Simple Summary
Energy homeostasis plays a crucial role in regulating plant defense responses. In this study, we characterized BrbZIP-S (S1-bZIP from Brassica rapa) as a key modulator of energy metabolism, including sugar and proline metabolism. In addition, plants overexpressing BrbZIP-S exhibited increased tolerance to darkness and heat stress, suggesting that BrbZIP-S regulates plant stress responses through a complex network mediated by abscisic acid, sugar, and proline.
Abstract
In higher plants, S1-basic region-leucine zipper (S1-bZIP) transcription factors fulfill crucial roles in the physiological homeostasis of carbon and amino acid metabolisms and stress responses. However, very little is known about the physiological role of S1-bZIP in cruciferous vegetables. Here, we analyzed the physiological function of S1-bZIP from Brassica rapa (BrbZIP-S) in modulating proline and sugar metabolism. Overexpression of BrbZIP-S in Nicotiana benthamiana resulted in delayed chlorophyll degradation during the response to dark conditions. Under heat stress or recovery conditions, the transgenic lines exhibited a lower accumulation of H2O2, malondialdehyde, and protein carbonyls compared to the levels in transgenic control plants. These results strongly indicate that BrbZIP-S regulates plant tolerance against dark and heat stress. We propose that BrbZIP-S is a modulator of proline and sugar metabolism, which are required for energy homeostasis in response to environmental stress conditions.
1. Introduction
Energy homeostasis in plant cells is regulated by diverse mechanisms concurring with the plant’s response to environmental conditions. Energy is available in the form of carbon fixed through photosynthesis, whereas various environmental stresses affect photosynthetic carbon metabolism by affecting photosynthesis, carbon allocation, respiration, and so on [1,2]. Thus, energy management systems, including catabolic processes and anabolism repression are required for plant growth and development under energy-deprived conditions [3]. As an energy sensor, sucrose non-fermenting-1-related kinases 1 (SnRK1) assists in transcriptional and metabolic reprogramming, which regulates the carbohydrate metabolism and energy balance under low-energy stress [4,5]. Importantly, members of the basic region-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor family have been found to be SnRK1-downstream mediators, which regulate the transcription of genes involved in various catabolic pathways providing alternative sources of energy and metabolites [3].
In the Arabidopsis genome, the bZIP family comprises 78 genes divided into 13 groups (A-K, M, and S). Most of these bZIP transcription factors have been found to regulate plant growth, development, senescence, seed maturation, metabolic reactions, and stress responses [6]. Among the plant bZIP family, the formation of heterodimers between S1 (a subgroup of the S group) and C bZIP group members is referred to as the C/S1 bZIP network, which play an important role in the plant low-energy management system [7]. Under starvation conditions, SnRK1 phosphorylated Arabidopsis bZIP63 (group C) to enhance heterodimerization with particular S1 group members [8] and improved the transcriptional potential of S1 group members, such as Arabidopsis bZIP11 [3]. However, the transcriptional responses induced by darkness include the induction of stress-related and metabolic target genes by S1-bZIPs in SnRK1-dependent and -independent ways [8]. In addition, S1-bZIPs were found to be transcriptionally induced by abiotic stresses, leading to enhanced tolerance against cold, salt, and drought [9,10,11]. For example, the analysis of loss-of-function and gain-of-function mutations in Arabidopsis S1-bZIP member (AtbZIP1) suggested that AtbZIP1 regulates plant tolerance to abiotic stresses including salt, osmotic, and drought stresses [9]. Similarly, rice S1-bZIP member (OsbZIP71) overexpression led to enhanced tolerance to drought, salt, and osmotic stresses [12], suggesting that S1-bZIPs are an available resource to improve environmental stress tolerance, although the functional specificities of individual S1-bZIPs remain unknown.
Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) is a vital cruciferous vegetable in Asia, particularly in China, Korea, and Japan. Its production yield is significantly affected by global climate change [13]. Although understanding the molecular mechanism of stress -tolerance modulation is essential, functional characterization of stress-induced genes in this plant remains a challenge. In a previous study, we identified 64 bZIPs as drought-induced differentially expressed genes. Among them, Brassica rapa S1-bZIP, known as BrbZIP-S, was induced by drought and salt stresses, indicating its possible involvement in abiotic stress responses [13]. To investigate the function of BrbZIP-S and evaluate its potential for engineering stress tolerance, we analyzed the impact of a heterologous gain-of-function approach of BrbZIP-S in Nicotiana benthamiana.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Growth Conditions
Seeds of Chinese cabbage (B. rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) cultivar (Chunkwang) and two lines of BrbZIP-S-overexpressing N. benthamiana (OX3 and OX7; T3 generation) were germinated and grown in a growth chamber (16 h light and 8 h dark) at 24 °C. In addition, we chose regenerated plants, which survived on the selection medium but exhibited no transcription of BrbZIP-S, as transgenic control plants (TC). Six- to eight-week-old transgenic or TC plants were incubated at 45 °C for six hours or treated with dark stress for five days. Three biological replicates (ten plants for each replicate) in each treatment were carried out.
2.2. cDNA Synthesis and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
Total RNA was isolated from the leaves of Chinese cabbage or N. benthamiana using FavorPrep Plant Total RNA Mini Kit (Favogen, Pingtung, Taiwan) and reverse-transcribed using the Toyobo cDNA synthesis kit (TOYOBO, Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan). qRT-PCR was performed using the Toyobo SYBR-Green Master Mix. Specific primer pairs for each gene were used (Table S1) and the transcription levels of target genes were normalized to NbEF1.
2.3. Plasmid Construction, Plant Transformation, and Analysis of Subcellular Localization
Using Chinese cabbage cDNA as a template, the full-length BrbZIP-S (accession number: XM_009140057) was cloned into the gateway binary vector pGWB505 for the expression of BrbZIP-S. The binary vector was introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 and used to transform N. benthamiana. Leaf disk explants of 3-week-old plants were inoculated into the Agrobacterium suspension, and co-cultivated in dark condition. After 48 h, leaf disks were selected with selection medium (MS medium containing 1 mg/L 6-benzylaminopurine, 0.1 mg/L indole-3-acetic acid, 300 mg/L cefotaxime, 30 mg/L hygromycin, 30 g/L sucrose, and 7.5 g/L plant agar). The transgenic lines showing hygromycin resistance were transplanted in soil and lines with a high level of BrbZIP-S-GFP protein were selected by RT-PCR.
GFP fluorescence was visualized using an Olympus FV1000 laser scanning confocal microscope (Tokyo, Japan). The DNA-binding reagent, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), was used for staining nuclei.
2.4. Analysis of Proline and Pyrroline-5-Carboxylate (P5C) Contents
Leaves of N. benthamiana were homogenized in 3% sulfosalicylic acid. After centrifugation, the supernatant was used for the analysis of proline and P5C contents. The content of proline was quantified using a colorimetric assay as described by Eom et al. [14] and expressed as ng/mg of fresh weight (F.W.).
For analysis of P5C content, the supernatant of each sample was mixed with 10 mM of 2-aminobenzaldehyde, as described by La et al. [15]. After incubation at 37 °C for two hours, the absorbance at 440 nm was determined, calculated by using an extinction coefficient of 2.58 mM−1 cm−1, and expressed as nM/mg of F.W.
2.5. Determination of Invertase Activity and Sucrose, Glucose, and Fructose Contents
To determine the activity of invertase, 0.5 g of leaf grinding material was mixed in 1 mL extraction buffer (200 mM HEPES, 3 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 2% glycerol, 0.1 mM PMSF, and 1 mM benzamidine) as described by Bonfig et al. [16]. After centrifugation, the supernatant was used to analyze the vacuolar invertase (NbV-inv) activity. The pellet was washed three times with distilled water, resuspended in the extraction buffer with 1 M NaCl, and subjected to another round of centrifugation. The supernatant was used to analyze the activity of extracellular invertase (NbC-inv). The activity of NbV-inv and NbC-inv was analyzed using GOD-POD reagent [16] and the absorbance at 595 nm was determined.
The contents of glucose, fructose, and sucrose were determined using the Sucrose/D-Fructose/D-Glucose Assay Kit (Megazyme, Wicklow, Ireland).
2.6. Determination of Chlorophyll (Chl), H2O2 Accumulation, Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content, and Protein Carbonyl Content
Ten milligrams of samples were extracted in 95% ethanol at 80 °C for 30 min, and an aliquot of the extracts was used to determine the chlorophyll (Chl) content. The contents of Chl a, b, and Chl a+b were calculated according to Czyczyło-Mysza et al. [17].
The accumulation of H2O2 in N. benthamiana leaves was carried out using the 3,3-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining method, as described by Ji et al. [18]. In addition, MDA content was analyzed as described by Eom et al. [13] and expressed as nmol/mg of F.W. using an absorbance coefficient of 155 mM−1 cm−1.
To determine the protein carbonyl content, protein from N. benthamiana leaves was extracted using an extraction buffer, as described by Eom et al. [13]. The same concentrations of protein were used for analyzing content of protein carbonyl using a fluorometric protein carbonyl content assay kit (BioVision, Milpitas, CA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sucrose-Induced Repression of Translation in BrbZIP-S
Among the plant bZIP family, the S group is the largest bZIP subfamily and is divided into three subgroups (S1, S2, and S3) [19]. As shown in Figure 1A, BrbZIP-S is phylogenetically closely related to the Arabidopsis S1-bZIP subgroup, which includes AtbZIP1, AtbZIP2, AtbZIP11, AtbZIP44, and AtbZIP53 [19]. Sucrose is a signaling molecule that negatively controls the translation of the S1-bZIP subgroup [20,21]. This sucrose-induced repression of translation (SIRT) is mediated by the presence of a highly conserved upstream open reading frame (uORF) found in the 5′ leader region of S1-bZIP transcripts, called the sucrose-controlled uORF (SC-uORF) [20,21]. BrbZIP-S contained four uORFs in its 5′ leader of which the third uORF showed high homology to the SC-uORF of Arabidopsis S1-bZIPs (Figure 1B), indicating that BrbZIP-S retains a SIRT mechanism mediated by a conserved SC-uORF.
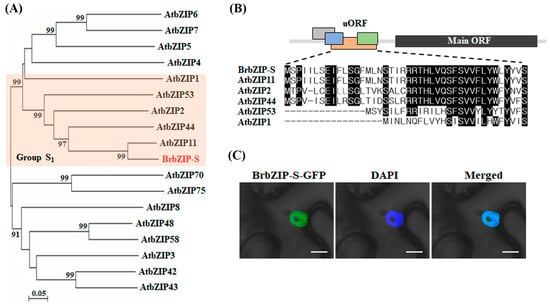
Figure 1.
Characterization of Brassica rapa bZIP-S (BrbZIP-S). (A) Phylogenetic analysis between Arabidopsis S bZIPs and BrbZIP-S. (B) Evolutionary conserved uORF in BrbZIP-S. The predicted amino acid sequence encoded by SC-uORF of BrbZIP-S was aligned with Arabidopsis S1-bZIPs. (C) Subcellular localization of BrbZIP-S in N. benthamiana plants. Co-localization of GFP with DAPI confirms the localization of BrbZIP-S in the nucleus. Scale bar = 10 μm.
Similar to other plant S1-bZIPs [22], BrbZIP-S-cGFP was localized in the nucleus (Figure 1C), indicating that BrbZIP-S is a nuclear protein. Although the basic region of bZIPs serves as a nuclear localization signal, phospho-mimicking mutations can disrupt the correct localization of bZIPs, indicating that phosphorylation regulates the subcellular localization of bZIP proteins, targeting either nuclear import or cytoplasmic retention [23,24]. However, the nuclear localization of AtbZIP53-cGFP was not changed by mimicking phosphorylation of conserved serines in the DNA-binding domain, suggesting that the functionality of the nuclear localization signal in S1-bZIPs is not disrupted by phosphorylation events [24].
3.2. BrbZIP-S Affects Sucrose Metabolism
Sucrose, the major form of carbon in higher plants, is used for internal regulation and physiological responses. As described above, S1-bZIPs, including BrbZIP-S, are known to be repressed by sucrose through translational inhibition [25,26], whereas overexpression of S1-bZIP increases the sugar content [26,27,28]. For example, fruit-specific expression of tomato S1-bZIP (SlbZIP1) or overexpression of strawberry S1-bZIP (strawberry bZIP11) resulted in tomato sweetening via the accumulation of sugar (sucrose, glucose, and fructose) [27,28]. Similarly, we found that the heterologous overexpression of BrbZIP-S induced sugar accumulation in N. benthamiana plants. As shown in Figure 2, the sucrose content was approximately 2.7- to 3-fold higher in transgenic lines (OX3 and OX7) than in TC plants. The transgenic plants also had higher levels of glucose (2.3- to 4-fold) and fructose (2.4- to 2.9-fold). In addition, overexpression of BrbZIP-S resulted in increased activity of vacuolar invertase. Furthermore, N. benthamiana vacuolar invertase 1 (NbV-inv 1) was upregulated in all transgenic lines (Figure 2), suggesting that BrbZIP-S affected carbohydrate partitioning via a mechanism that includes the regulation of NbV-inv 1 expression. These results suggest that BrbZIP-S is a potential gene for improving sweetness via the reprogramming of sugar metabolism.
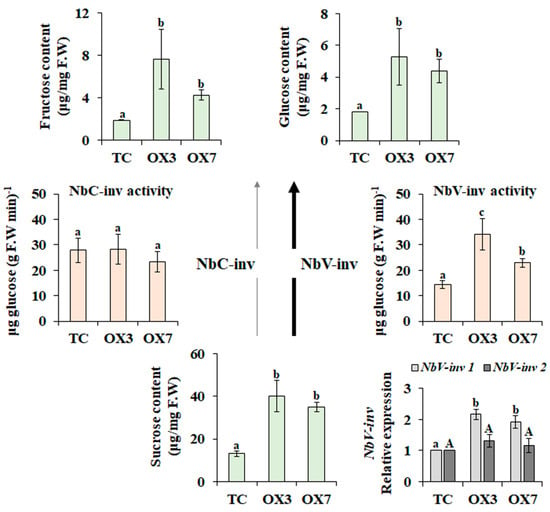
Figure 2.
Sucrose metabolism in BrbZIP-S-overexpressing N. benthamiana plants (OX3 and OX7 lines). Total content of sucrose, glucose, and fructose was determined. The activities of vacuolar invertase (NbV-inv) and extracellular invertase (NbC-inv) were determined. Normalized expression levels of NbV-inv 1 and 2 were expressed as relative to transgenic control (TC) plants. Means (±SE) with different letters are significantly different, according to Duncan’s multiple range test (<0.05).
3.3. Altered Proline Metabolism in BrbZIP-S Transgenic N. benthamiana Plants
One of the most important multifunctional amino acids in plants is proline, which is a proteinogenic amino acid synthesized from glutamate and ornithine [29]. Proline biosynthesis is induced by various stressors, and its catabolism is activated in darkness and during stress relief via TOR- and SnRK1-dependent signaling [30,31]. Overexpression of AtbZIP11 has been shown to lead to reduced proline content [32], indicating that S1-bZIP plays a role in coordinating sucrose and proline metabolism. We showed that OX plants contained a much lower proline level than the TC plants (Figure 3). In addition, P5C was slightly increased in OX plants, indicating that proline catabolism was activated by BrbZIP-S.
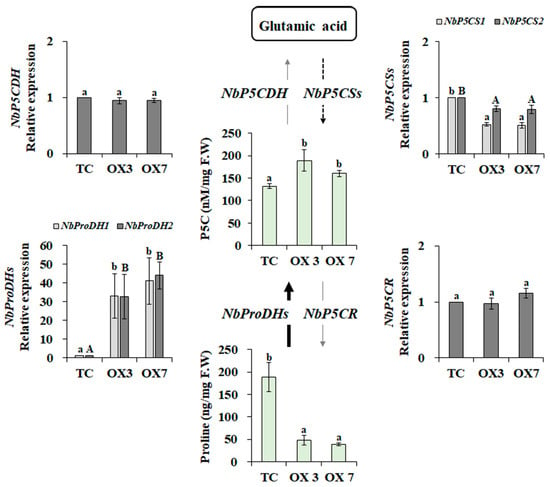
Figure 3.
Proline metabolism in BrbZIP-S overexpressing N. benthamiana plants (OX3 and OX7 lines). Proline and pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C) contents were determined in BrbZIP-S-overexpressing (OX3 and OX7) and transgenic control (TC) plants. Expression levels of ProDHs (proline dehydrogenases), P5CDH (delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase), P5CR (pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase), and P5CSs (pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetases) were expressed as relative to TC plants. Means (±SE) with different letters are significantly different (Duncan’s multiple range test, p < 0.05).
In higher plants, proline catabolism occurs in the mitochondria by the catalytic action of two enzymes, proline dehydrogenase (ProDH; EC 1.5.99.8), which produces pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C) from proline, and delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase (P5CDH; EC 1.5.1.12), which converts P5C to glutamate. The two enzymes pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS; EC not assigned) and pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase (P5CR; EC 1.5.1.2) are involved in proline biosynthesis catalyzing glutamate to proline [29,31]. In Arabidopsis, S1-bZIPs, including bZIP2, bZIP11, bZIP44, and bZIP53, function as transcriptional activators of ProDH genes [33], and the formation of the C/S1 bZIP network is required for controlling ProDH expression [11]. Here we showed that N. benthamiana ProDH (NbProDH) 1 and 2 were expressed at higher levels in OX plants compared to TC plants (Figure 3). In contrast, the expression levels of NbP5CS 1 and 2 were down-regulated (Figure 3). These results suggest that BrbZIP-S induces metabolic changes in proline metabolism.
3.4. BrbZIP-S Controls Darkness-Induced Senescence in Transgenic Plants
Various investigations have shown that unfavorable environmental stressors, including light deprivation, lead to rapid leaf senescence [34]. The understanding of darkness- or age-induced senescence is of high economic relevance as senescence can significantly decrease the post-harvest shelf-life of a plant as well as lead to yield loss in agriculture [35]. In Arabidopsis, the low content of trehalose 6-phosphate, a non-competitive inhibitor of SnRK1 [36], was shown to lead to delayed senescence [37]. During darkness-induced senescence, it was found that ProDH-mediated proline catabolism provides energy and glutamate, which play a crucial role in nitrogen remobilization [38]. Therefore, we presumed that the increasing proline catabolism by BrbZIP-S delays darkness-induced senescence. To test this hypothesis, we transferred six-week-old plants to extended darkness for five days and then analyzed the Chl levels, an integral part of leaf senescence [39]. As shown in Figure 4, the levels of Chl a, Chl b, and Chl a+b decreased by 58.2% (1.29 µg/mg F.W. to 0.54 µg/mg F.W.), 74.7% (0.57 g/mg F.W. to 0.14 g/mg F.W.), and 63.3% (1.87 µg/mg F.W. to 0.68 µg/mg F.W.), respectively, in plants kept in darkness, compared to those in normal growth conditions. However, the contents of Chl a, Chl b, and Chl a + b were significantly higher in OX3 and OX7 lines than in TC plants under dark conditions, indicating that BrbZIP-S overexpression delayed Chl degradation during darkness-induced senescence. It was previously shown that nutrient-deprivation-induced senescence and age-dependent senescence were delayed in plants overexpressing KIN10 (the main component of Arabidopsis SnRK1) and the rice SnRK1, respectively [3,40], suggesting the essential role of S1-bZIPs, including BrbZIP-S, in plant survival is through inducing remobilization of proline under darkness and nutrient deprivation conditions.
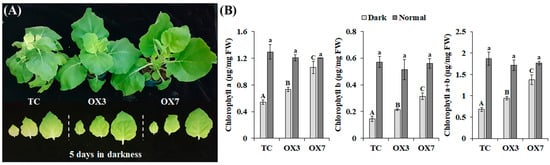
Figure 4.
BrbZIP-S overexpression delayed darkness-induced senescence in N. benthamiana plants. (A) The phenotype of BrbZIP-S-overexpressing plants (OX3 and OX7 lines) and transgenic control (TC) plants after five days in darkness. (B) Chlorophyll (Chl) contents of plants were determined. Uppercase denotes significance between the Chl levels under darkness, whereas lower-case denotes significance between the Chl levels under normal conditions (Duncan’s multiple range test, p < 0.05).
3.5. Overexpression of BrbZIP-S Increases the Heat Tolerance of N. benthamiana
Among unfavorable environmental conditions, higher temperatures above critical thresholds affect crop growth and development, leading to significant yield loss. Therefore, improving heat tolerance is of profound importance to the production yields of crops and will greatly secure food security [41]. Plant S1-bZIPs play a key role in plant innate immunity and the response to unfavorable environmental conditions [11]. In our previous study, BrbZIP-S was induced under abiotic stress conditions [13], indicating the possible involvement of BrbZIP-S in the stress response. To analyze the function of BrbZIP-S in heat stress responses, OX and TC plants were treated at 45 °C for six hours. As shown in Figure 5A, the leaves of the OX3 and OX7 lines were less wilted than those of the control plants. In addition, H2O2 was less accumulated in the OX3 and OX7 lines than in the TC plants (Figure 5B). After the subsequent recovery incubation at 25 °C, severe damage was observed in the TC plants, whereas only a slight wilting was seen in the OX3 and OX7 lines (Figure 5A). The levels of MDA and protein carbonyls were significantly lower in OX lines than in TC plants (Figure 5C,D), indicating that BrbZIP-S increased heat tolerance in N. benthamiana plants.

Figure 5.
BrbZIP-S overexpression improved heat tolerance in N. benthamiana plants. (A) The phenotype of BrbZIP-S-overexpressing plants (OX3 and OX7 lines) and transgenic control (TC) plants after exposure to 45 °C for six hours and recovery overnight at normal growth conditions. Changes in H2O2 level (B), malondialdehyde (MDA) level (C), and protein carbonyl content (D) were determined. Means (±SE) with different letters are significantly different (Duncan’s multiple range test, p < 0.05).
Soluble sugars are osmoprotectants, which can protect cell membranes by scavenging toxic reactive oxygen species generated under various stress conditions, including heat stress [42,43]. In addition, SlbZIP1 and OsbZIP71 exert important roles in abiotic stress tolerance via modulating abscisic acid (ABA)-mediated pathways [12,44]. Under heat stress conditions, the transcription levels of genes involved in sucrose metabolism including sucrose synthase and invertase, were increased by ABA [45]. Therefore, one possible explanation should be that the BrbZIP-S-induced sugar metabolism reprogramming seen above (Figure 2) contributes to improved heat tolerance.
4. Conclusions
Energy homeostasis under energy-deprived conditions is very common and important in regulating plant defense responses. In this study, we analyzed the physiological function BrbZIP-S, and suggested that BrbZIP-S acts as a positive factor in stress tolerance against darkness and heat stress. BrbZIP-S may be regulated by stress response pathways via a complex network mediated by ABA, sugar, and proline. Further functional dissection of S1-bZIP proteins, their targets, and their interplay in signaling pathways mediated by energy homeostasis will contribute to our understanding of plant responses under environmental stress conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology12040517/s1, Table S1: Primer sequences for cloning and qPCR analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H.E., H.B.L. and T.K.H.; investigation, S.H.E.; writing—original draft preparation, S.H.E., H.B.L. and T.K.H.; writing—review and editing, S.H.E., H.B.L. and T.K.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out with the support of the “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ01501905)” Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to reasons of privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bechtold, U.; Field, B. Molecular mechanisms controlling plant growth during abiotic stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2753–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.; Stitt, M.; Hotta, C.T. How stress affects your budget-stress impacts on starch metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 774060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baena-González, E.; Rolland, F.; Thevelein, J.M.; Sheen, J. A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature 2007, 448, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baena-Gonzalez, E. Energy signaling in the regulation of gene expression during stress. Mol. Plant. 2010, 3, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nukarinen, E.; Nägele, T.; Pedrotti, L.; Wurzinger, B.; Mair, A.; Landgraf, R.; Börnke, F.; Hanson, J.; Teige, M.; Baena-Gonzalez, E.; et al. Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveals the role of the AMPK plant ortholog SnRK1 as a metabolic master regulator under energy deprivation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dröge-Laser, W.; Snoek, B.L.; Snel, B.; Weiste, C. The Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor family-an update. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dröge-Laser, W.; Weiste, C. The C/S1 bZIP Network: A regulatory hub orchestrating plant energy homeostasis. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrotti, L.; Weiste, C.; Nägele, T.; Wolf, E.; Lorenzin, F.; Dietrich, K.; Mair, A.; Weckwerth, W.; Teige, M.; Baena-González, E.; et al. Snf1-RELATED KINASE1-controlled C/S1-bZIP signaling activates alternative mitochondrial metabolic pathways to ensure plant survival in extended darkness. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, H.; Bai, X.; Ji, W.; Ding, X.; Zhu, Y. The Arabidopsis AtbZIP1 transcription factor is a positive regulator of plant tolerance to salt, osmotic and drought stresses. J. Plant Res. 2021, 125, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, L.; Pedrotti, L.; Weiste, C.; Fekete, A.; Schierstaedt, J.; Göttler, J.; Kempa, S.; Krischke, M.; Dietrich, K.; Mueller, M.J.; et al. Crosstalk between two bZIP signaling pathways orchestrates salt-induced metabolic reprogramming in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2244–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Norris, A.; Jiang, C.Z. S1-bZIP Transcription factors play important roles in the regulation of fruit quality and stress response. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 802802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Mao, B.; Ou, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Chu, C.; Wang, X. OsbZIP71, a bZIP transcription factor, confers salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 84, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, S.H.; Baek, S.A.; Kim, J.K.; Hyun, T.K. Transcriptome analysis in Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis) provides the role of glucosinolate metabolism in response to drought stress. Molecules 2018, 23, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, S.H.; Ahn, M.A.; Kim, E.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Wi, S.H.; Kim, S.K.; Lim, H.B.; Hyun, T.K. Plant response to cold stress: Cold stress changes antioxidant metabolism in heading type kimchi cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. Pekinensis). Antioxidants 2022, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La, V.H.; Lee, B.R.; Islam, M.T.; Mamun, M.A.; Park, S.H.; Bae, D.W.; Kim, T.H. Characterization of glutamate-mediated hormonal regulatory pathway of the drought responses in relation to proline metabolism in Brassica napus L. Plants 2020, 9, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, M.; Guivarćh, A.; Hirsche, J.; Bauerfeind, M.A.; González, M.C.; Hyun, T.K.; Eom, S.H.; Chriqui, D.; Engelke, T.; Großkinsky, D.K.; et al. Metabolic Control of Tobacco Pollination by Sugars and Invertases. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyczyło-Mysza, I.; Tyrka, M.; Marcińska, I.; Skrzypek, E.; Karbarz, M.; Dziurka, M.; Hura, T.; Dziurka, K.; Quarrie, S.A. Quantitative trait loci for leaf chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, chlorophyll and carotenoid contents in relation to biomass and yield in bread wheat and their chromosome deletion bin assignments. Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.S.; Bang, S.G.; Ahn, M.A.; Kim, G.; Kim, E.; Eom, S.H.; Hyun, T.K. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of heat stress-responsive superoxide dismutases in garlic (Allium sativum L.). Antioxidants 2021, 10, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoby, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Tiedemann, J.; Kroj, T.; Parcy, F.; bZIP Research Group. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Takamatsu, S.; Glasbrenner, M.; Becker, T.; Naito, S.; Beckmann, R. Sucrose sensing through nascent peptide-meditated ribosome stalling at the stop codon of Arabidopsis bZIP11 uORF2. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalor, S.K.; Berberich, T.; Lee, S.S.; Yang, S.H.; Zhu, X.; Imai, R.; Takahashi, Y.; Kusano, T. Deregulation of sucrose-controlled translation of a bZIP-type transcription factor results in sucrose accumulation in leaves. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ali, Z.; Xu, L.; He, X.; Huang, Y.; Yi, J.; Shao, H.; Ma, H.; Zhang, D. The nuclear protein GmbZIP110 has transcription activation activity and plays important roles in the response to salinity stress in soybean. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorca, C.M.; Potschin, M.; Zentgraf, U. bZIPs and WRKYs: Two large transcription factor families executing two different functional strategies. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.; Kirchler, T.; Fillinger, S.; Wanke, F.; Stadelhofer, B.; Stahl, M.; Chaban, C. Targeted manipulation of bZIP53 DNA-binding properties influences Arabidopsis metabolism and growth. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5659–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peviani, A.; Lastdrager, J.; Hanson, J.; Snel, B. The phylogeny of C/S1 bZIP transcription factors reveals a shared algal ancestry and the pre-angiosperm translational regulation of S1 transcripts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hanssen, M.; Lundgren, K.; Hernández, L.; Delatte, T.; Ehlert, A.; Liu, C.M.; Schluepmann, H.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Moritz, T.; et al. The sucrose-regulated Arabidopsis transcription factor bZIP11 reprograms metabolism and regulates trehalose metabolism. New Phytol. 2011, 191, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagor, G.H.; Berberich, T.; Tanaka, S.; Nishiyama, M.; Kanayama, Y.; Kojima, S.; Muramoto, K.; Kusano, T. A novel strategy to produce sweeter tomato fruits with high sugar contents by fruit-specific expression of a single bZIP transcription factor gene. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; He, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Heterologous overexpression of strawberry bZIP11 induces sugar accumulation and inhibits plant growth of tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 292, 110634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavi Kishor, P.B.; Suravajhala, P.; Rathnagiri, P.; Sreenivasulu, N. Intriguing role of proline in redox potential conferring high temperature stress tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 867531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Asthir, B. Proline: A key player in plant abiotic stress tolerance. Biol. Plant. 2015, 59, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.E.; Savouré, A.; Szabados, L. Proline metabolism as regulatory hub. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.; Hanssen, M.; Wiese, A.; Hendriks, M.M.; Smeekens, S. The sucrose regulated transcription factor bZIP11 affects amino acid metabolism by regulating the expression of ASPARAGINE SYNTHETASE1 and PROLINE DEHYDROGENASE2. Plant J. 2008, 53, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, R.; Fujita, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. A novel subgroup of bZIP proteins functions as transcriptional activators in hypoosmolarity-responsive expression of the ProDH gene in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjertaas, A.C.; Preston, J.C.; Kainulainen, K.; Humphreys, A.M.; Fjellheim, S. Convergent evolution of the annual life history syndrome from perennial ancestors. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1048656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebsch, D.; Keech, O. Dark-induced leaf senescence: New insights into a complex light-dependent regulatory pathway. New Phytol. 2016, 212, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.J.; Watson, A.; Griffiths, C.A. Trehalose 6-phosphate signalling and impact on crop yield. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingler, A.; Delatte, T.L.; O’Hara, L.E.; Primavesi, L.F.; Jhurreea, D.; Paul, M.J.; Schluepmann, H. Trehalose 6-phosphate is required for the onset of leaf senescence associated with high carbon availability. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launay, A.; Cabassa-Hourton, C.; Eubel, H.; Maldiney, R.; Guivarc’h, A.; Crilat, E.; Planchais, S.; Lacoste, J.; Bordenave-Jacquemin, M.; Clément, G.; et al. Proline oxidation fuels mitochondrial respiration during dark-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 6203–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresson, J.; Bieker, S.; Riester, L.; Doll, J.; Zentgraf, U. A guideline for leaf senescence analyses: From quantification to physiological and molecular investigations. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.H.; Hong, J.W.; Kim, E.C.; Yoo, S.D. Regulatory functions of SnRK1 in stress-responsive gene expression and in plant growth and development. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaoui, M.; Jemo, M.; Datla, R.; Bekkaoui, F. Heat and drought stresses in crops and approaches for their mitigation. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keunen, E.; Peshev, D.; Vangronsveld, J.; Van Den Ende, W.; Cuypers, A. Plant sugars are crucial players in the oxidative challenge during abiotic stress: Extending the traditional concept. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, J.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Roles of osmoprotectants in improving salinity and drought tolerance in plants: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Meng, X.; Cai, J.; Li, G.; Dong, T.; Li, Z. Basic leucine zipper transcription factor SlbZIP1 mediates salt and drought stress tolerance in tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Euring, D.; Cha, J.Y.; Lin, Z.; Lu, M.; Huang, L.J.; Kim, W.Y. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of heat tolerance in response to global climate change. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 627969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).