Body Composition and Strength Symmetry of Kettlebell Sport Athletes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. The Sample
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Hand Grip Strength
2.4. Bioimpedance Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Practical Applications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Valen, L. A study of fluctuating asymmetry. Evolution 1962, XVI, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, P.; Petrick, M.; Connor, H.; Conklin, D. Grip Strength and Hand Dominance: Challenging the 10% Rule. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1989, 43, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilibeck, P.D.; Davison, K.S.; Sale, D.G.; Webber, C.E.; Faulkner, R.A. Effect of physical activity on bone mineral density assessed by limb dominance across the lifespan. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2000, 12, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepper, P.G. The developmental origins of laterality: Fetal handedness. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 55, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, J.; Peña, J.; Sá, M.; Virgile, A.; García-de-Alcaraz, A.; Bishop, C. Why Sports Should Embrace Bilateral Asymmetry: A Narrative Review. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, B.J.; Fan, B.; Ng, B.; Shepherd, J.A. Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry body composition reference values of limbs and trunk from NHANES 1999–2004 with additional visualization methods. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardigò, L.P.; Ouergui, I.; Nobari, H.; Formenti, D. Some Insights Regarding Symmetry Relevance in Biomedicine. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roi, G.S.; Bianchedi, D. The Science of Fencing. Sport. Med. 2008, 38, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moysi, S.J.; Dorado, C.; Olmedillas, H.; Serrano-Sanchez, J.A.; Calbet, J.A. Bone and lean mass inter-arm asymmetries in young male tennis players depend on training frequency. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fousekis, K.; Tsepis, E.; Vagenas, G. Lower limb strength in professional soccer players: Profile, asymmetry, and training age. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2010, 9, 364. [Google Scholar]
- Bahenský, P.; Marko, D.; Bunc, V.; Tlustý, P. Power, Muscle, and Take-Off Asymmetry in Young Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Hondt, J.; Chapelle, L.; Droogenbroeck, L.V.; Aerenhouts, D.; Clarys, P.; D’Hondt, E. Bioelectrical impedance analysis as a means of quantifying upper and lower limb asymmetry in youth elite tennis players: An explorative study. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2022, 22, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapelle, L.; Bishop, C.; D’Hondt, J.; D’Hondt, E.; Clarys, P. Morphological and functional asymmetry in elite youth tennis players compared to sex- and age-matched controls. J. Sport. Sci. 2022, 40, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z. The Effect of Application of Asymmetry Evaluation in Competitive Sports: A Systematic Review. J. Phys. Act. Health 2022, 6, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Bredin, S.S.D.; Taunton, J.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, N.; Warburton, D.E.R. Association between Inter-Limb Asymmetries in Lower-Limb Functional Performance and Sport Injury: A Systematic Review of Prospective Cohort Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helme, M.; Tee, J.; Emmonds, S.; Low, C. Does lower-limb asymmetry increase injury risk in sport? A systematic review. Phys. Ther. Sport 2021, 49, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, S.J. The Relationship Between Asymmetry and Athletic Performance: A Critical Review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2579–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, E.; Ceravolo, A.C.; Cavatton, A.; Quarantelli, M.; Ilika, O.; Varalda, C. Kettlebell Sport: Endurance weight lifting. Description and analysis of the performance model. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2020, 20, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonov, V.F.; Suhovey, A.V.; Leonov, D.V. Fundamentals of Kettlebell Sport: Teaching Motor Actions and Methods of Training: A Manual. Mosc. Sov. Sport. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- World Kettlebell Sport Federation (WKSF). Available online: https://wksf.site/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/WKSF-General-Competition-Rules-English.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Jay, K.; Frisch, D.; Hansen, K.; Zebis, M.K.; Andersen, C.H.; Mortensen, O.S.; Andersen, L.L. Kettlebell training for musculoskeletal and cardiovascular health: A randomized controlled trial. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2011, 37, 196–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.; Mac Innis, M.J.; Koch, S.; Mac Leod, K.E.; Lohse, K.R.; Gallo, M.E.; Sheel, A.W.; Koehle, M.S. Cardiopulmonary Demand of 16-kg Kettlebell Snatches in Simulated Girevoy Sport. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 34, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quednow, J.; Sedlak, T.; Meier, J.; Janot, J.; Braun, S. The Effects of High Intensity Interval-Based Kettlebells and Battle Rope Training on Grip Strength and Body Composition in College—Aged Adults. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2015, 8, 124–133. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, J.A.; Wilson, C.J.; Keogh, J.W.; Ho, K.W.; Lorenzen, C. Snatch trajectory of elite level girevoy (kettlebell) sport athletes and its implications to strength and conditioning coaching. Int. J. Sport. Sci. Coach 2015, 10, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostiantyn, P.; Grygoriy, G.; Prontenko, V.; Volodymyr, A.P.; Tkachenko, Y.; Kostyuk, Y.; Zhukovskyi, Y. Kettlebell lifting as a means of physical training of cadets at the higher military educational Institution. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2017, 17, 2685–2689. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.S.; Schoenfeld, B.; Schoenfeld, M.L. Applications of kettlebells in exercise program design. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 33, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meigh, N.J.; Keogh, J.W.L.; Schram, B.; Hing, W.A. Kettlebell training in clinical practice: A scoping review. BMC Sport. Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.T.; Wu, H.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Ho, S.Y.; Chung, Y.C. Effects of 8-week kettlebell training on body composition, muscle strength, pulmonary function, and chronic low-grade inflammation in elderly women with sarcopenia. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 112, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prontenko, K.; Prontenko, V.; Bondarenko, V.; Bezpaliy, S.; Bykova, G.; Zeleniuk, O.; Dvoretsky, V. Improvement of the physical state of cadets from higher educational establishments in the Ukranian armes forces due to to use ok the kettlebell. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2017, 17, 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Prontenko, K.; Griban, G.; Prontenko, V.; Bezpaliy, S.; Bondarenko, V.; Andreychuk, V.; Tkachenko, P. Correlation analysis of readiness indicators of the athletes and their competitive results in kettlebell sport. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2017, 17, 2123–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli, A.; Rossi, B.; Pillon, L.; Bucciante, G. A new method for monitoring body fluid variation by bioimpedance analysis: The RXc graph. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, R.; Saragat, B.; Cabras, S.; Rinaldi, A.C.; Marini, E. Accuracy of Specific BIVA for the Assessment of Body Composition in the United States Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, E.; Campa, F.; Buffa, R.; Stagi, S.; Matias, C.N.; Toselli, S.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Phase angle and bioelectrical impedance vector analysis in the evaluation of body composition in athletes. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagi, S.; Silva, A.M.; Jesus, F.; Campa, F.; Cabras, S.; Earthman, C.P.; Marini, E. Usability of classic and specific bioelectrical impedance vector analysis in measuring body composition of children. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Thomas, D.M.; Watts, K.; Clark, N.; Baller, D.; Morin, T.; Toselli, S.; Koury, J.C.; Melchiorri, G.; Andreoli, A.; et al. Reference Percentiles for Bioelectrical Phase Angle in Athletes. Biology 2022, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Pirlich, M.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Bioelectrical phase angle and impedance vector analysis clinical relevance and applicability of impedance parameters. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.C.; Barbosa-Silva, T.G.; Bielemann, R.M.; Gallagher, D.; Heymsfield, S.B. Phase angle and its determinants in healthy subjects: Influence of body composition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Lu, J.; Jia, G.; Zheng, J. Skeletal muscle mass and quality: Evolution of modern measurement concepts in the context of sarcopenia. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2015, 74, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, C.; Della-Morte, D.; Cacciatore, F.; Gargiulo, G.; Galizia, G.; Roselli, M.; Curcio, F.; Bonaduce, D.; Abete, P. Phase angle as bioelectrical marker to identify elderly patients at risk of sarcopenia. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 58, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagi, S.; Irurtia, A.; Rosales Rafel, J.; Cabras, S.; Buffa, R.; Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Castizo-Olier, J.; Marini, E. Segmental body composition estimated by specific BIVA and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagi, S.; Ibáñez-Zamacona, M.E.; Jelenkovic, A.; Marini, E.; Rebato, E. Association between self-perceived body image and body composition between the sexes and different age classes. Nutrition 2021, 82, 111030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagi, S.; Moroni, A.; Micheletti Cremasco, M.; Marini, E. Body Composition Symmetry in Long-Term Active Middle-Aged and Older Individuals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, T.G.; Roche, A.F.; Martorell, R. Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual; Human Kinetics Books: Champaign, IL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio: Report of a WHO Expert Consultation. Health Organization. 2008. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44583 (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Hillman, E.T.; Nunes, Q.M.; Hornby, S.T.; Stanga, Z.; Neal, K.R.; Rowlands, B.J.; Allison, S.P.; Lobo, D.N. A practical posture for hand grip dynamometry in the clinical setting. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Peolsson, A.; Massy-Westropp, N.; Desrosiers; JBear-Lehman, J. Reference values for adult grip strength measured with a Jamar dynamometer: A descriptive meta-analysis. Physiotherapy 2006, 92, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.; Lawton, T.; Harris, N.; Kilding, A.; McMaster, D.T. A brief review of handgrip strength and sport performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 3187–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIH. Bioelectrical impedance analysis in body composition measurement: National Institutes of Health Technology Assessment Conference Statement. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 524S–532S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, M.E.; Mereu, E.; Buffa, R.; Gualdi-Russo, E.; Zaccagni, L.; Cossu, S.; Rebato, E.; Marini, E. New specific bioelectrical impedance vector reference values for assessing body composition in the Italian-Spanish young adult population. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2015, 27, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, A.; Pastori, G. BIVA Software 2002; Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences, University of Padova: Padova, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, A.; Honnold, D.; Hudy, A.; Roberts, C.; Gallagher, P.; Vardiman, P.; Dellasega, C. Relationships between muscular strength and batting performances in collegiate baseball athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducher, G.; Courteix, D.; Meme, S.; Magni, C.; Viala, J.F.; Benhamou, C.L. Bone geometry in response to long-term tennis playing and its relationship with muscle volume: A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study in tennis players. Bone 2005, 37, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijewski, M.; Burdukiewicz, A.; Pietraszewska, J.; Andrzejewska, J.; Stachoń, A. Asymmetry of Muscle Mass Distribution and Grip Strength in Professional Handball Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.J.; Aagaard, P.; Herzog, W. Lower limb asymmetry in mechanical muscle function: A comparison between ski racers with and without ACL reconstruction. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2015, 25, e301–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzykała, M.; Leszczyńsk, P. Asymmetry in body composition in female hockey players. Homo 2015, 66, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
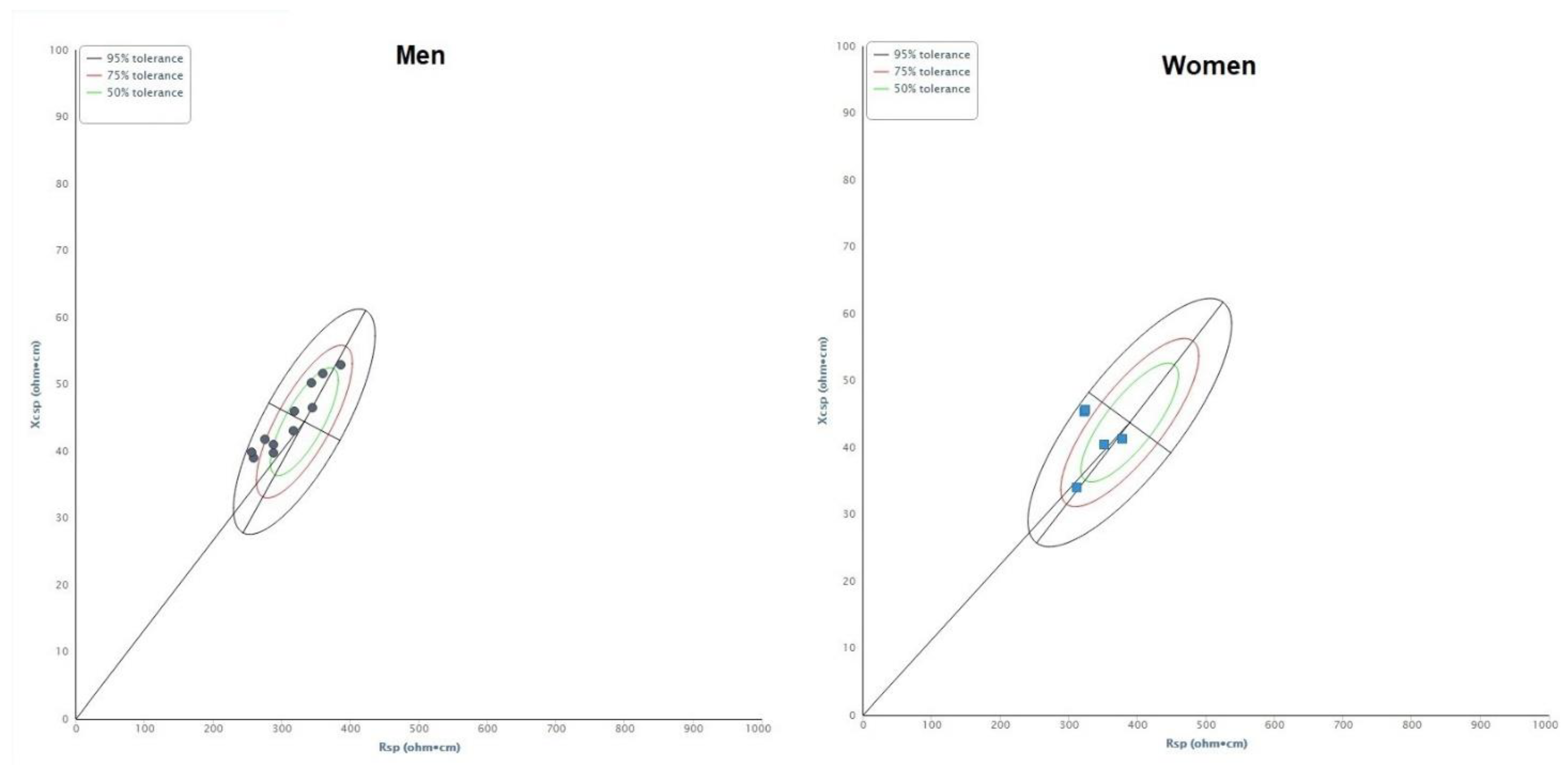
| Men (11) | Women (5) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Age (years) | 36.29 | 9.63 | 30.41 | 6.70 |
| Height (cm) | 175.33 | 6.34 | 161.86 | 9.92 |
| Weight (kg) | 79.23 | 6.98 | 56.90 | 12.36 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.80 | 2.30 | 21.55 | 3.51 |
| Waist crf (cm) | 83.01 | 5.32 | 67.24 | 5.39 |
| Hand grip R (kg) | 53.18 | 11.44 | 27.00 | 6.71 |
| Hand grip L (kg) | 49.82 | 9.21 | 27.40 | 8.47 |
| Rsp (ohm·cm) | 315.05 | 42.90 | 339.80 | 27.45 |
| Xcsp (ohm·cm) | 40.06 | 4.73 | 37.81 | 4.74 |
| Zsp (ohm·cm) | 317.59 | 43.12 | 341.93 | 27.31 |
| PhA (°) | 7.27 | 0.33 | 6.38 | 0.92 |
| Right Side | Left Side | Paired t-Test between Sides | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | Men | Women | |||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | t | p | |
| Hand grip (kg) | 53.18 | 11.44 | 27.00 | 6.71 | 49.82 | 9.21 | 27.40 | 8.47 | 1.742 | 0.102 |
| Arm crf (cm) | 32.35 | 1.64 | 26.14 | 2.02 | 32.33 | 1.92 | 26.42 | 2.55 | −0.475 | 0.642 |
| Thigh crf (cm) | 59.61 | 3.68 | 54.64 | 5.96 | 59.84 | 3.64 | 55.04 | 5.93 | −1.197 | 0.250 |
| Calf crf (cm) | 38.27 | 2.24 | 34.18 | 2.15 | 37.85 | 2.17 | 33.92 | 1.89 | 2.545 | 0.022 |
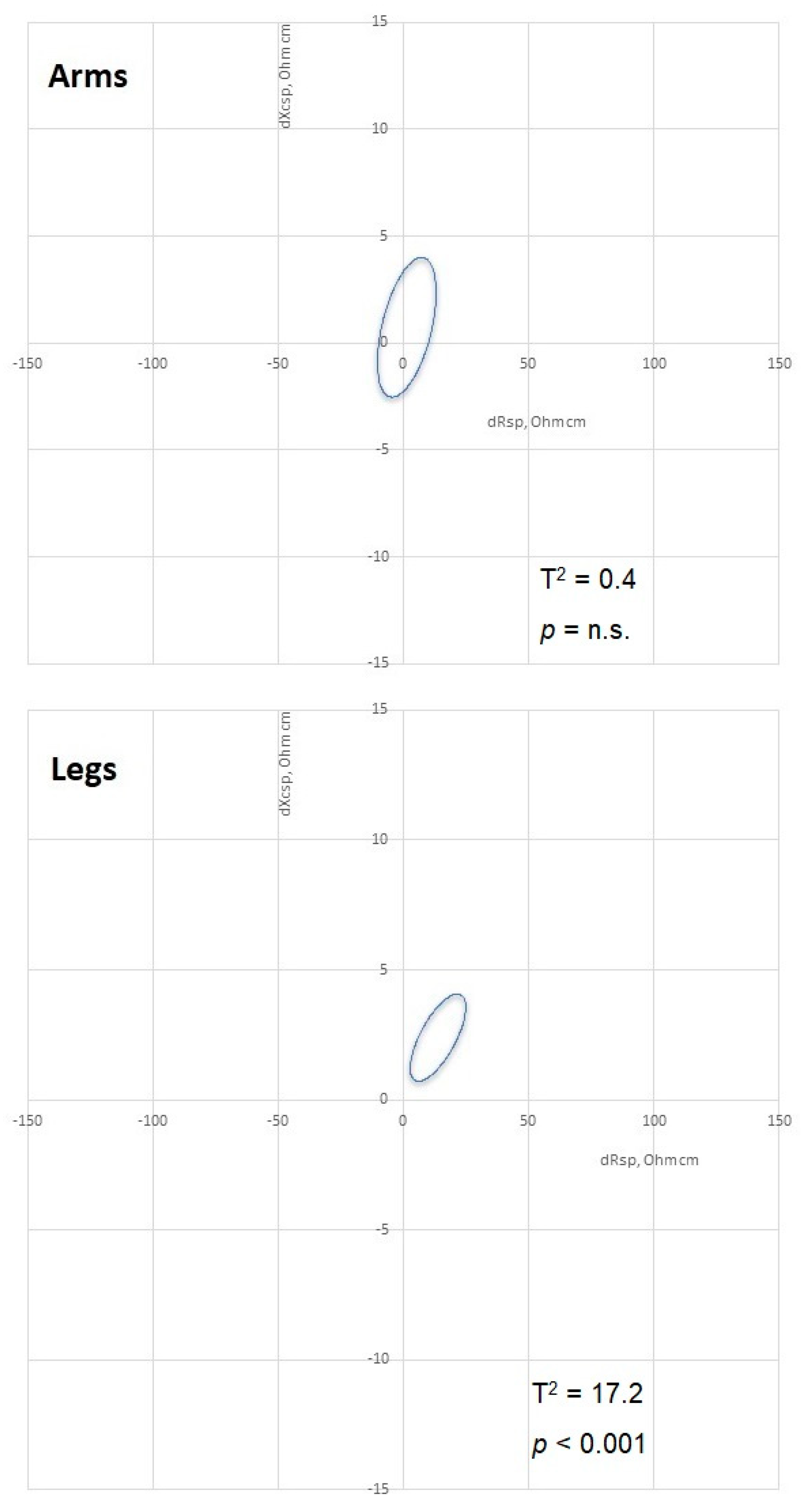
| Rsp arm (ohm·cm) | 233.85 | 30.09 | 243.56 | 25.64 | 232.95 | 27.08 | 254.07 | 33.98 | −1.558 | 0.585 |
| Xcsp arm (ohm·cm) | 30.96 | 4.85 | 26.84 | 2.31 | 30.16 | 4.22 | 27.57 | 4.43 | 0.451 | 0.658 |
| Zsp arm (ohm·cm) | 235.91 | 30.27 | 245.06 | 25.41 | 234.94 | 26.92 | 255.57 | 34.17 | −0.634 | 0.536 |
| PhA arm (°) | 7.57 | 0.89 | 6.36 | 0.98 | 7.45 | 1.31 | 6.20 | 0.58 | 0.488 | 0.633 |
| Rsp leg (ohm·cm) | 277.62 | 33.09 | 319.48 | 26.33 | 267.95 | 31.77 | 296.51 | 17.65 | 2.588 | 0.021 |
| Xcsp leg (ohm·cm) | 39.25 | 6.27 | 38.33 | 7.44 | 37.29 | 6.02 | 34.97 | 6.31 | 3.238 | 0.006 |
| Zsp leg (ohm·cm) | 280.39 | 33.59 | 321.82 | 26.70 | 270.54 | 32.25 | 298.61 | 17.77 | 3.556 | 0.003 |
| PhA leg (°) | 8.02 | 0.49 | 6.82 | 1.06 | 7.90 | 0.50 | 6.73 | 1.15 | 1.326 | 0.205 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stagi, S.; Mulliri, G.; Doneddu, A.; Ghiani, G.; Marini, E. Body Composition and Strength Symmetry of Kettlebell Sport Athletes. Biology 2023, 12, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030440
Stagi S, Mulliri G, Doneddu A, Ghiani G, Marini E. Body Composition and Strength Symmetry of Kettlebell Sport Athletes. Biology. 2023; 12(3):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030440
Chicago/Turabian StyleStagi, Silvia, Gabriele Mulliri, Azzurra Doneddu, Giovanna Ghiani, and Elisabetta Marini. 2023. "Body Composition and Strength Symmetry of Kettlebell Sport Athletes" Biology 12, no. 3: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030440
APA StyleStagi, S., Mulliri, G., Doneddu, A., Ghiani, G., & Marini, E. (2023). Body Composition and Strength Symmetry of Kettlebell Sport Athletes. Biology, 12(3), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030440







