Simple Summary
A bibliometric analysis of studies on the topic of earthworm in the soil ecosystem was conducted to reveal the research advances and trends in the field. The ecological effects of earthworms, the impact of agricultural activities on earthworms, earthworm ecotoxicology and earthworm invasion were four research hotspots on the topic and “impact”, ‘’biodiversity”, “oxidative stress”, “diversity”, “response”, “Eisenia fetida” and “exposure” have been the emerging active topics.
Abstract
The earthworm, as a soil engineer, plays highly important roles in the soil ecosystem for shaping soil structure, promoting soil fertility, regulating microbial community composition and activities and decomposing soil pollutants. However, the research progresses on this important soil fauna have rarely been reviewed so far. Therefore, we conducted a bibliometric analysis of the literature published during 1900–2022, which was collected from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoS). The results showed that three periods (1900–1990, 1991–2005 and 2006–2022) could be identified in terms of the intensity of publications on the topic, and the number of publications kept increasing since 2006. The United States produced the highest publication record at the country scale, whereas Chinese Academy of Sciences was the most productive institution. Chinese institutions and authors played an active and prominent role during 2018–2022. Soil Biology & Biochemistry was the most popular journal for the topic-related research. In these publications, Professor Lavelle P was the most influential author. Based on a citation network of the top 50 cited papers, four hotspots were identified, i.e., the ecological effects of earthworms, the impact of agricultural activities on earthworms, earthworm ecotoxicology and earthworm invasion. Moreover, “impact”, “biodiversity”, “oxidative stress”, “diversity”, “response”, “Eisenia fetida” and “exposure” were the emerging and active topics in recent years. This study can help us to better understand the relevant subject categories, journals, countries, institutions, authors and articles and identify the research hotspots and emerging trends in the field of soil earthworm research.
1. Introduction
Soil is a vital component of the terrestrial ecosystem, as the pedosphere intersect with the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere and lithosphere, and supports human health, food security and the agricultural economy [1]. However, global soil health is facing threat from soil acidification, salinization, climate change and large amounts of toxic substances, such as heavy metals and pesticides [2], which further affects the sustainable development of agriculture and food security. With accelerated urbanization and industrialization, for instance, soil heavy metal pollution becomes more and more severe and widespread [3], which changes the soil microbial community [4], affects crop growth [5], harms the agricultural environment [6] and consequently threatens the health of humans [7]. Soil acidification is a serious global environment problem in agriculture production [8] and the acidified soil area continues to expand due to the massive discharge of acid-causing substances [9], irrational use of chemical fertilizers [10] and intensive agricultural production [11]. These serious pollutions alter soil physicochemical properties and quality, limit nutrient supplies to plants, affect microbial community structure and interactively alter the biological activities and metabolic process of soil animals.
Earthworms, as the ecosystem engineer, are one of the most important soil fauna in terrestrial ecosystems [12]. As estimated, there are more than 4000 species of earthworms that belong to 12 families and 181 genera [13], which could be divided into three ecological types, i.e., epigeic, endogeic and anecic, according to the feeding habits and ecological functions [12]. They can modify soil structure and fertility, enhance soil organic matter content, speed up nutrient cycling, promote plant growth and improve soil properties by means of swallowing, digesting, excreting and burrowing in their habitats. Earthworm cast increases the aggregate stability and proportion of macroaggregates, likely due to the cementation of soil aggregates by high Ca in the soil [14,15]. The mucus secretion by earthworms’ guts is also beneficial for the formation of macroaggregates [16,17]. Christopher et al. showed that earthworms improved soil moisture and fertility and enhanced soil porosity to promote plant biomass by swallowing, excreting and burrowing [18]. The contents of total soil N and organic carbon were increased because of the decomposition and transformation of leaf litter by earthworms, thereby plants and microorganisms could obtain nutrients more easily [19]. Gong et al. [20] and Chen et al. [21] pointed out that earthworms affected the soil buffering capacity through changing soil aggregates and pH values and regulating the composition of the soil microbial community. Vermicompost has a high acid buffering capacity and therefore can improve the ability of soil to resist effects of exogenous acids [22,23]. Moreover, earthworms can work collaboratively with other soil organisms to promote ecosystem services. Compared with control without earthworms, the burrows of earthworms are beneficial for increasing the abundance, diversity and activity of the soil microbial community and consequently accelerating the decomposition of soil organic matter [24,25]. Therefore, it is of great significance to protect and utilize earthworms for improving soil environment and agriculture sustainable development.
In 1881, Charles Darwin highlighted the importance of earthworms and proposed that earthworms were highly important for soil formation and development. In spite of the high importance of earthworms, however, there are few reviews to completely outline the research advances in this field, leaving us unaware of the latest research hotspots and emerging topics. The existing literature often highlights a certain topic at a limited time scale. For instance, Lemtiri et al. [26] focused on the impacts of earthworms on soil components and dynamics, and Xiang et al. [27] analyzed the earthworm research worldwide from 2000 to 2015. In this study, we made a comprehensive summary of research on the topic of earthworms in the soil ecosystem from 1900 to 2022 by using CiteSpace and HitsCite software for bibliometric analyses. We mainly aimed to address three questions as follows: (1) Which subjects were the most popular areas in earthworm studies? (2) Which countries, institutions and authors made the greatest contribution to this field, and how about the collaboration network? (3) What are the emerging hotspots in soil and earthworm research?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Collection
In this study, we collected literature in the database of Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection, which covered Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-E) and Social Science Citation Index (SSCI). A topic search of “soil” and “earthworm” from the title, abstract, keywords and keyword plus of publications was conducted on 18 October 2022 to collect literature in the timespan from 1900 to 2022. Finally, 8674 records, including articles, proceeding papers, reviews, editorial materials and letters, were obtained and a text-based file of literature information was output from the WoS database for further bibliometric analyses.
2.2. Data Process and Analysis
We firstly analyzed the temporal trend of records during the whole investigation period and basic information including writing language and distribution of authors, institutes, countries or journals to know the development history and contribution of researchers, institutes and countries, as well as journals that had majorly published the topic-related work.
Furthermore, the collected data were imported into CiteSpace (version 5.2.R2), a popular bibliometric software that could help us to visualize the structural and temporal patterns or development trends in a given scientific field during a given investigation period [28]. It is often used to analyze the network structures of main countries, institutions or authors and bursting terms on the basis of keywords, countries, institutions or authors. Since the number of publications was intermittent and scarce before 1980, we set up the time slicing of 1980–2022 and years per slice = 1 year for further analyses. The top 20 most cited or occurring items were selected from each slice in order to obtain the most prominent items. “Pathfinder” and “pruning the merged network” were chosen for pruning. Other parameters were set up as default.
In the analyses of network structure, the centrality of the node that reflected the importance of a node was calculated on the basis of the percentage of shortest paths in the network for a given node [28]. For co-occurrence analysis of terms, the log-likelihood ratio (LLR) was calculated to cluster the highly related terms during the period [29], with the label size representing the number of terms in each cluster. We could consider that the results of the cluster were reliable and reasonable when the silhouette index was greater than 0.5 [30]. In burst detection analysis, the length of the whole line presented the research period (1980–2022) and the red part indicated the burst period of an emerging hotspot in a specific period.
Subsequently, HistCite (Pro 2.1), a citation analysis software that could be used to analyze the history of the citation of a publication and therefore underline highly important publications in a specific period [31], was utilized to examine the prominent authors and citation relationship of the top 50 most cited records. Local citation score (LCS) and global citation score (GCS) were employed to indicate the academic impact of these publications. The former represented the citation number of a given literature by other publications in the same research field, while the latter represented the total citation number in the whole WoS database, regardless of the research fields of citations [32]. Lastly, total local citation score (TLCS) was adopted to rank the publications and authors. The current status of development and hotspots in the earthworm-related research field were determined through analyzing the citation network of highly cited papers [33].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temporal Trend of Publication
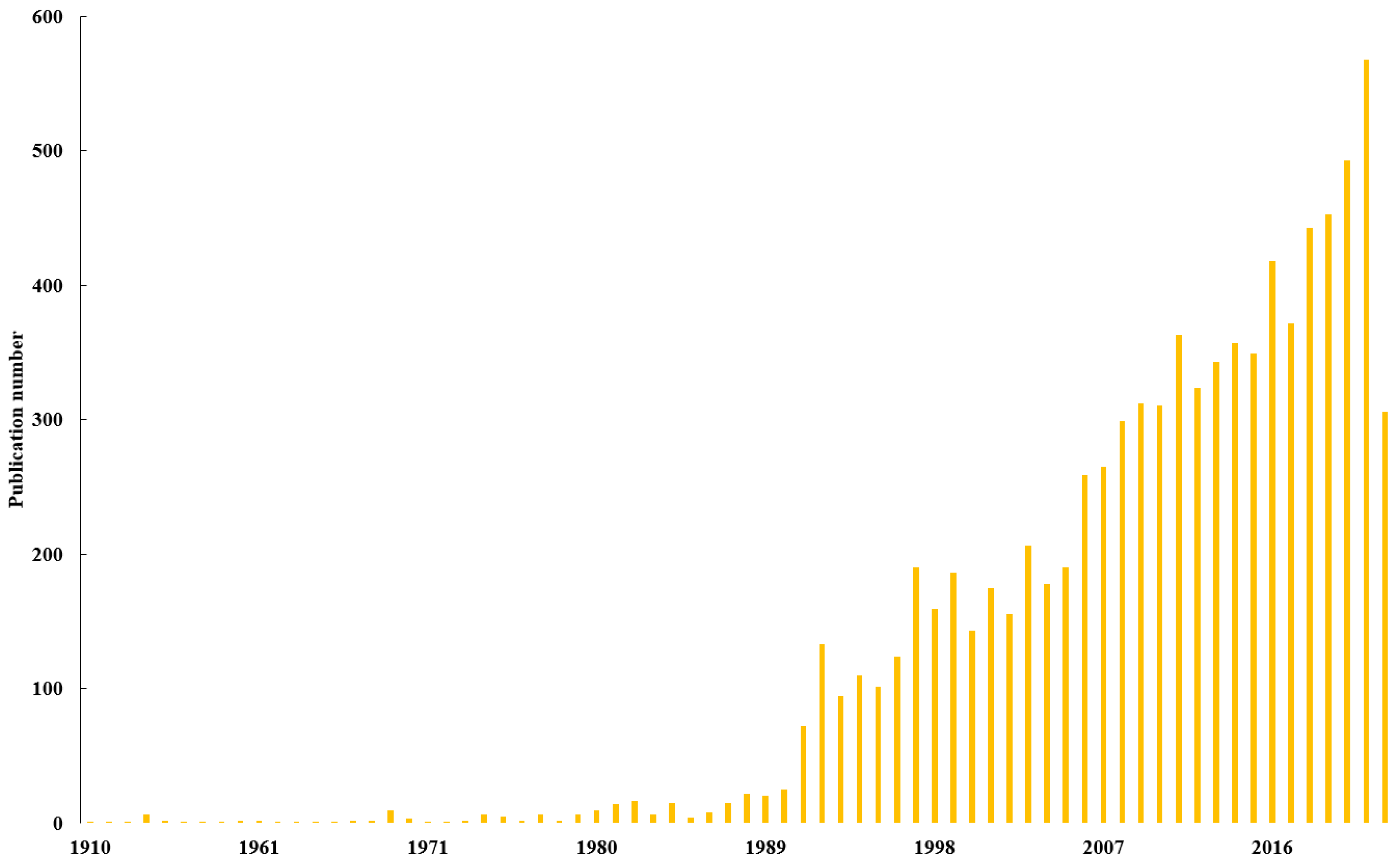
The year-scale number of publications indicates the level of researchers’ interest in a given topic. As shown in this study (Figure 1), the number of publications kept increasing during the investigation period, which could be roughly divided into three stages (i.e., periods of 1900–1990, 1991–2005 and 2006–2022).
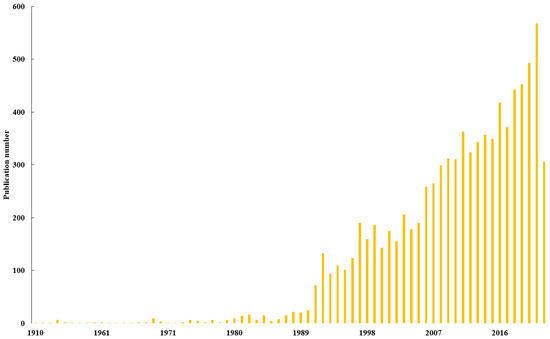
Figure 1.
Annual publication related to earthworm research collected in WoS from 1900 to 2022.
There were relatively few publications in the first period of 1900–1990. Despite that its high importance had been proposed by Darwin in 1881, earthworms did not draw much attention in the following 90 years, during which a total of 223 publications were published (on average 2.48 per year). In the earliest stage, researchers focused on the role of earthworms in shaping soil structure and fertility [34,35,36,37], and the publication record was extremely low and relatively constant. The first increase was observed in 1981, since the European Economic Community and Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development recommended earthworm as a bioindicator for the risk assessment of toxic substances in terrestrial environments in 1981 and 1984, respectively [38]. Then, researchers started to investigate the effect of chemicals on the ecotoxicology of earthworms [39,40] and were interested in their interactions with other soil organisms, such as nematodes and microorganisms [41,42].
The second stage was from 1991 to 2005, during which increasing attention was paid toward earthworm studies and the annual publication number obviously increased to range from 72 to 206. In this stage, several international symposiums with topics on earthworm ecotoxicology, soil animal science and earthworm ecology were held to encourage ecological risk assessment studies and revealed the potential of earthworms to remediate soil pollutants and improve soil quality by investigating the response of earthworms to environmental pollutants [38,43]. Related researches reported that the diversity, total number and biomass of earthworms greatly depend on the distance between the earthworms and source of heavy metals [44]. Moreover, different species of earthworms exhibited varying degrees of avoidance to heavy metal contamination due to their behavioral and ecological characteristics; for example, endogeic earthworms (A. tuberculate) were more sensitive to Cu and Zn contamination in the soil than epigeic earthworms (L. rubellus) [45]. In addition, numerous European earthworms were anthropogenically introduced to North America in this period, e.g., associated with alien plants and used as fishing bait [46,47], making the invasion of exotic earthworms to be a newly emerging research hotspot [48,49,50].
The last period ranged from 2006 to 2022 (the end point of literature searching). In this period, the number of publications increased exponentially, with more than 200 papers published every year, and numerous studies started to focus on the effects of earthworm invasion on soil structure, native soil food webs and nutrient availability, which explains the increase in the number of publications after 2006 [51,52,53]. This indicates that earthworm-related research topics constituted a bursting hotspot since then. In 2016, Earthworm Society of Britain proposed to designate 21 October of each year as the World Earthworm Day to announce the ecological value of earthworms and meanwhile commemorate Darwin as the pioneer of earthworm studies.
3.2. Document Types, Languages, Subject Categories and Journal Analysis
Research articles represented the majority (89.49%) of the total records in the WoS database, followed by proceeding papers (5.86%) and review papers (4.15%, Figure S1). The literatures were published in nine languages, with English being the most prevalent language, accounting for 97.71% of the records.
The publications covered 131 subject categories, with the top 10 categories being presented in Table 1. “Environmental Science” was the most popular subject category, with 37.51% of all the publications. The second was “Soil Science” (33.87%), followed by “Ecology” (17.82%). In WoS, 1013 journals were found to publish earthworm-related papers, and the top 10 journals are listed in Table 2. The most productive journal was Soil Biology & Biochemistry, with 612 records that accounted for 7.06% of the total. The following journals included Applied Soil Ecology, Pedobiologia, Environmental Pollution, Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety and Chemosphere, which comprised 5.72%, 4.65%, 3.47%, 3.39% and 3.38% of the total publications, respectively. The top 10 journals were categoried to Environment Science, Soil Science, Ecology, Soil Zoology and Ecotoxicology, a pattern consistent with the result of subject categories.

Table 1.
Top 10 subject categories and journals on earthworm-related research collected in WoS.

Table 2.
Top 10 records and centrality based on the published papers related to earthworm research by countries/regions collected in WoS.
3.3. Countries-, Institutions- and Authors-Based Outputs and Collaborations
3.3.1. Countries-Based Outputs and Collaborations Analysis
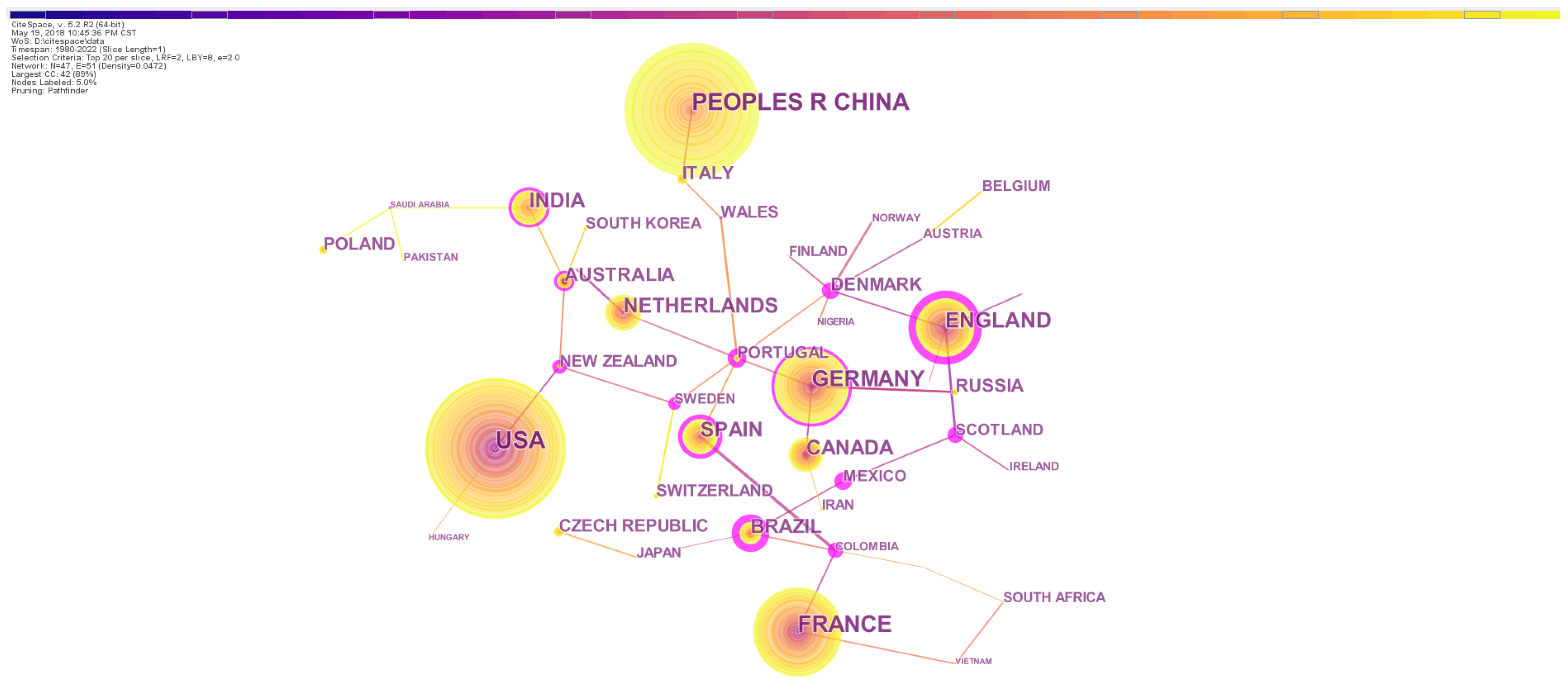
The countries-based statistics of publication can indicate the level of research activity of countries. The top 10 countries of publication records were the United States, China, France, Germany, England, Netherlands, Spain, India, Canada and Brazil. Researchers in these countries produced 79.17% of all the records. The United States and China were major contributors that produced 15.02% and 13.67% of the total records, respectively (Table 2), indicating that they were the most active on the topic. However, the centrality indices of publications of the United States and China were not high (0.47 and 0.06, respectively; Figure 2). Because the centrality index indicates international academic status and level of influence in a given field [54], the relatively low centrality implies that a considerable percentage of publications from the two countries had not made much academic influence at the global scale. Related studies in China were relatively late to start. China and the United States had less cooperation with other countries, likely implying that the authors in the two countries preferred to cooperate with domestic researchers (Figure 2).
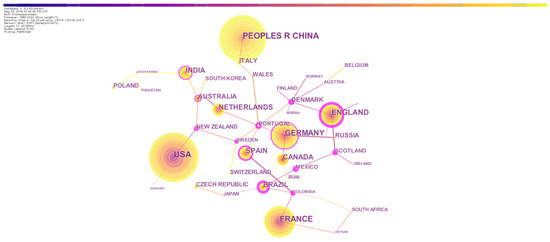
Figure 2.
The network of country/region collaborations on earthworm-related research collected in WoS. The nodes represent countries and regions. The size is proportional to the number of countries and regions and the color of node corresponds to the year. The connections between nodes indicate cooperation between these countries/regions. Nodes with high centrality are highlighted by the purple ring.
England had the highest level of influence in the field and highly cooperated with other countries, since both its publication record and country centrality were obviously high. England is the earliest contributor on the topic, and most of earthworm-related researches were originally conducted in England. This promoted cooperation among European countries, and many European countries such as Germany and the Netherlands also presented high influence and centrality.
3.3.2. Institutions-Based Outputs and Collaborations Analysis
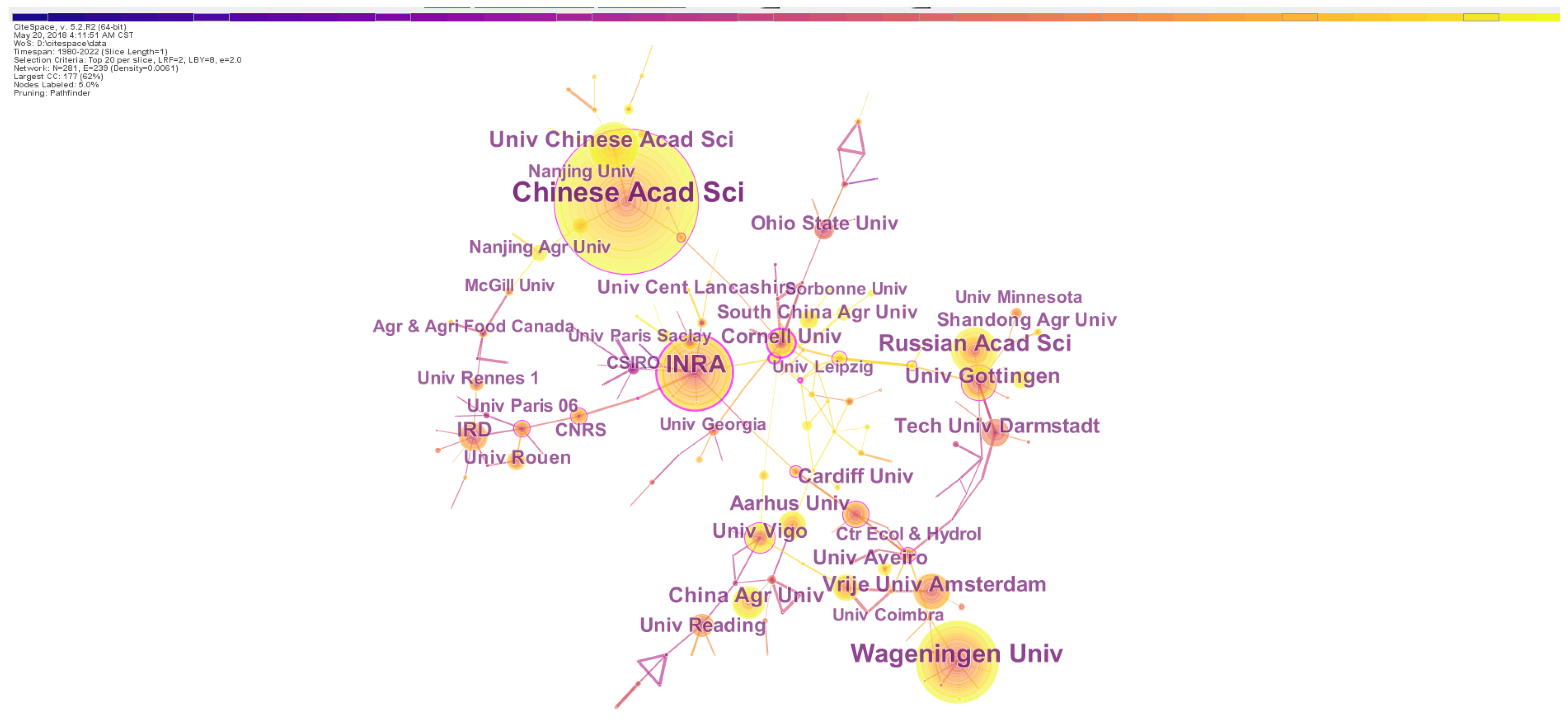
Analyzing institutions’ outputs can be used to assess the research capabilities and potential of an institution and identify the leading institutions on a given topic [33]. In the targeted field, the top 10 institutions constituted of 7 European and 3 Chinese institutions (Table 3). The institution with the most publications was the Chinese Academy of Sciences, which produced 317 records, and the second was the French National Institute of Agricultural Sciences (180 records), followed by the Russian Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Vrijie University Amsterdam, University of Gottingen, Wageningen University, China Agricultural University, University of Vigo and Aarhus University (Table 3). In spite of the high rank by the total publication record of the United States in the country-based statistics, the top 10 institutes did not cover any institute from the United States, suggesting that a large number of research institutions in the United States have been conducting earthworm-related studies.

Table 3.
Top 10 records and centrality based on the published papers related to earthworm research by institutions in WoS.
Interestingly, the US institutes played unneglectable roles in the research topic because three United States universities with high centrality (Cornell University, University of Florida and Rice University) were ranked in the top ten list (Table 3). Therein, Cornell University had the highest centrality and made frequent cooperations with other institutions (Figure 3). Moreover, two Chinese institutions (Nankai University and Chinese Academy of Sciences) and five European institutions (the French National Institute for Agricultural Research, University of Montpellier, Center for Ecology & Hydrology, Leizig University and University of Goettingen) were listed in the top ten institutes of high centrality. Generally, European institutions had high scores in both publication record and centrality, and collaborations started earlier among these institutes than those in other countries. The observation indicates that Europe is the leading pioneer in earthworm-related research.
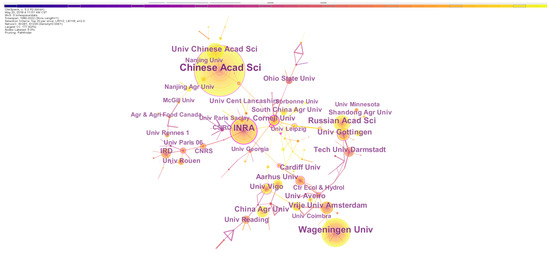
Figure 3.
The network of institution collaborations on earthworm-related research collected in WoS. The nodes represent institutions. The size is proportional to the number of institutions and the color of node corresponds to the year. The connections between nodes indicate cooperation between these institutions. Nodes with high centrality are highlighted by the purple ring.
3.3.3. Prominent Authors and Collaborations Analysis
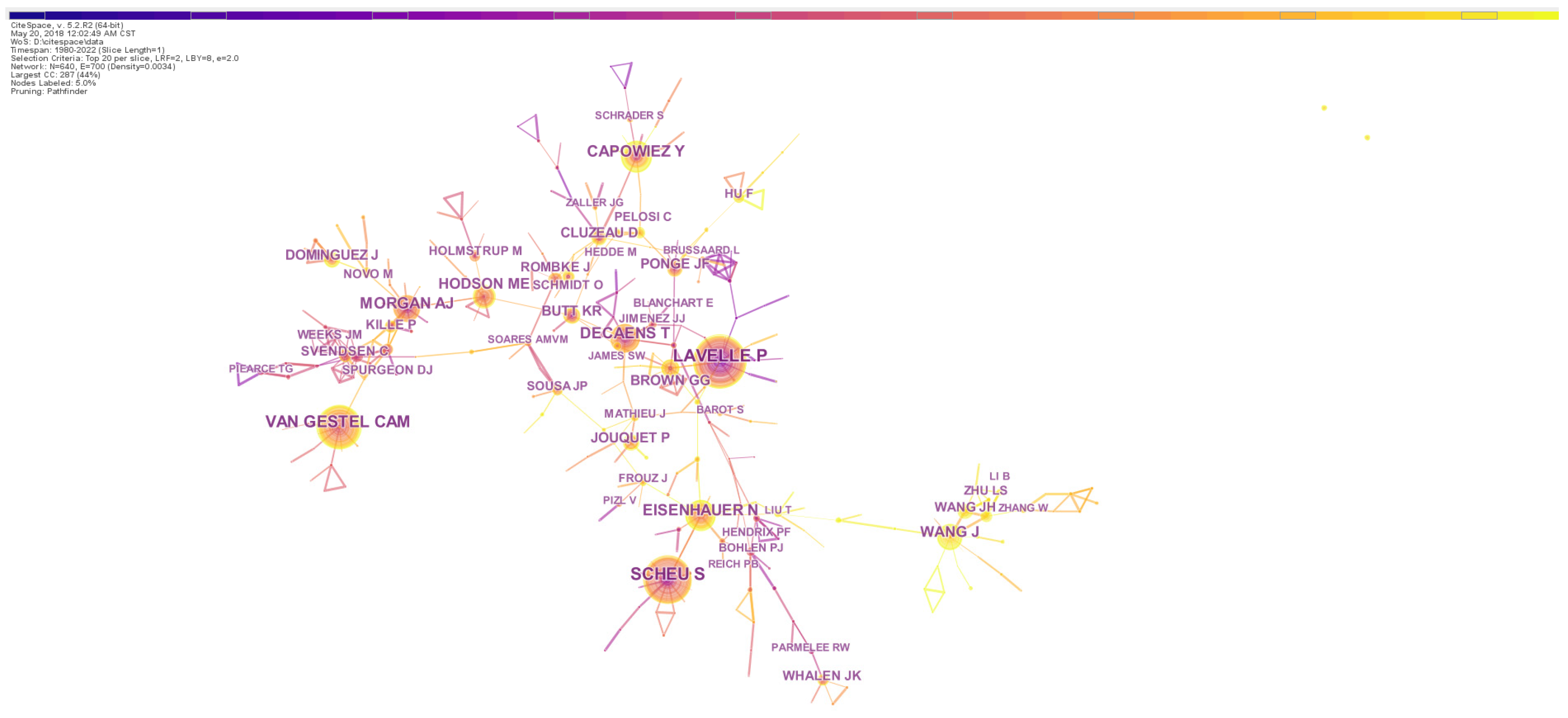
Highly influential authors were determined by calculating TLCS, and the top 10 influential authors are shown in Table 4. Professor Lavelle P, who had 140 publication records and a TLCS score of 4817, was the most influential researcher on the topic. The second and third top authors were Scheu S and Decaens T, with TLCS scores of 3258 and 1864, respectively. Eight of the ten most influential authors came from European institutes, suggesting that European researchers had played the leading role in this field. Moreover, collaborations were frequent among researchers (Figure 4), and the highly active groups were often headed by the most prominent researchers and led wide scientific cooperation. The color of the link indicates the closeness of cooperation between authors, and we could observe that the researchers in China started the topic relatively lately and had fewer collaborations compared with European researchers.

Table 4.
Rank of TLCS based on the published paper records related to earthworm research by authors collected in WoS.
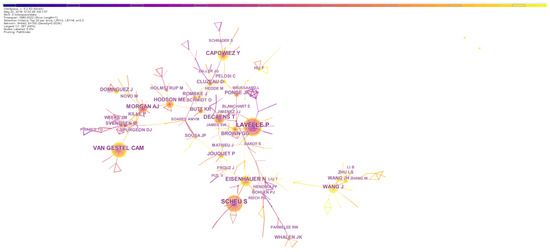
Figure 4.
The network of author collaborations on earthworm-related research collected in WoS. The nodes represent authors. The size is proportional to the publication number of authors and the color of node corresponds to the year. The connections between nodes indicate cooperation between these authors. Nodes with high centrality are highlighted by the purple ring.
3.4. Research Hotspots
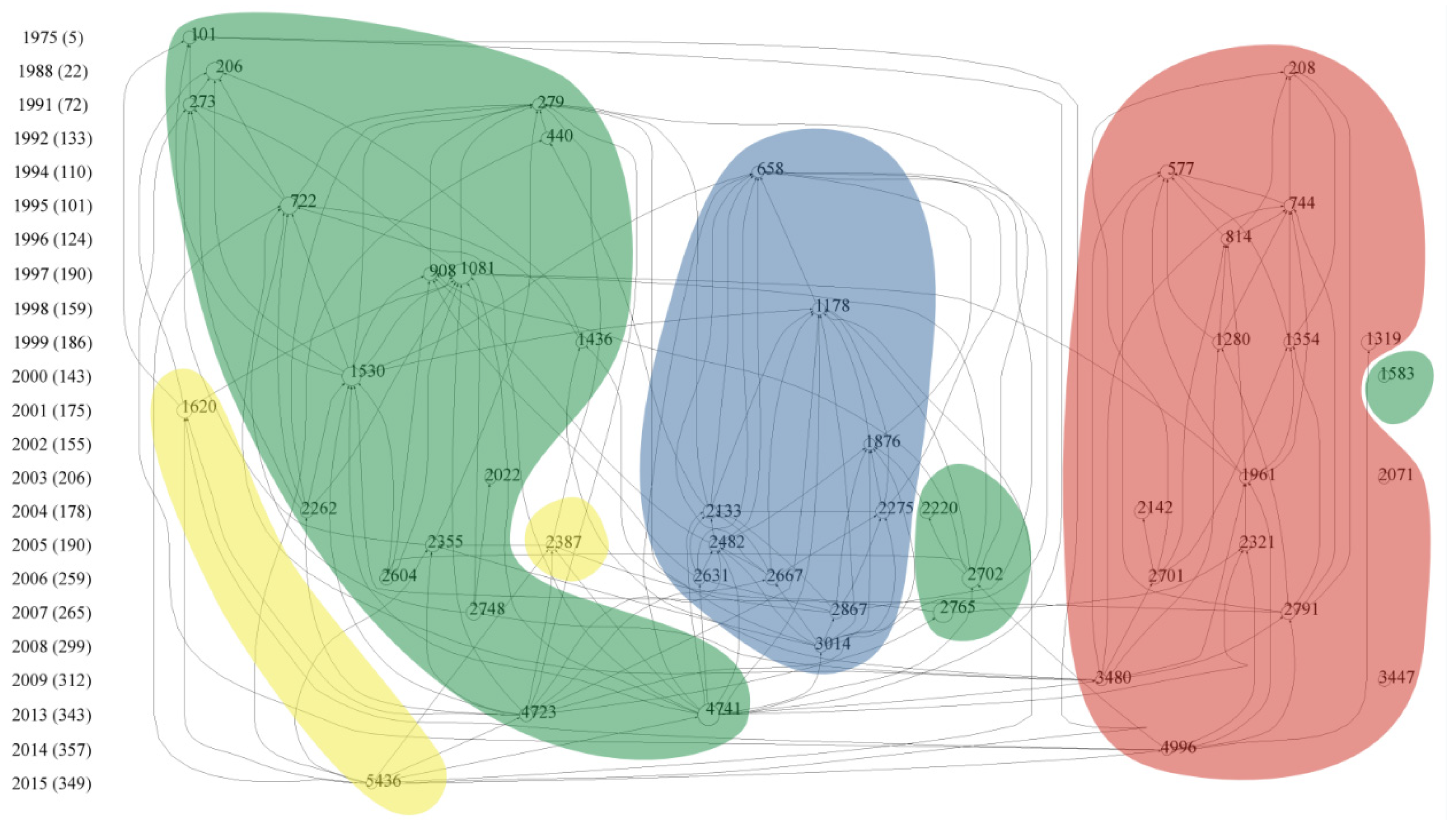
The citation network in WoS was constructed based on the research objective and content of the top 50 cited papers, which were divided into four sections. The four sections represent four research hotspots, which are marked as green, yellow, red and blue, respectively (Figure 5).
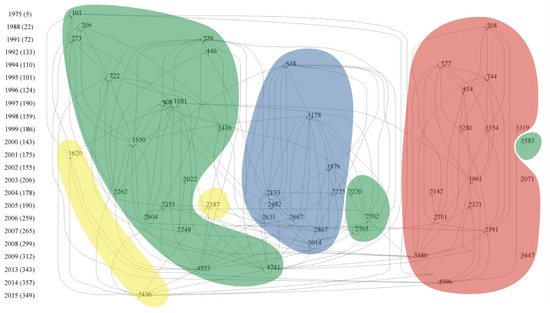
Figure 5.
The citation network on soil earthworm-related papers collected in WoS. Each node represents a highly cited paper. If there is a link between paper A and paper B, and the arrow points to paper B, then it means that paper A cited paper B. The size of node is proportional to the LCS of paper. Note: node = 50, links = 166, LCS min = 108, max = 378 (LCS scaled).
The literature in the green part mainly reports the ecological effect of earthworms on soil structure, nutrient cycling, soil biota, soil ecosystem services and greenhouse gas emissions. Node 101 was the earliest highly cited paper in which Ehlers indicated the positive effect of earthworm channels on soil drainage [55]. Another paper of node 273 also emphasized the effects of earthworms on soil structure (e.g., soil aggregates, microporosity and gas permeability) [56]. Nodes 206 and 440, authored by Lavelle [42], revealed that earthworm activities significantly affected functions of the soil system and could accelerate nutrition cycling. Earthworms were introduced into agricultural systems to improve soil fertility for crop growth due to the ecological linkage between aboveground and belowground parts [57,58]. In 1995, researchers started to study the interactive effects of earthworms and soil microbes. Earthworm activities could greatly accelerate the mineralization process of soil organic matter and provide more nutrients to soil microorganisms [59]. Moreover, soil macrofauna, including earthworms, could affect nitrogen cycling processes through regulating the composition and activity of soil microbial communities [60], e.g., by supporting specific groups of the N2O-producing soil bacteria [61]. Then, Ingrid et al. (node 4723) made a crucial review to discuss the possibility that earthworms increased the emission of greenhouse gases [62]. The ‘Sleeping Beauty Paradox’ was proposed by Lavelle et al. to explain why earthworms changed soil properties and affected soil microbial and faunal community diversity [63,64]. These publications highlighted the importance of soil invertebrates in shaping the diversity of soil organisms. Subsequently, several crucial reviews were made to clarify the ecological effects of earthworms on soil systems from different perspectives (e.g., soil function and ecosystem services) [65,66].
The second hotspot marked in yellow (Figure 5) focuses on the effects of agricultural activities on earthworms. Conventional tillage changed the abundance and diversity of the earthworm population and resulted in significant declines in the number of earthworms [67]. Differently, permanent pasture and organic management could favor the formation of soil organic matter and earthworm population to maintain high soil fertilization and sustainable utilization of land [68]. Michel et al. suggested that earthworm activities could enhance agricultural sustainability in intensive farming systems (node 5436) [69].
Earthworm ecotoxicology occurred as the third hotspot (marked in red in Figure 5). It is well known that soil degradation and soil pollutions were further exacerbated due to mining and smelting activities of humans and the use of chemicals in agriculture, and the effects on soil biota, including earthworms, were frequently investigated [38,70]. In 1981, the earthworm was proposed to be an excellent biological indicator of soil environmental conditions. Morgan et al. first proposed that earthworms could be used to indicate soil pollutions of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc (node 208) [71] and that earthworm tissues and feces could accumulate different concentrations of metals in contaminated soil (node 1354) [72]. Spurgeon et al. further pointed out that the conventional OECD tests overestimated the impact of metals on earthworm populations (node 577) [73] because of a higher bioavailability of metals in artificial soils [74]. Subsequently, Spurgeon et al. summarized the proposals in the first three International Workshops on Earthworm Ecotoxicology and highlighted the necessity to study the ecotoxicology of earthworms (node 1961) [75]. After that, a large number of ecotoxicological studies were conducted, which stimulated the need for earthworm supply. Thus, Christopher et al. reviewed the research progress of earthworm cultivation techniques for the development of ecotoxicology and soil restoration and investigated the growth rates and reproduction of four earthworm species under laboratory conditions (node 2321) [18]. In 2009, the oxidative stress and DNA damage of earthworms were used to evaluate the effects of toxic substances on the soil environment [76]. Eisenia fetida was the most widely used for toxicological tests, but further studies using different species and conducted in naturally contaminated rather than artificial soils are needed before expanding the application of research results [77].
Invasion effects of alien earthworms were the fourth hotspot (marked in blue; Figure 5) because invasive earthworms were observed to dramatically affect native ecosystems in North America [48]. Invasive species, introduced into new environments, could outcompete native species for resources and habitats, thereby changing the community structure [78]. Beginning with node 658, Alban et al. reported the invasive effects of exotic earthworms on a forest soil in northern Minnesota [79]. The invasion of earthworms reduced the weight and thickness of the forest floor but increased the soil density, since more humus was produced due to the intensified mixture of organic and mineral materials by earthworm activities. Moreover, invasive earthworms could decrease the density and number of microarthropods species, alter the distribution and community composition of soil microflora and change the competition among plant species [52,80]. Earthworm invasion also significantly changed the composition of the native earthworm community [81]. Bohlen et al. proposed that the invasion of exotic earthworms played an important role in regulating soil structure and function in northern temperate forest ecosystems in the last few decades and that the existence of earthworms needed to be included in regional risk assessment [49,82]. Exotic earthworms increased the leaf C/N ratio and the effects of earthworms on soil properties depended on the total biomass and the feeding and burrowing habitats of earthworms [83]. Paul et al. proposed some endogenous and exogenous factors to determine invasive earthworm species and suggested to predict the ecological effects of invasive earthworms by combining models with molecular techniques [50]. In spite of the known effects of invasive earthworms on native ecosystems, the potential risks of earthworm invasion remain to increase with the expansion of global commerce due to a lack of legal restrictions on targeted earthworms in most parts of the world [48].
3.5. Term Co-Occurrence
Similar terms that are located at a research field will be clustered as a group. The structure changes in a specific domain can be revealed by conducting term co-occurrence analysis [84]. In this study, 11 clusters were established and these clusters mainly focused on four topics (Table 5).

Table 5.
Top 11 clusters in terms of publications related to earthworm research fields during 1980–2022.
Until the 1990s, researchers concentrated on exploring the effects of earthworms on the soil ecosystem, and this research topic covered the cluster IDs 0, 2, 4 and 8. In these clusters, researchers focused on the decomposition of leaf litter and formation of soil organic matter that were influenced by activities of earthworms. Earthworms contribute to the decomposition and transformation of leaf litter, promote soil fertility by increasing organic carbon and total nitrogen content, and enhance soil microbiota diversity [19,85]. The role of earthworms in litter decomposition is commonly long-term and lasting, but in the short term, earthworms may have no significant effect on litter decomposition [86]. Moreover, advanced techniques such as isotope labeling could be used to trace soil nutrient transfer. By a stable isotope tracer, it was found that different earthworm species had different effects in the early stage of soil organic matter mineralization, and that their burrowing activities changed the soil structure and played an important role in the stabilization of soil organic matter [56,87]. Additionally, earthworm activities were observed to impact humus profile morphology. The mineral content of the soil humus profile increased with depth due to the mixing effect of earthworms in the soil [88]. Subsequently, the interactions among earthworms and other soil animals were paid more attention and ecological roles of earthworms were further reported. For instance, researchers found that earthworm activities were able to promote plant performance, thereby indirectly improving aphid reproduction [89,90].
The second topic focused on the effects of human activities (e.g., agricultural or pedestrian activity) on earthworms, including cluster IDs 5, 6 and 7. Since intensive agricultural activities result in degradation of soil structure and increase in soil pollution, adopting new farming systems with reduced tillage and adjusted chemical input will protect the stability of the soil structure. The effects of agricultural management could be further facilitated by the presence of enchytraeids [91]. In order to protect the quality of arable land, many countries carried out policies to reduce tillage. For example, Congress of the US passed a Conservation Reserve Program to improve soil fertility, reduce soil erosion and promote the sustainable development of agriculture in 1985 [92]. After that, people paid more attention to the effects of different arable farming systems on earthworms and found that earthworm abundance and biomass were increased in the agricultural soils by reducing tillage [93,94]. The effects of reduced tillage on earthworms may be influenced by earthworm species and soil physiochemical properties. In addition, cluster ID 6 demonstrated that the effects of pedestrian activities on earthworms in forests or urban greens were concerning. Due to excessive human trampling, the soil was heavily compacted with no herb vegetation in extensive paths, resulting in decreases in both the number and diversity of earthworm populations [95,96].
Cluster IDs 1, 3 and 9 constituted the third topic, which focused on earthworm ecotoxicology. The earthworm (specifically, Eisenia fetida) was recommended as a biological indicator to test the effects of chemicals (such as triazole) in the soil environment by European Union, OECD and the US Environmental Protection Agency [97,98]. Moreover, earthworms could be used to remove heavy metal in the sewage sludge due to the accumulation of earthworms’ tissue and the ingestion [99].
Cluster ID 10 concentrated on the effects of exotic earthworms, which was the fourth topic. Numerous exotic earthworms invaded North America, accelerated plant litter decomposition and changed the soil organic horizon to affect native plant growth, causing forest fragmentation [100,101,102].
3.6. Burst Detection
The abrupt changes in entity could be revealed by conducting burst detection analyses on keywords, countries, institutions and authors of the collected literature in a certain time zone [103]. The results of burst detection analyses are shown in Table 6, Table 7, Table S1 and Table S2 to present the emerging topics, active countries/regions, institutions and potential authors in the targeted field in the investigated period [104].

Table 6.
Keywords with bursts in the publications related to earthworm research in the last five years.

Table 7.
Top 10 countries/regions with bursts in terms of publication records related to earthworm research from 1980 to 2022.
3.6.1. Emerging Hotpots
We found that the emerging research hotspots since 2018 were related with “impact (2018–2022)”, “biodiversity (2018–2019)”, “oxidative stress (2018–2022)”, “diversity (2018–2019)”, “response (2019–2022)”, “Eisenia fetida (2020–2022)” and “exposure (2020–2022)” (Table 6). With the growth of population and urbanization, the continuous production of waste has become a popular environmental issue. Vermicomposting, as a solution for recycling the organic component of municipal solid waste, and its impacts on ecosystems have consequently attracted more attention [105]. Earthworms could serve as indicators of soil biodiversity, quality and productivity, and therefore numerous recent studies have been conducted to elucidate the impacts of anthropogenic activities, such as the use of chemicals and changes in soil management practices, on earthworm populations [106,107,108]. It was reported that soil biodiversity was deteriorating in Europe because of the agricultural intensification and climate change [109]. The presence of earthworms changed soil biodiversity [110], and invasive earthworms were found to significantly regulate soil biodiversity [111,112] and soil microbial communities [113]. In addition, the impact of interactions between earthworms and invasive plants was concerning because of the additive effects of both [114]. Moreover, an increasing number of studies reported that the presence of earthworms could modify soil microbial community activity and composition [20], and studied the diversity of gut microbiota in earthworms [115]. The response of earthworms with exposure to chemicals or other stress conditions has attracted much attention since 2018 [116,117,118]. As known, the earthworm is an important indicator for the evaluation of ecological risk and ecotoxicology, but indications of the toxicity endpoint by observing the behavior response of earthworms are time-consuming, tedious and may be influenced by the individual variations [119]. Therefore, the response of earthworms to oxidative stress has been developed rapidly for evaluating the ecotoxicological effect of chemicals [120], in which Eisenia fetida has been widely chosen for the ecotoxicological assessment of chemicals due to the recommendation of international organizations [121]. In short, the ecological effects of earthworms, earthworm ecotoxicology and earthworm invasion are currently research hotspots in the topic.
3.6.2. Active Countries/Regions, Institutions and Potential Authors
The top 10 active countries/regions and institutions from 1980 to 2022 were identified by the burst detection analysis (Table 7 and Table S1). In the early stage from 1980 to 1996, the burst of country/region occurred in USA, Australia and Finland, with a burst strength of 25.76, 29.27 and 21.77, respectively (Table 7). Although earthworm-related studies started late in China, the number of publications authorized by Chinese researchers has abruptly increased between 2018 and 2022, with a strength of 123.65 (Table 7), indicating that Chinese researchers paid increasing attention to earthworm studies in the last 5 years. Moreover, the number of publications from Iran, South Africa, Austria and Japan also increased rapidly in recent years.
In the top 10 active institutions, there were 4 institutions from China, 2 from France, and 1 from each of Australia, Germany, Unites States and Netherlands (Table S1). The bursting institutions from 1980 to 2016 were Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (Australia), Technical University of Darmstadt (Germany), Ohio State University (USA), Vrije University Amsterdam (Netherlands) and INRA (France). In the last five years, the burst occurred in University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (China), Chinese Academy of Sciences (China), Shandong Agricultural University (China) and Nanjing Agricultural University (China), showing that Chinese institutions played a prominent role in the period. Correspondingly, most of the bursting authors were from China in the last five years (Table S2), and they paid much attention to revealing the impact and potential mechanisms of earthworms on the soil ecosystem.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, a scientometrical review was conducted by collecting and analyzing 8674 publications on the topic of earthworms in the soil ecosystem during 1900–2022. The results showed that the number of publications had been exponentially increasing since 1900 and that three stages were identified, i.e., 1900–1990, 1991–2005 and 2006–2022, with different countries leading researches on the topic in these stages. A total of 1013 journals published papers on the topic, with the most papers in Soil Biology & Biochemistry. The highly productive institutions were Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wageningen University, French National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Russian Academy of Sciences and University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. At the global scale, Professor Lavelle P was the most influential author, but, in recent years, since 2018, Chinese institutions and authors had played an active role. Four main research hotspots were identified in the investigated period, i.e., effects of earthworms on the soil ecosystem, ecotoxicology of earthworms and soil remediation by earthworms, effects of alien earthworms, and effects of anthropogenic activities on earthworms. Furthermore, terms of “impact”, “biodiversity”, “oxidative stress”, “diversity”, “response”, “Eisenia fetida” and “exposure” had been the emerging active topics with obvious bursts since 2018, with the bursting of some terms, such as impacts, oxidative stress and exposure, lasting until the end point (2022) of searching in the present study. This observation indicates that these terms could be continuously highlighted at least in the following years. In summary, we clarified the research progress of earthworms in soil ecosystems, highly active research subjects on the topic, research hotspots in different period and emerging bursts in recent years by conducting these analyses. These results could help us to systematically understand the development progress of research on the earthworm and provide implications to allow us to know the following research hotspots at least in recent years.
Supplementary Materials
The following is available online at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology13060385/s1, Figure S1: Literature types of earthworm related publication collected in WoS from 1900 to 2022; Figure S2: The co-occurrence network of terms in earthworm related papers collected in WoS; Table S1: Top 10 institutions with bursts in terms of publication records related earthworm researches from 1980-2022; Table S2: Authors with burst in terms of publication records related earthworm researches in the last five years.
Author Contributions
J.C.: conceptualization, data collection, methodology, original draft, manuscript writing and revision. S.C.: data collection. Z.L.: data collection, methodology. L.W.: data collection. H.X.: methodology, revision. J.Z.: conceptualization, methodology, revision, funding acquisition, project administration. H.W.: conceptualization, methodology, revision, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 32071641 and U1701236), Guangdong Science and Technology Department (grant number 2021A1515012507) and the Laboratory of Lingnan Modern Agriculture Project (grant number NT2021010).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not application.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the finding of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lehmann, J.; Bossio, D.A.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Rillig, M.C. The concept and future prospects of soil health. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N.; Wood, S.A.; De Mesquita, C.P.B. How microbes can, and cannot, be used to assess soil health. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2021, 153, 108111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Han, Y.; Bate, B.; Ke, H.; Chen, Y. Soil heavy metal pollution of industrial legacies in China and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuaib, M.; Azam, N.; Bahadur, S.; Romman, M.; Yu, Q. Variation and succession of microbial communities under the conditions of persistent heavy metal and their survival mechanism. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Yu, X.; Tu, L. Effects of exogenous abscisic acid on the growth and cadmium accumulation of lettuce under cadmium-stress conditions. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 100, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Song, J.; Li, W.; Zheng, M. The accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural land and the associated potential ecological risks in Shenzhen, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, R. Effect of different industrial activities on soil heavy metal pollution, ecological risk, and health risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Zhang, G. Exploration and utilization of aluminum-tolerant barley germplasm. Explor. Identif. Util. Barley Germplasm 2016, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Adriano, D.; Curtin, D. Soil acidification and liming interactions with nutrient and heavy metal transformation and bioavailability. Adv. Agron. 2003, 78, 215–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, J.L.; Zhang, H.; Girma, K.; Raun, W.R.; Penn, C.J.; Payton, M.E. Soil acidification from long-term use of nitrogen fertilizers on winter wheat. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.M.; Yao, J.; Yan, F. Vegetable cultivation under greenhouse conditions leads to rapid accumulation of nutrients, acidification and salinity of soils and groundwater contamination in South-Eastern China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2009, 83, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P. Soil Ecology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, D.; Zhao, C. Functions of earthworm in ecosystem. Biodivers. Sci. 2007, 15, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Zeng, X.; Shengzhe, E.; Che, Z.; Bai, L.; Su, S.; Wang, Y. The stability mechanism for organic carbon of aggregate fractions in the irrigated desert soil based on the long-term fertilizer experiment of China. Catena 2019, 173, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Wang, J.; Shao, M.A. Application of earthworm cast improves soil aggregation and aggregate-associated carbon stability in typical soils from Loess Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. J. Soil. Sci. 1982, 33, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinissen, A. Biological and physico-chemical processes in excrements of soil animals. Geoderma 1993, 56, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, C.N.; Butt, K.R. Culture techniques for soil dwelling earthworms: A review. Pedobiologia 2005, 49, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Yin, X. Transformation of Carbon and Nitrogen by Earthworms in the Decomposition Processes of Broad-leaved Litters. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Hu, F.; Liu, M.; et al. Earthworms modify soil bacterial and fungal communities through enhancing aggregation and buffering pH. Geoderma 2019, 347, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, C.; Fu, X.; Cui, G.; Lei, X.; Huang, K. Impacts of earthworm on acidic and alkaline buffering capacity of pelletized dewatered sludge in vermicomposting. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2016, 36, 2941–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bayo, J.; Nogales, R.; Romero, E. Assessment of three vermicomposts as organic amendments used to enhance diuron sorption in soils with low organic carbon content. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2009, 60, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul Bachko, Y.L.; Didur, O.O.; Loza, I.M.; Pakhomov, O.E.; Bezrodnova, O.V. Environmental aspects of the effect of earthworm (Lumbricidae, Oligochaeta) tropho-metabolic activity on the pH buffering capacity of remediated soil (steppe zone, Ukraine). Biol. Bull. 2015, 42, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Al-Mutairi, K.A. Earthworms effect on microbial population and soil fertility as well as their interaction with agriculture practices. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binet, F.; Fayolle, L.; Pussard, M.; Crawford, J.J.; Traina, S.J.; Tuovinen, O.H. Significance of earthworms in stimulating soil microbial activity. Biol. Fert. Soils 1998, 27, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemtiri, A.; Colinet, G.; Alabi, T.; Cluzeau, D.; Francis, F. Impacts of earthworms on soil components and dynamics. A review. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2014, 18, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Q. Worldwide earthworm research: A scientometric analysis, 2000–2015. Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Li, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L. Knowledge domain and emerging trends in organic photovoltaic technology: A scientometric review based on citeSpace analysis. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, W.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, F.; Lin, C. Anthropogenic impact on diffuse trace metal accumulation in river sediments from agricultural reclamation areas with geochemical and isotopic approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, E.; Paris, S.W.; Stock, W.G. HistCite: A software tool for informetric analysis of citation linkage. Inf. Wiss. Prax. 2006, 57, 391–400. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Shi, S. Researching the development of Atanassov intuitionistic fuzzy set: Using a citation network analysis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 32, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, H.; Wei, H. A bibliometric analysis of research on acid rain. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, B.H.; Boström, U.; Klemedtson, L. Potential for higher rates of denitrification in earthworm casts than in the surrounding soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1986, 2, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, R. Mineralization of phosphorus by faecal phosphatases of some earthworms of Indian tropics. Proc. Indian. Acad. Sci. Anim. Sci. 1990, 99, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaby, R.J. The influence of earthworms on soil aggregation. J. Soil. Sci. 1950, 1, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syers, J.K.; Springett, J.A. Earthworms and soil fertility. Plant Soil. 1984, 76, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. Earthworms and their application in environment protection II. Ecotoxicology of earthworms. J. Shanghai Agric. Coll. 1999, 17, 310–318. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, A.; Ebing, W. Toxicity determination of pesticides to earthworms in the soil substrate. Z. Für Pflanzenkrankh. Und Pflanzenschutz/J. Plant Dis. Prot. 1983, 90, 395–408. [Google Scholar]
- van Gestel, C.A.M.; Ma, W. An approach to quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSARs) in earthworm toxicity studies. Chemosphere 1990, 21, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.D. Influence of Earthworms on Soil Microorganisms. Soil. Sci. 1950, 69, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P. Earthworm activities and the soil system. Biol. Fertil. 1988, 6, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.C.; Jury, W.; Luepromchai, E.; Yahng, C.S.; Crowley, D.E. Contribution of earthworms to PCB bioremediation. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukkari, T.; Taavitsainen, M.; Väisänen, A.; Haimi, J. Effects of heavy metals on earthworms along contamination gradients in organic rich soils. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2004, 59, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukkari, T.; Haimi, J. Avoidance of Cu- and Zn-contaminated soil by three ecologically different earthworm species. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2005, 62, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.W. The Earthworms (Lumbricidae and Sparganophilidae) of Ontario; The Hunter Rose Company: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1977; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, G.E. Farewell to north american megadriles. Megadrilogica 1982, 4, 12–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix, P.; Bohlen, P. Exotic earthworm invasions in North America: Ecological and policy implications. Bioscience 2002, 52, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlen, P.J.; Scheu, S.; Hale, C.M.; Mclean, M.A.; Migge, S.; Groffman, P.M.; Parkinson, D. Non-native invasive earthworms as agents of change in northern temperate forests. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, P.; Callaham, M.; Drake, J.; Huang, C.; James, S.; Snyder, B.; Zhang, W. Pandora’s box contained bait: The global problem of introduced earthworms. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 593–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migge-Kleian, S.; McLean, M.A.; Maerz, J.C.; Heneghan, L. The influence of invasive earthworms on indigenous fauna in ecosystems previously uninhabited by earthworms. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frelich, L.E.; Hale, C.M.; Scheu, S.; Holdsworth, A.R.; Heneghan, L.; Bohlen, P.J.; Reich, P.B. Earthworm invasion into previously earthworm-free temperate and boreal forests. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, M.A.; Migge-Kleian, S.; Parkinson, D. Earthworm invasions of ecosystems devoid of earthworms: Effects on soil microbes. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1257–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Xie, R. Biblimetric analysis of bioaccessibility of heavy metals on CiteSpace. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, W. Observations on earthworm channels and infiltration on tilled and untilled loess soil. Soil. Sci. 1975, 119, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Foster, R. Soil fauna and soil structure. Aust. J. Soil. Res. 1991, 29, 745–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A. Short- and long-term effects of the endogeic earthworm Millsonia anomala (Omodeo) (Megascolecid, Oligochta) of tropical savannas, on soil organic matter. Biol. Fert. Soils 1991, 11, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.G.; Baroisa, I.; Lavelle, P. Regulation of soil organic matter dynamics and microbial activity in the drilosphere and the role of interactions with other edaphic functional domains. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 2000, 36, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Martin, A. Small-scale and large-scale effects of endogeic earthworms on soil organic matter dynamics in soils of the humid tropics. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1992, 24, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, H.; Horn, M. As the worm turns: The earthworm gut as a transient habitat for soil microbial biomes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, M.; Schramm, A.; Drake, H. The earthworm gut: An ideal habitat for ingested N2O-producing microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2003, 69, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubbers, I.M.; Groenigen, K.V.; Fonte, S.J.; Six, J.; Brussaard, L.; Groenigen, J.V. Greenhouse-gas emissions from soils increased by earthworms. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Bignell, D.; Lepage, M.; Wolters, V.; Roger, P. Soil function in a changing world: The role of invertebrate ecosystem engineers. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 1997, 33, 159–193. [Google Scholar]
- Lavelle, P. Faunal activities and soil processes: Adaptive strategies that determine ecosystem function. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1997, 27, 93–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Deca Ns, T.; Aubert, M.; Barot, S.; Blouin, M.; Bureau, F.; Margerie, P.; Mora, P.; Rossi, J.P. Soil invertebrates and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 2006, 42, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, M.; Hodson, M.E.; Delgado, E.A.; Baker, G.; Brussaard, L.; Butt, K.R.; Dai, J.; Dendooven, L.; Peres, G.; Tondoh, J.E.; et al. A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2013, 64, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.Y. An overview of some tillage impacts on earthworm population abundance and diversity—Implications for functioning in soils. Soil. Tillage Res. 2001, 57, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulleman, M.M.; Six, J.; Uyl, A.; Marinissen, J.; Jongmans, A.G. Earthworms and management affect organic matter incorporation and microaggregate formation in agricultural soils. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2005, 29, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, M.; Barot, S.; Blouin, M.; Whalen, J.; Oliveira, T.D.; Roger-Estrade, J. Earthworm services for cropping systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Li, J.; He, C.; Hu, X.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Yang, S.; He, H.; et al. Distribution characteristics and relevance of heavy metals in soils and colloids around a mining area in Nanjing, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, J.E.; Morgan, A.J. Earthworms as biological monitors of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc in metalliferous soils. Environ. Pollut. 1988, 54, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.E.; Morgan, A.J. The accumulation of metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn and Ca) by two ecologically contrasting earthworm species (Lumbricus rubellus and Aporrectodea caliginosa): Implications for ecotoxicological testing. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 1999, 13, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Hopkin, S.P.; Jones, D.T. Effects of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc on growth, reproduction and survival of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny):Assessing the environmental impact of point-source metal contamination in terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1994, 84, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Hopkin, S.P. Extrapolation of the laboratory-based OECD earthworm toxicity test to metal-contaminated field sites. Ecotoxicology 1995, 4, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Weeks, J.M.; Van Gestel, C.A.M. A summary of eleven years progress in earthworm ecotoxicology. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, L.S.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, W.; Xie, H. DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahmani, J.; Hodson, M.E.; Black, S. A review of studies performed to assess metal uptake by earthworms. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polce, C.; Cardoso, A.C.; Deriu, I.; Gervasini, E.; Tsiamis, K.; Vigiak, O.; Zulian, G.; Maes, J. Invasive alien species of policy concerns show widespread patterns of invasion and potential pressure across European ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alban, D.H.; Berry, E.C. Effects of earthworm invasion on morphology, carbon, and nitrogen of a forest soil. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 1994, 1, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, N.; Partsch, S.; Parkinson, D.; Scheu, S. Invasion of a deciduous forest by earthworms: Changes in soil chemistry, microflora, microarthropods and vegetation. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, C.; Frelich, L.; Reich, P. Changes in hardwood forest understory plant communities in response to European earthworm invasions. Ecology 2006, 87, 1637–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlen, P.J.; Groffman, P.M.; Fahey, T.J.; Fisk, M.C.; Suarez, E.; Pelletier, D.M.; Fahey, R.T. Ecosystem consequences of exotic earthworm invasion of north temperate forests. Ecosystems 2004, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, C.M.; Frelich, L.E.; Reich, P.B.; Pastor, J. Effects of European earthworm invasion on soil characteristics in northern hardwood forests of minnesota, USA. Ecosystems 2005, 8, 911–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; He, M.; Hao, F.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W. Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: A scientometrics review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeffner, K.; Monard, C.; Santonja, M.; Cluzeau, D. Feeding behaviour of epi-anecic earthworm species and their impacts on soil microbial communities. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, Y.; Luizao, F.J.; Barros, E. Effect of earthworm addition on soil nitrogen availability, microbial biomass and litter decomposition in mesocosms. Biol. Fert. Soils 2004, 39, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, S.; Wolters, V. Influence of fragmentation and bioturbation on the decomposition of 14C-labelled beech leaf litter. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1991, 23, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdeshell, C.; Graham, R.C.; Peterson, A.C.; Hendrix, P.E.; Quideau, S.A. Morphology and Genesis of Humus Profiles under Chaparral Shrubs in Southern California. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, S.; Jones, A.T.H. Links between the detritivore and the herbivore system: Effects of earthworms and Collembola on plant growth and aphid development. Oecologia 1999, 119, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurst, S.; Jones, T.H. Indirect effects of earthworms (Aporrectodea caliginosa) on an above-ground tritrophic interaction. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topoliantz, S.; Ponge, J.F.O.; Viaux, P. Earthworm and enchytraeid activity under different arable farming systems, as exemplified by biogenic structures. Plant Soil. 2000, 225, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, T.L. America’s Conservation Reserve Program: Rural planning or just another subsidy? J. Rural. Stud. 1988, 4, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joschko, M.; Gebbers, R.; Barkusky, D.; Rogasik, J.; Höhn, W.; Hierold, W.; Fox, C.A.; Timmer, J. Location-dependency of earthworm response to reduced tillage on sandy soil. Soil. Till Res. 2009, 102, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moos, J.H.; Schrader, S.; Paulsen, H.M. Reduced tillage enhances earthworm abundance and biomass in organic farming: A meta-analysis. Landbauforsch.-J. Sustain. Org. Agric. Syst. 2017, 67, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuendet, G. Effect of pedestrian activity on earthworm populations of two forests in Switzerland. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1992, 24, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizl, V.; Schlaghamersky, J. The impact of pedestrian activity on soil annelids in urban greens. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 2007, 43, S68–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, F.; Moreira, J. Effects of glyphosate and 2,4-D on earthworms (Eisenia foetida) in laboratory tests. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Song, W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J. Effect on enzymes and histopathology in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by triazole fungicides. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 35, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, A.B.; Lim, M.P.M.; Noor, Z.M.; Abdullah, N. Vermiremoval of heavy metal in sewage sludge by utilising Lumbricus rubellus. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2013, 90, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundale, M.J. Influence of exotic earthworms on the soil organic horizon and the rare fern Botrychium mormo. Conserv. Biol. 2002, 16, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Zou, X.M. Exotic earthworms accelerate plant litter decomposition in a Puerto Rican pasture and a wet forest. Ecol. Appl. 2002, 12, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, P.F.; Baker, G.H.; Callaham, M.A.; Damoff, G.A.; Fragoso, C.; González, G.; James, S.W.; Lachnicht, S.L.; Winsome, T.; Zou, X. Invasion of exotic earthworms into ecosystems inhabited by native earthworms. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1287–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Dubin, R.; Kim, M.C. Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine: A scientometric update (2000–2014). Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2014, 14, 1295–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xu, C. Mapping research on carbon emissions trading: A co-citation analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducasse, V.; Capowiez, Y.; Peigné, J. Vermicomposting of municipal solid waste as a possible lever for the development of sustainable agriculture. A review. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litskas, V.D.; Karamanlis, X.N.; Prousali, S.P.; Koveos, D.S. The xenobiotic doxycycline affects nitrogen transformations in soil and impacts earthworms and cultivated plants. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2019, 54, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellnitz, T.; Barlow, J.L.; Dick, C.M.; Shaurette, T.R.; Weiher, E. Campsites, forest fires, and entry point distance affect earthworm abundance in the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness. Peerj 2020, 8, e8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vri, S.; Breznik, M.; Pulko, B.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Earthworm abundance changes depending on soil management practices in Slovenian vineyards. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaas, E.; Meyer-Wolfarth, F.; Banse, M.; Bengtsson, J.; Bergmann, H.; Faber, J.; Potthoff, M.; Runge, T.; Schrader, S.; Taylor, A. Towards valuation of biodiversity in agricultural soils: A case for earthworms. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 159, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thounaojam, R.S.; Thingbaijam, B.S. Biodiversity of ecologically important earthworms in subtropical forest ecosystems of East and West Imphal districts of Manipur. J. Environ. Biol. 2020, 41, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlian, O.; Eisenhauer, N.; Aguirrebengoa, M.; Camara, M.; Ramirez-Rojas, I.; Santos, F.; Tanalgo, K.; Thakur, M.P. Invasive earthworms erode soil biodiversity: A meta-analysis. J. Anim. Ecol. 2018, 87, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumack, K.; Ferlian, O.; Morselli Gysi, D.; Degrune, F.; Jauss, R.T.; Walden, S.; Ztoprak, H.; Wubet, T.; Bonkowski, M.; Eisenhauer, N. Contrasting protist communities (Cercozoa: Rhizaria) in pristine and earthworm-invaded North American deciduous forests. Biol. Invasions 2022, 24, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Sun, Y.; Qin, Q.; Sun, L.; Xue, Y. The Effects of Earthworms on Fungal Diversity and Community Structure in Farmland Soil with Returned Straw. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 594265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cope, C.G.; Eysenbach, S.R.; Faidiga, A.S.; Hausman, C.E.; Medeiros, J.S.; Murphy, J.E.; Burns, J.H. Potential interactive effects between invasive Lumbricus terrestris earthworms and the invasive plant Alliaria petiolata on a native plant Podophyllum peltatum in northeastern Ohio, USA. Aob Plants 2020, 13, a73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Lian, B.; Wu, C.; Guo, P. A comparative study of gut microbiota profiles of earthworms fed in three different substrates. Symbiosis 2018, 74, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, V.D.; Lankadurai, B.P.; Nagato, E.G.; Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J. Comparison of metabolomic responses of earthworms to sub-lethal imidacloprid exposure in contact and soil tests. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18846–18855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Qiao, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, C. Use of integrated biomarker response for studying the resistance strategy of the earthworm Metaphire californica in Cd-contaminated field soils in Hunan Province, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Saleem, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Ecotoxicity of herbicide carfentrazone-ethyl towards earthworm Eisenia fetida in soil. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2022, 253, 109250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.B.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z.J. Ecotoxicological effects of petroleum-contaminated soil on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, H.; O’Connor, G.; Ogram, A.; Kumar, K. Bioavailability of biosolids-borne ciprofloxacin and azithromycin to terrestrial organisms: Microbial toxicity and earthworm responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiao, R.; Li, R.; Amjad, A.; Zhang, Z. Bioremediation of Cd-contaminated soil by earthworms (Eisenia fetida): Enhancement with EDTA and bean dregs. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).