SMMDA: Predicting miRNA-Disease Associations by Incorporating Multiple Similarity Profiles and a Novel Disease Representation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
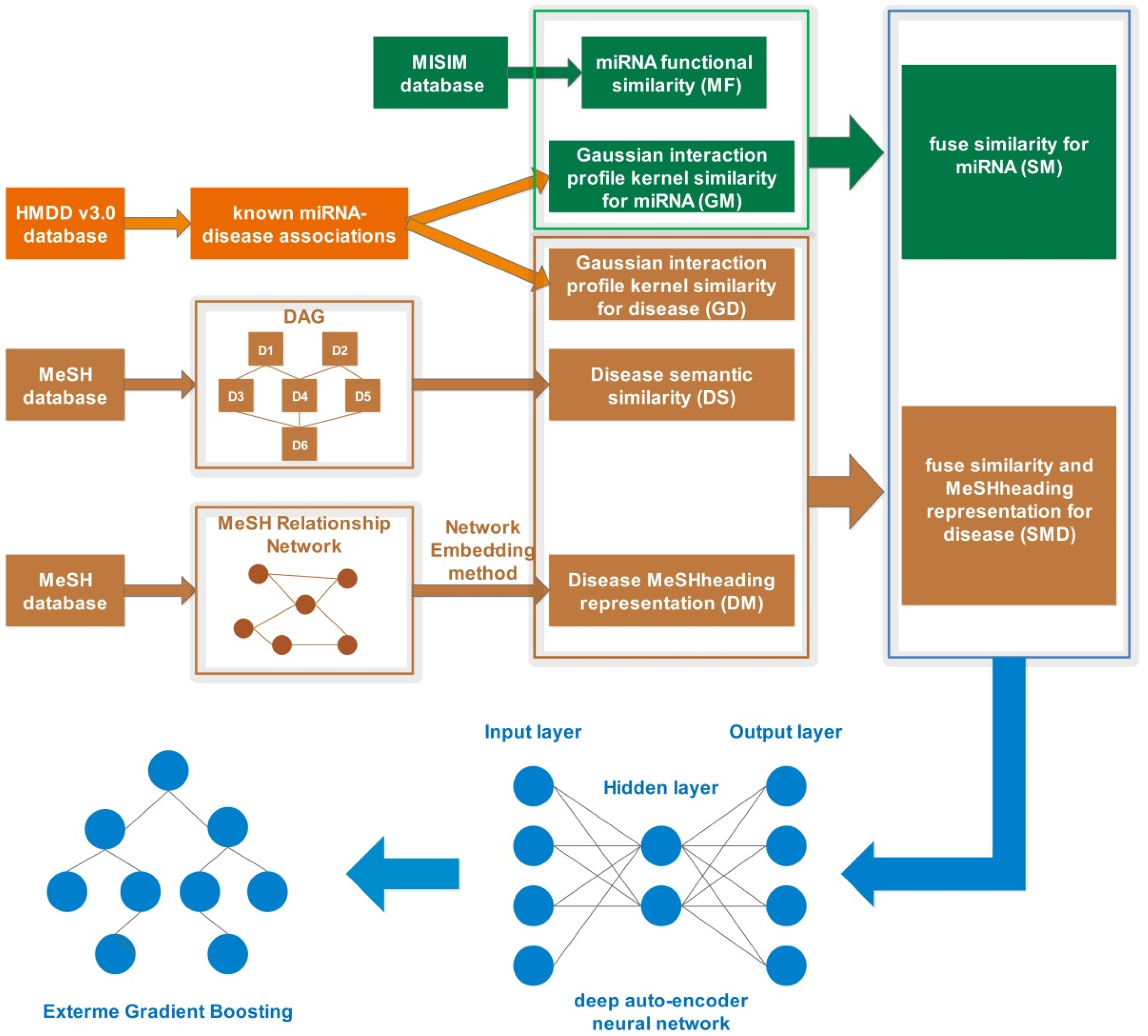
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human miRNA-Disease Associations
2.2. miRNA Functional Similarity
2.3. Gaussian Interaction Profile Kernel Similarity
2.4. Disease Semantic Similarity
2.5. MeSHHeading2vec Method
2.6. Incorporating Multiple Similarity Profiles and a Novel Disease Representation
2.7. Deep Auto-Encoder Learning Method
2.8. Exterme Gradient Boosting
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Detailed Prediction Performance of SMMDA
3.2. Comparison of Different Feature Combinations
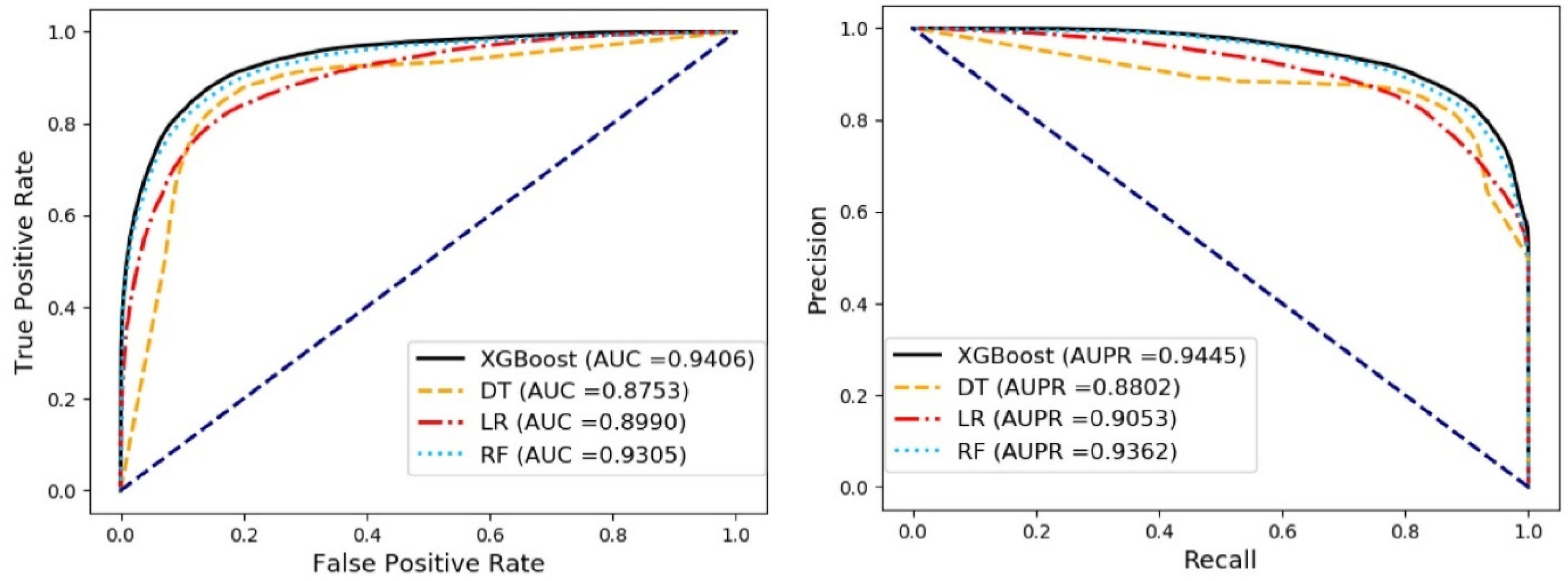
3.3. Comparison of Different Classifier Methods
3.4. Comparison of Previous Related Works
3.5. Case Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.M.; Byrom, M.W.; Shelton, J.; Ford, L.P. Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: microRNA sequences and annotation. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2010, 29, 12.9.1–12.9.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, X.; Ambros, V. Encountering microRNAs in cell fate signaling. Science 2005, 310, 1288–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Guo, M.; Hay, B.A. MicroRNAs and the regulation of cell death. TRENDS Genet. 2004, 20, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshalalfa, M.; Alhajj, R. Using context-specific effect of miRNAs to identify functional associations between miRNAs and gene signatures. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.; Rani, V. MicroRNAs: A critical regulator and a promising therapeutic and diagnostic molecule for diabetic cardiomyopathy. Curr. Gene Ther. 2021, 21, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tian, S.; Wang, H.-B.; Chu, D.-P.; Cao, J.-L.; Xia, H.-F.; Ma, X. MiR-185 is involved in human breast carcinogenesis by targeting Vegfa. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 4438–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.-Y.; You, Z.-H.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, J.-R.; Alghazzawi, D.; Li, L.-P. Predicting miRNA-disease association from heterogeneous information network with GraRep embedding model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.-H.; You, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.-B.; Huang, D.-S.; Yi, H.-C.; Chen, Z.-H. Bioentity2vec: Attribute-and behavior-driven representation for predicting multi-type relationships between bioentities. GigaScience 2020, 9, giaa032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.-H.; You, Z.-H.; Huang, D.-S.; Yi, H.-C.; Chen, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.-B. A learning based framework for diverse biomolecule relationship prediction in molecular association network. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, D.-H.; You, Z.-H. A heterogeneous label propagation approach to explore the potential associations between miRNA and disease. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xie, D.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Q.; You, Z.-H.; Liu, H. BNPMDA: Bipartite Network Projection for MiRNA–Disease Association prediction. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3178–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, B.-Y.; You, Z.-H.; Wang, L.; Wong, L.; Su, X.-R.; Zhao, B.-W. Predicting miRNA-Disease Associations via a New MeSH Headings Representation of Diseases and eXtreme Gradient Boosting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Shenzhen, China, 12–15 August 2021; pp. 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, B.-Y.; You, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.-W.; Wong, L. DANE-MDA: Predicting microRNA-disease associations via deep attributed network embedding. Iscience 2021, 24, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, C.-X.; Lv, J.-Y.; Li, Y.-S.; Xiao, Y.; Shao, T.-T.; Huo, X.; Li, X.; Zou, Y.; Han, Q.-L. Prioritizing candidate disease miRNAs by topological features in the miRNA target–dysregulated network: Case study of prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Yin, J. Prediction of potential mirna–disease associations through a novel unsupervised deep learning framework with variational autoencoder. Cells 2019, 8, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Shi, J.; Gao, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Q. HMDD v3. 0: A database for experimentally supported human microRNA–disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1013–D1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Lu, M.; Song, F.; Cui, Q. Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Laarhoven, T.; Nabuurs, S.B.; Marchiori, E. Gaussian interaction profile kernels for predicting drug–target interaction. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 3036–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Clarence Yan, C.; Luo, C.; Ji, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q. Constructing lncRNA functional similarity network based on lncRNA-disease associations and disease semantic similarity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.-H.; You, Z.-H.; Huang, D.-S.; Yi, H.-C.; Zheng, K.; Chen, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.-B. MeSHHeading2vec: A new method for representing MeSH headings as vectors based on graph embedding algorithm. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 22, 2085–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perozzi, B.; Al-Rfou, R.; Skiena, S. Deepwalk: Online learning of social representations. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD international Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 27 June 2014; pp. 701–710. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Qu, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M.; Yan, J.; Mei, Q. Line: Large-scale information network embedding. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on world Wide Web, Florence, Italy, 18–22 May 2015; pp. 1067–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Cui, P.; Zhu, W. Structural deep network embedding. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1225–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, M.; Cui, P.; Pei, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, W. Asymmetric transitivity preserving graph embedding. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1105–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Belkin, M.; Niyogi, P. Laplacian eigenmaps and spectral techniques for embedding and clustering. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3 January 2001; pp. 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, S.; Riedmiller, M. Deep auto-encoder neural networks in reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 July 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Brodley, C.E. Decision tree classification of land cover from remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W., Jr.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 398. [Google Scholar]
- Svetnik, V.; Liaw, A.; Tong, C.; Culberson, J.C.; Sheridan, R.P.; Feuston, B.P. Random forest: A classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modeling. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; You, Z.-H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.-P.; Li, Z.-W. MLMDA: A machine learning approach to predict and validate MicroRNA–disease associations by integrating of heterogenous information sources. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; You, Z.-H.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.-M.; Dong, Y.-N.; Li, L.-P.; Zheng, K. LMTRDA: Using logistic model tree to predict MiRNA-disease associations by fusing multi-source information of sequences and similarities. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; You, Z.-H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.-P.; Li, Z.-W. Dbmda: A unified embedding for sequence-based mirna similarity measure with applications to predict and validate mirna-disease associations. Mol. Ther. -Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, C.C.; Zhang, X.; You, Z.-H.; Deng, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q. WBSMDA: Within and between score for MiRNA-disease association prediction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.-H.; Huang, Z.-A.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, G.-Y.; Li, Z.-W.; Wen, Z.; Chen, X. PBMDA: A novel and effective path-based computational model for miRNA-disease association prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, P.; Han, K.; Guo, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Li, J.; Teng, Z. Prediction of microRNAs associated with human diseases based on weighted k most similar neighbors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yan, G.-Y. Semi-supervised learning for potential human microRNA-disease associations inference. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Ren, F.; Liu, C.; He, S.; Sun, G.; Gao, Q.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, R.; Cao, Y. dbDEMC: A database of differentially expressed miRNAs in human cancers. In BMC Genomics; BioMed Central: London, UK, 2010; p. S5. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Juan, L.; Teng, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. miR2Disease: A manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 37, D98–D104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelsey, J.L.; Horn-Ross, P.L. Breast cancer: Magnitude of the problem and descriptive epidemiology. Epidemiol. Rev. 1993, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Shi, A.; Lu, C.; Song, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J. Breast cancer: Epidemiology and etiology. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 72, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Seki, N.; Kikkawa, N.; Fujimura, L.; Hoshino, I.; Akutsu, Y.; Chiyomaru, T.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Matsubara, H. miR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b: Tumor-suppressive miRNAs target FSCN1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Yin, B.; Wang, B.; Xia, Z.; Chen, C.; Tang, J. MicroRNAs in esophageal cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 459–465. [Google Scholar]
- Dragovich, T.; Campen, C. Anti-EGFR-targeted therapy for esophageal and gastric cancers: An evolving concept. J. Oncol. 2009, 2009, 804108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Huang, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.; Qin, Y.; Duan, Y.; Gong, B. Salivary microRNAs as promising biomarkers for detection of esophageal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wu, W.; Che, Y.; Kang, N.; Zhang, R. Insights into the potential use of microRNAs as a novel class of biomarkers in esophageal cancer. Dis. Esophagus 2016, 29, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Fold | ACC. (%) | Spec. (%) | Sen.(%) | MCC (%) | Prec. (%) | AUC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 86.82 | 86.95 | 86.69 | 73.64 | 86.92 | 94.16 |
| 1 | 86.99 | 86.45 | 87.53 | 73.98 | 86.60 | 94.30 |
| 2 | 86.80 | 86.52 | 87.08 | 73.59 | 86.59 | 94.02 |
| 3 | 85.94 | 85.76 | 86.13 | 71.89 | 85.81 | 93.70 |
| 4 | 86.86 | 87.01 | 86.70 | 73.72 | 86.97 | 94.17 |
| Average | 86.68 ± 0.42 | 86.54 ± 0.50 | 86.83 ± 0.52 | 73.36 ± 0.84 | 86.58 ± 0.46 | 94.06 ± 0.23 |
| Fold | ACC. (%) | Spec. (%) | Sen. (%) | MCC (%) | Prec. (%) | AUC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 86.64 | 86.61 | 86.67 | 73.29 | 86.62 | 94.15 |
| 1 | 86.58 | 86.10 | 87.06 | 73.16 | 86.23 | 94.10 |
| 2 | 86.32 | 86.41 | 86.24 | 72.65 | 86.38 | 93.68 |
| 3 | 87.02 | 86.72 | 87.32 | 74.04 | 86.80 | 94.07 |
| 4 | 86.45 | 86.10 | 86.81 | 72.91 | 86.20 | 93.84 |
| Average | 86.60 ± 0.26 | 86.39 ± 0.29 | 86.82 ± 0.41 | 73.21 ± 0.52 | 86.45 ± 0.26 | 93.97 ± 0.20 |
| SMMDA | 86.68 ± 0.42 | 86.54 ± 0.50 | 86.83 ± 0.52 | 73.36 ± 0.84 | 86.58 ± 0.46 | 94.06 ± 0.23 |
| Classifier | ACC. (%) | Spec. (%) | Sen. (%) | MCC (%) | Prec. (%) | AUC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DT | 84.10 ± 0.15 | 83.30 ± 0.51 | 84.89 ± 0.33 | 68.20 ± 0.29 | 83.56 ± 0.38 | 87.53 ± 0.14 |
| LR | 82.50 ± 0.22 | 84.17 ± 0.66 | 80.82 ± 0.41 | 65.03 ± 0.45 | 83.62 ± 0.52 | 89.91 ± 0.21 |
| RF | 85.66 ± 0.36 | 85.61 ± 0.21 | 85.71 ± 0.63 | 71.32 ± 0.72 | 85.63 ± 0.22 | 93.05 ± 0.30 |
| XGBoost | 86.68 ± 0.42 | 86.54 ± 0.50 | 86.83 ± 0.52 | 73.36 ± 0.84 | 86.58 ± 0.46 | 94.06 ± 0.23 |
| Models | Average AUC (%) |
|---|---|
| DANE-MDA | 92.64 |
| MLMDA | 91.72 |
| MTDN | 91.89 |
| VAEMDA | 90.91 |
| LMTRDA | 90.54 |
| RLSMDA | 85.69 |
| PBMDA | 91.72 |
| WBSMDA | 81.85 |
| DBMDA | 91.29 |
| HDMP | 83.42 |
| SMMDA | 94.07 |
| miRNA | Evidence | miRNA | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-mir-122 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-451 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-146b | dbDemc | hsa-mir-494 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-34c | miR2Disease | hsa-mir-10a | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-375 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-320a | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-9 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-19b | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-16 | miR2Disease | hsa-mir-139 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-206 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-491 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-1 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-26b | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-183 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-212 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-182 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-193b | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-214 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-338 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-27b | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-199a-2 | miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-34b | miR2Disease | hsa-mir-20b | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-26a | miR2Disease | hsa-mir-497 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-199a | miR2Disease | hsa-mir-129 | miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-429 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-130b | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-29c | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-135a | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-96 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-328 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-99a | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-503 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-100 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-372 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-144 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-133a-1 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-483 | Unconfirmed | hsa-mir-449b | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-7 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-29 | Unconfirmed |
| hsa-let-7 | Unconfirmed | hsa-mir-98 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-196a-2 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-342 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| miRNA | Evidence | miRNA | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-mir-95 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-877 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-99b | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-337 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-190 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-138-1 | miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-217 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-650 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-206 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-449b | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-369 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-550a | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-19b-3p | dbDemc | hsa-mir-4717 | Unconfirmed |
| hsa-mir-517a | dbDemc | hsa-mir-329 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-422a | dbDemc | hsa-mir-639 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-133 | miR2Disease | hsa-mir-645 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-4324 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-1308 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-378b | dbDemc | hsa-mir-572 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-431 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-498 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-1908 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-561 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-188 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-1321 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-658 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-154 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-518e | dbDemc | hsa-mir-1825 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-636 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-504 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-362 | miR2Disease | hsa-mir-147b | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-487b | dbDemc | hsa-mir-454 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-501 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-208 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-665 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-208b | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-432 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-1236 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-30 | Unconfirmed | hsa-mir-323 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-511 | dbDemc; miR2Disease | hsa-mir-186 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| miRNA | Evidence | miRNA | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-mir-132 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-195 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-199a | dbDemc | hsa-mir-339 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-29a | dbDemc | hsa-mir-18b | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-19b | dbDemc | hsa-mir-101 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-23b | dbDemc | hsa-mir-146b | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-222 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-196a | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-16 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-103 | dbDemc; miR2Disease |
| hsa-mir-29b | dbDemc | hsa-mir-215 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-429 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-224 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-182 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-137 | Unconfirmed |
| hsa-mir-125a | dbDemc | hsa-mir-24 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-181b | dbDemc | hsa-mir-335 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-499 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-144 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-7 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-15b | dbDemc |
| hsa-let-7i | dbDemc | hsa-mir-497 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-133a | dbDemc | hsa-mir-106a | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-20b | dbDemc | hsa-mir-26a | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-221 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-218 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-204 | dbDemc | hsa-let-7f | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-181a | dbDemc | hsa-mir-139 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-302c | Unconfirmed | hsa-mir-124 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-378 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-206 | Unconfirmed |
| hsa-mir-1 | dbDemc | hsa-mir-372 | dbDemc |
| hsa-mir-18a | dbDemc | hsa-mir-23a | Unconfirmed |
| hsa-mir-199b | dbDemc | hsa-mir-10a | dbDemc |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, B.-Y.; Pan, L.-R.; Zhou, J.-R.; You, Z.-H.; Peng, S.-L. SMMDA: Predicting miRNA-Disease Associations by Incorporating Multiple Similarity Profiles and a Novel Disease Representation. Biology 2022, 11, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050777
Ji B-Y, Pan L-R, Zhou J-R, You Z-H, Peng S-L. SMMDA: Predicting miRNA-Disease Associations by Incorporating Multiple Similarity Profiles and a Novel Disease Representation. Biology. 2022; 11(5):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050777
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Bo-Ya, Liang-Rui Pan, Ji-Ren Zhou, Zhu-Hong You, and Shao-Liang Peng. 2022. "SMMDA: Predicting miRNA-Disease Associations by Incorporating Multiple Similarity Profiles and a Novel Disease Representation" Biology 11, no. 5: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050777
APA StyleJi, B.-Y., Pan, L.-R., Zhou, J.-R., You, Z.-H., & Peng, S.-L. (2022). SMMDA: Predicting miRNA-Disease Associations by Incorporating Multiple Similarity Profiles and a Novel Disease Representation. Biology, 11(5), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050777





