Rare Variants in LRP4 Are Associated with Mesiodens, Root Maldevelopment, and Oral Exostoses in Humans
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment
2.2. Whole Exome Sequencing, Mutation Analysis, and Bioinformatic Analyses
2.3. LRP4 Structural Analysis
2.4. Lrp4 Knockout Mice
3. Results
3.1. Whole Exome Sequence Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
3.2. Protein Models
3.3. Lrp4 Knockout Mice and Supernumerary Incisors
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hermans, F.; Hemeryck, L.; Lambrichts, I.; Bronckaers, A.; Vankelecom, H. Intertwined Signaling Pathways Governing Tooth Development: A Give-and-Take Between Canonical Wnt and Shh. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 758203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, B.T.; He, X. Frizzled and LRP5/6 receptors for Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a007880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
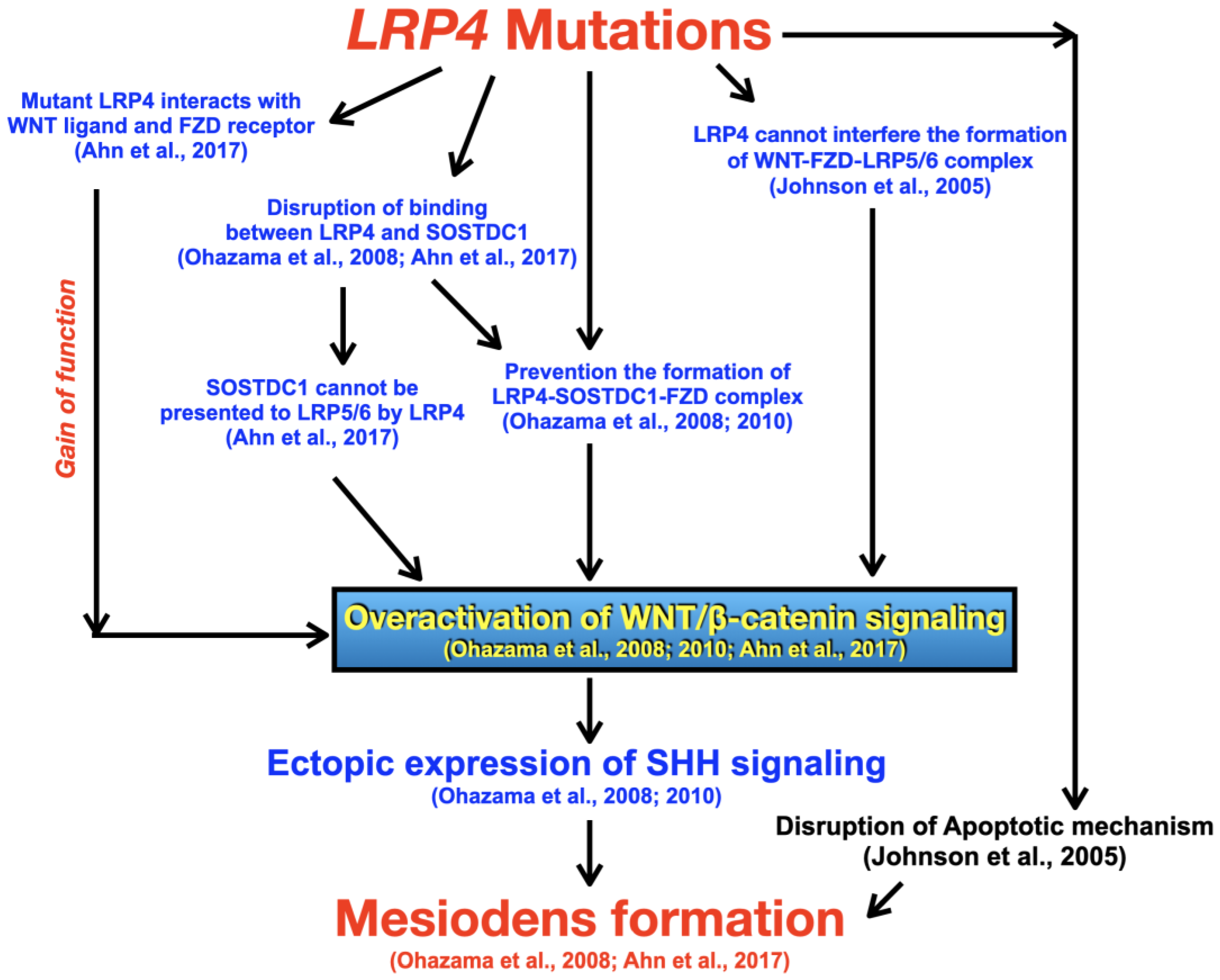
- Ohazama, A.; Johnson, E.B.; Ota, M.S.; Choi, H.Y.; Porntaveetus, T.; Oommen, S.; Itoh, N.; Eto, K.; Gritli-Linde, A.; Herz, J.; et al. Lrp4 modulates extracellular integration of cell signaling pathways in development. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Sims, C.; Murray, M.J.; Kuhlmann, P.K.; Fuentes-Antrás, J.; Weatherbee, S.D.; Krumlauf, R. Multiple modes of Lrp4 function in modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling during tooth development. Development 2017, 144, 2824–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassai, Y.; Munne, P.; Hotta, Y.; Penttilä, E.; Kavanagh, K.; Ohbayashi, N.; Takada, S.; Thesleff, I.; Jernvall, J.; Itoh, N. Regulation of mammalian tooth cusp patterning by ectodin. Science 2005, 309, 2067–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohazama, A.; Blackburn, J.; Porntaveetus, T.; Ota, M.S.; Choi, H.Y.; Johnson, E.B.; Myers, P.; Oommen, S.; Eto, K.; Kessler, J.A. A role for suppressed incisor cuspal morphogenesis in the evolution of mammalian heterodont dentition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langowska-Adamczyk, H.; Karmańska, B. Similar locations of impacted and supernumerary teeth in monozygotic twins: A report of 2 cases. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial. Orthop. 2001, 119, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaputra, P.N.; Guven, Y.; Tripuwabhrut, K.; Adisornkanj, P.; Hatsadaloi, A.; Kaewgahya, M.; Olsen, B.; Ngamphiw, C.; Jatooratthawichot, P.; Tongsima, S. Mutations in LRP5 and BMP4 are associated with mesiodens, tooth agenesis, root malformation, and oral exostoses. Clin. Genet. 2022, 102, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantaputra, P.; Jatooratthawichot, P.; Chintakanon, K.; Intachai, W.; Pradermdutsadeeporn, P.; Adisornkanj, P.; Tongsima, S.; Ngamphiw, C.; Olsen, B.; Tucker, A.S. Mutations in LRP6 highlight the role of WNT signaling in oral exostoses and dental anomalies. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2022, 142, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaputra, P.; Tripuwabhrut, K.; Jatooratthawichot, P.; Adisornkanj, P.; Hatsadaloi, A.; Porntrakoolsaree, N.; Kaewgaya, M.; Olsen, B.; Tongsima, S.; Ngamphiw, C. Mutations in the WLS are associated with dental anomalies, torus palatinus, and torus mandibularis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2022, cjac068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.B.; Hammer, R.E.; Herz, J. Abnormal development of the apical ectodermal ridge and polysyndactyly in Megf7-deficient mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 3523–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, D.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X. DANN: A deep learning approach for annotating the pathogenicity of genetic variants. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halevy, R.S.; Chien, H.C.; Heinz, B.; Bamshad, M.J.; Nickerson, D.A.; Kircher, M.; Ahituv, N. Mutations in the fourth β-propeller domain of LRP4 are associated with isolated syndactyly with fusion of the third and fourth fingers. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawara, B.; Cabrera-Serrano, M.; Nakata, T.; Milone, M.; Asai, N.; Ito, K.; Ito, M.; Masuda, A.; Ito, Y.; Engel, A.G. LRP4 third β-propeller domain mutations cause novel congenital myasthenia by compromising agrin-mediated MuSK signaling in a position-specific manner. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 1856–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leupin, O.; Piters, E.; Halleux, C.; Hu, S.; Kramer, I.; Morvan, F.; Bouwmeester, T.; Schirle, M.; Bueno-Lozano, M.; Fuentes, F.J. Bone overgrowth-associated mutations in the LRP4 gene impair sclerostin facilitator function. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 19489–19500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, M.P.; Amalnath, S.D.; McAlister, W.H.; Pedapati, R.; Muthupillai, V.; Duan, S.; Huskey, M.; Bijanki, V.N.; Mumm, S. Sclerosteosis: Report of type 1 or 2 in three Indian Tamil families and literature review. Bone 2018, 116, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonczek, O.; Krejci, P.; Izakovicova-Holla, L.; Cernochova, P.; Kiss, I.; Vojtesek, B. Tooth agenesis: What do we know and is there a connection to cancer? Clin. Genet. 2021, 99, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrman, J.M.; Morey, J.S.; Takeshita, R.; De Guise, S.; Wells, R.S.; McFee, W.; Speakman, T.; Townsend, F.; Smith, C.R.; Rowles, T. Age determination of common bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) using dental radiography pulp:tooth area ratio measurements. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Närhi, K.; Tummers, M.; Ahtiainen, L.; Itoh, N.; Thesleff, I.; Mikkola, M.L. Sostdc1 defines the size and number of skin appendage placodes. Dev. Biol. 2012, 364, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickels, M.R.; Zhang, X.; Mumm, S.; Whyte, M.P. Oropharyngeal skeletal disease accompanying high bone mass and novel LRP5 mutation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005, 20, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brance, M.L.; Brun, L.R.; Cóccaro, N.M.; Aravena, A.; Duan, S.; Mumm, S.; Whyte, M.P. High bone mass from mutation of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6). Bone 2020, 141, 115550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

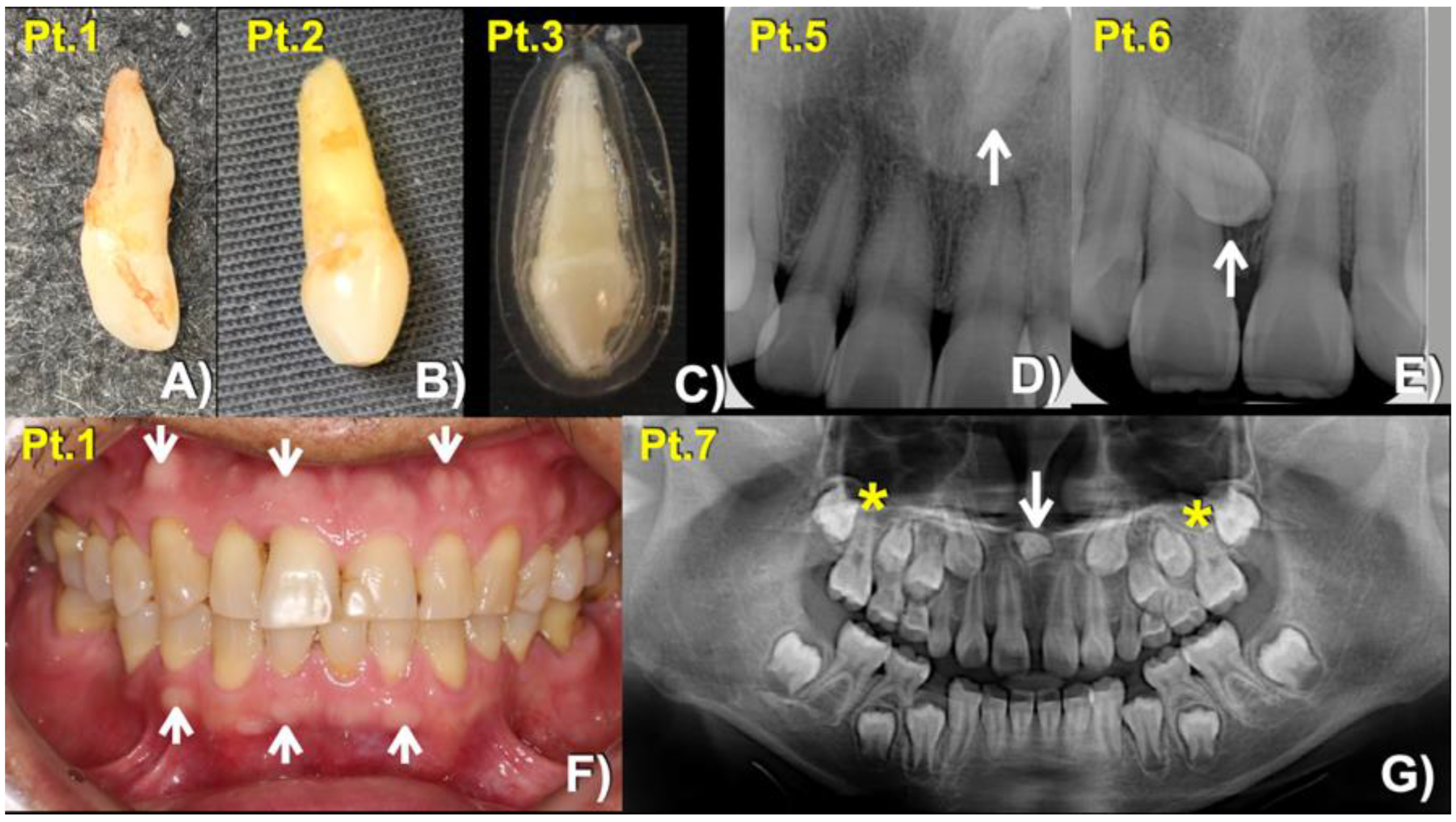
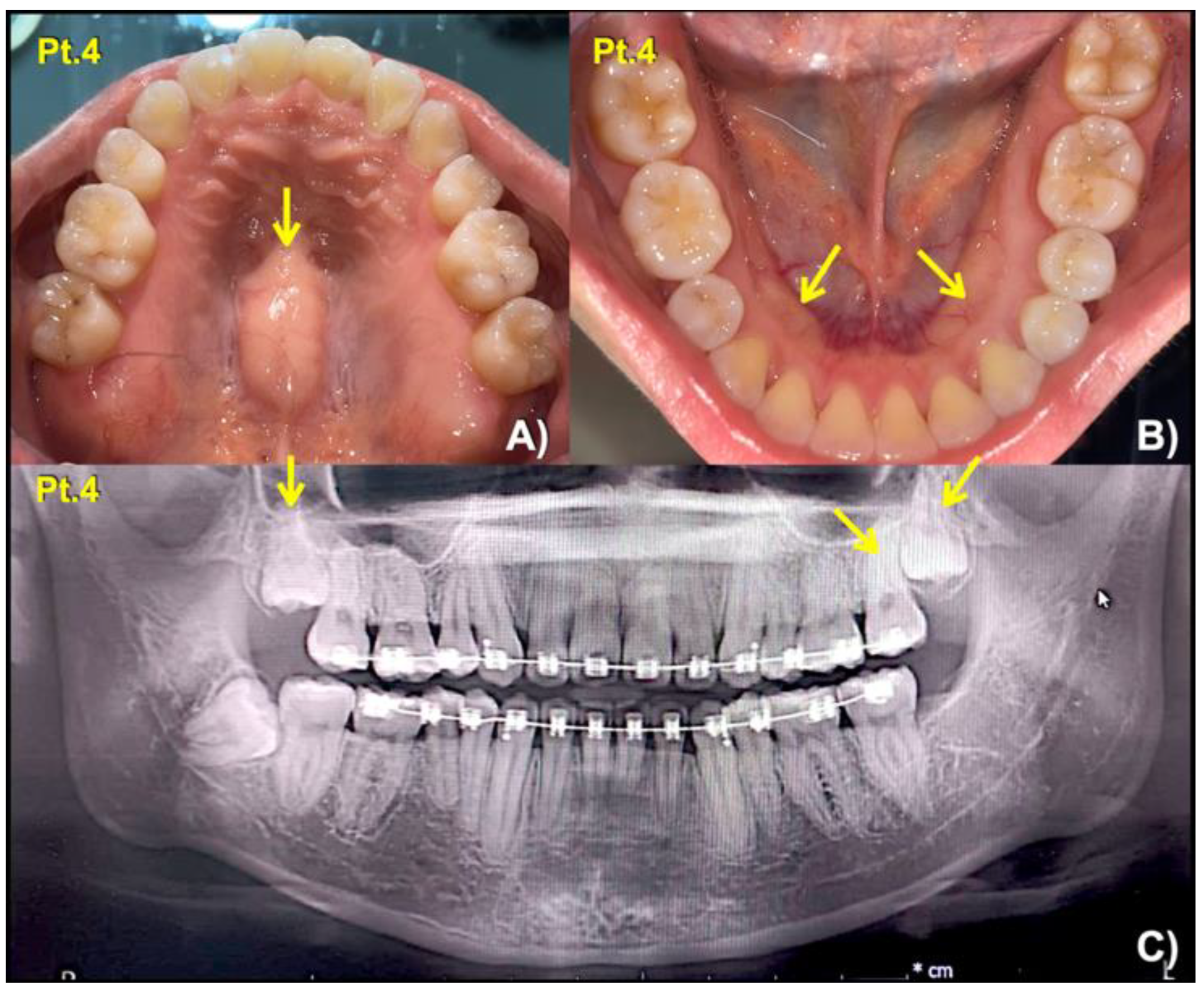



| Patients Gender/Age | Families | Phenotypes | LRP4 Variants | DANN Score | CADD Scores (GRCh38) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Male: 52 Yr) | 1 | Mesiodens (Conical; erupted) buccal exostoses | c.4154A > G; p.Asn1385Ser chr11:g.46896426T > C rs768733310, MAF: 0.00001768 | 0.9926 (pathogenic) | 22.3 |
| 2 (Female: 33 Yr) | Mesiodens (Conical; erupted) | ||||
| 3 (Female: 17 Yr) Homozygous | Mesiodens (Conical; erupted) | ||||
| 4 (Female: 30 Yr) | 2 | Mesiodens (Conical; unerupted) long roots of mandibular canines, short roots of second premolars, unseparated roots of second and third molars, torus mandibularis, and torus palatinus | c.3940G > A; p.Gly1314Ser chr11: g.46896640 C > T rs371961330 MAF = 0.00009579 | 0.9966 (pathogenic) | 18.11 |
| 5 (Female: 41 Yr) | 3 | Mesiodens (Inverted; unerupted) | |||
| 6 (Male: 13 Yr) | Mesiodens (Unerupted, tuberculate) | ||||
| 7 (Female: 9 Yr) | 4 | Mesiodens (inverted; unerupted) unseparated roots of the maxillary first molars | c.448G > A; p.Asp150Asn chr11:g.46921037C > T rs200746048, MAF: 0.00002787 | 0.9925 (pathogenic) | 22.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kantaputra, P.N.; Jatooratthawichot, P.; Adisornkanj, P.; Kitsadayurach, P.; Kaewgahya, M.; Olsen, B.; Ohazama, A.; Ngamphiw, C.; Tongsima, S.; Cox, T.C.; et al. Rare Variants in LRP4 Are Associated with Mesiodens, Root Maldevelopment, and Oral Exostoses in Humans. Biology 2023, 12, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12020220
Kantaputra PN, Jatooratthawichot P, Adisornkanj P, Kitsadayurach P, Kaewgahya M, Olsen B, Ohazama A, Ngamphiw C, Tongsima S, Cox TC, et al. Rare Variants in LRP4 Are Associated with Mesiodens, Root Maldevelopment, and Oral Exostoses in Humans. Biology. 2023; 12(2):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12020220
Chicago/Turabian StyleKantaputra, Piranit Nik, Peeranat Jatooratthawichot, Ploy Adisornkanj, Panita Kitsadayurach, Massupa Kaewgahya, Bjorn Olsen, Atsushi Ohazama, Chumpol Ngamphiw, Sissades Tongsima, Timothy C. Cox, and et al. 2023. "Rare Variants in LRP4 Are Associated with Mesiodens, Root Maldevelopment, and Oral Exostoses in Humans" Biology 12, no. 2: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12020220
APA StyleKantaputra, P. N., Jatooratthawichot, P., Adisornkanj, P., Kitsadayurach, P., Kaewgahya, M., Olsen, B., Ohazama, A., Ngamphiw, C., Tongsima, S., Cox, T. C., & Ketudat Cairns, J. R. (2023). Rare Variants in LRP4 Are Associated with Mesiodens, Root Maldevelopment, and Oral Exostoses in Humans. Biology, 12(2), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12020220











