from Dairy Wastewater. Biology 2024, 13, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080591
Hajri AK, Alsharif I, Albalawi MA, Alshareef SA, Albalawi RK, Jamoussi B. Utilizing Mixed Cultures of Microalgae to Up-Cycle and Remove Nutrients from Dairy Wastewater. Biology. 2024; 13(8):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080591
Chicago/Turabian StyleHajri, Amira K., Ifat Alsharif, Marzough A. Albalawi, Shareefa A. Alshareef, Raghad K. Albalawi, and Bassem Jamoussi. 2024. "Utilizing Mixed Cultures of Microalgae to Up-Cycle and Remove Nutrients from Dairy Wastewater" Biology 13, no. 8: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080591
APA StyleHajri, A. K., Alsharif, I., Albalawi, M. A., Alshareef, S. A., Albalawi, R. K., & Jamoussi, B. (2024). Utilizing Mixed Cultures of Microalgae to Up-Cycle and Remove Nutrients from Dairy Wastewater. Biology, 13(8), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080591







