Comparison of Antibody Responses against Two Molecules from Ascaris lumbricoides: The Allergen Asc l 5 and the Immunomodulatory Protein Al-CPI
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production of Recombinant Proteins
2.2. Peptide Analysis by Nano-Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
2.3. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
2.4. Serum Samples and Stool Examination by Kato-Katz
2.5. Evaluation of Antibody Responses (Specific IgE, IgG4 and IgG) by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Evaluation of Allergenicity
2.7. Production of Antibodies to Recombinant Asc l 5 or Al-CPI, Immunization Schedule and Determination of Titers by ELISA
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Circular Dichroism Reveals Recombinant Asc l 5 and Al-CPI Are Well-Folded Products That Differ in Their Thermostability
3.2. Lower IgE Levels but Higher IgG/IgG4 Response Was Found for Al-CPI Than for Asc l 5
3.3. The IgE Antibodies to Al-CPI Do Not Elicit an IgE-Mediated Reaction
3.4. The Antibody Responses to Al-CPI and Asc l 5 Are Not Associated with Asthma
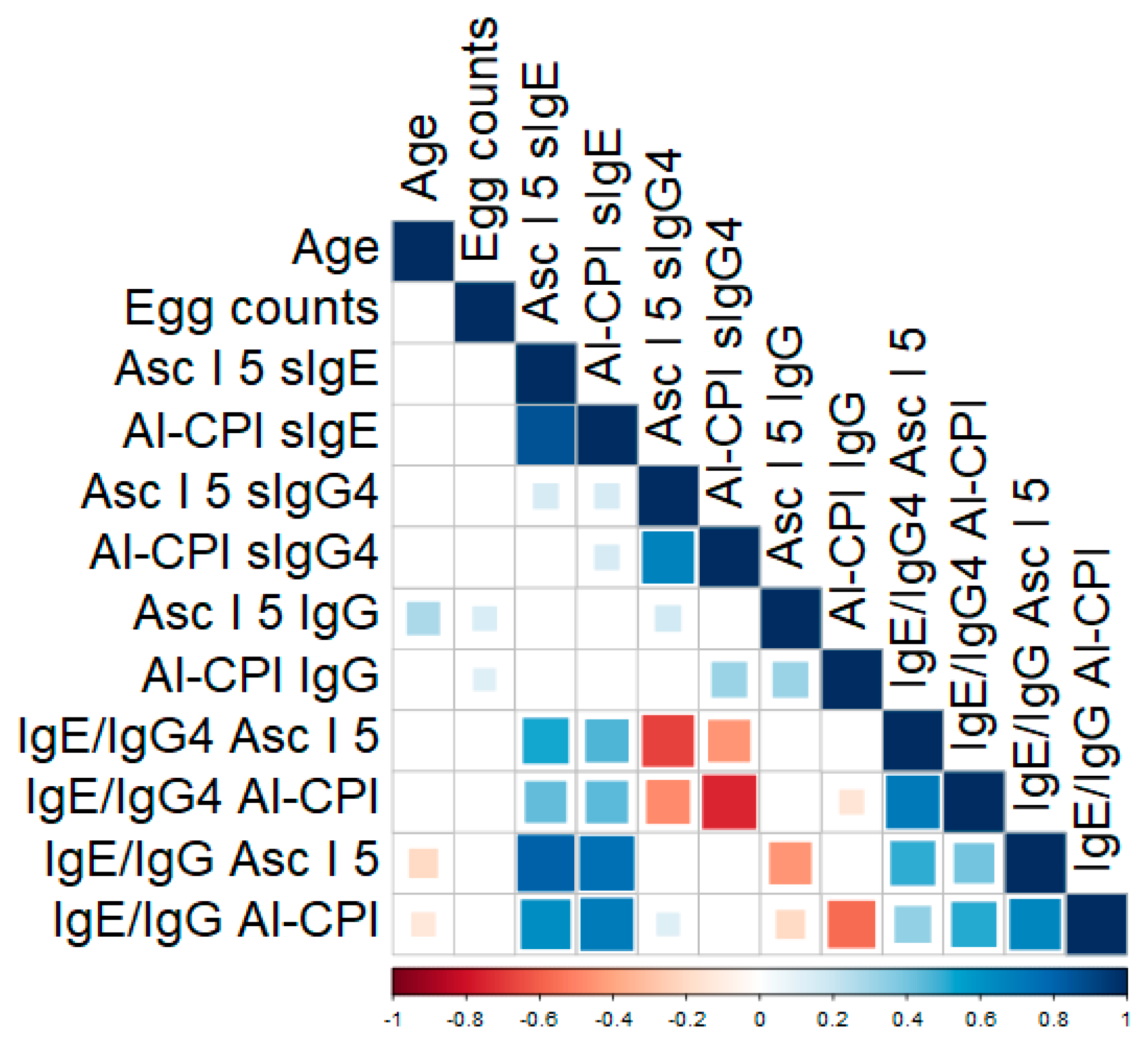
3.5. Humoral Responses to Asc l 5 and Al-CPI Are Associated with A. lumbricoides Egg Burden
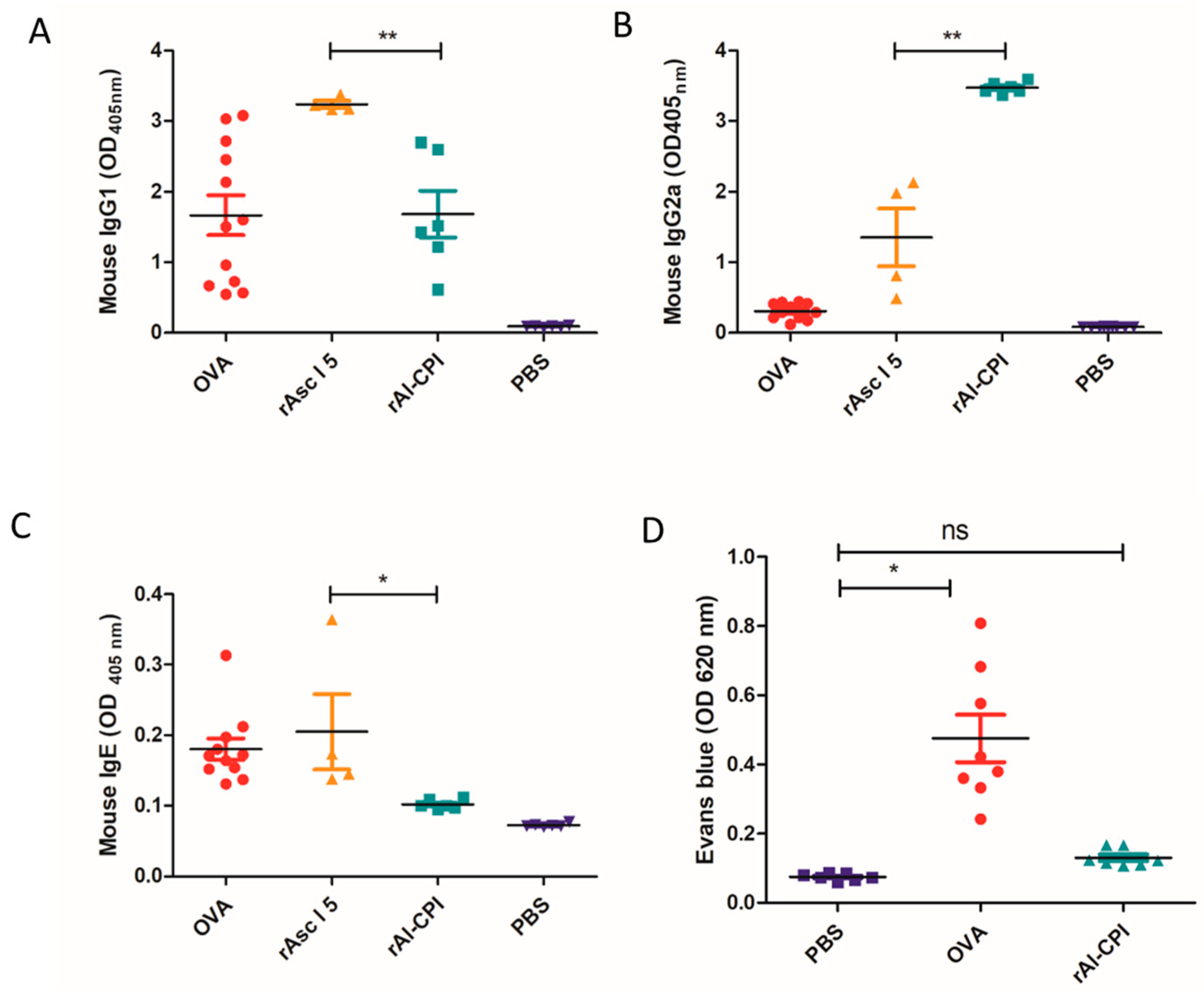
3.6. rAl-CPI Induces Lower IgE Response and Higher IgG2a Than rAsc l 5 in BALB/c Immunized Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pullan, R.L.; Smith, J.L.; Jasrasaria, R.; Brooker, S.J. Global numbers of infection and disease burden of soil transmitted helminth infections in 2010. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maizels, R.M.; Yazdanbakhsh, M. Immune regulation by helminth parasites: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Biggelaar, A.H.; Rodrigues, L.C.; van Ree, R.; van der Zee, J.S.; Hoeksma-Kruize, Y.C.; Souverijn, J.H.; Missinou, M.A.; Borrmann, S.; Kremsner, P.G.; Yazdanbakhsh, M. Long-term treatment of intestinal helminths increases mite skin-test reactivity in Gabonese schoolchildren. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcantara-Neves, N.M.; Veiga, R.V.; Dattoli, V.C.; Fiaccone, R.L.; Esquivel, R.; Cruz, A.A.; Cooper, P.J.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Barreto, M.L. The effect of single and multiple infections on atopy and wheezing in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 359–367.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Biggelaar, A.H.; van Ree, R.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Lell, B.; Deelder, A.M.; Kremsner, P.G.; Yazdanbakhsh, M. Decreased atopy in children infected with Schistosoma haematobium: A role for parasite-induced interleukin-10. Lancet 2000, 356, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, C.; Perini, A.; Martins, M.; Macedo, M.; Macedo-Soares, M.F. PAS-1, an Ascaris suum Protein, Modulates Allergic Airway Inflammation via CD8+ γδTCR+ and CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ T Cells. Scand. J. Immunol. 2010, 72, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, S.; Barrios, L.; Zakzuk, J.; Regino, R.; Ahumada, V.; Franco, L.; Ocampo, Y.; Caraballo, L. A recombinant cystatin from Ascaris lumbricoides attenuates inflammation of DSS-induced colitis. Parasite Immunol. 2017, 39, e12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, S.; Zakzuk, J.; Regino, R.; Ahumada, V.; Benedetti, I.; Angelina, A.; Palomares, O.; Caraballo, L. Ascaris lumbricoides Cystatin Prevents Development of Allergic Airway Inflammation in a Mouse Model. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, G.; Dong, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, M.; Liu, G.; Su, Z.; Liu, J. Structural basis for the immunomodulatory function of cysteine protease inhibitor from human roundworm Ascaris lumbricoides. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Dong, J.; Mei, G.; Liu, G.; Xu, W.; Su, Z.; Liu, J. Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic studies of a cysteine protease inhibitor from the human nematode parasite Ascaris lumbricoides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2011, 67 Pt 2, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainichi, T.; Maekawa, Y.; Ishii, K.; Zhang, T.; Nashed, B.F.; Sakai, T.; Takashima, M.; Himeno, K. Nippocystatin, a cysteine protease inhibitor from Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, inhibits antigen processing and modulates antigen-specific immune response. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 7380–7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoury, B.; Gregory, W.F.; Maizels, R.M.; Watts, C. Bm-CPI-2, a cystatin homolog secreted by the filarial parasite Brugia malayi, inhibits class II MHC-restricted antigen processing. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, S.; Kyewski, B.; Sonnenburg, B.; Lucius, R. A filarial cysteine protease inhibitor down-regulates T cell proliferation and enhances interleukin-10 production. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönemeyer, A.; Lucius, R.; Sonnenburg, B.; Brattig, N.; Sabat, R.; Schilling, K.; Bradley, J.; Hartmann, S. Modulation of human T cell responses and macrophage functions by onchocystatin, a secreted protein of the filarial nematode Onchocerca volvulus. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3207–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, L.; Zakzuk, J.; Acevedo, N. Helminth-derived cystatins: The immunomodulatory properties of an Ascaris lumbricoides cystatin. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1744–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, L.; Acevedo, N.; Zakzuk, J. Ascariasis as a model to study the helminth/allergy relationships. Parasite Immunol. 2019, 41, e12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontone, M.; Giovannini, M.; Barni, S.; Mori, F.; Venturini, E.; Galli, L.; Valleriani, C.; De las Vecillas, L.; Sackesen, C.; Lopata, A.L. IgE-mediated Anisakis allergy in children. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2023, 51, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahumada, V.; Manotas, M.; Zakzuk, J.; Aglas, L.; Coronado, S.; Briza, P.; Lackner, P.; Regino, R.; Araujo, G.; Ferreira, F.; et al. Identification and Physicochemical Characterization of a New Allergen from Ascaris lumbricoides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ishizaki, S.; Shimakura, K.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Molecular cloning and expression of two new allergens from Anisakis simplex. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 100, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, N.; Mercado, D.; Vergara, C.; Sanchez, J.; Kennedy, M.W.; Jimenez, S.; Fernandez, A.M.; Gutierrez, M.; Puerta, L.; Caraballo, L. Association between total immunoglobulin E and antibody responses to naturally acquired Ascaris lumbricoides infection and polymorphisms of immune system-related LIG4, TNFSF13B and IRS2 genes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 157, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSharry, C.; Xia, Y.; Holland, C.V.; Kennedy, M.W. Natural immunity to Ascaris lumbricoides associated with immunoglobulin E antibody to ABA-1 allergen and inflammation indicators in children. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakzuk, J.; Casadiego, S.; Mercado, A.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Caraballo, L. Ascaris lumbricoides infection induces both, reduction and increase of asthma symptoms in a rural community. Acta Trop. 2018, 187, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos da Silva, E.; Marques Ponte, J.C.; Barbosa da Silva, M.; Silva Pinheiro, C.; Carvalho Pacheco, L.G.; Ferreira, F.; Briza, P.; Alcantara-Neves, N.M. Proteomic Analysis Reveals Allergen Variability among Breeds of the Dust Mite Blomia tropicalis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 180, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asam, C.; Batista, A.; Moraes, A.; de Paula, V.; Almeida, F.; Aglas, L.; Kitzmüller, C.; Bohle, B.; Ebner, C.; Ferreira, F. Bet v 1–a Trojan horse for small ligands boosting allergic sensitization? Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.M.; Jess, T.J.; Price, N.C. How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1751, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmann, D.; Nagl, B.; Ebner, C.; Emminger, W.; Wöhrl, S.; Kitzmüller, C.; Vrtala, S.; Mangold, A.; Ankersmit, H.J.; Bohle, B. The quantity and quality of α-gal-specific antibodies differ in individuals with and without delayed red meat allergy. Allergy 2017, 72, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Versteeg, L.; Liu, Z.; Keegan, B.; Gazzinelli-Guimaraes, A.C.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Briggs, N.; Jones, K.M.; Strych, U.; Beaumier, C.M. Yeast-expressed recombinant As16 protects mice against Ascaris suum infection through induction of a Th2-skewed immune response. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stear, M.; Preston, S.; Piedrafita, D.; Donskow-Łysoniewska, K. The Immune Response to Nematode Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, N.; Mohr, J.; Zakzuk, J.; Samonig, M.; Briza, P.; Erler, A.; Pomes, A.; Huber, C.G.; Ferreira, F.; Caraballo, L. Proteomic and immunochemical characterization of glutathione transferase as a new allergen of the nematode Ascaris lumbricoides. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemert, D.J.; Pinto, A.G.; Freire, J.; Jariwala, A.; Santiago, H.; Hamilton, R.G.; Periago, M.V.; Loukas, A.; Tribolet, L.; Mulvenna, J.; et al. Generalized urticaria induced by the Na-ASP-2 hookworm vaccine: Implications for the development of vaccines against helminths. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 169–176.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjobimey, T.; Hoerauf, A. Induction of immunoglobulin G4 in human filariasis: An indicator of immunoregulation. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2010, 104, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mahillo, A.I.; Gonzalez-Muñoz, M.; Gomez-Aguado, F.; Rodriguez-Perez, R.; Corcuera, M.T.; Caballero, M.L.; Moneo, I. Cloning and characterisation of the Anisakis simplex allergen Ani s 4 as a cysteine-protease inhibitor. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newlands, G.; Skuce, P.; Knox, D.; Smith, W. Cloning and expression of cystatin, a potent cysteine protease inhibitor from the gut of Haemonchus contortus. Parasitology 2001, 122, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainichi, T.; Maekawa, Y.; Ishii, K.; Himeno, K. Molecular cloning of a cystatin from parasitic intestinal nematode, Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. J. Med. Investig. 2001, 48, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Hales, B.J.; Chai, L.Y.; Hazell, L.; Elliot, C.E.; Stone, S.; O’Neil, S.E.; Smith, W.-A.; Thomas, W.R. IgE and IgG binding patterns and T-cell recognition of Fel d 1 and Non–Fel d 1 cat allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2013, 1, 656–665.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, K.; Vailes, L.; Pomes, A.; Chapman, M. Molecular cloning, expression and modelling of cat allergen, cystatin (Fel d 3), a cysteine protease inhibitor. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2001, 31, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, P.G.; Strickland, D.; Bosco, A.; Belgrave, D.; Hales, B.; Simpson, A.; Hollams, E.; Holt, B.; Kusel, M.; Ahlstedt, S. Distinguishing benign from pathologic TH2 immunity in atopic children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamji, M.; Ljørring, C.; Francis, J.; Calderon, M.A.; Larche, M.; Kimber, I.; Frew, A.; Ipsen, H.; Lund, K.; Würtzen, P. Functional rather than immunoreactive levels of IgG4 correlate closely with clinical response to grass pollen immunotherapy. Allergy 2012, 67, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.K.; Shamji, M.H.; Walker, S.M.; Wilson, D.R.; Wachholz, P.A.; Francis, J.N.; Jacobson, M.R.; Kimber, I.; Till, S.J.; Durham, S.R. Long-term tolerance after allergen immunotherapy is accompanied by selective persistence of blocking antibodies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 509–516.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadermaier, E.; Staikuniene, J.; Scheiblhofer, S.; Thalhamer, J.; Kundi, M.; Westritschnig, K.; Swoboda, I.; Flicker, S.; Valenta, R. Recombinant allergen-based monitoring of antibody responses during injection grass pollen immunotherapy and after 5 years of discontinuation. Allergy 2011, 66, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strobl, M.R.; Demir, H.; Acosta, G.S.; Drescher, A.; Kitzmüller, C.; Möbs, C.; Pfützner, W.; Bohle, B. The role of IgG1 and IgG4 as dominant IgE-blocking antibodies shifts during allergen immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1371–1378.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.F.; James, L.K.; Bahnson, H.T.; Shamji, M.H.; Couto-Francisco, N.C.; Islam, S.; Houghton, S.; Clark, A.T.; Stephens, A.; Turcanu, V. IgG4 inhibits peanut-induced basophil and mast cell activation in peanut-tolerant children sensitized to peanut major allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollmann, E.; Hamsten, C.; Sibanda, E.; Ochome, M.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Asarnoj, A.; Önell, A.; Lilja, G.; Gallerano, D.; Lupinek, C. Natural clinical tolerance to peanut in African patients is caused by poor allergenic activity of peanut IgE. Allergy 2015, 70, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoguina, J.S.; Adjobimey, T.; Arndts, K.; Hoch, J.; Oldenburg, J.; Layland, L.E.; Hoerauf, A. Tr1 and naturally occurring regulatory T cells induce IgG4 in B cells through GITR/GITR-L interaction, IL-10 and TGF-β. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 3101–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarayal, B.; Schiller, D.; Möbs, C.; de Jong, N.W.; Ebner, C.; Reider, N.; Bartel, D.; Lidholm, J.; Pfützner, W.; Gerth van Wijk, R. Kinetics, cross-reactivity, and specificity of B et v 1-specific I g G 4 antibodies induced by immunotherapy with birch pollen. Allergy 2013, 68, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, V.; Dolecek, C.; Denépoux, S.; Le Mao, J.; Guret, C.; Rousset, F.; Guinnepain, M.-T.; Kraft, D.; Valenta, R.; Weyer, A. Human IgG monoclonal antibodies that modulate the binding of specific IgE to birch pollen Bet v 1. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M. A theoretical framework for the immunoepidemiology of blocking antibodies to helminth infection. Parasite Immunol. 1994, 16, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellweger, F.; Gasser, P.; Brigger, D.; Buschor, P.; Vogel, M.; Eggel, A. A novel bispecific DARPin targeting FcgammaRIIB and FcepsilonRI-bound IgE inhibits allergic responses. Allergy 2016, 72, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballeda-Sangiao, N.; Olivares, F.; Rodriguez-Mahillo, A.I.; Careche, M.; Tejada, M.; Moneo, I.; González-Muñuoz, M. Identification of autoclave-resistant Anisakis simplex allergens. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, A.C.; Mueller, G.A. Abundance and stability as common properties of allergens. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 769728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballeda-Sangiao, N.; Sánchez-Alonso, I.; Navas, A.; Arcos, S.C.; de Palencia, P.F.; Careche, M.; González-Muñoz, M. Anisakis simplex products impair intestinal epithelial barrier function and occludin and zonula occludens-1 localisation in differentiated Caco-2 cells. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo-Lopez, S.; Gómez-Rodríguez, L.; Coronado, X.; Orozco, A.; Valencia-Gutierrez, C.A.; Restrepo-Betancur, L.F.; Galvis-Gómez, L.A.; Botero-Palacio, L.E. Prevalencia de parasitosis intestinales y factores asociados en un corregimiento de la costa atlántica colombiana. Rev. Salud Pública 2008, 10, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Meenan, N.A.; Ball, G.; Bromek, K.; Uhrín, D.; Cooper, A.; Kennedy, M.W.; Smith, B.O. Solution structure of a repeated unit of the ABA-1 nematode polyprotein allergen of Ascaris reveals a novel fold and two discrete lipid-binding sites. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, L.; Kennedy, M.W.; McManus, D.P.; Bradley, J.E.; Cooper, A.; Storch, J. How helminth lipid-binding proteins offload their ligands to membranes: Differential mechanisms of fatty acid transfer by the ABA-1 polyprotein allergen and Ov-FAR-1 proteins of nematodes and Sj-FABPc of schistosomes. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 6706–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; McDERMOTT, L.; Price, N.C.; Kelly, S.M.; Cooper, A.; Kennedy, M.W. Sequence-divergent units of the ABA-1 polyprotein array of the nematode Ascaris suum have similar fatty-acid-and retinol-binding properties but different binding-site environments. Biochem. J. 1999, 340, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, E.; Donado, K.; Regino, R.; Hernandez, K.; Mercado, D.; Mercado, A.C.; Benedetti, I.; Puerta, L.; Zakzuk, J.; Caraballo, L. The Allergenic Activity of Blo t 2, a Blomia tropicalis IgE-Binding Molecule. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
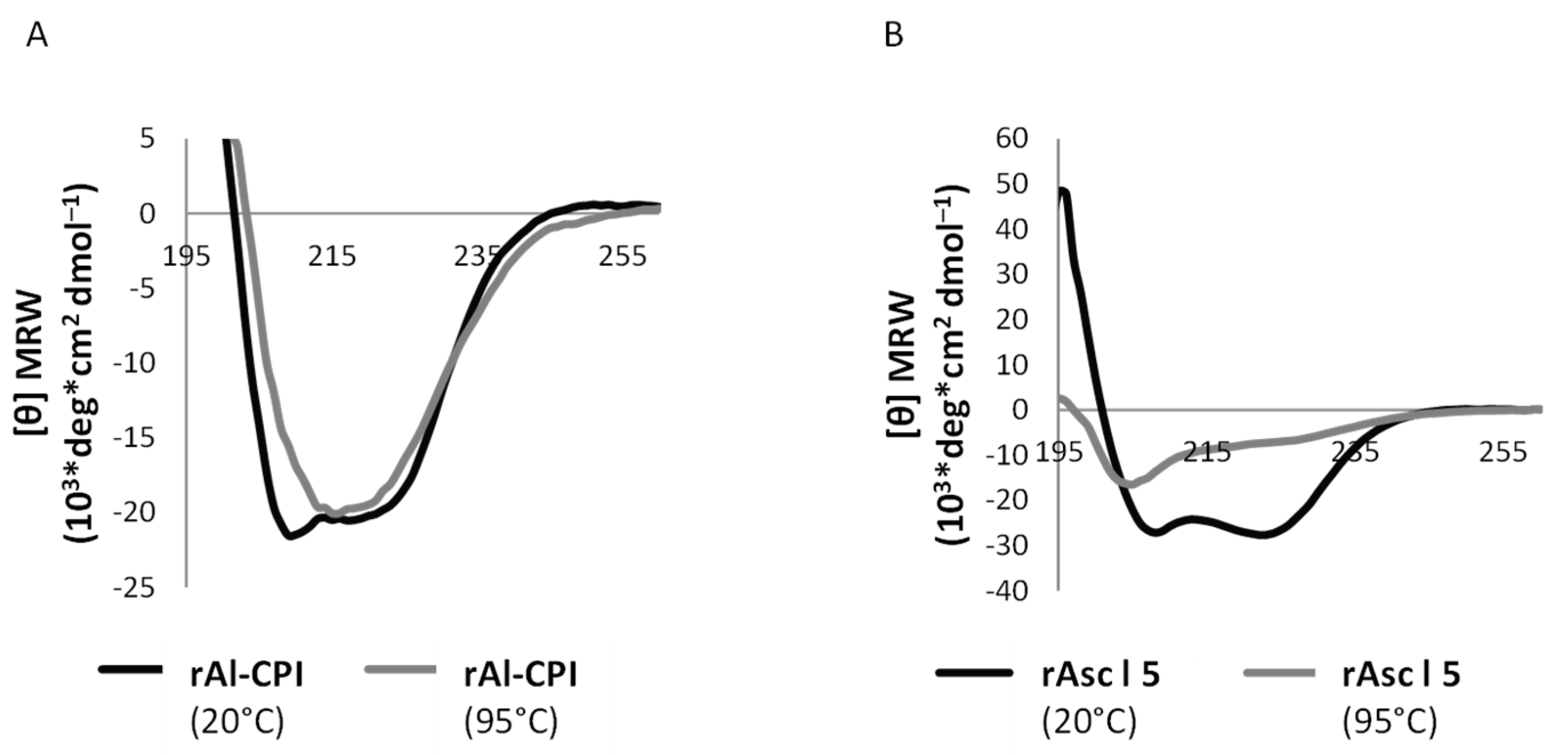
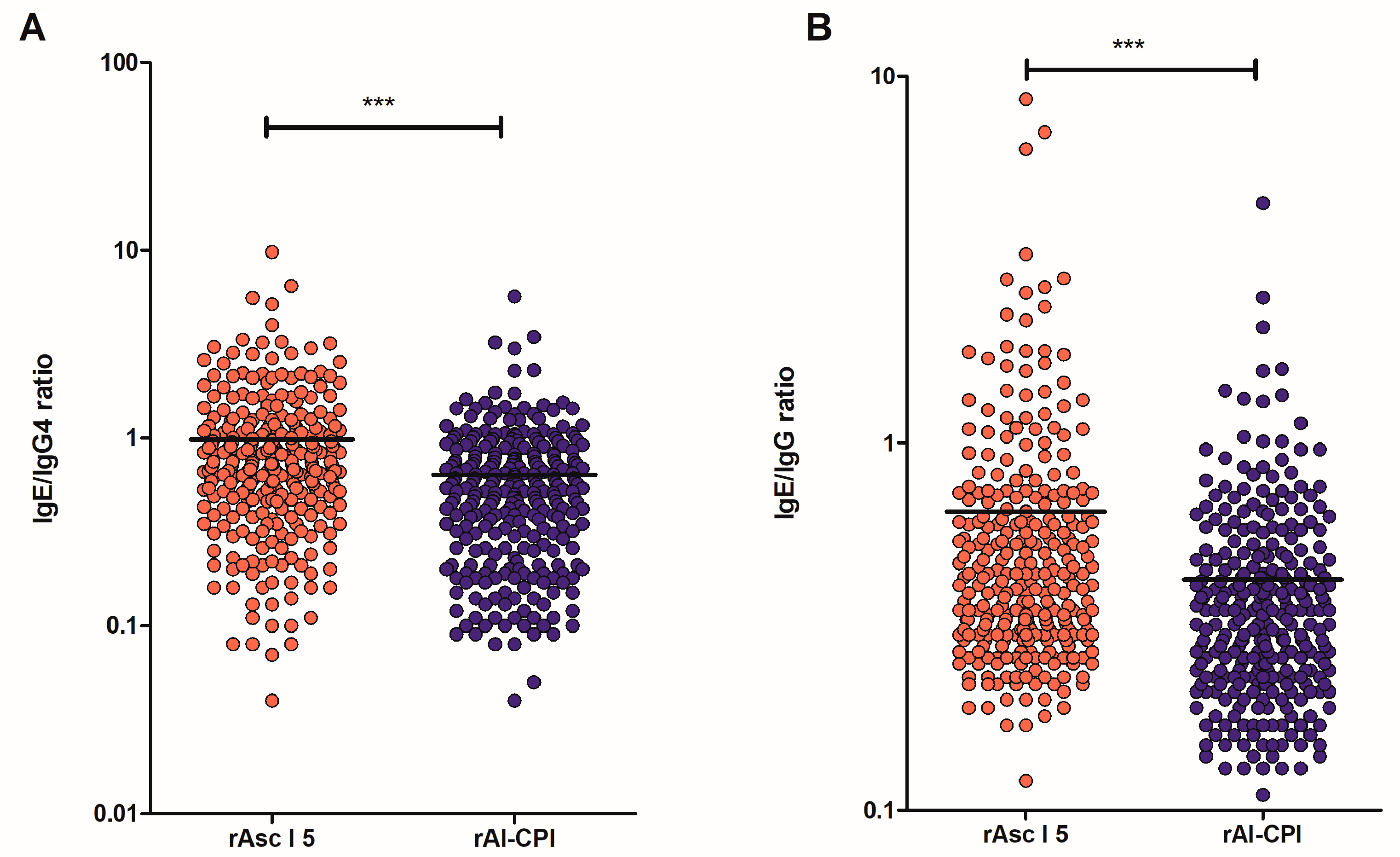
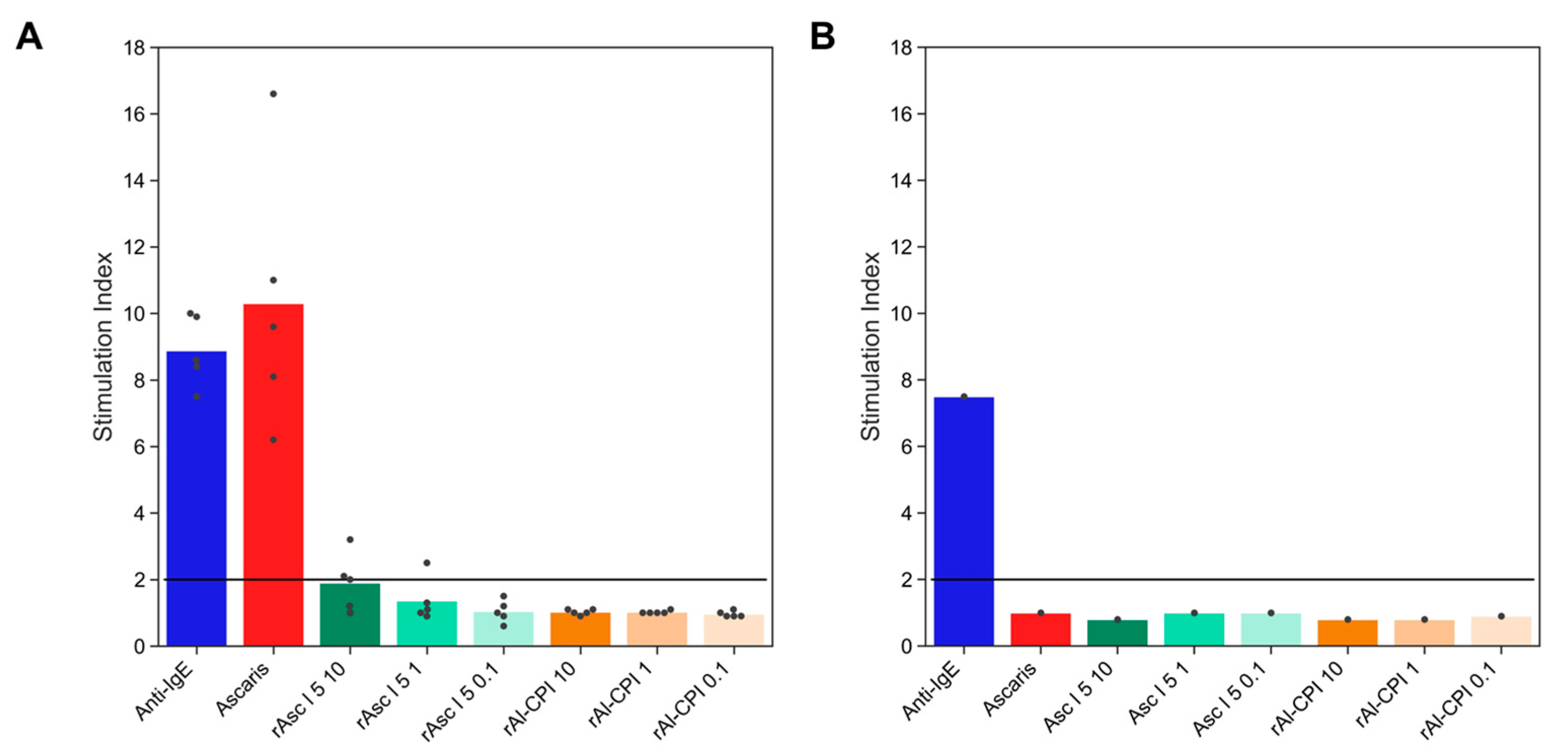
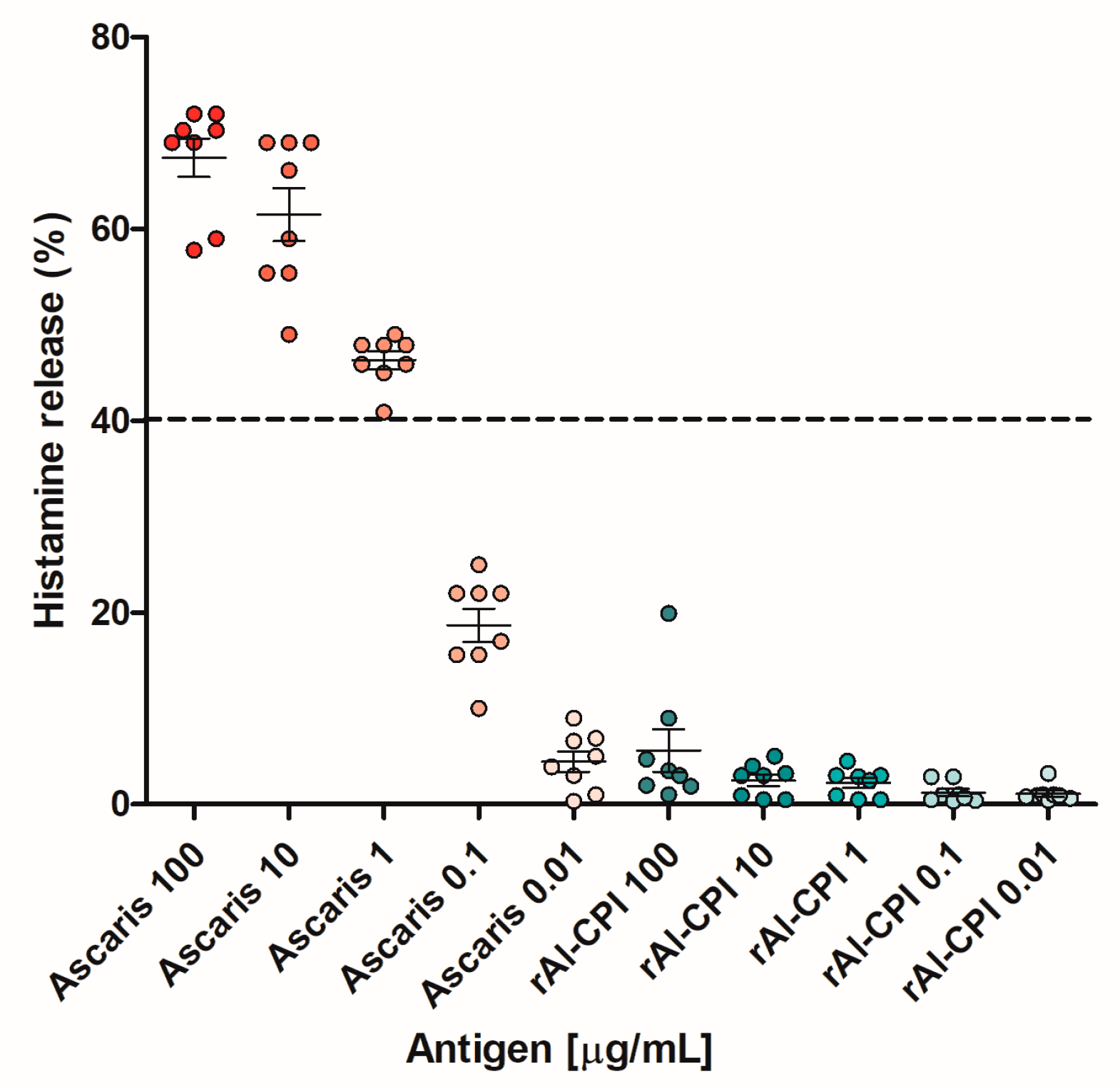
| Total Sample Size [N = 293] | Non-Asthmatics [n = 246] | Asthmatics [n = 47] | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age in years [mean ± SD] * | 30.9 ± 21.5 | 31.8 ±21.2 | 26.4 ± 22.3 | 0.13 |
| Sex, female n (%) ** | 208 (71) | 171 (69.5) | 37 (78.7) | 0.2 |
| Asc l 5 [n (%)] ** | ||||
| IgE+ | 153 (52.2%) | 125 (50.8%) | 28 (59.6%) | 0.27 |
| IgG4+ | 201 (68.6%) | 165 (67.1%) | 36 (76.6%) | 0.18 |
| IgG+ | 206 (70.3%) | 173 (70.3%) | 33 (70.2%) | 0.99 |
| Al-CPI [n (%)] ** | ||||
| IgE+ | 120 (41.0%) | 97 (39.4%) | 23 (48.9%) | 0.23 |
| IgG4+ | 237 (80.9%) | 200 (81.3%) | 37 (78.7%) | 0.68 |
| IgG+ | 222 (75.8%) | 184 (74.8%) | 38 (80.9%) | 0.38 |
| Variable | β | S.E. | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al-CPI | |||
| IgE/IgG4_ratio | −0.24 | 0.12 | 0.046 * |
| Gender | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.16 |
| Age (years) | 0.05 | 0.002 | 0.48 |
| Asc l 5 | |||
| IgE/IgG4_ratio | −0.08 | 0.07 | 0.28 |
| Gender | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| Age (years) | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahumada, V.; Zakzuk, J.; Aglas, L.; Coronado, S.; Briza, P.; Regino, R.; Ferreira, F.; Caraballo, L. Comparison of Antibody Responses against Two Molecules from Ascaris lumbricoides: The Allergen Asc l 5 and the Immunomodulatory Protein Al-CPI. Biology 2023, 12, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101340
Ahumada V, Zakzuk J, Aglas L, Coronado S, Briza P, Regino R, Ferreira F, Caraballo L. Comparison of Antibody Responses against Two Molecules from Ascaris lumbricoides: The Allergen Asc l 5 and the Immunomodulatory Protein Al-CPI. Biology. 2023; 12(10):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101340
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhumada, Velky, Josefina Zakzuk, Lorenz Aglas, Sandra Coronado, Peter Briza, Ronald Regino, Fátima Ferreira, and Luis Caraballo. 2023. "Comparison of Antibody Responses against Two Molecules from Ascaris lumbricoides: The Allergen Asc l 5 and the Immunomodulatory Protein Al-CPI" Biology 12, no. 10: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101340
APA StyleAhumada, V., Zakzuk, J., Aglas, L., Coronado, S., Briza, P., Regino, R., Ferreira, F., & Caraballo, L. (2023). Comparison of Antibody Responses against Two Molecules from Ascaris lumbricoides: The Allergen Asc l 5 and the Immunomodulatory Protein Al-CPI. Biology, 12(10), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101340







