Cytokinin and Metabolites Affect Rhizome Growth and Development in Kentucky Bluegrass (Poa pratensis)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
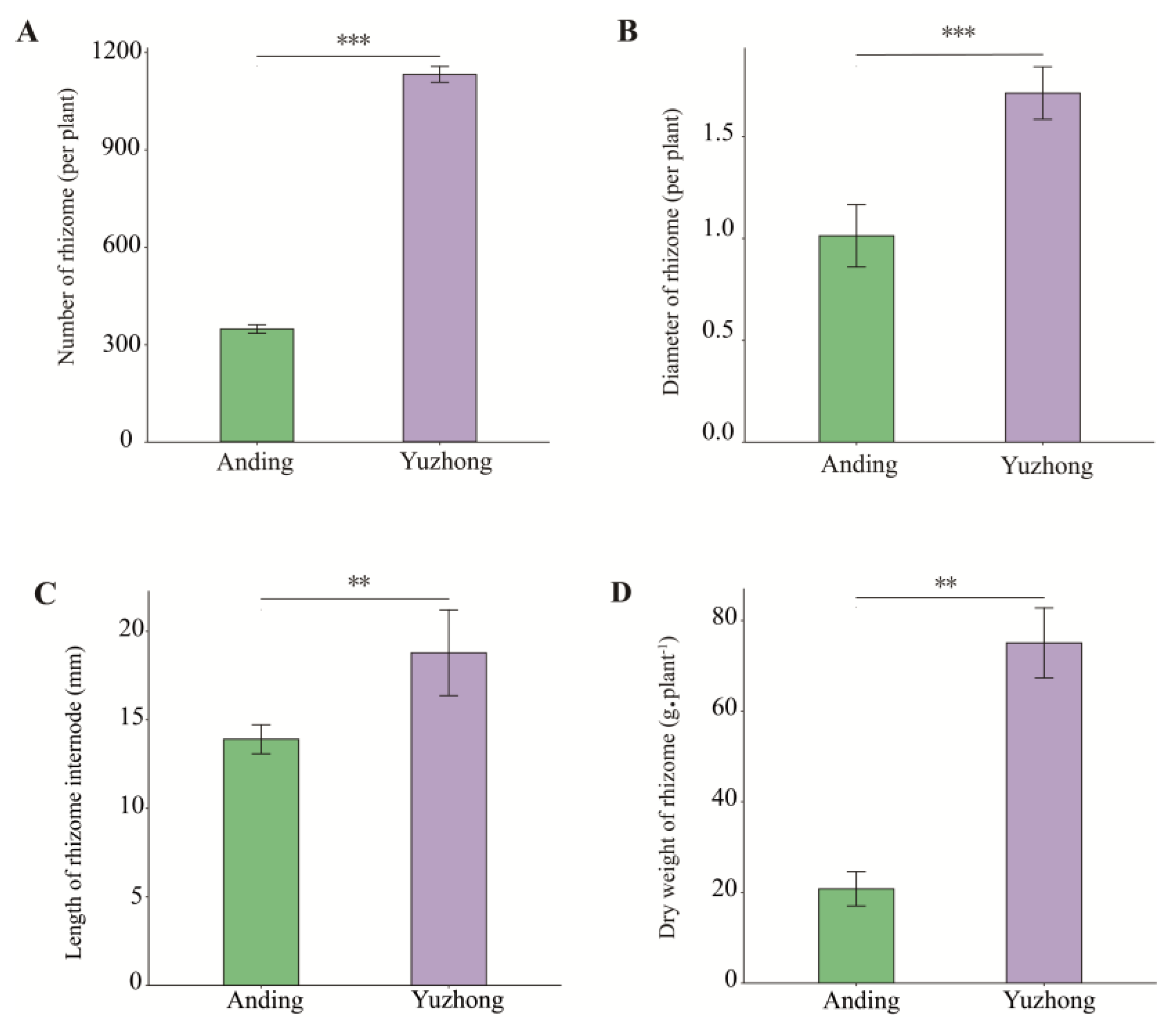
2.1. Morphology Difference of Rhizomes
2.2. Endogenous Phytohormone Content of Rhizome
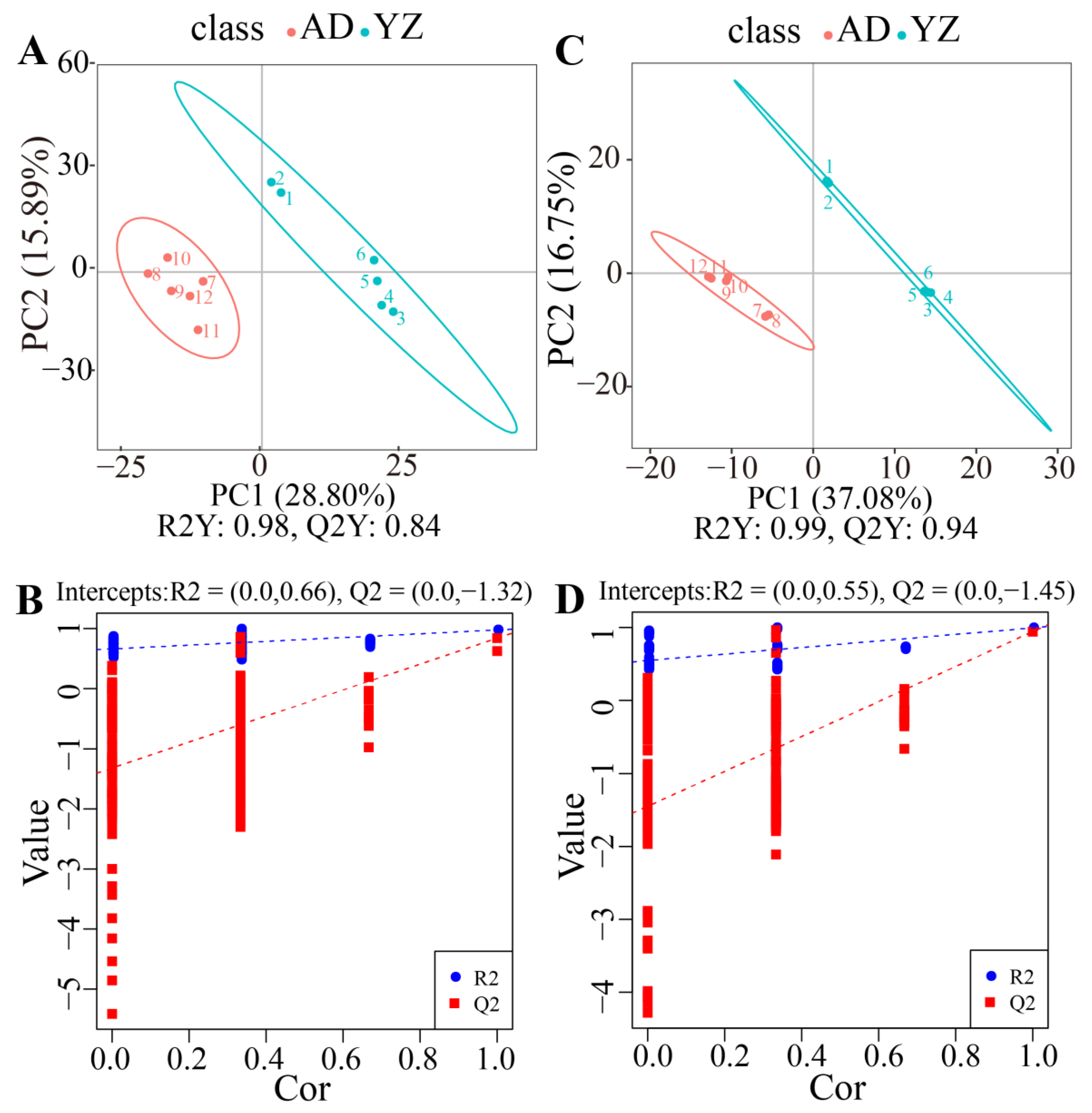
2.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Rhizome Metabolomics
2.4. Differentially Metabolites
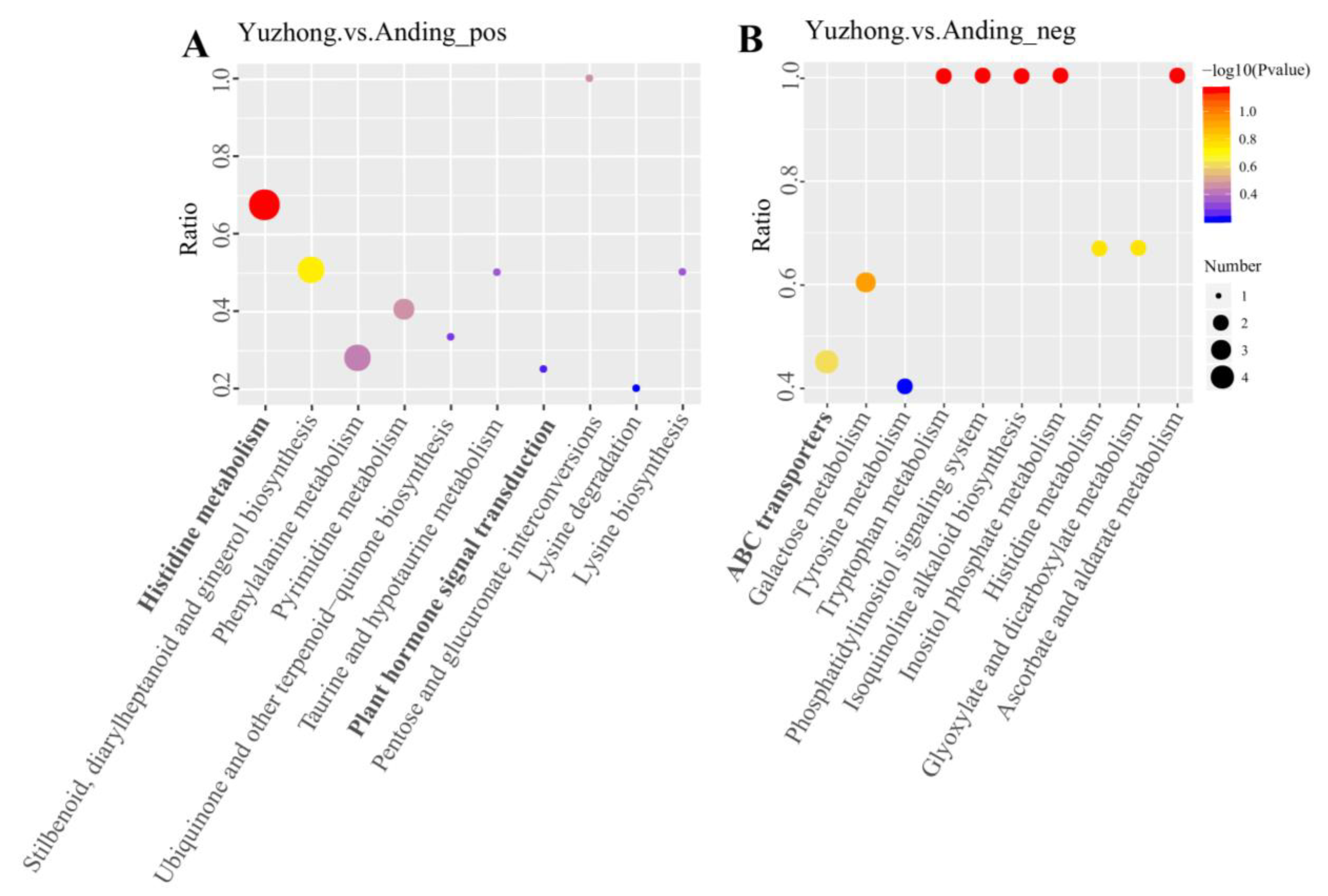
2.5. KEGG Pathway
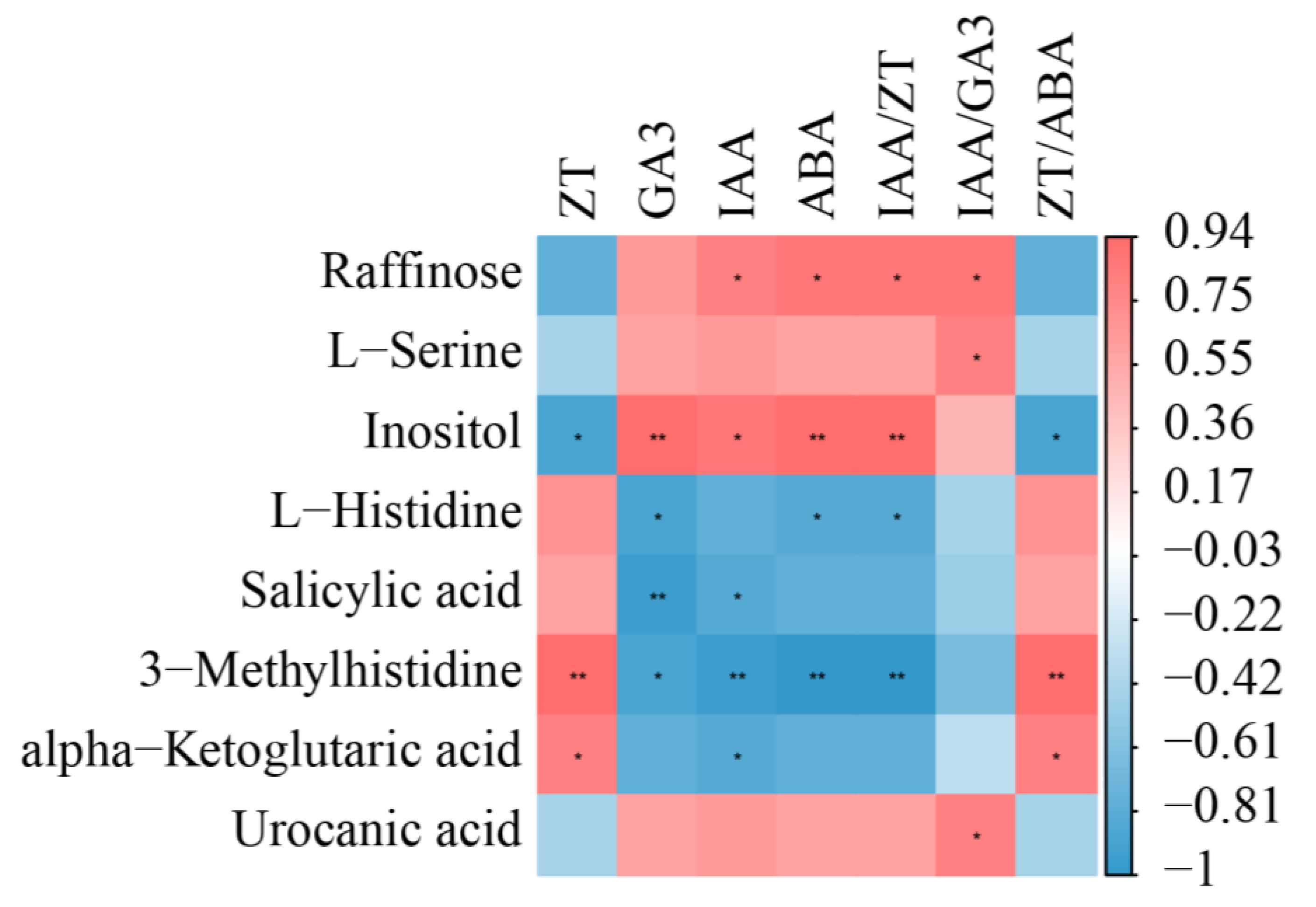
2.6. Interaction of Metabolites and Phytohormones
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Determination of Rhizome Morphology
4.3. Determination of Phytohormone
4.4. Metabolite Extraction
4.5. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patil, S.B.; Barbier, F.F.; Zhao, J.; Zafar, S.A.; Uzair, M.; Sun, Y.; Fang, J.; Perez-Garcia, M.D.; Bertheloot, J.; Sakr, S.; et al. Sucrose promotes D53 accumulation and tillering in rice. New Phytol. 2022, 234, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Plunkert, M.; Luo, X.; Liu, Z.C. Developmental regulation of stolon and rhizome. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 59, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toriba, T.; Tokunaga, H.; Nagasawa, K.; Nie, F.Y.; Yoshida, A.; Kyozuka, J. Suppression of Leaf Blade Development by BLAndingE-ON-PETIOLE Orthologs Is a Common Strategy for Underground Rhizome Growth. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Q.; Xu, Q.; Meyer, W.A.; Huang, B.R. Hormone regulation of rhizome development in tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea) associated with proteomic changes controlling respiratory and amino acid metabolism. Ann. Bot. 2016, 118, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimešová, J.; Martínková, J.; Herben, T. Horizontal growth: An overlooked dimension in plant trait space. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 32, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pausas, J.G.; Keeley, J.E. Evolutionary ecology of resprouting and seeding in fire prone ecosystems. New Phytol. 2014, 204, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, B.B.; Barbier, F.; Danieli, R.; Teper-Bamnolker, P.; Ziv, C.; Spíchal, L.; Aruchamy, K.; Shnaider, Y.; Leibman, D.; Shaya, F.; et al. Sucrose promotes stem branching through cytokinin. Plant Physiol. 2021, 185, 1708–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastdrager, J.; Hanson, J.; Smeekens, S. Sugar signals and the control of plant growth and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquès-Bueno, M.M.; Armengot, L.; Noack, L.C.; Bareille, J.; Rodriguez, L.; Platre, M.P.; Bayle, V.; Liu, M.; Opdenacker, D.; Vanneste, S.; et al. Auxin-Regulated Reversible Inhibition of TMK1 Signaling by MAKR2 Modulates the Dynamics of Root Gravitropism. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.M.; Luo, F.F.; Wu, D.X.; Zhang, X.H.; Lou, M.M.; Shen, D.F.; Yan, M.; Mao, C.Z.; Fan, X.R.; Xu, G.H.; et al. OsPIN9, an auxin efflux carrier, is required for the regulation of rice tiller bud outgrowth by ammonium. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.Y.; Chen, H.Q.; Dong, S.J.; Ma, Z.Y.; Ren, H.B.; Zhu, X.D.; Fang, X.H.; Chen, F. OsWUS promotes tiller bud growth by establishing weak apical dominance in rice. Plant J. 2020, 104, 1635–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.X.; Sun, L.P.; Chen, Y.Y.; Xue, P.; Yang, Q.Q.; Wang, B.F.; Yu, N.; Cao, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, K.; et al. Rice dwarf and low tillering 10 (OsDLT10) regulates tiller number by monitoring auxin homeostasis. Plant Sci. 2020, 297, 110502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Meng, X.P.; Liu, X.L.; Liu, T.N.; Wang, H.; Jia, Z.K.; Yang, D.Q.; Ren, X.L. Exogenous Hormonal Application Regulates the Occurrence of Wheat Tillers by Changing Endogenous Hormones. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.F.; Wu, B.; Xing, Y.Z.; Zhang, Z.X. Conservation and divergence: Regulatory networks underlying reproductive branching in rice and maize. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 41, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balla, J.; Medveďová, Z.; Kalousek, P.; Matiješčuková, N.; Friml, J.; Reinöhl, V.; Procházka, S. Auxin flow-mediated competition between axillary buds to restore apical dominance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbier, F.; Dun, E.; Kerr, S.; Chabikwa, T.; Beveridge, C. An Update on the Signals Controlling Shoot Branching. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Song, J.C.; Jameson, P.E. Cytokinin glucosyl transferases, key regulators of cytokinin homeostasis, have potential value for wheat improvement. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 878–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.T.; Guan, S.C.; Wen, C.J.; Li, P.; Gao, Z.; Chen, X. Auxin and cytokinin coordinate the dormancy and outgrowth of axillary bud in strawberry runner. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Chen, J.Q.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, T.; Li, W.Q.; Lin, L. Gibberellin A3 induces polyaerial shoot formation and increases the propagation rate in Paris polyphylla rhizomes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 167, 113511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenreira, T.; Lange, M.; Lange, T.; Bres, C.; Labadie, M.; Monfort, A.; Hernould, M.; Rothan, C.; Denoyes, B. A Specific Gibberellin 20-Oxidase Dictates the Flowering-Runnering Decision in Diploid Strawberry. Plant Cell. 2017, 29, 2168–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.G.; Yu, H.; Duan, J.B.; Yuan, K.; Yu, C.J.; Meng, X.B.; Kou, L.Q.; Chen, M.J.; Jing, Y.H.; Liu, G.F.; et al. SLR1 inhibits MOC1 degradation to coordinate tiller number and plant height in rice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameau, C.; Bertheloot, J.; Leduc, N.; Andrieu, B.; Foucher, F.; Sakr, S. Multiple pathways regulate shoot branching. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.W.; Chen, W.X.; Eggert, K.; Charnikhova, T.; Bouwmeester, H.; Schweizer, P.; Hajirezaei, M.; Seiler, C.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Wirén, N.; et al. Abscisic acid influences tillering by modulation of strigolactones in barley. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 3883–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Smith, S. Hormone Metabolism and Signaling in Plants; Academic Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Sun, X.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H.F.; Liu, Y.J.; Jiang, Y.W.; Xie, F.C.; Chen, Y.J. Mining of long non-coding RNAs with target genes in response to rust based on full-length transcriptome in Kentucky bluegrass. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1158035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.Q.; Yu, J.J.; Zhuang, L.L.; Shi, Y.; Meyer, W.; Huang, B.R. Differential regulatory pathways associated with drought-inhibition and post-drought recuperation of rhizome development in perennial grass. Ann. Bot. 2020, 126, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.J.; Hu, S.Q.; Zhao, X.Y.; Kumar, S.; Li, Y.X.; Yang, J.J.; Hou, H.W. Mechanisms of the Morphological Plasticity Induced by Phytohormones and the Environment in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpal, V.; Rathore, P.; Mehta, S.; Wadhwa, N.; Yadav, P.; Berry, E.; Goel, S.; Bhat, V.; Raina, S. Epigenetic variation: A major player in facilitating plant fitness under changing environmental conditions. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1020958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.B.; Ma, J.X. The genetic basis of shoot architecture in soybean. Mol. Breed. 2023, 43, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Smith, S.M.; Li, J. Genetic Regulation of Shoot Architecture. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 437–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprna, R.; Humplík, J.F.; Špíšek, Z.; Bryksová, M.; Zatloukal, M.; Mik, V.; Novák, O.; Nisler, J.; Doležal, K. Improvement of Tillering and Grain Yield by Application of Cytokinin Derivatives in Wheat and Barley. Agronomy 2021, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Weng, F.; Zha, M.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S. Relationship of the multi-tiller phenotype of a rice mutant D12W191with cytokinin. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2016, 39, 711–721. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, X.Q.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H.X.; Zhu, L.H.; Zhang, F.; Li, L.J.; Li, Q.; Tao, D.Y.; et al. Identification of rhizome-specific genes by genome-wide differential expression analysis in Oryza longistaminata. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, M.E.; Ramos-Montañez, S. Biosynthesis of Histidine. EcoSal Plus 2009, 3, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulis-Horn, R.; Persicke, M.; Kalinowski, J. Histidine biosynthesis, its regulation and biotechnological application in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microb. Biotechnol. 2013, 7, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Ma, Y.; Han, E.; Han, L.; Sun, L.; Peng, Z.; Wang, B. Research progress of ABC transporters in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. J. 2017, 53, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, R.J.; Bai, X.M.; Zhen, W.; Guo, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, C.N.; Lu, N. Study on rhizomes extensibility of 11 wild kentucky bluegrass collected in Gansu province. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2019, 27, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Anfang, M.; Shani, E. Transport mechanisms of plant hormones. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 102055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimann, K.; Skoog, F. Studies on the Growth Hormone of Plants: III. The Inhibiting Action of the Growth Substance on Bud Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1933, 19, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Yamagami, D.; Asami, T. Effects of gibberellin and strigolactone on rice tiller bud growth. J. Pestic. Sci. 2018, 43, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.L.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.J.; Yang, Z.M.; Huang, B.R. Gibberellic acid inhibition of tillering in tall fescue involving crosstalks with cytokinins and transcriptional regulation of genes controlling axillary bud outgrowth. Plant Sci. 2019, 287, 110168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotov, A.A.; Kotova, L.M.; Romanov, G.A. Signaling network regulating plant branching: Recent advances and new challenges. Plant Sci. 2021, 307, 110880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Q.; Luo, Y.L.; Kong, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Interactions Between Exogenous Cytokinin and Nitrogen Application Regulate Tiller Bud Growth via Sucrose and Nitrogen Allocation in Winter Wheat. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 40, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; Masson, P.; Michopoulos, F.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Loftus, N.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling of animal andhuman tissues via UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Total Differentially Expressed Metabolites (DEMs) | Up DEMs | Down DEMs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive ion mode | 163 | 60 | 103 |
| Negative ion mode | 75 | 36 | 39 |
| Metabolite Name | KEGG Pathway | VIP | log2FC | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imidazoleacetic acid | Histidine metabolism | 1.0594 | 0.7486 | 0.0304 |
| 3-Methylhistidine | Histidine metabolism | 1.7679 | 1.4103 | 0.0027 |
| Alpha-Ketoglutaric acid | Histidine metabolism | 1.4028 | 0.9658 | 0.0003 |
| Urocanic acid | Histidine metabolism | 1.0687 | −1.1618 | 0.0447 |
| Raffinose | ABC transporters | 1.6006 | −1.6531 | 0.0060 |
| L-Serine | ABC transporters | 1.3568 | −0.6028 | 0.0251 |
| Inositol | ABC transporters | 1.8831 | −2.6496 | 0.0000 |
| L-Histidine | ABC transporters | 1.4208 | 0.9078 | 0.0109 |
| Salicylic acid | Salicylic acid | 1.0364 | 0.8770 | 0.0448 |
| Phytohormone | Peak Time (min) | Regression Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IAA | 4.280 | Y = 1.66 × 104X − 1.98 × 103 | 0.999943 |
| ZT | 6.030 | Y = 4.36 × 10X + 1.34 × 103 | 0.999464 |
| GA3 | 7.987 | Y = 4.58 × 103X − 2.94 × 102 | 0.999656 |
| ABA | 8.794 | Y = 2.60 × 104X − 2.70 × 103 | 0.999934 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ran, F.; Bai, X.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Li, P.; Chen, H. Cytokinin and Metabolites Affect Rhizome Growth and Development in Kentucky Bluegrass (Poa pratensis). Biology 2023, 12, 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081120
Ran F, Bai X, Li J, Yuan Y, Li C, Li P, Chen H. Cytokinin and Metabolites Affect Rhizome Growth and Development in Kentucky Bluegrass (Poa pratensis). Biology. 2023; 12(8):1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081120
Chicago/Turabian StyleRan, Fu, Xiaoming Bai, Juanxia Li, Yajuan Yuan, Changning Li, Ping Li, and Hui Chen. 2023. "Cytokinin and Metabolites Affect Rhizome Growth and Development in Kentucky Bluegrass (Poa pratensis)" Biology 12, no. 8: 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081120
APA StyleRan, F., Bai, X., Li, J., Yuan, Y., Li, C., Li, P., & Chen, H. (2023). Cytokinin and Metabolites Affect Rhizome Growth and Development in Kentucky Bluegrass (Poa pratensis). Biology, 12(8), 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081120




