Insights into the Mitochondrial Genetic Makeup and Miocene Colonization of Primitive Flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes: Psettodidae) in the East Atlantic and Indo-West Pacific Ocean
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Species Identification
2.2. DNA Extraction, Mitogenome Sequencing, and Assembly
2.3. Mitogenomic Characterization
2.4. Genetic Distance, Phylogenetic Analyses, and TimeTree Estimation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mitogenomic Structure and Organization
3.2. Protein-Coding Genes
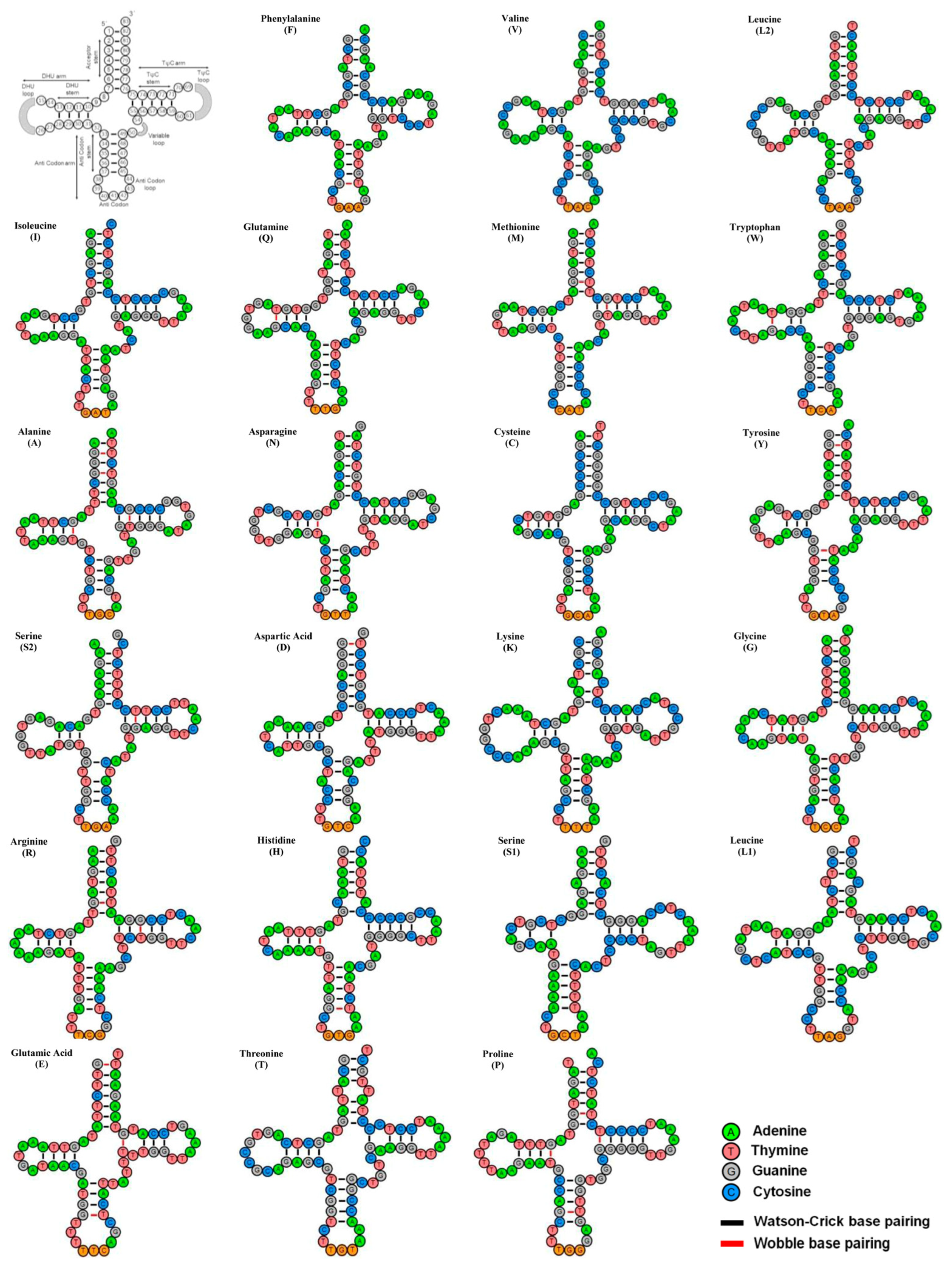
3.3. Ribosomal RNA and Transfer RNA Genes
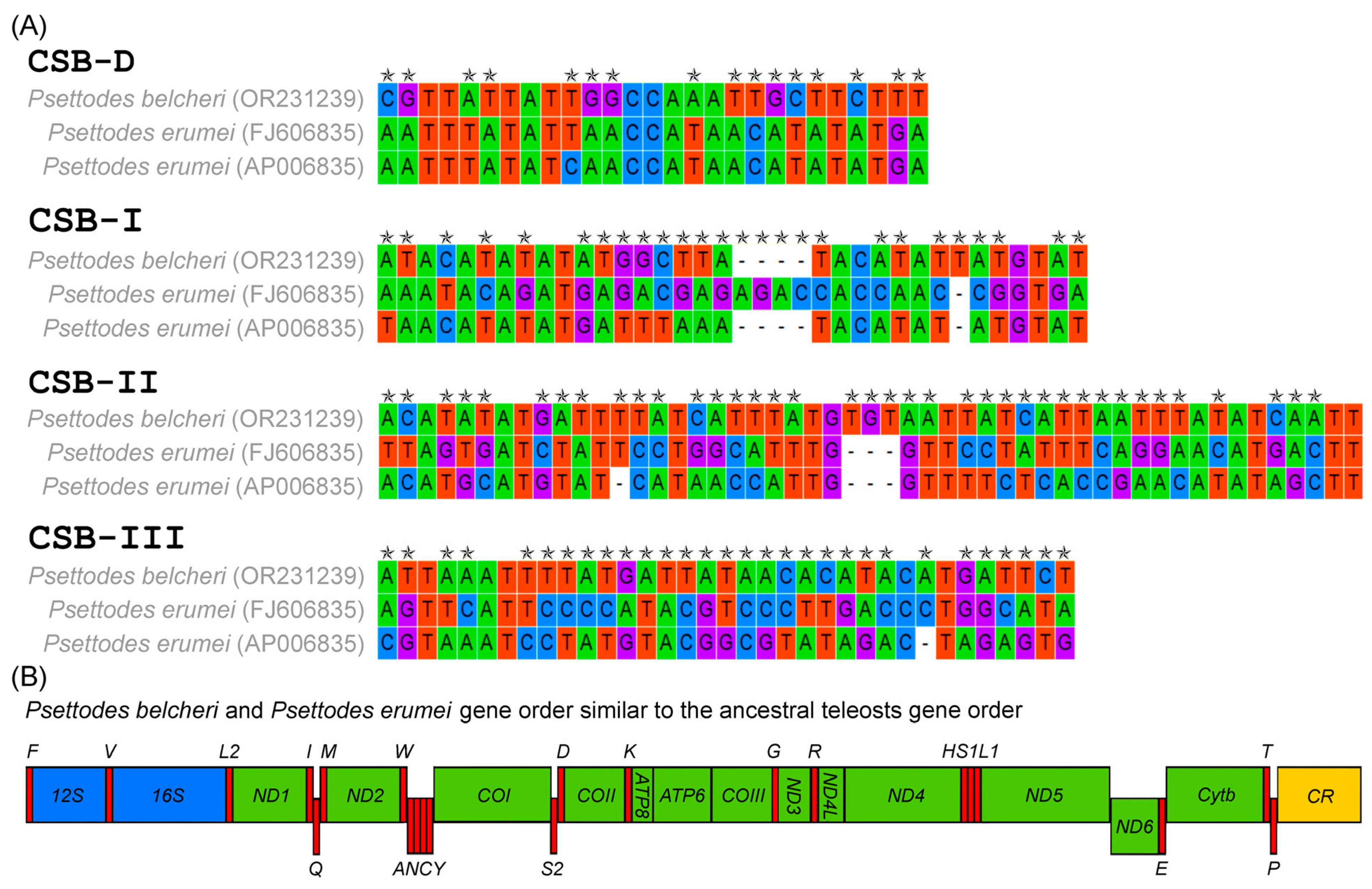
3.4. Features of Control Region and Gene Arrangements
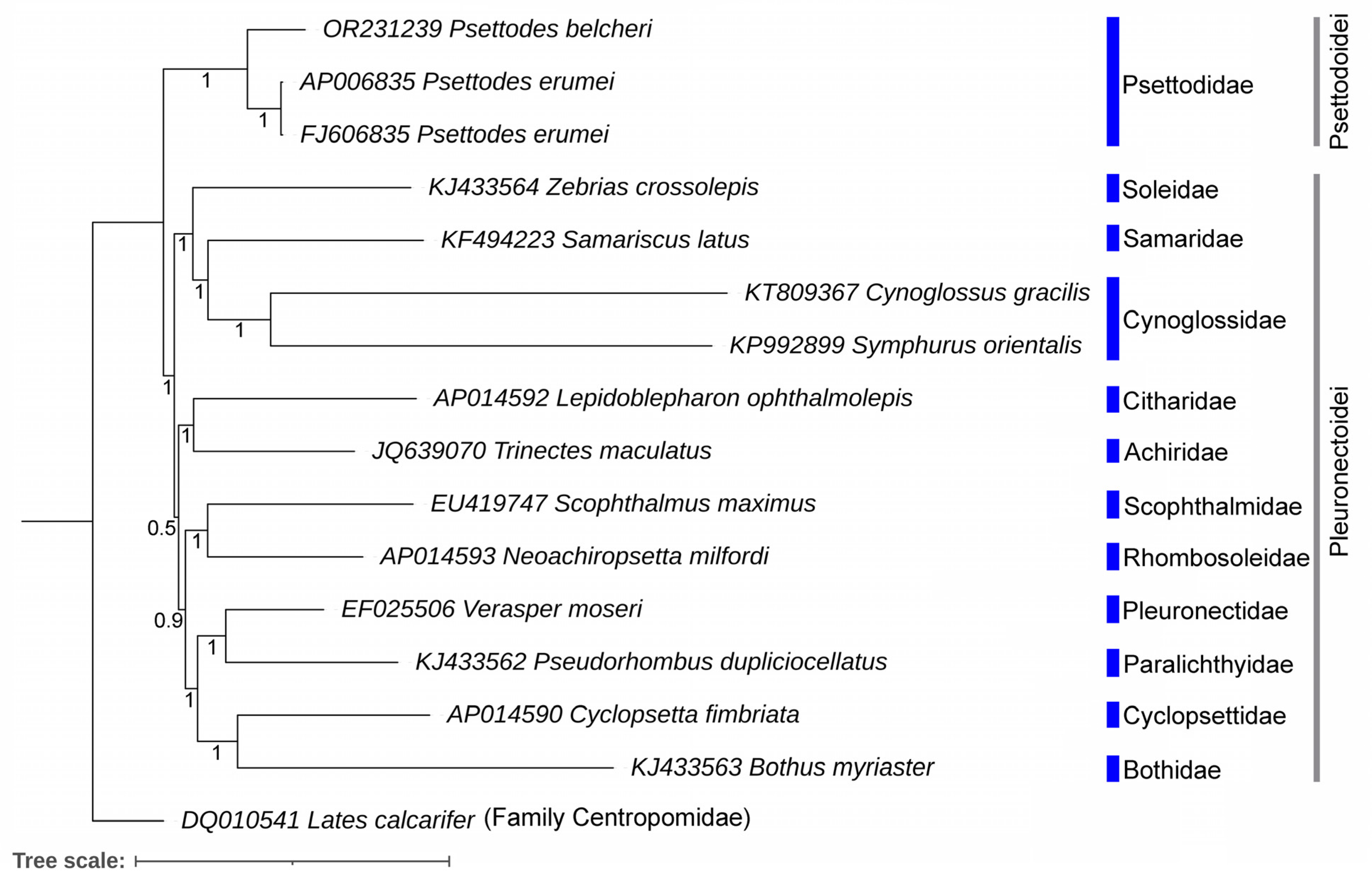
3.5. Genetic Distances and Mitogenomic Phylogeny
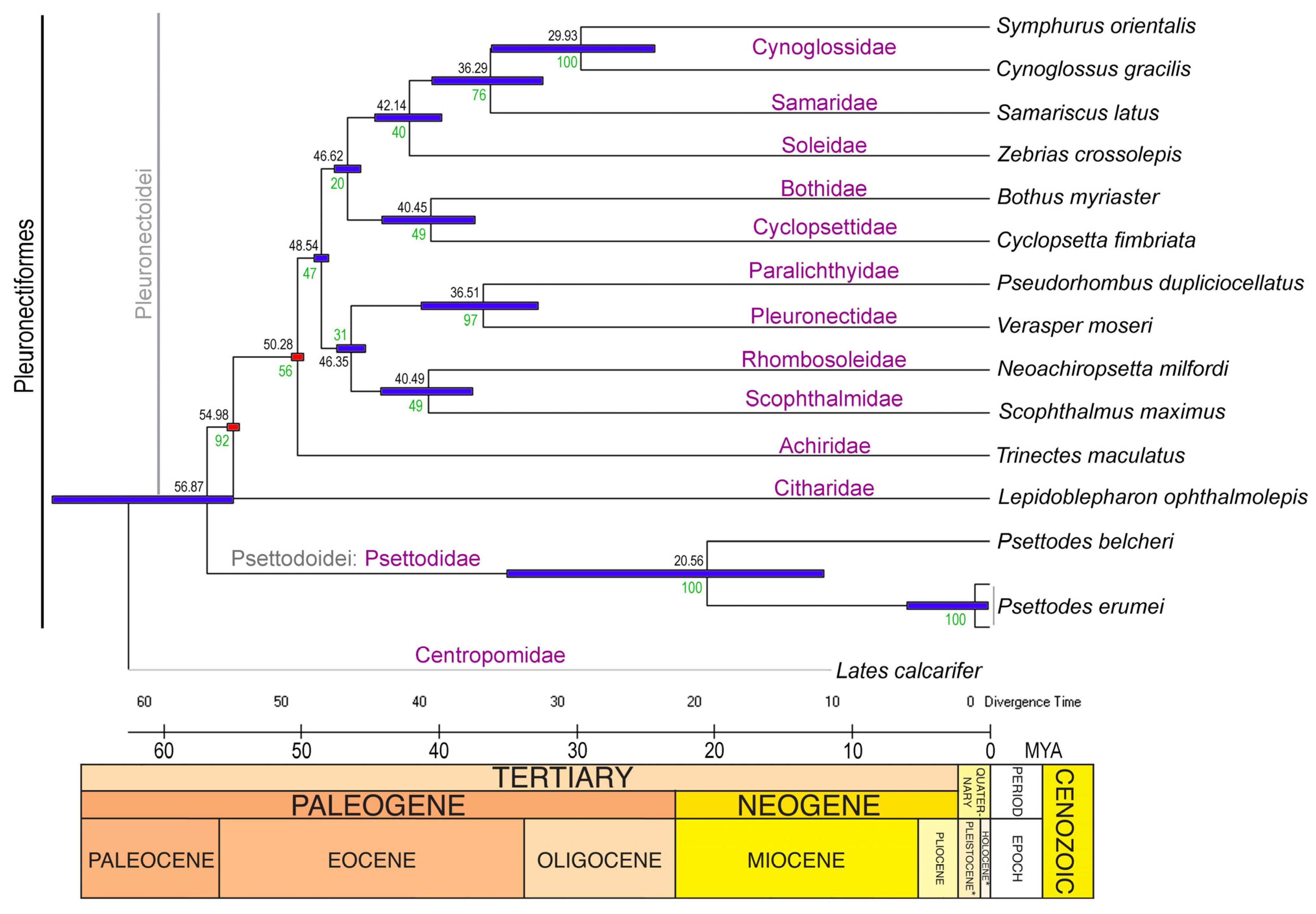
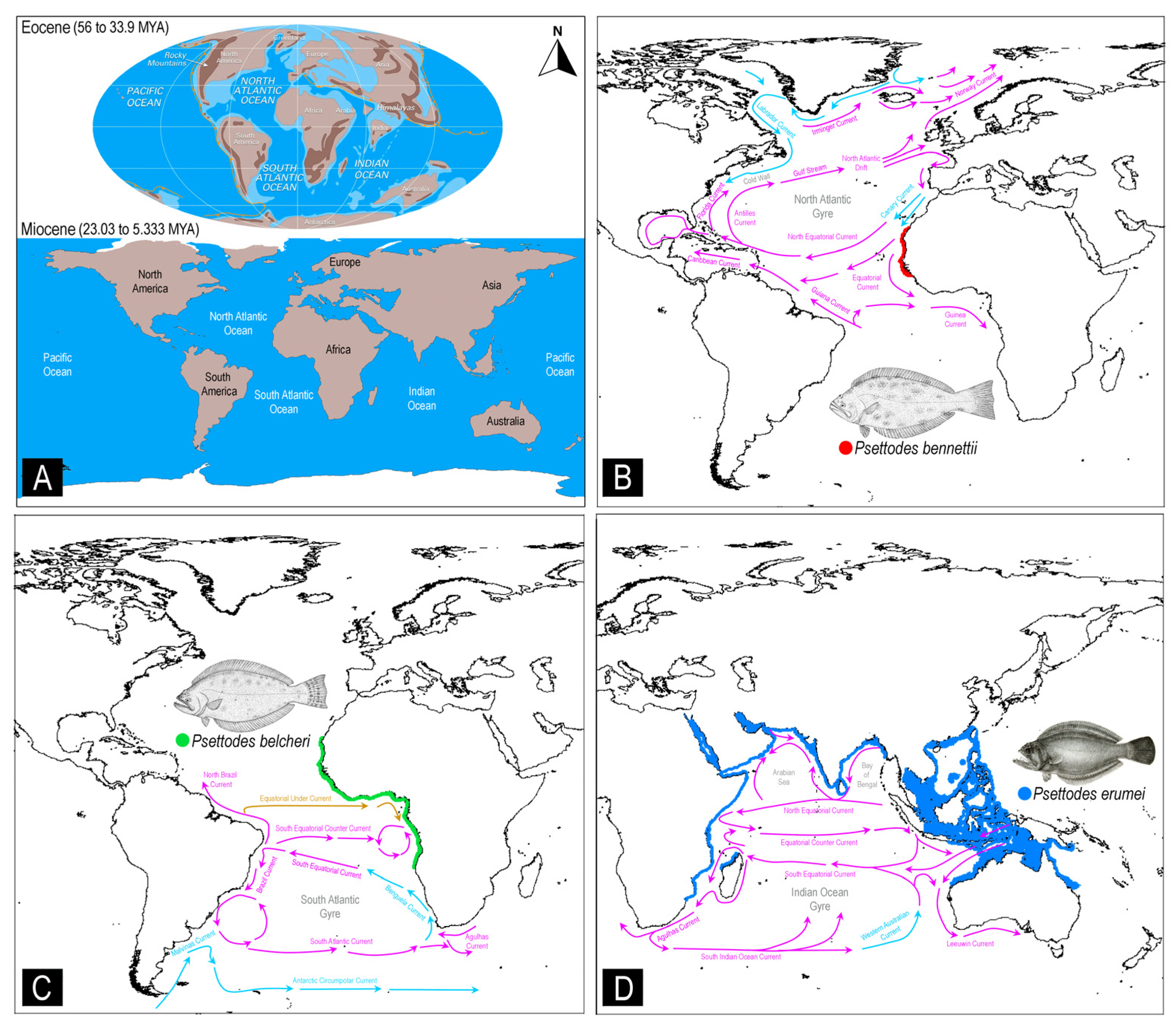
3.6. Divergence Time and Diversification
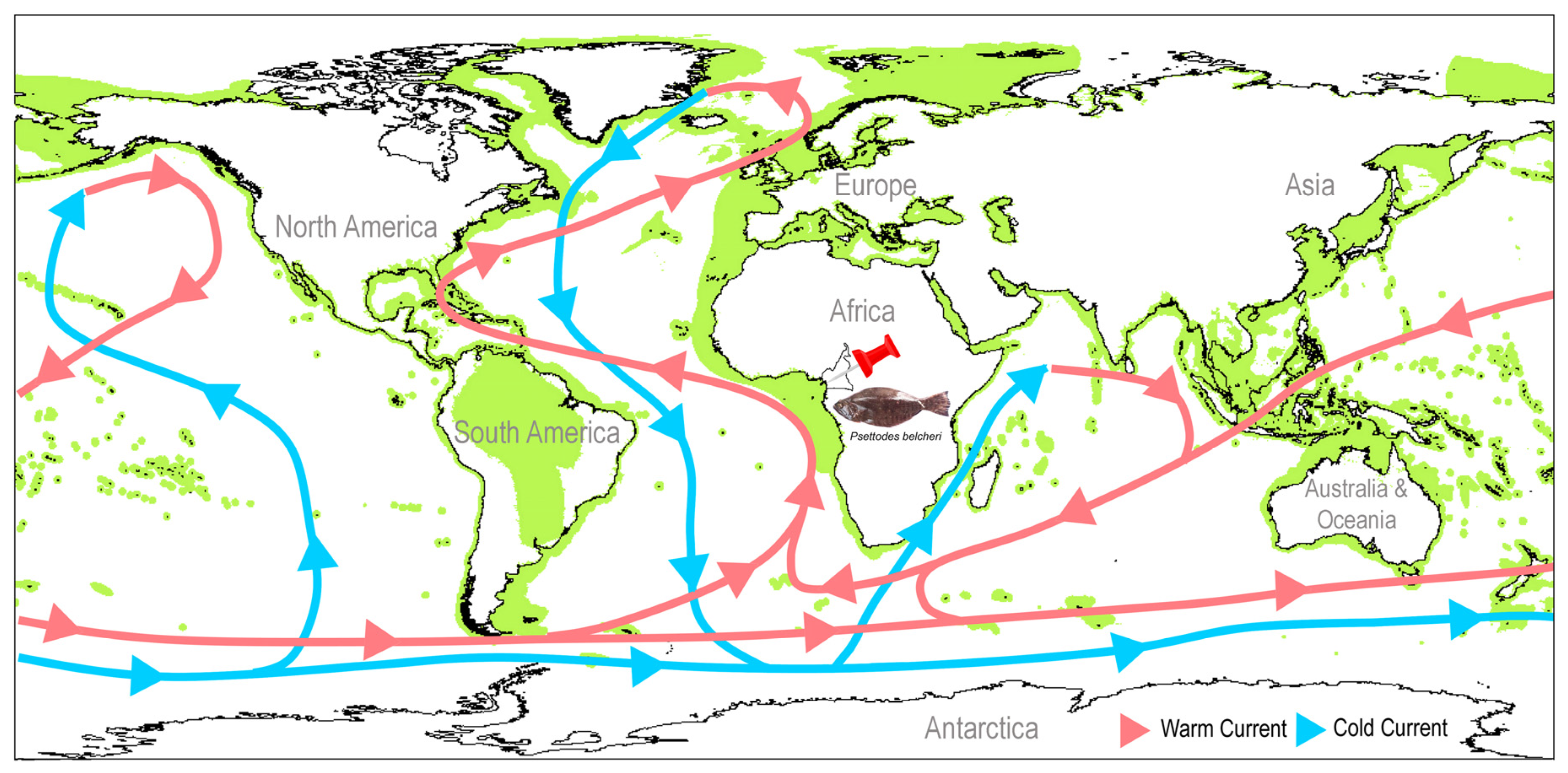
3.7. Conservation Implication
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fricke, R.; Eschmeyer, W.N.; Van der Laan, R. (Eds.) Eschmeyer’s Catalog of Fishes: Genera, Species. Electronic Version. 2022. Available online: http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Nelson, J.S.; Grande, T.C.; Wilson, M.V.H. Fishes of the World, 5th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; 752p. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, M. The evolutionary origin of flatfish asymmetry. Nature 2008, 454, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinner, M.; Kortmann, M.; Traini, C.; Gorb, S.N. Key role of scale morphology in flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes) in the ability to keep sand. Sci. Rep. 2016, 20, 26308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, K.M.; Larouche, O.; Watson, S.J.; Farina, S.; Habegger, M.L.; Friedman, M. Integration drives rapid phenotypic evolution in flatfishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101330118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.A.; Chapleau, F. Monophyly and intrarelationships of the family Pleuronectidae (Pleuronectiformes), with a revised classification. Fish. Bull. 1998, 96, 686–726. [Google Scholar]
- Eighani, M.; Paighambari, S.Y. Shrimp, bycatch and discard composition of fish caught by small-scale shrimp trawlers in the Hormuzgan coast of Iran in the Persian Gulf. Philipp. Agric. Sci. 2013, 96, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, R.N.; Nash, R.D.M.; Geffen, A.J.; Van der Veer, H.W. Flatfishes: Biology and Exploitation, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: West Sussex, UK, 2015; 576p. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; Version 2022-2; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Coulson, P.G.; Poad, J.A. Biological characteristics of the primitive flatfish Indian halibut (Psettodes erumei) from the tropical northeastern Indian Ocean, including implications of the use of incorrect aging methods on mortality estimates. Fish. Bull. 2021, 119, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, C.A.; Alba, J.; Pacheco, J.; Fritz, T.; Tamone, S.L. Polymorphism and multiple correlated characters: Do flatfish asymmetry morphs also differ in swimming performance and metabolic rate? Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 4772–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, T. Sexual dimorphism in scales of marbled flounder Pseudopleuronectes yokohamae (Pleuronectiformes: Pleuronectidae), with comments on the relevance to their spawning behaviour. J. Fish. Biol. 2013, 83, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.Y.; Munroe, T.A. Unraveling cryptic diversity among shallow-water tonguefishes (Pleuronectiformes: Cynoglossidae: Symphurus) from the Indo-West Pacific region, with descriptions of five new species. Zootaxa 2021, 5039, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur, R.R.; Li, C.; Munroe, T.A.; Ballesteros, J.A.; Ortí, G. Addressing gene tree discordance and non-stationarity to resolve a multi-locus phylogeny of the flatfishes (Teleostei: Pleuronectiformes). Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 763–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourt, J.A.; Affonso, P.R.A.M.; Ramos, R.T.C.; Schneider, H.; Sampaio, I. Phylogenetic relationships and the origin of New World soles (Teleostei: Pleuronectiformes: Achiridae): The role of estuarine habitats. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2023, 178, 107631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Gao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yanagimoto, T. Demographic History and Population Structure of Blackfin Flounder (Glyptocephalus stelleri) in Japan Revealed by Mitochondrial Control Region Sequences. Biochem. Genet. 2010, 48, 402–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robledo, D.; Hermida, M.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Fernández, C.; Blanco, A.; Bouza, C.; Martínez, P. Integrating genomic resources of flatfish (Pleuronectiformes) to boost aquaculture production. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2017, 21, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Zhao, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, R.; Yang, C.; Ma, W.; Wang, X.; Feng, M.; et al. Application of DNA barcoding in fish identification of supermarkets in Henan province, China: More and longer COI gene sequences were obtained by designing new primers. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerdà, J.; Douglas, S.; Reith, M. Genomic resources for flatfish research and their applications. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 1045–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-J.; Bonillo, C.; Lecointre, G. Repeatability of clades as a criterion of reliability: A case study for molecular phylogeny of Acanthomorpha (Teleostei) with larger number of taxa. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2003, 26, 262–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, R.; Miya, M.; Mabuchi, K.; Lavoue, S.; Inoue, J.G.; Satoh, T.P.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nishida, M. Interrelationships of the 11 gasterosteiform families (sticklebacks, pipefishes, and their relatives): A new perspective based on whole mitogenome sequences from 75 higher teleosts. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2008, 46, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, P.C.; Smith, W.L.; Price, S.A.; Tang, K.L.; Sparks, J.S.; Ferry, L.A.; Kuhn, K.L.; Eytan, R.I.; Near, T.J. The Evolution of Pharyngognathy: A Phylogenetic and Functional Appraisal of the Pharyngeal Jaw Key Innovation in Labroid Fishes and Beyond. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 1001–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.A.; Chen, W.J.; López, J.A. Are flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes) monophyletic? Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.A.; Chen, W.J.; López, J.A. Molecular data do not provide unambiguous support for the monophyly of flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes): A reply to Betancur-R and Ortí. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2014, 75, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur, R.R.; Orti, G. Molecular evidence for the monophyly of flatfishes (Carangimorpharia: Pleuronectiformes). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2014, 73, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.A.; Chanet, B.; Chen, J.N.; Lee, M.Y.; Chen, W.J. Origins and relationships of the Pleuronectoidei: Molecular and morphological analysis of living and fossil taxa. Zool. Scr. 2019, 48, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, R.C.; Faircloth, B.C.; Eytan, R.I.; Smith, W.L.; Near, T.J.; Alfaro, M.E.; Friedman, M. Phylogenomic analysis of carangimorph fishes reveals flatfish asymmetry arose in a blink of the evolutionary eye. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.A.; López, J.A.; Satoh, T.P.; Chen, W.-J.; Miya, M. Mitochondrial genomic investigation of flatfish monophyly. Gene 2014, 551, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Chen, S.; Kong, X.; Si, L.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Flatfish monophyly refereed by the relationship of Psettodes in Carangimorphariae. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potkamp, G.; Fransen, C.H.J.M. Speciation with gene flow in marine systems. Contrib. Zool. 2019, 88, 133–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, R.; Johannesson, K.; Stankowski, S. Speciation in marine environments: Diving under the surface. J. Evol. Biol. 2021, 34, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momigliano, P.; Jokinen, H.; Fraimout, A.; Florin, A.B.; Norkko, A.; Merilä, J. Extraordinarily rapid speciation in a marine fish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6074–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, K.E. The Living Marine Resources of the Eastern Central Atlantic. FAO Species Identification Guide for Fishery Purposes 2016; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, W.; Fukunaga, T.; Isagozawa, R.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Satoh, T.P.; Sado, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Takeshima, H.; Miya, M. MitoFish and MitoAnnotator: A Mitochondrial Genome Database of Fish with an Accurate and Automatic Annotation Pipeline. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.P.; Lin, B.Y.; Mak, A.J.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE 2.0: Improved detection and functional classification of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 9077–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laslett, D.; Canbäck, B. ARWEN: A program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2007, 24, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Lo, L.C.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Feng, F.; Chou, R.; Yue, G.H. The Complete Mitochondrial Genome Sequence and Characterization of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Control Region of the Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer). Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Han, J.; Ge, L.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, X.; Mu, Y.; Liu, W.; Cao, J.; Liu, Z. Sequence and organization of the complete mitochondrial genomes of spotted halibut (Verasper variegatus) and barfin flounder (Verasper moseri). DNA Seq. 2008, 19, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Miao, X.-G.; Kong, X.-Y. A novel model of double replications and random loss accounts for rearrangements in the Mitogenome of Samariscus latus (Teleostei: Pleuronectiformes). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Gong, L.; Wang, S.-Y.; Miao, X.-G.; Kong, X.-Y. Tandem Duplication and Random Loss for mitogenome rearrangement in Symphurus (Teleost: Pleuronectiformes). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Si, L.-Z.; Shi, W.; Kong, X.-Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of Zebrias crossolepis (Pleuronectiformes: Soleidae). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 1235–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Shi, W.; Yang, M.; Li, D.; Kong, X. Novel gene arrangement in the mitochondrial genome of Bothus myriaster (Pleuronectiformes: Bothidae): Evidence for the Dimer-Mitogenome and Non-random Loss model. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 3089–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhao, F.; Chen, S. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Cynoglossus gracilis and a comparative analysis with other Cynoglossinae fishes. Gene 2016, 591, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, L.-Z.; Gong, L.; Shi, W.; Yang, M.; Kong, X.-Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of Pseudorhombus dupliocellatus (Pleuronectiformes: Paralichthyidae). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2017, 28, 58–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redin, A.D.; Kartavtsev, Y.P. The Mitogenome Structure of Righteye Flounders (Pleuronectidae): Molecular Phylogeny and Systematics of the Family in East Asia. Diversity 2022, 14, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vences, M.; Miralles, A.; Brouillet, S.; Ducasse, J.; Fedosov, A.; Kharchev, V.; Kostadinov, I.; Kumari, S.; Patmanidis, S.; Scherz, M.D. iTaxoTools 0.1: Kickstarting a specimen-based software toolkit for taxonomists. Megataxa 2021, 6, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New Methods for Selecting Partitioned Models of Evolution for Molecular and Morphological Phylogenetic Analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Schwartz, T.; Pickett, B.E.; He, S.; Klem, E.B.; Scheuermann, R.H.; Passarotti, M.; Kaufman, S.; O’Leary, M.A. A RESTful API for Access to Phylogenetic Tools via the CIPRES Science Gateway. Evol. Bioinform. 2015, 11, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. JModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL): An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, B. Estimating TimeTrees with MEGA and the TimeTree Resource. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Battistuzzi, F.U.; Billing-Ross, P.; Murillo, O.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. Estimating divergence times in large molecular phylogenies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19333–19338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, B.; Tao, Q.; Tamura, K.; Kumar, S. Fast and Accurate Estimates of Divergence Times from Big Data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.; Binarao, J.D.; De Alwis, P.S.; Kim, A.R.; Lee, S.R.; Andriyono, S.; Gietbong, F.Z.; Kim, H.W. First Mitogenome of Endangered Enteromius thysi (Actinopterygii: Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae) from Africa: Characterization and Phylogeny. Fishes 2023, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alwis, P.S.; Kundu, S.; Gietbong, F.Z.; Amin, M.H.F.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, A.R. Mitochondriomics of Clarias Fishes (Siluriformes: Clariidae) with a New Assembly of Clarias camerunensis: Insights into the Genetic Characterization and Diversification. Life 2023, 13, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Tong, J. Evolutionary analysis of cyprinid mitochondrial genomes: Remarkable variation and strong adaptive evolution. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Quirós, J.L.; Hernández-Muñoz, S.; Baeza, J.A. The complete mitochondrial genome of the roosterfish Nematistius pectoralis Gill 1862: Purifying selection in protein coding genes, organization of the control region, and insights into family-level phylogenomic relationships in the recently erected order Carangiformes. Gene 2022, 845, 146847. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, N.S.; Hirabayashi, N.; Agmon, I.; Yonath, A.; Suzuki, T. Comprehensive genetic selection revealed essential bases in the peptidyl-transferase center. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15386–15391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.P.; Miya, M.; Mabuchi, K.; Nishida, M. Structure and variation of the mitochondrial genome of fishes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Kong, X.Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Jiang, J.X. Utility of tRNA genes from the complete mitochondrial genome of Psetta maxima for implying a possible sister-group relationship to the Pleuronectiformes. Zool. Stud. 2011, 50, 665–681. [Google Scholar]
- Varani, G.; McClain, W.H. The G-U wobble base pair: A fundamental building block of RNA structure crucial to RNA function in diverse biological systems. EMBO Rep. 2000, 1, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.; De Alwis, P.S.; Kim, A.R.; Lee, S.R.; Kang, H.-E.; Go, Y.; Gietbong, F.Z.; Wibowo, A.; Kim, H.-W. Mitogenomic Characterization of Cameroonian Endemic Coptodon camerunensis (Cichliformes: Cichlidae) and Matrilineal Phylogeny of Old-World Cichlids. Genes 2023, 14, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, D.A. Replication of animal mitochondrial DNA. Cell 1982, 28, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z. A novel rearrangement in the mitochondrial genome of tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis: Control region translocation and a tRNA gene inversion. Genome 2009, 52, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Dong, X.L.; Wang, Z.M.; Miao, X.G.; Wang, S.Y.; Kong, X.Y. Complete mitogenome sequences of four flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes) reveal a novel gene arrangement of L-strand coding genes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Gong, L.; Yu, H. Double control regions of some flatfish mitogenomes evolve in a concerted manner. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Lu, X.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Liu, L.; Lü, Z.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L. Novel gene rearrangement pattern in Cynoglossus melampetalus mitochondrial genome: New gene order in genus Cynoglossus (Pleuronectiformes: Cynoglossidae). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Tian, S.; Yang, C.; Chen, X. Novel Gene Rearrangement and the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Cynoglossus monopus: Insights into the Envolution of the Family Cynoglossidae (Pleuronectiformes). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinti, F.; Piccinetti, C.; Tommasini, S.; Vallisneri, M. Mitochondrial DNA Variation, Phylogenetic Relationships, and Evolution of Four Mediterranean Genera of Soles (Soleidae, Pleuronectiformes). Mar. Biotechnol. 2000, 2, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, K.; Hayashizaki, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Asahida, T.; Toyohara, H.; Yamashita, Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) mitochondrial genome: Structural properties and cue for resolving teleostean relationships. J. Hered. 2000, 91, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miya, M.; Takeshima, H.; Endo, H.; Ishiguro, N.B.; Inoue, J.G.; Mukai, T.; Satoh, T.P.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Mabuchi, K. Major patterns of higher teleostean phylogenies: A new perspective based on 100 complete mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, G.; Shao, C.; Huang, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, P.; Song, W.; An, N.; Chalopin, D.; Volff, J.N.; et al. Whole-genome sequence of a flatfish provides insights into ZW sex chromosome evolution and adaptation to a benthic lifestyle. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueras, A.; Robledo, D.; Corvelo, A.; Hermida, M.; Pereiro, P.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Gómez-Garrido, J.; Carreté, L.; Bello, X.; Gut, M.; et al. Whole genome sequencing of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus; Pleuronectiformes): A fish adapted to demersal life. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Bao, B.; Xie, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, B.; Jia, X.; Yao, Q.; Ortí, G.; Li, W.; Li, X.; et al. The genome and transcriptome of Japanese flounder provide insights into flatfish asymmetry. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Guo, H.; Jia, L.; Guo, B.; Zheng, D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B. Genome assembly and annotation at the chromosomal level of first Pleuronectidae: Verasper variegatus provides a basis for phylogenetic study of Pleuronectiformes. Genomics 2021, 113, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Z.; Gong, L.; Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Luo, H.; et al. Large-scale sequencing of flatfish genomes provides insights into the polyphyletic origin of their specialized body plan. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, C.J.; Yuan, H.; Li, C.; Arcila, D.; Betancur, R.R.; Hughes, L.C.; Ortí, G.; Tornabene, L. Exon-capture data and locus screening provide new insights into the phylogeny of flatfishes (Pleuronectoidei). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2022, 166, 107315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, G.; Barbut, L.; Volckaert, F.A.M. Complex effect of projected sea temperature and wind change on flatfish dispersal. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, A.; Primo, A.L.; Crespo, D.; Pardal, M.; Martinho, F. Interannual variability in early life phenology is driven by climate and oceanic processes in two NE Atlantic flatfishes. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Santos, P.; Tanner, S.E.; Aboim, M.A.; Vasconcelos, R.P.; Laroche, J.; Charrier, G.; Pérez, M.; Presa, P.; Gillanders, B.M.; Cabral, H.N. Reconciling differences in natural tags to infer demographic and genetic connectivity in marine fish populations. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, H.; Rohling, E.J.; Zhang, R.; Roberts, A.P.; Holbourn, A.E.; Ladant, J.B.; Dupont-Nivet, G.; Kuhnt, W.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; et al. Global warming-induced Asian hydrological climate transition across the Miocene–Pliocene boundary. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevenell, A.E.; Kennett, J.P.; Lea, D.W. Middle Miocene Southern Ocean Cooling and Antarctic Cryosphere Expansion. Science 2004, 305, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methner, K.; Campani, M.; Fiebig, J.; Löffler, N.; Kempf, O.; Mulch, A. Middle Miocene long-term continental temperature change in and out of pace with marine climate records. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, T.D.; Lawrence, K.T.; Tzanova, A.; Peterson, L.C.; Caballero-Gill, R.; Kelly, C.S. Late Miocene global cooling and the rise of modern ecosystems. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, I.S.; Aze, T.; Farnsworth, A.; Valdes, P.; Saupe, E.E. Origination of the modern-style diversity gradient 15 million years ago. Nature 2023, 614, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, T.D.; Lorenzoni, L.; Isensee, K.; Valdés, L. What are Marine Ecological Time Series telling us about the ocean. In A Status Report IOC-UNESCO 2017; IOC Technical Series, No. 129; IOC-UNESCO: Paris, France, 2017; 297p. [Google Scholar]
- Teske, P.R.; Sandoval-Castillo, J.; Golla, T.R.; Emami-Khoyi, A.; Tine, M.; von der Heyden, S.; Beheregaray, L.B. Thermal selection as a driver of marine ecological speciation. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20182023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.J.; Coll, M.; Danovaro, R.; Halpin, P.; Ojaveer, H.; Miloslavich, P. A Census of Marine Biodiversity Knowledge, Resources, and Future Challenges. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, J.A. Collapse and recovery of marine fishes. Nature 2000, 406, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, K.L.; Morét-Ferguson, S.; Maximenko, N.A.; Proskurowski, G.; Peacock, E.E.; Hafner, J.; Reddy, C.M. Plastic Accumulation in the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre. Science 2010, 329, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crego-Prieto, V.; Martinez, J.L.; Roca, A.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Interspecific Hybridization Increased in Congeneric Flatfishes after the Prestige Oil Spill. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feekings, J.; Bartolino, V.; Madsen, N.; Catchpole, T. Fishery Discards: Factors Affecting Their Variability within a Demersal Trawl Fishery. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pörtner, H.O.; Roberts, D.C.; Poloczanska, E.S.; Mintenbeck, K.; Tignor, M.; Alegría, A.; Craig, M.; Langsdorf, S.; Löschke, S.; Möller, V.; et al. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen, J.; Andersen, J.H.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Conley, D.J. Deoxygenation of the Baltic Sea during the last century. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5628–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissling, A.; Wallin, I. Recruitment variability in Baltic flounder (Platichthys solemdali)—Effects of salinity with implications for stock development facing climate change. J. Sea Res. 2020, 162, 10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
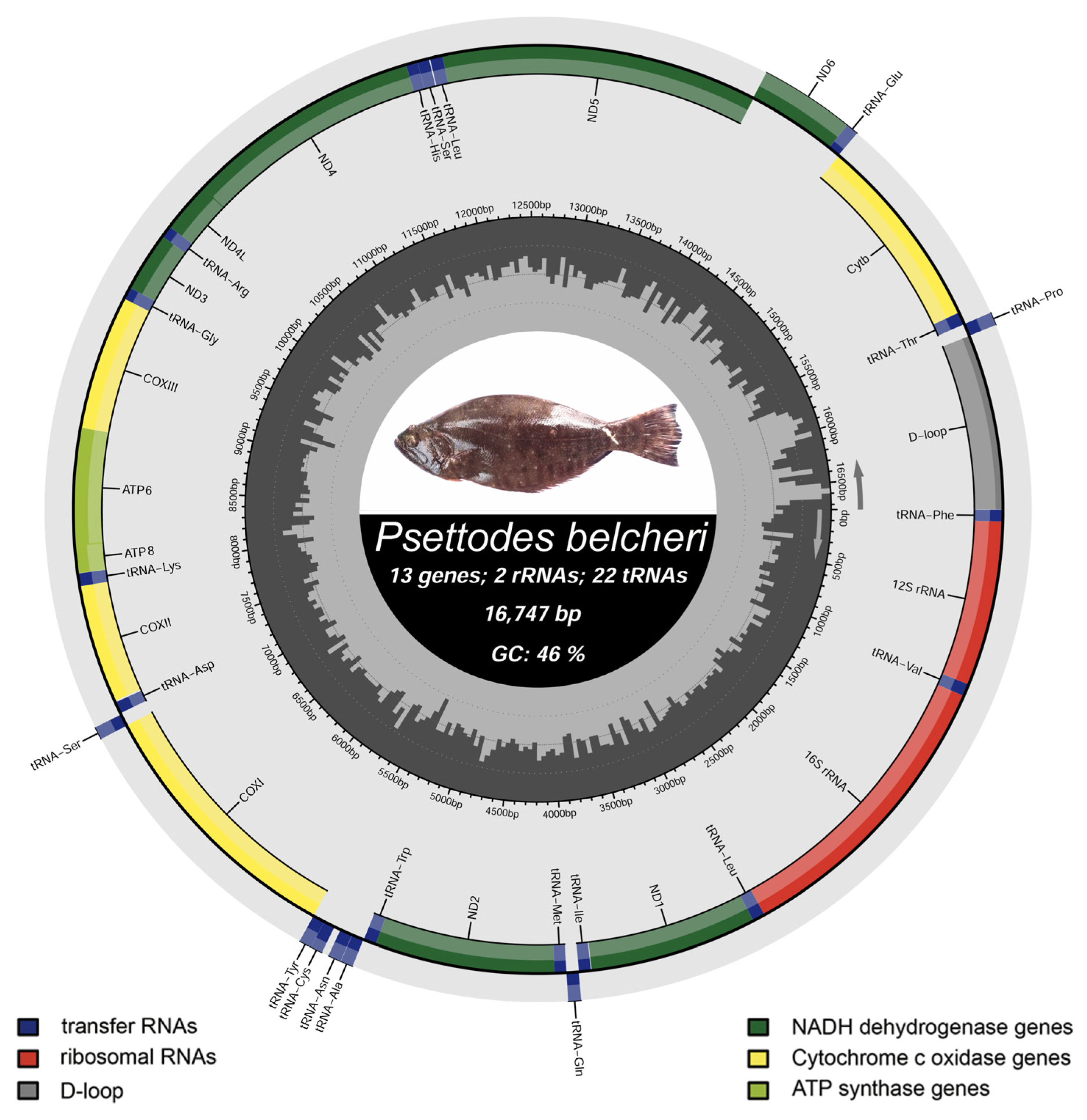
| Genes | Start | End | Strand | Size (bp) | Intergenic Nucleotide | Anti-Codon | Start Codon | Stop Codon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tRNA-Phe | 1 | 69 | H | 69 | 0 | TTC | . | . |
| 12S rRNA | 70 | 1030 | H | 961 | 0 | . | . | . |
| tRNA-Val | 1031 | 1102 | H | 72 | 26 | GTA | . | . |
| 16S rRNA | 1129 | 2830 | H | 1702 | 0 | . | . | . |
| tRNA-Leu | 2831 | 2903 | H | 73 | 0 | TTA | . | . |
| ND1 | 2904 | 3878 | H | 975 | 4 | . | ATG | AGG |
| tRNA-Ile | 3883 | 3952 | H | 70 | 1 | ATC | . | . |
| tRNA-Gln | 3954 | 4024 | L | 71 | −1 | CAA | . | . |
| tRNA-Met | 4024 | 4093 | H | 70 | 0 | ATG | . | . |
| ND2 | 4094 | 5138 | H | 1045 | 0 | . | ATG | T-- |
| tRNA-Trp | 5139 | 5211 | H | 73 | 2 | TGA | . | . |
| tRNA-Ala | 5214 | 5282 | L | 69 | 1 | GCA | . | . |
| tRNA-Asn | 5284 | 5356 | L | 73 | 38 | AAC | . | . |
| tRNA-Cys | 5395 | 5460 | L | 66 | 0 | TGC | . | . |
| tRNA-Tyr | 5461 | 5530 | L | 70 | 1 | TAC | . | . |
| COI | 5532 | 7082 | H | 1551 | 0 | . | GTG | TAA |
| tRNA-Ser | 7083 | 7153 | L | 71 | 8 | TCA | . | . |
| tRNA-Asp | 7162 | 7230 | H | 69 | 8 | GAC | . | . |
| COII | 7239 | 7929 | H | 691 | 0 | . | ATG | T-- |
| tRNA-Lys | 7930 | 8004 | H | 75 | 1 | AAA | . | . |
| ATP8 | 8006 | 8170 | H | 165 | −7 | . | ATG | TAA |
| ATP6 | 8164 | 8844 | H | 681 | 2 | . | ATG | TA- |
| COIII | 8847 | 9629 | H | 783 | 2 | . | ATG | TA- |
| tRNA-Gly | 9632 | 9702 | H | 71 | 0 | GGA | . | . |
| ND3 | 9703 | 10,050 | H | 348 | 1 | . | ATG | T-- |
| tRNA-Arg | 10,052 | 10,120 | H | 69 | 0 | CGA | . | . |
| ND4L | 10,121 | 10,414 | H | 294 | −4 | . | ATG | TAA |
| ND4 | 10,411 | 11,791 | H | 1381 | 0 | . | ATG | T-- |
| tRNA-His | 11,792 | 11,859 | H | 68 | 0 | CAC | . | . |
| tRNA-Ser | 11,860 | 11,927 | H | 68 | 6 | AGC | . | . |
| tRNA-Leu | 11,934 | 12,006 | H | 73 | 0 | CTA | . | . |
| ND5 | 12,007 | 13,845 | H | 1839 | −1 | . | ATG | TAA |
| ND6 | 13,845 | 14,363 | L | 519 | 0 | . | ATG | TAG |
| tRNA-Glu | 14,364 | 14,432 | L | 69 | 5 | GAA | . | |
| Cytb | 14,438 | 15,578 | H | 1141 | 0 | . | ATG | T-- |
| tRNA-Thr | 15,579 | 15,652 | H | 74 | −1 | ACA | . | . |
| tRNA-Pro | 15,652 | 15,724 | L | 73 | 0 | CCA | . | . |
| Control region | 15,725 | 16,747 | H | 1023 | . | . | . | . |
| Species Name | Size (bp) | A% | T% | G% | C% | A + T% | AT-Skew | GC-Skew |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complete mitogenome | ||||||||
| P. belcheri (OR231239) | 16,747 | 28.09 | 26.06 | 16.24 | 29.56 | 54.15 | 0.037 | −0.291 |
| P. erumei (FJ606835) | 17,315 | 28.83 | 24.78 | 15.71 | 30.68 | 53.61 | 0.076 | −0.323 |
| P. erumei (AP006835) | 16,683 | 28.57 | 24.50 | 15.78 | 31.15 | 53.07 | 0.077 | −0.328 |
| PCGs | ||||||||
| P. belcheri (OR231239) | 11,427 | 25.00 | 27.73 | 16.00 | 31.27 | 52.74 | −0.052 | −0.323 |
| P. erumei (FJ606835) | 11,427 | 25.37 | 25.75 | 15.62 | 33.25 | 51.13 | −0.008 | −0.361 |
| P. erumei (AP006835) | 11,426 | 25.33 | 25.62 | 15.62 | 33.43 | 50.95 | −0.006 | −0.363 |
| rRNAs | ||||||||
| P. belcheri (OR231239) | 2689 | 31.42 | 21.38 | 21.87 | 25.33 | 52.81 | 0.190 | −0.073 |
| P. erumei (FJ606835) | 2680 | 32.43 | 20.56 | 20.86 | 26.16 | 52.99 | 0.224 | −0.113 |
| P. erumei (AP006835) | 2680 | 32.43 | 20.45 | 20.90 | 26.23 | 52.87 | 0.227 | −0.113 |
| tRNAs | ||||||||
| P. belcheri (OR231239) | 1556 | 27.83 | 27.31 | 23.14 | 21.72 | 55.14 | 0.009 | 0.032 |
| P. erumei (FJ606835) | 1553 | 27.17 | 26.85 | 23.82 | 22.15 | 54.02 | 0.006 | 0.036 |
| P. erumei (AP006835) | 1554 | 27.28 | 26.83 | 23.68 | 22.20 | 54.12 | 0.008 | 0.032 |
| CRs | ||||||||
| P. belcheri (OR231239) | 1015 | 30.25 | 33.40 | 12.51 | 23.84 | 63.65 | −0.050 | −0.312 |
| P. erumei (FJ606835) | 1601 | 38.91 | 33.92 | 10.31 | 16.86 | 72.83 | 0.069 | −0.241 |
| P. erumei (AP006835) | 968 | 42.15 | 36.36 | 7.13 | 14.36 | 78.51 | 0.074 | −0.337 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kundu, S.; Palimirmo, F.S.; Kang, H.-E.; Kim, A.R.; Lee, S.R.; Gietbong, F.Z.; Song, S.H.; Kim, H.-W. Insights into the Mitochondrial Genetic Makeup and Miocene Colonization of Primitive Flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes: Psettodidae) in the East Atlantic and Indo-West Pacific Ocean. Biology 2023, 12, 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101317
Kundu S, Palimirmo FS, Kang H-E, Kim AR, Lee SR, Gietbong FZ, Song SH, Kim H-W. Insights into the Mitochondrial Genetic Makeup and Miocene Colonization of Primitive Flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes: Psettodidae) in the East Atlantic and Indo-West Pacific Ocean. Biology. 2023; 12(10):1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101317
Chicago/Turabian StyleKundu, Shantanu, Flandrianto Sih Palimirmo, Hye-Eun Kang, Ah Ran Kim, Soo Rin Lee, Fantong Zealous Gietbong, Se Hyun Song, and Hyun-Woo Kim. 2023. "Insights into the Mitochondrial Genetic Makeup and Miocene Colonization of Primitive Flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes: Psettodidae) in the East Atlantic and Indo-West Pacific Ocean" Biology 12, no. 10: 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101317
APA StyleKundu, S., Palimirmo, F. S., Kang, H.-E., Kim, A. R., Lee, S. R., Gietbong, F. Z., Song, S. H., & Kim, H.-W. (2023). Insights into the Mitochondrial Genetic Makeup and Miocene Colonization of Primitive Flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes: Psettodidae) in the East Atlantic and Indo-West Pacific Ocean. Biology, 12(10), 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101317









