Profiling the Physiological Roles in Fish Primary Cell Culture
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
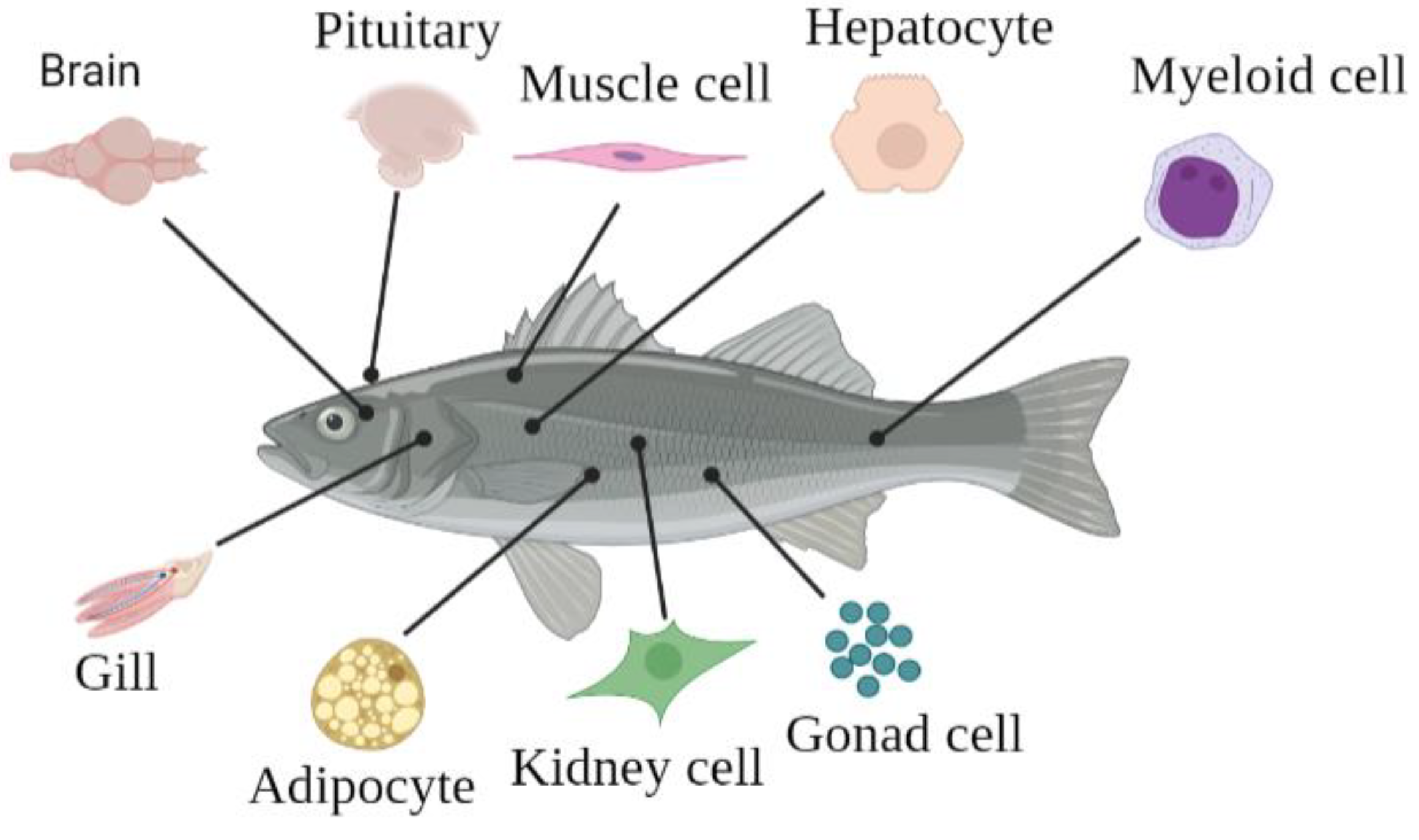
2. Primary Cells of Each Tissue
2.1. Fish Gonad Cells
2.2. Fish Pituitary Cells
2.3. Fish Muscle Cells
2.4. Fish Hepatocytes
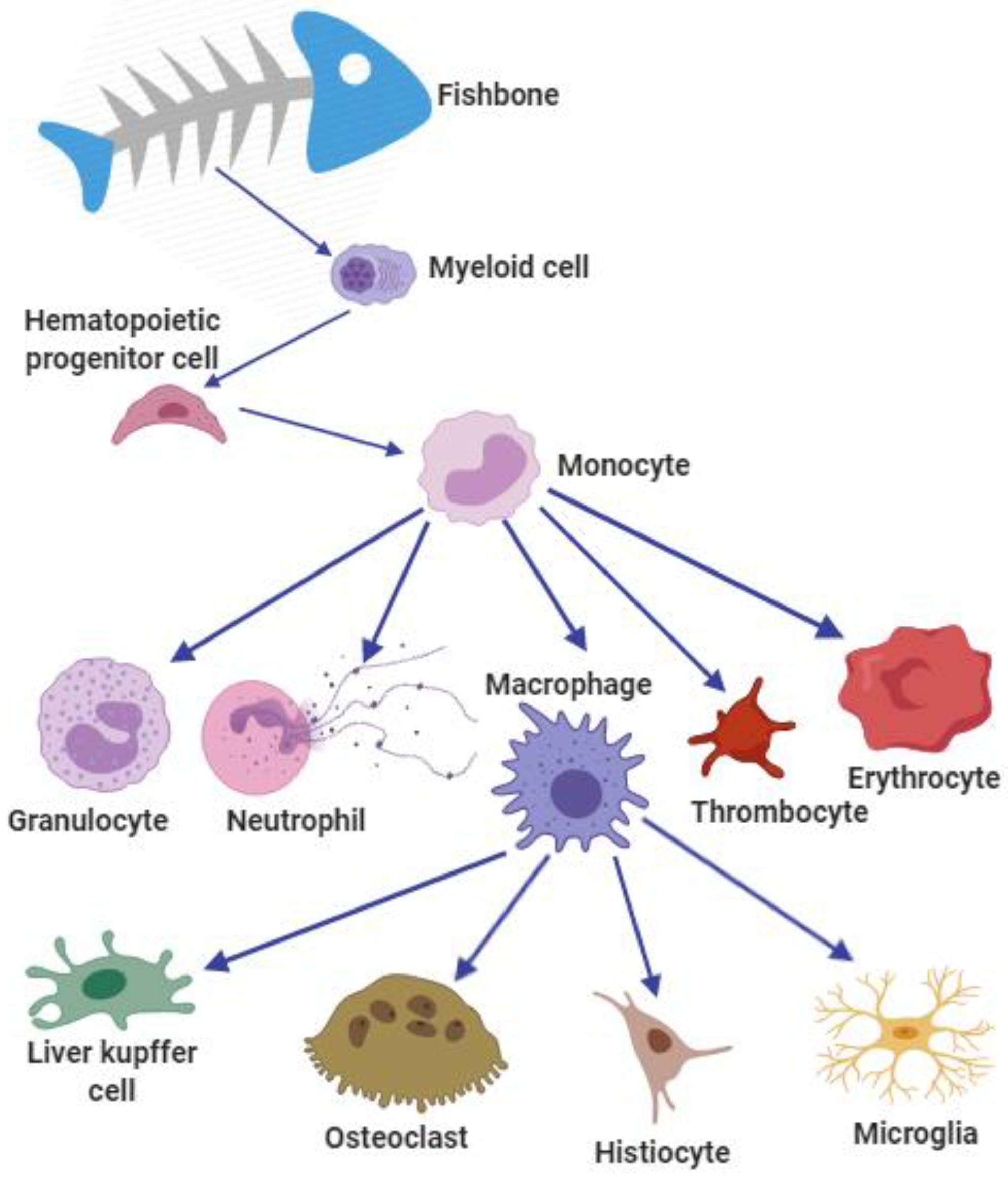
2.5. Fish Kidney and Immune Cells
2.6. Fish Adipocyte Cells and Myeloid Cells
2.7. Fish Brain Cells
2.8. Fish Gill Cells
2.9. Fish Intestinal Epithelial Cells
2.10. Other Cells
3. Common Methods for Fish Cell Isolation
3.1. Enzymatic Digestion
3.2. Tissue Block Adhesion Method
3.3. Mechanical Crushing
4. Perspectives and Future Developments
| Reference | Species | Tissue | Main Experimental Use | Culture Media | Serum | Antibiotics | Growth Factor, Hormone, and Others in Media |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [11] | Marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) | Pituitary, testis, and ovary | Rapid screening of environmental chemicals | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Fungizone, penicillin, and streptomycin | Insulin–transferrin–selenium-A, GlutaMAX |
| [29] | Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) | Pituitary | Optimizing the conditions of cell culture | M199 medium | Newborn calf serum | None | None |
| [27] | Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Pituitary | Signaling pathway validation | M199 medium | Fetal bovine serum | None | None |
| [23] | Medaka (Oryzias melastigma) | Pituitary | Rapid screening of environmental silver nanoparticles | M199 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Fungizone | 1 × GlutaMAX |
| [25] | Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) | Pituitary | Gene function analysis | L-15 medium | Newborn calf serum | None | None |
| [26] | Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) | Pituitary | Signaling pathway validation | L-15 medium | Bovine serum albumin | Penicillin, streptomycin | Sodium chloride |
| [10] | Medaka (Oryzias latipes) | Testis | Research of hormone metabolism | L-15 medium | Fetal calf serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | Steroid-free Ultroser SF |
| [87] | Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Testis | Analysis of spermatogenesis | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | None |
| [103] | Creekchub (Semotilus atromaculatus) | Skin | Rapid screening of environmental chemicals | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, Fungizone, kanamycin, and tetracycline | None |
| [31] | Gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) | Muscle | Signaling pathway validation | DMEM | Horse serum | Penicillin, streptomycin, fungizone, gentamycin | None |
| [34] | Brown trout (Salmo trutta) | Muscle | Signaling pathway validation | DMEM | Horse serum | Penicillin, streptomycin, amphotericin, and gentamycin | Poly-L-lysine, laminin |
| [30] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Muscle | Gene function analysis | DMEM | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | 100 nM of trout IGF1 |
| [32] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Muscle | Characterization of proliferation and differentiation | DMEM | Horse serum | Penicillin, streptomycin, Fungizone | None |
| [3] | Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) | Liver | Evaluation of the nonylphenol-induced oxidative stress | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | None |
| [41] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Liver | Toxicology research | L-15 medium | None | Amphotericin, streptomycin, penicillin | EE2, L-glutamine |
| [40] | Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) | Liver | Screening environmental contaminants | L-15 medium | None | Penicillin, streptomycin, amphotericin | L-glutamine |
| [42] | Brown trout (Salmo trutta) | Liver | Signaling pathway validation | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Streptomycin, penicillin | Poly-L-lysine (300 μg/mL) |
| [4] | Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) | Liver | Toxicology research | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | None |
| [47] | Yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) | Liver | Research of hormone metabolism | M199 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | L-glutamine |
| [49] | Brown trout (Salmo trutta) | Liver | Gene function analysis | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Streptomycin, penicillin | None |
| [51] | White sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus) | Liver | Test intracellular pH compensation | α-minimum essential medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin, Fungizone | None |
| [43] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Liver | Comparative cytotoxicity study of silver nanoparticles | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | L-glutamine, sodium pyruvate, NEAA |
| [44] | Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) | Liver | Toxicology research | DMEM/F12 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | None |
| [101] | Grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) | Intestine | Signaling pathway validation | DMEM | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, gentamycin, amphotericin B, gentamycin sulfate | None |
| [104] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Intestine | Cell culture method | Hanks’ balanced salt solution | Bovine serum albumin | None | None |
| [65] | Goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) | Kidney | Gene function analysis | MGFL-15 medium | Heat-inactivated carp serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | Mechano Growth Factor |
| [66] | Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) | Kidney | Immunological research | RPMI 1640 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | Heparin |
| [72] | Goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) | Kidney | Immunological research | NMGFL-15 medium | Calf serum and carp serum | None | Interleukin-3, granulocyte–macrophage-colony-stimulating factor |
| [60] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) | Kidney | Immunological research | DMEM | None | None | Antagonist receptors and/or hormones |
| [6] | Wolf fish (Hoplias malabaricus) | Kidney | Immunological research | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | None |
| [5] | Red carp (Cyprinus carpio) | Kidney | Immunological research | Hank’s balanced salt solution | None | Penicillin, streptomycin | Heparin |
| [64] | European eel (Anguilla anguilla) | Kidney | Immunological research | L-15 medium | Bovine serum albumin | None | Poly-L-lysine |
| [68] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Adipocyte | Toxicology research | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Antibiotic/antimycotic solution | Insulin |
| [69] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Adipocyte | Research of hormone metabolism | Krebs–HEPES buffer | Fetal bovine serum | Collagenase type II | Insulin |
| [67] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Adipocyte | Gene function analysis | Krebs–HEPES buffer | Bovine serum albumin | 1% antibiotic/antimycotic solution | L-glutamine, insulin |
| [106] | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | Brain | Electro-physiological studies | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | Ofloxacin |
| [74] | Giant groupers (Epinephelus lanceolatus) | Brain | Immunological research | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin | None |
| [48] | Half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis) | Brain | Gene function analysis | L-15 medium | Bovine serum albumin | Penicillin, streptomycin | Palmitic acid |
| [75] | Sole (Solea senegalensis) | Brain | Immunological research | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Gentamicin | Glutamine |
| [73] | Sea bream (Sparus aurata) | Bone | Research of hormone metabolism | DMEM | Fetal bovine serum | Antibiotic/antimycotic solution | L-ascorbic acid, β-glycerophosphate |
| [71] | Gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) | Bone | Gene function analysis | DMEM | Fetal bovine serum | Antibiotic/antimycotic solution | NaCl, porcine insulin, dexamethasone |
| [78] | Common carp (Cyprinus carpio) | Fin | Immunological research | DMEM | Fetal bovine serum | Phosphate, streptomycin | FGF |
| [97] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Gill | Environmental monitoring of urban streams | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin, gentamicin | None |
| [81] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Gill | Salinity/water regulation | Hanks’ balanced salt solution | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, Streptomycin, and amphotericin B | Glutamine |
| [82] | Puffer fish (Tetraodon nigroviridis) | Gill | Gene function analysis | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin, gentamicin | L-glutamine, cortisol |
| [90] | Japanese eels (Anguilla japonica) | Gill | Salinity/water regulation | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin, and Fungizone | None |
| [95] | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Gill | Toxicology research | L-15 medium | Fetal bovine serum | Penicillin, streptomycin, amphotericin B | Glycine |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolf, K.; Quimby, M.C. Established Eurythermic Line of Fish Cells in vitro. Science 1962, 135, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hightower, L.E.; Renfro, J.L. Recent applications of fish cell culture to biomedical research. J. Exp. Zool. 1988, 248, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshesh, N.; Movahedinia, A.; Salamat, N.; Hashemitabar, M.; Bayati, V. Using a liver cell culture from Epinephelus coioides as a model to evaluate the nonylphenol-induced oxidative stress. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshesh, N.; Salamat, N.; Movahedinia, A.; Hashemitabar, M.; Bayati, V. Exposure of liver cell culture from the orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides, to benzo[a]pyrene and light results in oxidative damage as measured by antioxidant enzymes. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, L.; Wu, M.; Yang, M. The primary culture of carp (Cyprinus carpio) macrophages and the verification of its phagocytosis activity. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2015, 52, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, J.L.C.; da Silva, C.A.; de Andrade, L.; Galvan, G.L.; Cestari, M.M.; Trindade, E.S.; Zampronio, A.R.; de Assis, H.C.S. Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs in primary kidney cell culture of a freshwater fish. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2014, 40, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Gutzeit, H.O. Effect of 17-alpha-ethynylestradiol on germ cell proliferation in organ and primary culture of medaka (Oryzias latipes) testis. Dev. Growth Differ. 2003, 45, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokalov, S.; Gutzeit, H. Spermatogenesis in testis primary cell cultures of the tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Dev. Dyn. 2005, 233, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, M.; Yashwanth, B.S.; Trudeau, V.; Lakra, W.S. Role and relevance of fish cell lines in advanced in vitro research. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 2393–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Gutzeit, H.O. Primary culture of medaka (Oryzias latipes) testis: A test system for the analysis of cell proliferation and differentiation. Cell Tissue Res. 2003, 313, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, A.C.; Lau, K.Y.; Ge, W.; Wu, R.S. A rapid screening test for endocrine disrupting chemicals using primary cell culture of the marine medaka. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 144–145, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ager-Wick, E.; Hodne, K.; Fontaine, R.; von Krogh, K.; Haug, T.M.; Weltzien, F.A. Preparation of a High-quality Primary Cell Culture from Fish Pituitaries. Jove-J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 138, e58159. [Google Scholar]
- Lakra, W.S.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Joy, K.P. Development, characterization, conservation and storage of fish cell lines: A review. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 37, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speirs, V.; Green, A.; Walton, D.; Kerin, M.; Fox, J.; Carleton, P.; Desai, S.; Atkin, S. Short-term primary culture of epithelial cells derived from human breast tumours. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 78, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G.; Morse, S.; Ararat, M.; Graham, F.L. Preferential transformation of human neuronal cells by human adenoviruses and the origin of HEK 293 cells. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2002, 16, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korch, C.; Hall, E.M.; Dirks, W.G.; Ewing, M.; Faries, M.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Robinson, S.; Storts, D.; Turner, J.A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Authentication of M14 melanoma cell line proves misidentification of MDA-MB-435 breast cancer cell line. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 142, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Watabe, S. Temperature-dependent enhancement of cell proliferation and mRNA expression for type I collagen and HSP70 in primary cultured goldfish cells. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2004, 138, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakers, S.; Ondrusch, A.-K.; Gruening, M.; Adamek, M.; Moeckel, B.; Gebert, M. Monitoring changing cellular characteristics during the development of a fin cell line from Cyprinus carpio. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 225, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Nogales, A.; Connolly, M.; Rosenkranz, P.; Fernández-Cruz, M.-L.; Navas, J.M. Negligible cytotoxicity induced by different titanium dioxide nanoparticles in fish cell lines. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 138, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Wang, T.Z.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.F.; Sha, Z.X.; Chen, S.L. Establishment and characterization of an ovarian cell line from half-smooth tongue sole Cynoglossus semilaevis. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 86, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, A.P.; Narvekar, S.S.; Goundadkar, B.B.; A Deshpande, P. IGF1 stimulates differentiation of primary follicles and their growth in ovarian explants of zebrafish (Danio rerio) cultured in vitro. J. Biosci. 2017, 42, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y. Establishment and characterization of the gonadal cell lines derived from large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) for gene expression studies. Aquaculture 2021, 546, 737300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degger, N.; Tse, A.C.; Wu, R.S. Silver nanoparticles disrupt regulation of steroidogenesis in fish ovarian cells. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 169, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Gómez, F.J.; Unceta, M.D.C.R.; Piñuela, C.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A.; Jiménez-Tenorio, N.; Sarasquete, C. Immunocytohistochemical characterization of pituitary cells of the bluefin tuna, Thunnus thynnus L. Histol. Histopathol. 2001, 16, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- von Krogh, K.; Bjørndal, G.T.; Nourizadeh-Lillabadi, R.; Ropstad, E.; Haug, T.M.; Weltzien, F.-A. Cortisol differentially affects cell viability and reproduction-related gene expression in Atlantic cod pituitary cultures dependent on stage of sexual maturation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2019, 236, 110517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qin, C.; Zhang, C.; Jia, J.; Sun, C.; Li, W. Differential involvement of signaling pathways in the regulation of growth hormone release by somatostatin and growth hormone-releasing hormone in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, A.; Li, X.; Jiang, Q. Irisin inhibition of growth hormone secretion in cultured tilapia pituitary cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 439, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Q. Tilapia adropin: The localization and regulation of growth hormone gene expression in pituitary cells. Peptides 2017, 97, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodne, K.; von Krogh, K.; Weltzien, F.-A.; Sand, O.; Haug, T.M. Optimized conditions for primary culture of pituitary cells from the Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). The importance of osmolality, pCO2, and pH. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2012, 178, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiliez, I.; Gutierrez, J.; Salmerón, C.; Skiba-Cassy, S.; Chauvin, C.; Dias, K.; Kaushik, S.; Tesseraud, S.; Panserat, S. An in vivo and in vitro assessment of autophagy-related gene expression in muscle of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 157, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montserrat, N.; Sánchez-Gurmaches, J.; de la Serrana, D.G.; Navarro, M.I.; Gutiérrez, J. IGF-I binding and receptor signal transduction in primary cell culture of muscle cells of gilthead sea bream: Changes throughout in vitro development. Cell Tissue Res. 2007, 330, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabillard, J.C.; Sabin, N.; Paboeuf, G. In vitro characterization of proliferation and differentiation of trout satellite cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 342, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Guo, L.; Guo, H. Establishment, characterization, and transfection potential of a new continuous fish cell line (CAM) derived from the muscle tissue of grass goldfish (Carassius auratus). Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2021, 57, 912–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnoni, L.J.; Vraskou, Y.; Palstra, A.P.; Planas, J.V. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Plays an Important Evolutionary Conserved Role in the Regulation of Glucose Metabolism in Fish Skeletal Muscle Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witters, H.; Berckmans, P.; Vangenechten, C. Immunolocalization of Na+, K+-ATPase in the gill epithelium of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Cell Tissue Res. 1996, 283, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiraççakali, A.N.; Oğuz, A.R. Determination of cytotoxic, genotoxic, and oxidative damage from deltamethrin on primary hepatocyte culture of Lake Van fish, Alburnus tarichi. Chem. Ecol. 2020, 36, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, H.; Umino, T. Molecular characterization of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and their gene expression in the differentiating adipocytes of red sea bream Pagrus major. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 151, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, B.; Xiao, K.; Tan, C.; Du, H. Establishment and characterization of a cell line derived from fin of the endangered Yangtze sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus). Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2020, 56, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nualart, D.P.; Dann, F.; Oyarzún-Salazar, R.; Morera, F.J.; Vargas-Chacoff, L. Immune Transcriptional Response in Head Kidney Primary Cell Cultures Isolated from the Three Most Important Species in Chilean Salmonids Aquaculture. Biology 2023, 12, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.; Hultman, M.T.; Tollefsen, K.E. Primary hepatocytes from Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) as a relevant Arctic in vitro model for screening contaminants and environmental extracts. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 187, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultman, M.T.; Song, Y.; Tollefsen, K.E. 17α-Ethinylestradiol (EE2) effect on global gene expression in primary rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 169, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, T.V.; Pinheiro, I.; Malhão, F.; Lopes, C.; Urbatzka, R.; Castro, L.F.C.; Rocha, E. Cross-interference of two model peroxisome proliferators in peroxisomal and estrogenic pathways in brown trout hepatocytes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 187, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, M.; Fernandez-Cruz, M.-L.; Quesada-Garcia, A.; Alte, L.; Segner, H.; Navas, J.M. Comparative Cytotoxicity Study of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) in a Variety of Rainbow Trout Cell Lines (RTL-W1, RTH-149, RTG-2) and Primary Hepatocytes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 5386–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Long, X.; Liu, Z.; Yan, S. Copper Nanoparticles and Copper Sulphate Induced Cytotoxicity in Hepatocyte Primary Cultures of Epinephelus coioides. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldatow, V.Y.; LeCluyse, E.L.; Griffith, L.G.; Rusyn, I. In vitro models for liver toxicity testing. Toxicol. Res. 2013, 2, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, M.G.; Mintram, K.S.; Owen, S.F.; Hetheridge, M.J.; Moody, A.J.; Purcell, W.M.; Jackson, S.K.; Jha, A.N. Pharmaceutical Metabolism in Fish: Using a 3-D Hepatic In Vitro Model to Assess Clearance. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, M.-Q.; Luo, Z.; Wu, K.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Zheng, J.-L.; Zhang, L.-H.; Chen, Q.-L. Regulation of insulin on lipid metabolism in freshly isolated hepatocytes from yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 177–178, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Yang, B.; Ji, R.; Xu, W.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids alleviate hepatic steatosis-induced inflammation through Sirt1-mediated nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B p65 subunit in hepatocytes of large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 71, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, T.V.; Pinheiro, I.; Malhão, F.; Castro, L.F.C.; Rocha, E.; Urbatzka, R. Silencing of PPARαBb mRNA in brown trout primary hepatocytes: Effects on molecular and morphological targets under the influence of an estrogen and a PPARα agonist. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 229, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Xu, W.-T.; Gan, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.-X.; Zhao, F.-Z.; Chen, S.-L. Cloning, expression prolife, and immune characterization of a novel stat family member (stat5bl) in Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 84, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, K.T.; Baker, D.W.; Harris, R.; Church, J.; Brauner, C.J. Capacity for intracellular pH compensation during hypercapnia in white sturgeon primary liver cells. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2011, 181, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Hogstrand, C.; Chen, G.; Lv, W.; Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Z. Zn Induces Lipophagy via the Deacetylation of Beclin1 and Alleviates Cu-Induced Lipotoxicity at Their Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4943–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-H.; Song, C.-C.; Zhao, T.; Hogstrand, C.; Wei, X.-L.; Lv, W.-H.; Song, Y.-F.; Luo, Z. Mitochondria-Dependent Oxidative Stress Mediates ZnO Nanoparticle (ZnO NP)-Induced Mitophagy and Lipotoxicity in Freshwater Teleost Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2407–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Gu, J.; Wang, D.; Liang, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Yin, S. Physiological mechanism of osmoregulatory adaptation in anguillid eels. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joerink, M.; Ribeiro, C.M.S.; Stet, R.J.M.; Hermsen, T.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Wiegertjes, G.F. Head Kidney-Derived Macrophages of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Show Plasticity and Functional Polarization upon Differential Stimulation. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Takizawa, F.; Parra, D.; Gómez, D.; Jørgensen, L.v.G.; LaPatra, S.E.; Sunyer, J.O. Mucosal immunoglobulins at respiratory surfaces mark an ancient association that predates the emergence of tetrapods. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Wang, K.R.; Nie, P.; Chen, X.H.; Ao, J.Q. Establishment and characterization of a head kidney cell line from large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 84, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeredo, R.; Serra, C.R.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Costas, B. Amino acids as modulators of the European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax, innate immune response: An in vitro approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontigo, J.; Vargas-Chacoff, L. Growth hormone (GH) and growth hormone release factor (GRF) modulate the immune response in the SHK-1 cell line and leukocyte cultures of head kidney in Atlantic salmon. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 300, 113631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansari, A.R.; Parra, D.; Reyes-López, F.E.; Tort, L. Cytokine modulation by stress hormones and antagonist specific hormonal inhibition in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) head kidney primary cell culture. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 250, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansari, A.R.; Parra, D.; Reyes-López, F.E.; Tort, L. Modulatory in vitro effect of stress hormones on the cytokine response of rainbow trout and gilthead sea bream head kidney stimulated with Vibrio anguillarum bacterin. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 70, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlenz, C.; Gatlin, D.M. Interrelationships between fish nutrition and health. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, C.J.; Gerwick, L. The acute phase response and innate immunity of fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callol, A.; Roher, N.; Amaro, C.; MacKenzie, S. Characterization of PAMP/PRR interactions in European eel (Anguilla anguilla) macrophage-like primary cell cultures. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 35, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgldnson, J.W.; Fibke, C.; Belosevic, M. Recombinant IL-4/13A and IL-4/13B induce arginase activity and down-regulate nitric oxide response of primary goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) macrophages. Develop. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 67, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, I.; Rodríguez, A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A. Adenosine arrests apoptosis in lymphocytes but not in phagocytes from primary leucocyte cultures of the teleost fish, Sparus aurata L. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2007, 31, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouraoui, L.; Cruz-Garcia, L.; Gutiérrez, J.; Capilla, E.; Navarro, I. Regulation of lipoprotein lipase gene expression by insulin and troglitazone in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) adipocyte cells in culture. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2012, 161, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfi, E.; Riera-Heredia, N.; Córdoba, M.; Porte, C.; Gutiérrez, J.; Capilla, E.; Navarro, I. Tributyltin and triphenyltin exposure promotes in vitro adipogenic differentiation but alters the adipocyte phenotype in rainbow trout. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 188, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmerón, C.; Johansson, M.; Asaad, M.; Angotzi, A.R.; Rønnestad, I.; Stefansson, S.O.; Jönsson, E.; Björnsson, B.T.; Gutiérrez, J.; Navarro, I.; et al. Roles of leptin and ghrelin in adipogenesis and lipid metabolism of rainbow trout adipocytes in vitro. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 188, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bou, M.; Montfort, J.; Le Cam, A.; Rallière, C.; Lebret, V.; Gabillard, J.-C.; Weil, C.; Gutiérrez, J.; Rescan, P.-Y.; Capilla, E.; et al. Gene expression profile during proliferation and differentiation of rainbow trout adipocyte precursor cells. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmerón, C.; Riera-Heredia, N.; Gutiérrez, J.; Navarro, I.; Capilla, E. Adipogenic Gene Expression in Gilthead Sea Bream Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Different Origin. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenback, B.A.; Katakura, F.; Belosevic, M. Goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) as a model system to study the growth factors, receptors and transcription factors that govern myelopoiesis in fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 58, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capilla, E.; Teles-García, A.; Acerete, L.; Navarro, I.; Gutiérrez, J. Insulin and IGF-I effects on the proliferation of an osteoblast primary culture from sea bream (Sparus aurata). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 172, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chi, S.-C. Interleukin-1 beta secreted from betanodavirus-infected microglia caused the death of neurons in giant grouper brains. Develop. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 70, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, S.; Olveira, J.G.; Vázquez-Salgado, L.; Dopazo, C.P.; Bandín, I. Betanodavirus infection in primary neuron cultures from sole. Veter-Res. 2018, 49, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, N.; Lai, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.; Wu, S.; Su, J. A novel fish cell line derived from the brain of Chinese perch Siniperca chuatsi: Development and characterization. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 86, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wu, Y.H.; Wei, S.N.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhang, N.W.; Li, P.F.; Qin, Q.W.; Chen, S.L. Establishment and characterization of a brain-cell line from kelp grouper Epinephelus moara. J. Fish Biol. 2018, 92, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Peng, L.; Liu, S.; Feng, H. Establishment of fin cell lines and their use to study the immune gene expression in cyprinid fishes with different ploidy in rhabdovirus infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 88, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jia, P.; Chen, X.; Lai, M.; Jin, F.; Liu, W.; Yi, M.; Jia, K. Establishment and characterization of a fin tissue cell line derived from silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, T.R.; Basheer, V.S.; Kumar, R.; Kathirvelpandian, A.; Sood, N.; Jena, J.K. Establishment and characterization of fin-derived cell line from ornamental carp, Cyprinus carpio koi, for virus isolation in India. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2015, 51, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leguen, I.; Cauty, C.; Odjo, N.; Corlu, A.; Pruneta, P. Trout gill cells in primary culture on solid and permeable supports. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 148, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, P.; Kelly, S.P. Claudins in a primary cultured puffer fish (Tetraodon nigroviridis) gill epithelium model alter in response to acute seawater exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 189, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K.P.; Zhu, P.; Boncan, D.A.T.; Yang, L.; Leung, C.C.T.; Ho, J.C.H.; Lin, X.; Chan, T.F.; Kong, R.Y.C.; Tse, W.K.F. Integrated Omics Approaches Revealed the Osmotic Stress-Responsive Genes and Microbiota in Gill of Marine Medaka. mSystems 2022, 7, e0004722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.M.; Kelly, S.P.; Zhou, B.; Fletcher, M.; O’Donnell, M.; Eletti, B.; Pärt, P. Cultured gill epithelia as models for the freshwater fish gill. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2002, 1566, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, W.K.F.; Chow, S.C.; Wong, C.K.C. The cloning of eel osmotic stress transcription factor and the regulation of its expression in primary gill cell culture. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 1964–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.; Sunyer, J.O.; Salinas, I. The mucosal immune system of fish: The evolution of tolerating commensals while fighting pathogens. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 35, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maunder, R.J.; Baron, M.G.; Owen, S.F.; Jha, A.N. Investigations to extend viability of a rainbow trout primary gill cell culture. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 1314–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa-Allah, K.A.; Otitoloju, A.; Hogstrand, C. Cultured rainbow trout gill epithelium as an in vitro method for marine ecosystem toxicological studies. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, S.C.; Ching, L.Y.; Wong, A.M.F.; Wong, C.K.C. Cloning and regulation of expression of the Na+–Cl––taurine transporter in gill cells of freshwater Japanese eels. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 3205–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, S.C.; Wong, C.K.C. Regulatory function of hyperosmotic stress-induced signaling cascades in the expression of transcription factors and osmolyte transporters in freshwater Japanese eel primary gill cell culture. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, W.S.; Ossum, C.G.; Hoffmann, E.K. Hypotonic shock mediation by p38 MAPK, JNK, PKC, FAK, OSR1 and SPAK in osmosensing chloride secreting cells of killifish opercular epithelium. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Lee, T.-H.; Tseng, D.-Y. Glucocorticoid Receptor Mediates Cortisol Regulation of Glycogen Metabolism in Gills of the Euryhaline Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Fishes 2023, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, W.-X. Physiological and immune profiling of tilapia Oreochromis niloticus gills by high-throughput single-cell transcriptome sequencing. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2023, 141, 109070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.D.; Hogstrand, C.; Miller, T.H.; Owen, S.F.; Bury, N.R. The Use of Molecular Descriptors to Model Pharmaceutical Uptake by a Fish Primary Gill Cell Culture Epithelium. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leguen, I.; Peron, S.; Prunet, P. Effects of iron on rainbow trout gill cells in primary culture. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2011, 27, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, J.I. Screening of Chilean fish-killing microalgae using a gill cell-based assay. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 48, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, S.; Bawa-Allah, K.; Otitoloju, A.; Hogstrand, C.; Miller, T.H.; Barron, L.P.; Bury, N.R. Environmental monitoring of urban streams using a primary fish gill cell culture system (FIGCS). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, S.; Stott, L.C.; Hogstrand, C.; Wood, C.M.; Kelly, S.P.; Pärt, P.; Owen, S.F.; Bury, N.R. Procedures for the reconstruction, primary culture and experimental use of rainbow trout gill epithelia. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieczynski, F.; Painefilú, J.C.; Venturino, A.; Luquet, C.M. Expression and Function of ABC Proteins in Fish Intestine. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 791834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenzel, D.; Yu, A.S.L. Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 525–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Tan, Q.; Liu, M.; Hu, P. Arginine affects growth and integrity of grass carp enterocytes by regulating TOR signaling pathway and tight junction proteins. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.; Peggs, D.; McGurk, C.; Martin, S. Immune responses to prebiotics in farmed salmonid fish: How transcriptomic approaches help interpret responses. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 127, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintz, H.A.; Weihing, C.; Bayer, R.; Lonzarich, D.; Bryant, W. Cultured fish epithelial cells are a source of alarm substance. MethodsX 2017, 4, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langan, L.M.; Owen, S.F.; Jha, A.N. Establishment and long-term maintenance of primary intestinal epithelial cells cultured from the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio032870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, C.; Wadsworth, S.; Burrells, C.; Secombes, C. Expression of immune genes in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) fed a nucleotide-supplemented diet. Aquaculture 2003, 221, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, M.E.; Roginsky, J.E.; Schulz, J.R. Primary cell culture of adult zebrafish spinal neurons for electrophysiological studies. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 322, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauger, P.-E.; Labbé, C.; Bobe, J.; Cauty, C.; Leguen, I.; Baffet, G.; Le Bail, P.-Y. Characterization of goldfish fin cells in culture: Some evidence of an epithelial cell profile. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 152, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K. Some Recent Developments and Applications of Fish Cell and Tissue Culture. Progress. Fish-Culturist 1965, 27, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.P.; Fletcher, M.; Pärt, P.; Wood, C.M. Procedures for the preparation and culture of ‘reconstructed’ rainbow trout branchial epithelia. Methods Cell Sci. 2000, 22, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Liu, L.; Tang, R.; Xian, D.; Zhong, J. A newly improved method of primary cell culture: Tissue block with continuous adhesion subculture in skin fibroblast. Acta Histochem. 2023, 125, 152090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.B.; Ye, Y.T.; Cai, C.F.; Yao, L.J.; Xu, F.; Liu, M.; Xiao, P.Z. Isolation and primary culture of intestinal mucosal epithelial cells of grass carp. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2013, 22, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Langan, L.M.; Dodd, N.J.F.; Owen, S.F.; Purcell, W.M.; Jackson, S.K.; Jha, A.N. Direct Measurements of Oxygen Gradients in Spheroid Culture System Using Electron Parametric Resonance Oximetry. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149492. [Google Scholar]
- Eldred, M.K.; Charlton-Perkins, M.; Muresan, L.; Harris, W.A. Self-organising aggregates of zebrafish retinal cells for investigating mechanisms of neural lamination. Development 2017, 144, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Winkler, C.; Schartl, M. Production of medakafish chimeras from a stable embryonic stem cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3679–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Hong, N.; Hong, Y. Generation of medaka fish haploid embryonic stem cells. Science 2009, 326, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, R.; Gui, J. Establishment of a normal medakafish spermatogonial cell line capable of sperm production in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8011–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, L.; Zhao, C.; Xiao, Q.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, J.; Cao, Q. Profiling the Physiological Roles in Fish Primary Cell Culture. Biology 2023, 12, 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12121454
He L, Zhao C, Xiao Q, Zhao J, Liu H, Jiang J, Cao Q. Profiling the Physiological Roles in Fish Primary Cell Culture. Biology. 2023; 12(12):1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12121454
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Lingjie, Cheng Zhao, Qi Xiao, Ju Zhao, Haifeng Liu, Jun Jiang, and Quanquan Cao. 2023. "Profiling the Physiological Roles in Fish Primary Cell Culture" Biology 12, no. 12: 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12121454
APA StyleHe, L., Zhao, C., Xiao, Q., Zhao, J., Liu, H., Jiang, J., & Cao, Q. (2023). Profiling the Physiological Roles in Fish Primary Cell Culture. Biology, 12(12), 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12121454








