Acute Inflammation Induces Neuroendocrine and Opioid Receptor Genes Responses in the Seabass Dicentrarchus labrax Brain
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Fish and Experimental Design
2.2. Gene Expression
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HPI-Axis Response
3.1.1. Telencephalon
3.1.2. Optic Tectum
3.1.3. Hypothalamus
3.1.4. Pituitary Gland
3.2. Opioid Receptors Response
3.2.1. Telencephalon
3.2.2. Optic Tectum
3.2.3. Hypothalamus
3.2.4. Pituitary Gland
4. Discussion
4.1. HPI-Axis Response
4.2. Opioid Receptors
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashley, P.J. Fish welfare: Current issues in aquaculture. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 104, 199–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneddon, L.; Wolfenden, D.; Thomson, J. Stress management and welfare. In Fish Physiology: Biology of Stress in Fish; Schreck, C.B., Tort, L., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 35, pp. 463–539. [Google Scholar]
- Sadoul, B.; Vijayan, M.M. Stress and Growth. In Fish Physiology: Biology of Stress in Fish; Schreck, C.B., Tort, L., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 167–205. [Google Scholar]
- Tort, L. Stress and immune modulation in fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg-Van Kemenade, B.M.L.; Stolte, E.H.; Metz, J.R.; Chadzinska, M. Neuroendocrine–immune interactions in teleost fish. In Fish Neuroendocrinology, 1st ed.; Bernier, N.J., Kraak, G.V.D., Farrell, A.P., Colin, J.B., Eds.; Fish Physiology; Academic Press: Burlington, ON, Canada, 2009; Volume 28, pp. 313–364. [Google Scholar]
- Costas, B.; Aragao, C.; Dias, J.; Afonso, A.; Conceicao, L.E.C. Interactive effects of a high-quality protein diet and high stocking density on the stress response and some innate immune parameters of Senegalese sole Solea senegalensis. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 39, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorissen, M.; Flik, G. The Endocrinology of the Stress Response in Fish. In Fish Physiology: Biology of Stress in Fish; Schreck, C.B., Tort, L., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 75–111. [Google Scholar]
- Azeredo, R.; Machado, M.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Martinez-Rodriguez, G.; Moura, J.; Peres, H.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Afonso, A.; Mancera, J.M.; Costas, B. Dietary tryptophan induces opposite health-related responses in the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) reared at low or high stocking densities with implications in disease resistance. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verburg-Van Kemenade, B.M.L.; Ribeiro, C.M.S.; Chadzinska, M. Neuroendocrine-immune interaction in fish: Differential regulation of phagocyte activity by neuroendocrine factors. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 172, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelsma, M.Y.; Huising, M.O.; van Muiswinkel, W.B.; Flik, G.; Kwang, J.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Verburg-van Kemenade, B.M.L. Neuroendocrine–immune interactions in fish: A role for interleukin-1. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2002, 87, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoglund, E.; Balm, P.H.M.; Winberg, S. Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of 5-HT1A receptors on adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisol secretion in a teleost fish, the Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus). Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 324, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winberg, S.; Nilsson, A.; Hylland, P.; Soderstom, V.; Nilsson, G.E. Serotonin as a regulator of hypothalamic-pituitary-interrenal activity in teleost fish. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 230, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Troutaud, D.; Moulinoux, J.P.; Deschaux, P. Characterization of serotonin receptors in fish brain: Polyamines inhibit the binding process. Neurosci. Res. Commun. 1996, 18, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timothy, M.; Forlano, P.M. Serotonin distribution in the brain of the plainfin midshipman: Substrates for vocal-acoustic modulation and a reevaluation of the serotonergic system in teleost fishes. J. Comp. Neurol. 2020, 528, 3451–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervova, L.S.; Lapshin, D.N. Nociceptive thresholds in fish and its modulation by opioids. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein, T.K. The Role of Opioid Receptors in Immune System Function. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chadzinska, M.; Hermsen, T.; Savelkou, H.F.J.; van Kemenade, B.M.L.V. Cloning of opioid receptors in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) and their involvement in regulation of stress and immune response. Brain Behav. Immun. 2009, 23, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verburg-van Kemenade, B.M.L.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Chadzinska, M. Function of the Opioid System during Inflammation in Carp. Trends Comp. Endocrinol. Neurobiol. 2009, 1163, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafalla, C.; Bogwald, J.; Dalmo, R.A. Adjuvants and immunostimulants in fish vaccines: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuhl, H.; Beck, A.; Wozniak, G.; Canario, A.V.M.; Volckaert, F.A.M.; Reinhardt, R. The European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax genome puzzle: Comparative BAC-mapping and low coverage shotgun sequencing. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzynska, A.K.; Maiorano, E.; Bastaroli, M.; Naderi, F.; Miguez, J.M.; Martinez-Rodriguez, G.; Mancera, J.M.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A. Impact of Air Exposure on Vasotocinergic and Isotocinergic Systems in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata): New Insights on Fish Stress Response. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.H.; Khansari, A.R.; Teles, M.; Martinez-Rodriguez, G.; Zhang, Y.G.; Mancera, J.M.; Reyes-Lopez, F.E.; Tort, L. Brain and Pituitary Response to Vaccination in Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, J. 60 YEARS OF POMC Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of POMC gene expression. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, T99–T112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Hu, F.; Denver, R.J. Distribution and corticosteroid regulation of glucocorticoid receptor in the brain of Xenopus laevis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 508, 967–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gądek-Michalska, A.; Spyrka, J.; Rachwalska, P.; Tadeusz, J.; Bugajski, J. Influence of chronic stress on brain corticosteroid receptors and HPA axis activity. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terova, G.; Gornati, R.; Rimoldi, S.; Bernardini, G.; Saroglia, M. Quantification of a glucocorticoid receptor in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) reared at high stocking density. Gene 2005, 357, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazzana, M.; Vizzini, A.; Sanfratello, M.A.; Celi, M.; Salerno, G.; Parrinello, N. Differential expression of two glucocorticoid receptors in seabass (teleost fish) head kidney after exogeneous cortisol inoculation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A-Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 157, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vazzana, M.; Vizzini, A.; Salerno, G.; Di Bella, M.L.; Celi, M.; Parrinello, N. Expression of a glucocorticoid receptor (D1GR1) in several tissues of the teleost fish Dicentrarchus labrax. Tissue Cell 2008, 40, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vizzini, A.; Vazzana, M.; Cammarata, M.; Parrinello, N. Peritoneal cavity phagocytes from the teleost sea bass express a glucocorticold receptor (cloned and sequenced) involved in genomic modulation of the in vitro chemiluminescence response to zymosan. Gen. Comp. Endocr. 2007, 150, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesto, M.; Lopez-Patino, M.A.; Hernandez, J.; Soengas, J.L.; Miguez, J.M. The response of brain serotonergic and dopaminergic systems to an acute stressor in rainbow trout: A time course study. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 4435–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moltesen, M.; Laursen, D.C.; Thornqvist, P.O.; Andersson, M.A.; Winberg, S.; Hoglund, E. Effects of acute and chronic stress on telencephalic neurochemistry and gene expression in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 3907–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medeiros, L.R.; McDonald, M.D. Cortisol-mediated downregulation of the serotonin 1A receptor subtype in the Gulf toadfish, Opsanus beta. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A-Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 164, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesaar, C. The serotonergic system in fish. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 41, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoglund, E.; Balm, P.H.M.; Winberg, S. Skin darkening, a potential social signal in subordinate Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus): The regulatory role of brain monoamines and pro-opiomelanocortin-derived peptides. J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 203, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overli, O.; Winberg, S.; Pottinger, T.G. Behavioral and neuroendocrine correlates of selection for stress responsiveness in rainbow trout—A review. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2005, 45, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, P.I.M.; Martins, C.I.M.; Khan, U.W.; Gjoen, H.M.; Overli, O.; Hoglund, E. Stress and fear responses in the teleost pallium. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 141, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanain, M.; Zalcman, S.; Bhatt, S.; Siegel, A. Interleukin-1 beta in the hypothalamus potentiates feline defensive rage: Role of serotonin-2 receptors. Neuroscience 2003, 120, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, R.J.; Mancera, J.M.; Munoz, J.L.; Bonga, S.E.W.; Flik, G. The stress response of the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) to air exposure and confinement. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 163, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.; Azeredo, R.; Fontinha, F.; Fernandez-Boo, S.; Conceicao, L.E.C.; Dias, J.; Costas, B. Dietary methionine improves the European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) immune status, inflammatory response, and disease resistance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Northmore, D.P.M. Holding visual attention for 400 million years: A model of tectum and torus longitudinalis in teleost fishes. Vis. Res. 2017, 131, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, O.; Vilchez, I.M.; Pottinger, T.G.; Winberg, S. Time-course of the effect of dietary L-tryptophan on plasma cortisol levels in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 3589–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przewlocki, R.; Przewlocka, B. Opioids in neuropathic pain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 3013–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chadzinska, M.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Verburg-van Kemenadea, B.M.L. Morphine affects the inflammatory response in carp by impairment of leukocyte migration. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, K. Pain management: Is opioid immuno suppression a clinical problem? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2006, 60, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneddon, L.U. Evolution of nociception in vertebrates: Comparative analysis of lower vertebrates. Brain Res. Rev. 2004, 46, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.-N.; Loh, H.H. Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of opioid receptor genes: Present and future. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 2011, 51, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, R.; Auerbach, S.B. Opioid receptor subtypes differentially modulate serotonin efflux in the rat central nervous system. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Northmore, D.P.M. The Optic Tectum. In Encyclopedia of Fish Physiology: From Genome to Environment; Farrell, A.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 131–142. [Google Scholar]
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). One-way ANOVA was performed to identify differences between i.p.-injected fish and the undisturbed group, followed by a Tukey post-hoc test. Different symbols (*, #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Two-way ANOVA was performed to identify significant differences within the i.p.-injected fish, followed by a Tukey post-hoc test. Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times (p ≤ 0.05).
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). One-way ANOVA was performed to identify differences between i.p.-injected fish and the undisturbed group, followed by a Tukey post-hoc test. Different symbols (*, #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Two-way ANOVA was performed to identify significant differences within the i.p.-injected fish, followed by a Tukey post-hoc test. Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times (p ≤ 0.05).
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). One-way ANOVA was performed to identify differences between i.p.-injected fish and the undisturbed group, followed by a Tukey post-hoc test. Different symbols (*, #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Two-way ANOVA was performed to identify significant differences within the i.p.-injected fish, followed by a Tukey post-hoc test. Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times (p ≤ 0.05).
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). One-way ANOVA was performed to identify differences between i.p.-injected fish and the undisturbed group, followed by a Tukey post-hoc test. Different symbols (*, #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Two-way ANOVA was performed to identify significant differences within the i.p.-injected fish, followed by a Tukey post-hoc test. Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times (p ≤ 0.05).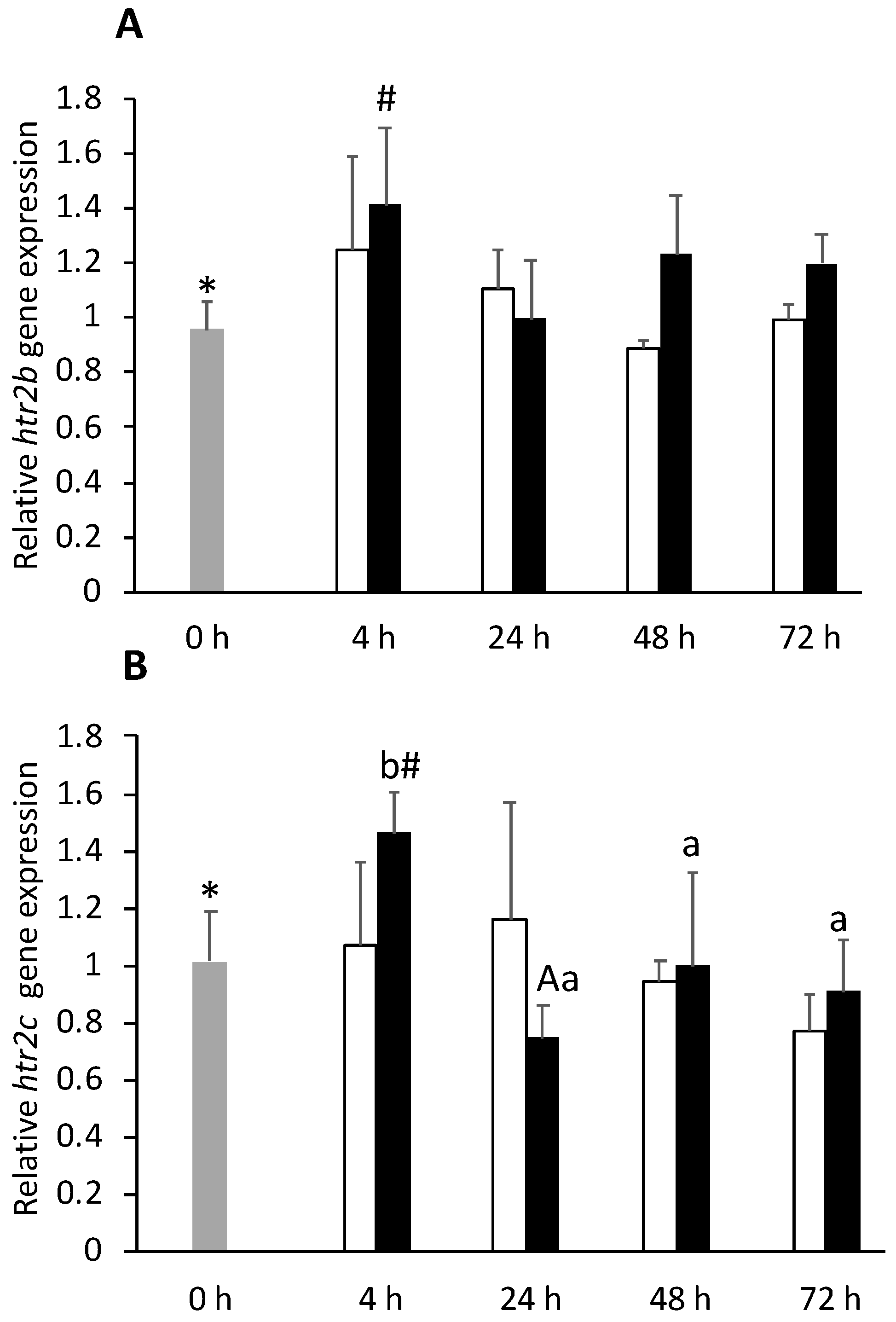
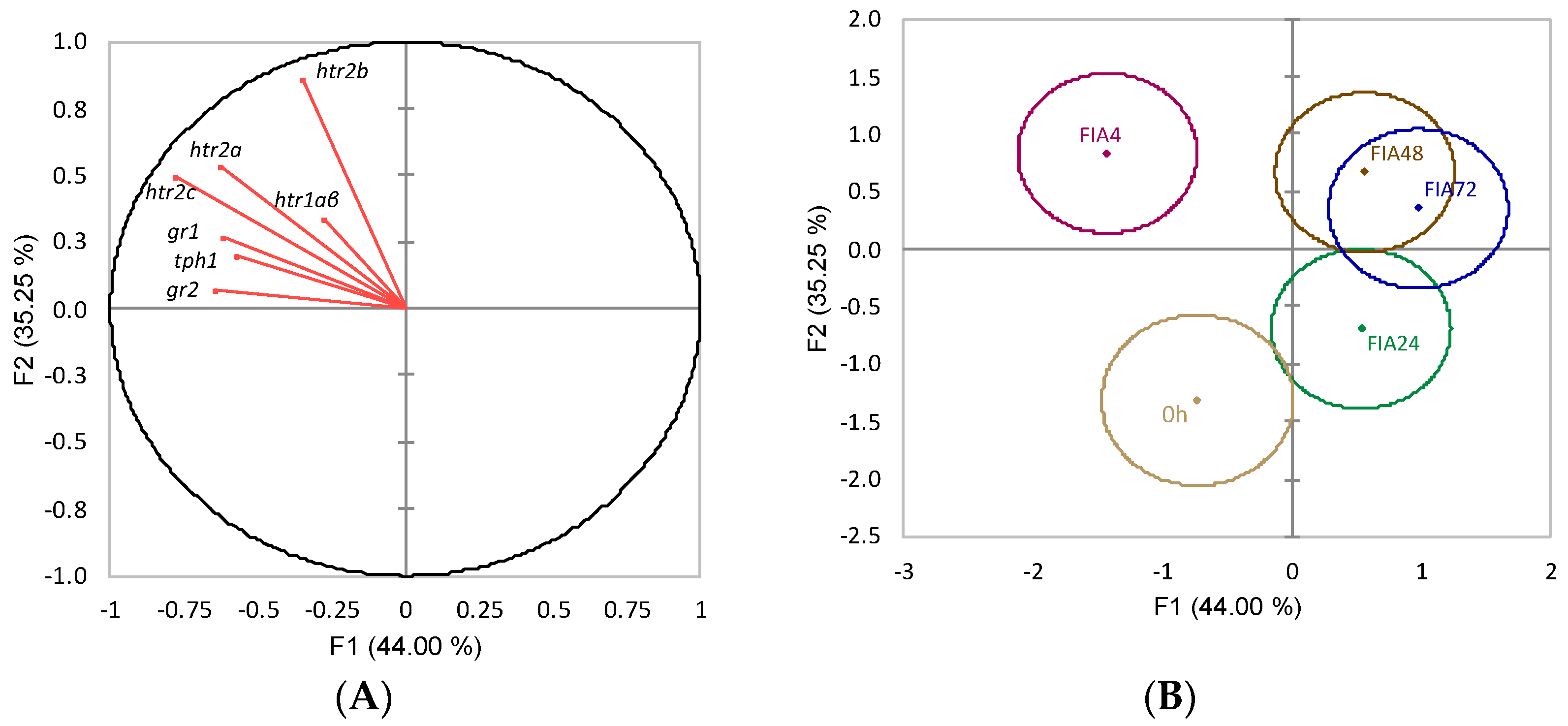
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.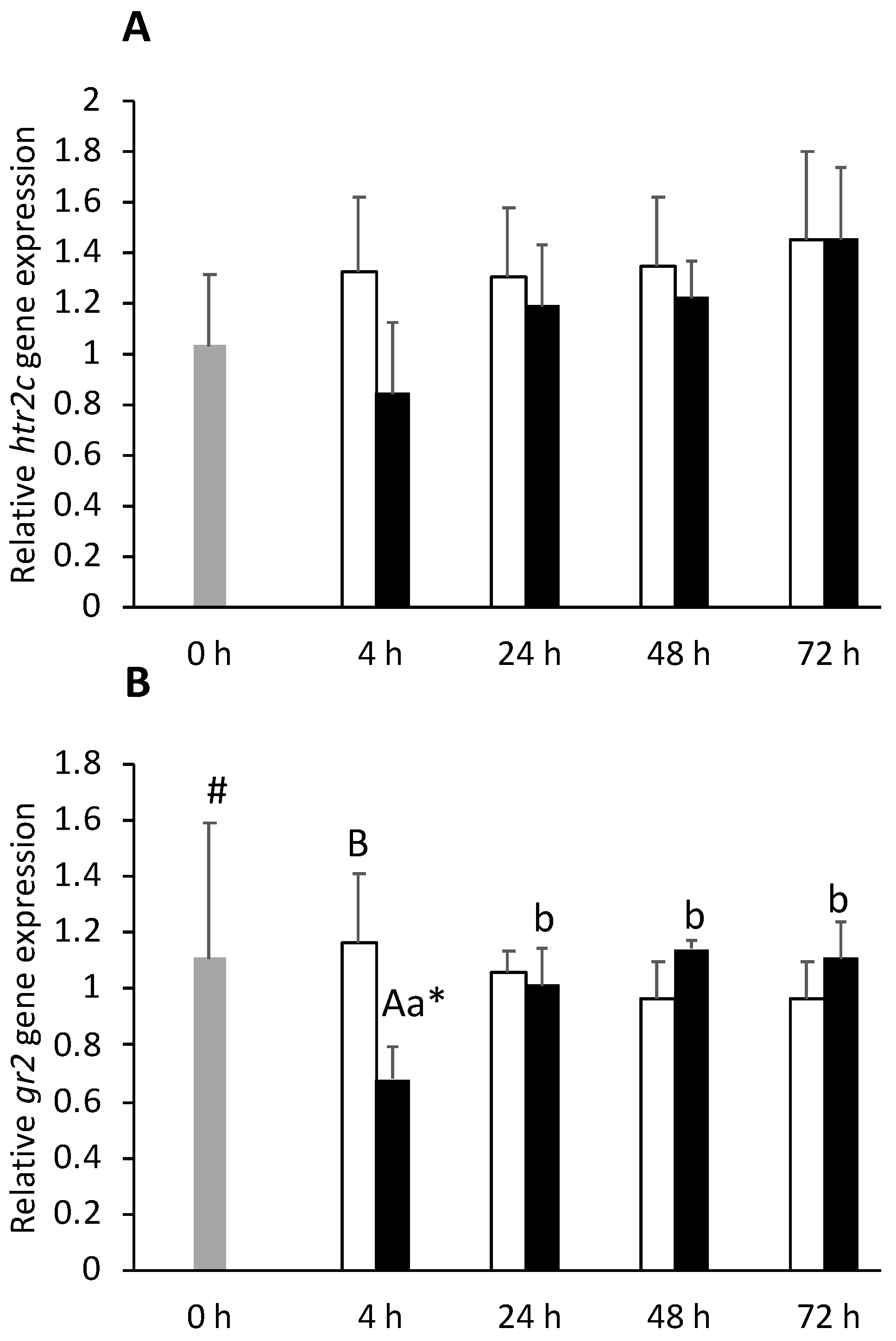
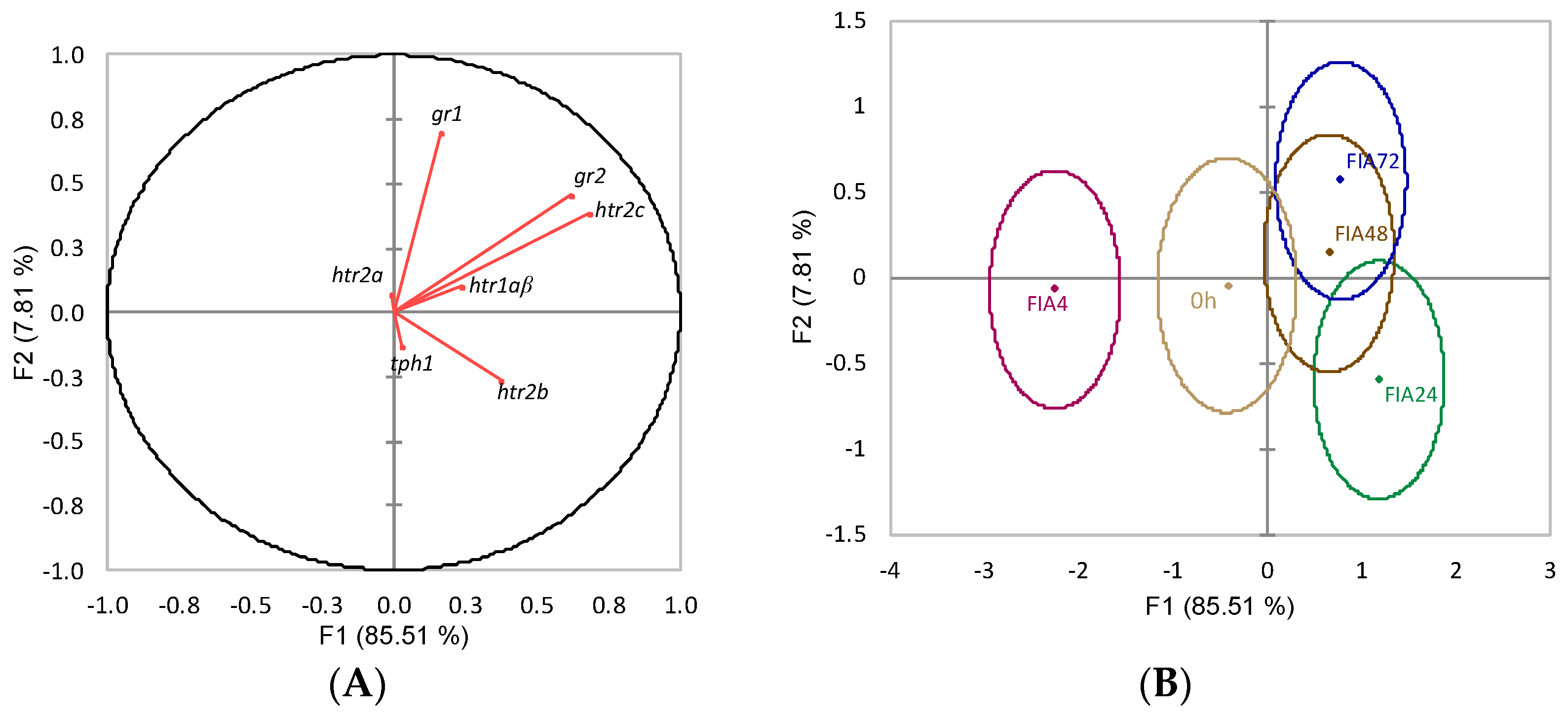
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.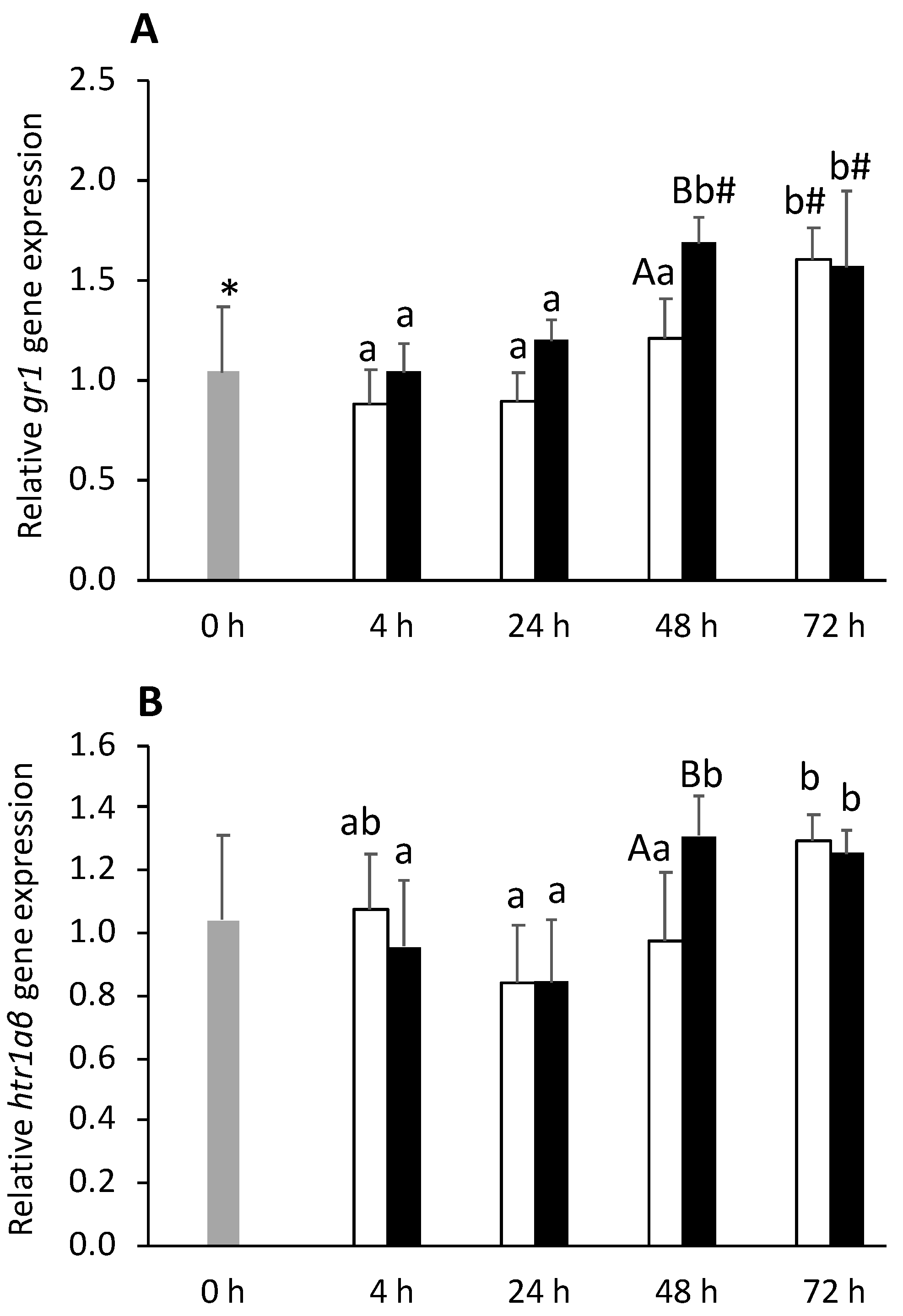
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
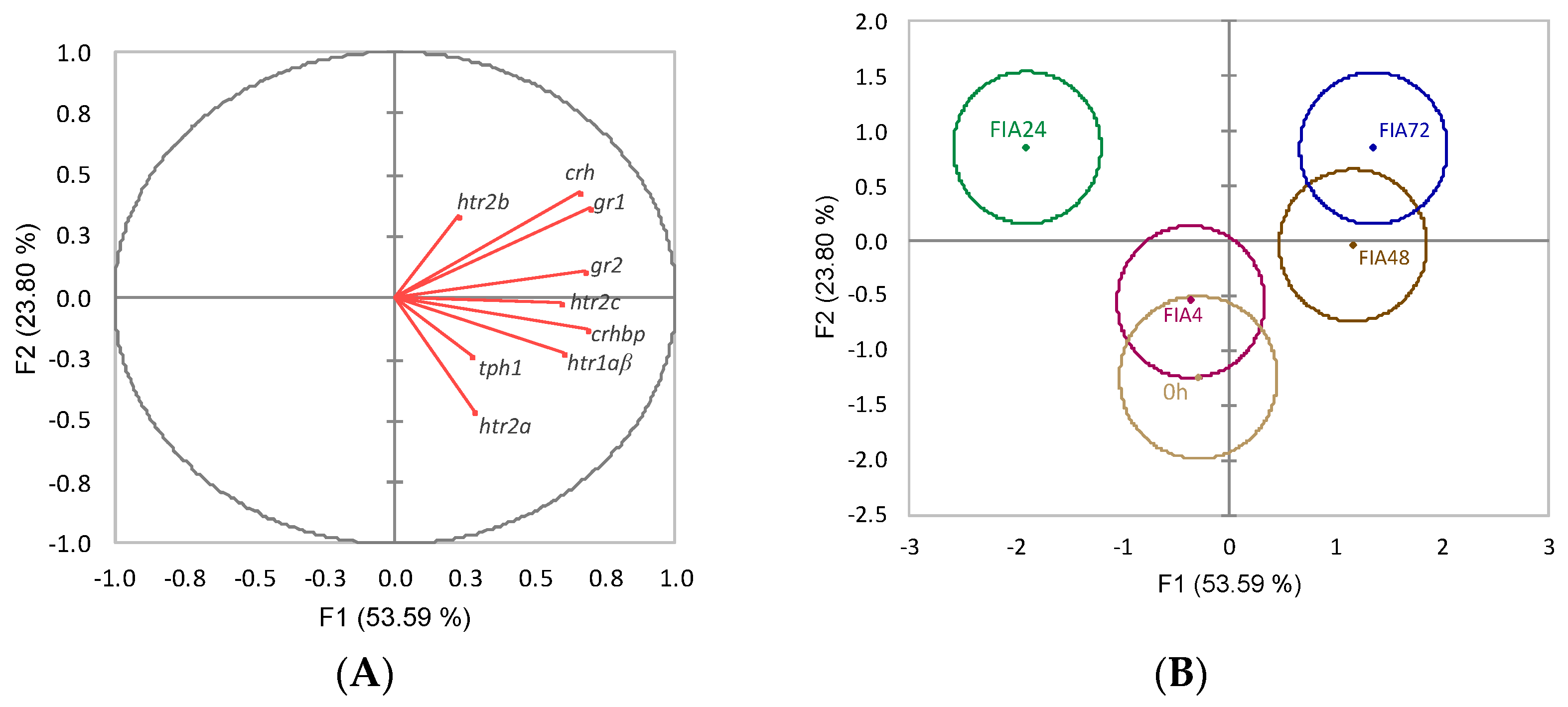
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.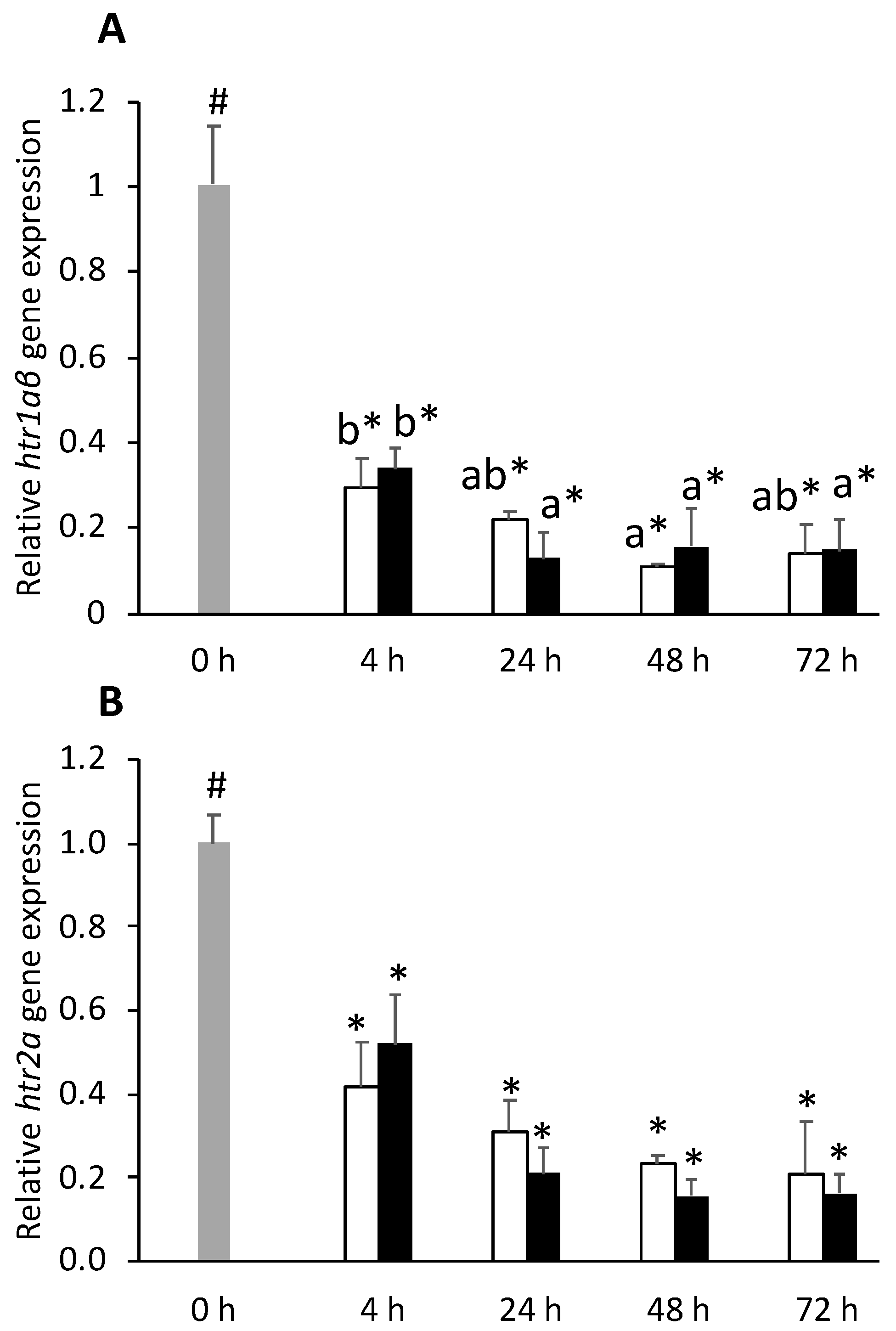
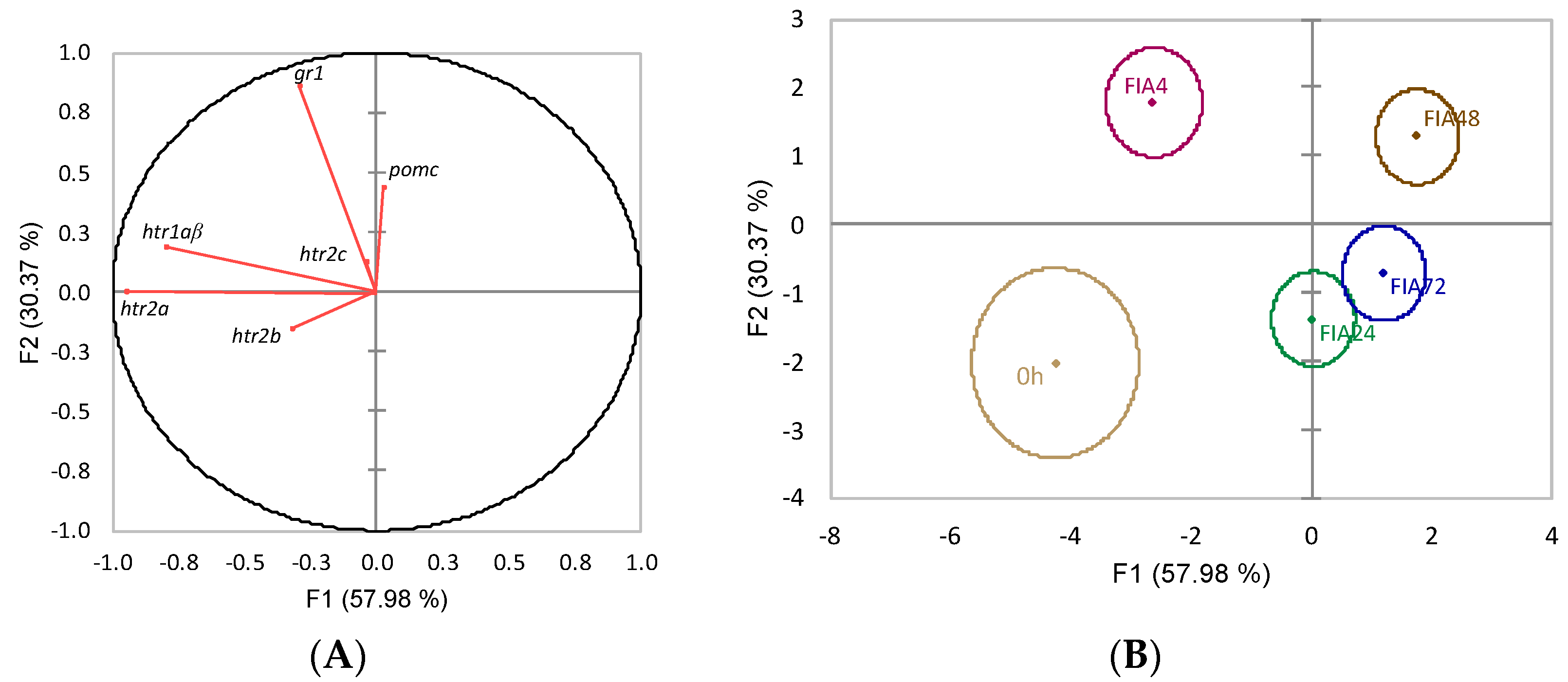
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
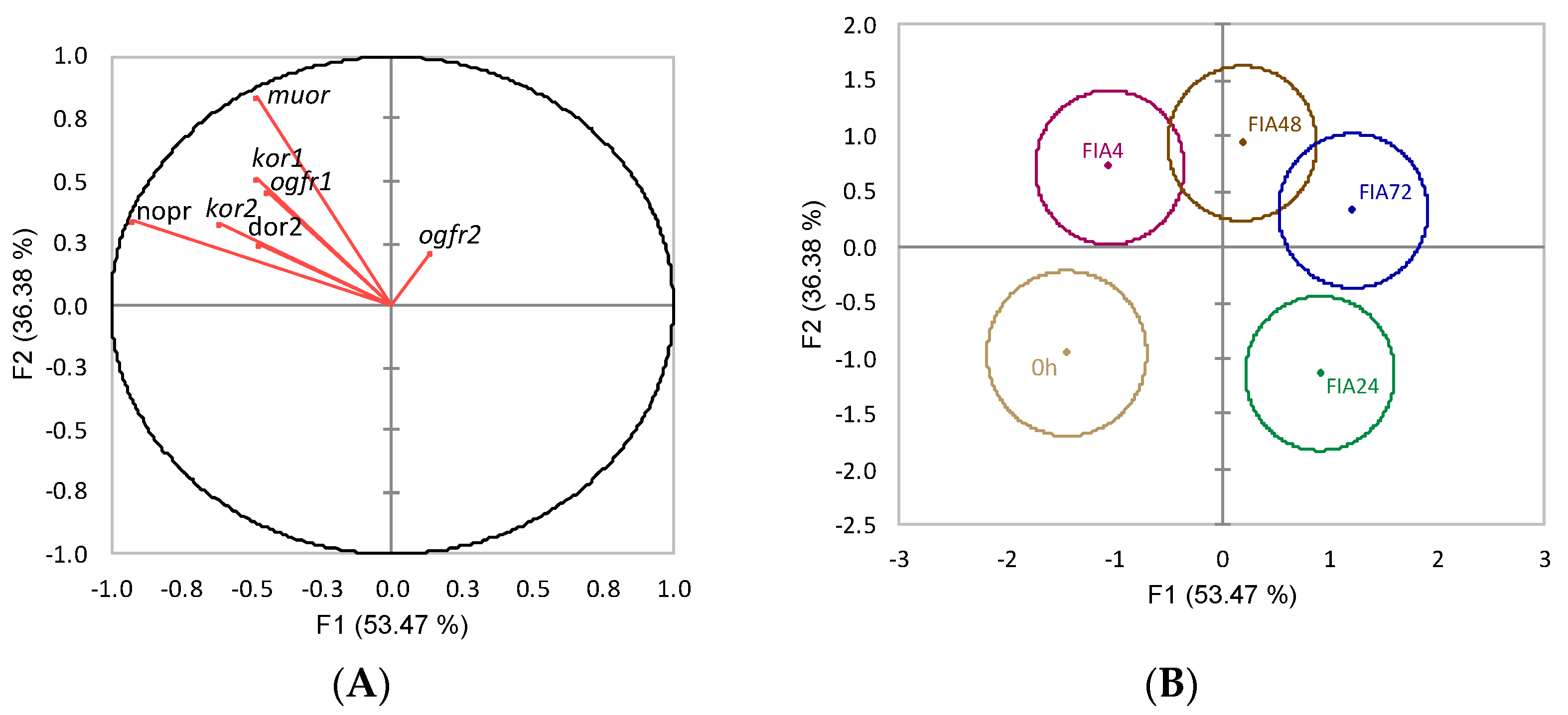
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.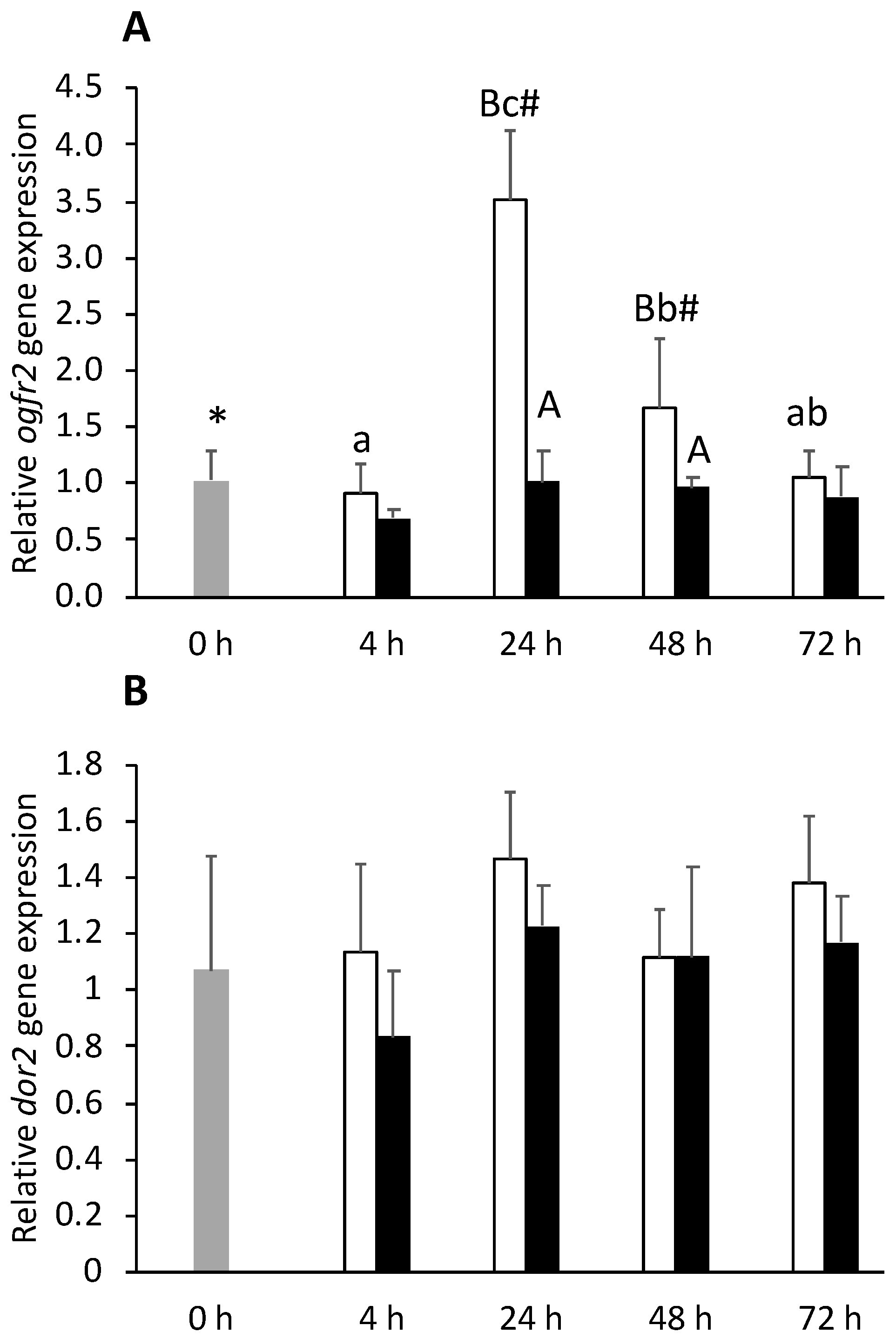
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Capital letters stand for significant differences between stimuli. Lower-case letters indicate significant differences between sampling times. Further details in legend of Figure 1.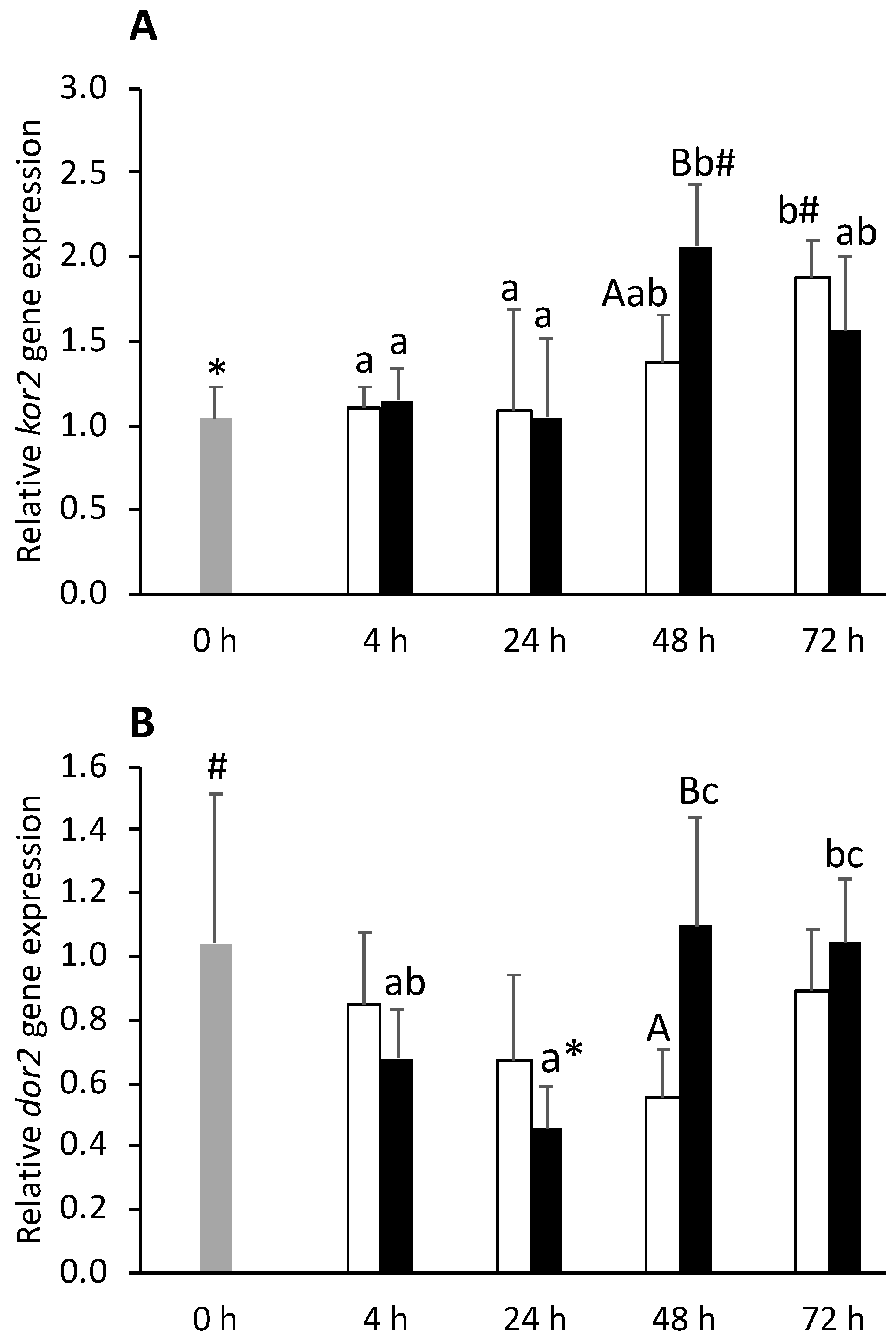
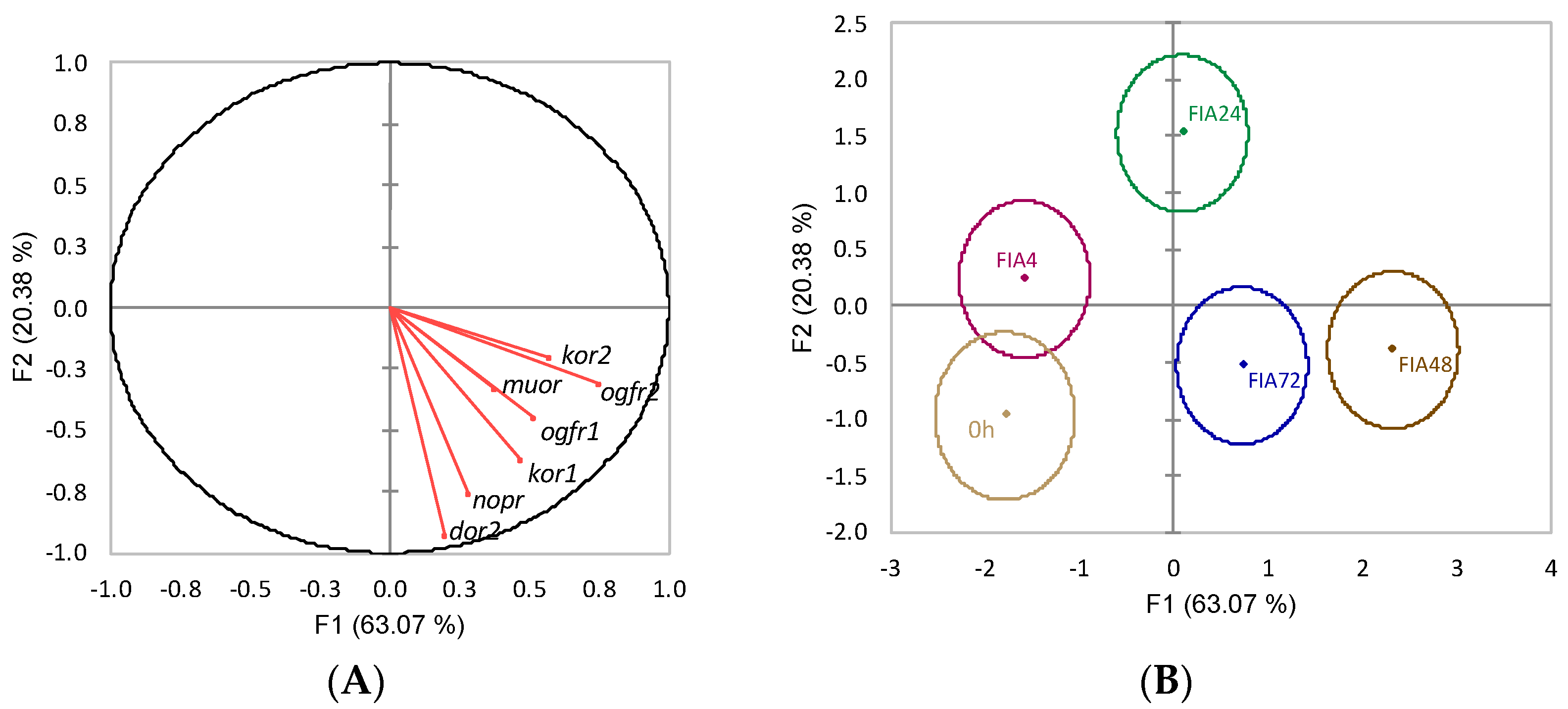
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Further details in legend of Figure 1.
 ) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Further details in legend of Figure 1.
) or i.p.-injected with a sham solution (CTRL, □) or Freund’s Incomplete Adjuvant (FIA, ∎) and sampled at 4, 24, 48, 72 h post-injection (means ± SD, n = 8). Different symbols (* and #) stand for significant differences between i.p.-injected groups and the undisturbed group (0 h). Further details in legend of Figure 1.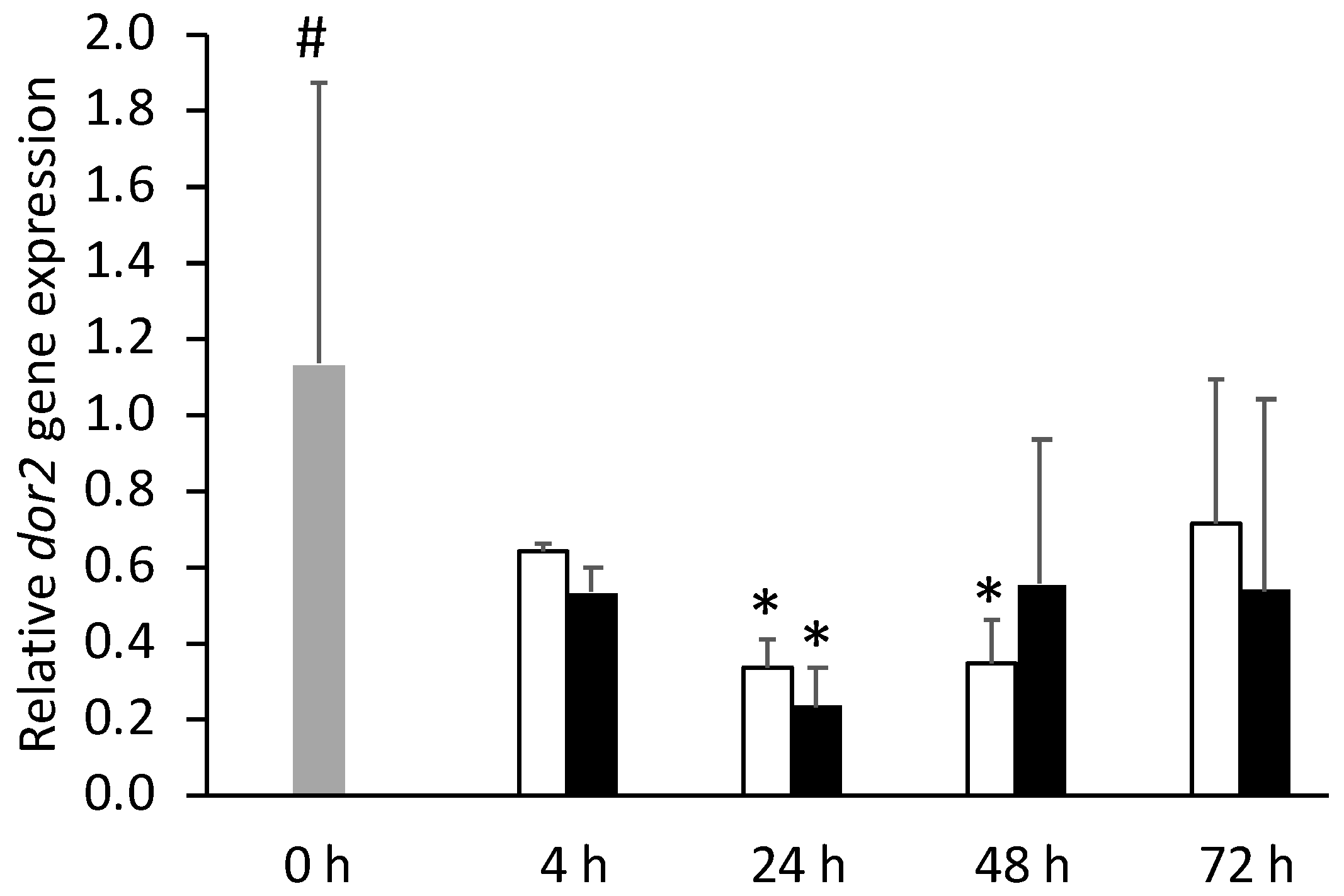
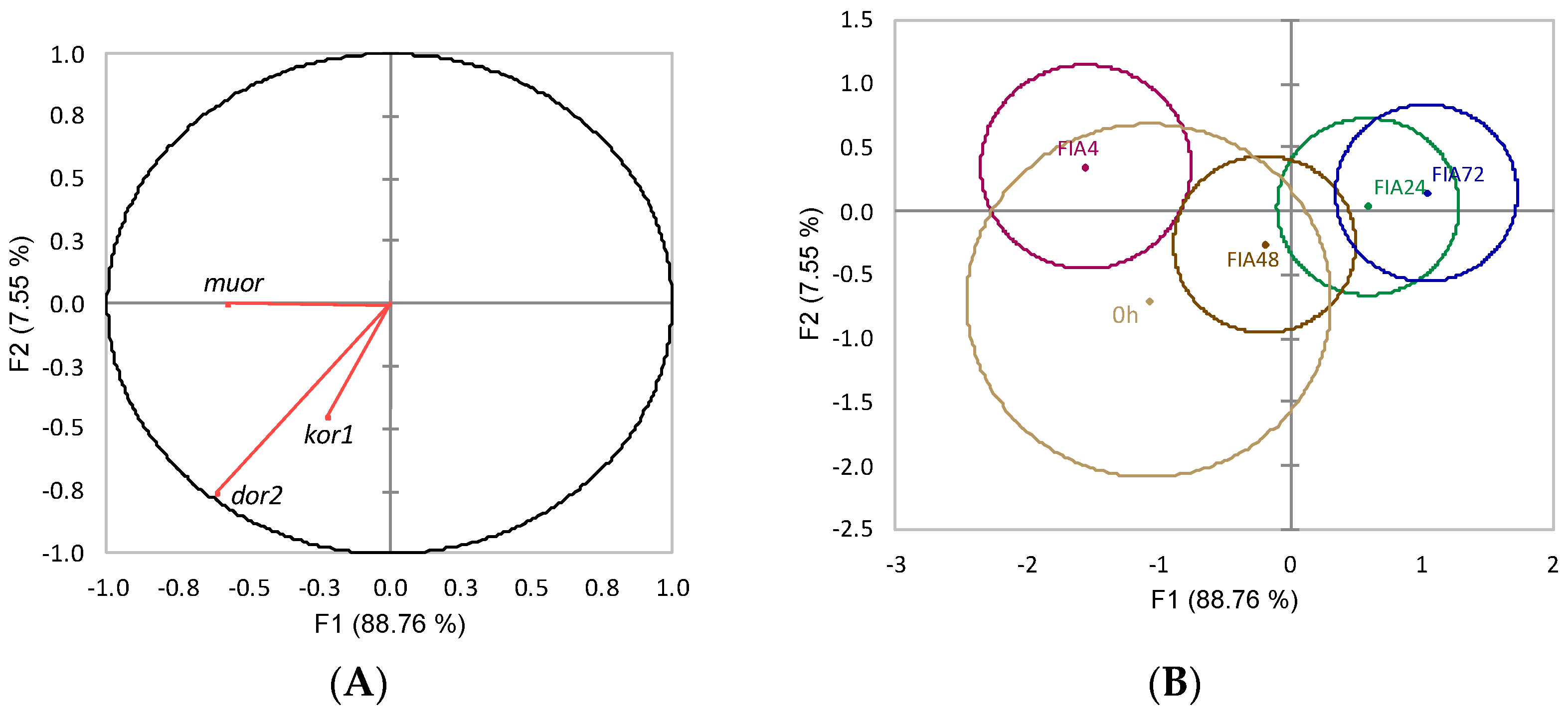
| Acronym | GenBank | Eff 2 | AT 3 | Product Length 4 | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40s | HE978789.1 | 108.8 | 60 | 79 | TGATTGTGACAGACCCTCGTG | CACAGAGCAATGGTGGGGAT |
| ef1α | AJ866727.1 | 92.8 | 57 | 144 | AACTTCAACGCCCAGGTCAT | CTTCTTGCCAGAACGACGGT |
| gr1 | AY619996.1 | 114.19 | 60 | 100 | AAATCTGCCTGGTGTGTTCC | TGCCCTTTCACTGCTCTCTT |
| gr2 | AY549305.1 | 109.4 | 55 | 142 | CTTCTACAGCACCAGCACCA | TCTCCTGTTTGACCACACCA |
| crh | JF274994.1 | 110.21 | 60 | 200 | AACCCAAAACTCCCAGCAG | TGTTCCCAACTTTCCCTTGT |
| crhbp | MG832822.1 | 105.47 | 60 | 199 | TGTCATCTCCCAGTCACCAG | GCCATTTCCTCCAAGCAAC |
| pomc | AY691808.1 | 101.98 | 60 | 158 | TCTTCCTCCTCCTCTCCACA | CGCCTTCTCATCTCTTCAGG |
| htr1aβ | DLAgn_00119560 1 | 102.0 | 60 | 176 | GGAGCGTAAAACGGTGAAAA | TGGGGTTGAGGAGAGAGTTG |
| htr2a | DLAgn_00222310 1 | 103.8 | 60 | 18 | CCTCTGACCTCTGTCCCATC | ACTGAAATCGTCCACACTGC |
| htr2b | DLAgn_00148380 1 | 109.4 | 60 | 165 | ATTGCCCTCGTCACTGTTCT | GCTGTGTTGGATTGGCTTCT |
| htr2c | DLAgn_00037670 1 | 118.0 | 60 | 195 | CATCCGCAACCCCATAGAG | ACGAAGGAGCCAATCAGCAT |
| tph1 | DLAgn_00154580 1 | 107.0 | 62 | 114 | CGCATAGACTTCACAACAGAGG | CAGCAGAGGGAGGTTCTTCA |
| ogfr1 | DLAgn_00128530 1 | 96.8 | 60 | 185 | GTTGGGAATGGAGATGGAAA | GCTTCAGATTTTGGCTCAGG |
| ogfr2 | DLAgn_00089660 1 | 96.6 | 60 | 146 | CTTGCCTTCCTGTCTCCAGT | CTTGTCTCGGTTTCCTTTGG |
| kor1 | DLAgn_00007470 1 | 89.7 | 60 | 249 | TCTGGTGCTTGTGGTAGTCG | TGGCAGTCTCTGTGTCCTTG |
| kor2 | DLAgn_00077520 1 | 82.0 | 60 | 163 | CTCGTCAGTGTCCCCGAAAC | CCCCCTTCAGTTTGGCCGAGAG |
| nopr | DLAgn_00125610 1 | 97.5 | 60 | 106 | CTCCTTTCTCATCCCTGTGG | GTTGCGGTCCTTTTCCTTG |
| muor | DLAgn_00015310 1 | 99.8 | 60 | 240 | GTCACCAGCACCCTACCATT | CGAGGAGAGAATCCAGTTGC |
| dor2 | DLAgn_00062690 1 | 108.1 | 60 | 81 | CGCTTCTCGGTCTCCATAACT | GGTCTCATTACTACTTGAAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azeredo, R.; Machado, M.; Pereiro, P.; Barany, A.; Mancera, J.M.; Costas, B. Acute Inflammation Induces Neuroendocrine and Opioid Receptor Genes Responses in the Seabass Dicentrarchus labrax Brain. Biology 2022, 11, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030364
Azeredo R, Machado M, Pereiro P, Barany A, Mancera JM, Costas B. Acute Inflammation Induces Neuroendocrine and Opioid Receptor Genes Responses in the Seabass Dicentrarchus labrax Brain. Biology. 2022; 11(3):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030364
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzeredo, Rita, Marina Machado, Patricia Pereiro, Andre Barany, Juan Miguel Mancera, and Benjamín Costas. 2022. "Acute Inflammation Induces Neuroendocrine and Opioid Receptor Genes Responses in the Seabass Dicentrarchus labrax Brain" Biology 11, no. 3: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030364
APA StyleAzeredo, R., Machado, M., Pereiro, P., Barany, A., Mancera, J. M., & Costas, B. (2022). Acute Inflammation Induces Neuroendocrine and Opioid Receptor Genes Responses in the Seabass Dicentrarchus labrax Brain. Biology, 11(3), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030364








